593:
743:
521:
555:
566:) at three levels of the continuous independent variable: high (one standard deviation above the mean), moderate (at the mean), and low (one standard deviation below the mean). If the scores of the continuous variable are not standardized, one can just calculate these three values by adding or subtracting one standard deviation of the original scores; if the scores of the continuous variable are standardized, one can calculate the three values as follows: high = the standardized score minus 1, moderate (mean = 0), low = the standardized score plus 1. Then one can explore the effects of gender on the dependent variable (
633:
118:
508:
ethnicity (0 = European
Americans, 1 = East Asians) and B represents the condition in the study (0 = control, 1 = experimental). Then the interaction effect shows whether the effect of condition on the dependent variable Y is different for European Americans and East Asians and whether the effect of ethnic status is different for the two conditions. The coefficient of A shows the ethnicity effect on Y for the control condition, while the coefficient of B shows the effect of imposing the experimental condition for European American participants.
110:
4183:
640:
648:
4169:
609:
586:
4207:
4195:
616:
coefficients is the difference in the dependent variable between one of the treatment groups and the mean of the reference group (or control group). This coding system is similar to ANOVA analysis, and is appropriate when researchers have a specific reference group and want to compare each of the other groups with it.
1105:
is still significant, we will be more confident in saying that there is indeed a moderation effect; however, if the interaction effect is no longer significant after adding the nonlinear term, we will be less certain about the existence of a moderation effect and the nonlinear model will be preferred
543:
is zero. However, a zero score on the
Satisfaction With Life Scale is meaningless as the range of the score is from 7 to 35. This is where centering comes in. If we subtract the mean of the SWLS score for the sample from each participant's score, the mean of the resulting centered SWLS score is zero.
623:
Contrast coding is used when one has a series of orthogonal contrasts or group comparisons that are to be investigated. In this case, the intercept is the unweighted mean of the individual group means. The unstandardized regression coefficient represents the difference between the unweighted mean of
511:
To probe if there is any significant difference between
European Americans and East Asians in the experimental condition, we can simply run the analysis with the condition variable reverse-coded (0 = experimental, 1 = control), so that the coefficient for ethnicity represents the ethnicity effect on
619:
Effects coding is used when one does not have a particular comparison or control group and does not have any planned orthogonal contrasts. The intercept is the grand mean (the mean of all the conditions). The regression coefficient is the difference between the mean of one group and the mean of all
399:
Like simple main effect analysis in ANOVA, in post-hoc probing of interactions in regression, we are examining the simple slope of one independent variable at the specific values of the other independent variable. Below is an example of probing two-way interactions. In what follows the regression
615:
Dummy coding is used when one has a reference group or one condition in particular (e.g. a control group in the experiment) that is to be compared to each of the other experimental groups. In this case, the intercept is the mean of the reference group, and each of the unstandardized regression
1357:
Schandelmaier, Stefan; Briel, Matthias; Varadhan, Ravi; Schmid, Christopher H.; Devasenapathy, Niveditha; Hayward, Rodney A.; Gagnier, Joel; Borenstein, Michael; van der
Heijden, Geert J.M.G.; Dahabreh, Issa J.; Sun, Xin; Sauerbrei, Willi; Walsh, Michael; Ioannidis, John P.A.; Thabane, Lehana
507:
If both of the independent variables are categorical variables, we can analyze the results of the regression for one independent variable at a specific level of the other independent variable. For example, suppose that both A and B are single dummy coded (0,1) variables, and that A represents
604:
When treating categorical variables such as ethnic groups and experimental treatments as independent variables in moderated regression, one needs to code the variables so that each code variable represents a specific setting of the categorical variable. There are three basic ways of coding:
1066:. In this case, low reliability of the interaction term leads to low power; therefore, we may not be able to find the interaction effects between A and B that actually exist. The solution for this problem is to use highly reliable measures for each independent variable.
624:
the means of one group (A) and the unweighted mean of another group (B), where A and B are two sets of groups in the contrast. This coding system is appropriate when researchers have an a priori hypothesis concerning the specific differences among the group means.
952:
667:. (Centering involves subtracting the overall sample mean score from the original score; standardizing does the same followed by dividing by the overall sample standard deviation.) By centering or standardizing the independent variables, the coefficient of
1288:
1096:
alone. If this is the case, it is worth testing a nonlinear regression model by adding nonlinear terms in individual variables into the moderated regression analysis to see if the interactions remain significant. If the interaction effect
698:
that are one standard deviation above and below the mean are chosen for this, but any sensible values can be used (and in some cases there are more meaningful values to choose). The plot is usually drawn by evaluating the values of
1109:
Moderated regression analyses also tend to include additional variables, which are conceptualized as covariates of no interest. However, the presence of these covariates can induce spurious effects when either (1) the covariate
302:
512:
Y in the experimental condition. In a similar vein, if we want to see whether the treatment has an effect for East Asian participants, we can reverse code the ethnicity variable (0 = East Asians, 1 = European
Americans).
592:
1894:
Hayes, A. F., & Matthes, J. (2009). "Computational procedures for probing interactions in OLS and logistic regression: SPSS and SAS implementations." Behavior
Research Methods, Vol. 41, pp. 924–936.
88:
analysis framework, a moderator is a third variable that affects the zero-order correlation between two other variables, or the value of the slope of the dependent variable on the independent variable. In
1064:
494:
577:
represents the effect of the SWLS score on the dependent variable for females. By reverse coding the gender variable, one can get the effect of the SWLS score on the dependent variable for males.
391:
Mean-centering (subtracting raw scores from the mean) may reduce multicollinearity, resulting in more interpretable regression coefficients. However, it does not affect the overall model fit.
773:
739:. A common technique for simple slope analysis is the Johnson-Neyman approach. Various internet-based tools exist to help researchers plot and interpret such two-way interactions.
1414:
Baron, R. M., & Kenny, D. A. (1986). "The moderator-mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: Conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations",
532:
If the first independent variable is a categorical variable (e.g. gender) and the second is a continuous variable (e.g. scores on the
Satisfaction With Life Scale (SWLS)), then
1140:
378:
1605:
755:
The principles for two-way interactions apply when we want to explore three-way or higher-level interactions. For instance, if we have a three-way interaction between
962:
It is worth noting that the reliability of the higher-order terms depends on the reliability of the lower-order terms. For example, if the reliability for variable
3304:
113:
Conceptual diagram of a simple moderation model in which the effect of the focal antecedent (X) on the outcome (Y) is influenced or dependent on a moderator (W).
3809:
1416:
3959:
3583:
179:
1134:. The solution is to include additional interaction terms in the model, for the interaction between each confounder and the primary variables as follows:
620:
the group means (e.g. the mean of group A minus the mean of all groups). This coding system is appropriate when the groups represent natural categories.
