631:, hemorrhage, edema) that exerts downward pressure on the brainstem, causing the nerve to stretch along the clivus. This type of traction injury can affect either side first. A right-sided brain tumor can produce either a right-sided or a left-sided sixth nerve palsy as an initial sign. Thus a right-sided sixth nerve palsy does not necessarily imply a right-sided cause. Sixth nerve palsies are infamous as "false localizing signs." Neurological signs are described as "false localizing" if they reflect dysfunction distant or remote from the expected anatomical location of pathology. Isolated sixth nerve palsies in children are assumed to be due to brain tumors until proven otherwise.
41:
369:
593:. The affected eye is pulled medially. In order to see without double vision, patients will turn their heads sideways so that both eyes are looking sideways. On formal testing, the affected eye cannot abduct past the midline – it cannot look sideways, toward the temple. Partial damage to the sixth nerve causes weak or incomplete abduction of the affected eye. The diplopia is worse on attempted lateral gaze, as would be expected (since the lateral gaze muscle is impaired).
1135:
1087:
1123:
1147:
1099:
1111:
29:
412:
564:. The affected eye is pulled to look towards the midline. In order to see without double vision, patients will rotate their heads so that both eyes are toward the temple. Partial damage to the abducens nerve causes weak or incomplete abduction of the affected eye. The diplopia is worse on attempts at looking laterally.
616:. Wernicke–Korsakoff syndrome is caused by thiamine deficiency, classically due to alcoholism. The characteristic ocular abnormalities are nystagmus and lateral rectus weakness. Tolosa-Hunt syndrome is an idiopathic granulomatous disease that causes painful oculomotor (especially sixth nerve) palsies.
647:
that affects both eyes simultaneously. The abducens nucleus contains two types of cells: motor neurons that control the lateral rectus muscle on the same side, and interneurons that cross the midline and connect to the contralateral oculomotor nucleus (which controls the medial rectus muscle of the
576:
The central anatomy of the sixth nerve predicts (correctly) that infarcts affecting the dorsal pons at the level of the abducens nucleus can also affect the facial nerve, producing an ipsilateral facial palsy together with a lateral rectus palsy. The anatomy also predicts (correctly) that infarcts
388:. Axons from the facial nerve loop around the abducens nucleus, creating a slight bulge (the facial colliculus) that is visible on the dorsal surface of the floor of the fourth ventricle. The abducens nucleus is close to the midline, like the other motor nuclei that control eye movements (the
577:
involving the ventral pons can affect the sixth nerve and the corticospinal tract simultaneously, producing a lateral rectus palsy associated with a contralateral hemiparesis. These rare syndromes are of interest primarily as useful summaries of the anatomy of the brainstem.
596:
Peripheral sixth nerve damage can be caused by tumors, aneurysms, or fractures – anything that directly compresses or stretches the nerve. Other processes that can damage the sixth nerve include strokes (infarctions), demyelination, infections (e.g.
605:. Iatrogenic injury is also known to occur, with the abducens nerve being the most commonly injured cranial nerve in halo orthosis placement. The resultant palsy is identified through loss of lateral gaze after application of the orthosis.
659:(MLF), a nerve tract that connects the three extraocular motor nuclei (abducens, trochlear and oculomotor) into a single functional unit. Lesions of the abducens nucleus and the MLF produce observable sixth nerve problems, most notably
572:
of the intracavernous carotid artery. Mass lesions that push the brainstem downward can damage the nerve by stretching it between the point where it emerges from the pons and the point where it hooks over the petrous temporal bone.
648:
opposite eye). In normal vision, lateral movement of one eye (lateral rectus muscle) is precisely coupled to medial movement of the other eye (medial rectus muscle), so that both eyes remain fixed on the same object.
567:
The long course of the abducens nerve between the brainstem and the eye makes it vulnerable to injury at many levels. For example, fractures of the petrous temporal bone can selectively damage the nerve, as can
904:Özveren, Mehmet Faik; Erol, Fatih Serhat; Alkan, Alpay; Kocak, Ayhan; Önal, Cagatay; Türe, Uğur (1 February 2007). "Microanatomical Architecture of Dorello's Canal and Its Clinical Implications".
691:
15–40% of people with tuberculosis have some resulting cranial nerve deficit. The sixth nerve is the most commonly affected cranial nerve in immunocompetent people with tuberculosis.
