96:
3494:
raised an army and marched against the Sultan, hoping to take his capital at
Iconium. Manuel made serious tactical errors, however, such as failing to properly scout the way ahead of him and taking predictable routes through Anatolia. He was thus ambushed at Myriokephalon by Kilij Arslan, and his army was soon routed in a humiliating defeat reminiscent of Manzikert a century earlier. Manuel, however, was able to rally his army and avoid the fate of Romanos Diogenes, and Kilij Arslan was quick to seek a peace treaty. Manuel could thus maintain his family's gains over the years in Anatolia, but his offensive drive was finished, and he added no further territory to Byzantine Anatolia.
3183:. Additionally, the Armenian allies had to deal with a separate Arab invasion that weakened their position against the Arabs. Combined with other difficulties, Leo was unable to make progress in Anatolia until 900, when he launched a new offensive against Tarsus. This campaign was successful, culminating in the capture of the emir of Tarsus and weakening the emirate. The next few years saw more offensives that gradually weakened the Arab presence in the east and allowed the empire to make its first eastern conquests in years. The empire's grip on Anatolia was stronger at Leo's death than it had been in a long time.
515:
2641:
3334:
2146:
3124:
25:
3569:, but he soon found himself unable to pay them. The Catalan mercenaries went on a destructive rampage in response. This only weakened Byzantine power in the area even further. Finally, new threats in the west and civil wars turned the attention of the Byzantine emperors inward and westward. The rest of the century witnessed the consolidation of Ottoman power and the taking of the last Byzantine holdings. In 1390, the fortress of
2993:
2780:
2138:
1580:
448:
3251:. Tzimiskes proved to be just as capable and active as Nikephoros. Aleppo soon submitted to the empire and became a Roman vassal, while remaining a Muslim state. This was an unprecedented development that further strengthened Anatolia's southern borders and demonstrated the new power of Byzantium. Tzimiskes continued the offensive with campaigns into Mesopotamia and into Syria against the
1907:
3309:, to become the new Emperor. Diogenes recognized the crumbling situation in Anatolia and quickly assembled an army to reverse it and push out the Seljuk Turks. For the next three years, Romanos campaigned against them, winning back some fortresses and pushing against them. He hoped to administer a fatal blow in 1071. Gathering an army of 40,000 men, Diogenes retook the town of
2078:. This would be the first in a series of raids into Anatolia that would last for hundreds of years. The desperate straits of the empire at this time caused a massive shift in strategic thinking for the Byzantines. For the next two centuries they would cease being an empire of conquest, of which they were largely incapable at the moment.
2246:. However his more limited resources and despotic nature ultimately proved his downfall as the last of the Heraclians. Initially he was able to continue his father's successes in the east leaving him free to concentrate on the Balkans where he was also successful. He then returned to the east but was soundly defeated at the
3407:. Alexios entrusted several cities to Turkish mercenaries such as Nicaea, but this strategy backfired on him when the Turks betrayed him and kept the cities for themselves. By 1095, the empire was reduced to only barely holding the coast with the Bosporus sea. Alexios now turned westward, working with Pope
3236:, which dealt a major blow to Sayf al-Dawla. By 965, Cilica was entirely back in Byzantine hands. al-Dawla faced continuous revolts for the rest of his reign that stymied his ability to fight back. The campaign of reconquest continued and culminated in 969 with the retaking of Antioch by Byzantine forces.
3258:
While neither
Tzimiskes nor Phokas had a unified strategy, their conquests tended to be territory that either posed a direct threat to Byzantine territory in Asia Minor, such as Cilcia, or territory that had a large Christian population such as Antioch. These territories, along with the vassalization
3359:
Weak leadership at the top would lead to civil war and a poor response to the waves of incoming Turks who now entered
Anatolia. The exact timeline is unclear due in part to a lack of sources during this time. For the year of 1072, the Byzantines did not have to deal with an organized invasion by the
2798:(780–797) was coemperor but only nine years old, and reigned with his mother Irene as regent. An unpopular ruler even after gaining majority, he was engaged in power struggles with his mother, who had been declared empress. Eventually his mother's supporters deposed him, leaving her as sole empress.
3389:
to apprehend him. He was successful, and in 1076 he captured
Roussel and returned to the capital. The wars with Roussel only served to expose the weakness of Roman presence within Anatolia, and throughout the decade, many Romans fled westwards away from the Turks. The combined threat of the Seljuks
3384:
to defeat
Roussel, the Byzantines were able to drive his army away from the capital and capture him. However, Roussel's wife was able to reach Artuk before the Empire and was able to ransom Roussel. Roussel now retreated to the Armeniakon theme and resumed his ambitions. In 1075, the imperial court
3283:
from
Byzantium. Yet Constantine did not react. He sent no armies to contest the Turkish raids. There is a lack of sources for his reign and thus the reason for this lack of reaction are unclear. In fact, it seems that Constantine may have actually weakened the armies that should have been defending
2824:
Following the deposition of Irene, there was founded a relatively short-lived dynasty for the era, the
Nikephorian dynasty. The empire was in a weaker and more precarious position than it had been for a long time and its finances were problematic. During this era Byzantium was almost continually at
2674:
Having overthrown
Theodosius, the first problem Leo faced was the Arab siege of Constantinople, which was abandoned in 718, Leo having continued his predecessors alliance with the Bulgars. His next pressing task was to consolidate his power to avoid being himself deposed and to restore order in the
2274:
Justinian then continued to reign for a further six years (705–711). His treatment of
Tiberios and his supporters had been brutal and he continued to rule in a manner that was despotic and cruel. He lost the ground regained by Tiberios in the east, and imposed his views on the pope. However, before
2203:
in 674. This first siege of
Constantinople demonstrated how vulnerable the city was to attack, but also its strengths which ultimately prevailed, the Arabs lifting the siege in 678, and after further setbacks signing another truce which allowed Constantine to concentrate on the Balkan threat. For a
3488:
John was succeeded by his son Manuel Komnenos in 1143. Manuel initially pursued a similar strategy to his father and grandfather, however the political situation he inherited from them, as well as his own ambitions to restore Roman power, demanded that his attention be primarily focused outside of
3434:
In 1097, the Crusaders launched an attack against Nicea. Before the city could be sacked, Alexios was able to negotiate a surrender by the city's Turkish garrison and a return of the city into Byzantine hands. The Crusaders then marched eastwards through Anatolia. They were opposed by the Turks at
3493:
established a truce which allowed Manuel to focus his attention elsewhere. The treaty proved to be a double edged sword, as Arslan was able to solidify his own position and defeat his rivals. Arslan gradually became more belligerent and refused to honor treaty obligations. Alarmed, Manuel quickly
3243:
Caliphate. This meant the caliphate was unable to offer a tangible response to Byzantine aggression. Furthermore, once Sayf al-Dawla was defeated, there was no other Arab state in the immediate region to slow the Byzantine efforts. Finally, Arab raids on the empire had ceased long ago, giving the
2721:
The traditional view was that Leo III issued an edict ordering the removal of images in 726, followed by prohibiting the veneration of images, but the controversy had existed in the church for some time and received some impetus from the rise of proximity of Islam and its attitude to imagery. The
2709:
One of the most significant influences of Leo III was his involvement with the Iconoclastic movement in about 726. This controversy, the removal and destruction of religious icons in favour of simple crosses, and the persecution of icon worshippers was to have a profound effect on the empire, its
2625:
It was surprising that the Byzantine Empire was able to survive, given its internal conflicts, the speedy collapse of the Sassanid Empire under Arab threat, and it was being threatened simultaneously on two fronts. However the strength of the military organisation within the empire, and factional
3471:
Alexios was succeeded by his son John in 1118. John continued his father's strategy of slowly taking back control over Anatolia. Contending with both the Seljuks and the Crusader states, John's strategy was one of patience, slowly chipping away at his enemies. By 1140, John had moved his eastern
2936:
In religious matters, despite early evidence of image veneration, he adopted iconoclasm, this precipitating the second phase of the divisive controversy (814–842). He appears to have been motivated by the observation that the return of image veneration coincided with a period of untimely ends of
2133:
tactics to defend against constant Arab raids into Anatolia for hundreds of years. Rather than attempting to defeat Arab armies head on, the troops would often ambush plunder laden Arab raiding parties as they made their way back out of Anatolia in the hope of retaking some plunder and deterring
2710:
religion and culture over most of the next century before being finally laid to rest in 842. Leo's exact role has been debated An opponent of image worship has been referred to as an εἰκονοκλάστης (iconoclast), while those supporting image worship have been variously described as εἰκονολάτραι (
1953:
by the same name, launched a revolt against Phocas, which weakened the eastern frontier. Heraclius was successful in overthrowing Phocas in 610, but in 611, the Persians succeeded in breaking through the Armenian frontier and invading Anatolia proper. Over the next four years, forces under the
2854:
had been the empire's finance minister and on Irene's deposition immediately embarked on a series of fiscal reforms. His administrative reforms included re-organisation of themata. He survived a civil war in 803 and like most of the Byzantine emperors, he found himself at war on three fronts,
2690:
on which it was based, was in Greek rather than in Latin. Administratively he subdivided a number of the themata, for reasons similar to that of his predecessors, smaller units meant less power to local officials and less threat to central authority. When Leo died he was succeeded by his son,
2882:
of Bulgaria that took the lives of his two predecessors, he engaged Krum once more and once more was defeated, severely weakening his position. Aware of a likely revolt he chose to abdicate given the grisly fate of so many prior overthrown emperors, ending the brief dynasty of Nikephoros.