2224:
3357:
1360:"Development of the Instrument to assess the Credibility of Effect Modification Analyses (ICEMAN) in randomized controlled trials and meta-analyses"
3796:
380:) is calculated. However, the new interaction term may be correlated with the two main effects terms used to calculate it. This is the problem of
659:
If both of the independent variables are continuous, it is helpful for interpretation to either center or standardize the independent variables,
1482:"Centering in Multiple Regression Does Not Always Reduce Multicollinearity: How to Tell When Your Estimates Will Not Benefit From Centering"
2219:
1919:
742:
2823:
1971:
520:
81:
4211:
1771:"Gene × Environment Interaction Studies Have Not Properly Controlled for Potential Confounders: The Problem and the (Simple) Solution"
3606:
3498:
1628:
1589:
1564:
1341:
554:
632:
3784:
3658:
985:
406:
3842:
3503:
3248:
2619:
2209:
2833:
3893:
3105:
2912:
2801:
2759:
1998:
46:) occurs when the relationship between two variables depends on a third variable. The third variable is referred to as the
4136:
3095:
3145:
947:{\displaystyle Y=b_{0}+b_{1}A+b_{2}B+b_{3}C+b_{4}A\cdot B+b_{5}A\cdot C+b_{6}B\cdot C+b_{7}A\cdot B\cdot C+\varepsilon .}
4233:
3687:
3636:
3621:
3611:
3480:
3352:
3319:
3100:
2930:
3756:
3057:
4031:
3832:
2811:
2480:
1944:
1643:
Dawson, J. F. (2013). Moderation in management research: What, why, when and how. Journal of
Business and Psychology.
1092:; consequently what appears to be a significant moderation effect might actually be a significant nonlinear effect of
3916:
3883:
562:
Cohen et al. (2003) recommended using the following to probe the simple effect of gender on the dependent variable (
117:
3888:
3631:
3390:
3296:
3276:
3184:
2895:
2713:
2196:
2068:
3062:
2828:
2686:
109:
3648:
3416:
3137:
2991:
2920:
2840:
2698:
2679:
2387:
2108:
3761:
4131:
3898:
3446:
3411:
3375:
3160:
2602:
2511:
2470:
2382:
2073:
1912:
732:
652:
340:
98:
94:
63:
3168:
3152:
605:
dummy-variable coding, effects coding, and contrast coding. Below is an introduction to these coding systems.
4040:
3653:
3593:
3530:
2890:
2752:
2742:
2592:
2506:
675:
can be interpreted as the effect of that variable on Y at the mean level of the other independent variable.
3801:
3738:
639:
551:
now represents the difference between males and females at the mean level of the SWLS score of the sample.
4078:
4008:
3493:
3380:
2377:
2274:
2181:
2060:
1959:
77:
4199:
3077:
4103:
4045:
3988:
3814:
3707:
3616:
3342:
3226:
3085:
2967:
2959:
2774:
2670:
2648:
2607:
2572:
2539:
2485:
2460:
2415:
2354:
2314:
2116:
1939:
1299:
1086:
4182:
3072:
647:
558:
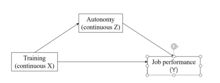
An example of conceptual moderation model with one categorical and one continuous independent variable.
570:) at high, moderate, and low levels of the SWLS score. As with two categorical independent variables,
4026:
3601:
3550:
3526:
3488:
3406:
3385:
3337:
3216:
3194:
3163:
2949:
2900:
2818:
2791:
2747:
2703:
2465:
2241:
2121:
90:
73:
69:
1851:"Moderator Variables in Personality Research: The Problem of Controlling for Plausible Alternatives"
4173:
4098:
4021:
3702:
3466:
3459:
3421:
3329:
3309:
3281:
3014:
2880:
2875:
2865:
2857:
2675:
2636:
2526:
2516:
2425:
2204:
2160:
2078:
2003:
1905:
1820:"Adjusting researchers' approach to adjustment: On the use of covariates when testing interactions"
1283:{\displaystyle Y=b_{0}+b_{1}A+b_{2}B+b_{3}C+b_{4}A\cdot B+b_{5}A\cdot C+b_{6}B\cdot C+\varepsilon }
384:
in moderated regression. Multicollinearity tends to cause coefficients to be estimated with higher
126:
35:
3748:
723:. Sometimes this is supplemented by simple slope analysis, which determines whether the effect of
4187:
3998:
3852:
3697:
3573:
3470:
3454:
3431:
3208:
2942:
2925:
2885:
2796:
2691:
2653:
2624:
2584:
2544:
2490:
2407:
2093:
2088:
1878:
1819:
1698:
1599:
746:
A conceptual diagram of a moderated moderation model, otherwise known as a three-way interaction.
1732:"Analysis of multiplicative combination rules when the causal variables are measured with error"
346:
1731:
4093:
4063:
4055:
3875:
3866:
3791:
3722:
3578:
3563:
3538:
3426:
3367:
3233:
3221:
2847:
2764:
2708:
2631:
2475:
2397:
2176:
2050:
1870:
1800:
1751:
1690:
1682:
1624:
1585:
1560:
1519:
1501:
1462:
1454:
1397:
1379:
1337:
540:
381:
334:
322:
137:. To quantify the effect of a moderating variable in multiple regression analyses, regressing
130:
1538:
1431:
Iacobucci, Dawn; Schneider, Matthew J.; Popovich, Deidre L.; Bakamitsos, Georgios A. (2016).
4118:
4073:
3837:
3824:
3717:
3692:
3626:
3558:
3436:
3044:
2937:
2870:
2783:
2730:
2549:
2420:
2214:
2013:
1980:
1862:
1831:
1790:
1782:
1743:
1674:
1644:
1509:
1493:
1444:
1387:
1371:
134:
1850:
4035:
3779:
3641:
3568:
3243:
3117:
3090:
3067:
3036:
2663:
2658:
2612:
2342:
1993:
138:
325:
for discussion of statistical evaluation of parameter estimates in regression analyses.
3984:
3979:
2442:
2372:
2018:
1795:
1770:
1514:
1481:
1392:
1359:
1329:
585:
385:
4227:
4141:
4108:
3971:
3932:
3743:
3712:
3176:
3130:
2735:
2437:
2264:
2028:
2023:
1882:
1122:), or (2) when the covariate itself is a moderator of the correlation between either
297:{\displaystyle Y=b_{0}+b_{1}x_{1}+b_{2}x_{2}+b_{3}(x_{1}\times x_{2})+\varepsilon \,}
2294:
1702:
4083:
4016:
3993:
3908:
3238:
2534:
2432:
2367:
2309:
2231:
2186:
1786:
608:
539:
represents the difference in the dependent variable between males and females when
101:
variable and a factor that specifies the appropriate conditions for its operation.
148:, an additional term is added to the model. This term is the interaction between
17:
4126:
4088:
3771:
3672:
3534:
3347:
3314:
2806:
2723:
2718:
2362:
2319:
2299:
2279:
2269:
2038:
85:
1835:
1747:
1584:(1. paperback print. ed.). Newbury Park, Calif. : Sage Publications, Inc.
80:
that is associated with the direction and/or magnitude of the relation between
2972:
2452:
2152:
2083:
2033:
2008:
1928:
1648:
1449:
1432:
1069:
Another caveat for interpreting the interaction effects is that when variable
31:
1874:
1866:
1755:
1686:
1505:
1497:
1458:
1383:
1114:) is correlated with one of the primary variables of interest (e.g. variable
3125:
2977:
2597:
2392:
2304:
2289:
2284:
2249:
1621:
Applied multiple regression/correlation analysis for the behavioral sciences
1557:
Applied multiple regression/correlation analysis for the behavioral sciences
1334:
Applied multiple regression/correlation analysis for the behavioral sciences
62:). The effect of a moderating variable is characterized statistically as an
1804:
1716:
1694:
1523:
1466:
1401:
678:
To probe the interaction effect, it is often helpful to plot the effect of
1433:"Mean centering helps alleviate "micro" but not "macro" multicollinearity"
2641:
2259:
2136:
2131:
2126:
2098:
1375:
4146:
3847:
1678:
4068:
3049:
3023:
3003:
2254:
2045:
1662:
1619:
Cohen Jacob; Cohen
Patricia; West Stephen G.; Aiken Leona S. (2003).