1134:
1086:
2080:
2075:
2004:
1859:
1839:
1122:
849:
299:
1844:
1445:
146:
2022:
1849:
1796:
1791:
671:
The sixth nerve is one of the final common pathways for numerous cortical systems that control eye movement in general. Cortical control of eye movement (
1854:
1664:
712:
1455:
2070:
1383:
1221:
1654:
2176:
1649:
1068:
825:
122:
2229:
1669:
1392:
1378:
545:
292:
2027:
1659:
1637:
463:
2144:
1975:
1970:
1926:
1921:
1632:
153:
609:
1952:
1947:
1098:
522:
2149:
2060:
656:
432:
2101:
2065:
285:
141:
1368:
601:), cavernous sinus diseases and various neuropathies. Perhaps the most common overall cause of sixth nerve impairment is
2214:
2209:
1214:
660:
403:(which runs longitudinally through the pons at this level) before exiting the brainstem at the pontomedullary junction.
40:
1110:
1880:
1146:
1324:
1285:
1999:
1697:
1622:
1450:
1172:
495:
1163:
613:
2137:
1992:
1987:
1982:
1577:
1460:
716:
475:
399:
Motor axons leaving the abducens nucleus run ventrally and caudally through the pons. They pass lateral to the
93:
748:
2219:
2204:
2199:
1711:
1207:
869:
711:"Abducens" is more common in recent literature, while "abducent" predominates in the older literature. The
549:
471:
272:
231:
2234:
1769:
1599:
1584:
1572:
906:
772:
705:
552:
of the right eye. This individual tries to look to his right, but the right eye fails to turn to the side.
237:
129:
117:
1176:
1048:
Wilson-Pauwels L, Akesson EJ, Stewart PA. Cranial Nerves: Anatomy and
Clinical Comments. Decker, 1998.
2040:
1827:
1140:
Dissection showing origins of right ocular muscles, and nerves entering by the superior orbital fissure.
740:
514:
483:
479:
337:
69:
1024:
Brodal A. Neurological
Anatomy in Relation to Clinical Medicine, 3rd ed. Oxford University Press, 1981
957:
368:
2035:
1757:
1687:
1612:
864:
590:
561:
352:
1092:
Dura mater and its processes exposed by removing part of the right half of the skull, and the brain.
110:
2168:
1552:
1470:
676:
628:
602:
400:
341:
2224:
1627:
1547:
1363:
976:
939:
843:
708:
officially recognizes two different
English translations: "abducent nerve" and "abducens nerve".
443:
389:
1183:
Animations of extraocular cranial nerve and muscle function and damage (University of
Liverpool)
1045:
Victor, M, Ropper, AH. Adam's and Victor's
Principles of Neurology, 7th ed. McGraw-Hill, 2001.
459:
2159:
1745:
1740:
1723:
1413:
1064:
996:
931:
923:
886:
831:
821:
640:
539:
428:
393:
385:
349:
345:
255:
1036:
Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM. Principles of Neural
Science, 4th ed. McGraw-Hill, 2000
521:. This muscle is responsible for outward gaze. The abducens nerve carries axons of type GSE,
2132:
2106:
2096:
1885:
1875:
1752:
1692:
1511:
1490:
1480:
1433:
1387:
1351:
1182:
988:
915:
878:
451:
381:
377:
213:
201:
59:
1030:
Butler AB, Hodos W. Comparative
Vertebrate Neuroanatomy, 2nd ed. Wiley-Interscience, 2005
2120:
1822:
1728:
1485:
1404:
1300:
1273:
467:
447:
249:
207:
189:
751:, which can retract the eye for protection. Homologous abducens nerves are found in all
1817:
1735:
1644:
1589:
1295:
1239:
1231:
919:
680:
652:
267:
183:
173:
1128:
Figure showing the mode of innervation of the Recti medialis and lateralis of the eye.
1013:
Federative
Committee on Anatomical Terminology. Terminologia Anatomica. Thieme, 1998
2193:
1939:
1910:
1832:
1809:
1780:
1594:
1251:
624:
333:
943:
1564:
1531:
1334:
436:
225:
470:. In the cavernous sinus, it runs anterior-ward alongside (inferolateral to) the
98:
1899:
1339:
1312:
1033:
Carpenter MB. Core Text of
Neuroanatomy, 4th ed. Williams & Wilkins, 1991.
