37:
385:
and particularly the dorsal raphe nucleus have long been implicated in depression. Some studies have suggested that the dorsal raphe may be decreased in size in people with depression and, paradoxically, an increased cell density in those who die by suicide.
846:
Steinbusch HW, Nieuwenhuys R, Verhofstad AA, Van der Kooy D (1981). "The nucleus raphe dorsalis of the rat and its projection upon the caudatoputamen. A combined cytoarchitectonic, immunohistochemical and retrograde transport study".
296:
exist in the dorsal raphe nucleus, and that it is a focal point as an ascending and descending regulator. Pourshanazari et al. showed in their 2000 paper that electrical stimulation of the dorsal raphe nucleus can partially alleviate
257:
are found in the rostral aspects, many of these co-express serotonin and substance P. There is also a population of catecholamine synthesizing neurons in the rostral dorsal raphe, and these cells appear to be relatively large.
304:
These are fascinating results; however no control was provided for the spread of electrical charge to other parts of the brain stem. It is quite possible that the charge spread to the nucleus raphes magnus and induced
507:
Baker KG, Halliday GM, Hornung JP, Geffen LB, Cotton RG, Törk I (1991). "Distribution, morphology and number of monoamine-synthesizing and substance P-containing neurons in the human dorsal raphe nucleus".
1312:
309:
upon the rats. Knowing that the spread of charge across such a short area is very plausible, as is an alternate connection to the raphe magnus, these results could be called into question.
329:
is the symptom of narcolepsy when full awareness of the environment is maintained, but all muscle tone is lost. This has thought to be a dissociation of what normally happens during
357:
respectively. These neurotransmitters are fully active during waking hours, partially active during non-REM sleep, and have almost ceased during REM sleep. In cats with
756:"A morphometric, immunohistochemical, and in situ hybridization study of the dorsal raphe nucleus in major depression, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, and suicide"
237:
The DRN issues serotonergic efferents to the hippocampal formation, limbic lobe, and amygdala (these efferents are involved in regulation of memory processing).
586:
Pourshanazari, A.A.; Alaei; Rafati (2000). "Effects of
Electrical Stimulation of Nucleus Raphe Dorsalis on initiation of morphine self-administration in rats".
172:
1464:
253:
Serotonergic neurons are found throughout the dorsal raphe nucleus and tend to be larger than other cells. A substantial population of cells synthesizing
1240:
365:
is not present, the dorsal raphe nucleus is fully active, as opposed to the cessation of action under normal conditions. A muscle relaxant, known as
950:
276:
705:"Serotonin 1A receptors, serotonin transporter binding and serotonin transporter mRNA expression in the brainstem of depressed suicide victims"
919:
491:
148:
250:
The dorsal raphe is the largest serotonergic nucleus and provides a substantial proportion of the serotonin innervation to the forebrain.
923:
803:
Ma QP, Yin GF, Ai MK, Han JS (December 1991). "Serotonergic projections from the nucleus raphe dorsalis to the amygdala in the rat".
1264:
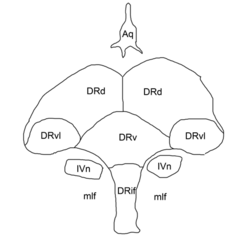
1173:
179:
1247:
1235:
439:
O'Hearn E, Molliver ME (December 1984). "Organization of raphe-cortical projections in rat: a quantitative retrograde study".
1289:
1204:
1156:
61:
333:
sleep, when all muscle tone is lost except for the eyes. The dorsal raphe nucleus has been known to project to the lateral
394:
An increased number of cells in the lateral aspects of the dorsal raphe is characteristic of primates (including humans).
167:
1269:
1459:
1332:
874:
Petzold GC, Hagiwara A, Murthy VN (June 2009). "Serotonergic modulation of odor input to the mammalian olfactory bulb".
292:
The dorsal raphe nucleus has also been implicated in naloxone-induced morphine withdrawal. It is known that endogenous
1161:
943:
1500:
1357:
1340:
342:
330:
106:
345:. The neurotransmitters of these three aforementioned nuclei, which project to the lateral hypothalamus, are
1322:
1054:
1281:
936:
155:
143:
1471:
1414:
1404:
1227:
1178:
607:"Activity of dorsal raphe cells across the sleep–waking cycle and during cataplexy in narcoleptic dogs"
1409:
979:
551:
Briley M, Moret C (October 1993). "Neurobiological mechanisms involved in antidepressant therapies".
