311:
specimen of just over 4 m (13 ft) weighed 36 kg (79 lb), a specimen of 4.5 m (15 ft) weighed 40 kg (88 lb), and a specimen of 5 m (16 ft) weighed 75 kg (165 lb). In comparison, length-weight comparisons for males found: a specimen of 2.8 m (9 ft 2 in) weighed 12 kg (26 lb), 2.97 m (9 ft 9 in) weighed 14.5 kg (32 lb), a specimen of 3 m (9.8 ft) weighed 7 kg (15 lb), and a specimen of 3.05 m (10.0 ft) weighed 18.5 kg (41 lb). In general, individuals over 5 m (16 ft) are rare. The record for maximum length of a
Burmese python is 5.79 m (19 ft 0 in) and was caught 10 July 2023 in South Florida's Big Cypress National Preserve. Widely published data of specimens reported to have been several feet longer are not verified. At her death, a Burmese named "Baby" was the heaviest snake recorded in the world at the time at 182.8 kg (403 lb), much heavier than any wild snake ever measured. Her length was measured at 5.74 m (18 ft 10 in) circa 1999. The minimum size for adults is 2.35 m (7 ft 9 in). Dwarf forms occur in
688:
as 18 months. As digestive tissues are energetically costly to maintain, they are downregulated during fasting periods to conserve energy when they are not in use. A fasting python has a reduced stomach volume and acidity, reduced intestinal mass, and a 'normal' heart volume. After ingesting prey, the entire digestive system undergoes a massive re-modelling, with rapid hypertrophy of the intestines, production of stomach acid, and a 40% increase in mass of the ventricle of the heart to fuel the digestive process. During digestion, the snake's oxygen consumption rises drastically as well, increasing with meal size by 17 to 40 times its resting rate. This dramatic increase is a result of the energetic cost of restarting many aspects of the digestive system, from rebuilding the stomach and small intestine to producing
763:
646:
561:. This was a month-long contest wherein a total of 68 pythons were removed. The contest offered incentives such as prizes for longest and greatest number of captured pythons. The purpose of the challenge was to raise awareness about the invasive species, increase participation from the public and agency cooperation, and to remove as many pythons as possible from the Florida Everglades. The challenge has run a few times again since then and is now an annual event over the duration of ten days. Recently, in 2023, it resulted in 209 pythons removed by 1,050 participants.
42:
463:
554:
cypress, overstory, and coniferous forest. Though aquatic marsh environments would be a great source for prey, the pythons seem to prioritize environments allowing for morphological and behavioral camouflage to be protected from predators. Also, the
Burmese pythons in Florida have been found to prefer elevated habitats, since this provides the optimal conditions for nesting. In addition to elevated habitats, edge habitats are common places where Burmese pythons are found for thermoregulation, nesting, and hunting purposes.
587:. It was more than 5.2 m (17 ft) long, weighed 64 kg (140 lb), and contained 73 developing eggs. In December 2021, a Burmese python was captured in Florida that weighed 98 kg (215 lb) and had a length of 5.5 m (18 ft); it contained a record 122 developing eggs. In July 2023, local hunters captured and killed a 5.8 m (19 ft) long Burmese python that weighed 57 kg (125 lb) in Florida's Big Cypress National Preserve.
471:
86:
218:
828:
61:
706:
657:. Its diet consists primarily of birds and mammals, but also includes amphibians and reptiles. It is a sit-and-wait predator, meaning it spends most of its time staying relatively still, waiting for prey to approach, then striking rapidly. The snake grabs a prey animal with its sharp teeth, then wraps its body around the animal to kill it through
796:
released into the wild, and become invasive species that devastate the environment. For this reason, some jurisdictions (including
Florida, due to the python invasion in the Everglades) have placed restrictions on the keeping of Burmese pythons as pets. Violators could be imprisoned for more than seven years or fined $ 500,000 if convicted.
692:
to be secreted in the stomach. Hydrochloric acid production is a significant component of the energetic cost of digestion, as digesting whole prey items requires the animal to be broken down without the use of teeth, either for chewing or tearing into smaller pieces. To compensate, once food has been
670:
as it grows. As an invasive species in
Florida, Burmese pythons primarily eat a variety of small mammals including foxes, rabbits, and raccoons. Due to their high predation levels, they have been implicated in the decline and even disappearance of many mammal species. In their invasive range, pythons
791:
Burmese pythons are often sold as pets, and are made popular by their attractive coloration and apparently easy-going nature. However, they have a rapid growth rate, and can exceed 2.1 m (6 ft 11 in) in length in a year if power fed. However this may cause health issues in the future.
839:
form is especially popular and is the most widely available morph. This morph is white with patterns in butterscotch yellow and burnt orange. Also, "labyrinth" specimens with maze-like patterns, khaki-colored "green", and "granite" with many small angular spots are available. Breeders have recently
687:
The digestive response of
Burmese pythons to such large prey has made them a model species for digestive physiology. Its sit-and-wait hunting style is characterized by long fasting periods in between meals, with Burmese pythons typically feeding every month or two, but sometimes fasting for as long
568:
Invasive
Burmese pythons also face certain physiological changes. Unlike their native South Asian counterparts who spend long periods fasting due to seasonal variation in prey availability, pythons in Florida feed year-round due to the constant availability of food. They are also vulnerable to cold
553:
Numerous efforts have been made to eliminate the
Burmese python population in the last decade. Understanding the preferred habitat of the species is needed to narrow down the python hunt. Burmese pythons have been found to select broad-leafed and low-flooded habitats. Broad-leafed habitats comprise
498:
in 1992 was deemed responsible for the destruction of a python-breeding facility and zoo, and these escaped snakes spread and populated areas into the
Everglades. More than 1,330 have been captured in the Everglades. A genetic study in 2017 revealed that the python population is composed of hybrids
818:
Although pythons are typically afraid of people due to their great stature, and generally avoid them, special care is still required when handling them. Given their adult strength, multiple handlers (up to one person per meter of snake) are usually recommended. Some jurisdictions require owners to
748:
To maintain
Burmese python populations, the IUCN recommends increased conservation legislation and enforcement at the national and international levels to reduce harvesting across the snake's native range. The IUCN also recommends increased research into its population ecology and threats. In Hong
611:
They tend to be solitary and are usually found in pairs only when mating. Burmese pythons breed in the early spring, with females laying clutches of 12–36 eggs in March or April. They remain with the eggs until they hatch, wrapping around them and twitching their muscles in such a way as to
607:
for some months during the cold season in a hollow tree, a hole in the riverbank, or under rocks. Brumation is biologically distinct from hibernation. While the behavior has similar benefits, allowing organisms to endure the winter without moving, it also involves the preparation of both male and
564:
A study from 2017 introduced a new method for identifying the presence of
Burmese pythons in southern Florida; this method involves the screening of mosquito blood. Since the introduction of the Burmese python in Florida, mosquito communities use the pythons as hosts even though they are recently
545:
By 2011, researchers identified up to 25 species of birds from nine avian orders in the digestive tract remains of 85 Burmese pythons found in Everglades National Park. Native bird populations are suffering a negative impact from the introduction of the Burmese python in Florida; among these bird
310:
in size; females average only slightly longer, but are considerably heavier and bulkier than the males. For example, length-weight comparisons in captive Burmese pythons for individual females have shown: at 3.47 m (11 ft 5 in) length, a specimen weighed 29 kg (64 lb), a
602:
dwellers. When young, they are equally at home on the ground and in trees, but as they gain girth, they tend to restrict most of their movements to the ground. They are also excellent swimmers, being able to stay submerged for up to half an hour. Burmese pythons spend the majority of their time
795:
Although the species has a reputation for docility, they are very powerful animals – capable of inflicting severe bites and even killing by constriction. They also consume large amounts of food, and due to their size, require large, often custom-built, secure enclosures. As a result, some are
771:
526:
by 94.1%." Road surveys between 2003 and 2011 indicated an 87.3% decrease in bobcat populations, and in some areas rabbits have not been detected at all. Experimental efforts to reintroduce rabbit populations to areas where rabbits have been eliminated have mostly failed "due to high (77% of
696:
The energy cost is highest in the first few days after eating when these regenerative processes are most active, meaning Burmese pythons rely on existing food energy storage to digest a new meal. Overall, the entire digestive process from food intake to defecation lasts 8–14 days.
