33:
57:
448:. MICs for triazole antifungals were higher than usual and cross-resistance to ITZ/VCZ and ITZ/VCZ/POS was observed for some isolates. Most of the time, aggressive therapy (itraconazole or posaconazole as monotherapy or combined with amphotericin B, or with amphotericin B and terbinafine) failed for cats. The majority were euthanased due to disease progression with severe signs.
1026:
342:
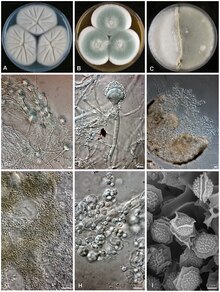
has greenish stipes and nodding heads. Vesicles have a diameter of 15–16.5 μm. Conidia are green, globose to subglobose, finely roughened and 1.5–2.5 μm in dimensions. Cleistothecia are white to creamish and have a diameter of 100–230 μm. Asci are globose, 8-spored, 12–16 μm in diameter. Ascospores
393:
is a thermotolerant fungus with a maximum growth temperature of 45°C and a minimum growth temperature of 20°C whereas species in the AVC have optimal growth between 35° and 42°C. Nevertheless, playing on temperatures is not as precise as molecular identification.
224:
infection is the cat. This may be explained by anatomical differences in the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses resulting in preferential deposition of inhaled fungal spores within the sinonasal cavity in cats compared to the lower respiratory tract in humans.
443:
isolates to amphotericin B, itraconazole, posaconazole, voriconazole, fluconazole, 5-flucytosine, terninafine, caspofungin, anidulafungin and micafungin were assessed in cats. No activity was observed for fluconazole or flucytosine against
402:
The use of PCR to amplify alpha and HMG domains of genes is mentioned in some articles but the best method remains comparative sequence analysis of multiple loci such as ITS-1, ITS-2, the 5.8S rDNA gene and parts of the β-tubulin
229:
is an important emerging agent of invasive aspergillosis in cats, dogs and humans because it is often refractory to aggressive antifungal treatment and its identification implies molecular and morphological techniques.
462:
The primary therapy that has been used for invasive aspergillosis in humans was voriconazole, with isavuconazole and amphotericin B as alternatives for treatment failures. A case of cranial aspergillosis with
426:
The gold standard method is using both molecular and morphological techniques to avoid misidentification with different species within the same complex which would explain why only a few clinical cases of
205:
in humans, dogs and cats. It was described for the first time in 2013 after being isolated from different hosts worldwide (North and South
America, Europe, Africa, Northeast Asia, and Asia-Pacific).
327:
MEA: Colonies reach a diameter of 5.5 cm in 7 days at 25°C. It is cream to light green and it is more or less velvety with abundant greenish sporulation occurring after 5 to 7 days.
467:
was reported in a 66-year-old male with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia and was successfully managed with voriconazole and surgery followed by maintenance with posaconazole.
220:
was then described in a dog with disseminated invasive aspergillosis and a human patient with chronic invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. The most common host described with
366:
all produce lenticular ascospores with two prominent equatorial crests and an echinulate convex surface. The use of different temperatures seems to be a solution as
1067:
988:
962:
801:
330:
CYA: Colonies have a diameter up to 5.0 - 5.5 cm in 7 days at 25°C. It is white and the texture is mostly floccose. Sporulation is often poor.
860:
841:
822:
257:
Cats: chronic invasive fungal rhinosinusitis and retrobulbar masses (chronic invasive pulmonary aspergillosis or sinonasal aspergillosis)
415:
can be reliably identified with ITS sequences only but the most commonly used genes that have been used for species descriptions are
1060:
1091:
802:"Aspergillus felis: new fungus found in Australia, causes infections in humans, cats | Aspergillus & Aspergillosis Website"
1101:
1053:
56:
993:
451:
Few cases of invasive disease in humans have been reported in the literature. Infections are often fatal because of
343:
are lenticular with two prominent equatorial crests and with short echinulate convex surfaces 5.0–7.0×3.5–5.0 μm.
208:
The first host infected was a domestic cat with invasive fungal rhinosinusitis who gave its name to this new
1096:
614:"A new fungal species causing invasive aspergillosis in cats and humans | Australian Veterinary Association"
876:
914:
613:
151:
1086:
954:
936:
567:
761:
Talbot JJ, Barrs VR (January 2018). "One-health pathogens in the
Aspergillus viridinutans complex".
