468:
860:
47:
765:
690:
744:(which helps focus vision on more proximal objects) is located caudally to that, at the level of the inferior colliculus, immediately lateral to the dorsal raphe nucleus. The oculomotor nerve emerges from the nucleus by traversing the ventral width of the tegmentum, while the trochlear nerve emerges via the tectum, just below the inferior colliculus itself; the trochlear is the only cranial nerve to exit the brainstem dorsally. The
1018:
757:
570:
807:– a narrow ribbon of fibres – passes through in a relatively constant axial position; at the level of the inferior colliculus it is near the lateral edge, on the ventral side, and retains a similar position rostrally (due to widening of the tegmentum towards the rostral end, the position can appears more medial). The
115:
811:– another ribbon-like region of fibres – are located at the lateral edge of the tegmentum; at the level of the inferior colliculus it is immediately dorsal to the medial lemiscus, but due to the rostral widening of the tegmentum, is lateral of the medial lemiscus at the level of the superior colliculus.
1056:
Throughout embryonic development, the cells within the midbrain continually multiply; this happens to a much greater extent ventrally than it does dorsally. The outward expansion compresses the still-forming cerebral aqueduct, which can result in partial or total obstruction, leading to congenital
550:
Sectioning of the midbrain is usually performed axially, at one of two levels – that of the superior colliculi, or that of the inferior colliculi. One common technique for remembering the structures of the midbrain involves visualizing these cross-sections (especially at the level of the superior
906:; however, the latter term actually covers all fibres communicating with the cerebrum (usually via the diencephalon), and therefore would include much of the tegmentum as well. The remainder of the crus pedunculi – small regions around the main cortical tracts – contain tracts from the
551:
colliculi) as the upside-down face of a bear, with the cerebral peduncles forming the ears, the cerebral aqueduct the mouth, and the tectum the chin; prominent features of the tegmentum form the eyes and certain sculptural shadows of the face.
822:
emerges from the red nucleus and descends caudally, primarily heading to the cervical portion of the spine, to implement the red nuclei's decisions. The area between the red nuclei, on the ventral side – known as the
2166:
1251:
1045:– the midbrain does not develop further subdivision for the remainder of neural development. It does not split into other brain areas. while the forebrain, for example, divides into the
941:), which serve a different role from one another within the basal ganglia system. The substantia nigra has extremely high production of melanin (hence the colour), dopamine, and
1109:
plays a role in movement, movement planning, excitation, motivation and habituation of species from humans to the most elementary animals such as insects. Laboratory
818:(which have a role in motor co-ordination) – are located in the rostral portion of the midbrain, somewhat medially, at the level of the superior colliculus. The
795:
The main bulk of the tegmentum contains a complex synaptic network of neurons, primarily involved in homeostasis and reflex actions. It includes portions of the
360:
2318:
784:, which enter at the caudal end, medially, on the ventral side; the cerebellar peduncles are distinctive at the level of the inferior colliculus, where they
2094:
1599:
925:
outside the forebrain. It is ventrally wider at the rostral end. By means of the basal ganglia, the substantia nigra is involved in motor-planning,
1804:
1264:
1489:
1415:
1236:
336:
729:
in response to certain neural activity) is located at the ventral side of the periaqueductal grey, at the level of the inferior colliculus.
1146:
776:
is the portion of the midbrain ventral to the cerebral aqueduct, and is much larger in size than the tectum. It communicates with the
1306:
913:
The portion of the lobes in connection with the tegmentum, except the most lateral portion, is dominated by a blackened band – the
748:(which controls the shape of the lens and size of the pupil) is located between the oculomotor nucleus and the cerebral aqueduct.
2118:
2027:
367:
2101:
2089:
1545:
1541:"Mice selectively bred for high voluntary wheel running have larger midbrains: support for the mosaic model of brain evolution"
1129:
The term "tectal plate" or "quadrigeminal plate" is used to describe the junction of the gray and white matter in the embryo. (
467:
2143:
2058:
2010:
1762:
871:
each form a lobe ventrally of the tegmentum, on either side of the midline. Beyond the midbrain, between the lobes, is the
781:
611:, which exerts some control over alertness, takes input from the tectum, and travels both rostrally and caudally from it.
