246:
469:
49:
115:
73:
484:
surface may be yellow, brown, gray, or blackish, with or without ragged or clearly defined cross bands. It can be olivaceous or brownish to black above with or without a yellow or orange-colored, O-shaped mark on the hood. It has a black spot on the lower surface of the hood on either side, and one
601:, snakes and fish. When disturbed it prefers to escape. However, when threatened it will raise the anterior portions of the body, spread its hood, usually hisses loudly and strikes in an attempt to bite and defend itself. It often hides in tree holes and areas where rodents are plentiful.
485:
or two black cross-bars on the belly behind it. The rest of the belly is usually the same color as the back, but paler. As age advances, the snake becomes paler, wherein the adult is brownish or olivaceous. A pair of fixed anterior fangs is present. The largest
752:
Between 1968 and 1974, 20 cases of cobra bites were observed in
Thailand; all the patients developed systemic envenoming and received treatment, but 19 patients survived. The monocled cobra causes the highest fatality due to snake venom poisoning in Thailand.
492:
Adult monocled cobras reach a length of 1.35 to 1.5 m (4.4 to 4.9 ft) with a tail length of 23 cm (9.1 in). Many larger specimens have been recorded, but they are rare. Adults can reach a maximum of 2.3 m (7.5 ft) in length.
513:. It typically has more than one cuneate scale on each side. The shape of the frontal scale is short and square. Ventrals in males range from 170 to 192, in females from 178 to 197. Subcaudals in males range from 48 to 61, in females from 46 to 59.
480:, which has the "spectacle" pattern (two circular ocelli connected by a curved line) on the rear of its hood. The elongated nuchal ribs enable a cobra to expand the anterior of the neck into a “hood”. Coloration in the young is more constant. The
731:, ventilatory failure or death could ensue rapidly, possibly as early as 60 minutes in very severe cases of envenomation. However, the presence of fang marks does not always imply that envenomation actually occurred.
624:. Incubation periods range from 55 to 73 days. Egg-laying takes place January through March. The females usually stay with the eggs. Some collaboration between males and females has been reported in
839:"Catalogue des Reptiles qui font partie d'une Collection zoologique recueillie dans l'Inde continental ou en Afrique, et apportée en France par M. Lamare-Piqout. Catalogue dressé (juillet 1831)"
680:
body weight. These results reflect the distinct difference in the lethal potency of the monocled cobra and response to antivenom neutralization. The major toxic components in cobra
660:, and its reported abundance. No major threats have been reported, and it is not thought to be undergoing a significant population decline. Monocled cobras are harvested for the
2200:
1757:
581:, but lives also in grasslands, shrublands, forests, agricultural land at elevations of up to 1,000 m (3,300 ft) and human settlements including cities.
968:
Ratnarathorn, N.; Harnyuttanakorn, P.; Chanhome, L.; Evans, S. E.; Day, J. J. (2019). "Geographical differentiation and cryptic diversity in the monocled cobra,
2156:
1749:
2236:
1541:
Pratanaphon, R.; Akesowan, S.; Khow, O.; Sriprapat, S.; Ratanabanangkoon, K. (1997). "Production of highly potent horse antivenom against the Thai cobra (
1506:
Trishnananda, M.; Oonsombat, P.; Dumavibhat, B.; Yongchaiyudha, S.; Boonyapisit, V. (1979). "Clinical manifestations of cobra bite in the Thai farmer".
2104:
2130:
569:. It can adapt to a range of habitats, from natural to anthropogenically impacted environments. It prefer habitats associated with water, such as
460:
in
Thailand have demonstrated surprising variation, with one population resulting in the species becoming paraphyletic with other Asiatic cobras.
1787:
2306:
1661:(Reptilia: Serpentes: Elapidae) in Indochina: Multivariate morphometrics and comparative mitochondrial DNA sequencing (cytochrome oxidase I)"
1490:
2251:
723:
and systemic manifestations to a lesser degree. Drowsiness, neurological and neuromuscular symptoms will usually manifest earliest;
2241:
1419:
672:
The venom of the monocled cobra from three different localities were reported to exhibit different intravenous and subcutaneous
360:
described a brownish monocled cobra with numerous faint yellow transverse stripes and a hood marked with a white ring under the
2256:
1149:
657:
727:, flushing of the face, warm skin, and pain around bite site typically manifest within one to four hours following the bite;
2135:
1383:
venom on skeletal muscle: Involvement of calcium-induced calcium release, sodium ion currents and phospholipases A2 and C".
