265:
37:
24:
283:
under acidic conditions in natural solvents, yet atheronal A is either not framed at all or is a minor part in the aqueous buffer. Practically the measures of both of the atheronals are equivalent were shaped by the response of cholesterol with human myeloperoxidase (MPO) within sight of its substrates hydrogen peroxide (H
291:) and Cl. There is five times more atheronal B that was created compare to atheronal A when cholesterol was incubated with hypochlorous corrosive (HOCl) and hydrogen peroxide. In any cases, in both the responses, immunoglobulin G (IgG) did not improve the arrangement of secosterols, recommending that singlet oxygen (O
315:
troposphere. Furthermore, such cholesterol oxidation items have been found in the brains of autopsy specimens from
Alzheimer’s disease patients. The ozonolyzed cholesterol quickens amyloidogenesis in these patients. They may play a crucial job in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis and neurodegenerative infections.
259:(ROS, for example, singlet oxygen, superoxide anion, hydroxyl radicals, and ozone). Atheronals, the major product of ozonolysis, when cholesterol is ozonized in the arrangement at high ozone fixations (>0.1%), are the substance that need be give extra care to since it have huge effect on the human body.
282:
that occur so smoothly in the biological system to produce atheronal B. Atheronal A and B were produced in an ozone-autonomous way using the Hock-cleavage of 5α-hydroperoxy cholesterol, which can emerge from the singlet oxygen ene reaction with cholesterol. However, atheronal B is shaped effectively
303:
When the ozonolysis of cholesterol reaction occurs, the atheronals as a product will quicken the normal conversion of monocytes to macrophages, are rapidly taken up by macrophages, hasten the inflammatory response on and increase the stickiness of the interior arterial walls, and contribute to the
314:
setting could lead to the recruitment, entrapment, dysfunction, and ultimate destruction of macrophages, with the major leukocyte player in inflammatory artery disease. Furthermore, atheronals have additionally been detected in lung tissue, potentially from exposure of lung surfactant to the
84:
92:
331:
Takeuchi, Cindy; Galvé, Roger; Nieva, Jorgé; Witter, Daniel; Wentworth, Anita; Troseth, Ryan; Lerner, Richard; Wentworth, Paul (17 May 2006). "Proatherogenic
Effects of the Cholesterol Ozonolysis Products, Atheronal-A and Atheronal-B".
459:
Tomono, Susumu; Miyoshi, Noriyuki; Sato, K; Ohba, Y; Ohshima, H (29 May 2009). "Formation of cholesterol ozonolysis products through an ozone-free mechanism mediated by the myeloperoxidase-H2O2-chloride system".
240:. Atheronal A (secosterol A) is the major product of ozonolysis which is 3β-hydroxy-5-oxo-5,6-secocholestan-6-al. Atheronal B (secosterol B) is formed by the intramolecular
140:
367:
Tomono, Susumu; Miyoshi, Noriyuki; Hidemi, Shiokawa; Tomoe, Iwabuchi; Yasuaki, Aratani; Tatsuya, Higashi; Hiroshi, Oshima (January 2011).
217:
264:
369:"Formation of cholesterol ozonolysis products in vitro and in vivo through a myeloperoxidase-dependent pathway"
295:) and perhaps another oxidant, however not an ozone-like oxidant, intervened the development of secosterols.
255:, a alkene that are located in aspiratory surfactant, anticipated in the attack by ozone among the different
256:
53:
308:, the hardening of the arteries. Atheronals possess biological effects that if translated to an
477:
400:
349:
500:
469:
439:
431:
390:
380:
341:
168:
305:
505:
444:
419:
395:
368:
279:
241:
211:
494:
126:
118:
244:
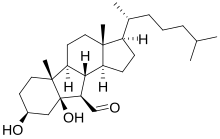
of atheronal A, which is 3β-hydroxy-5β-hydroxy-B-norcholestane-6β-carboxaldehyde.
252:
473:
275:
233:
196:
481:
404:
353:
435:
385:
36:
23:
310:
104:
345:
210:
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their
263:
237:
91:
83:
72:
274:
In the mechanism, atheronal A are produces from a process called
420:"Environmental Disease: Ozone: Good, Bad, or Indifferent?"
