35:
301:, by forming a sheet composed of two layers of lipids. Each layer forms by positioning their lypophilic chains to the same side of the layer. The two layers then stack such that their lyphphilic chains touch on the inside and their polar groups are outside facing the surrounding aqueous media. Thus the inside of the bilayer sheet is a non-polar region sandwiched between the two polar sheets.
20:
326:
Aβ proteins form antiparallel β sheets which are strongly amphiphilic, and which aggregate to form toxic oxidative Aβ fibrils. Aβ fibrils themselves are composed of amphiphilic 13-mer modular β sandwiches separated by reverse turns. Hydropathic waves optimize the description of the small (40,42 aa)
283:
273:
When placed in an immiscible biphasic system consisting of aqueous and organic solvents, the amphiphilic compound will partition the two phases. The extent of the hydrophobic and hydrophilic portions determines the extent of partitioning.
337:
analysis showed that amphipathicity best distinguished between AMPs with and without anti-gram-negative bacteria activities. The higher amphipathicity, the better chances for AMPs possessing antibacterial and antifungal dual activities.
323:, strongly interact with biological membranes by insertion of the hydrophobic part into the lipid membrane, while exposing the hydrophilic part to the aqueous medium, altering their physical behavior and sometimes disrupting them.
421:
is a common household amphiphilic surfactant compound. Soap mixed with water (polar, hydrophilic) is useful for cleaning oils and fats (non-polar, lipiphillic) from kitchenware, dishes, skin, clothing, etc.
42:
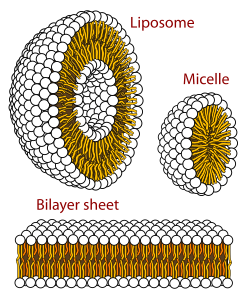
in aqueous solutions. Unlike this illustration, micelles are usually formed by non-biological, single-chain, amphiphiles, soaps or detergents, since it is difficult to fit two chains into this shape
1048:
723:
750:
671:"Large-scale analysis of antimicrobial activities in relation to amphipathicity and charge reveals novel characterization of antimicrobial peptides"
634:
Phillips, J.C. (20 May 2015). "Thermodynamic description of Beta amyloid formation using physicochemical scales and fractal bioinformatic scales".
503:
263:
As a result of having both lipophilic and hydrophilic portions, some amphiphilic compounds may dissolve in water and to some extent in
795:
743:
885:
1114:
1038:
297:. The amphiphilic nature of these molecules defines the way in which they form membranes. They arrange themselves into
968:
736:
1023:
915:
493:
34:
900:
835:
855:
238:
97:
Amphiphiles are the basis for a number of areas of research in chemistry and biochemistry, notably that of
953:
948:
805:
462:
377:
361:
316:, which are also included in these structures and give them different physical and biological properties.
245:
Often, amphiphilic species have several lipophilic parts, several hydrophilic parts, or several of both.
1053:
1033:
369:
330:
1119:
767:
759:
588:
880:
850:
294:
234:
27:
550:
78:) properties. Such a compound is called amphiphilic or amphipathic. Amphiphilic compounds include
457:
132:
98:
1058:
1017:
920:
702:
651:
616:
575:
Schubert, D; Behl, C; Lesley, R; Brack, A; Dargusch, R; Sagara, Y; Kimura, H (14 March 1995).
499:
308:
are the principal constituents of biological membranes, there are other constituents, such as
282:
59:
993:
988:
820:
780:
692:
682:
643:
606:
596:
202:
963:
895:
860:
845:
840:
825:
790:
978:
592:
526:
104:
Organic compounds containing hydrophilic groups at both ends of the molecule are called
1109:
1028:
983:
973:
890:
785:
775:
697:
670:
472:
447:
105:
1103:
1073:
910:
870:
815:
611:
576:
298:
91:
39:
930:
925:
392:
305:
290:
206:
87:
23:
260:) structures and hydrophilic polar functional groups (either ionic or uncharged).
