22:
453:
When the following driver reacts early when decelerating or reacts late when accelerating, the time and distance gap between the leader and the follower increases. The follower can be described as a cautious driver. In the other situation, the follower reacts later when decelerating or earlier when
419:
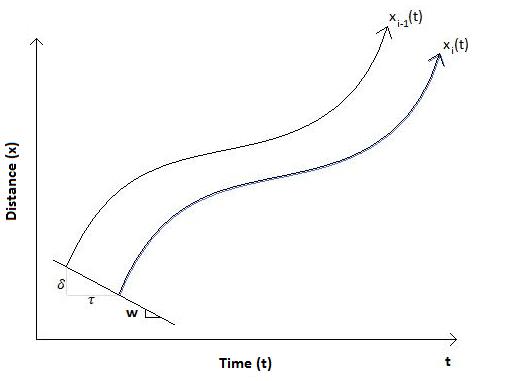
Under real-world conditions, a hypothetical following driver may drive improperly, resulting in deviations from the time-space trajectories proposed under Newell’s model. Time-space trajectories from data collected on roads and highways can be compared to its respective Newell’s car-following model
420:
trajectory to determine whether a driver is cautious or aggressive. The following figures show the trajectories of two vehicles (black) and the trajectory predicted by Newell’s car-following Model for the following vehicle (blue).
119:
is a method used to determine how vehicles follow one another on a roadway. The main idea of this model is that a vehicle will maintain a minimum space and time gap between it and the vehicle that precedes it. Thus, under
162:
can be assumed in the congestion region. The density on the roadway can be determined using the spacing between vehicles and is computed simply the equation:
296:
are constants defined by the wave speed and jam density, independent of the speed of the leading vehicle and the traffic state. The path of vehicle
496:
Newell G.F. (2002) A simplified car-following theory: a lower order model. Institute of
Transportation Studies, University of California, Berkeley.
32:
90:
62:
454:
accelerating decreasing the time and distance gap between the leader and follower. The follower can be described as an aggressive driver.
448:
438:
428:
243:
69:
124:
conditions, if the leading car changes its speed, the following vehicle will also change speed at a point in time-space along the
511:
76:
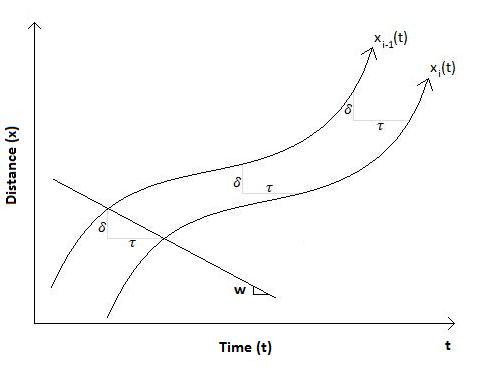
218:. The spacing between vehicles at traffic state A can be found using a geometric relationship found in the time-space diagram:
210:
In the time-space diagram, the trajectories of the leading (top) and following (bottom) vehicle are separated by the distance
47:
58:
463:
473:
83:
39:
178:
141:
112:
478:
121:
468:
505:
125:
447:
21:
437:
427:
242:
181:
can be used to calculate the density as well, given by the equation:
248:
Using relationships between the previous equations, variables
15:
300:, a function of time, can be determined using the equation:
144:(flow-density) is a triangular function, a traffic state
43:
443:Time-space trajectory for an aggressive driver:
433:Time-space trajectory for a cautious driver:
8:
48:introducing citations to additional sources
423:Time-space trajectory for a normal driver:
38:Relevant discussion may be found on the
489:
7:
14:
446:
436:
426:
241:
31:relies largely or entirely on a
20:
59:"Newell's car-following model"
1:
177:Geometric relations from the
464:Annual average daily traffic