974: = 0.2, then the reliability for the interaction variable
1539:"Testing and Interpreting Interactions in Regression-In a Nutshell"
741:
690:(some people prefer to also plot the effect at moderate values of
646:
638:
631:
607:
591:
584:
553:
519:
400:
equation with two variables A and B and an interaction term A*B,
116:
108:
1818:
Yzerbyt, Vincent Y.; Muller, Dominique; Judd, Charles M. (2004).
93:(ANOVA) terms, a basic moderator effect can be represented as an
1988:
3957:
3524:
3271:
2570:
2340:
1957:
1901:
600:
with three levels, as a multi-categorical independent variable.
1897:
1555:
Cohen Jacob; Cohen
Patricia; West Stephen G.; Aiken Leona S.
643:
A conceptual diagram of an additive multiple moderation model
1059:{\displaystyle ((0.7\times 0.8)+0.2^{2})/(1+0.2^{2})=0.577}
596:
A statistical diagram that depicts a moderation model with
524:
A statistical diagram that depicts a moderation model with
489:{\displaystyle Y=b_{0}+b_{1}A+b_{2}B+b_{3}A*B+\varepsilon }
1663:"The Johnson-Neyman technique, its theory and application"
1849:
Hull, Jay G.; Tedlie, Judith C.; Lehn, Daniel A. (1992).
321:, the parameter estimate for the interaction term. See
1623:(3. ed.). Mahwah, NJ : Erlbaum. pp. 302–353.
1559:(3. ed.). Mahwah, NJ : Erlbaum. pp. 255–301.
516:
One categorical and one continuous independent variable
314:
as a moderating variable is accomplished by evaluating
1143:
988:
776:
409:
349:
182:
3810:
Autoregressive conditional heteroskedasticity (ARCH)
711:, and creating two lines to represent the effect of
4117:
4054:
4007:
3970:
3925:
3907:
3874:
3865:
3823:
3770:
3731:
3680:
3671:
3592:
3549:
3479:
3445:
3399:
3366:
3328:
3295:
3207:
3116:
3035:
2990:
2958:
2911:
2856:
2782:
2773:
2583:
2525:
2499:
2451:
2406:
2353:
2240:
2195:
2169:
2151:
2107:
2059:
1979:
1970:
121:
A statistical diagram of a simple moderation model.
1282:
1058:
946:
488:
372:
296:
1730:Busemeyer, Jerome R.; Jones, Lawrence E. (1983).
3358:Multivariate adaptive regression splines (MARS)
1480:Olvera Astivia, Oscar L.; Kroc, Edward (2019).
1661:Johnson, Palmer O.; Fay, Leo C. (1950-12-01).
1582:Multiple regression testing and interpretation
767:, the regression equation will be as follows:
694:, but this is not necessary). Often values of
1913:
8:
1604:: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (
1417:Journal of Personality and Social Psychology
528:as a multicategorical independent variable.
3967:
3954:
3871:
3677:
3546:
3521:
3292:
3268:
2996:
2779:
2580:
2567:
2350:
2337:
1976:
1967:
1954:
1920:
1906:
1898:
1855:Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin
1824:Journal of Experimental Social Psychology
1794:
1513:
1486:Educational and Psychological Measurement
1448:
1391:
1336:. Hillsdale, N.J: L. Erlbaum Associates.
1259:
1237:
1215:
1199:
1183:
1167:
1154:
1142:
1041:
1023:
1014:
987:
914:
892:
870:
848:
832:
816:
800:
787:
775:
465:
449:
433:
420:
408:
364:
354:
348:
329:Multicollinearity in moderated regression
293:
278:
265:
252:
239:
229:
216:
206:
193:
181:
1085:term will be highly correlated with the
339:In moderated regression analysis, a new
1323:
1321:
1319:
1317:
1315:
1311:
3884:Kaplan–Meier estimator (product limit)
1597:
966:is 0.70, the reliability for variable
152:and the proposed moderating variable.
503:Two categorical independent variables
7:
4194:
3894:Accelerated failure time (AFT) model
1364:Canadian Medical Association Journal
628:Two continuous independent variables
4206:
3489:Analysis of variance (ANOVA, anova)
131:linear multiple regression analysis
82:dependent and independent variables
3584:Cochran–Mantel–Haenszel statistics
2210:Pearson product-moment correlation
1717:"Interpreting interaction effects"
970:is 0.80, and their correlation is
25:
1106:because it is more parsimonious.
72:(e.g., sex, ethnicity, class) or
4205:
4193:
4181:
4168:
4167:
1580:Aiken L.S., West., S.G. (1996).
1077:are highly correlated, then the
703:for high and low values of both
544:When the analysis is run again,
395:Post-hoc probing of interactions
3843:Least-squares spectral analysis
1328:Cohen, Jacob; Cohen, Patricia;
388:and hence greater uncertainty.
2824:Mean-unbiased minimum-variance
1787:10.1016/j.biopsych.2013.09.006
1047:
1028:
1020:
1004:
992:
989:
581:Coding in moderated regression
284:
258:
1:
4137:Geographic information system
3353:Simultaneous equations models
958:Spurious higher-order effects
735:at particular values of
76:(e.g., age, level of reward)
3320:Coefficient of determination
2931:Uniformly most powerful test
1421:5 (6), 1173–1182 (page 1174)
3889:Proportional hazards models
3833:Spectral density estimation
3815:Vector autoregression (VAR)
3249:Maximum posterior estimator
2481:Randomized controlled trial
1769:Keller, Matthew C. (2014).
1332:; West, Stephen H. (2003).
125:Moderation analysis in the
4250:
3649:Multivariate distributions
2069:Average absolute deviation
1836:10.1016/j.jesp.2003.10.001
1748:10.1037/0033-2909.93.3.549
686:at low and high values of
373:{\displaystyle x_{1}x_{2}}
332:
307:In this case, the role of
4163:
3966:
3953:
3637:Structural equation model
3545:
3520:
3291:
3267:
2999:
2973:Score/Lagrange multiplier
2579:
2566:
2388:Sample size determination
2349:
2336:
1966:
1953:
1935:
1649:10.1007/s10869-013-9308-7
1450:10.3758/s13428-015-0624-x
1437:Behavior Research Methods
751:Higher-level interactions
733:statistically significant
84:. Specifically within a
4132:Environmental statistics
3654:Elliptical distributions
3447:Generalized linear model
3376:Simple linear regression
3146:Hodges–Lehmann estimator
2603:Probability distribution
2512:Stochastic approximation
2074:Coefficient of variation
1867:10.1177/0146167292182001
1498:10.1177/0013164418817801
651:An example of a two-way
166:and moderating variable
3792:Cross-correlation (XCF)
3400:Non-standard predictors
2834:Lehmann–Scheffé theorem
2507:Adaptive clinical trial
4188:Mathematics portal
4009:Engineering statistics
3917:Nelson–Aalen estimator
3494:Analysis of covariance
3381:Ordinary least squares
3305:Pearson product-moment
2709:Statistical functional
2620:Empirical distribution
2453:Controlled experiments
2182:Frequency distribution
1960:Descriptive statistics
1736:Psychological Bulletin
1284:
1060:
948:
747:
656:
644:
636:
612:
601:
589:
559:
529:
490:
374:
298:
122:
114:
4104:Population statistics
4046:System identification
3780:Autocorrelation (ACF)
3708:Exponential smoothing
3622:Discriminant analysis
3617:Canonical correlation
3481:Partition of variance
3343:Regression validation
3187:(Jonckheere–Terpstra)
3086:Likelihood-ratio test
2775:Frequentist inference
2687:Location–scale family
2608:Sampling distribution
2573:Statistical inference
2540:Cross-sectional study
2527:Observational studies
2486:Randomized experiment
2315:Stem-and-leaf display
2117:Central limit theorem
1775:Biological Psychiatry
1300:Omitted-variable bias
1285:
1061:
949:
745:
719:at the two values of
650:
642:
635:
611:
595:
588:
557:
523:
491:
375:
333:Further information:
299:
155:Thus, for a response
120:
112:
4027:Probabilistic design
3612:Principal components
3455:Exponential families
3407:Nonlinear regression
3386:General linear model
3348:Mixed effects models
3338:Errors and residuals
3315:Confounding variable
3217:Bayesian probability
3195:Van der Waerden test
3185:Ordered alternative
2950:Multiple comparisons
2829:Rao–Blackwellization
2792:Estimating equations
2748:Statistical distance
2466:Factorial experiment
1999:Arithmetic-Geometric
1141:
986:
774:
499:will be considered.