2266:
857:
1449:
1053:
The Fauna of
British India, Ceylon and Burma, Including the Whole of the Indo-Chinese Sub-Region. Reptilia and Amphibia
2296:
2261:
1485:. Leipzig; English version NY, USA: Leipzig Publishing; English version published by Exeter Books (1982). p. 51.
1092:
1070:
699:
and even death by respiratory failure. The major α-neurotoxin in the monocled cobra's venom is a long neurotoxin, α-
2301:
2291:
2276:
1780:
1733:
1379:
Fletcher, J. E.; Jiang, M.-S.; Gong, Q.-H.; Yudkowsky, M.L.; Wieland, S.J. (1991). "Effects of a cardiotoxin from
1119:
593:
burrows in the dykes between fields and has become semi-aquatic in this type of habitat. Juveniles feed mostly on
2271:
2161:
746:
2286:
2281:
1196:
1179:
604:
Some monocled cobra populations have the ability to spit venom, earning them the name "Indian spitting cobra".
245:
114:
468:
2018:
692:
357:
343:
1044:
1773:
735:
664:, however, collection from the wild is minimal and not likely to cause significant population declines.
361:
293:
219:
880:
1297:
Ogay, A.; Rzhevskya, D.I.; Murasheva, A.N.; Tsetlinb, V.I.; Utkin, Y.N. (2005). "Weak neurotoxin from
838:
2091:
2065:
676:: Thailand, 0.18-0.22 μg/g; Malaysia, 0.90-1.11 μg/g; and Vietnam, 0.90-1.00 μg/g, of
433:
1336:
Mahanta, M.; Mukherjee, A.K. (2001). "Neutralisation of lethality, myotoxicity and toxic enzymes of
1015:
1958:
815:
704:
62:
1694:
Wüster, W. (1996). "Taxonomic changes and toxinology: Systematic revisions of the
Asiatic cobras (
929:
Wüster, W. (1996). "Taxonomic changes and toxinology: Systematic revisions of the
Asiatic cobras (
2056:
1902:
1881:
1682:
1120:"Dentitional phenomena in cobra revisited: spitting and fang structure in the Asiatic species of
989:
739:
673:
109:
1480:
1219:
Tan, K.Y.; Tan, C.H.; Fung, S.Y.; Tan, N.H. (2015). "Venomics, lethality and neutralization of
707:. The neurotoxins of this particular species are weak. The venom of this species also contains
2182:
2078:
1979:
1715:
1562:
1523:
1486:
1400:
1361:
1318:
1279:
1240:
1201:
950:
645:
589:
The monocled cobra is terrestrial and most active at dusk. In rice-growing areas, it hides in
2187:
319:
in 1831, when he described the monocled cobra as a beautiful snake that is distinct from the
2195:
2148:
1965:
1923:
1916:
1888:
1707:
1672:
1554:
1515:
1392:
1353:
1310:
1232:
1191:
981:
942:
810:
633:
510:
505:
on the neck, 19 to 21 on the body, and 17 or 15 on the front of the vent. It has 164 to 197
481:
339:
335:
320:
866:
Illustrations of Indian zoology chiefly selected from the collection of Maj.-Gen. Hardwicke
489:
recorded measured 6.78 mm (0.678 cm). Fangs are moderately adapted for spitting.
2169:
1972:
1895:
1825:
538:
436:
classified the monocled cobra as a subspecies of the spectacled cobra under the trinomial
327:
309:
48:
2000:
1993:
1986:
1874:
1811:
1677:
1656:
661:
506:
446:
316:
289:
235:
2070:
1558:
1427:
1357:
1223:(monocled cobra) venoms from three different geographical regions of Southeast Asia".
2246:
2230:
2143:
1867:
1853:
1818:
1711:
1396:
993:
946:
801:
792:
653:
649:
621:
617:
297:
82:
77:
1744:
1686:
476:
The monocled cobra has an O-shaped, or monocellate hood pattern, unlike that of the
2083:
1951:
1832:
1301:
cobra venom affects haemodynamic regulation by acting on acetylcholine receptors".
716:
502:
477:
453:
31:
1314:
2213:
2117:
2050:
1944:
1937:
1259:
1236:
724:
712:
656:
due to its large distribution, tolerance of a broad range of habitats including
570:
542:
1930:
1839:
1519:
700:
685:
546:
285:
1655:
Wüster, W.; Thorpe, R.S.; Cox, M.J.; Jintakune, P.; Nabhitabhata, J. (1995).
1258:
Wei, J.-F.; Lü, Q.-M.; Jin, Y.; Li, D.-S.; Xiong, Y.-L.; Wang, W.-Y. (2003).
17:
1909:
1860:
1846:
1457:
762:
749:. The average venom yield per bite is approximately 263 mg dry weight.