2158:
Card DC, Perry BW, Adams RH, Schield DR, Young AS, Andrew AL, Jezkova T, Pasquesi GI, Hales NR, Walsh MR, Rochford MR, Mazzotti FJ, Hart KM, Hunter ME, Castoe TA (2018). "Novel ecological and climatic conditions drive rapid adaptation in invasive Florida Burmese pythons".
535:. In addition to this correlational relationship, the pythons have also been experimentally shown to decrease marsh rabbit populations, further suggesting they are responsible for many of the recorded mammal declines. They may also outcompete native predators for food.
305:
The Burmese python is a dark-colored non-venomous snake with many brown blotches bordered by black down the back. In the wild, Burmese pythons typically grow to 5 m (16 ft), while specimens of more than 7 m (23 ft) are unconfirmed. This species is
665:
as a food source. However, its equal affinity for domesticated birds and mammals means it is often treated as a pest. In captivity, its diet consists primarily of commercially available appropriately sized rats, graduating to larger prey such as rabbits and
323:, with an average length of 2 m (6 ft 7 in) in Bali, and a maximum of 2.5 m (8 ft 2 in) on Sulawesi. Wild individuals average 3.7 m (12 ft) long, but have been known to reach 5.79 m (19 ft 0 in).
616:
to cut their way out of their eggs, no further maternal care is given. The newly hatched babies often remain inside their eggs until they are ready to complete their first shedding of skin, after which they hunt for their first meal.
753:
under Wild Animals Protection Ordinance Cap 170. It is also protected in Thailand, Vietnam, China, and Indonesia. However, it is still common only in Hong Kong and Thailand, with rare to very rare statuses in the rest of its range.
693:
ingested, Burmese pythons begin producing large amounts of acid to make the stomach acidic enough to turn the food into a semi-liquid that can be passed through to the small intestine and undergo the rest of the digestive process.
774:
779:
777:
773:
772:
778:
486:. Between 1996 and 2006, the Burmese python gained popularity in the pet trade, with more than 90,000 snakes imported into the U.S. The current number of Burmese pythons in the Florida Everglades may have reached a
569:
stress, with winter freezes resulting in mortality rates of up to 90%. Genomic data suggests natural selection on these populations favors increased thermal tolerance as a result of these high-mortality freezes.
1228:
Groot TV, Bruins E, Breeuwer JA. Molecular genetic evidence for parthenogenesis in the Burmese python, Python molurus bivittatus. Heredity (Edinb). 2003 Feb;90(2):130-5. doi: 10.1038/sj.hdy.6800210. PMID
844:
have slightly different coloring and pattern from their mainland relatives and do not grow much over 2.1 m (6 ft 11 in) in length. One of the most sought-after of these variations is the
776:
2607:
799:
Burmese pythons are opportunistic feeders; they eat almost any time food is offered, and often act hungry even when they have recently eaten. As a result, they are often overfed, causing
1750:
2427:
2229:
3720:
2309:
671:
also eat birds and occasionally other reptiles. Exceptionally large pythons may even require larger food items such as pigs or goats, and are known to have attacked and eaten
2790:
1554:
849:
Burmese. This particular variety is very rare, being entirely bright white with no pattern and blue eyes, and has only in 2008/2009 been reproduced in captivity as the
1780:
3650:
1520:
1476:
3702:
1405:
2000:
Mazzotti FJ, Rochford M, Vinci J, Jeffery BM, Eckles JK, Dove C, Sommers KP (2016). "Implications of the 2013 Python Challenge® for Ecology and Management of
3055:
2590:
1591:
1642:
2203:
819:
hold special licenses, and as with any wild animal being kept in captivity, treating them with the respect an animal of this size commands is important.
1432:
775:
3766:
810:, Burmese pythons are known to be easygoing or timid creatures, which means that if cared for properly, they can easily adjust to living near humans.
3624:
580:
parasitic disease, with them from Southeast Asia. Other reptiles in Florida have become infested, and the parasite appears to have become endemic.
3676:
792:
By age four, they will have reached their adult size, though they continue growing very slowly throughout their lives, which may exceed 20 years.
750:
2435:
2992:
2973:
3082:
2765:"Dr. D. H. Evans, Coroner of Ontario, "Inquest into the Death of Mark Nevilles: Verdict of Coroner's Jury" (Brampton, Ontario: June 1992)"
3781:
2732:
762:
542:, and numerous instances of alligators and pythons attacking—and in some cases, preying on—each other have been reported and recorded.
1798:
Dorcas ME, Willson JD, Reed RN, Snow RW, Rochford MR, Miller MA, Meshaka WE, Andreadis PT, Mazzotti FJ, Romagosa CM, Hart KM (2012).
2699:
1385:
1360:
1335:
3637:
3002:
Willson JD, Dorcas ME, Snow RW (2010-11-21). "Identifying plausible scenarios for the establishment of invasive Burmese pythons (
1049:"The corrected lengths of two well-known giant pythons and the establishment of a new maximum length record for Burmese Pythons,
741:
since 2012, as the wild population is estimated to have declined by at least 30% in the first decade of the 21st century due to
661:. The python then swallows its prey whole. It is often found near human habitation due to the presence of rats, mice, and other
645:
511:
2798:
1643:"Democrats Hold Hearing on Administration's Plan to Constrict Snakes in the Everglades - House Committee on Natural Resources"
444:, marshes, swamps, rocky foothills, woodlands, river valleys, and jungles with open clearings. It is a good climber and has a
3681:
1562:
1260:
514:. A 2012 report stated, "in areas where the snakes are well established, foxes, and rabbits have disappeared. Sightings of
584:
1607:
Walters TM, Mazzotti FJ, Fitz HC (2016). "Habitat selection by the invasive species Burmese python in Southern Florida".
1532:
3449:
3428:
2629:
1495:
1011:
The Fauna of British India, Ceylon and Burma, Including the Whole of the Indo-Chinese Sub-region. Reptilia and Amphibia
930:
3663:
3463:
1286:
2095:
Reeves LE, Krysko KL, Avery ML, Gillett-Kaufman JL, Kawahara AY, Connelly CR, Kaufman PE (2018-01-17). Paul R (ed.).
2873:
1162:
Marcellini, D.L. & Peters, A. (1982). "Preliminary observations on endogeneous heat production after feeding in
3707:
2550:"Gastric function and its contribution to the postprandial metabolic response of the Burmese python Python molurus"
457:
290:
1751:"Salazar Announces Ban on Importation and Interstate Transportation of Four Giant Snakes that Threaten Everglades"
1201:
Jacobson, E.R.; Homer, B. & Adams, W. (1991). "Endocarditis and congestive heart failure in a Burmese python (
894:
Stuart, B.; Nguyen, T.Q.; Thy, N.; Grismer, L.; Chan-Ard, T.; Iskandar, D.; Golynsky, E. & Lau, M.W. (2019) .
3786:
2764:
1048:
608:
female reproductive organs for the upcoming breeding season. The Florida population also goes through brumation.
487:
41:
3075:
1646:
558:
462:
85:
1693:
Hunter, M.E.; Johnson, N.A.; Smith, B.J.; Davis, M.C.; Butterfield, John S.S.; Snow, R.W.; Hart, K.M. (2017).
333:
3047:
1583:
1451:
3791:
3776:
3771:
3590:
3506:
1800:"Severe mammal declines coincide with proliferation of invasive Burmese pythons in Everglades National Park"
1303:
500:
1123:
Barker, D.G.; Murphy J.B. & Smith, K.W. (1979). "Social behavior in a captive group of Indian pythons,
3538:
3234:
3198:
3188:
866:
262:
3576:
190:
3227:
3220:
3111:
2837:
2168:
2112:
1870:
1811:
1299:
1001:
841:
626:
1380:. Frankfurt Contributions to Natural History (Band 25 ed.). Chimaira. pp. 23–27, 198–201.