556:"Aspergillus felis sp. nov., an emerging agent of invasive aspergillosis in humans, cats, and dogs"
237:
has a fully functioning reproductive cycle as induction of teleomorphs appears within 7 to 10 days
642:
Paccoud O, Guery R, Poirée S, Jouvion G, Bougnoux ME, Catherinot E, et al. (December 2019).
554:
Barrs VR, van Doorn TM, Houbraken J, Kidd SE, Martin P, Pinheiro MD, et al. (14 June 2013).
51:
507:
1001:
923:
856:
837:
818:
778:
738:
673:
595:
1037:
1006:
815:
Canine and Feline
Respiratory Medicine, An Issue of Veterinary Clinics: Small Animal Practice
770:
728:
720:
663:
655:
585:
575:
691:
Houbraken J, Kocsubé S, Visagie CM, Yilmaz N, Wang XC, Meijer M, et al. (March 2020).
32:
571:
350:. Nodding heads can be seen on cytological examination but this feature occurs in other
1033:
949:
733:
692:
668:
643:
590:
555:
118:
98:
1080:
281:
identification is difficult because of its resemblance with other species within the
202:
192:
423:. Currently, there is no gene accepted as a stand-alone method for identification.
928:
270:
causes infection in immunocompetent cats and dogs and immunocompromised patients.
899:
724:
580:
908:
197:
173:
128:
108:
88:
709:): An overview of families, genera, subgenera, sections, series and species"
68:
782:
742:
677:
659:
599:
489:
260:
Dog: disseminated invasive aspergillosis (IA), fungal rhinosinusitis (FRS)
975:
893:
774:
459:
species. Indeed, the right treatment is delayed leading to fatal issues.
312:
Many methods has to be used together in order to identify it correctly.
370:
is able to grow at 45°C while it has been shown in several studies that
967:
980:
78:
1025:
870:
941:
644:"Aspergillus felis in Patient with Chronic Granulomatous Disease"
346:
Morphological criteria alone are not enough to reliably identify
323:
can be isolated on malt extract agar (MEA) or Czapek agar (CYA).
874:
621:
307:
A. wyonmingesis A. aureoles, A. siamensis and A. arcoverdensis
180:
131F4, DTO 155G2, IFM 600, JV-2013, CBS 130245, CBS H-21125
253:
can give serious different diseases depending on hosts:
1041:
40:
Colonies growing 7 days at 25°C on CYA (A) and MEA (B);
263:
Human: chronic invasive pulmonary aspergillosis (IPA)
883:
834:
Clinical
Medicine of the Dog and Cat, Third Edition
385:is not. It can be a relevant method to distinguish
853:Ear, Nose and Throat Diseases of the Dog and Cat
42:Crossing of CBS 130245 and 130246 at 30°C (C);
1061:
756:
754:
752:
549:
547:
545:
8:
543:
541:
539:
537:
535:
533:
531:
529:
527:
525:
1068:
1054:
871:
283:Aspergillus viridinutans complex (A. felis
216:is a genus of cats in the family Felidae.
167:Barrs, van Doorn, Varga & Samson, 2013
31:
20:
732:
667:
589:
579:
484:
482:
480:
241:and there is also ascospore germination.
476:
44:Conidiophores and conidia (D, E and G);
431:in humans have been described so far.
46:Cleistothecium (F); Ascospores (H-I).
7:
1022:
1020:
455:being identified as another cryptic
233:According to mating-type analysis,
1040:. You can help Knowledge (XXG) by
14:
1024:
381:is able to grow at 50°C whereas
377:showed no growth at 45°C.
55:
195:species of fungus in the genus
851:Harvey RG, ter Haar G (2016).
1:
832:Schaer M, Gaschen FP (2016).
287:A. viridinutans sensu stricto
817:. Elsevier Health Sciences.
725:10.1016/j.simyco.2020.05.002
648:Emerging Infectious Diseases
581:10.1371/journal.pone.0064871
439:Susceptibilities of several
1118:
1019:
249:Among all cases reported,
389:from other species since
179:
172:
157:
150:
52:Scientific classification
50:
39:
30:
23:
398:Molecular identification
1092:Fungi described in 2013
1036:-related article is a
806:www.aspergillus.org.uk
660:10.3201/eid2512.191020
354:species. Furthermore,
303:A. pseudoviridinutans
1102:Eurotiomycetes stubs
705:and related genera (
813:Johnson LR (2014).