449:
The midbrain is the shortest segment of the brainstem, measuring at less than 2cm in length. It is situated mostly in the
355:
2123:
740:(which control the eyelid, and most eye movements) is located at the level of the superior colliculus, while the pair of
2313:
2186:
1592:
92:
2015:
1797:
96:
933:, and other functions. There are two regions within the substantia nigra – one where neurons are densely packed (the
618:
are four mounds, called colliculi, in two pairs – a superior and an inferior pair, on the surface of the tectum. The
1037:, while the interior of this portion of the tube becomes the cerebral aqueduct. Unlike the other two vesicles – the
2359:
1757:
1433:"The substantia nigra of the human brainII. Patterns of loss of dopamine-containing neurons in Parkinson's disease"
967:
717:. The cerebral aqueduct is a narrow channel located between the tectum and the tegmentum, and is surrounded by the
647:
2211:
1707:
1183:
1130:
981:
678:
666:; in those animals, the optic tectum integrates sensory information from the eyes and certain auditory reflexes.
393:
646:, and co-ordinates head and eye movements. Each superior colliculus also sends information to the corresponding
2194:
1749:
745:
294:
2176:
1908:
1585:
1514:
1188:
450:
31:
114:
2364:
2135:
1790:
1767:
1716:
1616:
1106:
946:
824:
343:
331:
2325:
2268:
2258:
2081:
2032:
1536:
1351:
1026:
922:
872:
677:– process certain auditory information. Each inferior colliculus sends information to the corresponding
80:
60:
859:
1268:
2263:
2204:
1833:
789:
722:
615:
608:
488:
311:
2253:
2156:
2053:
2022:
1858:
1853:
1846:
1841:
998:
895:
891:
890:
to caudal parts of the central nervous system; the central and medial ventral portions contain the
876:
808:
796:
718:
714:
689:
670:
663:
619:
564:
560:
426:
It is functionally associated with vision, hearing, motor control, sleep and wakefulness, arousal (
104:
100:
46:
1407:
764:
2106:
1971:
1942:
1406:(8th ed.). Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer/ Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Health. pp.
773:
737:
702:
651:
597:
2354:
2171:
2111:
2048:
2003:
1960:
1950:
1924:
1903:
1644:
1564:
1485:
1462:
1454:
1411:
1302:
1232:
1012:
868:
819:
741:
698:
635:
586:
540:
508:
500:
483:
416:
88:
68:
1196:
2284:
2248:
1998:
1554:
1444:
1399:
1339:
1114:
1102:
1078:
914:
907:
804:
710:
212:
206:
141:
84:
76:
2297:
1822:
1364:
1298:
1291:
945:; the loss of dopamine-producing neurons in this region contributes to the progression of
938:
898:, while the remainder of each crus primarily contains tracts connecting the cortex to the
836:
788:, but they dissipate more rostrally. Between these peduncles, on the ventral side, is the
706:
674:
454:
135:
1400:
1177:
1121:
have enlarged midbrains. The midbrain helps to relay information for vision and hearing.
1212:
Breedlove, Watson, & Rosenzweig. Biological
Psychology, 6th Edition, 2010, pp. 45-46
1878:
1734:
1608:
1321:
Collins
Dictionary of Biology, 3rd ed. © W. G. Hale, V. A. Saunders, J. P. Margham 2005
1151:
1017:
974:
639:
2348:
2292:
2240:
1724:
1695:
1331:
1118:
1086:
1058:
1046:
1030:
997:
as it passes around the peduncle. Some venous blood from the colliculi drains to the
934:
883:
832:
733:
1093:
in origin, meaning that its general architecture is shared with the most ancient of
30:
This article is about the midbrain in vertebrates. For the midbrain in insects, see
2236:
2199:
1980:
1888:
1739:
1671:
1090:
1082:
1050:
942:
848:
844:
840:
736:
are similarly located at the ventral side of the periaqueductal grey – the pair of
524:
516:
401:
324:
299:
2280:
2161:
2072:
1870:
1729:
1681:
1629:
1034:
973:
The central part of the tegmentum is supplied by the paramedian branches of the
815:
800:
785:
693:
Ventricular system anatomy showing the cerebral aqueduct, labelled centre right.
627:
72:
1535:
Kolb, E. M.; Rezende, E. L.; Holness, L.; Radtke, A.; Lee, S. K.; Obenaus, A.;
1449:
1432:
1654:
1134:
1110:
1094:
1062:
994:
777:
544:
306:
1458:
835:. The ventral tegmental area is in contact with parts of the forebrain – the
348:
17:
1666:
1639:
1157:
1074:
1042:
1038:
930:
726:
659:
654:
structure to the superior colliculus in non mammalian vertebrates including
623:
593:
532:
504:
427:
420:
397:
270:
1568:
1466:
756:
1782:
512:
1688:
1624:
1335:
1098:
926:
887:
828:
520:
474:
405:
318:
56:
1517:. National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. February 2008
1029:, the midbrain (also known as the mesencephalon) arises from the second
713:(caudally); as such it is responsible for continuing the circulation of
528:
1559:
1540:
1388:
Martin. Neuroanatomy Text and Atlas, Second edition. 1996, pp. 522-525.