3462:
would prove to be a new threat to Byzantine power in the region. In 1108, Alexios finally defeated Bohemond, who returned to Italy, but failed to return Antioch to Byzantine hands. Byzantium was thus given a foothold from which to attempt to reassert control over all of the peninsula.
3259:
of Aleppo, secured Anatolia from southern incursion and prevented any Muslim attempts to raid Anatolia from the south. Initially, it seemed that the empire would resume a defensive posture. However, the next emperor, Basil II, would soon address the north eastern borders of Anatolia.
2578:, which in turn alienated the empire from Rome. Militarily the Bulgars reached the walls of Constantinople, and moving troops to defend the capital allowed the Arabs to make incursions in the east. His reign ended abruptly when an army rebellion deposed him and replaced him with
2010:
when it was attacked by the Pannonian Avars and Persian forces in 626. Heraclius's continued offensives, combined with the failure to conquer Constantinople and suspected intrigues against Shahrbaraz, eventually brought about the fall of Khosrow II and the elevation of his son,
3398:
In 1081, Alexios Komnenos successfully led a coup against the government and became emperor. Alexios was a capable general and leader, but before he could deal with the situation in Anatolia, his attention was drawn westward by another Norman invasion and incursions by the
2271:(698–705). Tiberios managed to bolster the eastern frontier and reinforced the defences of Constantinople, but meanwhile Justinian was conspiring to make a comeback, and after forming an alliance with the Bulgars succeeded in taking Constantinople and executing Tiberios.
3535:
The Fourth Crusade would prove to be a grave challenge to the Byzantine Empire. The loss of a central authority figure shattered the empire, breaking it into four major successor states that each held sway over different parts of the empire. Two of these states, the
1884:. The Sassanid Empire, the largest opposing power to that of Byzantium in the region, would not make a determined effort to conquer Anatolia until the seventh century. Anatolia would occasionally receive the spillover of wars between Byzantium and Persia such as the
2061:
The loss of Egypt and Syria would prove catastrophic for the Byzantine Empire, but would dramatically heighten the importance of Anatolia. Previously, Egypt had been the main source of food and wealth for the empire, mainly due to the fertile lands watered by the
3523:. Alexios proved to be similarly incompetent and was unable to stop further advances into Anatolia by a resurgent Sultanate of Rum. In 1204, a new Byzantine state emerged in Anatolia based out of Trebizond. They were not met by any imperial response, due to the
3143:
and would see the Empire as a whole enter a new renisance and in particular would bring peace to Anatolia for the first time since the Arab conquests over the next hundred years. The first military success for the new emperor in Anatolia was the defeat of the
95:
3255:. By 975, Tzimiskes had campaigned far south into the Levant and Syria, pushing the borders away from Anatolia and extending Byzantine hegemony into Syria. Tzimiskes' strengthening of the armies also blunted the only serious attempt to take Antioch in 971.
3518:
travel through Anatolia, sacking Iconium along the way and defeating the Seljuks. Unfortunately for the Empire, Isaac was an incompetent emperor who failed to defeat his enemies and alienated those who could have been his friends. He was usurped in 1195 by
2679:
led an unsuccessful rebellion against him. Anastasius was executed. He then needed to secure the frontiers. In terms of domestic policies he embarked on a series of civil and legal reforms. The latter included a new codification in 726, referred to as the
2279:(711–713. Justinian was captured and executed as was his son and co-emperor, Tiberius (706–711), thus extinguishing the Heraclian line. Justinian had taken the Byzantine Empire yet further from his origins. He effectively abolished the historical role of
3004:, who claimed the throne. The ensuing civil war dragged on until 824, including a siege of Constantinople, when Thomas was defeated and killed. Michael continued the iconoclastic policy of Leo. After his death, he was succeeded by his son and coemperor,
1803:
2015:
in 628 CE. Within a month, Kavad surrendered to the Byzantine Empire and ordered his forces to withdraw from all Byzantine territory, including Anatolia. Heraclius had succeeded in defeating Persia and safeguarding Anatolia, but the peace was illusory.
2225:) in 680, which condemned Monotheletism. He also initiated a series of civil and military reform to cope with the shrunken and threatened empire. This was to do away with the original system of provinces with a new administrative structure based on
3211:
retook the island of Crete for the empire. This was the beginning of an era of reconquest for Byzantium and would extend its eastern frontiers to a length that had been unseen since 634. The main obstacle to Byzantine expansion was the emir of
3325:
to be captured alive. Alp Arslan was kind to Diogenes and released him eight days later, but his rivals in Constantinople moved against him. Diogenes was soon deposed, and after a brief civil war he was blinded and died. His replacement,
2801:
Irene (797–802), therefore was empress consort (775–780), empress dowager and regent (780–797) and empress regnant (797–80). As sole empress she was able to officially restore icon veneration during her regency in 787 by means of the
2567:
The years 711 to 717 were a troublesome time between the two dynasties, Heraclian and Isaurian and reflect a loss of leadership that had occurred under Justinian II, and could equally be dated from his first deposition in 695.
3552:
The 1300s would see the final end of the last Byzantine territory in Anatolia. The Nicean Empire had largely consisted of the northwestern corner of Anatolia, but these lands now came under threat from the rising power of the
3109:. This so alarmed Basil, in terms of potentially threatening the line of succession of which he was now the direct heir, that he had both Michael and Basiliskianos murdered, and ascended the throne as Basil I (867–886).
2179:(668–685 AD) had been made co-emperor in 654, and ruled in the east while his father campaigned in the west (662–668), succeeding him on the latter's death. In 646, almost immediately he had to deal with Arab attacks on
3372:. Roussel went on to attempt to create his own state in the center of Anatolia. In 1074, the empire sent an army against him led by Ioannes Doukas and Andronikos Doukas. The expedition was routed by Roussel at the
1970:
on the northwestern coast. in 617, Chalcedon itself fell. Rejecting a peace delegation sent by Heraclius, Shahin withdrew from Anatolia for the present to continue the war on other fronts, namely Egypt and Syria.
2220:
crossed the Danube and inflicted heavy losses on the Byzantine forces in 681. Faced with the uncompromising religious controversy that had perplexed his father he convened another ecumenical council, the sixth
2066:. With Egypt gone, Anatolia would become the main source of money, men, and food for the empire. Anatolia's peace was dealt a mortal blow by these staggering losses. In the late 640s under the caliph known as
3589:. In 1461, the Empire of Trebizond, the last Greek possession on Asia Minor, fell to the sultan as well. Thus came an end to Byzantine Anatolia and an end to over a millennium of Roman rule of Asia Minor.
3100:
Basil then arranged to murder Bardas in 866, and was adopted by Michael and crowned co-emperor a few months later. Michael and Basil were entangled in a complex sexual melange involving Michael's mistress
3026:, the Arab forces once again demonstrating their ability to penetrate deep into Anatolia and inflict significant losses on the Byzantine, if short lived, and vice versa. A significant Arab triumph was the
2644:
Byzantine Empire 717. 1. Ravenna 2. Venetia and Istria 3. Rome 4. Naples 5. Calabria 6. Hellas 7. Thrace 8. Opsikion 9. Thrakesion 10. Anatolikon 11. Karabisianoi 12. Armeniakon. Hatched area: Frequently
2871:(811). However he was severely wounded in the same battle in which his father died, and after much controversy regarding the succession was persuaded to abdicate later that year by his sister's husband,
1372:
3191:
In the tenth century, Byzantium gradually began regaining strength it had previously lost. On the eastern frontier, this meant a gradual pushing back of Arab power. The first major blow was struck by
2722:
iconoclastic movement in the east considerably exacerbated the rift between it and the western church. The first phase of iconoclasm coincided with the Isaurian dynasty, from the edict of Leo III to
1945:
to the Sassanid throne as Emperor, and upon his usurpation, Khosrow declared war with the casus belli of avenging Maurice. Phocas was successful in keeping the war out of Anatolia. However, in 608,
1382:
3380:. Roussell would march on Constantinople itself and attempt to set up a puppet emperor of his own, Ioannes Doukas, who had been taken prisoner at Sangarios. Turning to a Turkish mercenary named
2791:
an iconodule, resulting in a more conciliatory policy. Like his predecessors he had to defend his borders against both Arab and Bulgar, and like his father died campaigning against the Bulgars.