382:
703:
Arango V, Underwood MD, Boldrini M, Tamir H, Kassir SA, Hsiung S, Chen JJ, Mann JJ (December 2001).
407:
Ten percent of the axons from the dorsal raphe nucleus of the rat have been shown to project to the
123:
1399:
1302:
1199:
1168:
1004:
999:
992:
987:
223:
raphe have been found to vary topographically, and thus the subnuclei differ in their projections.
1505:
1252:
1117:
1088:
899:
828:
685:
533:
464:
325:. This is logical, as the raphe nuclei have been known to play a role in the sleep/wake cycle.
1317:
1257:
1194:
1149:
1106:
1096:
1070:
1049:
891:
856:
820:
785:
736:
677:
636:
568:
525:
487:
456:
75:
68:
1430:
1394:
1144:
883:
812:
775:
767:
726:
716:
667:
626:
618:
560:
517:
448:
293:
216:
raphe is further divided into interfascicular, ventral, ventrolateral and dorsal subnuclei.
1443:
968:
654:
Underwood MD, Khaibulina AA, Ellis SP, Moran A, Rice PM, Mann JJ, Arango V (August 1999).
338:
411:, while only medium cells seem to project to the caudate and putamen and olfactory bulb.
1024:
780:
755:
631:
350:
17:
721:
704:
672:
655:
279:(SSRIs) in this region is responsible for the latency of their antidepressant effect.
1494:
1438:
1386:
816:
606:
564:
521:
452:
272:
903:
689:
537:
1382:
1345:
1126:
1034:
832:
468:
420:
334:
262:
201:
656:"Morphometry of the dorsal raphe nucleus serotonergic neurons in suicide victims"
622:
301:
withdrawal symptoms via electrical stimulation of the raphe nucleus in question.
111:
1426:
1307:
1218:
1016:
254:
136:
771:
366:
322:
118:
160:
370:
354:
346:
326:
306:
205:
895:
789:
740:
681:
640:
928:
860:
824:
572:
529:
460:
960:
408:
298:
130:
369:, reduces activity of the dorsal nucleus, as well as microinjections of
185:
731:
605:
Wu MF, John J, Boehmer LN, Yau D, Nguyen GB, Siegel JM (January 2004).
362:
266:
887:
486:(2nd ed.). Hoboken, New Jersey: Wiley-Blackwell. p. 432.
94:
358:
932:
1313:
Rostral interstitial nucleus of medial longitudinal fasciculus
36:
208:
at the midline. It has rostral and caudal subdivisions:
321:
studied the dorsal raphe nucleus as it pertained to
1452:
1425:
1381:
1374:
1331:
1280:
1226:
1217:
1187:
1134:
1125:
1116:
1105:
1087:
1063:
1042:
1033:
1015:
978:
967:
166:
154:
142:
129:
117:
105:
93:
88:
83:
29:
100:nucleus raphes posterior, nucleus raphes dorsalis
482:Patestas, Maria A.; Gartner, Leslie P. (2016).
588:Medical Journal of Islamic Academy of Sciences
944:
8:
275:, and it's believed that the action of the
1378:
1223:
1131:
1122:
1113:
1039:
975:
951:
937:
929:
35:
779:
730:
720:
671:
630:
754:Matthews PR, Harrison PJ (March 2012).
431:
277:selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors
183:
26:
41:Outline of the dorsal raphe nucleus:
7:
373:(which induces atonia while awake).