631:
547:). In the rostral direction, the midbrain noticeably splays laterally.
1343:
768:
Cross-section of the midbrain at the level of the inferior colliculus.
373:
1676:
1504:
Martin. Neuroanatomy Text and Atlas, Second
Edition, 1996, pp. 35-36.
760:
Cross-section of the midbrain at the level of the superior colliculus
604:
496:
1431:
Damier, P.; Hirsch, E. C.; Agid, Y.; Graybiel, A. M. (1999-08-01).
569:
1634:
1016:
858:
763:
755:
688:
568:
466:
282:
1577:
1402:
Neuroanatomy : an atlas of structures, sections, and systems
1649:
899:
655:
643:
536:
478:
409:
64:
1786:
1581:
2167:
Rostral interstitial nucleus of medial longitudinal fasciculus
721:, which has a role in analgesia, quiescence, and bonding. The
831:-producing area in the brain, and is heavily involved in the
886:. The cerebral crus are the main tracts descending from the
251:
245:
239:
227:
221:
192:
174:
168:
156:
150:
1061:. The tectum is derived in embryonic development from the
993:
Venous blood from the midbrain is mostly drained into the
180:
630:(some fibres remain ipsilateral), and are involved with
1252:
Mosby's
Medical, Nursing & Allied Health Dictionary
1336:"Functions of the optic lobes or corpora quadrigemina"
803:
between other parts of the brain pass through it. The
119:
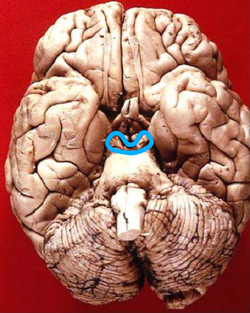
Inferior view in which the midbrain is encircled blue.
254:
242:
236:
230:
224:
215:
195:
189:
183:
171:
165:
159:
153:
144:
980:
The lateral part of the midbrain is supplied by the
962:
The midbrain is supplied by the following arteries:
248:
177:
2306:
2279:
2235:
2228:
2185:
2134:
2080:
2071:
2041:
1988:
1979:
1970:
1959:
1941:
1917:
1896:
1887:
1869:
1832:
1821:
1748:
1715:
1706:
1615:
354:
342:
330:
317:
305:
293:
281:
276:
266:
233:
218:
162:
147:
129:
124:
39:
1290:
1176:
814:A prominent pair of round, reddish, regions – the
592:The position of the tectum is contrasted with the
1254:,≈ Fourth Edition, Mosby-Year Book 1994, p. 981
902:. Older texts refer to the crus cerebri as the
863:Brain anatomy – forebrain, midbrain, hindbrain.
607:in response to visual or auditory stimuli. The
495:The principal regions of the midbrain are the
1798:
1593:
792:, which is involved in memory consolidation.
596:, which refers to the region in front of the
453:, with its superior part extending above the
8:
1073:The mesencephalon is considered part of the
585:) is the part of the midbrain dorsal to the
650:, with which it is directly connected. The
2232:
2077:
1985:
1976:
1967:
1893:
1829:
1805:
1791:
1783:
1712:
1600:
1586:
1578:
882:The majority of each lobe constitutes the
113:
45:
1558:
1448:
622:process some visual information, aid the
1168:
681:, with which it is directly connected.
638:connects the superior colliculi to the
1384:
1382:
1380:
1378:
1376:
1374:
1360:
1349:
371:
36:
1222:
1220:
1218:
27:Forward-most portion of the brainstem
7:
1208:
1206:
1197:participating institution membership
573:Principal connections of the tectum
1147:List of regions in the human brain
937:) and one where they are not (the
921:) – which is the only part of the
25:
875:, which is a cistern filled with
2028:Anterior trigeminothalamic tract
368:Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy
211:
140:
1546:Journal of Experimental Biology
430:), and temperature regulation.
2144:Rostromedial tegmental nucleus
1484:(12th ed.). p. 478.
1480:Sinnatamby, Chummy S. (2011).
1231:(12th ed.). p. 476.
1227:Sinnatamby, Chummy S. (2011).
966:The tectum is supplied by the
433:The name comes from the Greek
1:
1089:. The human mesencephalon is
1021:Mesencephalon of human embryo
782:superior cerebellar peduncles
2314:Superior cerebellar peduncle
2187:Midbrain reticular formation
1293:Principles of Neural Science
600:, or floor of the midbrain.