2054:, which they had occupied by 645. The loss of so much territory so quickly caused Heraclius to sink into depression, and he died later that year, becoming, in the judgement of English historian
2768:
in 754, followed by a concerted campaign against the iconodules and the suppression of monasteries which tended to be the centre of iconophilia. He continued his father's reorganisation of the
2307:
1990:, Heraclius engaged and defeated a Persian army under Shahrbaraz, forcing them out of Anatolia and winning a much needed victory. Heraclius was interrupted from continuing by an attack by the
3489:
Anatolia in Italy, Egypt, and the Balkans. However, he did not totally abandon Anatolia, both fortifying the border and launching limited raids into the Sultanate of Rum. By 1162, Manuel and
2899:(813) in which the Byzantines under Michael I were routed by the Bulgarians. Leo had already played a checkered role in imperial politics, rewarded by Nikephoros I for switching sides in the
2787:
Leo IV (775–780) also had to put down uprisings, in his case his half-brothers. His marriage epitomised the conflict in Byzantine society over icons, raised an iconoclast himself, he married
2264:(695–698) in 695, which deposed and exiled him, precipitating a series of events that led to a prolonged period of instability and anarchy, with seven emperors in twenty-two years.
3172:
in 882 ended in a defeat. Basil managed to make an alliance with Armenia that brought a measure of safety to the east of Asia Minor. Basil died in 886 and was succeeded by Leo VI.
2761:
between them. However Constantine managed to overcome his adversary by 743. The conflict was at least in part one over icons, Artabasdos being supported by the iconodule faction.
3267:
The Macedonian dynasty came to an end with the death of Theodora in 1059, who had no children or heirs to replace her. After a brief succession of emperors, she was replaced by
3864:
3544:, would contend for the remains of the empire in Anatolia, with the Nicean Empire holding the northwestern coast and the Trapezuntine empire holding the northeastern coast.
3390:
and the Normans had simply overwhelmed Roman capabilities to defend Anatolia from further incursion, and the 1080s would witness the near destruction of Byzantine Anatolia.
3317:. However, Arslan was much closer to the town than Diogenes anticipated, and launched a surprise attack. Owing both to this and to his appointment of the questionably loyal
3239:
The reconquest was due to several reasons. For one, the Abbasid Caliphate was in a fractured state at the time, facing multiple internal issues and the rise of the rival
4032:
2806:, although unofficially this had been the case since 781. A female head of state was not acceptable to the western church who promptly crowned an alternative emperor (
2300:
514:
1998:. For the next two years, Heraclius retreated to deal with the problem in Thrace. Returning in 624 , Heraclius renewed his offensive campaign by attacking through
419:
2122:(general) who functioned both as a commander of the Byzantine military forces in the area and a political governor of the geographic area covered by his theme.
2829:(802–811) himself died campaigning amongst the Bulgars to the north. Furthermore, Byzantium's influence continued to wane in the west with the formation of a
2772:
and embarked on aggressive and expensive foreign wars against both the Arabs and Bulgars. He died campaigning against the latter, being succeeded by his son,
1450:
1608:
476:
2753:(741–775) had a less successful reign than his father, for no sooner had he ascended the throne than he was attacked and defeated by his brother in law,
2293:
1533:
1438:
360:
2038:
began their first attacks against the frontiers of the Byzantine Empire. At first only consisting of minor raids, the Arabs won a major victory at the
3318:
1428:
3454:
The result of the First Crusade was a successful reconstruction of control over westernmost parts of Anatolia for the Byzantine Empire. However, the
3857:
4168:
3938:
3023:
1880:
were also sacked during this time, but the bulk of the carnage was confined to the easternmost part of Anatolia, as the main focus of the war was
2810:) in 800 further deepening the rift between east and west. With Irene ended the Isaurian dynasty when she was deposed by a patrician conspiracy.
4138:
3078:
2926:
2200:
3633:
3918:
1694:
as the empire gradually crumbled. The last Byzantine fortress of Philadelphia fell in 1399, and the last Byzantine presence in the area at
1352:
3472:
frontiers into central Anatolia and he was able to gain almost total control over the coasts. John was even able to launch campaigns into
3439:. The Crusaders were able to defeat the Turkish armies and open the way through Anatolia. They were assisted by a Byzantine general named
3228:, brother of Nikephoros, routed al-Dawla's armies and almost completely destroyed the Arab forces. Over the next two years, the region of
1772:. He has been called the greatest ruler of the Kingdom of Pontus. Further annexations by Rome, in particular of the Kingdom of Pontus by
3850:
2601:
1655:. Over the next two hundred and fifty years, the region suffered constant raids by Arab Muslim forces raiding mainly from the cities of
1491:
1342:
291:
2962:
The interlude of Leo V was followed by yet another short-lived dynasty, variously referred to as the Phrygian or Amorian dynasty after
3894:
3168:. However, the death of Basil's son Constantine profoundly affected the emperor, who went into a depression. A further attack against
3376:. This defeat broke the Byzantines' ability to recapture Asia Minor and would be the last army to move inland in Anatolia before the
2585:
Anastasius reversed his predecessor's religious policies and responded to Arab attacks by sea and land, this time reaching as far as
2675:
face of the chaos that had ensued from the years of civil strife. And indeed the need to do so became clear in 719 when the deposed
2593:
army) rose against him, proclaimed a new emperor and besieged Constantinople for six months, eventually forcing Anastasius to flee.
1516:
1408:
1690:. Following the retaking of Constantinople in 1261, the region gradually passed out of Byzantine control and into the hands of the
1849:, but on the whole the region would see little of the chaos that wracked other parts of the Empire during the next few centuries.
4204:
3510:. The primary source of attention for Isaac was a Bulgarian rebellion in the Balkans. The most notable event in Anatolia was the
1543:
414:
394:
3094:
4196:
3451:. Absent from their ranks, however, was Bohemond, who stayed behind in Antioch and became a rival once more to the Byzantines.
2938:
2222:
1715:
1601:
469:
41:
3175:
Leo's military record had a fairly unimpressive start. In 897, the emirate of Tarsus was able to sack the headquarters of the
356:
2112:, or "themes" in English. The exact date of this shift is unclear, but seems to have taken place during the reign of Emperor
1901:
1076:
3148:
in 873, who had been raiding western cities such as Nicaea and Ancyra. Basil's raid left only a few Paulicians in hiding at
2574:' rebellion extended beyond politics to religion, deposing the patriarch, reestablishing monothelitism and overturning the
3346:
3049:
2948:, on suspicion of conspiracy. Michael then organised the assassination of Leo, and assumed power as Michael II (820–829).
2739:
2657:
2635:
2007:
1570:
1521:
1322:
399:
3086:
2930:
4260:
4108:
4040:
3082:
2562:
1538:
1928:
37:
4309:
1418:
1206:
3052:
as regent (842–856). In 856 she was deposed from the regency with at least the acquiescence of Michael, by his uncle
2285:
3624:
Hewsen, Robert H. (2009). "Armenians on the Black Sea: The Province of Trebizond". In Richard G. Hovannisian (ed.).
2757:
who proceeded to seize the title resulting in civil war between the forces of the two emperors, who had divided the
1667:
near the Anatolian borders. However, the Byzantine Empire maintained control over the Anatolian peninsula until the
44:. It should focus on Anatolia, not the Empire as a whole except where developments impacted on the peninsula itself.
4113:
3611:
3443:
who ensured the handover of several towns to Byzantine hands. In 1098, the Crusaders made their way to Antioch and
2803:
2606:
2316:
2260:, however his land and taxation policies met with considerable opposition, eventually provoking a rebellion led by
2256:
2227:
2151:
2108:
1594:
1528:
1332:
494:
462:
434:
75:
3842:
4163:
3975:
3562:
2006:. For the next four years, Heraclius continued to push the offensive against the Persians, not even returning to
1699:
1553:
352:
322:
4123:
4103:
2727:
2575:
2051:
1777:
1641:
1637:
342:
310:
2640:
2042:
in 636. After the battle, Heraclius made the decision to withdraw his armies from Syria into Anatolia via the
2025:
1962:
defeated the Byzantines in several key battles, taking control of the southeastern part of Anatolia, known as
1785:
3899:
3704:
3423:
responded to Urban's call, arriving one by one to Constantinople. These were led by several leaders such as
3302:
2851:
2676:
2579:
1822:
376:
327:
236:
50:
3980:
3928:
3582:
3424:
3225:
2247:
2029:
1725:
1558:
569:
557:
542:
532:
2283:, merging it with emperor, thus strengthening the emperors' constitutional position as absolute monarch.
