352:
1317:
344:. In the unfolded state of proteins, the peptide groups are free to isomerize and adopt both isomers; however, in the folded state, only a single isomer is adopted at each position (with rare exceptions). The trans form is preferred overwhelmingly in most peptide bonds (roughly 1000:1 ratio in trans:cis populations). However, X-Pro peptide groups tend to have a roughly 30:1 ratio, presumably because the symmetry between the C and C atoms of
175:
97:
1311:
31:
1323:
541:
is usually much faster (typically 10–100 ms) than cis-trans isomerization (10–100 s). A nonnative isomer of some peptide groups can disrupt the conformational folding significantly, either slowing it or preventing it from even occurring until the native isomer is reached. However, not all
300:, although there are reports of peptide bond hydrolysis caused by conformational strain as the peptide/protein folds into the native structure. This non-enzymatic process is thus not accelerated by transition state stabilization, but rather by ground-state destabilization.
530:) by changes that favor the single-bonded form, such as placing the peptide group in a hydrophobic environment or donating a hydrogen bond to the nitrogen atom of an X-Pro peptide group. Both of these mechanisms for lowering the activation energy have been observed in
520:
451:
414:
1566:
481:
1410:
1007:
Radzicka, Anna; Wolfenden, Richard (1996-01-01). "Rates of
Uncatalyzed Peptide Bond Hydrolysis in Neutral Solution and the Transition State Affinities of Proteases".
381:
550:
Due to its resonance stabilization, the peptide bond is relatively unreactive under physiological conditions, even less than similar compounds such as
1528:
1455:
1136:
1042:
Sandberg A.; Johansson D. G.; Macao B.; Härd T. (April 2008). "SEA domain autoproteolysis accelerated by conformational strain: energetic aspects".
1559:
355:
Isomerization of an X-Pro peptide bond. Cis and trans isomers are at far left and far right, respectively, separated by the transition states.
813:
768:
735:
522:
requires that the partial double bond be broken, so that the activation energy is roughly 80 kJ/mol (20 kcal/mol). However, the
993:
1552:
1390:
1375:
1199:
351:
1226:
1579:
1187:
1177:
238:
1182:
542:
peptide groups have the same effect on folding; nonnative isomers of other peptide groups may not affect folding at all.
2229:
1129:
2392:
534:(PPIases), which are naturally occurring enzymes that catalyze the cis-trans isomerization of X-Pro peptide bonds.
1450:
1445:
2397:
2269:
1680:
1575:
1435:
1425:
1400:
1370:
1544:
1216:
457:
conformation). Amide groups can isomerize about the C'–N bond between the cis and trans forms, albeit slowly (
148:
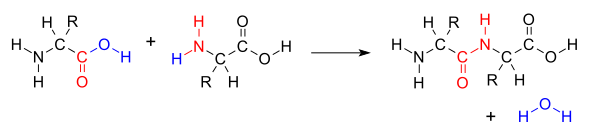
O) and two amino acids joined by a peptide bond (−CO−NH−). The two joined amino acids are called a dipeptide.
489:
2323:
1477:
1380:
1352:
1122:
565:, breaking the carbonyl double bond and forming a tetrahedral intermediate. This is the pathway followed in
2207:
423:
246:
187:
1521:
1482:
386:
168:
118:
1516:
980:
Martin R. B. (December 1998). "Free energies and equilibria of peptide bond hydrolysis and formation".
726:(hardcover) (Fourth ed.). Menlo Park, CA: The Benjamin/Cummings Publishing Company, Inc. p.
1598:
1440:
1331:
1194:
1153:
222:
207:
101:
1613:
1685:
1342:
1206:
1172:
598:
337:
2034:
1506:
460:
225:
as they are synthesized by specialized enzymes rather than ribosomes. For example, the tripeptide
2024:
1928:
1778:
1261:
823:
702:
140:
and oxygen from its carboxyl group (COOH) and the other loses a hydrogen from its amino group (NH
727:
721:
720:
Watson, James; Hopkins, Nancy; Roberts, Jeffrey; Agetsinger Steitz, Joan; Weiner, Alan (1987) .