1083:
998:
436:
431:
396:
356:
are an example group of amphiphilic compounds. Their polar region can be either
349:
309:
257:
171:
151:
129:
79:
63:
581:
Proceedings of the
National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
1068:
1063:
940:
687:
452:
404:
400:
381:
353:
313:
125:
71:
346:
There are several examples of molecules that present amphiphilic properties:
1088:
1043:
958:
408:
385:
250:
198:
189:
83:
706:
655:
601:
620:
19:
905:
441:
334:
320:
220:
214:
1008:
810:
800:
467:
412:
267:
246:
180:
161:
113:
109:
647:
728:
373:
264:
51:
164:. Examples, with the lipophilic part of the molecule represented by
830:
365:
281:
33:
724:
Estimating intestinal permeability by surface activity profiling
418:
732:
293:, a class of amphiphilic molecules, are the main components of
357:
577:"Amyloid peptides are toxic via a common oxidative mechanism"
286:
The lipid bilayer, the material that makes up cell membranes.
38:
Cross-section view of the structures that can be formed by
669:
Chien-Kuo Wang; Ling-Yi Shih; Kuan Y. Chang (2017-11-22).
360:, or non-ionic. Some typical members of this group are:
237:
with large R groups, such as diacyl glycerol (DAG), and
333:(AMPs) are another class of amphiphilic molecules, a
1049:
List of boiling and freezing information of solvents
1007:
939:
869:
766:
154:group falls into one of the following categories:
90:amphiphiles are the major structural component of
256:Amphiphilic compounds have lipophilic (typically
50:(from the Greek αμφις amphis, both, and φιλíα
744:
8:
16:Hydrophilic and lipophilic chemical compound
492:Betts, J. Gordon. "3.1 The cell membrane".
391:Many biological compounds are amphiphilic:
327:plaque-forming (aggregative) Aβ fragments.
751:
737:
729:
319:Many other amphiphilic compounds, such as
696:
686:
610:
600:
18:
484:
233:polar, uncharged groups. Examples are
135:, such as a long chain of the form CH
7:
14:
388:(long-chain alcohol, non-ionic).
112:they form in the aggregate are
1:
30:, have amphipathic character.
1039:Inorganic nonaqueous solvent
415:, local anaesthetics, etc.
128:group is typically a large
1136:
1024:Acid dissociation constant
688:10.3390/molecules22112037
636:ACS Chemical Neuroscience
551:"Structure of a Membrane"
531:Biology-Online Dictionary
495:Anatomy & physiology
54:, love, friendship), or
989:Solubility table (data)
856:Apparent molar property
241:with long alkyl chains.
954:Total dissolved solids
949:Solubility equilibrium
874:and related quantities
602:10.1073/pnas.92.6.1989
463:Sodium dodecyl sulfate
437:Bubbles in abiogenesis
378:cocamidopropyl betaine
362:sodium dodecyl sulfate
331:Antimicrobial peptides
287:
43:
40:biological amphiphiles
31:
1054:Partition coefficient
1034:Polar aprotic solvent
370:benzalkonium chloride
285:
239:oligo ethylene glycol
37:
22:
969:Enthalpy of solution
896:Volume concentration
891:Number concentration
555:The Lipid Chronicles
295:biological membranes
1115:Chemical properties
881:Molar concentration
851:Dilution (equation)
593:1995PNAS...92.1989S
253:are such examples.
28:glycerophospholipid
921:Isotopic abundance
886:Mass concentration
760:Chemical solutions
458:Lipid polymorphism
288:
99:lipid polymorphism
44:
32:
1097:
1096:
648:10.1021/cn5001793
557:. 5 November 2011
505:978-1-947172-04-3
147:, with n > 4.
