408:
416:
241:
141:
22:
280:
324:
272:
332:
340:
287:
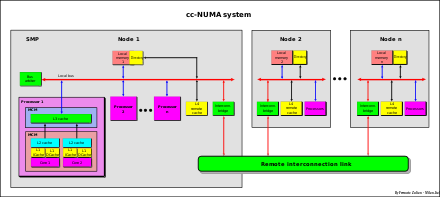
It is known that the SMP system has limited scalability. To overcome this limitation, the architecture called "cc-NUMA" (cache coherency–non-uniform memory access) is normally used. The main characteristic of a cc-NUMA system is having shared global memory that is distributed to each node, although
397:
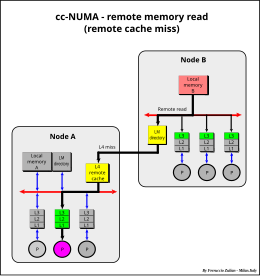
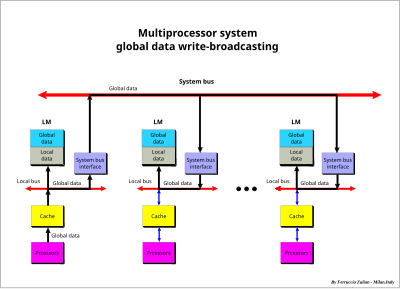
Each time the global data is modified in a local memory, a hardware write-broadcasting is sent to the system bus to all other local memories to maintain the global data coherency. Thus, global data may be read by each processor accessing its own local memory without involving the system bus. System
231:
contains multiple, but not homogeneous, processing units – central processing units (CPUs), graphics processing units (GPUs), digital signal processors (DSPs), or any type of application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs). The system architecture allows any accelerator – for instance, a graphics
291:
A cc–NUMA system is a cluster of SMP systems – each called a "node", which can have a single processor, a multi-core processor, or a mix of the two, of one or other kinds of architecture – connected via a high-speed "connection network" that can be a "link" that can be a single or double-reverse
255:
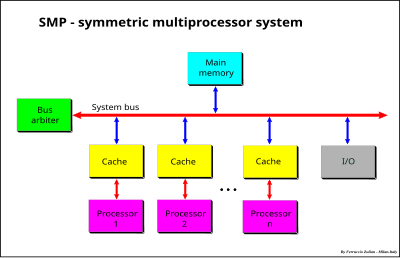
A symmetric multiprocessor system (SMP) is a system with a pool of homogeneous processors running under a single OS with a centralized, shared main memory. Each processor, executing different programs and working on different sets of data, has the ability to share common resources (memory, I/O
314:
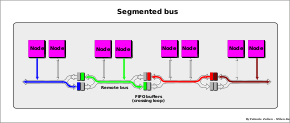
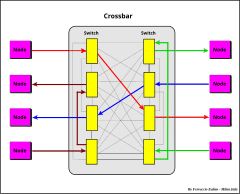
The difference in access times between local and remote memory can be also an order of magnitude, depending on the kind of connection network used (faster in segmented bus, crossbar, and point-to-point interconnection; slower in serial rings connection).
386:
This system (patented by F. Zulian ), used on the DPX/2 300 Unix based system (Bull Hn
Information Systems Italia (ex Honeywell)), is a mix of tightly and loosely coupled systems and makes use of all the advancements of these two architectures.
92:". While multiprocessing is a type of processing in which two or more processors work together to execute multiple programs simultaneously, multiprocessor refers to a hardware architecture that allows multiprocessing.
259:
Each processor has its own cache memory that acts as a bridge between the processor and main memory. The function of the cache is to alleviate the need for main-memory data access, thus reducing system-bus traffic.
382:
The common resources are accessible from all processors via the system bus, while local resources are only accessible to the local processor. Cache memories can be viewed in this perspective as local memories.
393:
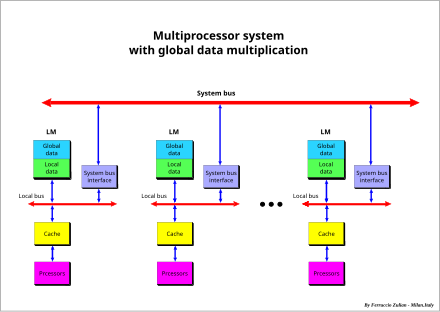
The basic concept of this architecture is to have global data, which is modifiable information, accessible by all processors. This information is duplicated and stored in each local memory of each processor.
288:
the effective "access" a processor has to the memory of a remote component subsystem, or "node", is slower compared to local memory access, which is why the memory access is "non-uniform".
82:
is defined as "a system with more than one processor", and, more precisely, "a number of central processing units linked together to enable parallel processing to take place".
379:
An intermediate approach, between those of the two previous architectures, is having common resources and local resources, such as local memories (LM), in each processor.
160:". Loosely-coupled multiprocessor systems are also known as distributed-memory systems, as the processors do not share physical memory and have individual I/O channels.