312:
of absorption for a peptide bond is 190–230 nm, which makes it particularly susceptible to
1882:
1768:
1727:
1492:
1281:
1241:
1231:
1100:
1059:
1024:
962:
921:
880:
809:
784:
764:
731:
694:
653:
645:
555:
554:. Nevertheless, peptide bonds can undergo chemical reactions, usually through an attack of an
523:
39:
940:
751:
Miller B. R.; Gulick A. M. (2016). "Structural
Biology of Nonribosomal Peptide Synthetases".
366:
2185:
2163:
2062:
1981:
1872:
1849:
1773:
1745:
1533:
1316:
1273:
1246:
1090:
1051:
1016:
989:
952:
911:
870:
862:
774:
756:
684:
635:
484:
333:
129:
58:
2296:
1996:
1887:
1763:
1722:
1385:
1256:
835:
538:
242:
199:
126:
85:
1511:
186:
The formation of the peptide bond consumes energy, which, in organisms, is derived from
2158:
2052:
2029:
1971:
1821:
1803:
1690:
1656:
1420:
1221:
875:
850:
779:
640:
623:
454:
360:
218:
152:
1095:
957:
348:
makes the cis and trans isomers nearly equal in energy, as shown in the figure below.
174:
2386:
2177:
2122:
2104:
2080:
2019:
2014:
1966:
1961:
1910:
1867:
1788:
1732:
1636:
1469:
1429:
1362:
1291:
1164:
1145:
706:
417:
261:(the addition of water). The hydrolysis of peptide bonds in water releases 8–16
214:
to produce proteins via reactions that differ in details from dehydration synthesis.
54:
51:
1976:
1793:
1608:
1415:
802:
Griffiths A. J.; Miller J. H.; Suzuki D. T.; Lewontin R. C.; Gelbart W. M. (2000).
673:"Glossary of terms used in physical organic chemistry (IUPAC Recommendations 1994)"
341:
278:
96:
363:
associated with the peptide group (defined by the four atoms C–C'–N–C) is denoted
121:. In this kind of condensation, two amino acids approach each other, with the non-
589:
or, more specifically, a thiacyclol, an oxacyclol or an azacyclol, respectively.
2098:
2057:
1986:
1951:
1946:
1905:
1877:
1844:
1826:
1798:
1651:
1641:
1631:
1603:
1501:
1251:
760:
672:
566:
274:
266:
226:
156:
1310:
803:
624:"Nomenclature and Symbolism for Amino Acids and Peptides. Recommendations 1983"
2338:
2244:
2221:
2217:
2173:
2137:
2114:
1897:
1701:
1667:
1623:
1055:
309:
258:
230:
195:
179:
122:
1028:
698:
649:
17:
2367:
2280:
2090:
2009:
1956:
1920:
1859:
1836:
1783:
1714:
1646:
1236:
1211:
1078:
689:
527:
325:
289:
282:
221:, are called ribosomal peptides as they are made by ribosomes, but many are
109:
1104:
1063:
925:
916:
899:
884:
788:
994:
10.1002/(SICI)1097-0282(19980415)45:5<351::AID-BIP3>3.0.CO;2-K
966:
851:"Ribosomal biosynthesis of the cyclic peptide toxins of Amanita mushrooms"
657:
30:
2355:
2351:
2347:
2284:
2257:
2199:
2150:
2146:
2044:
1991:
1813:
1755:
1737:
578:
559:
297:
211:
137:
66:
27:
Covalent chemical bond between amino acids in a peptide or protein chain
2315:
2307:
2288:
2261:
2072:
345:
270:
191:
159:
of the other amino acid molecule, causing the release of a molecule of
74:
70:
1020:
866:
2359:
2311:
2253:
2195:
1938:
1710:
898:
Wu G.; Fang Y. Z.; Yang S.; Lupton J. R.; Turner N. D. (March 2004).
586:
570:
569:
and, more generally, in N–O acyl exchange reactions such as those of
562:
293:
234:
203:
62:
1322:
2004:
1675:
582:
574:
551:
350:
329:
262:
173:
160:
133:
95:
47:
29:
1114:
1548:
1118:
755:. Methods in Molecular Biology. Vol. 1401. pp. 3–29.
88:, which is another type of amide bond between two amino acids.
573:. When the functional group attacking the peptide bond is a
1077:
Goldfarb A. R.; Saidel L. J.; Mosovich E. (November 1951).