59:
B: 3β-Hydroxy-5β-hydroxy-B-norcholestane-6β-carboxaldehyde
153:
B: C(CCCC(C)C)1CCC21(CCC3C2(4(3(CC(C4)O)C)O)C=O)C
462:
148:A: C(CCCC(C)C)1CC21(CC(2CC=O)3(CC(CC3=O)O)C)C
125:
117:
8:
236:formed in the reaction of cholesterol with
304:formation of arterial plaques. This cause
268:Mechanism of the ozonolysis of cholesterol
57:A: 3β-Hydroxy-5-oxo-5,6-secocholestan-6-al
15:
443:
394:
384:
323:
145:
7:
299:Effects of atheronals in human body
278:. Next, the atheronal A go through
107:
418:Weinhold, Bob (1 September 2006).
14:
424:Environmental Health Perspectives
180:
35:
22:
214:(at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
186:
174:
1:
522:
474:10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.03.155
232:are biologically relevant
373:Journal of Lipid Research
248:Ozonolysis of cholesterol
208:
161:
136:
64:
52:
47:
34:
21:
257:reactive oxygen species
269:
436:10.1289/ehp.114-a522b
267:
386:10.1194/jlr.M006775
204: g·mol
18:
270:
218:Infobox references
16:
346:10.1021/bi0604330
340:(23): 7162–7170.
226:Chemical compound
224:
223:
93:Interactive image
85:Interactive image
513:
486:
485:
456:
450:
449:
447:
415:
409:
408:
398:
388:
364:
358:
357:
328:
203:
188:
182:
176:
169:Chemical formula
129:
121:
109:
95:
87:
39:
26:
19:
521:
520:
516:
515:
514:
512:
511:
510:
491:
490:
489:
458:
457:
453:
417:
416:
412:
366:
365:
361:
330:
329:
325:
321:
306:atherosclerosis
301:
294:
290:
286:
250:
227:
220:
215:
201:
191:
185:
179:
171:
157:
154:
149:
144:
143:
132:
110:
98:
76:
60:
58:
43:
40:
30:
27:
12:
11:
5:
519:
517:
509:
508:
503:
493:
492:
488:
487:
451:
410:
359:
322:
320:
317:
300:
297:
292:
288:
284:
280:aldol reaction
272:
271:
249:
246:
242:aldol reaction
225:
222:
221:
216:
212:standard state
209:
206:
205:
199:
193:
192:
189:
183:
177:
172:
167:
164:
163:
159:
158:
156:
155:
152:
150:
147:
139:
138:
137:
134:
133:
131:
130:
122:
113:
111:
103:
100:
99:
97:
96:
88:
79:
77:
70:
67:
66:
62:
61:
56:
50:
49:
45:
44:
41:
32:
31:
28:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
518:
507:
504:
502:
499:
498:
496:
483:
479:
475:
471:
467:
463:
455:
452:
446:
441:
437:
433:
429:
425:
421:
414:
411:
406:
402:
397:
392:
387:
382:
378:
374:
370:
363:
360:
355:
351:
347:
343:
339:
335:
327:
324:
318:
316:
313:
312:
307:
298:
296:
281:
277:
266:
262:
261:
260:
258:
254:
247:
245:
243:
239:
235:
231:
219:
213:
207:
200:
198:
195:
194:
173:
170:
166:
165:
160:
151:
146:
142:
135:
128:
123:
120:
115:
114:
112:
106:
102:
101:
94:
89:
86:
81:
80:
78:
74:
69:
68:
63:
55:
51:
46:
38:
33:
25:
20:
468:(2): 222–7.
465:
461:
454:
427:
423:
413:
379:(1): 87–97.
376:
372:
362:
337:
334:Biochemistry
333:
326:
309:
302:
273:
251:
229:
228:
65:Identifiers
430:(9): A522.
253:Cholesterol
162:Properties
54:IUPAC names
42:Atheronal B
29:Atheronal A
17:Atheronals
495:Categories
319:References
276:ozonolysis
234:oxysterols
230:Atheronals
197:Molar mass
71:3D model (
482:19345674
405:20921334
354:16752907
127:24779591
124:B:
116:A:
90:B:
82:A:
501:Sterols
445:1570068
396:2999934
311:in vivo
202:418.662
119:6398884
105:PubChem
480:
442:
403:
393:
352:
141:SMILES
48:Names
506:Ozone
238:ozone
73:JSmol
478:PMID
401:PMID
350:PMID
470:doi
466:383
440:PMC
432:doi
428:114
391:PMC
381:doi
342:doi
108:CID
497::
476:.
464:.
438:.
426:.
422:.
399:.
389:.
377:52
375:.
371:.
348:.
338:45
336:.
184:46
178:27
484:.
472::
448:.
434::
407:.
383::
356:.
344::
293:2
289:2
287:O
285:2
190:3
187:O
181:H
175:C
75:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.