384:under congested conditions:
346:under free-flow conditions:
117:Newell’s car-following model
528:
474:Intelligent driver model
512:Road traffic management
415:Driver aggressiveness
380:Position of vehicle
342:Position of vehicle
44:improve this article
256:can be solved for:
179:fundamental diagram
142:fundamental diagram
113:traffic flow theory
479:Traffic simulation
109:
108:
94:
519:
497:
494:
450:
440:
430:
245:
104:
101:
95:
93:
52:
24:
16:
527:
526:
522:
521:
520:
518:
517:
516:
502:
501:
500:
495:
491:
487:
460:
417:
402:
391:
376:
364:
353:
333:
322:
307:
284:
267:
229:
225:
204:
196:
188:
173:
169:
160:
153:
138:
105:
99:
96:
53:
51:
37:
25:
12:
11:
5:
525:
523:
515:
514:
504:
503:
499:
498:
488:
486:
483:
482:
481:
476:
471:
466:
459:
456:
416:
413:
400:
389:
374:
362:
351:
331:
320:
305:
282:
265:
227:
223:
202:
194:
186:
171:
167:
158:
151:
137:
134:
107:
106:
42:. Please help
28:
26:
19:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
524:
513:
510:
509:
507:
493:
490:
484:
480:
477:
475:
472:
470:
467:
465:
462:
461:
457:
455:
451:
449:
444:
441:
439:
434:
431:
429:
424:
421:
414:
412:
411:
407:
403:
396:
392:
385:
383:
378:
373:
369:
365:
358:
354:
347:
345:
340:
338:
334:
327:
323:
316:
312:
308:
301:
299:
295:
291:
286:
285:
278:
274:
270:
268:
261:
257:
255:
251:
246:
244:
239:
238:
234:
230:
219:
217:
213:
208:
206:
198:
190:
182:
180:
175:
174:
163:
161:
154:
147:
143:
140:Assuming the
135:
133:
131:
127:
123:
118:
114:
103:
100:December 2009
92:
89:
85:
82:
78:
75:
71:
68:
64:
61: –
60:
56:
55:Find sources:
49:
45:
41:
35:
34:
33:single source
29:This article
27:
23:
18:
17:
492:
469:Gipps' model
452:
445:
442:
435:
432:
425:
422:
418:
409:
405:
398:
394:
387:
386:
381:
379:
371:
367:
360:
356:
349:
348:
343:
341:
336:
329:
325:
318:
314:
310:
303:
302:
297:
293:
289:
287:
280:
276:
272:
271:
263:
259:
258:
253:
249:
247:
240:
236:
232:
221:
220:
215:
211:
209:
200:
192:
184:
183:
176:
165:
164:
156:
155:and density
149:
145:
139:
129:
126:traffic wave
116:
110:
97:
87:
80:
73:
66:
54:
30:
148:with speed
485:References
70:newspapers
214:and time
122:congested
40:talk page
506:Category
458:See also
136:Overview
128:speed,
84:scholar
288:Thus,
86:
79:
72:
65:
57:
377:* τ
260:τ = 1
170:= 1/s
91:JSTOR
77:books
317:min(
292:and
252:and
63:news
410:- δ
406:t-τ
401:i-1
399:= x
370:) +
368:t-τ
361:= x
339:))
226:= v
199:)/(
111:In
46:by
508::
328:),
315:=
275:=
269:)
264:wk
262:/(
237:+δ
207:)
205:+w
132:.
130:-w
115:,
408:)
404:(
397:)
395:t
393:(
390:i
388:x
382:i
375:f
372:v
366:(
363:i
359:)
357:t
355:(
352:i
350:x
344:i
337:t
335:(
332:A
330:x
326:t
324:(
321:A
319:x
313:)
311:t
309:(
306:i
304:x
298:i
294:δ
290:τ
283:j
281:k
279:/
277:1
273:δ
266:j
254:δ
250:τ
235:)
233:τ
231:(
228:A
224:A
222:s
216:τ
212:δ
203:A
201:v
197:w
195:j
193:k
191:(
189:=
187:A
185:k
172:A
168:A
166:k
159:A
157:k
152:A
150:v
146:A
102:)
98:(
88:·
81:·
74:·
67:·
50:.
36:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.