44:
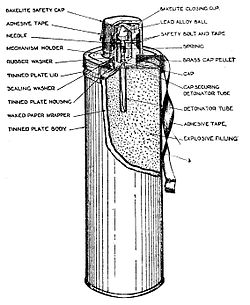
273:, from which the "Thermos bomb" nickname was derived. It was approximately 3.5 inches (89 mm) in diameter and 11 inches (280 mm) in length, and weighed 4.5 pounds (2.0 kg). Its explosive content consisted of 3.5 pounds (1.6 kg) of polar ammonal gelatine dynamite or nitrogelatine – both of which were highly flammable and could be detonated by the impact of small-arms fire. When thrown at a tank or other vehicle, a weighted tape held in the users hand unravelled and pulled free a safety pin, which was attached to a Type 247 "all-ways"
285:); this armed and then detonated the grenade. Its weight meant that it could only be thrown short distances, limiting its range to between 10 and 15 yards (9 and 14 m), and its detonation could injure the user if they did not find cover before it detonated. It was able to penetrate 2 inches (51 mm) of armour, and "damage severely any light tank." It was best used against the tracks of a tank, which it could easily blow off and force its crew to waste time by stopping and repairing it.
227:
was not well-equipped to defend the country in such an event; in the weeks after the
Dunkirk evacuation it could only field twenty-seven divisions. The Army was particularly short of anti-tank guns, 840 of which had been left behind in France leaving only 167 available in Britain; ammunition was so
293:
The No. 73 grenade was first issued in the last months of 1940, but it was rarely used as an anti-tank grenade; instead the fuze was usually removed and it was used as a demolition charge. It was withdrawn from service within a year, and reissued again in 1943 for the express purpose of being used
912:
311:
917:
932:
751:
261:(which simply uses a flammable liquid such as gasoline and a burning rag as a "fuse"). Ian Hogg states that the simplest of these grenades was the No. 73 grenade.
891:
927:
212:
744:
677:
592:
871:
737:
658:
639:
620:
573:
554:
247:
43:
922:
232:
251:
231:
As a result of these shortcomings, new anti-tank weapons had to be developed to equip the
British Army and the
242:, large numbers of which could be built in a very short space of time and for a low cost. They included the
246:, also known as the "sticky bomb", which was coated with a strong adhesive and stuck to a vehicle, and the
729:
295:
804:
789:
346:
269:
The No. 73 grenade had a roughly cylindrical shape and plastic screw-on cap, similar to that of a
886:
220:
216:
835:
673:
654:
635:
616:
588:
569:
550:
254:
188:
228:
scarce for the remaining guns that regulations forbade any being used for training purposes.
258:
208:
192:
101:
850:
819:
814:
325:
302:
threw it at
Heydrich's car in Prague. The bomb used for this purpose had been shortened.
840:
294:
for demolition work. On 27 May 1942, a modified version of the grenade was used in the
282:
906:
876:
809:
799:
257:
contained in a breakable glass container, like a more sophisticated variation of the
328: – World War II-era British anti-tank weapon invented by Lt Col Stewart Blacker
784:
779:
765:
545:
Bull, Stephen; Dennis, Peter; Delf, Brian; Chappell, Mike; Windrow, Martin (2004).
270:
239:
224:
196:
707:
299:
866:
845:
761:
278:
243:
881:
794:
724:
691:
17:
690:. Tank Hunting and Destruction, Military Training Manual No 42, Appendix D.
334:
236:
57:
60:
585:
The Last Ditch: Britain's Secret
Resistance and the Nazi Invasion Plan
316:
235:
with the means to repel German armoured vehicles. Many of these were
319: – soviet anti-tank hand-grenade used during the World War Two
355:
274:
733:
611:
Lowry, Bernard; Taylor, Chris; Boulanger, Vincent (2004).
377:
312:
British anti-invasion preparations of the Second World War
649:
Rottman, Gordon L.; Noon, Steve; Windrow, Martin (2005).
709:
School for Home Guard – news item featuring thermos bomb
296:
assassination of SS-Obergruppenführer
Reinhard Heydrich
688:
The Hand
Percussion Grenade (Anti-tank No. 73, Mark I)
892:
No. 42, No. 43 (Night), No 48, No 52 Signal
Grenades
360:
Pages displaying wikidata descriptions as a fallback
351:
Pages displaying wikidata descriptions as a fallback
339:
Pages displaying wikidata descriptions as a fallback
330:
Pages displaying wikidata descriptions as a fallback
321:
Pages displaying wikidata descriptions as a fallback
913:
World War II infantry weapons of the United
Kingdom
859:
828:
772:
566:
Tank
Killers: Anti-Tank Warfare by Men and Machines
461:
459:
457:
455:
453:
157:
149:
141:
128:
120:
112:
107:
97:
89:
79:
74:
66:
53:
34:
342:Pages displaying short descriptions with no spaces
48:Hand percussion grenade (anti-tank No. 73 Mark I)
632:The Home Guard: A Military and Political History
604:The Real Dad's Army: The Story of the Home Guard
195:. It got its nickname from the resemblance to a
145:Polar ammonal gelatine dynamite or nitrogelatine
745:
392:
390:
388:
386:
8:
531:Šolc, Jiří: Nikdo nás nezastaví. Prague 1992
918:World War II grenades of the United Kingdom
752:
738:
730:
668:Rottman, Gordon L.; Dennis, Peter (2008).
