189:
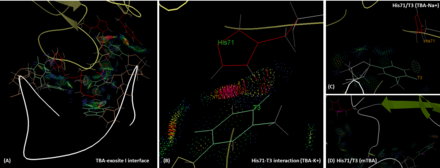
charged motif, engages in these interactions with the negatively charged backbone of HD1. Importantly, T3 interacts with His71, which plays a critical role for fibrinogen recognition, both through hydrogen bonding and hydrophobic interaction. However, in the presence of sodium ion, the hydrogen bonding between T3 and His71 is lost, and the intermolecular distance is longer than that in the potassium case. This reduces the affinity and functionality of TBA. Similar situation can be found in the case of mTBA. There are no interactions between mTBA and His71, which results in the reduction of anticoagulant activity. The results of In silico calculations with molecular mechanics
Poisson-Boltzmann surface area (MM-PBSA) method, suggest that the calculated binding energy (ΔG) of TBA to thrombin exosite I is slightly stronger is the presence of K+ (-66.73 kcal.mol-1) than in the case of Na+ (-60.29kcal.mol-1), however both states are likely to coexist.
97:, so this aptamer acts as an anti-coagulant agent inhibiting the activation of fibrinogen as well as platelet aggregation. In addition, TBA shows good affinity and specificity against thrombin. The dissociation constant of TBA-thrombin has been reported in nano-molar range, and TBA does not interact with other plasma proteins or thrombin analogues (e.g., gamma-thrombin). As a result, TBA has been used as a short-term anti-coagulant designed for the application in the coronary artery bypass graft surgery, and its optimized form (NU172) is now under the phase II of clinical trial by ARCA Biopharma (NCT00808964). Also, due to its high affinity and specificity, a variety of sensors was coupled with TBA and developed for thrombosis diagnostics.
301:
Val241 and Phe245 in thrombin are involved in the interaction. Since the exosite II is a positively charged motif, it creates many ion pairs with the HD22 backbone especially in the duplex region. Hydrophobic interactions are mainly observed in the G-quadruplex region (T9, T18 and T10), and this stabilizes the complex formation. Moreover, Interacting with thrombin improves the thermal stability of HD22 structure, and results in the increase of melting temperature (from 36 to 48 °C). Calculated binding energy of HD22 to thrombin exosite II is -88.37 -kcal.mol-1.
20:
180:
106:
155:
only interacts with four rather than eight oxygen atoms of two G-tetrad planes, and accordingly has two alternative position in the cavity. Thrombin shows similar influence as potassium ion. In the ion-deficient condition, thrombin helps TBA form into a stable G-quadruplex structure from a randomized coil, which results in conformational change. Some groups use this property to develop aptamer-based thrombin sensors. For this purpose, TBA is usually mounted with an additional sequence with a FRET (
224:
62:
267:). The nucleotides 1-3 and 25-27 with an additional C4-G23 form a duplex motif, and the sequence ranging from G5 to G20 folds into a G-quadruplex structure with four connection loops: T9-A10, T18-T19, G13-C14-A15 and a one-nucleotide loop (T6). In the core of G-quadruplex motif, two G-tetrad planes are formed by G5-G7-G12-G16 and G8-G11-G17-G20. The upper plane (G5-G7-G12-G16) is not a typical G-tetrad with the chain topology of
215:
330:. Ecarin activates prothrombin and accordingly produces meizothrombin. The exosite II is not accessible in meizothrombin, so thus the HD22 part cannot interact with meizothrombin directly. As a result, TBA-HD22 construct cannot improve the ecarin clotting time, which further demonstrates the improvement of aptamer functionality is due to TBA-HD22 avidity.
206:(now ARCA Biopharma) around 2005. Although it showed a rapid onset response with desired anticoagulation activity, the activity requires significantly high dosage of TBA. Thus, the companies redesigned the sequence of TBA and developed a second-generation 26-mer DNA aptamer known as NU172, which is now under phase II clinical trial.