332:
character. The partial double bond renders the amide group
313:
182:
to form a peptide bond (red) with expulsion of water (blue)
2297:
4-(p-hydroxybenzylidene)-5-imidazolinone (HBI) formation
900:"Glutathione metabolism and its implications for health"
941:"Glutathione metabolism and its selective modification"
198:
held together by peptide bonds (and sometimes by a few
492:
463:
426:
389:
369:
285:
at 25 °C of between 350 and 600 years per bond.
328:
of electrons on the nitrogen atom gives the group a
2346:
2336:
2306:
2279:
2252:
2242:
2216:
2194:
2172:
2145:
2135:
2113:
2089:
2071:
2043:
1937:
1919:
1896:
1858:
1835:
1812:
1754:
1709:
1699:
1666:
1622:
1586:
1491:
1468:
1399:
1361:
1341:
1330:
1290:
1272:
1163:
1152:
2270:p-Hydroxybenzylidene-imidazolinone (HBI) formation
514:
475:
445:
408:
375:
849:Walton J. D.; Hallen-Adams H. E.; Luo H. (2010).
1079:"The ultraviolet absorption spectra of proteins"
753:Nonribosomal Peptide and Polyketide Biosynthesis
144:). This reaction produces a molecule of water (H
1560:
1130:
288:In living organisms, the process is normally
8:
2230:Tryptophan tryptophylquinone (TTQ) formation
65:number one) of one alpha-amino acid and N2 (
281:. This process is extremely slow, with the
155:of one amino acid molecule reacts with the
132:of one coming near the non-side chain (N2)
2343:
2249:
2142:
1706:
1567:
1553:
1545:
1338:
1160:
1137:
1123:
1115:
1094:
956:
915:
874:
808:(7th ed.). New York: W. H. Freeman.
778:
688:
639:
585:, the resulting molecule may be called a
506:
491:
462:
437:
425:
400:
388:
368:
1529:Polyhedral skeletal electron pair theory
1009:Journal of the American Chemical Society
483: seconds at room temperature). The
2324:Methylidene-imidazolone (MIO) formation
610:
515:{\displaystyle \omega =\pm 90^{\circ }}
151:The amide bond is synthesized when the
831:
821:
526:can be lowered (and the isomerization
320:Cis/trans isomers of the peptide group
229:is synthesized in two steps from free
2208:Lysine tyrosylquinone (LTQ) formation
7:
618:
616:
614:
446:{\displaystyle \omega =180^{\circ }}
178:The dehydration condensation of two
1681:Glycosyl phosphatidylinositol (GPI)
1083:The Journal of Biological Chemistry
945:The Journal of Biological Chemistry
245:, which is not a peptide bond) and
641:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb07877.x
409:{\displaystyle \omega =0^{\circ }}
324:Significant delocalisation of the
25:
1992:Oxidative deamination to aldehyde
136:moiety of the other. One loses a
1321:
1315:
1309:
628:European Journal of Biochemistry
257:A peptide bond can be broken by
69:number two) of another, along a
1580:posttranslational modifications
723:Molecualar Biology of the Gene
1:
1096:10.1016/S0021-9258(19)52465-6
958:10.1016/S0021-9258(19)77815-6
1044:Journal of Molecular Biology
939:Meister A. (November 1988).
476:{\displaystyle \tau \sim 20}
107:When two amino acids form a
1799:Topaquinone (TPQ) formation
761:10.1007/978-1-4939-3375-4_1
167:O), hence the process is a
100:Peptide bond formation via
2414:
1227:Metal–ligand multiple bond
677:Pure and Applied Chemistry
532:peptidyl prolyl isomerases
336:, occurring in either the
84:to distinguish it from an
2243:Crosslinks between three
1576:Protein primary structure
1307:
1056:10.1016/j.jmb.2008.01.051
671:Muller, P. (1994-01-01).
239:glutamate–cysteine ligase
2337:Crosslinks between four
904:The Journal of Nutrition
249:(forms a peptide bond).