728:
696:
689:
613:
594:
126:
2041:
1365:
1322:
1283:
1244:
1205:
2174:
1719:
1566:
1404:
1055:. Vol. III (Serpentes). London: Taylor and Francis. pp. 428–432.
954:
2035:
1527:
1069:
Chanhome, L.; Cox, M. J.; Vasaruchaponga, T.; Chaiyabutra, N. S. (2011).
720:
708:
578:
566:
534:
372:
186:
166:
146:
1739:
2109:
1765:
1635:
Wüster, W. (1993). "A century of confusion: Asiatic cobras revisited".
554:
530:
383:
Several varieties of monocled cobras were described under the binomial
156:
2122:
985:
598:
590:
550:
368:
136:
2012:
745:
tested in mice is 0.373 mg/kg, and 0.225 mg/kg in case of
688:, which block the nerve transmission by binding specifically to the
1420:"Snakebite Protocols: Summary for Human Bite by Monocellate Cobra (
326:
Since then, several monocled cobras were described under different
2208:
681:
677:
574:
562:
526:
522:
467:
376:
176:
99:
93:
2096:
1796:
558:
486:
281:
196:
2016:
1769:
703:; the minor α-neurotoxin is different from cobrotoxin in one
1584:
Kyi, S.W.; Zug, G.R. (2003). "Unusual foraging behaviour of
1197:
10.1580/1080-6032(2001)012[0017:vshit]2.0.co;2
1178:
Chanhome, L; Jintkune, P.; Wilde, H.; Cox, M. J. (2001).
323:, with 188 ventral scales and 53 pairs of caudal scales.
450:, a name commonly used in older toxinological research.
440:. Reclassification in the 1990s further distinguished
1508:
The
American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene
719:
usually presents predominantly with extensive local
342:'s first illustration of a monocled cobra under the
2025:
1588:at the Moyingye Wetlands Bird Sanctuary, Myanmar".
1482:Snakes: Biology, Behavior, and Relationship to Man
1071:"Characterization of venomous snakes of Thailand"
1093:"Naja kaouthia: General Details and Information"
889:Proceedings of the Zoological Society of London
843:Bulletin des Sciences Naturelles et de Géologie
816:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2012-1.RLTS.T177487A1488122.en
1781:
1064:
1062:
8:
1601:Wüster, W. (1998). "The cobras of the genus
1657:"Population systematics of the snake genus
1038:
1036:
2013:
1788:
1774:
1766:
1649:Asiatic cobras: Systematics and snakebite.
1456:. University of Queensland. Archived from
1009:
1007:
1005:
1003:
244:
71:
47:
38:
1676:
1195:
814:
1016:"The cobras of the genus Naja in India"
774:
521:The monocled cobra is distributed from
1180:"Venomous snake husbandry in Thailand"
786:
784:
782:
780:
778:
658:anthropogenically altered environments
472:Characteristic monocle pattern on hood
1750:Clinical Toxinology Resources :
1184:Wilderness and Environmental Medicine
7:
1272:Acta Biochimica et Biophysica Sinica
2237:IUCN Red List least concern species
802:IUCN Red List of Threatened Species
1745:The Asiatic Cobra Systematics Page
1678:10.1046/j.1420-9101.1995.8040493.x
1118:Wüster, W.; Thorpe, R. S. (1992).
25:
868:. Vol. II. p. Plate 78.
1647:Wüster, W. Thorpe, R.S. (1991).
1097:WCH Clinical Toxinology Resource
644:The monocled cobra is listed on
501:The monocled cobra has 25 to 31
113:
1665:Journal of Evolutionary Biology
1148:Santra, V.; Wüster, W. (2017).
1454:Australian Venom Research Unit
791:Stuart, B.; Wogan, G. (2012).
616:species. Females lay 16 to 33
1:
1740:Reptarium.cz Reptile Database
1559:10.1016/S0264-410X(97)00098-4
1358:10.1016/S0378-8741(00)00373-1
1315:10.1016/j.toxicon.2004.09.014
597:whereas adults prey on small
1712:10.1016/0041-0101(95)00139-5
1397:10.1016/0041-0101(91)90005-C
1346:Journal of Ethnopharmacology
1268:snakes in different regions"
972:(Elapidae), from Thailand".
947:10.1016/0041-0101(95)00139-5
912:Records of the Indian Museum
1237:10.1016/j.jprot.2015.02.012
2323:
2252:Reptiles described in 1831
284:species widespread across
29:
2307:Taxa named by René Lesson
1806:
1520:10.4269/ajtmh.1979.28.165
1479:Engelmann, W.-E. (1981).