2016:Vestibulo-oculomotor fibers
1081:is closely associated with
732:The nuclei of two pairs of
55:) and surrounding regions;
51:Figure shows the midbrain (
2381:
1515:"Hydrocephalus Fact Sheet"
1113:from lines that have been
1010:
968:superior cerebellar artery
648:lateral geniculate nucleus
603:It is involved in certain
558:
29:
2212:Reticulotegmental nucleus
2152:
1708:Peripheral nervous system
1398:Haines, Duane E. (2012).
1184:Oxford English Dictionary
982:posterior cerebral artery
679:medial geniculate nucleus
673:– located just above the
626:of several fibres of the
515:the midbrain adjoins the
471:Brainstem (dorsal view).
366:
112:
44:
2195:dorsal tegmental nucleus
2124:Edinger–Westphal nucleus
1450:10.1093/brain/122.8.1437
1297:. McGraw-Hill. pp.
746:Edinger-Westphal nucleus
2177:Interpeduncular nucleus
1909:Central tegmental tract
1189:Oxford University Press
799:. A number of distinct
451:posterior cranial fossa
32:olfactory deutocerebrum
2136:Ventral tegmental area
1617:Central nervous system
1359:Cite journal requires
1107:ventral tegmental area
1022:
864:
825:ventral tegmental area
769:
761:
694:
632:saccadic eye movements
574:
492:
2326:Interpeduncular fossa
2269:Temporopontine fibers
2033:Dentatothalamic tract
1289:Kandel, Eric (2000).
1027:embryonic development
1020:
1011:Further information:
873:interpeduncular fossa
862:
767:
759:
709:(rostrally) with the
692:
572:
559:Further information:
470:
396:-most portion of the
61:cerebellar hemisphere
2264:Frontopontine fibers
2259:Corticopontine tract
1834:Corpora quadrigemina
1065:of the neural tube.
923:basal ganglia system
896:corticospinal tracts
833:neural reward system
790:median raphe nucleus
723:dorsal raphe nucleus
616:corpora quadrigemina
609:reticulospinal tract
2254:Corticobulbar tract
2249:Corticospinal tract
2157:Periaqueductal gray
2054:Rubro-olivary tract
2023:Spinothalamic tract
1989:Sensory / ascending
1897:Sensory / ascending
1854:Superior colliculus
1842:Inferior colliculus
1187:(Online ed.).
1117:for high voluntary
999:great cerebral vein
947:Parkinson's disease
877:cerebrospinal fluid
809:spinothalamic tract
797:reticular formation
719:periaqueductal grey
715:cerebrospinal fluid
701:is the part of the
565:Inferior colliculus
561:Superior colliculus
415:It consists of the
105:Superior colliculus
101:Inferior colliculus
2107:Oculomotor nucleus
2042:Motor / descending
1918:Motor / descending
1560:10.1242/jeb.076000
1023:
869:cerebral peduncles
865:
855:Cerebral peduncles
774:midbrain tegmentum
770:
762:
703:ventricular system
695:
671:inferior colliculi
620:superior colliculi
598:ventricular system
575:
509:cerebral peduncles
493:
417:cerebral peduncles
2360:Medical mnemonics
2342:
2341:
2338:
2337:
2334:
2333:
2224:
2223:
2220:
2219:
2172:Parabrachial area
2112:Trochlear nucleus
2067:
2066:
2049:Rubrospinal tract
1951:Cerebral aqueduct
1937:
1936:
1933:
1932:
1925:Tectospinal tract
1904:Spinotectal tract
1859:Superior brachium
1847:Inferior brachium
1780:
1779:
1776:
1775:
1491:978-0-7295-3752-0
1417:978-1-60547-653-7
1344:10.1037/12789-005
1238:978-0-7295-3752-0
1195:(Subscription or
1013:Isthmic organizer
904:cerebral peduncle
837:mammillary bodies
827:– is the largest
820:rubrospinal tract
738:oculomotor nuclei
699:cerebral aqueduct
685:Cerebral aqueduct
636:tectospinal tract
587:cerebral aqueduct
501:cerebral aqueduct
484:Medulla oblongata
382:
381:
377:
16:(Redirected from
2372:
2285:Substantia nigra
2233:
2078:
1986:
1977:
1968:
1894:
1830:
1807:
1800:
1793:
1784:
1713:
1602:
1595:
1588:
1579:
1573:
1572:
1562:
1532:
1526:
1525:
1523:
1522:
1511:
1505:
1502:
1496:
1495:
1477:
1471:
1470:
1452:
1443:(8): 1437–1448.