407:
347:
180:
129:involves the use of
91:analysis of variance
4234:Regression analysis
4099:Official statistics
4022:Methods engineering
3703:Seasonal adjustment
3471:Poisson regressions
3391:Bayesian regression
3330:Regression analysis
3310:Partial correlation
3282:Regression analysis
2881:Prediction interval
2876:Likelihood interval
2866:Confidence interval
2858:Interval estimation
2819:Unbiased estimators
2637:Model specification
2517:Up-and-down designs
2205:Partial correlation
2161:Index of dispersion
2079:Interquartile range
1376:10.1503/cmaj.200077
127:behavioral sciences
44:effect modification
36:regression analysis
4119:Spatial statistics
3999:Medical statistics
3899:First hitting time
3853:Whittle likelihood
3504:Degrees of freedom
3499:Multivariate ANOVA
3432:Heteroscedasticity
3244:Bayesian estimator
3209:Bayesian inference
3058:Kolmogorov–Smirnov
2943:Randomization test
2913:Testing hypotheses
2886:Tolerance interval
2797:Maximum likelihood
2692:Exponential family
2625:Density estimation
2585:Statistical theory
2545:Natural experiment
2491:Scientific control
2408:Survey methodology
2094:Standard deviation
1679:10.1007/BF02288864
1280:
1056:
944:
748:
657:
653:interaction effect
645:
637:
613:
602:
590:
560:
530:
486:
370:
294:
159:and two variables
123:
115:
48:moderator variable
27:Statistics concept
18:Moderator variable
4221:
4220:
4159:
4158:
4155:
4154:
4094:National accounts
4064:Actuarial science
4056:Social statistics
3949:
3948:
3945:
3944:
3941:
3940:
3876:Survival function
3861:
3860:
3723:Granger causality
3564:Contingency table
3539:Survival analysis
3516:
3515:
3512:
3511:
3368:Linear regression
3263:
3262:
3259:
3258:
3234:Credible interval
3203:
3202:
2986:
2985:
2802:Method of moments
2671:Parametric family
2632:Statistical model
2562:
2561:
2558:
2557:
2476:Random assignment
2398:Statistical power
2332:
2331:
2328:
2327:
2177:Contingency table
2147:
2146:
2014:Generalized/power
1370:(32): E901–E906.
541:life satisfaction
382:multicollinearity
335:Multicollinearity
323:linear regression
16:(Redirected from
4241:
4209:
4208:
4197:
4196:
4186:
4185:
4171:
4170:
4074:Crime statistics
3968:
3955:
3872:
3838:Fourier analysis
3825:Frequency domain
3805:
3752:
3718:Structural break
3678:
3627:Cluster analysis
3574:Log-linear model
3547:
3522:
3463:
3437:Homoscedasticity
3293:
3269:
3188:
3180:
3172:
3171:(Kruskal–Wallis)
3156:
3141:
3096:Cross validation
3081:
3063:Anderson–Darling
3010:
2997:
2968:Likelihood-ratio
2960:Parametric tests
2938:Permutation test
2921:1- & 2-tails
2812:Minimum distance
2784:Point estimation
2780:
2731:Optimal decision
2682:
2581:
2568:
2550:Quasi-experiment
2500:Adaptive designs
2351:
2338:
2215:Rank correlation
1977:
1968:
1955:
1922:
1915:
1908:
1899:
1887:
1886:
1846:
1840:
1839:
1815:
1809:
1808:
1798:
1766:
1760:
1759:
1727:
1721:
1720:
1713:
1707:
1706:
1658:
1652:
1641:
1635:
1634:
1616:
1610:
1609:
1603:
1595:
1577:
1571:
1570:
1552:
1546:
1545:
1543:
1534:
1528:
1527:
1517:
1477:
1471:
1470:
1452:
1443:(4): 1308–1317.
1428:
1422:
1412:
1406:
1405:
1395:
1354:
1348:
1347:
1325:
1289:
1287:
1286:
1281:
1264:
1263:
1242:
1241:
1220:
1219:
1204:
1203:
1188:
1187:
1172:
1171:
1159:
1158:
1087:omitted variable
1065:
1063:
1062:
1057:
1046:
1045:
1027:
1019:
1018:
953:
951:
950:
945:
919:
918:
897:
896:
875:
874:
853:
852:
837:
836:
821:
820:
805:
804:
792:
791:
495:
493:
492:
487:
470:
469:
454:
453:
438:
437:
425:
424:
379:
377:
376:
371:
369:
368:
359:
358:
303:
301:
300:
295:
283:
282:
270:
269:
257:
256:
244:
243:
234:
233:
221:
220:
211:
210:
198:
197:
135:causal modelling
97:between a focal
54:) or simply the
21:
4249:
4248:
4244:
4243:
4242:
4240:
4239:
4238:
4224:
4223:
4222:
4217:
4180:
4151:
4113:
4050:
4036:quality control
4003:
3985:Clinical trials
3962:
3937:
3921:
3909:Hazard function
3903:
3857:
3819:
3803:
3766:
3762:Breusch–Godfrey
3750:
3727:
3667:
3642:Factor analysis
3588:
3569:Graphical model
3541:
3508:
3475:
3461:
3441:
3395:
3362:
3324:
3287:
3286:
3255:
3199:
3186:
3178:
3170:
3154:
3139:
3118:Rank statistics
3112:
3091:Model selection
3079:
3037:Goodness of fit
3031:
3008:
2982:
2954:
2907:
2852:
2841:Median unbiased
2769:
2680:
2613:Order statistic
2575:
2554:
2521:
2495:
2447:
2402:
2345:
2343:Data collection
2324:
2236:
2191:
2165:
2143:
2103:
2055:
1972:Continuous data
1962:
1949:
1931:
1926:
1891:
1890:
1848:
1847:
1843:
1817:
1816:
1812:
1768:
1767:
1763:
1729:
1728:
1724:
1715:
1714:
1710:
1660:
1659:
1655:
1642:
1638:
1631:
1618:
1617:
1613:
1596:
1592:
1579:
1578:
1574:
1567:
1554:
1553:
1549:
1541:
1536:
1535:
1531:
1479:
1478:
1474:
1430:
1429:
1425:
1413:
1409:
1356:
1355:
1351:
1344:
1327:
1326:
1313:
1308:
1296:
1255:
1233:
1211:
1195:
1179:
1163:
1150:
1139:
1138:
1037:
1010:
984:
983:
960:
910:
888:
866:
844:
828:
812:
796:
783:
772:
771:
753:
630:
583:
576:
550:
538:
518:
505:
461:
445:
429:
416:
405:
404:
397:
386:standard errors
360:
350:
345:
344:
337:
331:
320:
313:
274:
261:
248:
235:
225:
212:
202:
189:
178:
177:
172:
165:
139:random variable
107:
52:effect modifier
42:(also known as
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
4247:
4245:
4237:
4236:
4226:
4225:
4219:
4218:
4216:
4215:
4203:
4191:
4177:
4164:
4161:
4160:
4157:
4156:
4153:
4152:
4150:
4149:
4144:
4139:
4134:
4129:
4123:
4121:
4115:
4114:
4112:
4111:
4106:
4101:
4096:
4091:
4086:
4081:
4076:
4071:
4066:
4060:
4058:
4052:
4051:
4049:
4048:
4043:
4038:
4029:
4024:
4019:
4013:
4011:
4005:
4004:
4002:
4001:
3996:
3991:
3982:
3980:Bioinformatics
3976:
3974:
3964:
3963:
3958:
3951:
3950:
3947:
3946:
3943:
3942:
3939:
3938:
3936:
3935:
3929:
3927:
3923:
3922:
3920:
3919:
3913:
3911:
3905:
3904:
3902:
3901:
3896:
3891:
3886:
3880:
3878:
3869:
3863:
3862:
3859:
3858:
3856:
3855:
3850:
3845:
3840:
3835:
3829:
3827:
3821:
3820:
3818:
3817:
3812:
3807:
3799:
3794:
3789:
3788:
3787:
3785:partial (PACF)
3776:
3774:
3768:
3767:
3765:
3764:
3759:
3754:
3746:
3741:
3735:
3733:
3732:Specific tests
3729:
3728:
3726:
3725:
3720:
3715:
3710:
3705:
3700:
3695:
3690:
3684:
3682:
3675:
3669:
3668:
3666:
3665:
3664:
3663:
3662:
3661:
3646:
3645:
3644:
3634:
3632:Classification
3629:
3624:
3619:
3614:
3609:
3604:
3598:
3596:
3590:
3589:
3587:
3586:
3581:
3579:McNemar's test
3576:
3571:
3566:
3561:
3555:
3553:
3543:
3542:
3525:
3518:
3517:
3514:
3513:
3510:
3509:
3507:
3506:
3501:
3496:
3491:
3485:
3483:
3477:
3476:
3474:
3473:
3457:
3451:
3449:
3443:
3442:
3440:
3439:
3434:
3429:
3424:
3419:
3417:Semiparametric
3414:
3409:
3403:
3401:
3397:
3396:
3394:
3393:
3388:
3383:
3378:
3372:
3370:
3364:
3363:
3361:
3360:
3355:
3350:
3345:
3340:
3334:
3332:
3326:
3325:
3323:
3322:
3317:
3312:
3307:
3301:
3299:
3289:
3288:
3285:
3284:
3279:
3273:
3272:
3265:
3264:
3261:
3260:
3257:
3256:
3254:
3253:
3252:
3251:
3241:
3236:
3231:
3230:
3229:
3224:
3213:
3211:
3205:
3204:
3201:
3200:
3198:
3197:
3192:
3191:
3190:
3182:
3174:
3158:
3155:(Mann–Whitney)
3150:
3149:
3148:
3135:
3134:
3133:
3122:
3120:
3114:
3113:
3111:
3110:
3109:
3108:
3103:
3098:
3088:
3083:
3080:(Shapiro–Wilk)
3075:
3070:
3065:
3060:
3055:
3047:
3041:
3039:
3033:
3032:
3030:
3029:
3021:
3012:
3000:
2994:
2992:Specific tests
2988:
2987:
2984:
2983:
2981:
2980:
2975:
2970:
2964:
2962:
2956:
2955:
2953:
2952:
2947:
2946:
2945:
2935:
2934:
2933:
2923:
2917:
2915:
2909:
2908:
2906:
2905:
2904:
2903:
2898:
2888:
2883:
2878:
2873:
2868:
2862:
2860:
2854:
2853:
2851:
2850:
2845:
2844:
2843:
2838:
2837:
2836:
2831:
2816:
2815:
2814:
2809:
2804:
2799:
2788:
2786:
2777:
2771:
2770:
2768:
2767:
2762:
2757:
2756:
2755:
2745:
2740:
2739:
2738:
2728:
2727:
2726:
2721:
2716:
2706:
2701:
2696:
2695:
2694:
2689:
2684:
2668:
2667:
2666:
2661:
2656:
2646:
2645:
2644:
2639:
2629:
2628:
2627:
2617:
2616:
2615:
2605:
2600:
2595:
2589:
2587:
2577:
2576:
2571:
2564:
2563:
2560:
2559:
2556:
2555:
2553:
2552:
2547:
2542:
2537:
2531:
2529:
2523:
2522:
2520:
2519:
2514:
2509:
2503:
2501:
2497:
2496:
2494:
2493:
2488:
2483:
2478:
2473:
2468:
2463:
2457:
2455:
2449:
2448:
2446:
2445:
2443:Standard error
2440:
2435:
2430:
2429:
2428:
2423:
2412:
2410:
2404:
2403:
2401:
2400:
2395:
2390:
2385:
2380:
2375:
2373:Optimal design
2370:
2365:
2359:
2357:
2347:
2346:
2341:
2334:
2333:
2330:
2329:
2326:
2325:
2323:
2322:
2317:
2312:
2307:
2302:
2297:
2292:
2287:
2282:
2277:
2272:
2267:
2262:
2257:
2252:
2246:
2244:
2238:
2237:
2235:
2234:
2229:
2228:
2227:
2222:
2212:
2207:
2201:
2199:
2193:
2192:
2190:
2189:
2184:
2179:
2173:
2171:
2170:Summary tables
2167:
2166:
2164:
2163:
2157:
2155:
2149:
2148:
2145:
2144:
2142:
2141:
2140:
2139:
2134:
2129:
2119:
2113:
2111:
2105:
2104:
2102:
2101:
2096:
2091:
2086:
2081:
2076:
2071:
2065:
2063:
2057:
2056:
2054:
2053:
2048:
2043:
2042:
2041:
2036:
2031:
2026:
2021:
2016:
2011:
2006:
2004:Contraharmonic
2001:
1996:
1985:
1983:
1974:
1964:
1963:
1958:
1951:
1950:
1948:
1947:
1942:
1936:
1933:
1932:
1927:
1925:
1924:
1917:
1910:
1902:
1896:
1895:
1889:
1888:
1861:(2): 115–117.
1841:
1830:(3): 424–431.
1810:
1761:
1742:(3): 549–562.
1722:
1708:
1673:(4): 349–367.
1653:
1636:
1629:
1611:
1590:
1572:
1565:
1547:
1537:Taylor, Alan.
1529:
1492:(5): 813–826.
1472:
1423:
1407:
1358:(2020-08-10).