60:chemical compound
1127:
994:Solubility chart
821:Phase separation
781:Aqueous solution
753:
746:
739:
730:
711:
710:
700:
690:
666:
660:
659:
631:
625:
624:
614:
604:
572:
566:
565:
563:
562:
547:
541:
540:
538:
537:
523:
517:
516:
514:
512:
489:
268:organic solvents
203:functional group
62:possessing both
1135:
1134:
1130:
1129:
1128:
1126:
1125:
1124:
1100:
1099:
1098:
1093:
1003:
964:Solvation shell
935:
873:
865:
861:Miscibility gap
846:Serial dilution
841:Supersaturation
791:Buffer solution
762:
757:
720:
715:
714:
668:
667:
663:
633:
632:
628:
574:
573:
569:
560:
558:
549:
548:
544:
535:
533:
525:
524:
520:
510:
508:
506:
491:
490:
486:
481:
428:
344:
280:
278:Biological role
249:and some block
226:
195:
186:
177:
158:charged groups
146:
142:
138:
122:
106:bolaamphiphilic
26:, such as this
17:
12:
11:
5:
1133:
1131:
1123:
1122:
1117:
1112:
1102:
1101:
1095:
1094:
1092:
1091:
1086:
1081:
1076:
1071:
1066:
1061:
1056:
1051:
1046:
1041:
1036:
1031:
1029:Protic solvent
1026:
1021:
1013:
1011:
1005:
1004:
1002:
1001:
996:
991:
986:
981:
976:
974:Lattice energy
971:
966:
961:
956:
951:
945:
943:
937:
936:
934:
933:
928:
923:
918:
913:
908:
903:
898:
893:
888:
883:
877:
875:
867:
866:
864:
863:
858:
853:
848:
843:
838:
833:
828:
826:Eutectic point
823:
818:
813:
808:
803:
798:
793:
788:
786:Solid solution
783:
778:
776:Ideal solution
772:
770:
764:
763:
758:
756:
755:
748:
741:
733:
727:
726:
719:
718:External links
716:
713:
712:
661:
626:
587:(6): 1989–93.
567:
542:
518:
504:
483:
482:
480:
477:
476:
475:
473:Viral envelope
470:
465:
460:
455:
450:
448:surface energy
444:
439:
434:
427:
424:
343:
340:
299:lipid bilayers
279:
276:
243:
242:
231:
230:
229:
228:
227:
224:
212:
211:
210:
196:
193:
187:
184:
178:
175:
144:
140:
136:
121:
118:
92:cell membranes
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1132:
1121:
1118:
1116:
1113:
1111:
1108:
1107:
1105:
1090:
1087:
1085:
1082:
1080:
1077:
1075:
1072:
1070:
1067:
1065:
1062:
1060:
1057:
1055:
1052:
1050:
1047:
1045:
1042:
1040:
1037:
1035:
1032:
1030:
1027:
1025:
1022:
1019:
1015:
1014:
1012:
1010:
1006:
1000:
997:
995:
992:
990:
987:
985:
982:
980:
977:
975:
972:
970:
967:
965:
962:
960:
957:
955:
952:
950:
947:
946:
944:
942:
938:
932:
929:
927:
924:
922:
919:
917:
916:Mass fraction
914:
912:
911:Mole fraction
909:
907:
904:
902:
899:
897:
894:
892:
889:
887:
884:
882:
879:
878:
876:
872:
871:Concentration
868:
862:
859:
857:
854:
852:
849:
847:
844:
842:
839:
837:
834:
832:
829:
827:
824:
822:
819:
817:
816:Phase diagram
814:
812:
809:
807:
804:
802:
799:
797:
796:Flory–Huggins
794:
792:
789:
787:
784:
782:
779:
777:
774:
773:
771:
769:
765:
761:
754:
749:
747:
742:
740:
735:
734:
731:
725:
722:
721:
717:
708:
704:
699:
694:
689:
684:
680:
676:
672:
665:
662:
657:
653:
649:
645:
642:(5): 745–50.