4191:
4128:
3503:
3333:
2600:(715–717) as the new emperor, and once he had overcome Anastasius was almost immediately faced with the
1846:
1838:
1834:
1814:
986:
1784:, which remained unstable for centuries, causing a series of military conflicts that culminated in the
3000:
No sooner had Michael deposed Leo, than he was confronted with revolt by a fellow military commander,
2878:
Michael I pursued more diplomatic than military solutions, however having survived the battle against
2604:(717–718), forcing him to seek assistance from the Bulgars. He in turn faced rebellion from two other
4070:
3989:
3578:
3570:
3515:
3411:
in the formation of a new kind of warfare: the crusade. Over the next two years, western armies from
3298:
3268:
3233:
3105:, and his sister Thekla. Michael also appointed, or announced he was going to appoint as co-emperor,
3061:
3017:
3005:
2896:
2704:
2669:
2649:
2619:
2571:
2482:
2276:
1959:
1857:
1152:
347:
317:
3279:. In 1064, the first major Turkish raid crossed over into Armenia and Anatolia, seizing the city of
3123:
2903:, and possibly later punished for a subsequent transgression, he had been appointed Governor of the
4219:
4214:
4178:
4044:
4027:
4017:
3541:
3520:
3428:
3361:
3306:
3221:
3176:
2945:
2819:
2512:
2500:
2494:
2399:
2387:
2208:
in the Balkans had been considered the frontier that must be defended to maintain the integrity of
2145:
2055:
1873:
1737:
1711:
1687:
1496:
1246:
976:
943:
835:
748:
424:
278:
154:
132:
125:
3368:
from the main expedition. The absence of Roussel would in part lead to the expedition's defeat at
3360:
Seljuks, but in 1073, an attempt to stabilize Anatolia would end in disaster. One of the leaders,
1982:
as well as Khosrow's refusal to accept a peace settlement, Heraclius took direct control over the
4158:
4083:
4074:
3966:
3923:
3890:
3386:
3322:
3140:
3118:
2916:
2892:
2731:
2447:
2352:
2126:
2035:
1797:
1506:
1362:
1166:
951:
227:
3301:
died with only two children who had not come to maturity to succeed him. His wife, the empress
3077:
Michael's reign included the usual wins and losses on the Arab front. However, despite Leo V's
2134:
further Arab raids. The empire simply lacked the strength to go on the offensive at this time.
4233:
4148:
4080:
3913:
3629:
3606:
3369:
3321:
who deserted him on the battlefield, Diogenes was defeated and became the first emperor since
3252:
3208:
2872:
2830:
2773:
2765:
2506:
2470:
2429:
2411:
2381:
2251:
2099:
1999:
1934:
1807:
1729:
1645:
1548:
1501:
1216:
1142:
1026:
1016:
996:
966:
503:
332:
285:
84:
4282:
4133:
4013:
3993:
3947:
3878:
3581:
both to be his vassal and to congratulate him upon his triumph. In 1453, the empire finally
3507:
3477:
3455:
3444:
3248:
3102:
2957:
2900:
2856:
2536:
2423:
2405:
2363:
2320:
2130:
2043:
2039:
1765:
1683:
1668:
1633:
1474:
1226:
1196:
1158:
658:
429:
409:
259:
218:
170:
138:
105:
3693:
3340:
humiliating Emperor Romanos IV. From a 15th-century illustrated French translation of
1841:. The Anatolian peninsula would see part of the conflict between Constantine and his rival
4228:
4173:
4058:
4049:
4021:
3961:
3566:
3537:
3490:
3459:
3447:
to it. Capturing the city in 1099, the Crusaders left Anatolia and proceeded southward to
3373:
3232:
was subjected to multiple campaigns led by Nikephoros. The campaign ended in 962 with the
3068:
3027:
3001:
2788:
2723:
2530:
2476:
2091:
2047:
2003:
1991:
1975:
1915:
1911:
1865:
1781:
1511:
1116:
1066:
1046:
1006:
865:
618:
366:
337:
252:
200:
3284:
the frontiers. By 1067, the frontiers were in bad shape and decisive action was needed.
2589:
in 714, with some success. However the very army that had placed him on the throne (the
24:
4270:
4264:
4246:
4199:
4091:
4066:
3943:
3933:
3524:
3192:
3153:
3090:
3081:
of 815, the empire was once again at war in the Balkans in 855. However the subsequent
2975:
2904:
2795:
2656:, restored order and stability to the empire, and the dynasty he founded, known as the
2597:
2518:
2488:
2464:
2435:
2348:
2342:
2213:
2176:
1983:
1853:
1769:
1741:
1679:
1660:
1314:
1086:
297:
209:
193:
3074:
During his reign important administrative reforms and reconstruction were undertaken.
4303:
4255:
4250:
4143:
3999:
3952:
3909:
3554:
3511:
3377:
3217:
3106:
3048:
Michael III however was only two years old, so effective control fell to his mother,
2825:
war on two frontiers which drained its resources, and like many of his predecessors,
2750:
2692:
2441:
2325:
2103:
2067:
1691:
1675:
1584:
1486:
1176:
452:
2992:
2921:
Leo's first task was to deal with the Bulgarian situation, who now occupied most of
2779:
2548:
Thrace and Macedonia were counted among the Eastern themes for hierarchical purposes
4278:
4243:
4209:
4153:
4062:
4009:
3971:
3957:
3874:
3272:
3152:, which was soon smashed in 879. Basil also campaigned against the Arab emirate of
2846:
2826:
2268:
2236:
2102:, the Byzantine Empire shifted its armies away from the classical structure of the
1877:
1826:
1286:
1256:
1106:
265:
3565:
attempted to retake parts of Anatolia with the assistance of mercenaries from the
2907:
from which he was able to orchestrate Michael's downfall and his own succession.
4288:
4238:
4186:
4118:
4054:
3327:
3165:
3132:
3043:
3031:
2855:
suffered a major defeat at the Battle of Krasos in Phrygia in 805 and died on a
2834:
2807:
2735:
2524:
2243:
2113:
1979:
1889:
1885:
1802:
1745:
1652:
1479:
1186:
1134:
708:
371:
2137:
1974:
In 622 AD, driven to desperation by shocking failures to hold onto classically
4095:
3985:
3337:
3314:
3276:
3161:
3149:
3145:
3071:
lost no time in putting an end to the iconoclastic movement once and for all.
2987:
2963:
2868:
2754:
2615:
2611:
2356:
2075:
2063:
1987:
1955:
1942:
1906:
1757:
1753:
1733:
1674:
The Byzantine Empire re-established control over parts of Anatolia during the
1296:
1266:
668:
589:
524:
112:
2116:. Anatolia was reorganized into several themes. Each theme was governed by a
4181:
3684:
Jenkins, Romilly (1966). Byzantium The Imperial centuries AD 610–1071. p. 56
3586:
3574:
3448:
3436:
3400:
3381:
3341:
3310:
2715:
2375:
2250:
in 692. Theologically he pursued non-orthodox thinking and convened another
2242:
Justinian was an ambitious ruler eager to emulate his illustrious ancestor,
2184:
2118:
1967:
1946:
1761:
1648:
1276:
1096:
956:
404:
4224:
4004:
3440:
3416:
3408:
3365:
3196:
3180:
3169:
2925:
and were blockading Constantinople. Eventually he was able to conclude a
2711:
2590:
2417:
2369:
2261:
2188:
2156:
2095:
2012:
1950:
1842:
1764:
region, waging several hard-fought but ultimately unsuccessful wars (the
1749:
1695:
1625:
1236:
1036:
816:
678:
608:
3904:
3558:
3404:
3240:
3229:
3136:
3089:. A new threat emerged further north in 860 with the appearance of the
2971:
2967:
2653:
2586:
2393:
2217:
2192:
2180:
2087:
2071:
1963:
1881:
1869:
1861:
1656:
1056:
845:
825:
758:
738:
698:
648:
638:
628:
2764:
Under Constantine, Iconoclasm became further entrenched following the
2231:(themes), the remaining parts of Anatolia being divided amongst seven
1671:(years 1080s), when imperial authority in the area began to collapse.
4100:
4088:
3412:
3213:
3053:
2922:
2682:
2280:
2209:
2205:
1995:
1938:
1773:
1664:
1629:
1400:
905:
875:
798:
728:
688:
3728:
Jenkins (1966). Byzantium The Imperial centuries AD 610-1071. p. 128
2730:(Seventh Ecumenical Council) in 787. Iconoclasm was then revived by
2622:(717–741) bringing an end to the cycle of violence and instability.
3827:
Treadgold. A History of the Byzantine State and Society. p. 941-944
3675:
Treadgold. A History of the Byzantine State and Society. p. 428-433
3657:
Treadgold. A History of the Byzantine State and Society. p. 401-409
3648:
Treadgold. A History of the Byzantine State and Society. p. 396-401
2046:. This opened the way for the forces of the Caliphate to take over
3473:
3420:
3332:
3220:. At first, al-Dawla was able to contain Byzantine forces until a
3157:
2196:
1905:
1818:
1801:
925:
915:
895:
885:
855:
788:
778:
768:
718:
2867:
On Nikephoros' death, he was succeeded by his son and coemperor,
4037:
3818:
John Julius Norwich. Byzantium: The Decline and Fall. P. 134-137
3809:
John Julius Norwich. Byzantium: The Decline and Fall. P. 124-126
3800:
Anthony Kaldellis. Streams of Gold, Rivers of Blood. P. 253-259.