1349:
1342:
1330:Leona S. Aiken
1310:
1309:
1307:
1304:
1303:
1302:
1295:
1292:
1291:
1290:
1279:
1276:
1273:
1270:
1267:
1262:
1258:
1254:
1251:
1248:
1245:
1240:
1236:
1232:
1229:
1226:
1223:
1218:
1214:
1210:
1207:
1202:
1198:
1194:
1191:
1186:
1182:
1178:
1175:
1170:
1166:
1162:
1157:
1153:
1149:
1146:
1055:
1052:
1049:
1044:
1040:
1036:
1033:
1030:
1026:
1022:
1017:
1013:
1009:
1006:
1003:
1000:
997:
994:
991:
959:
956:
955:
954:
943:
940:
937:
934:
931:
928:
925:
922:
917:
913:
909:
906:
903:
900:
895:
891:
887:
884:
881:
878:
873:
869:
865:
862:
859:
856:
851:
847:
843:
840:
835:
831:
827:
824:
819:
815:
811:
808:
803:
799:
795:
790:
786:
782:
779:
752:
749:
629:
626:
582:
579:
574:
548:
536:
517:
514:
504:
501:
497:
496:
485:
482:
479:
476:
473:
468:
464:
460:
457:
452:
448:
444:
441:
436:
432:
428:
423:
419:
415:
412:
396:
393:
367:
363:
357:
353:
330:
327:
318:
311:
305:
304:
292:
289:
286:
281:
277:
273:
268:
264:
260:
255:
251:
247:
242:
238:
232:
228:
224:
219:
215:
209:
205:
201:
196:
192:
188:
185:
170:
163:
106:
103:
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
4246:
4235:
4232:
4231:
4229:
4214:
4213:
4204:
4202:
4201:
4192:
4190:
4189:
4184:
4178:
4176:
4175:
4166:
4165:
4162:
4148:
4145:
4143:
4142:Geostatistics
4140:
4138:
4135:
4133:
4130:
4128:
4125:
4124:
4122:
4120:
4116:
4110:
4109:Psychometrics
4107:
4105:
4102:
4100:
4097:
4095:
4092:
4090:
4087:
4085:
4082:
4080:
4077:
4075:
4072:
4070:
4067:
4065:
4062:
4061:
4059:
4057:
4053:
4047:
4044:
4042:
4039:
4037:
4033:
4030:
4028:
4025:
4023:
4020:
4018:
4015:
4014:
4012:
4010:
4006:
4000:
3997:
3995:
3992:
3990:
3986:
3983:
3981:
3978:
3977:
3975:
3973:
3972:Biostatistics
3969:
3965:
3961:
3956:
3952:
3934:
3933:Log-rank test
3931:
3930:
3928:
3924:
3918:
3915:
3914:
3912:
3910:
3906:
3900:
3897:
3895:
3892:
3890:
3887:
3885:
3882:
3881:
3879:
3877:
3873:
3870:
3868:
3864:
3854:
3851:
3849:
3846:
3844:
3841:
3839:
3836:
3834:
3831:
3830:
3828:
3826:
3822:
3816:
3813:
3811:
3808:
3806:
3804:(Box–Jenkins)
3800:
3798:
3795:
3793:
3790:
3786:
3783:
3782:
3781:
3778:
3777:
3775:
3773:
3769:
3763:
3760:
3758:
3757:Durbin–Watson
3755:
3753:
3747:
3745:
3742:
3740:
3739:Dickey–Fuller
3737:
3736:
3734:
3730:
3724:
3721:
3719:
3716:
3714:
3713:Cointegration
3711:
3709:
3706:
3704:
3701:
3699:
3696:
3694:
3691:
3689:
3688:Decomposition
3686:
3685:
3683:
3679:
3676:
3674:
3670:
3660:
3657:
3656:
3655:
3652:
3651:
3650:
3647:
3643:
3640:
3639:
3638:
3635:
3633:
3630:
3628:
3625:
3623:
3620:
3618:
3615:
3613:
3610:
3608:
3605:
3603:
3600:
3599:
3597:
3595:
3591:
3585:
3582:
3580:
3577:
3575:
3572:
3570:
3567:
3565:
3562:
3560:
3559:Cohen's kappa
3557:
3556:
3554:
3552:
3548:
3544:
3540:
3536:
3532:
3528:
3523:
3519:
3505:
3502:
3500:
3497:
3495:
3492:
3490:
3487:
3486:
3484:
3482:
3478:
3472:
3468:
3464:
3458:
3456:
3453:
3452:
3450:
3448:
3444:
3438:
3435:
3433:
3430:
3428:
3425:
3423:
3420:
3418:
3415:
3413:
3412:Nonparametric
3410:
3408:
3405:
3404:
3402:
3398:
3392:
3389:
3387:
3384:
3382:
3379:
3377:
3374:
3373:
3371:
3369:
3365:
3359:
3356:
3354:
3351:
3349:
3346:
3344:
3341:
3339:
3336:
3335:
3333:
3331:
3327:
3321:
3318:
3316:
3313:
3311:
3308:
3306:
3303:
3302:
3300:
3298:
3294:
3290:
3283:
3280:
3278:
3275:
3274:
3270:
3266:
3250:
3247:
3246:
3245:
3242:
3240:
3237:
3235:
3232:
3228:
3225:
3223:
3220:
3219:
3218:
3215:
3214:
3212:
3210:
3206:
3196:
3193:
3189:
3183:
3181:
3175:
3173:
3167:
3166:
3165:
3162:
3161:Nonparametric
3159:
3157:
3151:
3147:
3144:
3143:
3142:
3136:
3132:
3131:Sample median
3129:
3128:
3127:
3124:
3123:
3121:
3119:
3115:
3107:
3104:
3102:
3099:
3097:
3094:
3093:
3092:
3089:
3087:
3084:
3082:
3076:
3074:
3071:
3069:
3066:
3064:
3061:
3059:
3056:
3054:
3052:
3048:
3046:
3043:
3042:
3040:
3038:
3034:
3028:
3026:
3022:
3020:
3018:
3013:
3011:
3006:
3002:
3001:
2998:
2995:
2993:
2989:
2979:
2976:
2974:
2971:
2969:
2966:
2965:
2963:
2961:
2957:
2951:
2948:
2944:
2941:
2940:
2939:
2936:
2932:
2929:
2928:
2927:
2924:
2922:
2919:
2918:
2916:
2914:
2910:
2902:
2899:
2897:
2894:
2893:
2892:
2889:
2887:
2884:
2882:
2879:
2877:
2874:
2872:
2869:
2867:
2864:
2863:
2861:
2859:
2855:
2849:
2846:
2842:
2839:
2835:
2832:
2830:
2827:
2826:
2825:
2822:
2821:
2820:
2817:
2813:
2810:
2808:
2805:
2803:
2800:
2798:
2795:
2794:
2793:
2790:
2789:
2787:
2785:
2781:
2778:
2776:
2772:
2766:
2763:
2761:
2758:
2754:
2751:
2750:
2749:
2746:
2744:
2741:
2737:
2736:loss function
2734:
2733:
2732:
2729:
2725:
2722:
2720:
2717:
2715:
2712:
2711:
2710:
2707:
2705:
2702:
2700:
2697:
2693:
2690:
2688:
2685:
2683:
2677:
2674:
2673:
2672:
2669:
2665:
2662:
2660:
2657:
2655:
2652:
2651:
2650:
2647:
2643:
2640:
2638:
2635:
2634:
2633:
2630:
2626:
2623:
2622:
2621:
2618:
2614:
2611:
2610:
2609:
2606:
2604:
2601:
2599:
2596:
2594:
2591:
2590:
2588:
2586:
2582:
2578:
2574:
2569:
2565:
2551:
2548:
2546:
2543:
2541:
2538:
2536:
2533:
2532:
2530:
2528:
2524:
2518:
2515:
2513:
2510:
2508:
2505:
2504:
2502:
2498:
2492:
2489:
2487:
2484:
2482:
2479:
2477:
2474:
2472:
2469:
2467:
2464:
2462:
2459:
2458:
2456:
2454:
2450:
2444:
2441:
2439:
2438:Questionnaire
2436:
2434:
2431:
2427:
2424:
2422:
2419:
2418:
2417:
2414:
2413:
2411:
2409:
2405:
2399:
2396:
2394:
2391:
2389:
2386:
2384:
2381:
2379:
2376:
2374:
2371:
2369:
2366:
2364:
2361:
2360:
2358:
2356:
2352:
2348:
2344:
2339:
2335:
2321:
2318:
2316:
2313:
2311:
2308:
2306:
2303:
2301:
2298:
2296:
2293:
2291:
2288:
2286:
2283:
2281:
2278:
2276:
2273:
2271:
2268:
2266:
2265:Control chart
2263:
2261:
2258:
2256:
2253:
2251:
2248:
2247:
2245:
2243:
2239:
2233:
2230:
2226:
2223:
2221:
2218:
2217:
2216:
2213:
2211:
2208:
2206:
2203:
2202:
2200:
2198:
2194:
2188:
2185:
2183:
2180:
2178:
2175:
2174:
2172:
2168:
2162:
2159:
2158:
2156:
2154:
2150:
2138:
2135:
2133:
2130:
2128:
2125:
2124:
2123:
2120:
2118:
2115:
2114:
2112:
2110:
2106:
2100:
2097:
2095:
2092:
2090:
2087:
2085:
2082:
2080:
2077:
2075:
2072:
2070:
2067:
2066:
2064:
2062:
2058:
2052:
2049:
2047:
2044:
2040:
2037:
2035:
2032:
2030:
2027:
2025:
2022:
2020:
2017:
2015:
2012:
2010:
2007:
2005:
2002:
2000:
1997:
1995:
1992:
1991:
1990:
1987:
1986:
1984:
1982:
1978:
1975:
1973:
1969:
1965:
1961:
1956:
1952:
1946:
1943:
1941:
1938:
1937:
1934:
1930:
1923:
1918:
1916:
1911:
1909:
1904:
1903:
1900:
1893:
1892:
1884:
1880:
1876:
1872:
1868:
1864:
1860:
1856:
1852:
1845:
1842:
1837:
1833:
1829:
1825:
1821:
1814:
1811:
1806:
1802:
1797:
1792:
1788:
1784:
1780:
1776:
1772:
1765:
1762:
1757:
1753:
1749:
1745:
1741:
1737:
1733:
1726:
1723:
1718:
1712:
1709:
1704:
1700:
1696:
1692:
1688:
1684:
1680:
1676:
1672:
1668:
1667:Psychometrika
1664:
1657:
1654:
1650:
1646:
1640:
1637:
1632:
1630:0-8058-2223-2
1626:
1622:
1615:
1612:
1607:
1601:
1593:
1591:0-7619-0712-2
1587:
1583:
1576:
1573:
1568:
1566:0-8058-2223-2
1562:
1558:
1551:
1548:
1540:
1533:
1530:
1525:
1521:
1516:
1511:
1507:
1503:
1499:
1495:
1491:
1487:
1483:
1476:
1473:
1468:
1464:
1460:
1456:
1451:
1446:
1442:
1438:
1434:
1427:
1424:
1420:
1418:
1411:
1408:
1403:
1399:
1394:
1389:
1385:
1381:
1377:
1373:
1369:
1365:
1361:
1353:
1350:
1345:
1343:0-8058-2223-2
1339:
1335:
1331:
1324:
1322:
1320:
1318:
1316:
1312:
1305:
1301:
1298:
1297:
1293:
1277:
1274:
1271:
1268:
1265:
1260:
1256:
1252:
1249:
1246:
1243:
1238:
1234:
1230:
1227:
1224:
1221:
1216:
1212:
1208:
1205:
1200:
1196:
1192:
1189:
1184:
1180:
1176:
1173:
1168:
1164:
1160:
1155:
1151:
1147:
1144:
1137:
1136:
1135:
1133:
1129:
1125:
1121:
1117:
1113:
1107:
1104:
1100:
1095:
1091:
1088:
1084:
1081: *
1080:
1076:
1073:and variable
1072:
1067:
1053:
1050:
1042:
1038:
1034:
1031:
1024:
1015:
1011:
1007:
1001:
998:
995:
981:
978: *
977:
973:
969:
965:
957:
941:
938:
935:
932:
929:
926:
923:
920:
915:
911:
907:
904:
901:
898:
893:
889:
885:
882:
879:
876:
871:
867:
863:
860:
857:
854:
849:
845:
841:
838:
833:
829:
825:
822:
817:
813:
809:
806:
801:
797:
793:
788:
784:
780:
777:
770:
769:
768:
766:
762:
758:
750:
744:
740:
738:
734:
730:
726:
722:
718:
714:
710:
706:
702:
697:
693:
689:
685:
681:
676:
674:
670:
666:
662:
654:
649:
641:
634:
627:
625:
621:
617:
610:
606:
599:
594:
587:
580:
578:
573:
569:
565:
556:
552:
547:
542:
535:
527:
522:
515:
513:
509:
502:
500:
483:
480:
477:
474:
471:
466:
462:
458:
455:
450:
446:
442:
439:
434:
430:
426:
421:
417:
413:
410:
403:
402:
401:
394:
392:
389:
387:
383:
365:
361:
355:
351:
342:
336:
328:
326:
324:
317:
310:
290:
287:
279:
275:
271:
266:
262:
253:
249:
245:
240:
236:
230:
226:
222:
217:
213:
207:
203:
199:
194:
190:
186:
183:
176:
175:
174:
169:
162:
158:
153:
151:
147:
143:
140:
136:
132:
128:
119:
111:
104:
102:
100:
96:
92:
87:
86:correlational
83:
79:
75:
71:
68:; that is, a
67:
66:
61:
57:
53:
49:
45:
41:
37:
33:
19:
4210:
4198:
4179:
4172:
4084:Econometrics
4034: /
4017:Chemometrics
3994:Epidemiology
3987: /
3960:Applications
3802:ARIMA model
3749:Q-statistic
3698:Stationarity
3594:Multivariate
3537: /
3533: /
3531:Multivariate
3529: /
3469: /
3465: /
3239:Bayes factor
3138:Signed rank
3050:
3024:
3016:
3004:
2699:Completeness
2535:Cohort study
2433:Opinion poll
2368:Missing data
2355:Study design
2310:Scatter plot
2232:Scatter plot
2225:Spearman's ρ
2187:Grouped data
1858:
1854:
1844:
1827:
1823:
1813:
1781:(1): 18–24.
