407:
157:, to spatially separate the colors of light. It usually has a mechanism for directing the selected color to an exit slit. Usually the grating or the prism is used in a reflective mode. A reflective prism is made by making a right triangle prism (typically, half of an equilateral prism) with one side mirrored. The light enters through the hypotenuse face and is reflected back through it, being refracted twice at the same surface. The total refraction, and the total dispersion, is the same as would occur if an equilateral prism were used in transmission mode.
232:
224:
22:
30:
304:) contains the entire image of the entrance slit of the selected color plus parts of the entrance slit images of nearby colors. A rotation of the dispersing element causes the band of colors to move relative to the exit slit, so that the desired entrance slit image is centered on the exit slit. The range of colors leaving the exit slit is a function of the width of the slits. The entrance and exit slit widths are adjusted together.
98:
177:. In a practical monochromator, however, the light source is close by, and an optical system in the monochromator converts the diverging light of the source to collimated light. Although some monochromator designs do use focusing gratings that do not need separate collimators, most use collimating mirrors. Reflective optics are preferred because they do not introduce dispersive effects of their own.
377:
a master grating is a long, expensive process because the grooves must be of identical size, exactly parallel, and equally spaced over the length of the grating (3–10 cm). A grating for the ultraviolet and visible region typically has 300–2000 grooves/mm, however 1200–1400 grooves/mm is most common. For the infrared region, gratings usually have 10–200 grooves/mm. When a
240:
368:
cutoff about one millionth of the peak value, the product of the two cutoffs of the individual sections. The intensity of the light of other colors in the exit beam is referred to as the stray light level and is the most critical specification of a monochromator for many uses. Achieving low stray light is a large part of the art of making a practical monochromator.
712:
492:. This configuration allows the simultaneous analysis of the intensities of a wide band of colors. Photographic film or an array of photodetectors can be used, for instance to collect the light. Such an instrument can record a spectral function without mechanical scanning, although there may be tradeoffs in terms of resolution or sensitivity for instance.
428:
might have a focal length of 2 meters. Building such monochromators requires exceptional attention to mechanical and thermal stability. For many applications a monochromator of about 0.4 meters' focal length is considered to have excellent resolution. Many monochromators have a focal length less than 0.1 meters.
507:
Absorption spectrophotometers have many everyday uses in chemistry, biochemistry, and biology. For example, they are used to measure the concentration or change in concentration of many substances that absorb light. Critical characteristics of many biological materials, many enzymes for instance, are
427:
The narrowness of the band of colors that a monochromator can generate is related to the focal length of the monochromator collimators. Using a longer focal length optical system also unfortunately decreases the amount of light that can be accepted from the source. Very high resolution monochromators
389:
was a large undertaking (as well as exceedingly difficult, in past decades), and good gratings were very expensive. The slope of the triangular groove in a ruled grating is typically adjusted to enhance the brightness of a particular diffraction order. This is called blazing a grating. Ruled gratings
381:
is used, care must be taken in the design of broadband monochromators because the diffraction pattern has overlapping orders. Sometimes broadband preselector filters are inserted in the optical path to limit the width of the diffraction orders so they do not overlap. Sometimes this is done by using a
376:
Grating monochromators disperse ultraviolet, visible, and infrared radiation typically using replica gratings, which are manufactured from a master grating. A master grating consists of a hard, optically flat, surface that has a large number of parallel and closely spaced grooves. The construction of
367:
It is common for two monochromators to be connected in series, with their mechanical systems operating in tandem so that they both select the same color. This arrangement is not intended to improve the narrowness of the spectrum, but rather to lower the cutoff level. A double monochromator may have a
342:
The dispersion of a monochromator is characterized as the width of the band of colors per unit of slit width, 1 nm of spectrum per mm of slit width for instance. This factor is constant for a grating, but varies with wavelength for a prism. If a scanning prism monochromator is used in a constant
299:
At the exit slit, the colors of the light are spread out (in the visible this shows the colors of the rainbow). Because each color arrives at a separate point in the exit-slit plane, there are a series of images of the entrance slit focused on the plane. Because the entrance slit is finite in width,
445:
Monochromators are often calibrated in units of wavelength. Uniform rotation of a grating produces a sinusoidal change in wavelength, which is approximately linear for small grating angles, so such an instrument is easy to build. Many of the underlying physical phenomena being studied are linear in
113:
A device that can produce monochromatic light has many uses in science and in optics because many optical characteristics of a material are dependent on wavelength. Although there are a number of useful ways to select a narrow band of wavelengths (which, in the visible range, is perceived as a pure
540:
Monochromatic light allows for the measurement of the quantum efficiency (QE) of an imaging device (e.g. CCD or CMOS imager). Light from the exit slit is passed either through diffusers or an integrating sphere on to the imaging device while a calibrated detector simultaneously measures the light.