747:intraperitoneal injection
648:and has been assessed as
252:
243:
225:
218:
110:Scientific classification
108:
91:
69:
60:
55:
46:
41:
1099:. University of Adelaide
537:. It also occurs on the
517:Distribution and habitat
30:Not to be confused with
2242:Fauna of Southeast Asia
1758:Thailand Snakes :
1651:Experientia 47: 205–209
525:in the west through to
387:between 1895 and 1913:
2257:Reptiles of Bangladesh
1124:(Serpentes: Elapidae)"
906:Smith, M. A. (1940). "
837:Lesson, R.-P. (1831).
693:acetylcholine receptor
473:
358:Theodore Edward Cantor
1624:Herpetological Review
1225:Journal of Proteomics
1161:Herpetological Review
1043:Smith, M. A. (1943).
809:: e.T177487A1488122.
736:intravenous injection
695:, leading to flaccid
585:Behaviour and ecology
471:
278:Indian spitting cobra
2267:Reptiles of Cambodia
856:Gray, J. E. (1834).
434:Malcolm Arthur Smith
1959:Naja philippinensis
1618:Cox, M.J. (1995). "
1014:Wüster, W. (1998).
933:species complex)".
879:Cantor, T. (1839).
640:Conservation status
63:Conservation status
2297:Snakes of Thailand
2262:Reptiles of Bhutan
1903:Naja multifasciata
1882:Naja mandalayensis
1422:Naja naja kaouthia
1260:"α-Neurotoxins of
1154:behavior/spitting"
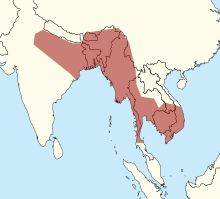
1047:Naja naja kaouthia
908:Naja naja kaouthia
674:median lethal dose
474:
438:Naja naja kaouthia
2302:Snakes of Vietnam
2292:Snakes of Myanmar
2277:Reptiles of Nepal
2224:
2223:
2183:Open Tree of Life
2019:Taxon identifiers
2010:
2009:
1980:Naja senegalensis
1553:(14): 1523–1528.
1492:978-0-89673-110-3
1391:(12): 1489–1500.
1075:Asian Biomedicine
986:10.1111/zsc.12378
974:Zoologica Scripta
684:are postsynaptic
646:CITES Appendix II
541:and is native to
274:monocellate cobra
260:
259:
103:
86:
16:(Redirected from
2314:
2272:Reptiles of Laos
2217:
2216:
2204:
2203:
2191:
2190:
2178:
2177:
2165:
2164:
2152:
2151:
2139:
2138:
2126:
2125:
2113:
2112:
2100:
2099:
2087:
2086:
2074:
2073:
2061:
2060:
2059:
2046:
2045:
2044:
2014:
1966:Naja sagittifera
1924:Naja nigricollis
1917:Naja nigricincta
1889:Naja melanoleuca
1790:
1783:
1776:
1767:
1723:
1690:
1680:
1644:
1631:
1614:
1597:
1571:
1570:
1538:
1532:
1531:
1503:
1497:
1496:
1476:
1470:
1469:
1467:
1465:
1460:on 13 April 2012
1445:
1439:
1438:
1436:
1435:
1426:. Archived from
1415:
1409:
1408:
1376:
1370:
1369:
1344:root extracts".
1333:
1327:
1326:
1294:
1288:
1287:
1255:
1249:
1248:
1216:
1210:
1209:
1199:
1175:
1169:
1168:
1158:
1145:
1139:
1138:
1128:
1115:
1109:
1108:
1106:
1104:
1089:
1083:
1082:
1066:
1057:
1056:
1040:
1031:
1030:
1020:
1011:
998:
997:
965:
959:
958:
926:
920:
919:
903:
897:
896:
876:
870:
869:
853:
847:
846:
834:
828:
827:
825:
823:
818:
788:
511:subcaudal scales
340:Thomas Hardwicke
336:John Edward Gray
328:scientific names
321:spectacled cobra
315:was proposed by
280:, is a venomous
248:
231:
211:N. kaouthia
118:
117:
97:
80:
75:
74:
51:
39:
27:Species of snake
21:
2322:
2321:
2317:
2316:
2315:
2313:
2312:
2311:
2287:Snakes of India
2282:Snakes of China
2227:
2226:
2225:
2220:
2212:
2207:
2199:
2194:
2186:
2181:
2173:
2170:Observation.org
2168:
2160:
2155:
2147:
2142:
2134:
2129:
2121:
2116:
2108:
2103:
2095:
2090:
2082:
2077:
2069:
2064:
2055:
2054:
2049:
2040:
2039:
2034:
2021:
2011:
2006:
1973:Naja samarensis
1896:Naja mossambica
1826:Naja annulifera
1802:
1800:(cobra) species
1794:
1730:
1693:
1654:
1634:
1617:
1600:
1583:
1580:
1578:Further reading
1575:
1574:
1540:
1539:
1535:
1505:
1504:
1500:
1493:
1478:
1477:
1473:
1463:
1461:
1447:
1446:
1442:
1433:
1431:
1417:
1416:
1412:
1378:
1377:
1373:
1335:
1334:
1330:
1296:
1295:
1291:
1257:
1256:
1252:
1218:
1217:
1213:
1177:
1176:
1172:
1156:
1147:
1146:
1142:
1126:
1117:
1116:
1112:
1102:
1100:
1091:
1090:
1086:
1068:
1067:
1060:
1042:
1041:
1034:
1018:
1013:
1012:
1001:
967:
966:
962:
928:
927:
923:
905:
904:
900:
878:
877:
873:
855:
854:
850:
845:(XXV): 119–123.