752:
620:
243:
195:
992:
882:
1167:
644:
598:
556:
Damage to the peripheral part of the abducens nerve will cause double vision (
455:
450:) when it emerges from the brainstem. It runs upward between the pons and the
105:
28:
1187:
927:
835:
134:
1027:
Brodal P. The
Central Nervous System, 3rded. Oxford University Press, 2004
1021:
Blumenfeld H. Neuroanatomy Through Clinical Cases. Sinauer Associates, 2002
760:
569:
544:
518:
420:
1000:
935:
372:
Axial section of the Brainstem (Pons) at the level of the Facial Colliculus
890:
1192:
756:
672:
586:
557:
1042:
Patten J. Neurological Differential Diagnosis, 2nd ed. Springer, 1996.
2052:
744:
720:
704:
The Latin name for the sixth cranial nerve is "nervus abducens". The
336:
in humans and various other animals that controls the movement of the
159:
2014:
1199:
794:
792:
790:
788:
724:
499:
1039:
Martin JH. Neuroanatomy Text and Atlas, 3rd ed. McGraw-Hill, 2003.
439:. It runs upwards and forwards from this position to reach the eye.
45:
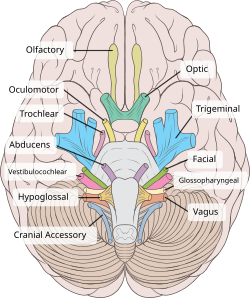
Inferior view of the human brain, with the cranial nerves labelled.
863:
Umansky, Felix; Elidan, Josef; Valarezo, Alberto (1 August 1991).
543:
411:
410:
367:
81:
739:
The abducens nerve controls the movement of a single muscle, the
619:
Indirect damage to the sixth nerve can be caused by any process (
1962:
1190:
at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (
502:
424:
1203:
639:
Damage to the abducens nucleus does not produce an isolated
1059:
Susan Standring; Neil R. Borley; et al., eds. (2008).
585:
Complete interruption of the peripheral sixth nerve causes
981:
Optometry (Journal of the American Optometric Association)
1061:
Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical practice
977:"Acquired abducens nerve palsy secondary to tuberculosis"
715:
uses "abducens nerve" in its Medical Subject Heading (
958:"Halo Orthosis Immobilization – Spine – Orthobullets"
589:(double vision), due to the unopposed action of the
2158:
2119:
2089:
2051:
2013:
1961:
1937:
1908:
1898:
1868:
1807:
1778:
1768:
1710:
1680:
1610:
1561:
1540:
1530:
1501:
1432:
1403:
1350:
1311:
1272:
1238:
1104:
Superficial dissection of brain-stem. Ventral view.
608:Rare causes of isolated sixth nerve damage include
140:
128:
116:
104:
92:
80:
75:
65:
55:
50:
21:
798:
474:. It enters the orbit through (medial end of) the
1063:(40th ed.). London: Churchill Livingstone.
975:Smith, Daniel E.; Blasi, Ashley (August 2009).
458:to run between the dura and the skull through
1215:
494:The human abducens nerve is derived from the
466:, it makes a sharp turn forward to enter the
293:
8:
380:is located in the pons, on the floor of the
1116:Hind- and mid-brains; postero-lateral view.
727:biomedical databases. The 39th edition of
560:), due to the unopposed muscle tone of the
1905:
1775:
1537:
1222:
1208:
1200:
865:"Dorello's canal: a microanatomical study"
848:: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (
713:United States National Library of Medicine
300:
286:
169:
39:
27:
1082:
784:
172:
1152:Cerebrum.Inferior view.Deep dissection
914:(suppl_2): ONS1-7, discussion ONS7-8.
841:
731:(2005) also prefers "abducens nerve."
157:
18:
7:
818:Last's anatomy: regional and applied
811:
809:
807:
655:is mediated in the brainstem by the
419:The abducens nerve emerges from the
16:Cranial nerve VI, for eye movements
920:10.1227/01.neu.0000249229.89988.4d
14:
464:petrous part of the temporal bone
1145:
1133:
1121:
1109:
1097:
1085:
513:The abducens nerve supplies the
154:Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy
1177:GrossAnatomy/h_n/cn/cn1/cn6.htm
719:) vocabulary to index the vast
683:, not unilateral eye movement.
