26:
319:
only with actin filaments and do not promote filament depolymerisation or fragmentation. Although these proteins are biochemically distinct and play different roles in actin dynamics, they all appear to use the ADF-H domain for their interactions with
328:
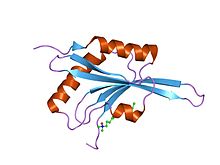
in which the four central strands (beta2-beta5) are anti-parallel and the two edge strands (beta1 and beta6) run parallel with the neighbouring strands. The sheet is surrounded by two
174:
86:
110:
406:"Structural conservation between the actin monomer-binding sites of twinfilin and actin-depolymerizing factor (ADF)/cofilin"
194:
316:
233:
486:
Liu L, Wei Z, Wang Y, Wan M, Cheng Z, Gong W (November 2004). "Crystal structure of human coactosin-like protein".
130:
541:
182:
281:
257:
277:
225:
178:
123:
135:
91:
404:
Paavilainen VO, Merckel MC, Falck S, Ojala PJ, Pohl E, Wilmanns M, Lappalainen P (November 2002).
245:
249:
503:
468:
427:
383:
265:
253:
169:
495:
458:
417:
373:
365:
161:
302:
273:
269:
463:
446:
311:
composed of an N-terminal ADF-H domain followed by a variable region and a C-terminal
535:
378:
353:
214:
115:
54:
157:
67:
527:
79:
329:
499:
447:"Structure and expression of a novel filarial gene for glia maturation factor"
325:
312:
285:
222:
211:
218:
507:
431:
422:
405:
472:
387:
354:"The ADF homology (ADF-H) domain: a highly exploited actin-binding module"
119:
25:
523:
369:
308:
74:
298:
292:
261:
241:
237:
103:
98:
210:(actin-depolymerising factor homology domain) is an approximately 150
189:
289:
276:
by depolymerising/fragmenting actin filaments. ADF/cofilins bind
519:
151:
61:
49:
352:
Lappalainen P, Kessels MM, Cope MJ, Drubin DG (August 1998).
260:(GMFs) beta and gamma. ADF/cofilins are small actin-binding
445:
Liu LX, Xu H, Weller PF, Shi A, Debnath I (February 1997).
518:
This article incorporates text from the public domain
188:
168:
150:
145:
129:
109:
97:
85:
73:
60:
48:
40:
35:
30:
crystal structure of adf1 from arabidopsis thaliana
18:
324:The ADF-H domain consists of a six-stranded mixed
399:
397:
347:
345:
8:
297:Twinfilins, which are actin monomer-binding
307:Abp1/Drebrins, which are relatively large
142:
24:
462:
421:
377:
264:composed of a single ADF-H domain. They
341:
272:and promote rapid filament turnover in
15:
7:
284:-actin and inhibit the spontaneous
14:
280:-actin with higher affinity than
301:that are composed of two ADF-H
1:
464:10.1016/S0378-1119(96)00585-9
146:Available protein structures:
232:ADF/cofilins, which include
558:
517:
500:10.1016/j.jmb.2004.09.036
217:that is present in three
141:
23:
268:both actin-monomers and
258:glia maturation factors
423:10.1074/jbc.M208225200
226:actin-binding proteins
206:In molecular biology,
370:10.1091/mbc.9.8.1951
221:distinct classes of
204:
203:
200:
199:
195:structure summary
549:
512:
511:
483:
477:
476:
466:
442:
436:
435:
425:
416:(45): 43089–95.
401:
392:
391:
381:
349:
315:. Abp1/Drebrins
219:phylogenetically
143:
28:
16:
557:
556:
552:
551:
550:
548:
547:
546:
542:Protein domains
532:
531:
530:
516:
515:
485:
484:
480:
444:
443:
439:
403:
402:
395:
358:Mol. Biol. Cell
351:
350:
343:
338:
332:on each side .
31:
12:
11:
5:
555:
553:
545:
544:
534:
533:
514:
513:
478:
437:
393:
340:
339:
337:
334:
322:
321:
305:
295:
202:
201:
198:
197:
192:
186:
185:
172:
166:
165:
155:
148:
147:
139:
138:
133:
127:
126:
113:
107:
106:
101:
95:
94:
89:
83:
82:
77:
71:
70:
65:
58:
57:
52:
46:
45:
42:
38:
37:
33:
32:
29:
21:
20:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
554:
543:
540:
539:
537:
529:
525:
521:
509:
505:
501:
497:
494:(2): 317–23.
493:
489:
482:
479:
474:
470:
465:
460:
456:
452:
448:
441:
438:
433:
429:
424:
419:
415:
411:
410:J. Biol. Chem
407:
400:
398:
394:
389:
385:
380:
375:
371:
367:
364:(8): 1951–9.
363:
359:
355:
348:
346:
342:
335:
333:
331:
330:alpha-helices
327:
318:
314:
310:
306:
304:
300:
296:
294:
291:
287:
283:
279:
275:
271:
267:
263:
259:
255:
251:
247:
243:
239:
235:
231:
230:
229:
227:
224:
220:
216:
213:
209:
196:
193:
191:
187:
184:
180:
176:
173:
171:
167:
163:
159:
156:
153:
149:
144:
140:
137:
134:
132:
128:
125:
121:
117:
114:
112:
108:
105:
102:
100:
96:
93:
90:
88:
84:
81:
78:
76:
72:
69:
66:
63:
59:
56:
53:
51:
47:
43:
39:
34:
27:
22:
17:
491:
488:J. Mol. Biol
487:
481:
454:
450:
440:
413:
409:
361:
357:
323:
288:exchange on
208:ADF-H domain
207:
205:
44:Cofilin_ADF
36:Identifiers
19:Cofilin_ADF
457:(1): 1–5.
336:References
326:beta-sheet
313:SH3 domain
286:nucleotide
246:actophorin
223:eukaryotic
212:amino acid
158:structures
528:IPR002108
270:filaments
250:coactosin
104:PDOC00297
80:IPR002108
536:Category
524:InterPro
508:15522287
432:12207032
317:interact
309:proteins
299:proteins
293:monomers
262:proteins
254:depactin
175:RCSB PDB
75:InterPro
473:9047337
388:9693358
303:domains
242:destrin
238:cofilin
136:cd00013
99:PROSITE
55:PF00241
506:
471:
430:
386:
376:
320:actin.
190:PDBsum
164:
154:
124:SUPFAM
68:CL0092
41:Symbol
379:25446
290:actin
274:cells
215:motif
120:SCOPe
111:SCOP2
87:SMART
522:and
520:Pfam
504:PMID
469:PMID
451:Gene
428:PMID
384:PMID
266:bind
256:and
183:PDBj
179:PDBe
162:ECOD
152:Pfam
116:2prf
64:clan
62:Pfam
50:Pfam
496:doi
492:344
459:doi
455:186
418:doi
414:277
374:PMC
366:doi
282:ATP
278:ADP
234:ADF
170:PDB
131:CDD
92:ADF
538::
526::
502:.
490:.
467:.
453:.
449:.
426:.
412:.
408:.
396:^
382:.
372:.
360:.
356:.
344:^
252:,
248:,
244:,
240:,
236:,
228:.
181:;
177:;
160:/
122:/
118:/
510:.
498::
475:.
461::
434:.
420::
390:.
368::
362:9
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.