836:
835:
831:
821:
819:
790:
789:
776:
771:
759:
743:
670:
642:
610:
587:
539:Malay Peninsula
519:
499:
466:
464:Characteristics
385:Naja tripudians
347:Naja tripudians
310:scientific name
306:
272:), also called
239:
233:
227:
214:
112:
104:
87:
76:
72:
65:
56:Monocled cobra
42:Monocled cobra
35:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
2320:
2318:
2310:
2309:
2304:
2299:
2294:
2289:
2284:
2279:
2274:
2269:
2264:
2259:
2254:
2249:
2244:
2239:
2229:
2228:
2222:
2221:
2219:
2218:
2205:
2192:
2179:
2166:
2153:
2140:
2127:
2114:
2101:
2088:
2075:
2062:
2047:
2031:
2029:
2023:
2022:
2017:
2008:
2007:
2005:
2004:
2001:Naja sumatrana
1997:
1994:Naja sputatrix
1990:
1987:Naja siamensis
1983:
1976:
1969:
1962:
1955:
1948:
1941:
1934:
1927:
1920:
1913:
1906:
1899:
1892:
1885:
1878:
1875:Naja katiensis
1871:
1864:
1857:
1850:
1843:
1836:
1829:
1822:
1815:
1812:Naja anchietae
1807:
1804:
1803:
1795:
1793:
1792:
1785:
1778:
1770:
1764:
1763:
1755:
1747:
1742:
1729:
1728:External links
1726:
1725:
1724:
1706:(4): 399–406.
1691:
1671:(4): 493–510.
1652:
1645:
1632:
1615:
1598:
1579:
1576:
1573:
1572:
1533:
1514:(1): 165–166.
1498:
1491:
1471:
1440:
1410:
1371:
1328:
1289:
1278:(8): 683–688.
1250:
1211:
1170:
1140:
1110:
1084:
1058:
1032:
999:
980:(6): 711–726.
960:
941:(4): 399–406.
921:
898:
871:
848:
829:
773:
772:
770:
767:
766:
765:
758:
755:
741:
669:
666:
662:wildlife trade
641:
638:
609:
606:
586:
583:
518:
515:
507:ventral scales
498:
495:
465:
462:
447:Naja siamensis
430:
429:
419:
409:
399:
381:
380:
354:
305:
302:
292:and listed as
290:Southeast Asia
264:monocled cobra
258:
257:
250:
249:
241:
240:
234:
223:
222:
216:
215:
208:
206:
202:
201:
194:
190:
189:
184:
180:
179:
174:
170:
169:
164:
160:
159:
154:
150:
149:
144:
140:
139:
134:
130:
129:
124:
120:
119:
106:
105:
92:
89:
88:
70:
67:
66:
61:
58:
57:
53:
52:
44:
43:
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2319:
2308:
2305:
2303:
2300:
2298:
2295:
2293:
2290:
2288:
2285:
2283:
2280:
2278:
2275:
2273:
2270:
2268:
2265:
2263:
2260:
2258:
2255:
2253:
2250:
2248:
2245:
2243:
2240:
2238:
2235:
2234:
2232:
2215:
2210:
2206:
2202:
2197:
2193:
2189:
2184:
2180:
2176:
2171:
2167:
2163:
2158:
2154:
2150:
2145:
2141:
2137:
2132:
2128:
2124:
2119:
2115:
2111:
2106:
2102:
2098:
2093:
2089:
2085:
2080:
2076:
2072:
2071:Naja_kaouthia
2067:
2063:
2058:
2057:Naja kaouthia
2052:
2048:
2043:
2037:
2033:
2032:
2030:
2028:
2027:Naja kaouthia
2024:
2020:
2015:
2003:
2002:
1998:
1996:
1995:
1991:
1989:
1988:
1984:
1982:
1981:
1977:
1975:
1974:
1970:
1968:
1967:
1963:
1961:
1960:
1956:
1954:
1953:
1949:
1947:
1946:
1942:
1940:
1939:
1935:
1933:
1932:
1928:
1926:
1925:
1921:
1919:
1918:
1914:
1912:
1911:
1907:
1905:
1904:
1900:
1898:
1897:
1893:
1891:
1890:
1886:
1884:
1883:
1879:
1877:
1876:
1872:
1870:
1869:
1868:Naja kaouthia
1865:
1863:
1862:
1858:
1856:
1855:
1854:Naja christyi
1851:
1849:
1848:
1844:
1842:
1841:
1837:
1835:
1834:
1830:
1828:
1827:
1823:
1821:
1820:
1819:Naja annulata
1816:
1814:
1813:
1809:
1808:
1805:
1801:
1799:
1791:
1786:
1784:
1779:
1777:
1772:
1771:
1768:
1762:
1761:
1760:Naja kaouthia
1756:
1754:
1753:
1752:Naja kaouthia
1748:
1746:
1743:
1741:
1737:
1736:
1735:Naja kaouthia
1732:
1731:
1727:
1721:
1717:
1713:
1709:
1705:
1701:
1697:
1692:
1688:
1684:
1679:
1674:
1670:
1666:
1662:
1660:
1653:
1650:
1646:
1642:
1638:
1633:
1630:(3): 156–157.
1629:
1625:
1621:
1620:Naja kaouthia
1616:
1612:
1608:
1604:
1599:
1596:(2): 265–266.
1595:
1591:
1587:
1586:Naja kaouthia
1582:
1581:
1577:
1568:
1564:
1560:
1556:
1552:
1548:
1544:
1543:Naja kaouthia
1537:
1534:
1529:
1525:
1521:
1517:
1513:
1509:
1502:
1499:
1494:
1488:
1484:
1483:
1475:
1472:
1459:
1455:
1451:
1444:
1441:
1430:on 2012-12-03
1429:
1425:
1423:
1418:Davidson, T.
1414:
1411:
1406:
1402:
1398:
1394:
1390:
1386:
1382:
1381:Naja kaouthia
1375:
1372:
1367:
1363:
1359:
1355:
1351:
1347:
1343:
1342:Mimosa pudica
1339:
1338:Naja kaouthia
1332:
1329:
1324:
1320:
1316:
1312:
1308:
1304:
1300:
1299:Naja kaouthia
1293:
1290:
1285:
1281:
1277:
1273:
1269:
1267:
1266:Naja kaouthia
1263:
1254:
1251:
1246:
1242:
1238:
1234:
1230:
1226:
1222:
1221:Naja kaouthia
1215:
1212:
1207:
1203:
1198:
1193:
1189:
1185:
1181:
1174:
1171:
1166:
1162:
1155:
1153:
1152:Naja kaouthia
1144:
1141:
1137:(4): 424–434.
1136:
1132:
1131:Herpetologica
1125:
1123:
1114:
1111:
1098:
1094:
1088:
1085:
1081:(3): 311–328.