500:
relates the absorption of light to the concentration of the light-absorbing material, the optical path length, and an intrinsic property of the material called molar absorptivity. According to this relation the decrease in intensity is exponential in concentration and path length. The decrease is
312:
The ideal transfer function of such a monochromator is a triangular shape. The peak of the triangle is at the nominal wavelength selected, so that the image of the selected wavelength completely fills the exit slit. The intensity of the nearby colors then decreases linearly on either side of this
557:
that emit light generated by atoms of a specific element, for instance iron or lead or calcium. The available colors are fixed, but are very monochromatic and are excellent for measuring the concentration of specific elements in a sample. These instruments behave as if they contained a very high
476:
Monochromators are used in many optical measuring instruments and in other applications where tunable monochromatic light is wanted. Sometimes the monochromatic light is directed at a sample and the reflected or transmitted light is measured. Sometimes white light is directed at a sample and the
436:
The most common optical system uses spherical collimators and thus contains optical aberrations that curve the field where the slit images come to focus, so that slits are sometimes curved instead of simply straight, to approximate the curvature of the image. This allows taller slits to be used,
418:
region. Prism monochromators are favored in some instruments that are principally designed to work in the far UV region. Most monochromators use gratings, however. Some monochromators have several gratings that can be selected for use in different spectral regions. A double monochromator made by
508:
measured by starting a chemical reaction that produces a color change that depends on the presence or activity of the material being studied. Optical thermometers have been created by calibrating the change in absorbance of a material against temperature. There are many other examples.
501:
linear in these quantities when the inverse logarithm of transmission is used. The old nomenclature for this value was optical density (OD), current nomenclature is absorbance units (AU). One AU is a tenfold reduction in light intensity. Six AU is a millionfold reduction.
260:). The amount of light energy available for use depends on the intensity of the source in the space defined by the slit (width × height) and the acceptance angle of the optical system. The slit is placed at the effective focus of a curved mirror (the
526:
In the UV, visible and near IR, absorbance and reflectance spectrophotometers usually illuminate the sample with monochromatic light. In the corresponding IR instruments, the monochromator is usually used to analyze the light coming from the sample.
334:, abbreviated as FWHM). A typical spectral bandwidth might be one nanometer; however, different values can be chosen to meet the need of analysis. A narrower bandwidth does improve the resolution, but it also decreases the signal-to-noise ratio.
495:
An absorption spectrophotometer measures the absorption of light by a sample as a function of wavelength. Sometimes the result is expressed as percent transmission and sometimes it is expressed as the inverse logarithm of the transmission. The
437:
gathering more light, while still achieving high spectral resolution. Some designs take another approach and use toroidal collimating mirrors to correct the curvature instead, allowing higher straight slits without sacrificing resolution.
390:
have imperfections that produce faint "ghost" diffraction orders that may raise the stray light level of a monochromator. A later photolithographic technique allows gratings to be created from a holographic interference pattern.
450:
have a reciprocal relationship, spectral patterns that are simple and predictable when plotted as a function of energy are distorted when plotted as a function of wavelength. Some monochromators are calibrated in units of
467:
built with a high quality double monochromator can produce light of sufficient purity and intensity that the instrument can measure a narrow band of optical attenuation of about one million fold (6 AU, Absorbance Units).
484:
An automatic scanning spectrometer includes a mechanism to change the wavelength selected by the monochromator and to record the resulting changes in the measured quantity as a function of the wavelength.