1428:
1422:
1421:
1405:
1395:
1389:
1386:
1369:
1368:
1362:
1357:
1355:
1347:
1328:
1322:
1319:
1313:
1312:
1296:
1286:
1280:
1279:
1277:
1276:
1267:. Archived from
1261:
1255:
1249:
1243:
1242:
1224:
1213:
1210:
1201:
1200:
1192:
1180:
1173:
1115:selectively bred
1103:substantia nigra
1101:produced in the
1085:pathways of the
1079:substantia nigra
915:substantia nigra
908:internal capsule
805:medial lemniscus
742:trochlear nuclei
725:(which releases
711:fourth ventricle
705:which links the
662:, is called the
487:7 and 8 are the
437:, "middle", and
374:edit on Wikidata
261:
260:
257:
256:
253:
250:
247:
244:
241:
238:
235:
232:
229:
226:
223:
220:
217:
210:
202:
201:
198:
197:
194:
191:
186:
185:
182:
179:
176:
173:
170:
167:
164:
161:
158:
155:
152:
149:
146:
139:
117:
77:Fourth ventricle
49:
37:
21:
2380:
2379:
2375:
2374:
2373:
2371:
2370:
2369:
2345:
2344:
2343:
2330:
2302:
2298:Pars reticulata
2275:
2216:
2181:
2148:
2130:
2063:
2037:
1963:
1955:
1929:
1913:
1883:
1865:
1825:
1817:
1813:Anatomy of the
1811:
1781:
1772:
1763:Parasympathetic
1744:
1702:
1611:
1606:
1576:
1534:
1533:
1529:
1520:
1518:
1513:
1512:
1508:
1503:
1499:
1492:
1479:
1478:
1474:
1430:
1429:
1425:
1418:
1397:
1396:
1392:
1387:
1372:
1358:
1348:
1330:
1329:
1325:
1320:
1316:
1309:
1288:
1287:
1283:
1274:
1272:
1263:
1262:
1258:
1250:
1246:
1239:
1226:
1225:
1216:
1211:
1204:
1194:
1178:"mesencephalon"
1175:
1174:
1170:
1166:
1143:
1127:
1071:
1015:
1009:
991:
989:Venous drainage
960:
958:Arterial supply
955:
939:pars reticulata
919:black substance
857:
754:
707:third ventricle
687:
675:trochlear nerve
640:cervical nerves
567:
557:
531:it adjoins the
527:, etc.), while
486:
481:
472:
465:
455:tentorial notch
447:
400:connecting the
378:
214:
205:
204:
188:
143:
134:
133:
120:
108:
35:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
2378:
2376:
2368:
2367:
2362:
2357:
2347:
2346:
2340:
2339:
2336:
2335:
2332:
2331:
2329:
2328:
2323:
2322:
2321:
2310:
2308:
2304:
2303:
2301:
2300:
2295:
2289:
2287:
2277:
2276:
2274:
2273:
2272:
2271:
2266:
2256:
2251:
2245:
2243:
2230:
2226:
2225:
2222:
2221:
2218:
2217:
2215:
2214:
2209:
2208:
2207:
2197:
2191:
2189:
2183:
2182:
2180:
2179:
2174:
2169:
2164:
2159:
2153:
2150:
2149:
2147:
2146:
2140:
2138:
2132:
2131:
2129:
2128:
2127:
2126:
2116:
2115:
2114:
2109:
2099:
2098:
2097:
2086:
2084:
2082:cranial nuclei
2075:
2069:
2068:
2065:
2064:
2062:
2061:
2059:Descending MLF
2056:
2051:
2045:
2043:
2039:
2038:
2036:
2035:
2030:
2025:
2020:
2019:
2018:
2008:
2007:
2006:
2001:
1992:
1990:
1983:
1974:
1965:
1957:
1956:
1954:
1953:
1947:
1945:
1939:
1938:
1935:
1934:
1931:
1930:
1928:
1927:
1921:
1919:
1915:
1914:
1912:
1911:
1906:
1900:
1898:
1891:
1885:
1884:
1882:
1881:
1879:Pretectal area
1875:
1873:
1867:
1866:
1864:
1863:
1862:
1861:
1851:
1850:
1849:
1838:
1836:
1827:
1819:
1818:
1812:
1810:
1809:
1802:
1795:
1787:
1778:
1777:
1774:
1773:
1771:
1770:
1765:
1760:
1754:
1752:
1746:
1745:
1743:
1742:
1737:
1735:Cranial nerves
1732:
1727:
1721:
1719:
1710:
1704:
1703:
1701:
1700:
1699:
1698:
1693:
1692:
1691:
1686:
1685:
1684:
1679:
1664:
1659:
1658:
1657:
1652:
1647:
1632:
1627:
1621:
1619:
1613:
1612:
1609:Nervous system
1607:
1605:
1604:
1597:
1590:
1582:
1575:
1574:
1553:(3): 515–523.