3499:
3169:
3068:
2072:"ICYMI: Lieutenant Governor Jeanette Nuñez Announces Winners of the 2023 Florida Python Challenge®"
1953:
Dove CJ, Snow RW, Rochford MR, Mazzotti FJ (2011). "Birds Consumed by the Invasive Burmese Python (
50:
3485:
3421:
3292:
3023:
2855:
2530:
2029:
2021:
1982:
1974:
1624:
1183:
1144:
1105:
734:
714:
539:
307:
274:
230:
80:
65:
612:
raise the ambient temperature around the eggs by several degrees. Once the hatchlings use their
3655:
835:
The Burmese python is frequently captive-bred for color, pattern, and more recently, size. Its
3598:
3356:
3342:
2988:
2969:
2740:
2707:
2648:
2599:
2571:
2522:
2481:
2384:
2184:
2140:
1932:
1903:"Marsh rabbit mortalities tie pythons to the precipitous decline of mammals in the Everglades"
1839:
1732:
1381:
1356:
1331:
975:
730:
689:
523:
507:
470:
3743:
1378:
The Snakes of Sulawesi: A Field Guide to the Land Snakes of Sulawesi with Identification Keys
3715:
3694:
3435:
3400:
3368:
3335:
3042:
3015:
2845:
2561:
2512:
2473:
2374:
2176:
2130:
2120:
2013:
1966:
1922:
1914:
1878:
1829:
1819:
1722:
1714:
1616:
1325:
1175:
1136:
1097:
857:
trait. The caramel Burmese python has a caramel-colored pattern with "milk-chocolate" eyes.
629:
when in captivity. Offspring are clones of their mother and reproduction appears to be by a
510:. The importation of Burmese pythons was banned in the United States in January 2012 by the
495:
491:
840:
begun working with an island lineage of Burmese pythons. Early reports indicate that these
3520:
3492:
3378:
3349:
3311:
3263:
1668:
630:
532:
506:
By 2007, the Burmese python was found in northern Florida and in the coastal areas of the
2204:"A 17-foot, 140-pound python was captured in a Florida park. Officials say it's a record"
2841:
2501:"Digestive physiology of the Burmese python: broad regulation of integrated performance"
2172:
2116:
1874:
1815:
557:
One of the Burmese python eradication movements with the biggest influence was the 2013
3390:
3328:
3321:
3118:
2965:
The Lizard King: The True Crimes and Passions of the World's Greatest Reptile Smugglers
2135:
2096:
1927:
1902:
1834:
1799:
1727:
1694:
1009:
895:
854:
827:
270:
217:
167:
2403:
2230:"Caught! Record-breaking 18-foot Burmese python pulled from Collier County wilderness"
3760:
3689:
3513:
3442:
3414:
3027:
2859:
1410:
1261:"A record-breaking Burmese python — as long as a giraffe is tall — caught in Florida"
904:
738:
603:
hidden in the underbrush. In the northern parts of its range, the Burmese python may
479:
282:
278:
241:
207:
70:
2071:
2033:
1986:
1628:
948:
Jacobs, H.J.; Auliya, M.; Böhme, W. (2009). "On the taxonomy of the Burmese Python,
349:
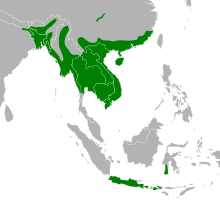
The Burmese python occurs throughout Southern and Southeast Asia, including eastern
3642:
3603:
3299:
3282:
3270:
3256:
3125:
2534:
742:
658:
583:
In April 2019, researchers captured and killed a large Burmese python in Florida's
2462:"Structural flexibility of the intestine of Burmese python in response to feeding"
2283:
1084:
Van Mierop, L.H. & Barnard, S.M. (1976). "Observations on the reproduction of
705:
2963:
2656:
2254:
2125:
3733:
3570:
3456:
3176:
2332:
1859:"Indirect effects of invasive Burmese pythons on ecosystems in southern Florida"
1014:. Vol. III.—Serpentes. London: Secretary of State for India. Taylor and Francis.
836:
807:
784:
3561:
2932:
2850:
2821:
2461:
3210:
3092:
3019:
850:
599:
577:
547:
483:
445:
440:
It is an excellent swimmer and needs a permanent source of water. It lives in
362:
338:
157:
17:
2826:) are novel nest predators in wading bird colonies of the Florida Everglades"
2744:
2711:
2652:
2603:
3611:
3159:
3101:
1883:
1858:
1824:
1695:"Cytonuclear discordance in the Florida Everglades invasive Burmese python (
1327:
Tales of Giant Snakes: A Historical Natural History of Anacondas and Pythons
846:
710:
672:
654:
613:
596:
441:
418:
414:
398:
294:
97:
3668:
2933:"Captive Animals - Most states have no laws governing captive wild animals"
2575:
2526:
2485:
2379:
2362:
2188:
2144:
1936:
1918:
1843:
1736:
1307:
2477:
2388:
2017:
3555:
2885:
2706:. Toronto: Canadian Broadcasting Commission. Canadian Press. 2013-04-13.
1901:
McCleery RA, Sovie A, Reed RN, Cunningham MW, Hunter ME, Hart KM (2015).
722:
426:
386:
378:
370:
320:
137:
117:
2025:
1978:
936:
499:
between the Burmese python and Indian python. The species also displays
3629:
3475:
3147:
3137:
2907:
2674:
2517:
2500:
1781:"Pythons are squeezing the life out of the Everglades, scientists warn"
1187:
1148:
1109:
800:
667:
634:
604:
519:
515:
430:
406:
394:
382:
366:
286:
127:
3043:
Burmese python (Python molurus) - EDDMapS State Distribution - EDDMapS
2566:
2549:
2363:"Adaptive responses to feeding in Burmese pythons: pay before pumping"
2180:
1718:
1406:"Bloodsucking worms in pythons are killing Florida snakes, study says"
3585:
3246:
1970:
662:
528:
434:
410:
402:
390:
358:
107:
3532:
3060:
1699:) population reveals possible hybridization with the Indian python (
1179:
1140:
1101:
853:
form (referred to as "super" by reptile keepers) of the co-dominant
503:
which has made phylogenetic studies of its origin more complicated.
448:
tail. It can stay in water for 30 minutes but mostly stays on land.
3616:
2316:. In Shaul, Travis R.; Shaul, Kylienne A.; Weaver, Ella M. (eds.).
1620:
1047:
Barker, D.G.; Barten, S.L.; Ehrsam, J.P. & Daddono, L. (2012).
3728:
1127:(Serpentes, Boidae) with formation of a linear social hierarchy".
826:
769:
761:
704:
644:
482:, where a large number of pythons can now be found in the Florida
469:
461:
354:
350:
266:
147:
2047:
676:
478:
Python invasion has been particularly extensive, notably across
422:
374:
316:
312:
3536:
3064:
2733:"Python-linked Deaths Raise Questions over Exotic Animal Laws"
2675:"The Keeping of Large Pythons: Realities and Responsibilities"
2630:"A Fatal Attack on a Teenage Boy by a Captive Burmese Python (
2428:"Photo in the News: Python Bursts After Eating Gator (Update)"
3056:
U.S. Department of Agriculture National Agricultural Library
550:
is of specific concern, now listed as federally endangered.
803:-related problems to be common in captive Burmese pythons.
649:
Burmese python photographed in Bardiya National Park, Nepal
531:
populations may be threatened, as well as the already-rare
538:
For example, Burmese pythons also compete with the native
331:
In both their native and invasive range they suffer from
2908:"Playing with the Big Boys: Handling Large Constrictors"
2820:
Orzechowski SC, Romagosa CM, Frederick PC (2019-07-01).
1669:"(US National Park Service website - December 31, 2009)"
2101:
Kuhl, and the local mosquito community in Florida, USA"
1907:
Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences
1355:. Krieger Publishing Company. pp. 13, 14, 18, 86.
952:
KUHL, 1820, specifically on the Sulawesi population".
527:
mortalities) rates of predation by pythons." Bird and
1239:
Saint Girons, H. (1972). "Les serpents du Cambodge".
2591:"Python Kills Careless Student Zookeeper in Caracas"
1353:
A Field Guide to the Amphibians and Reptiles of Bali
281:. Until 2009, it was considered a subspecies of the
3545:
3473:
3388:
3366:
3309:
3280:
3244:
3208:
3186:
3157:
3135:
3099:
2097:"Interactions between the invasive Burmese python,
766:
Audience volunteers holding an adult Burmese python
474:
A captured Burmese python in the Florida Everglades
2700:"Python Caused Death in Ontario Home in 1992 Case"
2641:The Bulletin of the Chicago Herpetological Society
2628:Chiszar D, Smith HM, Petkus A, Doughery J (1993).
2589:
1645:. Naturalresources.house.gov. 2010. Archived from
1330:. Krieger Pub. Co. pp. 2, 19, 37, 42, 55–56.