363:
Loosely-coupled architectures feature high performances of each individual processor but do not enable for easy real-time balancing of the load among processors.
95:
Multiprocessor systems are classified according to how processor memory access is handled and whether system processors are of a single type or various ones.
256:
device, interrupt system, and so on) that are connected using a system bus, a crossbar, or a mix of the two, or an address bus and data crossbar.
85:
The key objective of a multiprocessor is to boost a system's execution speed. The other objectives are fault tolerance and application matching.
398:
bus access is only required when global data is modified in a local memory to update the copy of this data stored in the other local memories.
43:
475:
370:
and distribution among processors but suffer from the bottleneck consisting in the sharing of common resources through one or more buses.
407:
228:
65:
415:
548:
191:
A symmetric multiprocessing system is a system with centralized shared memory called main memory (MM) operating under a single
674:
669:
36:
30:
367:
297:
156:. Processors exchange data over a high-speed communication network by sending messages via a technique known as "
47:
240:
140:
602:
536:
436:
351:) is normally used. With this solution, the cc-NUMA system becomes very close to a large SMP system.
589:
Bull HN F. Zulian – A. Zulian patent – Computer system with a bus having a segmented structure –
173:
578:
549:
http://www.intel.ie/content/dam/doc/white-paper/quick-path-interconnect-introduction-paper.pdf
483:
293:
497:
279:
249:
192:
169:
These systems are able to perform multiple-instructions-on-multiple-data (MIMD) programming.
153:
628:
402:
305:
157:
89:
646:
419:
Multiprocessor system with global data multiplication - global data write-broadcasting
252:) with two or more homogeneous processors and with a centralized shared main memory.
663:
390:
The local memory is divided into two sectors, global data (GD) and local data (LD).
148:
In loosely-coupled multiprocessor systems, each processor has its own local memory,
131:
Hybrid system – shared system memory for global data and local memory for local data
454:
348:
323:
149:
614:
476:"multiprocessor – Definition of multiprocessor in English by Oxford Dictionaries"
590:
515:
188:
Multiprocessor system with a shared memory closely connected to the processors.
560:
301:
271:
331:
292:
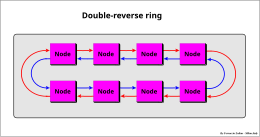
ring, or multi-ring, point-to-point connections, or a mix of these (e.g.
232:
processor – to operate at the same processing level as the system's CPU.
359:
Both architectures have trade-offs which may be summarized as follows:
311:
cc-NUMA is also called "distributed shared memory" (DSM) architecture.
603:
http://www.dba-oracle.com/real_application_clusters_rac_grid/numa.html
437:"Multiprocessor definition and meaning - Collins English Dictionary"
339:
263:
Use of shared memory allows for a uniform memory-access time (UMA).
537:
http://www.cse.wustl.edu/~roger/569M.s09/28_AMD_Hammer_MP_HC_v8.pdf
414:
406:
338:
330:
322:
296:), bus interconnection (e.g. NUMAq), "crossbar", "segmented bus" (
278:
270:
239:
139:
516:"Multiprocessor dictionary definition - multiprocessor defined"
15:
579:
http://lse.sourceforge.net/numa/faq/system_descriptions.html
401:
Local data can be exchanged in a loosely coupled system via
615:"Multiprocessor system featuring global data multiplation"
375:
Multiprocessor system featuring global data multiplication
136:
Loosely-coupled (distributed memory) multiprocessor system
88:
The term "multiprocessor" can be confused with the term "
498:"What is a Multiprocessor? - Definition from Techopedia"
547:
411:
Multiprocessor system with global data multiplication
184:
Tightly-coupled (shared memory) multiprocessor system
355:
Tightly-coupled versus loosely-coupled architecture
347:To overcome this limit, a large remote cache (see
103:There are many types of multiprocessor systems:
591:http://www.freepatentsonline.com/6314484.html
8:
366:Tightly-coupled architectures feature easy
179:The distributed memory is highly scalable.
195:with two or more homogeneous processors.
66:Learn how and when to remove this message
122:Distributed memory multiprocessor system
29:This article includes a list of general
535:AMD Opteron Shared Memory MP Systems –
428:
531:
529:
218:Symmetric multiprocessing system (SMP)
248:Systems operating under a single OS (
144:Loosely coupled multiprocessor system
110:Tightly coupled multiprocessor system
107:Loosely coupled multiprocessor system
7:
229:heterogeneous multiprocessing system
215:Heterogeneous multiprocessing system
223:Heterogeneous multiprocessor system
119:Shared memory multiprocessor system
116:Heterogeneous multiprocessor system
210:Uniform memory access (UMA) system
202:Uniform memory-access (UMA) system
125:Uniform memory access (UMA) system
35:it lacks sufficient corresponding
14:
172:This type of architecture allows
113:Homogeneous multiprocessor system
244:Symmetric multiprocessing system
198:There are two types of systems:
20:
236:Symmetric multiprocessor system
1:
480:Oxford Dictionaries - English
561:"IBM POWER Systems Overview"
319:Examples of interconnection
99:Multiprocessor system types
691:
283:cc-NUMA remote memory read
441:www.collinsdictionary.com
50:more precise citations.