1527:
1506:
1497:
1490:
1482:Last's Anatomy
1472:
1423:
1416:
1390:
1370:
1361:|journal=
1332:Ferrier, David
1323:
1314:
1307:
1281:
1256:
1244:
1237:
1229:Last's Anatomy
1214:
1202:
1167:
1165:
1162:
1161:
1160:
1155:
1152:Pretectal area
1149:
1142:
1139:
1126:
1123:
1070:
1067:
1008:
1005:
990:
987:
986:
985:
978:
975:basilar artery
971:
959:
956:
954:
951:
856:
853:
753:
750:
734:cranial nerves
686:
683:
556:
553:
464:
461:
446:
443:
423:, and tectum.
380:
379:
370:
364:
363:
358:
352:
351:
346:
340:
339:
334:
328:
327:
322:
315:
314:
309:
303:
302:
297:
291:
290:
285:
279:
278:
274:
273:
268:
264:
263:
131:
127:
126:
122:
121:
118:
110:
109:
93:Posterior lobe
50:
42:
41:
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2377:
2366:
2365:Brain anatomy
2363:
2361:
2358:
2356:
2353:
2352:
2350:
2327:
2324:
2320:
2317:
2316:
2315:
2312:
2311:
2309:
2305:
2299:
2296:
2294:
2293:Pars compacta
2291:
2290:
2288:
2286:
2282:
2278:
2270:
2267:
2265:
2262:
2261:
2260:
2257:
2255:
2252:
2250:
2247:
2246:
2244:
2242:
2241:Cerebral crus
2238:
2234:
2231:
2227:
2213:
2210:
2206:
2203:
2202:
2201:
2198:
2196:
2193:
2192:
2190:
2188:
2184:
2178:
2175:
2173:
2170:
2168:
2165:
2163:
2160:
2158:
2155:
2154:
2151:
2145:
2142:
2141:
2139:
2137:
2133:
2125:
2122:
2121:
2120:
2117:
2113:
2110:
2108:
2105:
2104:
2103:
2100:
2096:
2095:Mesencephalic
2093:
2092:
2091:
2088:
2087:
2085:
2083:
2079:
2076:
2074:
2070:
2060:
2057:
2055:
2052:
2050:
2047:
2046:
2044:
2040:
2034:
2031:
2029:
2026:
2024:
2021:
2017:
2014:
2013:
2012:
2011:Ascending MLF
2009:
2005:
2002:
2000:
1997:
1996:
1994:
1993:
1991:
1987:
1984:
1982:
1978:
1975:
1973:
1969:
1966:
1962:
1958:
1952:
1949:
1948:
1946:
1944:
1940:
1926:
1923:
1922:
1920:
1916:
1910:
1907:
1905:
1902:
1901:
1899:
1895:
1892:
1890:
1886:
1880:
1877:
1876:
1874:
1872:
1868:
1860:
1857:
1856:
1855:
1852:
1848:
1845:
1844:
1843:
1840:
1839:
1837:
1835:
1831:
1828:
1824:
1820:
1816:
1808:
1803:
1801:
1796:
1794:
1789:
1788:
1785:
1769:
1766:
1764:
1761:
1759:
1756:
1755:
1753:
1751:
1747:
1741:
1738:
1736:
1733:
1731:
1728:
1726:
1725:Sensory nerve
1723:
1722:
1720:
1718:
1714:
1711:
1709:
1705:
1697:
1696:Limbic system
1694:
1690:
1687:
1683:
1680:
1678:
1675:
1674:
1673:
1670:
1669:
1668:
1665:
1663:
1660:
1656:
1653:
1651:
1648:
1646:
1643:
1642:
1641:
1638:
1637:
1636:
1633:
1631:
1628:
1626:
1623:
1622:
1620:
1618:
1614:
1610:
1603:
1598:
1596:
1591:
1589:
1584:
1583:
1580:
1570:
1566:
1561:
1556:
1552:
1548:
1547:
1542:
1538:
1531:
1528:
1516:
1510:
1507:
1501:
1498:
1493:
1487:
1483:
1476:
1473:
1468:
1464:
1460:
1456:
1451:
1446:
1442:
1438:
1434:
1427:
1424:
1419:
1413:
1409:
1404:
1403:
1394:
1391:
1385:
1383:
1381:
1379:
1377:
1375:
1371:
1366:
1353:
1345:
1341:
1337:
1333:
1327:
1324:
1318:
1315:
1310:
1308:0-8385-7701-6
1304:
1300:
1295:
1294:
1285:
1282:
1271:on 2011-04-27
1270:
1266:
1260:
1257:
1253:
1248:
1245:
1240:
1234:
1230:
1223:
1221:
1219:
1215:
1209:
1207:
1203:
1198:
1190:
1186:
1185:
1179:
1172:
1169:
1163:
1159:
1156:
1153:
1150:
1148:
1145:
1144:
1140:
1138:
1136:
1132:
1125:Related terms
1124:
1122:
1120:
1119:wheel running
1116:
1112:
1108:
1104:
1100:
1096:
1092:
1088:
1087:basal ganglia
1084:
1080:
1076:
1068:
1066:
1064:
1060:
1059:hydrocephalus
1054:
1052:
1048:
1047:telencephalon
1044:
1040:
1036:
1032:
1028:
1019:
1014:
1006:
1004:
1003:
1000:
996:
988:
983:
979:
976:
972:
969:
965:
964:
963:
957:
952:
950:
948:
944:
940:
936:
935:pars compacta
932:
928:
924:
920:
916:
911:
909:
905:
901:
897:
893:
892:corticobulbar
889:
885:
884:cerebral crus
880:
878:
874:
870:
861:
854:
852:
850:
846:
842:
838:
834:
830:
826:
821:
817:
812:
810:
806:
802:
798:
793:
791:
787:
783:
779:
775:
766:
758:
751:
749:
747:
743:
739:
735:
730:
728:
724:
720:
716:
712:
708:
704:
700:
691:
684:
682:
680:
676:
672:
667:
665:
661:
657:
653:
649:
645:
641:
637:
633:
629:
625:
621:
617:
612:
610:
606:
601:
599:
595:
591:
588:
584:
580:
571:
566:
562:
554:
552:
548:
546:
542:
538:
534:
530:
526:
522:
518:
514:
510:
506:
502:
498:
490:
485:
480:
477:B:Midbrain C:
476:
469:
462:
460:
459:
456:
452:
444:
442:
440:
436:
431:
429:
424:
422:
418:
414:
411:
407:
403:
399:
395:
391:
390:mesencephalon
387:
375:
369:
365:
362:
359:
357:
353:
350:
347:
345:
341:
338:
335:
333:
329:
326:
323:
320:
316:
313:
310:
308:
304:
301:
298:
296:
292:
289:
288:mesencephalon
286:
284:
280:
275:
272:
269:
265:
259:
208:
200:
137:
132:
130:Pronunciation
128:
123:
116:
111:
106:
102:
98:
97:Anterior lobe
94:
90:
86:
82:
78:
74:
70:
66:
62:
58:
54:
48:
43:
38:
33:
19:
18:Mesencephalon
2200:Raphe nuclei
1981:White matter
1889:White matter
1814:
1740:Spinal nerve
1672:Diencephalon
1661:
1550:
1544:
1530:
1519:. Retrieved
1509:
1500:
1481:
1475:
1440:
1436:
1426:
1401:
1393:
1352:cite journal
1326:
1317:
1292:
1284:
1273:. Retrieved
1269:the original
1259:
1247:
1228:
1182:
1171:
1128:
1091:archipallian
1083:motor system
1072:
1055:
1051:diencephalon
1024:
1002:
992:
961:
943:noradrenalin
918:
912:
903:
881:
866:
849:diencephalon
845:hypothalamus
841:Diencephalon
813:
801:nerve tracts
794:
771:
731:
696:
668:
664:optic tectum
613:
602:
590:
582:
578:
576:
549:
525:hypothalamus
517:diencephalon
494:
458:
448:
438:
434:
432:
425:
413:
402:diencephalon
389:
385:
383:
337:A14.1.03.005
325:birnlex_1667
287:
59:view of one
52:
2319:Decussation
2162:Red nucleus
2073:Grey matter
1871:Grey matter
1758:Sympathetic
1730:Motor nerve
1682:Optic nerve
1630:Spinal cord
1338:: 149–173.
1154:(Pretectum)
1095:vertebrates
1035:neural tube
1007:Development
953:Vasculature
917:(literally
628:optic nerve
624:decussation
581:(Latin for
441:, "brain".