1778:
1774:
1764:
1739:
1735:
1725:
1711:
1670:
1666:
1656:
1639:
1620:
1614:
1581:
1575:
1556:
1550:
1532:
1489:
1485:
1475:
1440:
1436:
1426:
1415:
1410:
1367:
1363:
1352:
1333:
1131:
1127:
1123:
1119:
1115:
1111:
1108:
1102:
1098:
1093:
1089:
1082:
1078:
1074:
1070:
1068:
979:
975:
971:
967:
963:
961:
764:
760:
756:
754:
736:
728:
724:
720:
716:
712:
708:
704:
700:
695:
691:
687:
683:
679:
677:
672:
668:
664:
660:
658:
622:
618:
614:
603:
597:
571:
567:
563:
561:
545:
533:
531:
525:
510:
506:
498:
398:
390:
338:
315:
308:
306:
167:
160:
156:
154:
149:
145:
141:
124:
64:
59:
55:
51:
47:
43:
39:
29:
4212:WikiProject
4127:Cartography
4089:Jurimetrics
4041:Reliability
3772:Time domain
3751:(Ljung–Box)
3673:Time-series
3551:Categorical
3535:Time-series
3527:Categorical
3462:(Bernoulli)
3297:Correlation
3277:Correlation
3073:Jarque–Bera
3045:Chi-squared
2807:M-estimator
2760:Asymptotics
2704:Sufficiency
2471:Interaction
2383:Replication
2363:Effect size
2320:Violin plot
2300:Radar chart
2280:Forest plot
2270:Correlogram
2220:Kendall's τ
343:predictor (
341:interaction
99:independent
95:interaction
70:categorical
65:interaction
4079:Demography
3797:ARMA model
3602:Regression
3179:(Friedman)
3140:(Wilcoxon)
3078:Normality
3068:Lilliefors
3015:Student's
2891:Resampling
2765:Robustness
2753:divergence
2743:Efficiency
2681:(monotone)
2676:Likelihood
2593:Population
2426:Stratified
2378:Population
2197:Dependence
2153:Count data
2084:Percentile
2061:Dispersion
1994:Arithmetic
1929:Statistics
1306:References
74:continuous
40:moderation
32:statistics
3460:Logistic
3227:posterior
3153:Rank sum
2901:Jackknife
2896:Bootstrap
2714:Bootstrap
2649:Parameter
2598:Statistic
2393:Statistic
2305:Run chart
2290:Pie chart
2285:Histogram
2275:Fan chart
2250:Bar chart
2132:L-moments
2019:Geometric
1883:145366173
1875:0146-1672
1756:1939-1455
1687:1860-0980
1600:cite book
1506:0013-1644
1459:1554-3528
1384:0820-3946
1278:ε
1269:⋅
1247:⋅
1225:⋅
999:×
939:ε
930:⋅
924:⋅
902:⋅
880:⋅
858:⋅
484:ε
475:∗
291:ε
272:×
56:moderator
4228:Category
4174:Category
3867:Survival
3744:Johansen
3467:Binomial
3422:Isotonic
3009:(normal)
2654:location
2461:Blocking
2416:Sampling
2295:Q–Q plot
2260:Box plot
2242:Graphics
2137:Skewness
2127:Kurtosis
2099:Variance
2029:Heronian
2024:Harmonic
1805:24135711
1703:43748836
1695:14797902
1524:31488914
1467:26148824
1402:32778601
1294:See also
78:variable
60:modifier
4200:Commons
4147:Kriging
4032:Process
3989:studies
3848:Wavelet
3681:General
2848:Plug-in
2642:L space
2421:Cluster
2122:Moments
1940:Outline
1796:3859520
1515:6713984
1393:7829020
105:Example
4069:Census
3659:Normal
3607:Manova
3427:Robust
3177:2-way
3169:1-way
3007:-test
2678:
2255:Biplot
2046:Median
2039:Lehmer
1981:Center
1881:
1873:
1803:
1793:
1754:
1701:
1693:
1685:
1627:
1588:
1563:
1522:
1512:
1504:
1465:
1457:
1400:
1390:
1382:
1340:
763:, and
3693:Trend
3222:prior
3164:anova
3053:-test
3027:-test
3019:-test
2926:Power
2871:Pivot
2664:shape
2659:scale
2109:Shape
2089:Range
2034:Heinz
2009:Cubic
1945:Index
1879:S2CID
1699:S2CID
1542:(PDF)
1130:with
1054:0.577
3926:Test
3126:Sign
2978:Wald
2051:Mode
1989:Mean
1871:ISSN
1801:PMID
1752:ISSN
1691:PMID
1683:ISSN
1625:ISBN
1606:link
1586:ISBN
1561:ISBN
1520:PMID
1502:ISSN
1463:PMID
1455:ISSN
1398:PMID
1380:ISSN
1338:ISBN
707:and
663:and
655:plot
58:(or
50:(or
34:and
3106:BIC
3101:AIC
1863:doi
1832:doi
1791:PMC
1783:doi
1744:doi
1675:doi
1645:doi
1510:PMC
1494:doi
1445:doi
1388:PMC
1372:doi
1368:192
1126:or
1118:or
1039:0.2
1012:0.2
1002:0.8
996:0.7
982:is
731:is
727:on
715:on
682:on
671:or
173:,:
144:on
133:or
30:In
4230::
1877:.
1869:.
1859:18
1857:.
1853:.
1828:40
1826:.
1822:.
1799:.
1789:.
1779:75
1777:.
1773:.
1750:.
1740:93
1738:.
1734:.
1697:.
1689:.
1681:.
1671:15
1669:.
1665:.
1602:}}
1598:{{
1518:.
1508:.
1500:.
1490:79
1488:.
1484:.
1461:.
1453:.
1441:48
1439:.
1435:.
1396:.
1386:.
1378:.
1366:.
1362:.
1314:^
759:,
38:,
3051:G
3025:F
3017:t
3005:Z
2724:V
2719:U
1921:e
1914:t
1907:v
1885:.
1865::
1838:.
1834::
1807:.
1785::
1758:.
1746::
1719:.
1705:.
1677::
1651:.
1647::
1633:.
1608:)
1594:.
1569:.
1544:.
1526:.
1496::
1469:.
1447::
1419:,
1404:.
1374::
1346:.
1275:+
1272:C
1266:B
1261:6
1257:b
1253:+
1250:C
1244:A
1239:5
1235:b
1231:+
1228:B
1222:A
1217:4
1213:b
1209:+
1206:C
1201:3
1197:b
1193:+
1190:B
1185:2
1181:b
1177:+
1174:A
1169:1
1165:b
1161:+
1156:0
1152:b
1148:=
1145:Y
1132:Y
1128:B
1124:A
1120:B
1116:A
1112:C
1110:(
1103:B
1101:*
1099:A
1094:A
1090:A
1083:B
1079:A
1075:B
1071:A
1051:=
1048:)
1043:2
1035:+
1032:1
1029:(
1025:/
1021:)
1016:2
1008:+
1005:)
993:(
990:(
980:B
976:A
972:r
968:B
964:A
942:.
936:+
933:C
927:B
921:A
916:7
912:b
908:+
905:C
899:B
894:6
890:b
886:+
883:C
877:A
872:5
868:b
864:+
861:B
855:A
850:4
846:b
842:+
839:C
834:3
830:b
826:+
823:B
818:2
814:b
810:+
807:A
802:1
798:b
794:+
789:0
785:b
781:=
778:Y
765:C
761:B
757:A
737:Z
729:Y
725:X
721:Z
717:Y
713:X
709:Z
705:X
701:Y
696:Z
692:Z
688:Z
684:Y
680:X
673:Z
669:X
665:Z
661:X
598:W
575:2
572:b
568:Y
564:Y
549:1
546:b
537:1
534:b
526:X
481:+
478:B
472:A
467:3
463:b
459:+
456:B
451:2
447:b
443:+
440:A
435:1
431:b
427:+
422:0
418:b
414:=
411:Y
366:2
362:x
356:1
352:x
319:3
316:b
312:2
309:x
288:+
285:)
280:2
276:x
267:1
263:x
259:(
254:3
250:b
246:+
241:2
237:x
231:2
227:b
223:+
218:1
214:x
208:1
204:b
200:+
195:0
191:b
187:=
184:Y
171:2
168:x
164:1
161:x
157:Y
150:X
146:X
142:Y
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.