300:
The nucleotides G23, T24, G25, A26, C27 in the duplex and T9, T18, T19, G20 in G-quadruplex contribute to the interaction with the exosite II of thrombin. On the protein side, the residues Tyr89, His91, Pro92, Arg93, Tyr94, Asn95, Trp96, Arg97, Arg126, Leu130, Arg165, Lys169, His230, Arg233, Trp237,
183:
The interface between TBA and the exosite I of thrombin. (A) The interface. Involved protein residues and aptamer nucleotides are labeled with red and green, respectively. (B) The interaction between His71 and T3 (TBA) in the presence of potassium ion. (C) The positions of His 71 and T3 (TBA) in the
154:
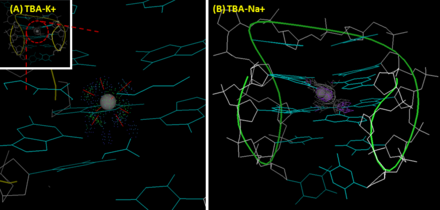
ion and potassium are 24 °C and 53 °C, respectively. Compared with sodium, potassium ion fits perfectly to the cavity between two G-tetrad plane and is coordinately bound to four O6 atoms in each plane. This enhances the structural stability of TBA. In contrast, due to its small size, sodium ion can
197:
It has been demonstrated that TBA can inhibit the thrombin-induced platelet aggregation and clot-bound thrombin activity. The IC50 of TBA for the inhibition of platelet aggregation (0.5 U/mL thrombin) is around 70 to 80 nmol/L, which is much lower than that of hirudin (~1.7 umol/L). Also, compared
159:) pair to form a transient duplex structure. Once the TBA part interacts with thrombin, the conformational change would change the distance between the FRET pair and lead to a fluorescent output. This approach provides nano-molar sensitivity and is capable of sensing thrombin in the spiked serum.
291:
conformation. Additionally, the one-nucleotide loop inserted between G5 and G7. These make G-tetrad formed not through a typically cyclic pattern. This unusual G-tetrad plan is formed by four hydrogen bonds: one on N2:N7(G5-G16), two on O6:N7(G12-G7; G16-G12) and one on O6:N2 (G7-G5). Some other
188:
TBA is bound to the exosite I of thrombin majorly via its two TT loops (T3, T4 and T12, T13) through polar and hydrophobic interactions. The residues His71, Arg75, Tyr76, Arg77, Asn78, Ile79, Tyr117 in the exosite I epitope are involved in the interaction with TBA. Exosite 1, being a positively
254:
binding. Therefore, HD22 inhibits the activations of factors V/VIII rather than that of fibrinogen. Despite that this aptamer only shows moderate effect on fibrinogen regulation, the affinity of this aptamer is slightly higher than TBA (KD~0.5 nM), and nowadays this aptamer is widely used for
122:
interacts with one another through non Watson-Crick-like hydrogen bonds (more likely
Hoogsteen-like hydrogen bonds). In the structure of TBA, G1, G6, G10 and G15 form the top layer of G-tetrad; G2, G5, G11 and G14 form the second layer. The first crystallographic images with 2.9 Å resolution
109:
The interactions between TBA and ions. (A) TBA-potassium ion complex. Potassium ion fits the cavity between the two G-tetrad planes of TBA properly and coordinately interacts with eight O6 atoms in G-quadruplex. (insert: the whole structure of TBA-K+ complex) (B) TBA-sodium ion complex. Two
313:
effect against thrombin after dimerization. When TBA and HD22 are conjugated with an optimal linker or co-printed on the sensor surface with an optimal density, the affinity against thrombin could be significantly enhanced by 100 to 10,000 fold. Furthermore, the dimerization improves the
292:
interactions could be found in the G-quadruplex motif: two Watson-Crick base pairs (T6-A15 and A10-T19) and a G-fork (G5-G21). Importantly, because of the interaction between G5 and G21, there is a 90-degree turn between the G-qudruplex and duplex motifs.