651:www.feb-patrimoine.com
633:www.feb-patrimoine.com
520:www.yourdictionary.com
420:
412:
344:
336:
328:
284:
276:
245:
164:System characteristics
145:
418:
410:
342:
334:
326:
282:
274:
243:
143:
80:multiprocessor system
675:Classes of computers
601:NUMA Architecture –
486:on November 4, 2018.
327:Double-reverse ring
174:parallel processing
670:Parallel computing
565:computing.llnl.gov
421:
413:
345:
337:
329:
285:
277:
246:
150:input/output (I/O)
146:
294:IBM Power Systems
76:
75:
68:
682:
655:
654:
643:
637:
636:
625:
619:
618:
611:
605:
599:
593:
587:
581:
575:
569:
568:
557:
551:
545:
539:
533:
524:
523:
512:
506:
505:
494:
488:
487:
482:. Archived from
472:
466:
465:
459:
451:
445:
444:
433:
250:operating system
193:operating system
154:operating system
71:
64:
60:
57:
51:
46:this article by
37:inline citations
24:
23:
16:
690:
689:
685:
684:
683:
681:
680:
679:
660:
659:
658:
645:
644:
640:
629:"UNIX and Bull"
627:
626:
622:
613:
612:
608:
600:
596:
588:
584:
576:
572:
559:
558:
554:
546:
542:
534:
527:
514:
513:
509:
496:
495:
491:
474:
473:
469:
457:
453:
452:
448:
435:
434:
430:
426:
403:message-passing
377:
357:
321:
300:Bull HN ISI ex
269:
238:
225:
212:
186:
166:
158:message passing
138:
101:
90:multiprocessing
72:
61:
55:
52:
42:Please help to
41:
25:
21:
12:
11:
5:
688:
686:
678:
677:
672:
662:
661:
657:
656:
638:
620:
606:
594:
582:
577:SourceForge –
570:
552:
540:
525:
507:
502:Techopedia.com
489:
467:
446:
427:
425:
422:
376:
373:
372:
371:
368:load-balancing
364:
356:
353:
320:
317:
275:cc-NUMA system
268:
267:cc-NUMA system
265:
237:
234:
224:
221:
220:
219:
216:
211:
208:
207:
206:
203:
185:
182:
181:
180:
177:
170:
165:
162:
152:channels, and
137:
134:
133:
132:
129:
128:cc–NUMA system
126:
123:
120:
117:
114:
111:
108:
100:
97:
74:
73:
28:
26:
19:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
687:
676:
673:
671:
668:
667:
665:
652:
648:
642:
639:
634:
630:
624:
621:
616:
610:
607:
604:
598:
595:
592:
586:
583:
580:
574:
571:
566:
562:
556:
553:
550:
544:
541:
538:
532:
530:
526:
521:
517:
511:
508:
503:
499:
493:
490:
485:
481:
477:
471:
468:
463:
456:
450:
447:
442:
438:
432:
429:
423:
417:
409:
405:
404:
399:
395:
391:
388:
384:
380:
374:
369:
365:
362:
361:
360:
354:
352:
350:
341:
335:Segmented bus
333:
325:
318:
316:
312:
309:
307:
303:
299:
295:
289:
281:
273:
266:
264:
261:
257:
253:
251:
242:
235:
233:
230:
222:
217:
214:
213:
209:
204:
201:
200:
199:
196:
194:
189:
183:
178:
175:
171:
168:
167:
163:
161:
159:
155:
151:
142:
135:
130:
127:
124:
121:
118:
115:
112:
109:
106:
105:
104:
98:
96:
93:
91:
86:
83:
81:
70:
67:
59:
49:
45:
39:
38:
32:
27:
18:
17:
650:
641:
632:
623:
609:
597:
585:
573:
564:
555:
543:
519:
510:
501:
492:
484:the original
479:
470:
462:www.cs.vu.nl
461:
449:
440:
431:
400:
396:
392:
389:
385:
381:
378:
358:
349:Remote cache
346:
313:
310:
290:
286:
262:
258:
254:
247:
226:
197:
190:
187:
147:
102:
94:
87:
84:
79:
77:
62:
56:January 2019
53:
34:
306:mesh router
205:NUMA system
48:introducing
664:Categories
647:"Bull DPX"
424:References
31:references
302:Honeywell
343:Crossbar
308:", etc.
44:improve
455:"Data"
33:, but
458:(PDF)
304:,) "
298:NUMA
666::
649:.
631:.
563:.
528:^
518:.
500:.
478:.
460:.
439:.
227:A
78:A
653:.
635:.
617:.
567:.
522:.
504:.
464:.
443:.
176:.
69:)
63:(
58:)
54:(
40:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.