46:
33:
235:
forward to the anterior end, back to the posterior end and then forward again to the anterior end, before opening at the female gonopore. Small testes and yolk cells are scattered throughout most of the tissue. The male gonopore is at the posterior end, and there is no gut. The larvae have ten wrench-shaped hooks and these are retained at the posterior end of the adult body.
234:
Unlike other tapeworms, the body of amphilinids is not divided into segments, instead being leaf-shaped and laterally flattened. There is a proboscis and several frontal glands at the anterior end, and an ovary and a seminal receptacle at the posterior end. The uterus extends from the posterior end,
257:), and there may be as many as thirty worms in one turtle host. It is uncertain how the worm's eggs are released into the open water, but somehow they do emerge. When the eggs hatch, the developing larvae seek out an intermediate host, a suitable freshwater
265:
by chemical action and by sawing through the shell with miniature hooks. The young tapeworm then continues its development in the crustacean, and if the crayfish is eaten by a turtle, the larva forces its way through the turtle's
546:
322:
639:
533:
652:
559:
422:
711:
678:
585:
300:
657:
564:
45:
442:
250:
213:
330:
241:
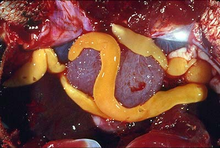
is bright yellow and can grow to a length of 150 mm (6 in) and a width of 15 mm (0.6 in).
473:
140:
511:
683:
590:
288:
162:
40:
32:
665:
626:
572:
551:
520:
418:
670:
577:
412:
706:
194:
700:
631:
525:
197:
107:
97:
617:
496:
505:
356:
267:
209:
205:
190:
57:
611:
490:
258:
220:). It is found in eastern Australia. It is the only species in the genus
201:
77:
644:
538:
386:
262:
87:
67:
467:
414:
Encyclopedic
Reference of Parasitology: Biology, Structure, Function
249:
The adult stage of this tapeworm is found in the body cavity of the
212:. It is an internal parasite of freshwater turtles including the
326:
208:, because their bodies are unsegmented and are not divided into
471:
323:"The Amphilinidea, a small group of aberrant tapeworms"
417:. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 72.
601:
480:
436:
434:
8:
200:. Amphilinids are commonly considered to be
204:, yet differ from true tapeworms, subclass
468:
31:
20:
350:
348:
279:
7:
14:
441:Rhode, Klaus (18 February 2010).
301:World Register of Marine Species
44:
270:into the turtle's body cavity.
1:
391:The Tree of Life Web Project
387:"Amphilinidea: Amphilinidae"
365:The Tree of Life Web Project
321:Rohde, Klaus (2 June 2011).
728:
251:eastern long-necked turtle
214:eastern long-necked turtle
712:Animals described in 1931
603:Australamphilina elongata
291:Australamphilina elongata
186:Australamphilina elongata
168:
161:
150:Australamphilina elongata
146:
139:
41:Scientific classification
39:
30:
25:Australamphilina elongata
23:
411:Mehlhorn, Heinz (2001).
385:Rohde, Klaus (2000).
355:Rohde, Klaus (2000).
255:Chelodina longicollis
218:Chelodina longicollis
445:Gigantolina elongata
359:Gigantolina elongata
261:, and penetrate its
175:Gigantolina elongata
451:Parasite of the Day
16:Species of flatworm
287:Bray, Rod (2018).