65:
The G-quadruplex structure adopted by TBA. (A) The crystallographic structure and (B) the schematic illustration of TBA (PDB file 4DII). Insert: the top layer of G-tetrad (The
Hoogsteen-like hydrogen bonds are highlighted with green dashed
1129:
Russo Krauss, Irene; Pica, Andrea; Merlino, Antonello; Mazzarella, Lelio; Sica, Filomena (2013). "Duplex–quadruplex motifs in a peculiar structural organization cooperatively contribute to thrombin binding of a DNA aptamer".
622:
Nagatoishi, Satoru; Tanaka, Yoshikazu; Tsumoto, Kouhei (2007). "Circular dichroism spectra demonstrate formation of the thrombin-binding DNA aptamer G-quadruplex under stabilizing-cation-deficient conditions".
218:
HD22 structure and interbase interaction. (A) Overall structure of HD22. (B) Top G-tetrad plane (C) The Watson-Crick base pairs in the G-quadruplex motif. (D) G-fork interaction between G-quadruplex and duplex
198:
with heparin, TBA is more efficient in the inhibition of clot-bound thrombin. Furthermore, TBA recognizes and inhibits prothrombin with similar affinity against alpha-thrombin. As a result, TBA prolongs the
171:). This improves the thermal stability of G-quadruplex structure, and increases the melting temperature by 4 °C. In spite of this, the anticoagulant activity is affected and reduced by the inversion design.
150:(CD) spectrum. Also, potassium ion improves the thermal stability of TBA. The melting temperature of TBA's G-quadruplex (measuring the intensity change of the peak at 295 nm by CD) in the presence of
227:
HD22-exosite II interaction. (A) Overall interface between HD22 and the exosite II. (B) The interface at the duplex motif. (C) The interface at the G-quadruplex motif. Dots represent the interactions.
658:
Chi, Chun-Wei; Lao, Yeh-Hsing; Li, Yi-Shan; Chen, Lin-Chi (2011). "A quantum dot-aptamer beacon using a DNA intercalating dye as the FRET reporter: Application to label-free thrombin detection".
46:
127:) was reported in 1993. It showed that the T7-G8-T9 loop and TT loops (T3-T4 and T12-T13) connected the narrow and the wide grooves, respectively. However, since the improved NMR (
23:
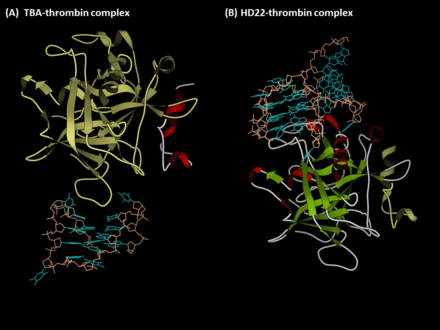
The complexes of (A) TBA-thrombin and (B) HD22-thrombin (PDB files 4DII and 4I7Y). The protein and aptamer were represented in the ribbon and ball&stick formats, respectively.
49:) technology in 1992 by L.C. Bock, J.J. Toole and colleagues. A second thrombin-binding aptamer, HD22, recognizes thrombin exosite II and was discovered in 1997 by NeXstar (now
350:
Bock, Louis C.; Griffin, Linda C.; Latham, John A.; Vermaas, Eric H.; Toole, John J. (1992). "Selection of single-stranded DNA molecules that bind and inhibit human thrombin".
495:
Padmanabhan, K.; Padmanabhan, K. P.; Ferrara, J. D.; Sadler, J. E.; Tulinsky, A. (1993). "The structure of alpha-thrombin inhibited by a 15-mer single-stranded DNA aptamer".
242:) or 27 (lacking the first and the last nucleotides of 29-mer form) nucleotides. This aptamer recognizes the exosite II of thrombin, which is involved in the activation of
693:
Martino, Luigi; Virno, Ada; Randazzo, Antonio; Virgilio, Antonella; Esposito, Veronica; Giancola, Concetta; Bucci, Mariarosaria; Cirino, Giuseppe; Mayol, Luciano (2006).
53:). These two aptamers have high affinity and good specificity and have been widely studied and used for the development of aptamer-based therapeutics and diagnostics.