31:
933:Weapons and ammunition introduced in 1940
404:
402:
790:Nos. 3, 20, 24, 35 "Hales rifle grenade"
712:(Newsreel). British Pathé. 7 August 1941
425:
423:
651:World War II Infantry Anti-Tank Tactics
511:World War II Infantry Anti-Tank Tactics
370:
670:World War II Infantry Assault Tactics
489:World War II Infantry Assault Tactics
467:World War II Infantry Assault Tactics
7:
928:Hand grenades of the United Kingdom
815:Nos. 8, 9 double cylinder "jam tin"
219:between 26 May and 4 June 1940, a
25:
248:No. 76 special incendiary grenade
358: – rocket-propelled grenade
221:German invasion of Great Britain
42:
244:grenade, hand, anti-tank No. 74
606:. Hutchinson Library Services.
378:Military Training Manual No 42
1:
785:No. 2 grenade "Hales Pattern"
613:British Home Defences 1940–45
547:World War II Infantry Tactics
634:. Oxford University Press.
277:(the same type used in the
213:British Expeditionary Force
949:
725:Home Guard website article
211:and the evacuation of the
602:Longmate, Norman (1974).
136:
67:Place of origin
41:
630:Mackenzie, S.P. (1995).
349: – grenade launcher
153:3.5 pounds (1.6 kg)
116:4.5 pounds (2.0 kg)
795:Nos. 5, 23, 36 "Mills"
250:, essentially a simple
185:hand percussion grenade
132:3.5 inches (89 mm)
124:11 inches (280 mm)
672:. Osprey Publishing.
653:. Osprey Publishing.
615:. Osprey Publishing.
583:Lampe, David (1968).
549:. Osprey Publishing.
175:, also known as the "
846:No. 74 "sticky bomb"
760:British grenades of
207:With the end of the
851:No. 75 AT "Hawkins"
805:No. 15 ball grenade
587:. Greenhill Books.
347:Northover Projector
298:, when paratrooper
289:Operational history
223:seemed likely. The
217:the port of Dunkirk
150:Filling weight
923:Anti-tank grenades
887:Bomb, ground, 6 lb
564:Hogg, Ian (1995).
900:
899:
836:No. 68 AT (rifle)
679:978-1-84603-191-5
594:978-1-85367-730-4
568:. Pan Macmillan.
447:Hogg, pp. 239–240
438:Hogg, pp. 237–239
337: – artillery
189:anti-tank grenade
187:", was a British
169:
168:
29:Anti-tank grenade
16:(Redirected from
940:
841:No. 73 "Thermos"
754:
747:
740:
731:
721:
719:
717:
695:
694:. February 1941.
683:
664:
645:
626:
607:
598:
579:
560:
532:
529:
523:
520:
514:
507:
501:
498:
492:
485:
479:
476:
470:
463:
448:
445:
439:
436:
430:
427:
418:
417:Mackenzie, p. 20
415:
409:
406:
397:
396:Mackenzie, p. 92
394:
381:
375:
361:
352:
343:
340:
331:
322:
259:Molotov cocktail
252:white phosphorus
209:Battle of France
193:Second World War
191:used during the
102:Second World War
46:
37:
32:
21:
948:
947:
943:
942:
941:
939:
938:
937:
903:
902:
901:
896:
867:No. 82 "Gammon"
855:
824:
820:Garland grenade
768:
758:
715:
713:
706:
703:
698:
686:
680:
667:
661:
648:
642:
629:
623:
610:
601:
595:
582:
576:
563:
557:
544:
540:
535:
530:
526:
522:Bull, pp. 30–31
521:
517:
508:
504:
499:
495:
486:
482:
478:Longmate, p. 77
477:
473:
464:
451:
446:
442:
437:
433:
428:
421:
416:
412:
407:
400:
395:
384:
376:
372:
368:
359:
350:
341:
338:
329:
326:Blacker Bombard
320:
308:
291:
267:
205:
162:
160:
137:
84:
80:In service
75:Service history
49:
35:
30:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
946:
944:
936:
935:
930:
925:
920:
915:
905:
904:
898:
897:
895:
894:
889:
884:
879:
874:
869:
863:
861:
857:
856:
854:
853:
848:
843:
838:
832:
830:
826:
825:
823:
822:
817:
812:
807:
802:
797:
792:
787:
782:
780:Grenade, No. 1
776:
774:
773:Anti-personnel
770:
769:
759:
757:
756:
749:
742:
734:
728:
727:
722:
702:
701:External links
699:
697:
696:
684:
678:
665:
659:
646:
640:
627:
621:
608:
599:
593:
580:
574:
561:
555:
541:
539:
536:
534:
533:
524:
515:
502:
493:
480:
471:
449:
440:
431:
419:
410:
398:
382:
369:
367:
364:
363:
362:
353:
344:
332:
323:
314:
307:
304:
290:
287:
283:No. 69 grenade
266:
263:
204:
201:
181:Woolworth bomb
173:No. 73 grenade
167:
166:
163:
158:
155:
154:
151:
147:
146:
143:
139:
138:
134:
133:
130:
126:
125:
122:
118:
117:
114:
110:
109:
108:Specifications
105:
104:
99:
95:
94:
93:United Kingdom
91:
87:
86:
81:
77:
76:
72:
71:
70:United Kingdom
68:
64:
63:
55:
51:
50:
47:
39:
38:
28:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
945:
934:
931:
929:
926:
924:
921:
919:
916:
914:
911:
910:
908:
893:
890:
888:
885:
883:
880:
878:
875:
873:
870:
868:
865:
864:
862:
860:Special types
858:
852:
849:
847:
844:
842:
839:
837:
834:
833:
831:
827:
821:
818:
816:
813:
811:
808:
806:
803:
801:
800:No. 6 grenade
798:
796:
793:
791:
788:
786:
783:
781:
778:
777:
775:
771:
767:
763:
755:
750:
748:
743:
741:
736:
735:
732:
726:
723:
711:
710:
705:
704:
700:
693:
689:
685:
681:
675:
671:
666:
662:
660:1-84176-842-1
656:
652:
647:
643:
641:0-19-820577-5
637:
633:
628:
624:
622:1-84176-767-0
618:
614:
609:
605:
600:
596:
590:
586:
581:
577:
575:0-330-35316-0
571:
567:
562:
558:
556:1-84176-663-1
552:
548:
543:
542:
537:
528:
525:
519:
516:
512:
506:
503:
497:
494:
490:
484:
481:
475:
472:
468:
462:
460:
458:
456:
454:
450:
444:
441:
435:
432:
426:
424:
420:
414:
411:
405:
403:
399:
393:
391:
389:
387:
383:
379:
374:
371:
365:
357:
354:
348:
345:
336:
333:
327:
324:
318:
315:
313:
310:
309:
305:
303:
301:
297:
288:
286:
284:
280:
276:
272:
271:Thermos flask
264:
262:
260:
256:
253:
249:
245:
241:
240:hand grenades
238:
234:
229:
226:
222:
218:
214:
210:
202:
200:
198:
197:Thermos flask
194:
190:
186:
182:
178:
174:
164:
156:
152:
148:
144:
140:
135:
131:
127:
123:
119:
115:
111:
106:
103:
100:
96:
92:
88:
82:
78:
73:
69:
65:
62:
59:
56:
52:
45:
40:
33:
27:
19:
18:No 73 Grenade
766:World War II
714:. Retrieved
708:
687:
669:
650:
631:
612:
603:
584:
565:
546:
538:Bibliography
527:
518:
510:
505:
496:
488:
483:
474:
466:
443:
434:
413:
408:Hogg, p. 239
373:
292:
268:
230:
225:British Army
206:
184:
180:
176:
172:
170:
90:Used by
26:
877:No. 77 (WP)
872:No. 76 (WP)
762:World War I
500:Bull, p. 30
429:Lampe, p. 3
279:Gammon bomb
203:Development
907:Categories
882:Lewes bomb
692:War Office
366:References
255:incendiary
233:Home Guard
159:Detonation
85:1943–?1945
829:Anti-tank
509:Rottman,
487:Rottman,
465:Rottman,
335:Smith Gun
300:Jan Kubiš
237:anti-tank
161:mechanism
83:1940–1941
58:Anti-tank
306:See also
129:Diameter
716:8 March
513:, p. 62
491:, p. 62
469:, p. 25
183:", or "
177:Thermos
142:Filling
61:grenade
36:No. 73
810:No. 69
764:&
676:
657:
638:
619:
591:
572:
553:
317:RPG-40
265:Design
165:Impact
121:Length
215:from
718:2010
674:ISBN
655:ISBN
636:ISBN
617:ISBN
589:ISBN
570:ISBN
551:ISBN
356:PIAT
281:and
275:fuze
179:", "
171:The
113:Mass
98:Wars
54:Type
909::
452:^
422:^
401:^
385:^
199:.
753:e
746:t
739:v
720:.
682:.
663:.
644:.
625:.
597:.
578:.
559:.
380:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.