694:
693:
666:Open Tree of Life
573:Open Tree of Life
474:Taxon identifiers
424:978-3-540-66819-0
182:
181:
719:
687:
686:
674:
673:
661:
660:
648:
647:
635:
634:
622:
621:
620:
594:
593:
581:
580:
568:
567:
555:
554:
542:
541:
529:
528:
516:
515:
514:
512:Australamphilina
501:
500:
499:
482:Australamphilina
469:
462:
461:
459:
457:
438:
429:
428:
408:
402:
401:
399:
397:
382:
376:
375:
373:
371:
352:
343:
342:
340:
338:
329:. Archived from
318:
312:
311:
309:
307:
284:
223:Australamphilina
189:is a species of
152:
132:A. elongata
119:Australamphilina
49:
48:
35:
21:
727:
726:
722:
721:
720:
718:
717:
716:
697:
696:
695:
690:
682:
677:
669:
664:
656:
651:
643:
638:
630:
625:
616:
615:
610:
597:
589:
584:
576:
571:
563:
558:
550:
545:
537:
532:
524:
519:
510:
509:
504:
495:
494:
489:
476:
466:
465:
455:
453:
440:
439:
432:
425:
410:
409:
405:
395:
393:
384:
383:
379:
369:
367:
354:
353:
346:
336:
334:
320:
319:
315:
305:
303:
293:Johnston, 1931"
286:
285:
281:
276:
247:
232:
157:
154:
148:
135:
78:Platyhelminthes
43:
17:
12:
11:
5:
725:
723:
715:
714:
709:
699:
698:
692:
691:
689:
688:
675:
662:
649:
636:
623:
607:
605:
599:
598:
596:
595:
582:
569:
556:
543:
530:
517:
502:
486:
484:
478:
477:
472:
464:
463:
430:
423:
403:
377:
344:
313:
278:
277:
275:
272:
246:
243:
231:
228:
180:
179:
178:
177:
166:
165:
159:
158:
155:
144:
143:
137:
136:
129:
127:
123:
122:
115:
111:
110:
105:
101:
100:
95:
91:
90:
85:
81:
80:
75:
71:
70:
65:
61:
60:
55:
51:
50:
37:
36:
28:
27:
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
724:
713:
710:
708:
705:
704:
702:
685:
680:
676:
672:
667:
663:
659:
654:
650:
646:
641:
637:
633:
628:
624:
619:
613:
609:
608:
606:
604:
600:
592:
587:
583:
579:
574:
570:
566:
561:
557:
553:
548:
544:
540:
535:
531:
527:
522:
518:
513:
507:
503:
498:
492:
488:
487:
485:
483:
479:
475:
470:
452:
448:
446:
437:
435:
431:
426:
420:
416:
415:
407:
404:
392:
388:
381:
378:
366:
362:
360:
351:
349:
345:
333:on 2011-08-13
332:
328:
324:
317:
314:
302:
298:
294:
292:
283:
280:
273:
271:
269:
264:
260:
256:
252:
244:
242:
240:
236:
229:
227:
225:
224:
219:
215:
211:
207:
203:
199:
196:
192:
188:
187:
176:
173:
172:
171:
167:
164:
160:
156:Johnson, 1831
153:
151:
145:
142:
141:Binomial name
138:
134:
133:
128:
125:
124:
121:
120:
116:
113:
112:
109:
106:
103:
102:
99:
96:
93:
92:
89:
86:
83:
82:
79:
76:
73:
72:
69:
66:
63:
62:
59:
56:
53:
52:
47:
42:
38:
34:
29:
26:
22:
19:
602:
481:
454:. Retrieved
450:
444:
413:
406:
394:. Retrieved
390:
380:
368:. Retrieved
364:
358:
335:. Retrieved
331:the original
316:
304:. Retrieved
296:
290:
282:
254:
248:
238:
237:
233:
222:
221:
217:
198:Amphilinidea
193:worm in the
185:
184:
183:
174:
169:
149:
147:
131:
130:
118:
117:
108:Amphilinidae
98:Amphilinidea
24:
18:
506:Wikispecies
239:A. elongata
230:Description
210:proglottids
701:Categories
274:References
268:oesophagus
245:Life cycle
170:(Species)
618:Q55604498
497:Q61493679
206:Eucestoda
202:tapeworms
191:parasitic
126:Species:
64:Kingdom:
58:Eukaryota
612:Wikidata
491:Wikidata
259:crayfish
163:Synonyms
104:Family:
74:Phylum:
68:Animalia
54:Domain:
707:Cestoda
684:1026453
671:7985940
658:1059790
645:9386976
591:1026451
578:7985939
565:1058894
552:1454852
539:7013062
263:cuticle
114:Genus:
94:Order:
88:Cestoda
84:Class:
456:27 May
421:
396:27 May
370:26 May
337:26 May
306:26 May
679:WoRMS
632:689M4
586:WoRMS
547:IRMNG
526:7NQ6G
297:WoRMS
195:order
653:ITIS
640:GBIF
560:ITIS
534:GBIF
458:2018
419:ISBN
398:2018
372:2018
339:2018
327:Knol
308:2018
627:CoL
521:CoL
703::
681::
668::
655::
642::
629::
614::
588::
575::
562::
549::
536::
523::
508::
493::
449:.
433:^
389:.
363:.
347:^
325:.
299:.
295:.
226:.
460:.
447:"
443:"
427:.
400:.
374:.
361:"
357:"
341:.
310:.
289:"
253:(
216:(
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.