3746:
Anthony Kaldellis. Streams of Gold, Rivers of Blood. p. 141-143.
2879:
2267:
Leontios proved equally unpopular and was in turn overthrown by
1810:
598:
3846:
3836:
John Julius Norwich. Byzantium: The Decline and Fall. P 346-347
3755:
Treadgold. A History of the Byzantine State and Society. P. 808
3364:, a Norman, led a group of his fellow mercenaries away east to
2289:
1941:. Maurice had previously been instrumental in the accession of
1682:, Anatolia became the heartland of the successor states of the
1636:. Anatolia was of vital importance to the empire following the
3737:
Anthony Kaldellis. Streams of Gold, Rivers of Blood. p. 75-78.
3502:
The Komnenian dynasty came to an end in 1186 with the fall of
3280:
1986:
and began to pursue an offensive strategy. Leading his men to
18:
3719:
Jenkins. Byzantium The Imperial Centuries AD 610-1071. p. 117
3628:. Costa Mesa, CA: Mazda Publishers, Inc. pp. 41, 37–66.
3275:
had coalesced into a powerful force united under the sultan
3056:, who became very influential, and was eventually appointed
1833:
Anatolia's prosperity largely continued during the reign of
3782:
Anthony Kaldellis. Streams of Gold, Rivers of Blood. P. 251
2199:(670), as well as Smyrna and other coastal cities, finally
3313:
from the Seljuks with the intent of defeating the Sultan,
3271:. To the east, a new threat had slowly been emerging. The
2254:
in 692. Domestically he continued the organisation of the
3139:
the Macedonian in 867. Basil's dynasty would be known as
3030:
in 838. When he died in 842, he was succeeded by his son
3330:, was seen as a weak emperor who was unfit for the job.
3085:
and the peace of 864 brought a long lasting lull in the
2626:
struggles within the Arab world enabled this situation.
2070:, the Arabs launched raids into Anatolia, advancing to
46:
3764:
Kaldellis. Streams of Gold, Rivers of Blood p. 232-235
3247:
In 969, Nikephoros was overthrown by his subordinate,
1678:, and following the sack of Constantinople during the
40:, as currently, the article is a very poor variant of
2944:
His downfall was the jailing of one of his generals,
2891:
The Nikephorian dynasty was overthrown by a general,
1892:, but the region would never be directly threatened.
3626:
Armenian Pontus: The Trebizond-Black Sea Communities
2456:
2334:
2235:. When he died in 668 he was succeeded by his son,
3773:Kaldellis. Streams of Gold, Rivers of Blood p. 238
2171:The first siege of Constantinople and Justinian II
3531:The Fourth Crusade and Byzantine successor states
3498:The Angeloi and disintegration of Byzantine power
2086:Constantly menaced by the Arabs to the east, the
1852:The first major disruption of this peace was the
3022:Theophilus was now faced with a flare-up of the
2783:Asia Minor 780 showing administrative boundaries
2618:in 717, and chose to resign, being succeeded by
1780:, except for the southeastern frontier with the
3394:The Komnenian Restoration and the First Crusade
1966:and eventually opening the way to lay siege to
16:History of Anatolia under the Byzantine Empire
3858:
3244:Byzantines time to assemble a powerful army.
3038:The demise of iconoclasm: Michael III 842–867
2734:, and it persisted until 842 in the reign of
2301:
2141:Territories of the Byzantine Empire in 650 AD
2050:by the year 638 In 641, the Arabs began the
1896:Heraclian dynasty and the Barbarian invasions
1602:
470:
8:
3709:Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2011.
3083:conversion of the Bulgarians to Christianity
2937:emperors. He made this official through the
1768:) to break Roman dominion over Asia and the
3707:Byzantium in the Iconoclast Era, c. 680-850
3028:sacking of the dynastic homeland of Amorium
3865:
3851:
3843:
3060:that year. Another influential figure was
2308:
2294:
2286:
2239:(685–695, 705–711), co-emperor since 681.
1756:region. Mithridates VI sought to dominate
1732:in northern Anatolia, otherwise known as "
1609:
1595:
488:
477:
463:
69:
2895:(813–820), suspected of treachery in the
2557:The non-dynastic years of anarchy 711–717
2034:In 633, the Arab Muslim forces under the
1994:, who threatened the empire's holding in
1792:From Constantine to Phocas: 324 to 602 AD
3427:. The most important, however, would be
3288:The Battle of Manzikert and the Crusades
3122:
2991:
2778:
2639:
2144:
2136:
3598:
3355:The Crisis of the Normans and the Turks
1937:was overthrown by the usurper known as
1821:together with Christian bishops at the
502:
491:
83:
72:
3484:Manuel and the Battle of Myriokephalon
2191:. This was followed by the capture of
1798:Classical Anatolia § Roman period
1748:in order to halt the advance of Roman
7:
4174:Palestine (Classical ~ Late Antique)
3666:Norwich: Byzantium: The Early Years.
3156:in the same year, defeating them at
2660:, was to last for nearly a century.
2630:Iconoclasm: Isaurian dynasty 717–802
2602:Second Arab siege of Constantinople
2082:Introduction of the thematic system
2002:into the Sassanid heartland of the
4114:Lebanon (Classical ~ Late Antique)
2952:Phrygian (Amorian) dynasty 820–867
2745:
14:
4050:Israel (Classical ~ Late Antique)
3458:remained on the plateau, and the
2862:
2275:long he faced a rebellion led by
1933:In 602 AD, the Byzantine Emperor
1157:(330–1453; 1204-1261 in exile as
36:to comply with Knowledge (XXG)'s
4239:Syria (Classical ~ Late Antique)
3981:Egypt (Classical ~ Late Antique)
3694:Encyclopædia Britannica: Leo III
3135:"the Drunkard", was murdered by
2718:) or εἰκονόφιλοι (iconophiles).
2058:, "the man who lived too long."
1864:was sacked by the forces of the
1776:, brought all of Anatolia under
1578:
1121:224–651 AD (briefly in Anatolia)
513:
446:
94:
23:
3195:and his sacking of the city of
3067:Theodora, like her predecessor
2887:Leo V and the Phrygians 820–867
2857:campaign against the Bulgarians
2223:Third Council of Constantinople
2125:These thematic troops utilized
1872:. Several other cities such as
1716:History of the Byzantine Empire
42:History of the Byzantine Empire
2875:(811–813), who succeeded him.
2863:Nikephoros' successors 811–813
1902:Byzantium under the Heraclians
977:Kingdom of Alexander the Great
1:
3548:The end of Byzantine Anatolia
3347:De Casibus Virorum Illustrium
3305:, married a disgraced noble,
2160:
2106:to a new system known as the
1910:Arab Muslim invasions in the
547:
175:
159:
143:
3561:. Additionally, the emperor
3127:The Byzantine Empire, c. 867
2563:The Years of Anarchy 711-717
3705:L. Brubaker and J. Haldon,
3431:, an old rival of Alexios.
3113:Macedonian dynasty 867–1056
2814:Nikephorian dynasty 802–813
2686:, which unlike Justinian's
1949:, the son of a governor of
1624:refers to the peninsula of
1492:Ancient peoples of Anatolia
1207:Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia
4326:
3131:The last Amorian emperor,
3116:
3079:treaty with the Bulgarians
3041:
3015:
2985:
2955:
2914:
2844:
2817:
2804:Seventh Ecumenical Council
2702:
2667:
2652:(717–741), a general from
2633:
2596:The troops had proclaimed
2560:
2457:Western or European themes
2252:council in Constantinople.
2023:
1926:
1899:
1795:
1709:
3886:
3577:, who forced the emperor
2966:, who like Leo came from
2939:Council of Constantinople
2738:(842–867) and regency of
2546:
2094:to the north, and by the
1632:) during the rule of the
1373:Decline and modernization
1323:Periods of Ottoman Empire
266:Frankish and Latin states
2931:Byzantine–Bulgarian wars
2746:Leo's successors 741–802
2728:Second Council of Nicaea
2576:Sixth Ecumenical Council
2201:attacking Constantinople
2052:Muslim invasion of Egypt
1740:, waged war against the
1644:during the reign of the
1638:Muslim invasion of Syria
1628:(located in present-day
343:Second Hellenic Republic
53:may contain suggestions.