263:
Unlike TBA, HD22 holds a duplex/G-quadruplex mixed structure. The X-ray crystallographic image of HD22 (27mer form) with 2.4 Å resolution was reported recently (
572:"High-resolution structures of two complexes between thrombin and thrombin-binding aptamer shed light on the role of cations in the aptamer inhibitory activity"
167:
A modified TBA with chain polarity inversion was reported in 1996, which is known as mTBA. A 5'-5' inversion was designed between T3 and T4 in mTBA sequence (
139:) were provided, another topology with the TGT loop on the wide side and the TT loops on the narrow sites has been considered as a correct structure of TBA.
146:
ion helps TBA fold into a G-quadruplex structure, which results in a significant positive band at 295 nm and a negative band at 270 nm on its
315:
156:
1375:
404:
Tasset, Diane M.; Kubik, Mark F.; Steiner, Walter (1997). "Oligonucleotide inhibitors of human thrombin that bind distinct epitopes".
314:
anticoagulant activity as well. The TBA-HD22 construct (linked with 16-mer polyA) shows significant improvement both in the assay of
979:"HD1, a Thrombin-directed Aptamer, Binds Exosite 1 on Prothrombin with High Affinity and Inhibits Its Activation by Prothrombinase"
202:
when interacting with prothrombin. TBA entered the phase I clinical trial for coronary artery bypass graft surgery by
Archemix and
114:
The tertiary structure of TBA is an anti-parallel G-quadruplex. This chair-like structure is folded through the stacking of two
184:
presence of sodium ion. (D) The positions of His71 and T3 (mTBA). Dots represent the interactions between thrombin and aptamer.
930:"A novel nucleotide-based thrombin inhibitor inhibits clot-bound thrombin and reduces arterial platelet thrombus formation"
834:
Russo Krauss, Irene; Merlino, Antonello; Giancola, Concetta; Randazzo, Antonio; Mazzarella, Lelio; Sica, Filomena (2011).
570:
Russo Krauss, Irene; Merlino, Antonello; Randazzo, Antonio; Novellino, Ettore; Mazzarella, Lelio; Sica, Filomena (2012).
318:, clotting time and thrombin-induced platelet-aggregation. TBA-HD22 construct shows comparable efficacy compared with
1317:"Anticoagulant characteristics of HD1-22, a bivalent aptamer that specifically inhibits thrombin and prothrombinase"
439:
Li, Jianwei J.; Fang, Xiaohong; Tan, Weihong (2002). "Molecular
Aptamer Beacons for Real-Time Protein Recognition".
478:"Phase 2 Study of NU172 Anticoagulation in Patients Undergoing Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery OFF-Pump"
477:
110:
alternative positions of sodium observed, and sodium can only interacts with four rather than eight oxygens.
742:
Rangnekar, Abhijit; Nash, Jessica A.; Goodfred, Bethany; Yingling, Yaroslava G.; Labean, Thomas H. (2016).
1370:
1167:"Thrombin detection in murine plasma using engineered fluorescence resonance energy transfer aptadimers"
19:
1077:"Beyond G-Quadruplexes—The Effect of Junction with Additional Structural Motifs on Aptamers Properties"
1227:
1178:
902:
887:
359:
327:
179:
105:
1346:
1057:
959:
530:
Padmanabhan, K.; Tulinsky, A. (1996). "An
Ambiguous Structure of a DNA 15-mer Thrombin Complex".
383:
147:
1338:
1297:
1275:"Enhancement of Aptamer Microarray Sensitivity through Spacer Optimization and Avidity Effect"
1274:
1255:
1196:
1147:
1108:
1049:
1000:
951:
865:
816:
775:
724:
675:
640:
601:
547:
512:
456:
421:
375:
264:
128:
124:
1328:
1289:
1245:
1235:
1186:
1139:
1098:
1088:
1039:
1031:
990:
941:
910:
855:
847:
806:
765:
755:
714:
706:
667:
632:
591:
583:
539:
504:
448:
413:
367:
199:
223:
50:
38:
1231:
1182:
1044:
1019:
906:
888:"Binding modes of thrombin binding aptamers investigated by simulations and experiments"
744:"Design of Potent and Controllable Anticoagulants Using DNA Aptamers and Nanostructures"
363:
93:. It interacts with the exosite I of human alpha-thrombin, which is the binding site of
1250:
1215:
1214:
Hasegawa, Hijiri; Taira, Ken-ichi; Sode, Koji; Ikebukuro, Kazunori (19 February 2008).