694:
Lodish H, Berk A, Zipursky SL, et al. Molecular Cell
Biology. 4th edition. New York: W. H. Freeman; 2000. Section 3.5, Purifying, Detecting, and Characterizing Proteins. Available from:
537:
Lasers produce light which is much more monochromatic than the optical monochromators discussed here, but only some lasers are easily tunable, and these lasers are not as simple to use.
394:
have sinusoidal grooves and so are not as bright, but have lower scattered light levels than blazed gratings. Almost all the gratings actually used in monochromators are carefully made
530:
Monochromators are also used in optical instruments that measure other phenomena besides simple absorption or reflection, wherever the color of the light is a significant variable.
541:
Coordination of the imager, calibrated detector, and monochromator allows one to calculate the carriers (electrons or holes) generated for a photon of a given wavelength, QE.
504:
Absorption spectrophotometers often contain a monochromator to supply light to the sample. Some absorption spectrophotometers have automatic spectral analysis capabilities.
406:
102:
343:
bandwidth mode, the slit width must change as the wavelength changes. Dispersion depends on the focal length, the grating order and grating resolving power.
109:
in
Australia. It is made by slabs of oriented Germanium crystals which are inclined towards each other in order to focus down the Bragg reflected beam.
106:
169:, that is if all the rays of light are parallel, or practically so. A source, like the sun, which is very far away, provides collimated light.
679:
419:
placing a prism and a grating monochromator in series typically does not need additional bandpass filters to isolate a single grating order.
202:
481:; one monochromator is used to select the excitation wavelength and a second monochromator is used to analyze the emitted light.
562:
550:
268:) so that the light from the slit reflected from the mirror is collimated (focused at infinity). The collimated light is
410:
The internal structure of a
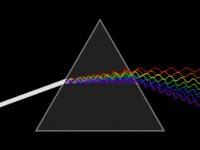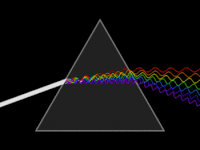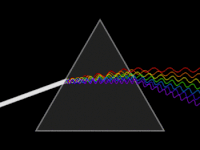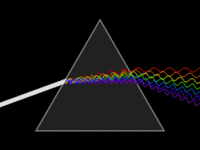
Reflecting monochromator using a single prism.The yellow line indicates the path of light.
42:
519:
of colored objects. They are used to characterize the performance of sunglasses, laser protective glasses, and other
243:
A Littrow grating monochromator. This is similar to the Czerny–Turner but uses a common collimator/refocusing mirror.
359:(IR) spectra, although monochromators are built for a great variety of optical ranges, and to a great many designs.
331:
351:
A monochromator's adjustment range might cover the visible spectrum and some part of both or either of the nearby
716:
185:
There are grating/prism configurations that offer different tradeoffs between simplicity and spectral accuracy.
757:
589:– a technique for producing "monochromatic" electron beams, where all the electrons have nearly the same energy
565:
IR, or FTIR, does not use a monochromator. Instead, the measurement is performed in the time domain, using the
231:
577:
566:
192:
21:
330:
is defined as the width of the triangle at the points where the light has reached half the maximum value (
207:
38:
477:
monochromator is used to analyze the reflected or transmitted light. Two monochromators are used in many
762:
130:
497:
212:
619:
114:
color), there are not as many other ways to easily select any wavelength band from a wide range. See
217:
197:
722:
554:
512:
395:
391:
378:
273:
154:
313:
peak until some cutoff value is reached, where the intensity stops decreasing. This is called the
635:
531:
516:
327:
142:
729:
558:
quality monochromator, but their use is limited to analyzing the elements they are equipped for.
671:
385:
The original high-resolution diffraction gratings were ruled. The construction of high-quality
675:
464:
223:
126:
663:
627:
581:
261:
29:
16:
Optical device which allows selection of a narrow band of wavelengths from a wider spectrum
744:- contains an extended discussion of the design rationale of this UV-VIS-NIR monochromator
607:
520:
386:
249:
623:
488:
If an imaging device replaces the exit slit, the result is the basic configuration of a
97:
146:
82:
70:
319:
level. The cutoff level is typically about one thousandth of the peak value, or 0.1%.