1080:
1076:
1072:
1065:
1063:
1059:
1054:
1050:
1048:
1039:
1037:
1033:
1028:
1024:
1017:
1010:
1008:
1006:
1004:
1000:
995:
991:
987:
983:
979:
975:
971:
970:Naja kaouthia
964:
961:
956:
952:
948:
944:
940:
936:
932:
925:
922:
917:
913:
909:
902:
899:
894:
890:
886:
884:
875:
872:
867:
863:
861:
860:Cobra Capella
852:
849:
844:
840:
833:
830:
817:
812:
808:
804:
803:
798:
796:
795:Naja kaouthia
787:
785:
783:
781:
779:
775:
768:
764:
761:
760:
756:
754:
750:
748:
744:
737:
732:
730:
726:
722:
718:
714:
710:
706:
702:
698:
694:
691:
687:
683:
679:
675:
667:
665:
663:
659:
655:
654:IUCN Red List
651:
650:Least Concern
647:
639:
637:
635:
631:
630:Naja kaouthia
627:
623:
619:
615:
607:
605:
602:
600:
596:
592:
584:
582:
580:
576:
572:
568:
564:
560:
556:
552:
548:
544:
540:
536:
532:
528:
524:
516:
514:
512:
509:and 43 to 58
508:
504:
496:
494:
490:
488:
483:
479:
470:
463:
461:
459:
458:Naja kaouthia
455:
451:
449:
448:
443:
442:Naja kaouthia
439:
435:
427:
423:
420:
417:
413:
410:
407:
403:
400:
397:
393:
390:
389:
388:
386:
378:
374:
370:
366:
363:
359:
355:
352:
348:
345:
341:
337:
333:
332:
331:
329:
324:
322:
318:
314:
313:Naja kaouthia
311:
303:
301:
299:
298:IUCN Red List
295:
294:Least Concern
291:
287:
283:
279:
275:
271:
270:
269:Naja kaouthia
265:
256:distribution
255:
254:Naja kaouthia
251:
247:
242:
237:
232:
230:
229:Naja kaouthia
224:
221:
220:Binomial name
217:
213:
212:
207:
204:
203:
200:
199:
195:
192:
191:
188:
185:
182:
181:
178:
175:
172:
171:
168:
165:
162:
161:
158:
155:
152:
151:
148:
145:
142:
141:
138:
135:
132:
131:
128:
125:
122:
121:
116:
111:
107:
101:
95:
90:
84:
79:
78:Least Concern
68:
64:
59:
54:
50:
45:
40:
37:
33:
19:
18:Naja kaouthia
2026:
1999:
1992:
1985:
1978:
1971:
1964:
1957:
1952:Naja pallida
1950:
1943:
1936:
1929:
1922:
1915:
1908:
1901:
1894:
1887:
1880:
1873:
1866:
1859:
1852:
1845:
1838:
1833:Naja arabica
1831:
1824:
1817:
1810:
1797:
1759:
1751:
1734:
1703:
1699:
1695:
1668:
1664:
1658:
1648:
1640:
1636:
1627:
1623:
1619:
1610:
1606:
1602:
1593:
1589:
1585:
1550:
1546:
1542:
1536:
1511:
1507:
1501:
1481:
1474:
1462:. Retrieved
1458:the original
1453:
1443:
1432:. Retrieved
1428:the original
1421:
1413:
1388:
1384:
1380:
1374:
1352:(1): 55–60.
1349:
1345:
1341:
1337:
1331:
1309:(1): 93–99.
1306:
1302:
1298:
1292:
1275:
1271:
1265:
1261:
1253:
1228:
1224:
1220:
1214:
1190:(1): 17–23.
1187:
1183:
1173:
1164:
1160:
1151:
1143:
1134:
1130:
1121:
1113:
1101:. Retrieved
1096:
1087:
1078:
1074:
1052:
1046:
1026:
1022:
977:
973:
969:
963:
938:
934:
930:
924:
915:
911:
907:
901:
892:
888:
883:Naja larvata
882:
874:
865:
859:
851:
842:
832:
820:. Retrieved
806:
800:
794:
751:
733:
717:Envenomation
713:cardiotoxins
671:
643:
629:
625:
611:
608:Reproduction
603:
588:
571:paddy fields
520:
500:
491:
478:Indian cobra
475:
457:
454:Phylogenetic
452:
445:
441:
437:
431:
425:
421:
415:
411:
405:
401:
395:
391:
384:
382:
365:Naja larvata
364:
350:
346:
325:
312:
307:
277:
273:
268:
267:
263:
261:
253:
228:
226:
210:
209:
197:
36:
32:Indian cobra
2118:iNaturalist
2051:Wikispecies
1945:Naja oxiana
1938:Naja nubiae
1698:complex)".
1643:(4): 14–18.
1613:(1): 15–32.
1605:in India".
1464:25 December
1450:"LD50 Menu"
1231:: 105–125.
1029:(1): 15–32.
734:In case of
725:hypotension
686:neurotoxins
612:This is an
543:West Bengal
456:studies of
426:sagittifera
367:, found in
317:René Lesson
96:Appendix II
2231:Categories
1931:Naja nivea
1840:Naja ashei
1448:Fry, B.G.
1434:2011-11-10
1103:3 February
822:29 January
769:References
701:cobratoxin
595:amphibians
547:Bangladesh
396:scopinucha
338:published
173:Suborder:
1910:Naja naja
1861:Naja haje
1847:Naja atra
1696:Naja naja
1607:Hamadryad
1590:Hamadryad
1340:venom by
1262:Naja atra
1167:(2): 455.