657:medial longitudinal fasciculus
33:The path of the abducens nerve
1:
2102:Dorsal nucleus of vagus nerve
816:Chummy S. Sinnatamby (2011).
820:(12th ed.). Edinburgh.
661:internuclear ophthalmoplegia
2230:Nerves of the head and neck
1881:Inferior salivatory nucleus
743:of the eye. In most other
610:Wernicke–Korsakoff syndrome
482:to reach and innervate the
2251:
1325:lateral geniculate nucleus
1286:anterior olfactory nucleus
993:10.1016/j.optm.2009.02.012
883:10.3171/jns.1991.75.2.0294
770:
643:, but rather a horizontal
537:
2005:Superior cervical cardiac
1698:Superior salivary nucleus
1451:spinal trigeminal nucleus
152:
38:
26:
2138:spinal accessory nucleus
1578:pterygopalatine ganglion
1369:Edinger–Westphal nucleus
749:musculus retractor bulbi
523:general somatic efferent
476:superior orbital fissure
344:responsible for outward
1520:no significant branches
1422:no significant branches
1262:no significant branches
870:Journal of Neurosurgery
747:it also innervates the
472:internal carotid artery
454:, and then pierces the
423:at the junction of the
1840:Stylopharyngeal branch
1600:submandibular ganglion
1585:Nerve to the stapedius
907:Operative Neurosurgery
773:anatomical terminology
706:Terminologia Anatomica
553:
478:, passing through the
416:
384:, at the level of the
373:
741:lateral rectus muscle
547:
529:Clinical significance
515:lateral rectus muscle
484:lateral rectus muscle
480:common tendinous ring
462:. At the apex of the
446:(more precisely, the
442:The nerve enters the
414:
371:
338:lateral rectus muscle
70:Lateral rectus muscle
1688:Facial motor nucleus
1384:parasympathetic root
962:www.orthobullets.com
667:Supranuclear lesions
614:Tolosa–Hunt syndrome
591:medial rectus muscle
562:medial rectus muscle
435:, and medial to the
320:, also known as the
2215:Human head and neck
2210:Otorhinolaryngology
2000:Recurrent laryngeal
1845:Pharyngeal branches
1623:Posterior auricular
1471:trigeminal ganglion
799:Gray's Anatomy 2008
629:pseudotumor cerebri
603:diabetic neuropathy
401:corticospinal tract
342:extraocular muscles
322:sixth cranial nerve
1983:Superior laryngeal
1850:Tonsillar branches
1548:Intermediate nerve
1364:oculomotor nucleus
771:This article uses
675:, smooth pursuit,
581:Peripheral lesions
554:
444:subarachnoid space
431:, superior to the
417:
374:
2187:
2186:
2115:
2114:
2081:Posterior gastric
1976:pharyngeal plexus
1971:Pharyngeal branch
1894:
1893:
1758:Scarpa's ganglion
1746:lateral lemniscus
1741:striae medullares
1724:vestibular nuclei
1712:Vestibulocochlear
1706:
1705:
1079:Additional images
1070:978-0-8089-2371-8
827:978-0-7020-4839-5
801:, pp. 666–7.
641:sixth nerve palsy
540:Sixth nerve palsy
433:medullary pyramid
386:facial colliculus
310:
309:
232:Vestibulocochlear
168:
167:
163:
2242:
2133:nucleus ambiguus
2107:Solitary nucleus
2097:Nucleus ambiguus
2076:Anterior gastric
2023:Inferior cardiac
1953:Auricular branch
1948:Meningeal branch
1906:
1886:Solitary nucleus
1876:Nucleus ambiguus
1855:Lingual branches
1776:
1770:Glossopharyngeal
1693:Solitary nucleus
1573:Greater petrosal
1538:
1388:ciliary ganglion
1224:
1217:
1210:
1201:
1149:
1137:
1125:
1113:
1101:
1089:
1074:
1014:
1011:
1005:
1004:
972:
966:
965:
954:
948:
947:
901:
895:
894:
860:
854:
853:
847:
839:
813:
802:
796:
394:trochlear nuclei
382:fourth ventricle
378:abducens nucleus
326:cranial nerve VI
302:
295:
288:
238:Glossopharyngeal
170:
160:edit on Wikidata
60:Abducens nucleus
43:
31:
19:
2250:
2249:
2245:
2244:
2243:
2241:
2240:
2239:
2190:
2189:
2188:
2183:
2154:
2111:
2085:
2047:
2009:
1957:
1933:
1890:
1864:
1828:lesser petrosal
1823:tympanic plexus
1803:
1764:
1729:cochlear nuclei
1702:
1676:
1614:
1606:
1563:
1557:
1526:
1497:
1428:
1399:
1346:
1307:
1301:olfactory tract
1268:
1234:
1228:
1173:MedEd at Loyola
1160:
1153:
1150:
1141:
1138:
1129:
1126:
1117:
1114:
1105:
1102:
1093:
1090:
1081:
1071:
1058:
1018:
1017:
1012:
1008:
987:(10): 567–571.