1103:
1076:
860:
835:
793:
Tsiang, M.; Jain, A. K.; Dunn, K. E.; Rojas, M. E.; Leung, L. L.; Gibbs, C. S. (1995).
770:
743:
719:
695:"A new modified thrombin binding aptamer containing a 5′–5′ inversion of polarity site"
694:
596:
571:
115:
136:
132:
1364:
1333:
1316:
977:
Kretz, Colin A.; Stafford, Alan R.; Fredenburgh, James C.; Weitz, Jeffrey I. (2006).
1350:
1061:
963:
61:
387:
79:
34:
946:
929:
319:
247:
671:
636:
1143:
1035:
760:
543:
323:
94:
1200:
811:
794:
214:
143:
1342:
1301:
1259:
1151:
1112:
1053:
1004:
995:
978:
928:
Li, W. X.; Kaplan, A. V.; Grant, G. W.; Toole, J. J.; Leung, L. L. (1994).
869:
779:
728:
679:
644:
605:
551:
460:
452:
417:
955:
820:
516:
508:
425:
379:
1093:
851:
710:
587:
243:
45:. The first anti-thrombin aptamer, TBA, was generated through via SELEX (
42:
310:
251:
231:
The aptamer HD22 (also known as HTDQ) is an optimized aptamer with 29 (
119:
29:
1293:
1191:
1166:
914:
1240:
371:
203:
151:
142:
In addition to protein-selectivity, TBA also shows ion preference. A
75:
71:
222:
213:
178:
104:
60:
18:
16:
Oligonucleotides which recognize the exosites of human thrombin
1020:"Direct thrombin inhibitors – a survey of recent developments"
795:"Functional mapping of the surface residues of human thrombin"
283:
alternation. Instead, three guanines (G5, G7 and G16) adopt
47:
Systematic
Evolution of Ligands by Exponential Enrichment
1315:
Müller, J.; Freitag, D.; Mayer, G.; Pötzsch, B. (2008).
326:. In addition, the TBA-HD22 avidity can be examined by
836:"Thrombin–aptamer recognition: A revealed ambiguity"
82:) is a 15-mer single-stranded DNA with the sequence
1273:Lao, Yeh-Hsing; Peck, Konan; Chen, Lin-Chi (2009).
625:
441:
1216:"Improvement of Aptamer Affinity by Dimerization"
309:Similar to antibody, aptamers TBA and HD22 show
287:conformation, and only one guanine (G12) adopts
74:(also known as G15D, HTQ, HD1, ARC183, GS522,
1075:Kotkowiak, Weronika; Pasternak, Anna (2021).
886:Trapaidze, A.; Bancaud, A.; Brut, M. (2015).
210:Aptamer HD22 (the exosite II-binding aptamer)
8:
1081:International Journal of Molecular Sciences
57:Aptamer TBA (the exosite I-binding aptamer)
1332:
1249:
1239:
1190:
1102:
1092:
1043:
994:
945:
859:
810:
769:
759:
718:
595:
41:, which recognizes the exosites of human
339:
1124:
1122:
881:
879:
296:Interactions between HD22 and thrombin
131:) and X-ray crystallographic images (
1321:Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis
316:activated partial thromboplastin time
175:Interactions between TBA and thrombin
7:
1024:Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences
617:
615:
565:
563:
561:
472:
470:
399:
397:
345:
343:
1165:Trapaidze, A.; et al. (2015).
799:The Journal of Biological Chemistry
497:The Journal of Biological Chemistry
14:
157:Förster resonance energy transfer
1334:10.1111/j.1538-7836.2008.03162.x
1132:Acta Crystallographica Section D
532:Acta Crystallographica Section D
255:developments of aptamer sensor.