69:
chosen from a wider range of wavelengths available at the input. The name is from
751:
664:
639:
572:
447:
289:
489:
174:
170:
586:
478:
352:
315:
269:
150:
740:
695:
452:
293:
166:
58:
580:– a monochromator that compensates for path length delays that would stretch
66:
652:
Keppy, N. K. and Allen M., Thermo Fisher
Scientific, Madison, WI, USA, 2008
610:; Turner, A. F. (1930). "Über den astigmatismus bei spiegelspektrometern".
239:
711:
356:
34:
631:
292:
takes the place of the diffraction grating, in which case the light is
54:
382:
prism as one of the monochromators of a dual monochromator design.
165:
The dispersion or diffraction is only controllable if the light is
405:
238:
230:
122:
96:
62:
25:
Conceptual animation of the dispersion (or breaking down) of light
300:
parts of nearby images overlap. The light leaving the exit slit (
284:), which refocuses the light, now dispersed, on the exit slit (
57:
device that transmits a mechanically selectable narrow band of
455:
or some other energy units, but the scale may not be linear.
415:
118:
for a discussion of some of the uses of monochromators.
133:
are used to define wave conditions on the instruments.
181:
Geometrical design of a prism or grating monochromator
534:
spectrometers contain a monochromator, for example.
252:–Turner design, the broad-band illumination source (
235:A combined reflecting-focusing diffraction grating
141:A monochromator can use either the phenomenon of
723:Discusses monochromator design in great detail
738:Double folded-z-configuration monochromator.
8:
696:https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK21589/
511:Spectrophotometers are used to measure the
280:) and then is collected by another mirror (
288:). In a prism monochromator, a reflective
398:of ruled or holographic master gratings.
446:energy though, and since wavelength and
372:Diffraction gratings and blazed gratings
227:Diagram of a Czerny–Turner monochromator
222:
28:
20:
599:
670:. Belmont, CA: Brooks/Cole. pp.
414:Prisms have higher dispersion in the
7:
666:Principles of Instrumental Analysis
561:A major IR measurement technique,
14:
523:. There are many other examples.
115:
710:
256:) is aimed at an entrance slit (
189:Czerny–Turner (discussed below)
101:Neutron monochromator for the
1:
553:spectrometers use light from
734:(8th ed.). MKS Newport.
731:Diffraction Grating Handbook
728:Palmer, Christopher (2020).
89: 'denoting an agent'.
81: 'colour' and
43:Argonne National Laboratory
779:
332:full width at half maximum
33:Monochromator in an x-ray
105:powder diffractometer at
662:Skoog, Douglas (2007).
578:Ultrafast monochromator
612:Zeitschrift für Physik
453:reciprocal centimeters
411:
244:
236:
228:
131:crystal monochromators
110:
46:
39:Advanced Photon Source
26:
567:field autocorrelation
441:Wavelength vs. energy
409:
363:Double monochromators
242:
234:
226:
173:used sunlight in his
100:
32:
24:
741:U.S. patent RE26053E
719:at Wikimedia Commons
555:hollow cathode lamps
513:specular reflectance
392:Holographic gratings
624:1930ZPhy...61..792C
517:diffuse reflectance
515:of mirrors and the
379:diffraction grating
155:diffraction grating
77: 'single'
632:10.1007/BF01340206
618:(11–12): 792–797.
532:Circular dichroism
412:
328:Spectral bandwidth
323:Spectral bandwidth
245:
237:
229:
175:famous experiments
143:optical dispersion
111:
47:
27:
715:Media related to
681:978-0-495-01201-6
582:ultrashort pulses
563:Fourier transform
551:Atomic absorption
465:spectrophotometer
770:
743:
735:
714:
698:
692:
686:
685:
669:
659:
653:
650:
644:
643:
604:
498:Beer–Lambert law
347:Wavelength range
778:
777:
773:
772:
771:
769:
768:
767:
758:Optical devices
748:
747:
739:
727:
707:
702:
701:
693:
689:
682:
661:
660:
656:
651:
647:
606:
605:
601:
596:
547:
521:optical filters
474:
461:
443:
434:
425:
404:
374:
365:
349:
340:
325:
310:
247:
183:
163:
139:
95:
17:
12:
11:
5:
776:
774:
766:
765:
760:
750:
749:
746:
745:
736:
725:
720:
717:Monochromators
706:
705:External links
703:
700:
699:
687:
680:
654:
645:
598:
597:
595:
592:
591:
590:
584:
575:
570:
559:
546:
543:
473:
470:
460:
457:
442:
439:
433:
430:
424:
421:
403:
400:
387:ruling engines
373:
370:
364:
361:
348:
345:
339:
336:
324:
321:
309:
306:
296:by the prism.