2791:"New law makes Burmese python illegal in Florida"
2076:Florida Fish And Wildlife Conservation Commission
3054:, National Invasive Species Information Center,
1241:Mémoires du Muséum national d'Histoire naturelle
2284:"Glossary of reptile and amphibian terminology"
1804:Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
2739:. Toronto: Canadian Broadcasting Corporation.
1957:) in Everglades National Park, Florida, USA".
1590:National Invasive Species Information Center,
1488:Bulletin of the Chicago Herpetological Society
1444:Bulletin of the Chicago Herpetological Society
1399:
1397:
1060:Bulletin of the Chicago Herpetological Society
3076:
2048:"Florida Python Challenge - Python Challenge"
980:Berkeley Rausser College of Natural Resources
8:
2647:(#12). Chicago Herpetological Society: 261.
1292:), with emphasis on its reproductive Biology
1224:
1222:
1220:
1042:
1040:
1038:
1036:
1030:. Washington, District of Columbia. pp. 8–9.
1028:A Field Guide to the Snakes of South Vietnam
1592:United States National Agricultural Library
1324:Murphy, J.C. & Henderson, R.W. (1997).
3533:
3083:
3069:
3061:
216:
59:
40:
31:
2849:
2565:
2516:
2378:
2320:. Vol. 2. The Ohio State University.
2134:
2124:
1926:
1882:
1833:
1823:
1726:
1477:"The distribution of the Burmese Python,
1433:"The Distribution of the Burmese Python,
1022:
1020:
1774:
1772:
1288:The life history of the green anaconda (
1254:
1252:
1250:
997:
995:
879:
653:Like all snakes, the Burmese python is
2455:
2453:
2356:
2354:
2352:
2350:
2310:"1.4 Invasive species Burmese python (
1896:
1894:
1519:Breuer, H.; Murphy, W.C. (2009–2010).
889:
887:
885:
883:
285:, but is now recognized as a distinct
1948:
1946:
1602:
1600:
969:
967:
7:
1376:De Lang, R. & Vogel, G. (2005).
1207:Journal of Zoo and Wildlife Medicine
633:that involves a modification of the
2554:The Journal of Experimental Biology
2466:The Journal of Experimental Biology
2367:The Journal of Experimental Biology
1475:Barker, D.G.; Barker, T.M. (2008).
1431:Barker, D.G.; Barker, T.M. (2010).
976:"Burmese Pythons in the Everglades"
905:IUCN Red List of Threatened Species
869:, a viral disease affecting pythons
27:Species of large, nonvenomous snake
3048:Species profile - Burmese Python (
1584:Species Profile - Burmese Python (
269:. It is native to a large area of
25:
2361:Secor, S.M.; Diamond, J. (1995).
1959:The Wilson Journal of Ornithology
3767:IUCN Red List vulnerable species
2460:Starck, J.M.; Beese, K. (2001).
1088:(Reptilia, Serpentes, Boidae)".
787:Burmese python at a zoo in Japan
729:The Burmese python is listed on
84:
2610:from the original on 2022-01-12
2505:Journal of Experimental Biology
512:U.S. Department of the Interior
433:. It has also been reported in
3379:Nyctophilopython oenpelliensis
2004:(Burmese python) in Florida".
1259:Jones, Dustin (13 July 2023).
625:The Burmese python is able to
1:
937:Reptarium.cz Reptile Database
585:Big Cypress National Preserve
225:Native distribution in green
2314:) and its effect in Florida"
2126:10.1371/journal.pone.0190633
2822:"Invasive Burmese pythons (
595:Burmese pythons are mainly
466:United States range in 2007
291:invasive species in Florida
3808:
3782:Reptiles described in 1820
2851:10.1007/s10530-019-01979-x
2789:Burrage G (30 June 2010).
2598:. London. AP. 2008-08-26.
2318:Environmental ScienceBites
1863:Journal of Applied Ecology
1494:(3): 33–38. Archived from
1450:(5): 86–88. Archived from
458:Burmese pythons in Florida
455:
3020:10.1007/s10530-010-9908-3
2937:Animal Legal Defense Fund
2632:Python molurus bivittatus
2002:Python molorus bivittatus
1955:Python molurus bivittatus
1586:Python molurus bivittatus
1555:"Top 10 Invasive Species"
1523:Python molurus bivittatus
1479:Python molurus bivittatus
1203:Python molurus bivittatus
1086:Python molurus bivittatus
1006:Python molurus bivittatus
950:Python molurus bivittatus
631:parthenogenetic mechanism
488:minimum viable population
239:Python molurus bivittatus
236:
229:
224:
215:
196:
189:
81:Scientific classification
79:
57:
48:
39:
34:
3300:Malayopython timoriensis
3293:Malayopython reticulatus
3170:Aspidites melanocephalus
3006:) in Southern Florida".
2731:Davison J (2013-08-07).
2432:National Geographic News
2331:Ghosh A (11 July 2012).
2052:Florida Python Challenge
1026:Campden-Main SM (1970).
733:. It has been listed as
719:Malayopython reticulatus
574:Raillietiella orientalis
559:Florida Python Challenge
389:, and southern China in
345:Distribution and habitat
334:Raillietiella orientalis
2006:Southeastern Naturalist
1884:10.1111/1365-2664.12844
1825:10.1073/pnas.1115226109
1304:University of Tennessee
713:of Burmese pythons and
501:cytonuclear discordance
385:, northern continental
3235:Leiopython fredparkeri
2681:. Herp Care Collection
2434:. 2006. Archived from
2380:10.1242/jeb.198.6.1313
2263:The deep Scaly Project
1919:10.1098/rspb.2015.0120
1609:Journal of Herpetology
1561:. 2010. Archived from
1168:Journal of Herpetology
1090:Journal of Herpetology
867:Inclusion body disease
832:
831:Caramel Burmese python
806:Like the much smaller
788:
767:
726:
650:
475:
467:
452:As an invasive species
3221:Leiopython albertisii
2478:10.1242/jeb.204.2.325
2308:Krusling, Lindsey A.
2018:10.1656/058.015.sp807
1757:(Press release). 2012
1707:Ecology and Evolution
912:: e.T193451A151341916
842:dwarf Burmese pythons
830:
782:
765:
745:and over-harvesting.
721:) at a local shop at
708:
648:
473:
465:
3415:Python breitensteini
3228:Leiopython biakensis
3126:Antaresia perthensis
3008:Biological Invasions
2968:. New York: TWELVE.
2830:Biological Invasions
2548:Secor, S.M. (2003).
2499:Secor, S.M. (2008).
2265:. Digital Morphology
2202:Mettler, K. (2019).
1857:Willson, J. (2017).
1649:on 16 September 2012
1351:McKay, J.L. (2006).
1285:Rivas, J.A. (2000).
413:. It also occurs in
341:parasitic disease).
3500:Simalia clastolepis
3486:Simalia amethistina
3112:Antaresia childreni
2983:Mattison C (1999).
2842:2019BiInv..21.2333O
2438:on October 21, 2018
2402:Szalay, J. (2016).
2373:(Pt 6): 1313–1325.
2208:The Washington Post
2173:2018MolEc..27.4744C
2117:2018PLoSO..1390633R
1875:2017JApEc..54.1251W
1816:2012PNAS..109.2418D
1565:on February 6, 2010
1404:Waymer, J. (2019).
974:Sarill, M. (2016).
715:reticulated pythons
627:reproduce asexually
518:are down by 99.3%,
293:as a result of the
51:Conservation status
3422:Python brongersmai
3119:Antaresia maculosa
2888:on 22 October 2018
2518:10.1242/jeb.023754
1913:(1805): 20150120.
1779:Adams, G. (2012).
1008:", pp. 108–109 in
833:
789:
768:
727:
709:Leather goods and
651:
572:They have carried
540:American alligator
476:
468:
308:sexually dimorphic
182:P. bivittatus
3754:
3753:
3591:python-bivittatus
3577:Python bivittatus
3547:Python bivittatus
3539:Taxon identifiers
3530:
3529:
3507:Simalia kinghorni
3450:Python natalensis
3408:Python bivittatus
3343:Morelia imbricata
3177:Aspidites ramsayi
2994:978-0-7894-4660-2
2987:. DK Publishing.
2975:978-0-446-58095-3
2876:Python bivittatus
2824:Python bivittatus
2795:Abcactionnews.com
2769:documentcloud.org
2673:Kaplan M (1994).