288:Naloxone-induced morphine withdrawal
261:The dorsal raphe nucleus is rich in
381:The rostral raphe nuclei, both the
924:Neuroscience Information Framework
25:
920:NIF Search - Dorsal Raphe Nucleus
1174:Anterior trigeminothalamic tract
565:10.1097/00002826-199310000-00002
180:Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy
1290:Rostromedial tegmental nucleus
246:Serotonergic neurotransmission
62:medial longitudinal fasciculus
1:
722:10.1016/S0893-133X(01)00310-4
673:10.1016/S0006-3223(99)00043-8
1460:Superior cerebellar peduncle
1333:Midbrain reticular formation
817:10.1016/0304-3940(91)90499-J
623:10.1113/jphysiol.2003.052134
522:10.1016/0306-4522(91)90043-N
453:10.1016/0361-9230(84)90232-6
45:interfascicular subnucleus,
1162:Vestibulo-oculomotor fibers
1522:
484:A Textbook of Neuroanatomy
212:The rostral aspect of the
53:ventrolateral subnucleus,
1358:Reticulotegmental nucleus
1298:
772:10.1016/j.jad.2011.10.043
178:
34:
1341:dorsal tegmental nucleus
1270:Edinger–Westphal nucleus
343:tuberomammillary nucleus
204:. It is situated in the
1323:Interpeduncular nucleus
1055:Central tegmental tract
709:Neuropsychopharmacology
219:The projections of the
18:Nucleus raphes dorsalis
1282:Ventral tegmental area
377:Depression and suicide
361:lesions, their normal
1472:Interpeduncular fossa
1415:Temporopontine fibers
1179:Dentatothalamic tract
1410:Frontopontine fibers
1405:Corticopontine tract
980:Corpora quadrigemina
383:median raphe nucleus
198:dorsal raphe nucleus
49:ventral subnucleus,
30:Dorsal raphe nucleus
1400:Corticobulbar tract
1395:Corticospinal tract
1303:Periaqueductal gray
1200:Rubro-olivary tract
1169:Spinothalamic tract
1135:Sensory / ascending
1043:Sensory / ascending
1000:Superior colliculus
988:Inferior colliculus
849:J. Physiol. (Paris)
553:Clin Neuropharmacol
57:dorsal subnucleus,
1253:Oculomotor nucleus
1188:Motor / descending
1064:Motor / descending
1488:
1487:
1484:
1483:
1480:
1479:
1370:
1369:
1366:
1365:
1318:Parabrachial area
1258:Trochlear nucleus
1213:
1212:
1195:Rubrospinal tract
1097:Cerebral aqueduct
1083:
1082:
1079:
1078:
1071:Tectospinal tract
1050:Spinotectal tract
1005:Superior brachium
993:Inferior brachium
493:978-1-118-67746-9
337:, along with the
194:
193:
189:
76:trochlear nucleus
69:cerebral aqueduct
16:(Redirected from
1513:
1501:Brainstem nuclei
1431:Substantia nigra
1379:
1224:
1132:
1123:
1114:
1040:
976:
953:
946:
939:
930:
908:
907:
871:
865:
864:
843:
837:
836:
800:
794:
793:
783:
766:(1–3): 125–134.
751:
745:
744:
734:
724:
700:
694:
693:
675:
651:
645:
644:
634:
617:(Pt 1): 202–15.
602:
596:
595:
583:
577:
576:
548:
542:
541:
504:
498:
497:
479:
473:
472:
436:
294:opioid receptors
186:edit on Wikidata
39:
27:
21:
1521:
1520:
1516:
1515:
1514:
1512:
1511:
1510:
1491:
1490:
1489:
1476:
1448:
1444:Pars reticulata
1421:
1362:
1327:
1294:
1276:
1209:
1183:
1109:
1101:
1075:
1059:
1029:
1011:
971:
963:
959:Anatomy of the
957:
916:
911:
888:10.1038/nn.2335
873:
872:
868:
855:(2–3): 157–74.
845:
844:
840:
802:
801:
797:
760:J Affect Disord
753:
752:
748:
702:
701:
697:
660:Biol Psychiatry
653:
652:
648:
604:
603:
599:
585:
584:
580:
550:
549:
545:
506:
505:
501:
494:
481:
480:
476:
441:Brain Res. Bull
438:
437:
433:
429:
417:
405:
400:
392:
379:
339:locus coeruleus
315:
290:
285:
270:
248:
243:
241:Neurophysiology
235:
230:
190:
79:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
1519:
1517:
1509:
1508:
1503:
1493:
1492:
1486:
1485:
1482:
1481:
1478:
1477:
1475:
1474:
1469:
1468:
1467:
1456:
1454:
1450:
1449:
1447:
1446:
1441:
1435:
1433:
1423:
1422:
1420:
1419:
1418:
1417:
1412:
1402:
1397:
1391:
1389:
1376:
1372:
1371:
1368:
1367:
1364:
1363:
1361:
1360:
1355:
1354:
1353:
1343:
1337:
1335:
1329:
1328:
1326:
1325:
1320:
1315:
1310:
1305:
1299:
1296:
1295:
1293:
1292:
1286:
1284:
1278:
1277:
1275:
1274:
1273:
1272:
1262:
1261:
1260:
1255:
1245:
1244:
1243:
1232:
1230:
1228:cranial nuclei
1221:
1215:
1214:
1211:
1210:
1208:
1207:
1205:Descending MLF
1202:
1197:
1191:
1189:
1185:
1184:
1182:
1181:
1176:
1171:
1166:
1165:
1164:
1154:
1153:
1152:
1147:
1138:
1136:
1129:
1120:
1111:
1103:
1102:
1100:
1099:
1093:
1091:
1085:
1084:
1081:
1080:
1077:
1076:
1074:
1073:
1067:
1065:
1061:
1060:
1058:
1057:
1052:
1046:
1044:
1037:
1031:
1030:
1028:
1027:
1025:Pretectal area
1021:
1019:
1013:
1012:
1010:
1009:
1008:
1007:
997:
996:
995:
984:
982:
973:
965:
964:
958:
956:
955:
948:
941:
933:
927:
926:
915:
914:External links
912:
910:
909:
866:
838:
805:Neurosci. Lett
795:
746:
715:(6): 892–903.