248:In the common
221:
220:
215:
210:
205:
200:
195:
190:
182:
179:
162:
159:
138:
135:
94:
91:
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
775:
764:
761:
759:
756:
755:
753:
742:
737:
733:
732:
726:
724:
721:
718:
713:
709:
708:
704:
697:
691:
688:
683:
677:
673:
668:
667:
658:
655:
649:
646:
641:
637:
633:
629:
625:
621:
617:
613:
609:
603:
600:
593:
588:
585:
583:
579:
576:
574:
573:Polychromator
571:
568:
564:
560:
556:
552:
549:
548:
544:
542:
538:
535:
533:
528:
524:
522:
518:
514:
509:
505:
502:
499:
493:
491:
486:
482:
480:
471:
469:
466:
459:Dynamic range
458:
456:
454:
449:
448:photon energy
440:
438:
431:
429:
422:
420:
417:
408:
401:
399:
397:
393:
388:
383:
380:
371:
369:
362:
360:
358:
354:
346:
344:
337:
335:
333:
329:
322:
320:
318:
317:
307:
305:
303:
297:
295:
291:
290:Littrow prism
287:
283:
279:
275:
271:
267:
263:
259:
255:
251:
241:
233:
225:
219:
216:
214:
211:
209:
206:
204:
201:
199:
196:
194:
193:Paschen-Runge
191:
188:
187:
186:
180:
178:
176:
172:
168:
160:
158:
156:
152:
149:, or that of
148:
144:
136:
134:
132:
128:
124:
119:
117:
108:
104:
99:
92:
90:
88:
84:
80:
76:
72:
68:
64:
60:
56:
52:
51:monochromator
44:
40:
36:
31:
23:
19:
763:Spectroscopy
730:
690:
665:
657:
648:
615:
611:
602:
539:
536:
529:
525:
510:
506:
503:
494:
490:spectrograph
487:
483:
479:fluorometers
475:
472:Applications
462:
444:
435:
426:
423:Focal length
413:
384:
375:
366:
350:
341:
326:
314:
311:
301:
298:
285:
281:
277:
265:
257:
253:
246:
184:
164:
140:
120:
112:
86:
78:
74:
50:
48:
18:
587:Wien filter
432:Slit height
353:ultraviolet
316:stray light
308:Stray light
208:Ebert-Fasti
161:Collimation
151:diffraction
59:wavelengths
752:Categories
608:Czerny, M.
594:References
569:technique.
338:Dispersion
270:diffracted
262:collimator
167:collimated
137:Techniques
640:126259668
355:(UV) and
294:refracted
272:from the
203:Wadsworth
67:radiation
65:or other
545:See also
396:replicas
357:infrared
153:using a
129:optics,
121:In hard
35:beamline
620:Bibcode
274:grating
213:Littrow
127:neutron
103:ECHIDNA
55:optical
37:at the
678:
674:–183.
638:
402:Prisms
250:Czerny
171:Newton
79:chroma
53:is an
636:S2CID
218:Pfund
198:Eagle
147:prism
145:in a
123:X-ray
116:below
87:-ator
85:
83:Latin
75:mono-
73:
71:Greek
63:light
676:ISBN
125:and
107:OPAL
93:Uses
672:182
628:doi
61:of
754::
634:.
626:.
616:61
614:.
463:A
416:UV
264:,
49:A
41:,
684:.
642:.
630::
622::
302:F
286:F
282:E
278:D
276:(
266:C
258:B
254:A
45:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.