713:Studies in Mycology
693:"Classification of
572:2013PLoSO...864871B
490:"Aspergillus felis"
372:A. viridinutans and
775:10.1093/mmy/myx016
407:) and calmodulin (
279:Aspergillus felis’
1049:
1048:
1017:
1016:
1002:Open Tree of Life
915:Aspergillus felis
885:Aspergillus felis
877:Taxon identifiers
862:978-1-315-35575-7
843:978-1-482-22606-5
824:978-0-323-26421-1
654:(12): 2319–2321.
510:Aspergillus felis
340:Aspergillus felis
235:Aspergillus felis
218:Apsergillus felis
188:Aspergillus felis
184:
183:
161:Aspergillus felis
25:Aspergillus felis
16:Species of fungus
1109:
1070:
1063:
1056:
1028:
1021:
1010:
1009:
997:
996:
984:
983:
971:
970:
958:
957:
945:
944:
932:
931:
919:
918:
917:
904:
903:
902:
872:
866:
847:
828:
809:
787:
786:
763:Medical Mycology
758:
747:
746:
736:
688:
682:
681:
671:
639:
633:
632:
630:
629:
620:. Archived from
610:
604:
603:
593:
583:
551:
520:
519:
504:
498:
497:
486:
201:which can cause
163:
60:
59:
35:
21:
1117:
1116:
1112:
1111:
1110:
1108:
1107:
1106:
1077:
1076:
1075:
1074:
1018:
1013:
1005:
1000:
992:
987:
979:
974:
966:
961:
953:
948:
940:
935:
927:
922:
913:
912:
907:
898:
897:
892:
879:
869:
863:
850:
844:
831:
825:
812:
800:
796:
794:Further reading
791:
790:
760:
759:
750:
690:
689:
685:
641:
640:
636:
627:
625:
612:
611:
607:
553:
552:
523:
506:
505:
501:
488:
487:
478:
473:
437:
400:
337:
318:
276:
247:
168:
165:
159:
146:
54:
45:
43:
41:
17:
12:
11:
5:
1115:
1113:
1105:
1104:
1099:
1097:Fungus species
1094:
1089:
1079:
1078:
1073:
1072:
1065:
1058:
1050:
1047:
1046:
1034:Eurotiomycetes
1029:
1015:
1014:
1012:
1011:
998:
985:
972:
959:
946:
933:
920:
905:
889:
887:
881:
880:
875:
868:
867:
861:
848:
842:
829:
823:
810:
797:
795:
792:
789:
788:
748:
683:
634:
618:www.ava.com.au
605:
521:
499:
475:
474:
472:
469:
436:
433:
399:
396:
336:
333:
332:
331:
328:
317:
314:
295:A. pseudofelis
275:
274:Identification
272:
265:
264:
261:
258:
246:
243:
182:
181:
177:
176:
170:
169:
166:
155:
154:
148:
147:
140:
138:
134:
133:
126:
122:
121:
119:Aspergillaceae
116:
112:
111:
106:
102:
101:
99:Eurotiomycetes
96:
92:
91:
86:
82:
81:
76:
72:
71:
66:
62:
61:
48:
47:
37:
36:
28:
27:
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1114:
1103:
1100:
1098:
1095:
1093:
1090:
1088:
1085:
1084:
1082:
1071:
1066:
1064:
1059:
1057:
1052:
1051:
1045:
1043:
1039:
1035:
1030:
1027:
1023:
1008:
1003:
999:
995:
990:
986:
982:
977:
973:
969:
964:
960:
956:
951:
947:
943:
938:
934:
930:
925:
921:
916:
910:
906:
901:
895:
891:
890:
888:
886:
882:
878:
873:
864:
858:
855:. CRC Press.
854:
849:
845:
839:
836:. CRC Press.
835:
830:
826:
820:
816:
811:
807:
803:
799:
798:
793:
784:
780:
776:
772:
768:
764:
757:
755:
753:
749:
744:
740:
735:
730:
726:
722:
718:
714:
710:
708:
704:
700:
696:
687:
684:
679:
675:
670:
665:
661:
657:
653:
649:
645:
638:
635:
624:on 2017-02-02
623:
619:
615:
609:
606:
601:
597:
592:
587:
582:
577:
573:
569:
566:(6): e64871.