277:Identifiers
81:Arbor vitae
73:Spinal cord
2349:Categories
1655:Cerebellum
1521:2011-03-23
1275:2011-03-05
1199:required.)
1164:References
1135:NeuroNames
1111:house mice
1063:alar plate
995:basal vein
839:(from the
816:red nuclei
778:cerebellum
660:amphibians
652:homologous
545:cerebellum
507:, and the
439:enkephalos
307:NeuroNames
1995:Lemnisci
1972:Tegmentum
1964:(Ventral)
1750:Autonomic
1667:Forebrain
1640:Hindbrain
1459:0006-8950
1265:"Slide 5"
1158:Tegmentum
1131:ancil-453
1075:brainstem
1043:hindbrain
1039:forebrain
931:addiction
786:decussate
752:Tegmentum
727:serotonin
594:tegmentum
533:hindbrain
513:Rostrally
505:tegmentum
489:colliculi
463:Structure
428:alertness
421:tegmentum
408:with the
398:brainstem
271:Brainstem
2355:Midbrain
1961:Peduncle
1826:(Dorsal)
1815:midbrain
1689:Cerebrum
1662:Midbrain
1625:Meninges
1569:23325861
1539:(2013).
1467:10430830
1334:(1886).
1141:See also
1099:Dopamine
1069:Function
1049:and the
927:learning
888:thalamus
847:(of the
829:dopamine
605:reflexes
529:caudally
521:thalamus
475:Thalamus
406:cerebrum
386:midbrain
319:NeuroLex
57:sagittal
40:Midbrain
2307:Surface
2004:Lateral
1768:Enteric
1717:Somatic
1645:Medulla
1537:Garland
1033:of the
1031:vesicle
1025:During
780:by the
642:of the
541:medulla
445:Anatomy
394:rostral
392:is the
300:D008636
267:Part of
125:Details
69:Medulla
2205:dorsal
1999:Medial
1823:Tectum
1677:Retina
1567:
1488:
1465:
1457:
1414:
1305:
1235:
1077:. Its
843:) and
634:. The
579:tectum
555:Tectum
499:, the
497:tectum
89:Tonsil
85:Nodule
2237:White
1635:Brain
1437:Brain
1193:
435:mesos
372:[
361:61993
283:Latin
103:. L:
99:. K:
95:. J:
91:. I:
87:. H:
83:. G:
79:. F:
75:. E:
71:. D:
67:. C:
63:. B:
2281:Grey
2229:Base
1650:Pons
1565:PMID
1486:ISBN
1463:PMID
1455:ISSN
1412:ISBN
1365:help
1303:ISBN
1233:ISBN
1105:and
1041:and
900:pons
894:and
867:The
772:The
697:The
669:The
658:and
656:fish
644:neck
614:The
583:roof
577:The
563:and
543:and
537:pons
479:Pons
410:pons
404:and
384:The
349:5874
332:TA98
295:MeSH
65:Pons
2119:GVE
2102:GSE
2090:GSA
1943:CSF
1555:doi
1551:216
1445:doi
1441:122
1340:doi
1299:669
1133:at
851:).
388:or
356:FMA
344:TA2
312:462
2351::
2283:/
2239:/
1563:.
1549:.
1543:.
1461:.
1453:.
1439:.
1435:.
1410:.
1408:42
1373:^
1356::
1354:}}
1350:{{
1301:.
1217:^
1205:^
1181:.
1137:)
1097:.
1053:.
949:.
929:,
910:.
879:.
539:,
523:,
511:.
503:,
482:D:
473:A:
419:,
321:ID
209::
207:US
203:,
199:-/
187:,-
138::
136:UK
1806:e
1799:t
1792:v
1601:e
1594:t
1587:v
1571:.
1557::
1524:.
1494:.
1469:.
1447::
1420:.
1367:)
1363:(
1346:.
1342::
1311:.
1278:.
1241:.
1191:.
1001:.
984:.
977:.
970:.
589:.
535:(
519:(
491:.
457:.
412:.
376:]
262:;
258:/
255:n
252:ə
249:l
246:ə
243:f
240:ɛ
237:s
234:ˈ
231:n
228:ə
225:z
222:ɛ
219:m
216:ˌ
213:/
196:f
193:ɛ
190:k
184:n
181:ɒ
178:l
175:ə
172:f
169:ɛ
166:s
163:ˈ
160:n
157:ɛ
154:s
151:ɛ
148:m
145:ˌ
142:/
107:.
53:A
34:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.