80:It can also be called a
57:linking two consecutive
2136:Crosslinks between two
690:10.1351/pac199466051077
376:{\displaystyle \omega }
296:known as peptidases or
1784:Porphyrin ring linkage
516:
477:
453:for the trans isomer (
447:
410:
377:
356:
247:glutathione synthetase
183:
104:
35:
1845:Succinimide formation
517:
478:
448:
411:
378:
354:
223:nonribosomal peptides
208:nonribosomal peptides
177:
169:dehydration synthesis
119:condensation reaction
99:
33:
1599:Protein biosynthesis
1217:Coordinate (dipolar)
917:10.1093/jn/134.3.489
490:
461:
424:
416:for the cis isomer (
387:
367:
217:Some peptides, like
102:dehydration reaction
1391:C–H···O interaction
1173:Electron deficiency
951:(33): 17205–17208.
599:The Proteolysis Map
420:conformation), and
330:partial double-bond
1929:Transglutamination
1376:Resonance-assisted
546:Chemical reactions
512:
473:
443:
406:
373:
357:
184:
117:, it is a type of
105:
36:
2393:Protein structure
2380:
2379:
2376:
2375:
2332:
2331:
2238:
2237:
2131:
2130:
1883:Polyglutamylation
1769:Dephosphorylation
1728:Dephosphorylation
1542:
1541:
1493:Electron counting
1464:
1463:
1353:London dispersion
1305:
1304:
1282:Metal aromaticity
1021:10.1021/ja954077c
1015:(26): 6105–6109.
867:10.1002/bip.21416
815:978-0-7167-3520-5
805:Protein synthesis
770:978-1-4939-3373-0
737:978-0-8053-9614-0
634:(1): 9–37. 1984.
524:activation energy
485:transition states
202:). Organisms use
59:alpha-amino acids
40:organic chemistry
16:(Redirected from
2405:
2398:Chemical bonding
2344:
2250:
2186:Sulfilimine bond
2164:ADP-ribosylation
2143:
2063:ADP-ribosylation
1982:ADP-ribosylation
1873:ADP-ribosylation
1850:ADP-ribosylation
1774:ADP-ribosylation
1746:ADP-ribosylation
1707:
1700:Single specific
1569:
1562:
1555:
1546:
1534:Jemmis mno rules
1386:Dihydrogen bonds
1339:
1325:
1319:
1313:
1247:Hyperconjugation
1161:
1139:
1132:
1125:
1116:
1109:
1108:
1098:
1074:
1068:
1067:
1050:(4): 1117–1129.
1039:
1033:
1032:
1004:
998:
997:
977:
971:
970:
960:
936:
930:
929:
919:
895:
889:
888:
878:
846:
840:
839:
833:
829:
827:
819:
799:
793:
792:
782:
748:
742:
741:
717:
711:
710:
692:
683:(5): 1077–1184.
668:
662:
661:
643:
620:
521:
519:
518:
513:
511:
510:
482:
480:
479:
474:
452:
450:
449:
444:
442:
441:
415:
413:
412:
407:
405:
404:
382:
380:
379:
374:
200:isopeptide bonds
21:
2413:
2412:
2408:
2407:
2406:
2404:
2403:
2402:
2383:
2382:
2381:
2372:
2328:
2302:
2275:
2234:
2212:
2190:
2168:
2127:
2123:C-mannosylation
2109:
2085:
2067:
2039:
2005:Imine formation
1933:
1915:
1892:
1888:Polyglycylation
1854:
1831:
1808:
1764:Phosphorylation
1750:
1723:Phosphorylation
1695:
1662:
1618:
1582:
1573:
1543:
1538:
1487:
1460:
1403:
1395:
1357:
1344:
1334:
1326:
1320:
1314:
1301:
1286:
1268:
1156:
1148:
1143:
1113:
1112:
1076:
1075:
1071:
1041:
1040:
1036:
1006:
1005:
1001:
979:
978:
974:
938:
937:
933:
897:
896:
892:
848:
847:
843:
830:
820:
816:
801:
800:
796:
771:
750:
749:
745:
738:
719:
718:
714:
670:
669:
665:
622:
621:
612:
607:
595:
556:electronegative
548:
539:protein folding
537:Conformational
502:
488:
487:
459:
458:
433:
422:
421:
396:
385:
384:
365:
364:
322:
306:
255:
243:isopeptide bond
190:. Peptides and
166:
147:
143:
127:carboxylic acid
94:
86:isopeptide bond
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
2411:
2409:
2401:
2400:
2395:
2385:
2384:
2378:
2377:
2374:
2373:
2371:
2370:
2364:
2362:
2341:
2334:
2333:
2330:
2329:
2327:
2326:
2320:
2318:
2304:
2303:
2301:
2300:
2293:
2291:
2277:
2276:
2274:
2273:
2266:
2264:
2247:
2240:
2239:
2236:
2235:
2233:
2232:
2226:
2224:
2214:
2213:
2211:
2210:
2204:
2202:
2192:
2191:
2189:
2188:
2182:
2180:
2170:
2169:
2167:
2166:
2161:
2159:Disulfide bond
2155:
2153:
2140:
2133:
2132:
2129:
2128:
2126:
2125:
2119:
2117:
2111:
2110:
2108:
2107:
2102:
2095:
2093:
2087:
2086:
2084:
2083:
2077:
2075:
2069:
2068:
2066:
2065:
2060:
2055:
2053:Citrullination
2049:
2047:
2041:
2040:
2038:
2037:
2032:
2030:Propionylation
2027:
2022:
2017:
2012:
2007:
2002:
2000:-glycosylation
1994:
1989:
1984:
1979:
1974:
1972:Ubiquitination
1969:
1964:
1959:
1954:
1949:
1943:
1941:
1935:
1934:
1932:
1931:
1925:
1923:
1917:
1916:
1914:
1913:
1908:
1902:
1900:
1894:
1893:
1891:
1890:
1885:
1880:
1875:
1870:
1864:
1862:
1856:
1855:
1853:
1852:
1847:
1841:
1839:
1833:
1832:
1830:
1829:
1824:
1822:Palmitoylation
1818:
1816:
1810:
1809:
1807:
1806:
1804:Detyrosination
1801:
1796:
1794:Flavin linkage
1791:
1786:
1781:
1776:
1771:
1766:
1760:
1758:
1752:
1751:
1749:
1748:
1743:
1735:
1730:
1725:
1719:
1717:
1704:
1697:
1696:
1694:
1693:
1691:Detyrosination
1688:
1683:
1678:
1672:
1670:
1664:
1663:
1661:
1660:
1657:Myristoylation
1654:
1649:
1644:
1639:
1634:
1628:
1626:
1620:
1619:
1617:
1616:
1614:N–O acyl shift
1611:
1606:
1601:
1596:
1590:
1588:
1584:
1583:
1574:
1572:
1571:
1564:
1557:
1549:
1540:
1539:
1537:
1536:
1531:
1526:
1525:
1524:
1519:
1514:
1509:
1498:
1496:
1489:
1488:
1486:
1485:
1480:
1474:
1472:
1466:
1465:
1462:
1461:
1459:
1458:
1453:
1448:
1443:
1438:
1433:
1423:
1418:
1413:
1407:
1405:
1397:
1396:
1394:
1393:
1388:
1383:
1378:
1373:
1367:
1365:
1359:
1358:
1356:
1355:
1349:
1347:
1336:
1332:Intermolecular
1328:
1327:
1308:
1306:
1303:
1302:
1300:
1299:
1296:
1294:
1288:
1287:
1285:
1284:
1278:
1276:
1270:
1269:
1267:
1266:
1265:
1264:
1259:
1249:
1244:
1239:
1234:
1229:
1224:
1219:
1214:
1209:
1204:
1203:
1202:
1192:
1191:
1190:
1185:
1180:
1169:
1167:
1158:
1154:Intramolecular
1150:
1149:
1146:Chemical bonds
1144:
1142:
1141:
1134:
1127:
1119:
1111:
1110:
1089:(1): 397–404.
1069:
1034:
999:
988:(5): 351–353.
972:
931:
910:(3): 489–492.
890:
861:(5): 659–664.