695:
646:
597:
578:
559:(5): 387–400.
543:
499:
492:
474:
430:
428:
425:
424:
423:
416:
413:
404:
401:
399:
396:
391:
388:
378:
375:
351:norepinephrine
314:
311:
289:
286:
284:
281:
268:
247:
244:
242:
239:
234:
231:
229:
226:
225:
224:
217:
200:is one of the
192:
191:
182:
176:
175:
170:
164:
163:
158:
152:
151:
146:
140:
139:
134:
127:
126:
121:
115:
114:
109:
103:
102:
97:
91:
90:
86:
85:
81:
80:
40:
32:
31:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1518:
1507:
1504:
1502:
1499:
1498:
1496:
1473:
1470:
1466:
1463:
1462:
1461:
1458:
1457:
1455:
1451:
1445:
1442:
1440:
1439:Pars compacta
1437:
1436:
1434:
1432:
1428:
1424:
1416:
1413:
1411:
1408:
1407:
1406:
1403:
1401:
1398:
1396:
1393:
1392:
1390:
1388:
1387:Cerebral crus
1384:
1380:
1377:
1373:
1359:
1356:
1352:
1349:
1348:
1347:
1344:
1342:
1339:
1338:
1336:
1334:
1330:
1324:
1321:
1319:
1316:
1314:
1311:
1309:
1306:
1304:
1301:
1300:
1297:
1291:
1288:
1287:
1285:
1283:
1279:
1271:
1268:
1267:
1266:
1263:
1259:
1256:
1254:
1251:
1250:
1249:
1246:
1242:
1241:Mesencephalic
1239:
1238:
1237:
1234:
1233:
1231:
1229:
1225:
1222:
1220:
1216:
1206:
1203:
1201:
1198:
1196:
1193:
1192:
1190:
1186:
1180:
1177:
1175:
1172:
1170:
1167:
1163:
1160:
1159:
1158:
1157:Ascending MLF
1155:
1151:
1148:
1146:
1143:
1142:
1140:
1139:
1137:
1133:
1130:
1128:
1124:
1121:
1119:
1115:
1112:
1108:
1104:
1098:
1095:
1094:
1092:
1090:
1086:
1072:
1069:
1068:
1066:
1062:
1056:
1053:
1051:
1048:
1047:
1045:
1041:
1038:
1036:
1032:
1026:
1023:
1022:
1020:
1018:
1014:
1006:
1003:
1002:
1001:
998:
994:
991:
990:
989:
986:
985:
983:
981:
977:
974:
970:
966:
962:
954:
949:
947:
942:
940:
935:
934:
931:
925:
921:
918:
917:
913:
905:
901:
897:
893:
889:
885:
882:(6): 784–91.
881:
877:
876:Nat. Neurosci
870:
867:
862:
858:
854:
850:
842:
839:
834:
830:
826:
822:
818:
814:
810:
806:
799:
796:
791:
787:
782:
777:
773:
769:
765:
761:
757:
750:
747:
742:
738:
733:
728:
723:
718:
714:
710:
706:
699:
696:
691:
687:
683:
679:
674:
669:
666:(4): 473–83.
665:
661:
657:
650:
647:
642:
638:
633:
628:
624:
620:
616:
612:
608:
601:
598:
593:
589:
582:
579:
574:
570:
566:
562:
558:
554:
547:
544:
539:
535:
531:
527:
523:
519:
516:(3): 757–75.
515:
511:
503:
500:
495:
489:
485:
478:
475:
470:
466:
462:
458:
454:
450:
447:(6): 709–26.