974:
973:
969:
956:
955:
951:
903:
902:
898:
862:
861:
857:
840:
828:
815:
814:
805:
797:
786:
781:
776:
769:
737:
702:
697:
689:
669:
651:The control of
637:
635:Nuclear lesions
583:
542:
536:
531:
511:
492:
468:cavernous sinus
460:Dorello's canal
448:pontine cistern
409:
366:
361:
306:
277:
164:
87:nervus abducens
46:
34:
17:
12:
11:
5:
2248:
2246:
2238:
2237:
2232:
2227:
2222:
2220:Nervous system
2217:
2212:
2207:
2205:Cranial nerves
2202:
2200:Abducens nerve
2192:
2191:
2185:
2184:
2182:
2181:
2180:
2179:
2171:
2165:
2163:
2156:
2155:
2153:
2152:
2147:
2142:
2141:
2140:
2135:
2126:
2124:
2117:
2116:
2113:
2112:
2110:
2109:
2104:
2099:
2093:
2091:
2087:
2086:
2084:
2083:
2078:
2073:
2068:
2063:
2057:
2055:
2049:
2048:
2046:
2045:
2044:
2043:
2038:
2030:
2025:
2019:
2017:
2011:
2010:
2008:
2007:
2002:
1997:
1996:
1995:
1990:
1980:
1979:
1978:
1967:
1965:
1959:
1958:
1956:
1955:
1950:
1944:
1942:
1935:
1934:
1932:
1931:
1930:
1929:
1924:
1915:
1913:
1903:
1896:
1895:
1892:
1891:
1889:
1888:
1883:
1878:
1872:
1870:
1866:
1865:
1863:
1862:
1857:
1852:
1847:
1842:
1837:
1836:
1835:
1830:
1825:
1814:
1812:
1805:
1804:
1802:
1801:
1800:
1799:
1794:
1785:
1783:
1773:
1766:
1765:
1763:
1762:
1761:
1760:
1750:
1749:
1748:
1743:
1736:Cochlear nerve
1733:
1732:
1731:
1726:
1717:
1715:
1708:
1707:
1704:
1703:
1701:
1700:
1695:
1690:
1684:
1682:
1678:
1677:
1675:
1674:
1673:
1672:
1667:
1662:
1657:
1652:
1645:Parotid plexus
1642:
1641:
1640:
1635:
1625:
1619:
1617:
1608:
1607:
1605:
1604:
1603:
1602:
1597:
1590:Chorda tympani
1587:
1582:
1581:
1580:
1569:
1567:
1559:
1558:
1556:
1555:
1550:
1544:
1542:
1535:
1528:
1527:
1525:
1524:
1523:
1522:
1514:
1508:
1506:
1499:
1498:
1496:
1495:
1494:
1493:
1488:
1483:
1475:
1474:
1473:
1465:
1464:
1463:
1458:
1453:
1448:
1439:
1437:
1430:
1429:
1427:
1426:
1425:
1424:
1416:
1410:
1408:
1401:
1400:
1398:
1397:
1396:
1395:
1390:
1381:
1373:
1372:
1371:
1366:
1357:
1355:
1348:
1347:
1345:
1344:
1343:
1342:
1337:
1329:
1328:
1327:
1318:
1316:
1309:
1308:
1306:
1305:
1304:
1303:
1298:
1296:olfactory bulb
1290:
1289:
1288:
1279:
1277:
1270:
1269:
1267:
1266:
1265:
1264:
1256:
1255:
1254:
1245:
1243:
1236:
1235:
1232:cranial nerves
1229:
1227:
1226:
1219:
1212:
1204:
1198:
1197:
1185:
1180:
1170:
1159:
1158:External links
1156:
1155:
1154:
1151:
1144:
1142:
1139:
1132:
1130:
1127:
1120:
1118:
1115:
1108:
1106:
1103:
1096:
1094:
1091:
1084:
1080:
1077:
1076:
1075:
1069:
1055:
1054:
1050:
1049:
1046:
1043:
1040:
1037:
1034:
1031:
1028:
1025:
1022:
1016:
1015:
1006:
967:
949:
896:
877:(2): 294–298.