2567:10.1242/jeb.00300
2560:(10): 1621–1630.
2511:(24): 3767–3774.
2312:Python bivittatus
2259:, Burmese Python"
2181:10.1111/mec.14885
2167:(23): 4744–4757.
2161:Molecular Ecology
2099:Python bivittatus
1719:10.1002/ece3.4423
1713:(17): 9034–9047.
1697:Python bivittatus
1435:Python bivittatus
1243:. Série A: 40–41.
1051:Python bivittatus
932:Python bivittatus
898:Python bivittatus
780:
751:protected species
731:CITES Appendix II
690:hydrochloric acid
524:white-tailed deer
508:Florida Panhandle
273:and is listed as
258:Python bivittatus
249:
248:
200:Python bivittatus
74:
16:(Redirected from
3799:
3787:Reptiles as pets
3747:
3746:
3737:
3736:
3724:
3723:
3711:
3710:
3698:
3697:
3685:
3684:
3672:
3671:
3659:
3658:
3646:
3645:
3633:
3632:
3620:
3619:
3607:
3606:
3594:
3593:
3581:
3580:
3579:
3566:
3565:
3564:
3534:
3436:Python kyaiktiyo
3401:Python anchietae
3369:Nyctophilopython
3336:Morelia carinata
3271:Liasis olivaceus
3199:Bothrochilus boa
3085:
3078:
3071:
3062:
3031:
3014:(7): 1493–1504.
2998:
2979:
2962:Christy (2008).
2948:
2947:
2945:
2943:
2929:
2923:
2922:
2920:
2918:
2904:
2898:
2897:
2895:
2893:
2884:. Archived from
2870:
2864:
2863:
2853:
2836:(7): 2333–2344.
2817:
2811:
2810:
2808:
2806:
2797:. Archived from
2786:
2780:
2779:
2777:
2775:
2761:
2755:
2754:
2752:
2751:
2728:
2722:
2721:
2719:
2718:
2702:. Toronto News.
2696:
2690:
2689:
2687:
2686:
2670:
2664:
2663:
2661:
2655:. Archived from
2638:
2625:
2619:
2618:
2616:
2615:
2593:
2586:
2580:
2579:
2569:
2545:
2539:
2538:
2520:
2496:
2490:
2489:
2457:
2448:
2447:
2445:
2443:
2424:
2418:
2417:
2415:
2414:
2399:
2393:
2392:
2382:
2358:
2345:
2344:
2342:
2340:
2335:. AnimalSpot.net
2333:"Burmese Python"
2328:
2322:
2321:
2305:
2299:
2298:
2296:
2294:
2280:
2274:
2273:
2271:
2270:
2253:Evans S (2003).
2250:
2244:
2243:
2241:
2240:
2228:Williams, A. B.
2225:
2219:
2218:
2216:
2214:
2199:
2193:
2192:
2155:
2149:
2148:
2138:
2128:
2092:
2086:
2085:
2083:
2082:
2068:
2062:
2061:
2059:
2058:
2044:
2038:
2037:
1997:
1991:
1990:
1971:10.1676/10-092.1
1950:
1941:
1940:
1930:
1898:
1889:
1888:
1886:
1869:(4): 1251–1258.
1854:
1848:
1847:
1837:
1827:
1810:(7): 2418–2422.
1795:
1789:
1788:
1776:
1767:
1766:
1764:
1762:
1747:
1741:
1740:
1730:
1690:
1684:
1683:
1681:
1679:
1665:
1659:
1658:
1656:
1654:
1639:
1633:
1632:
1604:
1595:
1581:
1575:
1574:
1572:
1570:
1551:
1545:
1544:
1542:
1540:
1531:. Archived from
1529:Snakes of Taiwan
1516:
1510:
1509:
1507:
1506:
1500:
1485:
1472:
1466:
1465:
1463:
1462:
1456:
1441:
1428:
1422:
1421:
1419:
1418:
1401:
1392:
1391:
1373:
1367:
1366:
1348:
1342:
1341:
1321:
1315:
1314:
1312:
1306:. Archived from
1297:
1290:Eunectes murinus
1282:
1276:
1275:
1273:
1271:
1256:
1245:
1244:
1236:
1230:
1226:
1215:
1214:
1198:
1192:
1191:
1159:
1153:
1152:
1120:
1114:
1113:
1081:
1075:
1074:
1072:
1071:
1057:
1044:
1031:
1024:
1015:
999:
990:
989:
987:
986:
971:
962:
961:
945:
939:
928:
922:
921:
919:
917:
891:
781:
496:Hurricane Andrew
492:invasive species
261:) is one of the
220:
202:
89:
88:
68:
63:
62:
44:
32:
21:
3807:
3806:
3802:
3801:
3800:
3798:
3797:
3796:
3757:
3756:
3755:
3750:
3742:
3740:
3732:
3727:
3719:
3714:
3706:
3701:
3693:
3688:
3680:
3675:
3667:
3662:
3654:
3649:
3641:
3636:
3628:
3623:
3615:
3610:
3602:
3597:
3589:
3584:
3575:
3574:
3569:
3560:
3559:
3554:
3541:
3531:
3526:
3521:Simalia tracyae
3493:Simalia boeleni
3469:
3384:
3362:
3357:Morelia viridis
3350:Morelia spilota
3305:
3276:
3264:Liasis mackloti
3240:
3204:
3182:
3153:
3148:Apodora papuana
3131:
3095:
3089:
3039:
3034:
3001:
2995:
2982:
2976:
2961:
2957:
2955:Further reading
2952:
2951:
2941:
2939:
2931:
2930:
2926:
2916:
2914:
2912:www.anapsid.org
2906:
2905:
2901:
2891:
2889:
2872:
2871:
2867:
2819:
2818:
2814:
2804:
2802:
2788:
2787:
2783:
2773:
2771:
2763:
2762:
2758:
2749:
2747:
2730:
2729:
2725:
2716:
2714:
2698:
2697:
2693:
2684:
2682:
2679:www.anapsid.org
2672:
2671:
2667:
2659:
2636:
2627:
2626:
2622:
2613:
2611:
2588:
2587:
2583:
2547:
2546:
2542:
2498:
2497:
2493:
2459:
2458:
2451:
2441:
2439:
2426:
2425:
2421:
2412:
2410:
2401:
2400:
2396:
2360:
2359:
2348:
2338:
2336:
2330:
2329:
2325:
2307:
2306:
2302:
2292:
2290:
2282:
2281:
2277:
2268:
2266:
2252:
2251:
2247:
2238:
2236:
2227:
2226:
2222:
2212:
2210:
2201:
2200:
2196:
2157:
2156:
2152:
2111:(1): e0190633.