237:-AGTCCGTGGTAGGGCAGGTTGGGGTGACT-3
983:Journal of Biological Chemistry
305:Avidity effect of TBA and HD22
1:
660:Biosensors and Bioelectronics
406:Journal of Molecular Biology
322:, but much more potent than
947:10.1182/blood.V83.3.677.677
169:3′-GGT-5′-5′TGGTGTGGTTGG-3′
1392:
1376:Direct thrombin inhibitors
672:10.1016/j.bios.2011.01.015
637:10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.11.088
1144:10.1107/S0907444913022269
1036:10.1007/s00018-006-6219-z
1018:Schwienhorst, A. (2006).
761:10.3390/molecules21020202
544:10.1107/S0907444995013977
812:10.1074/jbc.270.28.16854
193:Therapeutic applications
1171:Applied Physics Letters
895:Applied Physics Letters
996:10.1074/jbc.M607359200
840:Nucleic Acids Research
699:Nucleic Acids Research
576:Nucleic Acids Research
453:10.1006/bbrc.2002.6581
418:10.1006/jmbi.1997.1275
228:
220:
185:
111:
67:
24:
226:
217:
182:
108:
64:
22:
1282:Analytical Chemistry
1094:10.3390/ijms22189948
328:ecarin clotting time
1232:2008Senso...8.1090H
1183:2015ApPhL.107w3701T
989:(49): 37477–37485.
907:2015ApPhL.106d3702T
805:(28): 16854–16863.
509:10.2210/pdb1hut/pdb
503:(24): 17651–17654.
482:Clinical Trials.gov
364:1992Natur.355..564B
116:guanine (G)-tetrads
852:10.1093/nar/gkr522
711:10.1093/nar/gkl915
588:10.1093/nar/gks512
229:
221:
186:
148:circular dichroism
112:
88:-GGTTGGTGTGGTTGG-3
68:
25:
1327:(12): 2105–2112.
1294:10.1021/ac801285a
1192:10.1063/1.4937351
1138:(12): 2403–2411.
1030:(23): 2773–2791.
915:10.1063/1.4906594
846:(17): 7858–7867.
705:(22): 6653–6662.
582:(16): 8119–8128.
358:(6360): 564–566.
250:and mediates the
1383:
1355:
1354:
1336:
1312:
1306:
1305:
1288:(5): 1747–1754.
1279:
1270:
1264:
1263:
1253:
1243:
1241:10.3390/s8021090
1226:(2): 1090–1098.
1211:
1205:
1204:
1194:
1162:
1156:
1155:
1126:
1117:
1116:
1106:
1096:
1072:
1066:
1065:
1047:
1015:
1009:
1008:
998:
974:
968:
967:
949:
925:
919:
918:
892:
883:
874:
873:
863:
831:
825:
824:
814:
790:
784:
783:
773:
763:
739:
733:
732:
722:
690:
684:
683:
666:(7): 3346–3352.
655:
649:
648:
619:
610:
609:
599:
567:
556:
555:
527:
521:
520:
492:
486:
485:
474:
465:
464:
436:
430:
429:
401:
392:
391:
372:10.1038/355564a0
347:
240:
236:
200:prothrombin time
91:
87:
39:oligonucleotides
1391:
1390:
1386:
1385:
1384:
1382:
1381:
1380:
1361:
1360:
1359:
1358:
1314:
1313:
1309:
1277:
1272:
1271:
1267:
1213:
1212:
1208:
1164:
1163:
1159:
1128:
1127:
1120:
1074:
1073:
1069:
1017:
1016:
1012:
976:
975:
971:
927:
926:
922:
890:
885:
884:
877:
833:
832:
828:
792:
791:
787:
741:
740:
736:
692:
691:
687:
657:
656:
652:
621:
620:
613:
569:
568:
559:
529:
528:
524:
494:
493:
489:
476:
475:
468:
438:
437:
433:
403:
402:
395:
349:
348:
341:
336:
307:
298:
261:
238:
234:
212:
195:
177:
165:
103:
89:
85:
59:
51:Gilead Sciences
17:
12:
11:
5:
1389:
1387:
1379:
1378:
1373:
1363:
1362:
1357:
1356:
1307:
1265:
1206:
1177:(23): 233701.