855:
826:
803:
783:
782:
780:
777:
768:
765:
736:
733:
729:Gray's Anatomy
701:
698:
696:
693:
688:
685:
681:conjugate gaze
668:
665:
653:conjugate gaze
636:
633:
582:
579:
548:Limitation of
538:Main article:
535:
532:
530:
527:
510:
507:
491:
488:
408:
405:
365:
362:
360:
357:
353:efferent nerve
318:abducent nerve
314:abducens nerve
308:
307:
305:
304:
297:
290:
282:
279:
278:
276:
275:
270:
264:
261:
260:
259:
258:
252:
246:
240:
234:
228:
222:
216:
210:
204:
198:
192:
186:
177:
176:
174:Cranial nerves
166:
165:
156:
150:
149:
144:
138:
137:
132:
126:
125:
120:
114:
113:
108:
102:
101:
96:
90:
89:
84:
78:
77:
73:
72:
67:
63:
62:
57:
53:
52:
48:
47:
44:
36:
35:
32:
24:
23:
22:Abducens nerve
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2247:
2236:
2235:Ophthalmology
2233:
2231:
2228:
2226:
2223:
2221:
2218:
2216:
2213:
2211:
2208:
2206:
2203:
2201:
2198:
2197:
2195:
2178:
2175:
2174:
2172:
2170:
2167:
2166:
2164:
2161:
2157:
2151:
2148:
2146:
2143:
2139:
2136:
2134:
2131:
2130:
2128:
2127:
2125:
2122:
2118:
2108:
2105:
2103:
2100:
2098:
2095:
2094:
2092:
2088:
2082:
2079:
2077:
2074:
2072:
2069:
2067:
2064:
2062:
2059:
2058:
2056:
2054:
2050:
2042:
2039:
2037:
2034:
2033:
2032:Vagal trunks
2031:
2029:
2026:
2024:
2021:
2020:
2018:
2016:
2012:
2006:
2003:
2001:
1998:
1994:
1991:
1989:
1986:
1985:
1984:
1981:
1977:
1974:
1973:
1972:
1969:
1968:
1966:
1964:
1960:
1954:
1951:
1949:
1946:
1945:
1943:
1941:
1940:jugular fossa
1936:
1928:
1925:
1923:
1920:
1919:
1917:
1916:
1914:
1912:
1911:jugular fossa
1907:
1904:
1901:
1897:
1887:
1884:
1882:
1879:
1877:
1874:
1873:
1871:
1867:
1861:
1860:Carotid sinus
1858:
1856:
1853:
1851:
1848:
1846:
1843:
1841:
1838:
1834:
1833:otic ganglion
1831:
1829:
1826:
1824:
1821:
1820:
1819:
1816:
1815:
1813:
1811:
1810:jugular fossa
1806:
1798:
1795:
1793:
1790:
1789:
1787:
1786:
1784:
1782:
1781:jugular fossa
1777:
1774:
1771:
1767:
1759:
1756:
1755:
1754:
1751:
1747:
1744:
1742:
1739:
1738:
1737:
1734:
1730:
1727:
1725:
1722:
1721:
1719:
1718:
1716:
1713:
1709:
1699:
1696:
1694:
1691:
1689:
1686:
1685:
1683:
1679:
1671:
1668:
1666:
1663:
1661:
1658:
1656:
1653:
1651:
1648:
1647:
1646:
1643:
1639:
1636:
1634:
1631:
1630:
1629:
1626:
1624:
1621:
1620:
1618:
1616:
1609:
1601:
1598:
1596:
1595:lingual nerve
1593:
1592:
1591:
1588:
1586:
1583:
1579:
1576:
1575:
1574:
1571:
1570:
1568:
1566:
1560:
1554:
1551:
1549:
1546:
1545:
1543:
1539:
1536:
1533:
1529:
1521:
1518:
1517:
1515:
1513:
1510:
1509:
1507:
1504:
1500:
1492:
1489:
1487:
1484:
1482:
1479:
1478:
1476:
1472:
1469:
1468:
1466:
1462:
1459:
1457:
1454:
1452:
1449:
1447:
1444:
1443:
1441:
1440:
1438:
1435:
1431:
1423:
1420:
1419:
1417:
1415:
1412:
1411:
1409:
1406:
1402:
1394:
1391:
1389:
1385:
1382:
1380:
1377:
1376:
1374:
1370:
1367:
1365:
1362:
1361:
1359:
1358:
1356:
1353:
1349:
1341:
1338:
1336:
1333:
1332:
1330:
1326:
1323:
1322:
1320:
1319:
1317:
1314:
1310:
1302:
1299:
1297:
1294:
1293:
1291:
1287:
1284:
1283:
1281:
1280:
1278:
1275:
1271:
1263:
1260:
1259:
1257:
1253:
1252:septal nuclei
1250:
1249:
1247:
1246:
1244:
1241:
1237:
1233:
1225:
1220:
1218:
1213:
1211:
1206:
1205:
1202:
1195:
1194:
1189:
1188:cranialnerves
1186:
1184:
1181:
1179:
1178:
1174:
1171:
1169:
1165:
1162:
1161:
1157:
1148:
1143:
1136:
1131:
1124:
1119:
1112:
1107:
1100:
1095:
1088:
1083:
1078:
1072:
1066:
1062:
1057:
1056:
1052:
1051:
1047:
1044:
1041:
1038:
1035:
1032:
1029:
1026:
1023:
1020:
1019:
1010:
1007:
1002:
998:
994:
990:
986:
982:
978:
971:
968:
963:
959:
953:
950:
945:
941:
937:
933:
929:
925:
921:
917:
913:
909:
908:
900:
897:
892:
888:
884:
880:
876:
872:
871:
866:
859:
856:
851:
845:
837:
833:
829:
823:
819:
812:
810:
808:
804:
800:
795:
793:
791:
789:
785:
778:
774:
766:
764:
762:
758:
754:
750:
746:
742:
735:Other animals
734:
732:
730:
726:
722:
718:
714:
709:
707:
699:
694:
692:
686:
684:
682:
678:
677:accommodation
674:
666:
664:
662:
658:
654:
649:
646:
642:
634:
632:
630:
626:
625:hydrocephalus
622:
617:
615:
611:
606:
604:
600:
594:
592:
588:
580:
578:
574:
571:
565:
563:
559:
551:
546:
541:
533:
528:
526:
524:
520:
516:
508:
506:
504:
501:
497:
489:
487:
485:
481:
477:
473:
469:
465:
461:
457:
453:
449:
445:
440:
438:
434:
430:
426:
422:
413:
406:
404:
402:
397:
395:
391:
387:
383:
379:
370:
363:
358:
356:
354:
351:
347:
343:
340:, one of the
339:
335:
334:cranial nerve
331:
327:
323:
319:
315:
303:
298:
296:
291:
289:
284:
283:
281:
280:
274:
271:
269:
266:
265:
263:
262:
257:
253:
251:
247:
245:
241:
239:
235:
233:
229:
227:
223:
221:
217:
215:
211:
209:
205:
203:
199:
197:
193:
191:
187:
185:
181:
180:
179:
178:
175:
171:
161:
155:
151:
148:
145:
143:
139:
136:
133:
131:
127:
124:
121:
119:
115:
112:
109:
107:
103:
100:
97:
95:
91:
88:
85:
83:
79:
74:
71:
68:
64:
61:
58:
54:
49:
42:
37:
30:
25:
20:
1613:stylomastoid
1565:facial canal
1519:
1502:
1421:
1335:optic chiasm
1261:
1191:
1175:
1060:
1009:
984:
980:
970:
961:
952:
911:
905:
899:
874:
868:
858:
817:
738:
728:
710:
703:
690:
687:Tuberculosis
670:
650:
638:
618:
607:
595:
584:
575:
566:
555:
512:
493:
486:of the eye.