2094:
2093:
2089:
2080:
2078:
2070:
2069:
2065:
2056:
2054:
2046:
2045:
2041:
1999:
1998:
1994:
1952:
1951:
1944:
1900:
1899:
1892:
1856:
1855:
1851:
1797:
1796:
1792:
1785:The Independent
1778:
1777:
1770:
1760:
1758:
1749:
1748:
1744:
1692:
1691:
1687:
1677:
1675:
1667:
1666:
1662:
1652:
1650:
1641:
1640:
1636:
1606:
1605:
1598:
1582:
1578:
1568:
1566:
1553:
1552:
1548:
1538:
1536:
1535:on 26 June 2012
1518:
1517:
1513:
1504:
1502:
1498:
1483:
1474:
1473:
1469:
1460:
1458:
1454:
1439:
1430:
1429:
1425:
1416:
1414:
1403:
1402:
1395:
1388:
1375:
1374:
1370:
1363:
1350:
1349:
1345:
1338:
1323:
1322:
1318:
1310:
1295:
1284:
1283:
1279:
1269:
1267:
1258:
1257:
1248:
1238:
1237:
1233:
1227:
1218:
1200:
1199:
1195:
1180:10.2307/1563914
1161:
1160:
1156:
1141:10.2307/1443224
1122:
1121:
1117:
1102:10.2307/1563071
1083:
1082:
1078:
1069:
1067:
1055:
1046:
1045:
1034:
1025:
1018:
1000:
993:
984:
982:
973:
972:
965:
947:
946:
942:
929:
925:
915:
913:
893:
892:
881:
876:
863:
825:
816:
770:
760:
703:
685:
643:
635:meiotic process
623:
621:Parthenogenesis
593:
533:Florida panther
460:
454:
361:, southeastern
353:, southeastern
347:
329:
303:
263:largest species
211:
204:
198:
185:
83:
75:
64:
60:
53:
35:Burmese python
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
3805:
3803:
3795:
3794:
3792:Apex predators
3789:
3784:
3779:
3777:Snakes of Asia
3774:
3772:Python (genus)
3769:
3759:
3758:
3752:
3751:
3749:
3748:
3738:
3725:
3712:
3699:
3686:
3673:
3660:
3647:
3634:
3621:
3608:
3595:
3582:
3567:
3551:
3549:
3543:
3542:
3537:
3528:
3527:
3525:
3524:
3517:
3510:
3503:
3496:
3489:
3481:
3479:
3471:
3470:
3468:
3467:
3460:
3453:
3446:
3443:Python molurus
3439:
3432:
3425:
3418:
3411:
3404:
3396:
3394:
3386:
3385:
3383:
3382:
3374:
3372:
3364:
3363:
3361:
3360:
3353:
3346:
3339:
3332:
3329:Morelia bredli
3325:
3322:Morelia azurea
3317:
3315:
3307:
3306:
3304:
3303:
3296:
3288:
3286:
3278:
3277:
3275:
3274:
3267:
3260:
3252:
3250:
3242:
3241:
3239:
3238:
3231:
3224:
3216:
3214:
3206:
3205:
3203:
3202:
3194:
3192:
3184:
3183:
3181:
3180:
3173:
3165:
3163:
3155:
3154:
3152:
3151:
3143:
3141:
3133:
3132:
3130:
3129:
3122:
3115:
3107:
3105:
3097:
3096:
3090:
3088:
3087:
3080:
3073:
3065:
3059:
3058:
3050:Python molurus
3045:
3038:
3037:External links
3035:
3033:
3032:
3004:Python molurus
2999:
2993:
2980:
2974:
2958:
2956:
2953:
2950:
2949:
2924:
2899:
2865:
2812:
2781:
2756:
2723:
2691:
2665:
2662:on 2019-02-18.
2634:) in Colorado"
2620:
2581:
2540:
2491:
2472:(2): 325–335.
2449:
2419:
2404:"Python Facts"
2394:
2346:
2323:
2300:
2275:
2257:Python molurus
2245:
2234:The News-Press
2220:
2194:
2150:
2087:
2063:
2039:
2012:(sp8): 63–74.
1992:
1965:(1): 126–131.
1942:
1890:
1849:
1790:
1768:
1742:
1685:
1660:
1634:
1621:10.1670/14-098
1596:
1576:
1546:
1511:
1467:
1423:
1393:
1386:
1368:
1361:
1343:
1336:
1316:
1313:on 2016-03-03.
1277:
1246:
1231:
1216:
1193:
1164:Python molurus
1154:
1135:(3): 466–471.
1125:Python molurus
1115:
1096:(4): 333–340.
1076:
1032:
1016:
991:
963:
940:
923:
878:
877:
875:
872:
871:
870:
862:
859:
855:hypomelanistic
824:
821:
815:
812:
759:
756:
749:Kong, it is a
702:
699:
684:
681:
642:
639:
622:
619:
592:
589:
522:by 98.9%, and
490:and become an
456:Main article:
453:
450:
346:
343:
328:
325:
302:
299:
271:Southeast Asia
253:Burmese python
247:
246:
234:
233:
227:
226:
222:
221:
213:
212:
205:
194:
193:
187:
186:
179:
177:
173:
172:
165:
161:
160:
155:
151:
150:
145:
141:
140:
135:
131:
130:
125:
121:
120:
115:
111:
110:
105:
101:
100:
95:
91:
90:
77:
76:
58:
55:
54:
49:
46:
45:
37:
36:
26:
24:
18:Burmese Python
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
3804:
3793:
3790:
3788:
3785:
3783:
3780:
3778:
3775:
3773:
3770:
3768:
3765:
3764:
3762:
3745:
3739:
3735:
3730:
3726:
3722:
3717:
3713:
3709:
3704:
3700:
3696:
3691:
3687:
3683:
3678:
3674:
3670:
3665:
3661:
3657:
3652:
3648:
3644:
3639:
3635:
3631:
3626:
3622:
3618:
3613:
3609:
3605:
3600:
3596:
3592:
3587:
3583:
3578:
3572:
3568:
3563:
3557:
3553:
3552:
3550:
3548:
3544:
3540:
3535:
3523:
3522:
3518:
3516:
3515:
3514:Simalia nauta
3511:
3509:
3508:
3504:
3502:
3501:
3497:
3495:
3494:
3490:
3488:
3487:
3483:
3482:
3480:
3478:
3477:
3472:
3466:
3465:
3461:
3459:
3458:
3457:Python regius
3454:
3452:
3451:
3447:
3445:
3444:
3440:
3438:
3437:
3433:
3431:
3430:
3429:Python curtus
3426:
3424:
3423:
3419:
3417:
3416:
3412:
3410:
3409:
3405:
3403:
3402:
3398:
3397:
3395:
3393:
3392:
3387:
3381:
3380:
3376:
3375:
3373:
3371:
3370:
3365:
3359:
3358:
3354:
3352:
3351:
3347:
3345:
3344:
3340:
3338:
3337:
3333:
3331:
3330:
3326:
3324:
3323:
3319:
3318:
3316:
3314:
3313:
3308:
3302:
3301:
3297:
3295:
3294:
3290:
3289:
3287:
3285:
3284:
3279:
3273:
3272:
3268:
3266:
3265:
3261:
3259:
3258:
3257:Liasis fuscus
3254:
3253:
3251:
3249:
3248:
3243:
3237:
3236:
3232:
3230:
3229:
3225:
3223:
3222:
3218:
3217:
3215:
3213:
3212:
3207:
3201:
3200:
3196:
3195:
3193:
3191:
3190:
3185:
3179:
3178:
3174:
3172:
3171:
3167:
3166:
3164:
3162:
3161:
3156:
3150:
3149:
3145:
3144:
3142:
3140:
3139:
3134:
3128:
3127:
3123:
3121:
3120:
3116:
3114:
3113:
3109:
3108:
3106:
3104:
3103:
3098:
3094:
3086:
3081:
3079:
3074:
3072:
3067:
3066:
3063:
3057:
3053:
3051:
3046:
3044:
3041:
3040:
3036:
3029:
3025:
3021:
3017:
3013:
3009:
3005:
3000:
2996:
2990:
2986:
2981:
2977:
2971:
2967:
2966:
2960:
2959:
2954:
2938:
2934:
2928:
2925:
2913:
2909:
2903:
2900:
2887:
2883:
2879:
2878:(Kuhl, 1820)"
2877:
2869:
2866:
2861:
2857:
2852:
2847:
2843:
2839:
2835:
2831:
2827:
2825:
2816:
2813:
2801:on 2013-05-01
2800:
2796:
2792:
2785:
2782:
2770:
2766:
2760:
2757:
2746:
2742:
2738:
2734:
2727:
2724:
2713:
2709:
2705:
2701:
2695:
2692:
2680:
2676:
2669:
2666:
2658:
2654:
2650:
2646:
2642:
2635:
2633:
2624:
2621:
2609:
2605:
2601:
2597:
2596:The Telegraph
2592:
2585:
2582:
2577:
2573:
2568:
2563:
2559:
2555:
2551:
2544:
2541:
2536:
2532:
2528:
2524:
2519:
2514:
2510:
2506:
2502:
2495:
2492:
2487:
2483:
2479:
2475:
2471:
2467:
2463:
2456:
2454:
2450:
2437:
2433:
2429:
2423:
2420:
2409:
2405:
2398:
2395:
2390:
2386:
2381:
2376:
2372:
2368:
2364:
2357:
2355:
2353:
2351:
2347:
2334:
2327:
2324:
2319:
2315:
2313:
2304:
2301:
2289:
2288:Kingsnake.com
2285:
2279:
2276:
2264:
2260:
2258:
2249:
2246:
2235:
2231:
2224:
2221:
2209:
2205:
2198:
2195:
2190:
2186:
2182:
2178:
2174:
2170:
2166:
2162:
2154:
2151:
2146:
2142:
2137:
2132:
2127:
2122:
2118:
2114:
2110:
2106:
2102:
2100:
2091:
2088:
2077:
2073:
2067:
2064:
2053:
2049:
2043:
2040:
2035:
2031:
2027:
2023:
2019:
2015:
2011:
2007:
2003:
1996:
1993:
1988:
1984:
1980:
1976:
1972:
1968:
1964:
1960:
1956:
1949:
1947:
1943:
1938:
1934:
1929:
1924:
1920:
1916:
1912:
1908:
1904:
1897:
1895:
1891:
1885:
1880:
1876:
1872:
1868:
1864:
1860:
1853:
1850:
1845:
1841:
1836:
1831:
1826:
1821:
1817:
1813:
1809:
1805:
1801:
1794:
1791:
1786:
1782:
1775:
1773:
1769:
1756:
1752:
1746:
1743:
1738:
1734:
1729:
1724:
1720:
1716:
1712:
1708:
1704:
1702:
1698:
1689:
1686:
1674:
1670:
1664:
1661:
1648:
1644:
1638:
1635:
1630:
1626:
1622:
1618:
1614:
1610:
1603:
1601:
1597:
1593:
1589:
1587:
1580:
1577:
1564:
1560:
1556:
1550:
1547:
1534:
1530:
1526:
1524:
1515:
1512:
1501:on 2014-05-20
1497:
1493:
1489:
1482:
1480:
1471:
1468:
1457:on 2016-03-03
1453:
1449:
1445:
1438:
1436:
1427:
1424:
1413:
1412:
1411:Florida Today
1407:
1400:
1398:
1394:
1389:
1387:3-930612-85-2
1383:
1379:
1372:
1369:
1364:
1362:1-57524-190-0
1358:
1354:
1347:
1344:
1339:
1337:0-89464-995-7
1333:
1329:
1328:
1320:
1317:
1309:
1305:
1301:
1294:
1293:
1289:
1281:
1278:
1266:
1262:
1255:
1253:
1251:
1247:
1242:
1235:
1232:
1225:
1223:
1221:
1217:
1212:
1208:
1204:
1197:
1194:
1189:
1185:
1181:
1177:
1173:
1169:
1165:
1158:
1155:
1150:
1146:
1142:
1138:
1134:
1130:
1126:
1119:
1116:
1111:
1107:
1103:
1099:
1095:
1091:
1087:
1080:
1077:
1065:
1061:
1054:
1052:
1043:
1041:
1039:
1037:
1033:
1029:
1023:
1021:
1017:
1013:
1012:
1007:
1003:
998:
996:
992:
981:
977:
970:
968:
964:
959:
955:
951:
944:
941:
938:
934:
933:
927:
924:
911:
907:
906:
901:
899:
890:
888:
886:
884:
880:
873:
868:
865:
864:
860:
858:
856:
852:
848:
843:
838:
829:
822:
820:
813:
811:
809:
804:
802:
797:
793:
786:
764:
757:
755:
752:
746:
744:
740:
739:IUCN Red List
736:
732:
724:
720:
716:
712:
707:
700:
698:
694:
691:
682:
680:
678:
674:
669:
664:
660:
656:
647:
640:
638:
636:
632:
628:
620:
618:
615:
609:
606:
601:
598:
590:
588:
586:
581:
579:
575:
570:
566:
562:
560:
555:
551:
549:
546:species, the
543:
541:
536:
534:
530:
525:
521:
517:
513:
509:
504:
502:
497:
493:
489:
485:
481:
480:South Florida
472:
464:
459:
451:
449:
447:
443:
438:
436:
432:
428:
424:
420:
416:
412:
408:
404:
400:
396:
392:
388:
384:
380:
376:
372:
368:
364:
360:
356:
352:
344:
342:
340:
336:
335:
326:
324:
322:
318:
314:
309:
300:
298:
296:
292:
288:
284:
283:Indian python
280:
279:IUCN Red List
276:
272:
268:
264:
260:
259:
254:
245:
243:
240:
235:
232:
228:
223:
219:
214:
209:
203:
201:
195:
192:
191:Binomial name
188:
184:
183:
178:
175:
174:
171:
170:
166:
163:
162:
159:
156:
153:
152:
149:
146:
143:
142:
139:
136:
133:
132:
129:
126:
123:
122:
119:
116:
113:
112:
109:
106:
103:
102:
99:
96:
93:
92:
87:
82:
78:
72:
67:
56:
52:
47:
43:
38:
33:
30:
19:
3546:
3519:
3512:
3505:
3498:
3491:
3484:
3474:
3464:Python sebae
3462:
3455:
3448:
3441:
3434:
3427:
3420:
3413:
3407:
3406:
3399:
3389:
3377:
3367:
3355:
3348:
3341:
3334:
3327:
3320:
3310:
3298:
3291:
3283:Malayopython
3281:
3269:
3262:
3255:
3245:
3233:
3226:
3219:
3209:
3197:
3189:Bothrochilus
3187:
3175:
3168:
3158:
3146:
3136:
3124:
3117:
3110:
3100:
3049:
3011:
3007:
3003:
2984:
2964:
2940:. Retrieved
2936:
2927:
2915:. Retrieved
2911:
2902:
2890:. Retrieved
2886:the original
2882:www.gbif.org
2881:
2875:
2868:
2833:
2829:
2823:
2815:
2803:. Retrieved
2799:the original
2794:
2784:
2772:. Retrieved
2768:
2759:
2748:. Retrieved
2736:
2726:
2715:. Retrieved
2703:
2694:
2683:. Retrieved
2678:
2668:
2657:the original
2644:
2640:
2631:
2623:
2612:. Retrieved
2595:
2584:
2557:
2553:
2543:
2508:
2504:
2494:
2469:
2465:
2440:. Retrieved
2436:the original
2431:
2422:
2411:. Retrieved
2408:Live Science
2407:
2397:
2370:
2366:
2337:. Retrieved
2326:
2317:
2311:
2303:
2291:. Retrieved
2287:
2278:
2267:. Retrieved
2262:
2256:
2248:
2237:. Retrieved
2233:
2223:
2211:. Retrieved
2207:
2197:
2164:
2160:
2153:
2108:
2104:
2098:
2090:
2079:. Retrieved
2075:
2066:
2055:. Retrieved
2051:
2042:
2009:
2005:
2001:
1995:
1962:
1958:
1954:
1910:
1906:
1866:
1862:
1852:
1807:
1803:
1793:
1784:
1759:. Retrieved
1754:
1745:
1710:
1706:
1700:
1696:
1688:
1676:. Retrieved
1672:
1663:
1651:. Retrieved
1647:the original
1637:
1615:(1): 50–56.
1612:
1608:
1585:
1579:
1567:. Retrieved
1563:the original
1558:
1549:
1537:. Retrieved
1533:the original
1528:
1522:
1514:
1503:. Retrieved
1496:the original
1491:
1487:
1478:
1470:
1459:. Retrieved
1452:the original
1447:
1443:
1434:
1426:
1415:. Retrieved
1409:
1377:
1371:
1352:
1346:
1326:
1319:
1308:the original
1291:
1287:
1280:
1268:. Retrieved
1264:
1240:
1234:
1210:
1206:
1202:
1196:
1174:(1): 92–95.
1171:
1167:
1163:
1157:
1132:
1128:
1124:
1118:
1093:
1089:
1085:
1079:
1068:. Retrieved
1063:
1059:
1050:
1027:
1010:
1005:
983:. Retrieved
979:
957:
953:
949:
943:
931:
926:
914:. Retrieved
909:
903:
897:
834:
817:
805:
798:
794:
790:
758:In captivity
747:
743:habitat loss
728:
718:
701:Conservation
695:
686:
679:in Florida.
659:constriction
652:
624:
610:
594:
582:
573:
571:
567:
565:introduced.
563:
556:
552:
544:
537:
505:
477:
439:
429:, Bali, and
348:
332:
330:
304:
257:
256:
252:
250:
238:
237:
199:
197:
181:
180:
168:
29:
3571:Wikispecies
2917:8 September
2339:27 December
1437:, in China"
837:amelanistic
808:ball python
785:amelanistic
655:carnivorous
425:, southern
301:Description
289:. It is an
3761:Categories
3721:bivittatus
3211:Leiopython
3093:Pythonidae
2750:2019-02-17
2717:2019-02-17
2685:2019-02-18
2614:2019-02-18
2413:2021-03-17
2269:2007-07-25
2239:2022-06-25
2081:2024-03-29
2057:2024-03-29
1701:P. molurus
1539:17 October
1505:2012-10-17
1461:2012-06-26
1417:2021-12-16
1213:: 245–248.
