46:
425:
32:
405:
256:
39:
248:
239:
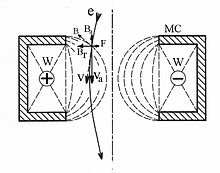
which in turn focus the electron. Note that the magnetic field is inhomogeneous, particles close to the center are less strongly deflected than those passing the lens far from the axis.
237:
210:
183:
156:
462:
377:
496:
491:
455:
481:
506:
501:
486:
448:
409:
320:
300:
251:
A deflection yoke (copper coils and white plastic former) around the rear neck of a cathode ray tube television
290:
117:
93:
315:
278:
89:
45:
373:
310:
109:
62:
50:
432:
389:
Proc. Institute of
Physics Electron Microscopy and Analysis Group Conf., Cavendish Laboratory
264:
113:
85:
215:
188:
161:
134:
369:
295:
269:
212:
causes the particle to spiral through the lens, and this spiraling expose the electron to
121:
24:
20:
344:
124:. From this configuration a customized magnetic field can be formed to manipulate the
475:
125:
78:
74:
387:
John M. Rodenburg (2–5 September 1997). "Electron microscopy and analysis 1997".
363:
274:
424:
105:
38:
104:
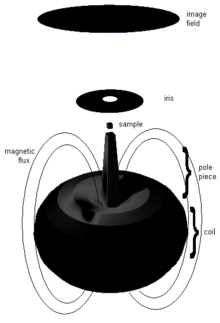
A magnetic lens typically consists of several electromagnets arranged in a
31:
404:
305:
66:
255:
254:
246:
44:
37:
30:
247:
70:
365:
Electron energy-loss spectroscopy in the electron microscope
436:
131:
The passing particle is subjected to two vector forces
84:
Magnetic lenses are used in diverse applications, from
343:
Characterization
Facility, University of Minnesota – "
341:
218:
191:
164:
137:
61:
is a device for the focusing or deflection of moving
231:
204:
177:
150:
120:are placed at the vertices of a square or another
77:. Its strength can often be varied by usage of
456:
8:
259:View inside the yoke, with the tube removed
463:
449:
53:) in the Maier-Leibnitz laboratory, Munich
223:
217:
196:
190:
169:
163:
142:
136:
332:
431:This electronics-related article is a
185:(parallel to the radius of the lens).
267:use a magnetic lens in the form of a
7:
421:
419:
435:. You can help Knowledge (XXG) by
14:
423:
403:
281:it vertically and horizontally.
273:to enable an electron beam to
49:A subtype of a magnetic lens (
1:
158:(parallel to the core), and
523:
418:
263:Television sets employing
18:
16:Lens for charged particles
73:, by use of the magnetic
321:Quadrupole mass analyzer
301:Electron beam technology
116:, or higher format; the
391:. Institute of Physics.
362:Egerton, R. F. (1996).
260:
252:
233:
206:
179:
152:
54:
42:
35:
497:Television technology
492:Electromagnetic coils
291:Charged particle beam
258:
250:
234:
232:{\displaystyle H_{Z}}
207:
205:{\displaystyle H_{R}}
180:
178:{\displaystyle H_{R}}
153:
151:{\displaystyle H_{Z}}
118:electromagnetic coils
94:particle accelerators
48:
41:
34:
412:at Wikimedia Commons
216:
189:
162:
135:
482:Accelerator physics
316:Quadrupole ion trap
90:electron microscopy
261:
253:
229:
202:
175:
148:
55:
43:
36:
507:Electronics stubs
444:
443:
408:Media related to
339:Hafner B., 2008,
311:Mass spectrometry
265:cathode ray tubes
110:quadrupole magnet
86:cathode ray tubes
63:charged particles
51:quadrupole magnet
514:
502:Types of magnets
487:Cathode ray tube
465:
458:
451:
427:
420:
407:
392:
383:
368:(2nd ed.).
348:
337:
238:
236:
235:
230:
228:
227:
211:
209:
208:
203:
201:
200:
184:
182:
181:
176:
174:
173:
157:
155:
154:
149:
147:
146:
522:
521:
517:
516:
515:
513:
512:
511:
472:
471:
470:
469:
416:
400:
395:
386:
380:
370:Springer Verlag
361:
357:
352:
351:
338:
334:
329:
296:Electron optics
287:
270:deflection yoke
245:
219:
214:
213:
192:
187:
186:
165:
160:
159:
138:
133:
132:
122:regular polygon
102:
27:
25:Strong focusing
21:Electron optics
17:
12:
11:
5:
520:
518:
510:
509:
504:
499:
494:
489:
484:
474:
473:
468:
467:
460:
453:
445:
442:
441:
428:
414:
413:
399:
398:External links
396:
394:
393:
384:
378:
358:
356:
353:
350:
349:
331:
330:
328:
325:
324:
323:
318:
313:
308:
303:
298:
293:
286:
283:
244:
241:
226:
222:
199:
195:
172:
168:
145:
141:
101:
98:
79:electromagnets
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
519:
508:
505:
503:
500:
498:
495:
493:
490:
488:
485:
483:
480:
479:
477:
466:
461:
459:
454:
452:
447:
446:
440:
438:
434:
429:
426:
422:
417:
411:
410:Magnetic lens
406:
402:
401:
397:
390:
385:
381:
379:9780306452239
375:
371:
367:
366:
360:
359:
354:
346:
342:
336:
333:
326:
322:
319:
317:
314:
312:
309:
307:
304:
302:
299:
297:
294:
292:
289:
288:
284:
282:
280:
277:the image by
276:
272:
271:
266:
257:
249:
242:
240:
224:
220:
197:
193:
170:
166:
143:
139:
129:
127:
126:particle beam
123:
119:
115:
111:
107:
99:
97:
95:
91:
87:
82:
80:
76:
75:Lorentz force
72:
68:
64:
60:
59:magnetic lens
52:
47:
40:
33:
29:
26:
22:
437:expanding it
430:
415:
388:
364:
340:
335:
268:
262:
130:
103:
83:
58:
56:
28:
476:Categories
355:References
279:deflecting
106:quadrupole
65:, such as
19:See also:
345:Reference
114:sextupole
67:electrons
306:Ion beam
285:See also
376:
100:Design
327:Notes
108:(see
88:over
433:stub
374:ISBN
275:scan
243:Uses
71:ions
23:and
112:),
92:to
69:or
478::
372:.
128:.
96:.
81:.
57:A
464:e
457:t
450:v
439:.
382:.
347:"
225:Z
221:H
198:R
194:H
171:R
167:H
144:Z
140:H
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.