22:
87:
221:
203:
51:
262:
156:
through the remaining controller, port or switch transparently and with no changes visible to the applications, other than perhaps resulting in increased
296:
291:
255:
73:
281:
286:
248:
163:
Multipath software layers can leverage the redundant paths to provide performance-enhancing features, including dynamic
164:
34:
122:
is a fault-tolerance and performance-enhancement technique that defines more than one physical path between the
44:
38:
30:
123:
55:
157:
107:
185:
95:
228:
115:
103:
86:
168:
145:
141:
232:
152:
ports. Should one controller, port or switch fail, the operating system can route the
220:
275:
209:
180:
149:
153:
131:
127:
197:
85:
138:
91:
15:
134:, controllers, switches, and bridge devices connecting them.
171:, automatic path management, and dynamic reconfiguration.
236:
148:on the same computer, or a disk may connect to two
43:but its sources remain unclear because it lacks
256:
8:
263:
249:
74:Learn how and when to remove this message
7:
217:
215:
200:, Linux Symposium 2005 p. 147
14:
219:
20:
297:Fault-tolerant computer systems
206:, Veritas Dynamic Multi pathing
1:
292:Computer storage technologies
126:in a computer system and its
235:. You can help Knowledge by
210:Linux Multipath Usage guide
313:
214:
144:may connect to two SCSI
29:This article includes a
282:Computer hardware stubs
58:more precise citations.
111:
90:Multipath access to a
287:Computer data storage
89:
130:devices through the
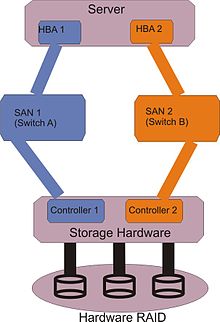
108:Storage area network
198:Linux Multipathing
186:Linux DM Multipath
112:
96:Linux DM Multipath
31:list of references
244:
243:
229:computer hardware
204:VxDMP white paper
137:As an example, a
84:
83:
76:
304:
265:
258:
251:
223:
216:
116:computer storage
104:Host bus adapter
79:
72:
68:
65:
59:
54:this article by
45:inline citations
24:
23:
16:
312:
311:
307:
306:
305:
303:
302:
301:
272:
271:
270:
269:
194:
177:
169:traffic shaping
142:hard disk drive
80:
69:
63:
60:
49:
35:related reading
25:
21:
12:
11:
5:
310:
308:
300:
299:
294:
289:
284:
274:
273:
268:
267:
260:
253:
245:
242:
241:
224:
213:
212:
207:
201:
193:
192:External links
190:
189:
188:
183:
176:
173:
165:load balancing
82:
81:
39:external links
28:
26:
19:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
309:
298:
295:
293:
290:
288:
285:
283:
280:
279:
277:
266:
261:
259:
254:
252:
247:
246:
240:
238:
234:
231:article is a
230:
225:
222:
218:
211:
208:
205:
202:
199:
196:
195:
191:
187:
184:
182:
181:Device mapper
179:
178:
174:
172:
170:
166:
161:
159:
155:
151:
150:Fibre Channel
147:
143:
140:
135:
133:
129:
125:
121:
120:multipath I/O
117:
109:
105:
101:
97:
93:
88:
78:
75:
67:
57:
53:
47:
46:
40:
36:
32:
27:
18:
17:
237:expanding it
226:
162:
136:
128:mass-storage
119:
113:
99:
70:
61:
50:Please help
42:
146:controllers
56:introducing
276:Categories
106:, "SAN" =
64:April 2016
175:See also
102:"HBA" =
158:latency
100:Legend:
52:improve
94:using
227:This
132:buses
37:, or
233:stub
139:SCSI
92:RAID
154:I/O
124:CPU
114:In
278::
167:,
160:.
118:,
41:,
33:,
264:e
257:t
250:v
239:.
110:)
98:(
77:)
71:(
66:)
62:(
48:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.