1070:2020-03-02
985:2021-03-17
960:(3): 5–11.
874:References
851:homozygous
823:Variations
735:vulnerable
675:and adult
673:alligators
600:rainforest
578:pentastome
548:wood stork
484:Everglades
446:prehensile
442:grasslands
363:Bangladesh
357:, western
339:pentastome
275:Vulnerable
158:Pythonidae
144:Suborder:
66:Vulnerable
3160:Aspidites
3102:Antaresia
3028:207096799
2860:102350541
2745:0708-9392
2712:0708-9392
2653:0009-3564
2604:0307-1235
1787:. London.
1761:April 26,
1302:thesis).
1004:(1943). "
847:leucistic
725:, Myanmar
683:Digestion
614:egg tooth
597:nocturnal
419:Indonesia
417:, and in
415:Hong Kong
399:Guangdong
295:pet trade
176:Species:
148:Serpentes
104:Kingdom:
98:Eukaryota
3729:Species+
3656:10476314
3562:Q2716137
3556:Wikidata
2805:9 August
2737:CBC News
2735:. News.
2704:CBC News
2608:Archived
2576:12682094
2527:19043049
2486:11136618
2189:30269397
2145:29342169
2105:PLOS ONE
2034:90352897
2026:26454670
1987:55495469
1979:23033493
1937:25788598
1844:22308381
1737:30271564
1653:9 August
1629:86327588
1569:27 April
1229:12634818
1066:(1): 1–6
1002:Smith MA
861:See also
814:Handling
723:Mandalay
591:Behavior
520:opossums
516:raccoons
427:Sulawesi
387:Malaysia
379:Cambodia
371:Thailand
327:Diseases
321:Sulawesi
231:Synonyms
154:Family:
138:Squamata
128:Reptilia
118:Chordata
114:Phylum:
108:Animalia
94:Domain:
71:IUCN 3.1
3744:8055835
3682:1094050
3630:4820533
3476:Simalia
3312:Morelia
3138:Apodora
3091:Family
2942:8 April
2892:8 April
2838:Bibcode
2774:8 April
2535:5545174
2442:8 April
2389:7782719
2293:8 April
2169:Bibcode
2136:5771569
2113:Bibcode
1928:4389622
1871:Bibcode
1835:3289325
1812:Bibcode
1755:doi.gov
1728:6157680
1678:8 April
1673:nps.gov
1270:14 July
1188:1563914
1149:1443224
1110:1563071
935:at the
916:6 April
801:obesity
737:on the
668:poultry
605:brumate
431:Sumbawa
407:Guangxi
395:Jiangxi
383:Vietnam
367:Myanmar
287:species
277:on the
244:, 1820
210:, 1820)
164:Genus:
134:Order:
124:Class:
69: (
3741:uBio:
3708:176946
3695:193451
3617:PYTNBI
3586:ARKive
3391:Python
3247:Liasis
3026:
2991:
2972:
2858:
2743:
2710:
2651:
2602:
2574:
2533:
2525:
2484:
2387:
2213:23 May
2187:
2143:
2133:
2032:
2024:
1985:
1977:
1935:
1925:
1842:
1832:
1735:
1725:
1627:
1384:
1359:
1334:
1186:
1147:
1129:Copeia
1108:
954:Sauria
663:vermin
529:coyote
435:Kinmen
411:Yunnan
409:, and
403:Hainan
391:Fujian
359:Bhutan
319:, and
267:snakes
169:Python
3669:66412
3651:IRMNG
3604:4QY48
3024:S2CID
2985:Snake
2856:S2CID
2660:(PDF)
2637:(PDF)
2531:S2CID
2030:S2CID
2022:JSTOR
1983:S2CID
1975:JSTOR
1625:S2CID
1499:(PDF)
1484:(PDF)
1455:(PDF)
1440:(PDF)
1311:(PDF)
1300:Ph.D.
1296:(PDF)
1184:JSTOR
1145:JSTOR
1106:JSTOR
1056:(PDF)
711:skins
355:Nepal
351:India
3734:8396
3703:NCBI
3690:IUCN
3677:ITIS
3643:1207
3638:GISD
3625:GBIF
3612:EPPO
2989:ISBN
2970:ISBN
2944:2019
2919:2017
2894:2019
2807:2012
2776:2019
2741:ISSN
2708:ISSN
2649:ISSN
2600:ISSN
2572:PMID
2523:PMID
2482:PMID
2444:2019
2385:PMID
2341:2012
2295:2019
2215:2020
2185:PMID
2141:PMID
1933:PMID
1840:PMID
1763:2022
1733:PMID
1680:2019
1655:2012
1571:2010
1559:Time
1541:2012
1382:ISBN
1357:ISBN
1332:ISBN
1272:2023
1205:)".
1133:1979
918:2021
910:2019
677:deer
641:Diet
576:, a
423:Java
375:Laos
317:Bali
313:Java
251:The
242:Kuhl
208:Kuhl
3664:ISC
3599:CoL
3016:doi
2846:doi
2562:doi
2558:206
2513:doi
2509:211
2474:doi
2470:204
2375:doi
2371:198
2177:doi
2131:PMC
2121:doi
2014:doi
1967:doi
1963:123
1923:PMC
1915:doi
1911:282
1879:doi
1830:PMC
1820:doi
1808:109
1723:PMC
1715:doi
1617:doi
1265:NPR
1176:doi
1166:".
1137:doi
1098:doi
783:An
421:on
337:(a
265:of
3763::
3731::
3718::
3716:RD
3705::
3692::
3679::
3666::
3653::
3640::
3627::
3614::
3601::
3588::
3573::
3558::
3022:.
3012:13
3010:.
2935:.
2910:.
2880:.
2854:.
2844:.
2834:21
2832:.
2828:.
2793:.
2767:.
2677:.
2645:28
2643:.
2639:.
2606:.
2594:.
2570:.
2556:.
2552:.
2529:.
2521:.
2507:.
2503:.
2480:.
2468:.
2464:.
2452:^
2430:.
2406:.
2383:.
2369:.
2365:.
2349:^
2286:.
2261:.
2232:.
2206:.
2183:.
2175:.
2165:27
2163:.
2139:.
2129:.
2119:.
2109:13
2107:.
2103:.
2074:.
2050:.
2028:.
2020:.
2010:15
2008:.
1981:.
1973:.
1961:.
1945:^
1931:.
1921:.
1909:.
1905:.
1893:^
1877:.
1867:54
1865:.
1861:.
1838:.
1828:.
1818:.
1806:.
1802:.
1783:.
1771:^
1753:.
1731:.
1721:.
1709:.
1705:.
1703:)"
1671:.
1623:.
1613:50
1611:.
1599:^
1588:).
1557:.
1527:.
1492:43
1490:.
1486:.
1448:45
1446:.
1442:.
1408:.
1396:^
1263:.
1249:^
1219:^
1211:22
1209:.
1182:.
1172:16
1170:.
1143:.
1131:.
1104:.
1094:10
1092:.
1064:47
1062:.
1058:.
1035:^
1019:^
994:^
978:.
966:^
958:31
956:.
908:.
902:.
882:^
637:.
494:.
437:.
405:,
401:,
397:,
393:,
381:,
377:,
373:,
369:,
365:,
315:,
297:.
3084:e
3077:t
3070:v
3052:)
3030:.
3018::
2997:.
2978:.
2946:.
2921:.
2896:.
2874:"
2862:.
2848::
2840::
2809:.
2778:.
2753:.
2720:.
2688:.
2617:.
2578:.
2564::
2537:.
2515::
2488:.
2476::
2446:.
2416:.
2391:.
2377::
2343:.
2297:.
2272:.
2255:"
2242:.
2217:.
2191:.
2179::
2171::
2147:.
2123::
2115::
2084:.
2060:.
2036:.
2016::
1989:.
1969::
1939:.
1917::
1887:.
1881::
1873::
1846:.
1822::
1814::
1765:.
1739:.
1717::
1711:8
1682:.
1657:.
1631:.
1619::
1594:.
1573:.
1543:.
1525:"
1521:"
1508:.
1481:"
1464:.
1420:.
1390:.
1365:.
1340:.
1298:(
1274:.
1190:.
1178::
1151:.
1139::
1112:.
1100::
1073:.
1053:"
988:.
920:.
900:"
896:"
717:(
255:(
206:(
73:)
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.