641:
637:
630:
627:
622:
618:
613:
608:
603:
598:
594:
590:
586:
582:
578:
571:
568:
556:
552:
546:
543:
532:
528:
527:"Amphipathic"
522:
519:
507:
501:
497:
496:
488:
485:
478:
474:
471:
469:
466:
464:
461:
459:
456:
454:
451:
449:
445:
443:
440:
438:
435:
433:
430:
429:
425:
423:
420:
416:
414:
410:
406:
402:
398:
394:
393:phospholipids
389:
387:
383:
379:
375:
371:
367:
363:
359:
355:
351:
347:
341:
339:
336:
332:
328:
324:
322:
317:
315:
311:
307:
306:phospholipids
302:
300:
296:
292:
291:Phospholipids
284:
277:
275:
271:
269:
266:
261:
259:
254:
252:
248:
240:
236:
232:
222:
219:
218:
216:
213:
208:
207:phospholipids
204:
201:(the charged
200:
197:
191:
188:
182:
179:
173:
170:
169:
167:
163:
160:
159:
157:
156:
155:
153:
148:
134:
131:
127:
119:
117:
115:
111:
107:
102:
100:
95:
93:
89:
85:
81:
77:
73:
70:, polar) and
69:
65:
61:
57:
53:
49:
41:
36:
29:
25:
24:Phospholipids
21:
1078:
979:Raoult's law
931:Ternary plot
926:Mixing ratio
681:(11): 2037.
678:
674:
664:
639:
635:
629:
584:
580:
570:
559:. Retrieved
554:
545:
534:. Retrieved
530:
521:
509:. Retrieved
498:. OpenStax.
494:
487:
417:
390:
382:zwitterionic
348:
345:
329:
325:
318:
303:
289:
272:
262:
255:
244:
217:. Examples:
172:carboxylates
165:
149:
123:
103:
96:
88:phospholipid
75:
68:water-loving
67:
55:
47:
45:
1120:Surfactants
1084:Lyonium ion
999:Miscibility
984:Henry's law
432:Amphoterism
405:fatty acids
401:glycolipids
397:cholesterol
354:surfactants
350:Hydrocarbon
314:glycolipids
310:cholesterol
258:hydrocarbon
152:hydrophilic
130:hydrocarbon
80:surfactants
64:hydrophilic
1104:Categories
1079:Amphiphile
1074:Lipophilic
1069:Hydrophile
1064:Hydrophobe
941:Solubility
836:Saturation
806:Suspension
561:2020-06-02
536:2016-11-17
479:References
453:Surfactant
409:bile acids
251:copolymers
199:phosphates
190:sulfonates
126:lipophilic
84:detergents
76:fat-loving
72:lipophilic
48:amphiphile
1089:Lyate ion
1044:Solvation
959:Solvation
901:Normality
675:Molecules
386:1-octanol
321:pepducins
304:Although
265:non-polar
221:ammoniums
120:Structure
56:amphipath
1059:Polarity
1018:Category
906:Molality
768:Solution
707:29165350
656:25702750
442:Emulsion
426:See also
413:saponins
374:cationic
342:Examples
335:big data
247:Proteins
235:alcohols
215:cationic
181:sulfates
110:micelles
1009:Solvent
811:Colloid
801:Mixture
698:6150348
621:7892213
589:Bibcode
468:Wetting
384:), and
366:anionic
352:-based
168:, are:
162:anionic
114:prolate
58:, is a
705:
695:
654:
619:
609:
511:14 May
502:
133:moiety
108:. The
86:. The
52:philia
1110:Soaps
831:Alloy
612:42408
446:Free
358:ionic
223:: RNH
192:: RSO
183:: RSO
174:: RCO
703:PMID
652:PMID
617:PMID
513:2023
500:ISBN
419:Soap
312:and
150:The
124:The
82:and
693:PMC
683:doi
644:doi
607:PMC
597:doi
376:),
368:),
205:in
139:(CH
46:An
1106::
701:.
691:.
679:22
677:.
673:.
650:.
638:.
615:.
605:.
595:.
585:92
583:.
579:.
553:.
529:.
411:,
407:,
403:,
399:,
395:,
270:.
116:.
101:.
94:.
1020:)
1016:(
752:e
745:t
738:v
709:.
685::
658:.
646::
640:6
623:.
599::
591::
564:.
539:.
515:.
380:(
372:(
364:(
225:3
209:)
194:3
185:4
176:2
166:R
145:n
143:)
141:2
137:3
74:(
66:(
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.