1157:
1118:
1067:
1010:
969:
940:(3): 677–682.
920:
875:
826:
785:
734:
685:
650:
631:(3): 812–817.
611:
557:
538:(2): 272–282.
522:
487:
484:. 8 June 2011.
466:
431:
412:(5): 688–698.
393:
338:
337:
335:
332:
306:
303:
297:
294:
260:
259:HD22 structure
257:
211:
208:
194:
191:
176:
173:
164:
161:
102:
99:
58:
55:
28:Anti-thrombin
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1388:
1377:
1374:
1372:
1371:Nucleic acids
1369:
1368:
1366:
1352:
1348:
1344:
1340:
1335:
1330:
1326:
1322:
1318:
1311:
1308:
1303:
1299:
1295:
1291:
1287:
1283:
1276:
1269:
1266:
1261:
1257:
1252:
1247:
1242:
1237:
1233:
1229:
1225:
1221:
1217:
1210:
1207:
1202:
1198:
1193:
1188:
1184:
1180:
1176:
1172:
1168:
1161:
1158:
1153:
1149:
1145:
1141:
1137:
1133:
1125:
1123:
1119:
1114:
1110:
1105:
1100:
1095:
1090:
1086:
1082:
1078:
1071:
1068:
1063:
1059:
1055:
1051:
1046:
1041:
1037:
1033:
1029:
1025:
1021:
1014:
1011:
1006:
1002:
997:
992:
988:
984:
980:
973:
970:
965:
961:
957:
953:
948:
943:
939:
935:
931:
924:
921:
916:
912:
908:
904:
901:(4): 043702.
900:
896:
889:
882:
880:
876:
871:
867:
862:
857:
853:
849:
845:
841:
837:
830:
827:
822:
818:
813:
808:
804:
800:
796:
789:
786:
781:
777:
772:
767:
762:
757:
753:
749:
745:
738:
735:
730:
726:
721:
716:
712:
708:
704:
700:
696:
689:
686:
681:
677:
673:
669:
665:
661:
654:
651:
646:
642:
638:
634:
630:
626:
618:
616:
612:
607:
603:
598:
593:
589:
585:
581:
577:
573:
566:
564:
562:
558:
553:
549:
545:
541:
537:
533:
526:
523:
518:
514:
510:
506:
502:
498:
491:
488:
483:
479:
473:
471:
467:
462:
458:
454:
450:
446:
442:
435:
432:
427:
423:
419:
415:
411:
407:
400:
398:
394:
389:
385:
381:
377:
373:
369:
365:
361:
357:
353:
346:
344:
340:
333:
331:
329:
325:
321:
317:
312:
304:
302:
295:
293:
290:
286:
282:
278:
274:
270:
266:
258:
256:
253:
249:
245:
241:
225:
216:
209:
207:
205:
201:
192:
190:
181:
174:
172:
170:
162:
160:
158:
153:
149:
145:
140:
138:
134:
130:
126:
121:
117:
107:
101:TBA structure
100:
98:
96:
92:
81:
77:
73:
63:
56:
54:
52:
48:
44:
40:
36:
32:
31:
21:
1324:
1320:
1310:
1285:
1281:
1268:
1223:
1219:
1209:
1174:
1170:
1160:
1135:
1131:
1087:(18): 9948.
1084:
1080:
1070:
1027:
1023:
1013:
986:
982:
972:
937:
933:
923:
898:
894:
843:
839:
829:
802:
798:
788:
751:
747:
737:
702:
698:
688:
663:
659:
653:
628:
624:
579:
575:
535:
531:
525:
500:
496:
490:
481:
447:(1): 31–40.
444:
440:
434:
409:
405:
355:
351:
308:
299:
288:
284:
280:
276:
272:
268:
262:
232:
230:
196:
187:
168:
166:
141:
113:
83:
80:Rovunaptabin
70:The aptamer
69:
35:G-quadruplex
27:
26:
320:bivalirudin
248:factor VIII
118:, and four
1365:Categories
754:(2): 202.