441:
437:facial nerve
418:
398:
375:
329:
328:, or simply
325:
321:
317:
313:
311:
219:
123:A14.2.01.098
86:
2160:Hypoglossal
1541:Near origin
1340:optic tract
753:vertebrates
679:) involves
621:brain tumor
496:basal plate
490:Development
256:Hypoglossal
76:Identifiers
2194:Categories
1753:Vestibular
1665:mandibular
1638:stylohyoid
1628:Suprahyoid
1553:Geniculate
1491:mandibular
1481:ophthalmic
1434:Trigeminal
1352:Oculomotor
1168:NeuroNames
779:References
645:gaze palsy
599:meningitis
456:dura mater
415:The Clivus
390:oculomotor
348:. It is a
230:CN VIII –
214:Trigeminal
202:Oculomotor
106:NeuroNames
66:Innervates
2225:Neurology
2173:Branches
2121:Accessory
2041:posterior
2028:Pulmonary
1714:(CN VIII)
1655:zygomatic
1633:digastric
1516:Branches
1486:maxillary
1477:Branches
1418:Branches
1405:Trochlear
1375:Branches
1274:Olfactory
928:2332-4252
844:cite book
836:764565702
761:hagfishes
700:Etymology
570:aneurysms
550:abduction
519:human eye
500:embryonic
421:brainstem
359:Structure
254:CN XII –
250:Accessory
224:CN VII –
208:Trochlear
200:CN III –
190:Olfactory
2162:(CN XII)
2036:anterior
1993:internal
1988:external
1927:inferior
1922:superior
1918:Ganglia
1818:Tympanic
1797:inferior
1792:superior
1788:Ganglia
1670:cervical
1650:temporal
1534:(CN VII)
1503:Abducens
1393:inferior
1379:superior
1354:(CN III)
1240:Terminal
1164:hier-541
1001:19801340
944:36731926
936:17297359
767:See also
757:lampreys
673:saccades
587:diplopia
558:diplopia
509:Function
427:and the
268:Overview
248:CN XI –
236:CN IX –
220:Abducens
218:CN VI –
206:CN IV –
194:CN II –
184:Terminal
2177:lingual
2169:Nucleus
2145:Cranial
2129:Nuclei
2123:(CN XI)
2071:Hepatic
2053:Abdomen
1909:Before
1779:Before
1772:(CN IX)
1720:Nuclei
1615:foramen
1512:Nucleus
1505:(CN VI)
1467:Course
1442:Nuclei
1414:Nucleus
1407:(CN IV)
1360:Nuclei
1331:Course
1321:Nuclei
1315:(CN II)
1292:Course
1282:Nuclei
1258:Course
1248:Nuclei
891:2072168
755:except
745:mammals
721:MEDLINE
695:History
663:(INO).
517:of the
498:of the
429:medulla
364:Nucleus
350:somatic
332:, is a
242:CN X –
212:CN V –
188:CN I –
182:CN 0 –
99:D000010
51:Details
2150:Spinal
2090:Nuclei
2061:Celiac
2015:Thorax
1938:After
1902:(CN X)
1869:Nuclei
1808:After
1681:Nuclei
1660:buccal
1562:Inside
1532:Facial
1436:(CN V)
1276:(CN I)
1242:(CN 0)
1067:
999:
942:
934:
926:
889:
834:
824:
725:PubMed
534:Damage
452:clivus
407:Course
226:Facial
2066:Renal
1900:Vagus
1313:Optic
1053:Books
940:S2CID
330:CN VI
273:Table
244:Vagus
196:Optic
158:[
147:50867
82:Latin
1963:Neck
1230:The
1065:ISBN
997:PMID
932:PMID
924:ISSN
887:PMID
850:link
832:OCLC
822:ISBN
759:and
723:and
717:MeSH
612:and
503:pons
425:pons
392:and
376:The
346:gaze
312:The
135:6283
118:TA98
94:MeSH
56:From
1611:At
1461:TMN
1446:PSN
1386:of
1166:at
989:doi
916:doi
879:doi
396:).
316:or
142:FMA
130:TA2
111:550
2196::
1456:MN
1193:VI
995:.
985:80
983:.
979:.
960:.
938:.
930:.
922:.
912:60
910:.
885:.
875:75
873:.
867:.
846:}}
842:{{
830:.
806:^
787:^
763:.
627:,
623:,
525:.
505:.
355:.
324:,
1223:e
1216:t
1209:v
1196:)
1073:.
1003:.
991::
964:.
946:.
918::
893:.
881::
852:)
838:.
775:.
301:e
294:t
287:v
162:]
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.