446:
442:
435:
432:
426:
422:
419:
418:
414:
412:
410:
402:
397:
395:
390:Other animals
389:
387:
384:
376:
374:
372:
368:
364:
360:
356:
352:
348:
344:
340:
336:
332:
328:
324:
320:
312:
310:
308:
302:
300:
295:
287:
282:
280:
278:
274:
273:autoreceptors
271:
264:
259:
256:
251:
245:
240:
238:
232:
227:
222:
218:
215:
211:
210:
209:
207:
203:
199:
187:
181:
177:
174:
171:
169:
165:
162:
159:
157:
153:
150:
147:
145:
141:
138:
135:
132:
128:
125:
122:
120:
116:
113:
110:
108:
104:
101:
98:
96:
92:
87:
82:
77:
74:
70:
67:
63:
60:
56:
52:
48:
44:
38:
33:
28:
19:
1350:
1346:Raphe nuclei
1127:White matter
1035:White matter
879:
875:
869:
852:
848:
841:
808:
804:
798:
763:
759:
749:
712:
708:
698:
663:
659:
649:
614:
610:
600:
591:
587:
581:
556:
552:
546:
513:
510:Neuroscience
509:
502:
483:
477:
444:
440:
434:
421:Raphe nuclei
406:
393:
380:
335:hypothalamus
318:
316:
303:
291:
263:pre-synaptic
260:
252:
249:
236:
220:
213:
202:raphe nuclei
197:
195:
149:A14.1.05.604
99:
72:
65:
58:
54:
50:
46:
42:
1465:Decussation
1308:Red nucleus
1219:Grey matter
1017:Grey matter
811:(1): 21–4.
732:2158/200883
255:substance P
137:birnlex_982
89:Identifiers
1495:Categories
611:J. Physiol
594:(2): 63–7.
427:References
367:Mephenesin
323:narcolepsy
313:Narcolepsy
265:serotonin
119:NeuroNames
1506:Serotonin
1141:Lemnisci
1118:Tegmentum
1110:(Ventral)
371:carbachol
355:histamine
347:serotonin
327:Cataplexy
307:analgesia
233:Efferents
206:brainstem
1107:Peduncle
972:(Dorsal)
961:midbrain
922:via the
904:33863055
896:19430472
790:22129767
741:11750182
690:19780741
682:10459396
641:14678502
538:23034680
415:See also
409:amygdala
403:Research
341:and the
317:Wu M.F.
299:morphine
283:Research
131:NeuroLex
1453:Surface
1150:Lateral
861:6169825
833:5713957
825:1815148
781:3314923
632:1664742
573:8221701
530:1720227
469:4761755
461:6099744
359:pontine
228:Anatomy
112:D065847
84:Details
1351:dorsal
1145:Medial
969:Tectum
902:
894:
859:
831:
823:
788:
778:
739:
688:
680:
639:
629:
571:
536:
528:
490:
467:
459:
363:atonia
319:et al.
221:dorsal
214:dorsal
1383:White
900:S2CID
829:S2CID
686:S2CID
534:S2CID
465:S2CID
184:[
173:68462
95:Latin
1427:Grey
1375:Base
892:PMID
857:PMID
821:PMID
786:PMID
737:PMID
678:PMID
637:PMID
569:PMID
526:PMID
488:ISBN
457:PMID
353:and
267:5-HT
196:The
161:5957
144:TA98
107:MeSH
51:DRvl
43:DRif
1265:GVE
1248:GSE
1236:GSA
1089:CSF
884:doi
813:doi
809:134
776:PMC
768:doi
764:137
727:hdl
717:doi
668:doi
627:PMC
619:doi
615:554
561:doi
518:doi
449:doi
398:Rat
331:REM
168:FMA
156:TA2
124:512
73:IVn
59:mlf
55:DRd
47:DRv
1497::
1429:/
1385:/
898:.
890:.
880:12
878:.
853:77
851:.
827:.
819:.
807:.
784:.
774:.
762:.
758:.
735:.
725:.
713:25
711:.
707:.
684:.
676:.
664:46
662:.
658:.
635:.
625:.
613:.
609:.
592:13
590:.
567:.
557:16
555:.
532:.
524:.
514:42
512:.
463:.
455:.
445:13
443:.
349:,
269:1A
133:ID
71:,
66:Aq
64:,
952:e
945:t
938:v
906:.
886::
863:.
835:.
815::
792:.
770::
743:.
729::
719::
692:.
670::
643:.
621::
575:.
563::
540:.
520::
496:.
471:.
451::
188:]
78:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.