334:References
324:argatroban
95:fibrinogen
1201:0003-6951
748:Molecules
144:potassium
37:-bearing
1351:24628635
1343:18826387
1302:19193102
1260:27879754
1152:24311581
1113:34576112
1062:45046164
1054:17103113
1045:11135997
1005:17046833
964:29862655
870:21715374
780:26861277
729:17145716
680:21306887
645:17150180
606:22669903
552:15299700
461:11890667
244:factor V
120:guanines
43:thrombin
30:aptamers
1251:3927496
1228:Bibcode
1220:Sensors
1179:Bibcode
1104:8466185
956:8298130
903:Bibcode
861:3177225
821:7622501
771:6273181
720:1751544
597:3439905
517:8102368
426:9368651
388:4349607
380:1741036
360:Bibcode
311:avidity
252:heparin
66:lines).
1349:
1341:
1300:
1258:
1248:
1199:
1150:
1111:
1101:
1060:
1052:
1042:
1003:
962:
954:
868:
858:
819:
778:
768:
727:
717:
678:
643:
604:
594:
550:
515:
459:
424:
386:
378:
352:Nature
219:motifs
204:Nuvelo
152:sodium
76:BC-007
1347:S2CID
1278:(PDF)
1058:S2CID
960:S2CID
934:Blood
891:(PDF)
384:S2CID
239:'
235:'
90:'
86:'
78:, or
1339:PMID
1298:PMID
1256:PMID
1197:ISSN
1148:PMID
1109:PMID
1050:PMID
1001:PMID
952:PMID
866:PMID
817:PMID
776:PMID
725:PMID
676:PMID
641:PMID
602:PMID
548:PMID
513:PMID
457:PMID
422:PMID
376:PMID
289:anti
277:anti
269:anti
265:4I7Y
246:and
163:mTBA
137:4DII
133:4DIH
129:1HAO
125:1HUT
33:are
1329:doi
1290:doi
1246:PMC
1236:doi
1187:doi
1175:107
1140:doi
1099:PMC
1089:doi
1040:PMC
1032:doi
991:doi
987:281
942:doi
911:doi
899:106
856:PMC
848:doi
807:doi
803:270
766:PMC
756:doi
715:PMC
707:doi
668:doi
633:doi
629:352
592:PMC
584:doi
540:doi
505:doi
501:268
449:doi
445:292
414:doi
410:272
368:doi
356:355
285:syn
281:syn
273:syn
72:TBA
1367::
1345:.
1337:.
1323:.
1319:.
1296:.
1286:81
1284:.
1280:.
1254:.
1244:.
1234:.
1222:.
1218:.
1195:.
1185:.
1173:.
1169:.
1146:.
1136:69
1134:.
1121:^
1107:.
1097:.
1085:22
1083:.
1079:.
1056:.
1048:.
1038:.
1028:63
1026:.
1022:.
999:.
985:.
981:.
958:.
950:.
938:83
936:.
932:.
909:.
897:.
893:.
878:^
864:.
854:.
844:39
842:.
838:.
815:.
801:.
797:.
774:.
764:.
752:21
750:.
746:.
723:.
713:.
703:34
701:.
697:.
674:.
664:26
662:.
639:.
627:.
614:^
600:.
590:.
580:40
578:.
574:.
560:^
546:.
536:52
534:.
511:.
499:.
480:.
469:^
455:.
443:.
420:.
408:.
396:^
382:.
374:.
366:.
354:.
342:^
135:;
1353:.
1331::
1325:6
1304:.
1292::
1262:.
1238::
1230::
1224:8
1203:.
1189::
1181::
1154:.
1142::
1115:.
1091::
1064:.
1034::
1007:.
993::
966:.
944::
917:.
913::
905::
872:.
850::
823:.
809::
782:.
758::
731:.
709::
682:.
670::
647:.
635::
608:.
586::
554:.
542::
519:.
507::
463:.
451::
428:.
416::
390:.
370::
362::
279:-
275:-
271:-
233:5
123:(
84:5
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.