841:
832:|journal=
814:
794:
769:
743:
736:
712:
663:
609:
608:
606:
603:
602:
601:
594:
591:
547:
544:
509:
505:
501:
498:
495:
472:
469:
466:
455:antiperiplanar
440:
436:
432:
429:
403:
399:
395:
392:
372:
361:dihedral angle
321:
318:
305:
302:
254:
251:
219:alpha-amanitin
194:are chains of
164:
153:carboxyl group
145:
141:
93:
90:
82:eupeptide bond
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2410:
2399:
2396:
2394:
2391:
2390:
2388:
2369:
2366:
2365:
2363:
2361:
2357:
2353:
2349:
2345:
2342:
2340:
2335:
2325:
2322:
2321:
2319:
2317:
2313:
2309:
2305:
2299:(chromophore)
2298:
2295:
2294:
2292:
2290:
2286:
2282:
2278:
2272:(chromophore)
2271:
2268:
2267:
2265:
2263:
2259:
2255:
2251:
2248:
2246:
2241:
2231:
2228:
2227:
2225:
2223:
2219:
2215:
2209:
2206:
2205:
2203:
2201:
2197:
2193:
2187:
2184:
2183:
2181:
2179:
2178:Hydroxylysine
2175:
2171:
2165:
2162:
2160:
2157:
2156:
2154:
2152:
2148:
2144:
2141:
2139:
2134:
2124:
2121:
2120:
2118:
2116:
2112:
2106:
2105:Adenylylation
2103:
2100:
2097:
2096:
2094:
2092:
2088:
2082:
2081:Hydroxylation
2079:
2078:
2076:
2074:
2070:
2064:
2061:
2059:
2056:
2054:
2051:
2050:
2048:
2046:
2042:
2036:
2033:
2031:
2028:
2026:
2023:
2021:
2020:Succinylation
2018:
2016:
2015:Carbamylation
2013:
2011:
2008:
2006:
2003:
2001:
1999:
1995:
1993:
1990:
1988:
1985:
1983:
1980:
1978:
1975:
1973:
1970:
1968:
1967:Hydroxylation
1965:
1963:
1962:Adenylylation
1960:
1958:
1955:
1953:
1950:
1948:
1945:
1944:
1942:
1940:
1936:
1930:
1927:
1926:
1924:
1922:
1918:
1912:
1911:Glycosylation
1909:
1907:
1904:
1903:
1901:
1899:
1895:
1889:
1886:
1884:
1881:
1879:
1876:
1874:
1871:
1869:
1868:Carboxylation
1866:
1865:
1863:
1861:
1857:
1851:
1848:
1846:
1843:
1842:
1840:
1838:
1834:
1828:
1825:
1823:
1820:
1819:
1817:
1815:
1811:
1805:
1802:
1800:
1797:
1795:
1792:
1790:
1789:Adenylylation
1787:
1785:
1782:
1780:
1777:
1775:
1772:
1770:
1767:
1765:
1762:
1761:
1759:
1757:
1753:
1747:
1744:
1742:
1740:
1736:
1734:
1733:Glycosylation
1731:
1729:
1726:
1724:
1721:
1720:
1718:
1716:
1712:
1708:
1705:
1703:
1698:
1692:
1689:
1687:
1686:O-methylation
1684:
1682:
1679:
1677:
1674:
1673:
1671:
1669:
1665:
1658:
1655:
1653:
1650:
1648:
1645:
1643:
1640:
1638:
1637:Carbamylation
1635:
1633:
1630:
1629:
1627:
1625:
1621:
1615:
1612:
1610:
1607:
1605:
1602:
1600:
1597:
1595:
1592:
1591:
1589:
1585:
1581:
1577:
1570:
1565:
1563:
1558:
1556:
1551:
1550:
1547:
1535:
1532:
1530:
1527:
1523:
1520:
1518:
1515:
1513:
1510:
1508:
1507:Hückel's rule
1505:
1504:
1503:
1500:
1499:
1497:
1494:
1490:
1484:
1481:
1479:
1476:
1475:
1473:
1471:
1470:Bond cleavage
1467:
1457:
1454:
1452:
1449:
1447:
1444:
1442:
1439:
1437:
1436:Intercalation
1434:
1431:
1427:
1426:Metallophilic
1424:
1422:
1419:
1417:
1414:
1412:
1409:
1408:
1406:
1402:
1398:
1392:
1389:
1387:
1384:
1382:
1379:
1377:
1374:
1372:
1369:
1368:
1366:
1364:
1360:
1354:
1351:
1350:
1348:
1346:
1343:Van der Waals
1340:
1337:
1333:
1329:
1324:
1318:
1312:
1298:
1297:
1295:
1293:
1289:
1283:
1280:
1279:
1277:
1275:
1271:
1263:
1260:
1258:
1255:
1254:
1253:
1250:
1248:
1245:
1243:
1240:
1238:
1235:
1233:
1230:
1228:
1225:
1223:
1220:
1218:
1215:
1213:
1210:
1208:
1205:
1201:
1198:
1197:
1196:
1193:
1189:
1186:
1184:
1181:
1179:
1176:
1175:
1174:
1171:
1170:
1168:
1166:
1162:
1159:
1155:
1151:
1147:
1140:
1135:
1133:
1128:
1126:
1121:
1120:
1117:
1106:
1102:
1097:
1092:
1088:
1084:
1080:
1073:
1070:
1065:
1061:
1057:
1053:
1049:
1045:
1038:
1035:
1030:
1026:
1022:
1018:
1014:
1010:
1003:
1000:
995:
991:
987:
983:
976:
973:
968:
964:
959:
954:
950:
946:
942:
935:
932:
927:
923:
918:
913:
909:
905:
901:
894:
891:
886:
882:
877:
872:
868:
864:
860:
856:
852:
845:
842:
837:
825:
817:
811:
807:
806:
798:
795:
790:
786:
781:
776:
772:
766:
762:
758:
754:
747:
744:
739:
733:
729:
725:
724:
716:
713:
708:
704:
700:
696:
691:
686:
682:
678:
674:
667:
664:
659:
655:
651:
647:
642:
637:
633:
629:
625:
619:
617:
615:
611:
604:
600:
597:
596:
592:
590:
588:
584:
580:
576:
572:
568:
564:
561:
557:
553:
545:
543:
540:
535:
533:
529:
525:
507:
503:
499:
496:
493:
486:
470:
467:
464:
456:
438:
434:
430:
427:
419:
418:synperiplanar
401:
397:
393:
390:
370:
362:
353:
349:
347:
343:
342:trans isomers
339:
335:
331:
327:
319:
317:
315:
311:
303:
301:
299:
295:
291:
286:
284:
280:
276:
272:
268:
264:
260:
252:
250:
248:
244:
240:
236:
232:
228:
224:
220:
215:
213:
209:
205:
201:
197:
193:
189:
181:
176:
172:
170:
162:
158:
154:
149:
139:
135:
131:
128:
124:
120:
116:
112:
111:
103:
98:
91:
89:
87:
83:
78:
76:
72:
68:
64:
60:
56:
55:chemical bond
53:
49:
45:
41:
32:
19:
18:Amide linkage
2035:Butyrylation
1997:
1738:
1609:Racemization
1594:Peptide bond
1593:
1512:Baird's rule
1232:Charge-shift
1195:Hypervalence
1086:
1082:
1072:
1047:
1043:
1037:
1012:
1008:
1002:
985:
981:
975:
948:
944:
934:
907:
903:
893:
858:
854:
844:
804:
797:
752:
746:
722:
715:
680:
676:
666:
631:
627:
558:atom on the
549:
536:
531:
358:
323:
307:
287:
279:Gibbs energy
256:
216:
185:
150:
115:peptide bond
114:
108:
106:
81:
79:
44:peptide bond
43:
37:
34:Peptide bond
2099:Diphthamide
2058:Methylation
2025:Lactylation
1987:Deamination
1977:Sumoylation
1952:Acetylation
1947:Methylation
1906:Deamidation
1878:Methylation
1827:Prenylation
1652:Methylation
1642:Formylation
1632:Acetylation
1604:Proteolysis
1502:Aromaticity
1478:Heterolysis
1456:Salt bridge
1401:Noncovalent
1371:Low-barrier
1252:Aromaticity
1242:Conjugation
1222:Pi backbond
982:Biopolymers
855:Biopolymers
567:proteolysis
316:radiation.
253:Degradation
231:amino acids
227:glutathione
206:to produce
196:amino acids
180:amino acids
157:amino group
2387:Categories
2222:Tryptophan
2218:Tryptophan
2174:Methionine
2115:Tryptophan
1898:Asparagine
1668:C terminus
1624:N terminus
1430:aurophilic
1411:Mechanical
605:References
310:wavelength
269:(2–4
259:hydrolysis
241:(forms an
171:reaction.