565:
561:
557:
550:
548:
546:
544:
542:
540:
538:
536:
534:
532:
530:
528:
526:
522:
517:
513:
511:
503:
500:
495:
491:
485:
483:
481:
477:
470:
468:
466:
460:
458:
454:
449:
447:
442:
434:
432:
430:
424:
422:
418:
414:
410:
406:
397:
395:
392:
388:
384:
380:
376:
373:
369:
365:
361:
357:
353:
349:
344:
341:
334:
329:
326:
325:
324:
322:
315:
313:
311:
308:
304:
300:
296:
292:
288:
284:
280:
273:
271:
269:
262:
259:
256:
255:
254:
252:
245:Pathogenicity
244:
242:
240:
236:
231:
228:
223:
219:
215:
211:
206:
204:
203:aspergillosis
200:
199:
194:
193:heterothallic
190:
189:
178:
175:
171:
164:
162:
156:
153:
152:Binomial name
149:
145:
144:
143:A. felis
139:
136:
135:
132:
131:
127:
124:
123:
120:
117:
114:
113:
110:
107:
104:
103:
100:
97:
94:
93:
90:
87:
84:
83:
80:
77:
74:
73:
70:
67:
64:
63:
58:
53:
49:
38:
34:
29:
26:
22:
19:
1042:expanding it
1031:
884:
852:
833:
814:
805:
766:
762:
716:
712:
706:
702:
698:
694:
686:
651:
647:
637:
626:. Retrieved
622:the original
617:
608:
563:
559:
515:
509:
502:
493:
464:
461:
456:
452:
450:
445:
440:
438:
428:
425:
420:
416:
412:
408:
404:
401:
390:
386:
382:
379:A. fumigatus
378:
374:
371:
367:
363:
359:
355:
351:
347:
345:
339:
338:
320:
319:
309:
306:
302:
299:A. parafelis
298:
294:
290:
286:
282:
278:
277:
267:
266:
250:
248:
238:
234:
232:
226:
221:
217:
213:
209:
207:
196:
187:
186:
185:
160:
158:
142:
141:
129:
24:
18:
1087:Aspergillus
909:Wikispecies
769:(1): 1–12.
703:Talaromyces
699:Penicillium
695:Aspergillus
457:Aspergillus
375:A. udagawae
364:A. udagawae
291:A. udagawae
210:Aspergillus
198:Aspergillus
174:Type strain
130:Aspergillus
1081:Categories
707:Eurotiales
628:2017-01-29
471:References
360:N. aureola
335:Morphology
109:Eurotiales
89:Ascomycota
85:Division:
900:Q14130295
719:: 5–169.
435:Treatment
137:Species:
75:Kingdom:
69:Eukaryota
976:MycoBank
950:Fungorum
942:39973953
894:Wikidata
783:28379569
743:32855739
678:31742513
600:23798996
560:PLOS ONE
516:MycoBank
465:A. felis
453:A. felis
446:A. felis
441:A. felis
429:A. felis
413:A. felis
411:) gene.
391:A. felis
387:A. felis
383:A. felis
368:A. felis
356:A. felis
352:Fumigati
348:A. felis
251:A. felis
239:in vitro
222:A. felis
115:Family:
65:Domain:
1007:4061493
994:1287682
968:9082758
734:7426331
669:6874246
591:3683053
568:Bibcode
494:UniProt
321:A.felis
316:Culture
268:A.felis
227:A.felis
125:Genus:
105:Order:
95:Class:
981:560382
955:560382
859:
840:
821:
781:
741:
731:
676:
666:
598:
588:
1032:This
214:Felis
191:is a
79:Fungi
1038:stub
989:NCBI
963:GBIF
929:HC2H
857:ISBN
838:ISBN
819:ISBN
779:PMID
739:PMID
674:PMID
596:PMID
419:and
417:benA
409:calM
405:benA
362:and
937:EoL
924:CoL
771:doi
729:PMC
721:doi
664:PMC
656:doi
586:PMC
576:doi
421:caM
212:as
1083::
1004::
991::
978::
965::
952::
939::
926::
911::
896::
804:.
777:.
767:56
765:.
751:^
737:.
727:.
717:95
715:.
711:.
701:,
697:,
672:.
662:.
652:25
650:.
646:.
616:.
594:.
584:.
574:.
562:.
558:.
524:^
514:.
492:.
479:^
358:,
310:).
305:,
301:,
297:,
293:,
289:,
285:,
1069:e
1062:t
1055:v
1044:.
865:.
846:.
827:.
808:.
785:.
773::
745:.
723::
680:.
658::
631:.
602:.
578::
570::
564:8
518:.
512:"
508:"
496:.
403:(
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.