1023:Hamadryad
994:201199120
931:Naja naja
763:Snakebite
729:paralysis
709:myotoxins
697:paralysis
690:nicotinic
626:Naja naja
614:oviparous
579:mangroves
497:Scalation
432:In 1940,
356:In 1839,
344:trinomial
334:In 1834,
205:Species:
177:Serpentes
133:Kingdom:
127:Eukaryota
2209:Species+
2201:kaouthia
2036:Wikidata
1687:58939700
1637:Vivarium
1366:11282444
1323:15581687
1284:12897961
1245:25748141
1206:11294550
895:: 32–33.
757:See also
721:necrosis
567:Thailand
535:Cambodia
406:unicolor
373:Calcutta
362:binomial
351:fasciata
304:Taxonomy
187:Elapidae
183:Family:
167:Squamata
157:Reptilia
147:Chordata
143:Phylum:
137:Animalia
123:Domain:
83:IUCN 3.1
2188:1053579
2110:2470368
2097:1055811
1738:at the
1720:8735239
1700:Toxicon
1567:9330463
1547:Vaccine
1405:1666202
1385:Toxicon
1303:Toxicon
955:8735239
935:Toxicon
705:residue
652:on the
634:hybrids
599:mammals
555:Myanmar
531:Vietnam
416:viridis
296:on the
193:Genus:
163:Order:
153:Class:
98: (
81: (
2175:101590
2149:177487
2136:700628
2123:106447
2042:Q41165
1718:
1685:
1565:
1528:434309
1526:
1489:
1403:
1364:
1321:
1282:
1243:
1204:
992:
953:
918:: 485.
682:venoms
622:clutch
591:rodent
575:swamps
565:, and
551:Bhutan
503:scales
482:dorsal
375:, and
369:Bombay
238:, 1831
236:Lesson
2214:10754
2084:45KX4
1683:S2CID
1157:(PDF)
1127:(PDF)
1019:(PDF)
990:S2CID
678:mouse
668:Venom
563:Nepal
527:China
523:India
444:from
424:var.
422:N. j.
414:var.
412:N. j.
404:var.
402:N. j.
394:var.
392:N. j.
377:Assam
349:var.
286:South
282:cobra
100:CITES
94:CITES
2247:Naja
2162:8649
2157:NCBI
2144:IUCN
2131:ITIS
2105:GBIF
1798:Naja
1716:PMID
1659:Naja
1603:Naja
1563:PMID
1545:)".
1524:PMID
1487:ISBN
1466:2011
1401:PMID
1362:PMID
1319:PMID
1280:PMID
1264:and
1241:PMID
1202:PMID
1122:Naja
1105:2012
951:PMID
916:XLII
824:2022
807:2012
738:the
711:and
620:per
618:eggs
577:and
559:Laos
533:and
487:fang
428:1913
418:1913
408:1876
398:1895
308:The
288:and
276:and
262:The
198:Naja
2092:EoL
2079:CoL
2066:ADW
1708:doi
1673:doi
1622:".
1555:doi
1516:doi
1393:doi
1354:doi
1311:doi
1233:doi
1229:120
1192:doi
982:doi
943:doi
910:".
893:VII
811:doi
2233::
2211::
2198::
2196:RD
2185::
2172::
2159::
2146::
2133::
2120::
2107::
2094::
2081::
2068::
2053::
2038::
1714:.
1704:34
1702:.
1681:.
1667:.
1663:.
1639:.
1628:26
1626:.
1611:23
1609:.
1594:27
1592:.
1561:.
1551:15
1549:.
1522:.
1512:28
1510:.
1452:.
1424:)"
1399:.
1389:29
1387:.
1360:.
1350:75
1348:.
1317:.
1307:45
1305:.
1276:35
1274:.
1270:.
1239:.
1227:.
1200:.
1188:12
1186:.
1182:.
1165:48
1163:.
1159:.
1135:48
1133:.
1129:.
1095:.
1077:.
1073:.
1061:^
1051:.
1035:^
1027:23
1025:.
1021:.
1002:^
988:.
978:48
976:.
949:.
939:34
937:.
914:.
891:.
887:.
864:.
841:.
805:.
799:.
777:^
742:50
740:LD
715:.
636:.
632:-
628:x
573:,
561:,
557:,
553:,
549:,
545:,
529:,
371:,
330::
300:.
1789:e
1782:t
1775:v
1722:.
1710::
1689:.
1675::
1669:8
1641:4
1569:.
1557::
1530:.
1518::
1495:.
1468:.
1437:.
1407:.
1395::
1368:.
1356::
1325:.
1313::
1286:.
1247:.
1235::
1208:.
1194::
1150:"
1107:.
1079:5
1049:"
1045:"
996:.
984::
957:.
945::
885:"
881:"
862:"
858:"
826:.
813::
797:"
793:"
379:.
353:.
266:(
102:)
85:)
34:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.