123:side chain
113:through a
2368:Desmosine
2281:Histidine
2101:formation
2091:Histidine
2010:Glycation
1957:Acylation
1921:Glutamine
1860:Glutamate
1837:Aspartate
1779:Sulfation
1715:Threonine
1676:Amidation
1647:Glycation
1522:spherical
1483:Homolysis
1446:Cation–pi
1421:Chalcogen
1381:Symmetric
1237:Hapticity
1029:0002-7863
834:ignored (
824:cite book
707:195819485
699:1365-3075
650:0014-2956
528:catalyzed
508:∘
500:±
494:ω
468:∼
465:τ
439:∘
428:ω
402:∘
391:ω
371:ω
326:lone pair
298:proteases
290:catalyzed
283:half life
233:, by two
212:ribosomes
110:dipeptide
92:Synthesis
61:from C1 (
2356:Allysine
2352:Allysine
2348:Allysine
2285:Tyrosine
2258:Tyrosine
2200:Tyrosine
2151:Cysteine
2147:Cysteine
2045:Arginine
1814:Cysteine
1756:Tyrosine
1451:Anion–pi
1441:Stacking
1363:Hydrogen
1274:Metallic
1165:Covalent
1157:(strong)
1105:14907727
1064:18308334
926:14988435
885:20564017
789:26831698
593:See also
579:hydroxyl
560:carbonyl
192:proteins
138:hydrogen
67:nitrogen
52:covalent
50:type of
2316:Glycine
2308:Alanine
2289:Glycine
2262:Glycine
2073:Proline
1741:-GlcNAc
1587:General
1416:Halogen
1262:bicyclo
1207:Agostic
967:3053703
876:4001729
780:4760355
658:6692818
571:inteins
346:proline
304:Spectra
294:enzymes
235:enzymes
204:enzymes
77:chain.
75:protein
71:peptide
2360:Lysine
2312:Serine
2254:Serine
2196:Lysine
1939:Lysine
1711:Serine
1517:Möbius
1345:forces
1335:(weak)
1103:
1062:
1027:
965:
924:
883:
873:
812:
787:
777:
767:
734:
705:
697:
656:
648:
587:cyclol
563:carbon
552:esters
334:planar
210:, and
130:moiety
63:carbon
46:is an
1659:(Gly)
1495:rules
1404:other
1292:Ionic
1200:3c–4e
1188:8c–2e
1183:4c–2e
1178:3c–2e
703:S2CID
583:amine
575:thiol
277:) of
161:water
134:amino
125:(C1)
48:amide
1578:and
1257:homo
1212:Bent
1101:PMID
1060:PMID
1025:ISSN
963:PMID
922:PMID
881:PMID
836:help
810:ISBN
785:PMID
765:ISBN
732:ISBN
695:ISSN
654:PMID
646:ISSN
359:The
308:The
271:kcal
42:, a
2339:AAs
2245:AAs
2138:AAs
1702:AAs
1091:doi
1087:193
1052:doi
1048:377
1017:doi
1013:118
990:doi
953:doi
949:263
912:doi
908:134
871:PMC
863:doi
775:PMC
757:doi
728:168
685:doi
636:doi
632:138
581:or
435:180
340:or
338:cis
292:by
275:mol
267:mol
188:ATP
73:or
38:In
2389::
1099:.
1085:.
1081:.
1058:.
1046:.
1023:.
1011:.
986:45
984:.
961:.
947:.
943:.
920:.
906:.
902:.
879:.
869:.
859:94
857:.
853:.
828::
826:}}
822:{{
783:.
773:.
763:.
730:.
701:.
693:.
681:66
679:.
675:.
652:.
644:.
630:.
626:.
613:^
577:,
504:90
471:20
383:;
314:UV
263:kJ
237::
163:(H
2358:–
2354:–
2350:–
2314:–
2310:–
2287:–
2283:–
2260:–
2256:–
2220:–
2198:–
2176:–
2149:–
1998:O
1739:O
1713:/
1568:e
1561:t
1554:v
1432:)
1428:(
1138:e
1131:t
1124:v
1107:.
1093::
1066:.
1054::
1031:.
1019::
996:.
992::
969:.
955::
928:.
914::
887:.
865::
838:)
818:.
791:.
759::
740:.
709:.
687::
660:.
638::
497:=
431:=
398:0
394:=
273:/
265:/
165:2
146:2
142:2
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.