34:may need to be rewritten
3612:Encyclopædia Britannica
3476:, echoing his namesake
3303:Eudokia Makrembolitissa
2794:When Leo died his son,
2335:Eastern or Asian themes
1929:Byzantine–Sasanian wars
1923:Byzantine–Sasanian wars
1825:in 325 CE, holding the
1823:First Council of Nicaea
1698:ended in 1461 with the
377:Third Hellenic Republic
357:Collaborationist regime
328:First Hellenic Republic
292:Venetian Ionian Islands
4096:Late Antique/Medieval)
3939:Bosnia and Herzegovina
3607:Mithradates VI Eupator
3585:to the Ottomans under
3425:Raymond IV of Toulouse
3351:
3226:Leo Phokas the Younger
3128:
2997:
2974:), the capital of the
2929:, to the long-running
2831:new empire in the west
2784:
2646:
2248:Battle of Sebastopolis
2167:
2142:
2030:Early Muslim conquests
1919:
1830:
1726:Mithridates VI Eupator
1544:Constitutional history
1429:Provisional government
1383:Defeat and dissolution
533:Prehistory of Anatolia
3881:in modern territories
3506:. He was replaced by
3504:Andronikos I Komnenos
3336:
3297:In 1068, the emperor
3160:and continuing on to
3126:
2995:
2782:
2643:
2148:
2140:
2020:Arab Muslim invasions
2008:defend Constantinople
1909:
1860:. The border city of
1847:Battle of Chrysopolis
1835:Constantine the Great
1815:Constantine the Great
1805:
1651:in the years 634–645
987:Kingdom of Cappadocia
543:Palaeolithic Anatolia
3516:Frederick Barbarossa
3385:sent a new general,
3299:Constantine X Doukas
3269:Constantine X Doukas
3263:Prelude to Manzikert
3234:Sack of Aleppo (962)
3207:In 961, the general
3062:Basil the Macedonian
2897:Battle of Versinicia
2841:Nikephoros I 802–811
2705:Byzantine iconoclasm
2277:Philippikos Bardanes
1858:Anastasius I Dicorus
1856:during the reign of
1153:Eastern Roman Empire
348:4th of August Regime
318:Septinsular Republic
4071:Sardinia (Classical
3944:Bulgaria (Classical
3542:Empire of Trebizond
3521:Alexios III Angelos
3429:Bohemond of Taranto
3362:Roussel de Bailleul
3307:Romanos IV Diogenes
3203:Reconquest 961-1025
3177:Theme of Cappadocia
3095:Rus'–Byzantine wars
3024:Byzantine–Arab wars
2946:Michael the Amorian
2927:peace treaty in 815
2820:Nikephorian dynasty
2056:John Julius Norwich
2026:Arab–Byzantine wars
1786:Roman–Parthian Wars
1738:Classical antiquity
1712:History of Anatolia
1688:Empire of Trebizond
1497:History of Anatolia
1419:War of Independence
1247:Empire of Trebizond
1111:133 BC-27 BC–330 AD
558:Mesolithic Anatolia
323:War of Independence
279:Early modern Greece
133:Helladic chronology
4310:Byzantine Anatolia
3990:Corsica (Classical
3910:Armenia (Classical
3891:Albania (Classical
3514:, which witnessed
3387:Alexios I Komnenos
3352:
3141:Macedonian Dynasty
3129:
3119:Macedonian dynasty
3012:Theophilus 829–842
2998:
2982:Michael II 820–829
2837:(800–814) in 800.
2785:
2647:
2168:
2143:
2127:asymmetric warfare
2036:Rashidun Caliphate
1920:
1831:
1788:(54 BC – 217 AD).
1622:Byzantine Anatolia
1539:Diplomatic history
1451:Multi-party period
1401:Republic of Turkey
1177:Great Seljuk State
1167:Rashidun Caliphate
952:Classical Anatolia
570:Neolithic Anatolia
228:Hellenistic Greece
4297:
4296:
4279:Thrace (Classical
4271:Turkey (Classical
4063:Sicily (Classical
4010:Greece (Classical
3972:Cyprus (Classical
3958:Crimea (Classical
3953:Britain (England)
3791:Çoban 2020, p. 51
3635:978-1-56859-155-1
3571:Philadelphia fell
3319:Andronikos Doukas
3253:Fatimid Caliphate
3222:disastrous ambush
3209:Nikephoros Phokas
2766:Council of Hieria
2714:), εἰκονόδουλοι (
2699:Iconclasm 730–842
2553:
2552:
2430:Cibyrrhaeot Theme
2382:Bucellarian Theme
2100:Italian Peninsula
1730:Kingdom of Pontus
1700:fall of Trebizond
1646:Byzantine Emperor
1619:
1618:
1585:Turkey portal
1502:History of Thrace
1459:
1458:
1409:Periods of Turkey
1391:
1390:
1305:
1304:
1217:Anatolian beyliks
1143:Medieval Anatolia
1125:
1124:
1027:Kingdom of Pontus
1017:Ptolemaic Kingdom
967:Achaemenid Empire
934:
933:
807:
806:
580:
579:
487:
486:
453:Greece portal
333:Kingdom of Greece
241:
232:
223:
214:
205:
182:
166:
150:
68:
67:
38:quality standards
4317:
4225:Spain (Classical
4055:Italy (Classical
4018:Crete (Classical
3879:Byzantine Empire
3867:
3860:
3853:
3844:
3837:
3834:
3828:
3825:
3819:
3816:
3810:
3807:
3801:
3798:
3792:
3789:
3783:
3780:
3774:
3771:
3765:
3762:
3756:
3753:
3747:
3744:
3738:
3735:
3729:
3726:
3720:
3717:
3711:
3702:
3696:
3691:
3685:
3682:
3676:
3673:
3667:
3664:
3658:
3655:
3649:
3646:
3640:
3639:
3621:
3615:
3603:
3508:Isaac II Angelos
3478:John I Tzimiskes
3467:John II Komnenos
3456:Sultanate of Rum
3249:John I Tzimiskes
3187:Ending the raids
3103:Eudokia Ingerina
2958:Phrygian dynasty
2636:Isaurian dynasty
2364:Thracesian Theme
2321:Byzantine Empire
2310:
2303:
2296:
2287:
2165:
2162:
2131:guerilla warfare
2044:Taurus Mountains
2040:Battle of Yarmuk
1766:Mithridatic Wars
1684:Empire of Nicaea
1669:High Middle Ages
1634:Byzantine Empire
1611:
1604:
1597:
1583:
1582:
1581:
1549:Cultural history
1534:Military history
1529:Economic history
1475:Turkic migration
1439:One-party period
1415:
1414:
1329:
1328:
1227:County of Edessa
1197:Sultanate of Rum
1159:Empire of Nicaea
1149:
1148:
963:
962:
957:Classical Thrace
822:
821:
659:Achaeans (Homer)
595:
594:
562:c. 11,000–
549:
539:
538:
517:
507:
489:
479:
472:
465:
451:
450:
449:
389:History by topic
260:Byzantine Greece
239:
230:
221:
219:Classical Greece
212:
204:(1100 BC–750 BC)
203:
180:
179: 1750–1050
177:
173:
164:
163: 3100–1100
161:
157:
148:
147: 3100–1000
145:
141:
126:Greek Bronze Age
106:Neolithic Greece
98:
88:
70:
63:
60:
54:
27:
19:
4325:
4324:
4320:
4319:
4318:
4316:
4315:
4314:
4300:
4299:
4298:
4293:
4251:Early Medieval)
4164:The Netherlands
4075:Early Medieval)
3994:Early Medieval)
3882:
3873:History of the
3871:
3841:
3840:
3835:
3831:
3826:
3822:
3817:
3813:
3808:
3804:
3799:
3795:
3790:
3786:
3781:
3777:
3772:
3768:
3763:
3759:
3754:
3750:
3745:
3741:
3736:
3732:
3727:
3723:
3718:
3714:
3703:
3699:
3692:
3688:
3683:
3679:
3674:
3670:
3665:
3661:
3656:
3652:
3647:
3643:
3636:
3623:
3622:
3618:
3604:
3600:
3595:
3567:Catalan Company
3550:
3538:Empire of Nicea
3533:
3500:
3491:Kilij Arslan II
3486:
3469:
3460:Crusader States
3396:
3374:Sangarios River
3357:
3295:
3290:
3265:
3224:by the general
3205:
3189:
3121:
3115:
3093:and subsequent
3046:
3040:
3020:
3014:
3002:Thomas the Slav
2990:
2984:
2960:
2954:
2919:
2913:
2889:
2865:
2849:
2843:
2822:
2816:
2748:
2707:
2701:
2672:
2666:
2664:Leo III 717–741
2638:
2632:
2565:
2559:
2554:
2549:
2542:
2531:Cherson/Klimata
2452:
2330:
2314:
2183:in Phrygia and
2175:Constans's son
2173:
2163:
2092:Pannonian Avars
2084:
2048:Byzantine Syria
2032:
2024:Main articles:
2022:
2004:Persian Plateau
1992:Pannonian Avars
1976:Roman provinces
1931:
1925:
1916:Byzantine Syria
1912:Sassanid Empire
1904:
1898:
1866:Sassanid Empire
1800:
1794:
1782:Parthian Empire
1744:in the year 88
1728:, ruler of the
1723:
1718:
1710:Main articles:
1708:
1615:
1579:
1577:
1565:
1564:
1563:
1554:Genetic history
1469:
1461:
1460:
1444:
1413:
1403:
1393:
1392:
1327:
1317:
1307:
1306:
1147:
1137:
1127:
1126:
1117:Sasanian Empire
1077:Armenian Empire
1067:Parthian Empire
1047:Attalid kingdom
1007:Seleucid Empire
961:
946:
936:
935:
819:
809:
808:
619:Akkadian Empire
592:
582:
581:
575:
574:c. 8,000–
563:
551:
537:
527:
505:
498:
483:
447:
445:
440:
439:
390:
382:
381:
353:Axis occupation
338:National Schism
313:
303:
302:
294:
288:
281:
271:
270:
262:
255:
253:Medieval Greece
245:
244:
240:(146 BC–330 AD)
233:
224:
222:(500 BC–323 BC)
215:
213:(800 BC–480 BC)
206:
201:Greek Dark Ages
196:
186:
185:
178:
167:
162:
151:
146:
135:
128:
118:
117:
108:
86:
79:
64:
58:
55:
45:
28:
17:
12:
11:
5:
4323:
4321:
4313:
4312:
4302:
4301:
4295:
4294:
4292:
4291:
4286:
4268:
4265:Roman Carthage
4258:
4253:
4241:
4236:
4231:
4222:
4217:
4212:
4207:
4202:
4194:
4189:
4184:
4176:
4171:
4166:
4161:
4156:
4151:
4146:
4141:
4136:
4131:
4126:
4121:
4116:
4111:
4106:
4098:
4086:
4078:
4052:
4047:
4035:
4030:
4025:
4007:
4002:
3997:
3983:
3978:
3969:
3964:
3955:
3950:
3948:High Medieval)
3941:
3936:
3931:
3926:
3921:
3916:
3907:
3902:
3897:
3887:
3884:
3883:
3872:
3870:
3869:
3862:
3855:
3847:
3839:
3838:
3829:
3820:
3811:
3802:
3793:
3784:
3775:
3766:
3757:
3748:
3739:
3730:
3721:
3712:
3697:
3686:
3677:
3668:
3659:
3650:
3641:
3634:
3616:
3597:
3596:
3594:
3591:
3573:to the sultan
3549:
3546:
3532:
3529:
3525:Fourth Crusade
3499:
3496:
3485:
3482:
3468:
3465:
3395:
3392:
3356:
3353:
3294:
3291:
3289:
3286:
3264:
3261:
3204:
3201:
3193:John Kourkouas
3188:
3185:
3117:Main article:
3114:
3111:
3087:Bulgarian wars
3042:Main article:
3039:
3036:
3016:Main article:
3013:
3010:
2986:Main article:
2983:
2980:
2976:Anatolic Theme
2956:Main article:
2953:
2950:
2915:Main article:
2912:
2909:
2905:Anatolic theme
2888:
2885:
2864:
2861:
2845:Main article:
2842:
2839:
2818:Main article:
2815:
2812:
2796:Constantine VI
2747:
2744:
2703:Main article:
2700:
2697:
2668:Main article:
2665:
2662:
2634:Main article:
2631:
2628:
2598:Theodosius III
2561:Main article:
2558:
2555:
2551:
2550:
2547:
2544:
2543:
2541:
2540:
2533:
2527:
2521:
2515:
2509:
2503:
2497:
2491:
2485:
2479:
2473:
2467:
2460:
2458:
2454:
2453:
2451:
2450:
2444:
2438:
2432:
2426:
2420:
2414:
2408:
2402:
2396:
2390:
2384:
2378:
2372:
2370:Opsician Theme
2366:
2360:
2349:Armeniac Theme
2345:
2343:Anatolic Theme
2338:
2336:
2332:
2331:
2315:
2313:
2312:
2305:
2298:
2290:
2204:long time the
2177:Constantine IV
2172:
2169:
2083:
2080:
2021:
2018:
1984:Byzantine army
1927:Main article:
1924:
1921:
1900:Main article:
1897:
1894:
1862:Theodosiopolis
1854:Anastasian War
1839:his successors
1796:Main article:
1793:
1790:
1770:Hellenic world
1742:Roman Republic
1722:
1719:
1707:
1704:
1680:Fourth Crusade
1617:
1616:
1614:
1613:
1606:
1599:
1591:
1588:
1587:
1574:
1573:
1567:
1566:
1562:
1561:
1556:
1551:
1546:
1541:
1536:
1531:
1526:
1525:
1524:
1519:
1514:
1504:
1499:
1494:
1489:
1484:
1483:
1482:
1471:
1470:
1467:
1466:
1463:
1462:
1457:
1456:
1455:(1945–present)
1453:
1447:
1446:
1441:
1435:
1434:
1431:
1425:
1424:
1421:
1412:
1411:
1405:
1404:
1399:
1398:
1395:
1394:
1389:
1388:
1385:
1379:
1378:
1375:
1369:
1368:
1365:
1359:
1358:
1355:
1353:Transformation
1349:
1348:
1345:
1339:
1338:
1335:
1326:
1325:
1319:
1318:
1313:
1312:
1309:
1308:
1303:
1302:
1299:
1293:
1292:
1289:
1283:
1282:
1279:
1273:
1272:
1269:
1263:
1262:
1259:
1253:
1252:
1249:
1243:
1242:
1239:
1233:
1232:
1229:
1223:
1222:
1219:
1213:
1212:
1209:
1203:
1202:
1199:
1193:
1192:
1189:
1183:
1182:
1179:
1173:
1172:
1169:
1163:
1162:
1155:
1146:
1145:
1139:
1138:
1133:
1132:
1129:
1128:
1123:
1122:
1119:
1113:
1112:
1109:
1103:
1102:
1099:
1093:
1092:
1089:
1087:Roman Republic
1083:
1082:
1079:
1073:
1072:
1069:
1063:
1062:
1059:
1053:
1052:
1049:
1043:
1042:
1039:
1033:
1032:
1029:
1023:
1022:
1019:
1013:
1012:
1009:
1003:
1002:
999:
993:
992:
989:
983:
982:
979:
973:
972:
969:
960:
959:
954:
948:
947:
942:
941:
938:
937:
932:
931:
928:
922:
921:
918:
912:
911:
910:859–595/585 BC
908:
902:
901:
898:
892:
891:
888:
882:
881:
878:
872:
871:
868:
862:
861:
858:
852:
851:
848:
842:
841:
838:
832:
831:
828:
820:
815:
814:
811:
810:
805:
804:
803:859–595/585 BC
801:
795:
794:
791:
785:
784:
781:
775:
774:
771:
765:
764:
761:
755:
754:
751:
745:
744:
741:
735:
734:
731:
725:
724:
721:
715:
714:
711:
705:
704:
701:
695:
694:
691:
685:
684:
681:
675:
674:
671:
665:
664:
661:
655:
654:
651:
645:
644:
641:
635:
634:
631:
625:
624:
621:
615:
614:
611:
605:
604:
601:
593:
588:
587:
584:
583:
578:
577:
572:
566:
565:
560:
554:
553:
550:500,000–
545:
536:
535:
529:
528:
523:
522:
519:
518:
510:
509:
500:
499:
492:
485:
484:
482:
481:
474:
467:
459:
456:
455:
442:
441:
438:
437:
432:
427:
422:
417:
412:
407:
402:
397:
391:
388:
387:
384:
383:
380:
379:
374:
372:Military Junta
369:
364:
350:
345:
340:
335:
330:
325:
320:
314:
309:
308:
305:
304:
301:
300:
298:Ottoman Greece
295:
289:
286:Venetian Crete
282:
277:
276:
273:
272:
269:
268:
263:
256:
251:
250:
247:
246:
243:
242:
234:
231:(323 BC–31 BC)
225:
216:
210:Archaic Greece
207:
197:
194:Ancient Greece
192:
191:
188:
187:
184:
183:
168:
152:
136:
129:
124:
123:
120:
119:
116:
115:
109:
104:
103:
100:
99:
91:
90:
81:
80:
73:
66:
65:
31:
29:
22:
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
4322:
4311:
4308:
4307:
4305:
4290:
4287:
4284:
4280:
4276:
4272:
4269:
4266:
4262:
4259:
4257:
4254:
4252:
4248:
4245:
4242:
4240:
4237:
4235:
4232:
4230:
4229:Late Antique)
4226:
4223:
4221:
4218:
4216:
4213:
4211:
4208:
4206:
4203:
4201:
4198:
4195:
4193:
4190:
4188:
4185:
4183:
4180:
4177:
4175:
4172:
4170:
4167:
4165:
4162:
4160:
4157:
4155:
4152:
4150:
4147:
4145:
4142:
4140:
4137:
4135:
4132:
4130:
4127:
4125:
4124:Liechtenstein
4122:
4120:
4117:
4115:
4112:
4110:
4107:
4105:
4102:
4099:
4097:
4093:
4090:
4087:
4085:
4082:
4079:
4076:
4072:
4068:
4064:
4060:
4056:
4053:
4051:
4048:
4046:
4042:
4039:
4036:
4034:
4031:
4029:
4026:
4023:
4019:
4015:
4011:
4008:
4006:
4003:
4001:
3998:
3995:
3991:
3987:
3984:
3982:
3979:
3977:
3973:
3970:
3968:
3965:
3963:
3959:
3956:
3954:
3951:
3949:
3945:
3942:
3940:
3937:
3935:
3932:
3930:
3927:
3925:
3922:
3920:
3917:
3915:
3914:Late Antique)
3911:
3908:
3906:
3903:
3901:
3898:
3896:
3892:
3889:
3888:
3885:
3880:
3876:
3868:
3863:
3861:
3856:
3854:
3849:
3848:
3845:
3833:
3830:
3824:
3821:
3815:
3812:
3806:
3803:
3797:
3794:
3788:
3785:
3779:
3776:
3770:
3767:
3761:
3758:
3752:
3749:
3743:
3740:
3734:
3731:
3725:
3722:
3716:
3713:
3710:
3708:
3701:
3698:
3695:
3690:
3687:
3681:
3678:
3672:
3669:
3663:
3660:
3654:
3651:
3645:
3642:
3637:
3631:
3627:
3620:
3617:
3614:
3613:
3608:
3602:
3599:
3592:
3590:
3588:
3584:
3580:
3576:
3572:
3568:
3564:
3563:Andronikos II
3560:
3556:
3555:Ottoman Turks
3547:
3545:
3543:
3539:
3530:
3528:
3526:
3522:
3517:
3513:
3512:Third Crusade
3509:
3505:
3497:
3495:
3492:
3483:
3481:
3479:
3475:
3466:
3464:
3461:
3457:
3452:
3450:
3446:
3442:
3438:
3432:
3430:
3426:
3422:
3418:
3414:
3410:
3406:
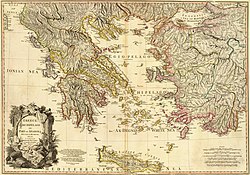
3402:
3393:
3391:
3388:
3383:
3379:
3378:First Crusade
3375:
3371:
3367:
3363:
3354:
3349:
3348:
3343:
3339:
3335:
3331:
3329:
3324:
3320:
3316:
3312:
3308:
3304:
3300:
3292:
3287:
3285:
3282:
3278:
3274:
3270:
3262:
3260:
3256:
3254:
3250:
3245:
3242:
3237:
3235:
3231:
3227:
3223:
3219:
3218:Sayf al-Dawla
3215:
3210:
3202:
3200:
3198:
3194:
3186:
3184:
3182:
3178:
3173:
3171:
3167:
3163:
3159:
3155:
3151:
3147:
3142:
3138:
3134:
3125:
3120:
3112:
3110:
3108:
3107:Basiliskianos
3104:
3098:
3096:
3092:
3088:
3084:
3080:
3075:
3072:
3070:
3065:
3063:
3059:
3055:
3051:
3045:
3037:
3035:
3033:
3029:
3025:
3019:
3011:
3009:
3007:
3003:
2994:
2989:
2981:
2979:
2977:
2973:
2969:
2965:
2959:
2951:
2949:
2947:
2942:
2940:
2934:
2932:
2928:
2924:
2918:
2911:Leo V 813–820
2910:
2908:
2906:
2902:
2901:803 civil war
2898:
2894:
2886:
2884:
2881:
2876:
2874:
2870:
2860:
2858:
2853:
2848:
2840:
2838:
2836:
2832:
2828:
2821:
2813:
2811:
2809:
2805:
2799:
2797:
2792:
2790:
2781:
2777:
2775:
2771:
2767:
2762:
2760:
2756:
2752:
2751:Constantine V
2743:
2741:
2737:
2733:
2729:
2725:
2719:
2717:
2713:
2706:
2698:
2696:
2694:
2693:Constantine V
2689:
2685:
2684:
2678:
2677:Anastasius II
2671:
2663:
2661:
2659:
2655:
2651:
2642:
2637:
2629:
2627:
2623:
2621:
2617:
2613:
2609:
2608:
2603:
2599:
2594:
2592:
2588:
2583:
2581:
2580:Anastasius II
2577:
2573:
2569:
2564:
2556:
2545:
2538:
2534:
2532:
2528:
2526:
2522:
2520:
2516:
2514:
2510:
2508:
2504:
2502:
2498:
2496:
2492:
2490:
2486:
2484:
2480:
2478:
2474:
2472:
2468:
2466:
2462:
2461:
2459:
2455:
2449:
2445:
2443:
2439:
2437:
2433:
2431:
2427:
2425:
2421:
2419:
2415:
2413:
2409:
2407:
2403:
2401:
2397:
2395:
2391:
2389:
2385:
2383:
2379:
2377:
2373:
2371:
2367:
2365:
2361:
2358:
2354:
2350:
2346:
2344:
2340:
2339:
2337:
2333:
2328:
2327:
2326:De Thematibus
2323:according to
2322:
2318:
2311:
2306:
2304:
2299:
2297:
2292:
2291:
2288:
2284:
2282:
2278:
2272:
2270:
2265:
2263:
2259:
2258:
2253:
2249:
2245:
2240:
2238:
2234:
2230:
2229:
2224:
2219:
2215:
2211:
2207:
2202:
2198:
2194:
2190:
2186:
2182:
2178:
2170:
2164: 750 AD
2158:
2154:
2153:
2147:
2139:
2135:
2132:
2128:
2123:
2121:
2120:
2115:
2111:
2110:
2105:
2104:Roman legions
2101:
2097:
2093:
2089:
2081:
2079:
2077:
2073:
2069:
2065:
2059:
2057:
2053:
2049:
2045:
2041:
2037:
2031:
2027:
2019:
2017:
2014:
2009:
2005:
2001:
1997:
1993:
1989:
1985:
1981:
1977:
1972:
1969:
1965:
1961:
1957:
1952:
1948:
1944:
1940:
1936:
1930:
1922:
1917:
1913:
1908:
1903:
1895:
1893:
1891:
1887:
1883:
1879:
1875:
1871:
1867:
1863:
1859:
1855:
1850:
1848:
1844:
1840:
1836:
1828:
1824:
1820:
1816:
1813:representing
1812:
1809:
1804:
1799:
1791:
1789:
1787:
1783:
1779:
1778:Roman control
1775:
1771:
1767:
1763:
1759:
1755:
1751:
1747:
1743:
1739:
1735:
1731:
1727:
1720:
1717:
1713:
1705:
1703:
1701:
1697:
1693:
1692:Ottoman Turks
1689:
1685:
1681:
1677:
1676:First Crusade
1672:
1670:
1666:
1662:
1658:
1654:
1650:
1647:
1643:
1639:
1635:
1631:
1627:
1623:
1612:
1607:
1605:
1600:
1598:
1593:
1592:
1590:
1589:
1586:
1576:
1575:
1572:
1569:
1568:
1560:
1557:
1555:
1552:
1550:
1547:
1545:
1542:
1540:
1537:
1535:
1532:
1530:
1527:
1523:
1520:
1518:
1515:
1513:
1510:
1509:
1508:
1505:
1503:
1500:
1498:
1495:
1493:
1490:
1488:
1487:Turkification
1485:
1481:
1478:
1477:
1476:
1473:
1472:
1465:
1464:
1454:
1452:
1449:
1448:
1442:
1440:
1437:
1436:
1432:
1430:
1427:
1426:
1422:
1420:
1417:
1416:
1410:
1407:
1406:
1402:
1397:
1396:
1386:
1384:
1381:
1380:
1376:
1374:
1371:
1370:
1366:
1364:
1361:
1360:
1356:
1354:
1351:
1350:
1346:
1344:
1343:Classical Age
1341:
1340:
1336:
1334:
1331:
1330:
1324:
1321:
1320:
1316:
1311:
1310:
1300:
1298:
1295:
1294:
1290:
1288:
1285:
1284:
1280:
1278:
1275:
1274:
1270:
1268:
1265:
1264:
1260:
1258:
1255:
1254:
1250:
1248:
1245:
1244:
1240:
1238:
1235:
1234:
1230:
1228:
1225:
1224:
1220:
1218:
1215:
1214:
1210:
1208:
1205:
1204:
1200:
1198:
1195:
1194:
1190:
1188:
1185:
1184:
1180:
1178:
1175:
1174:
1170:
1168:
1165:
1164:
1160:
1156:
1154:
1151:
1150:
1144:
1141:
1140:
1136:
1131:
1130:
1120:
1118:
1115:
1114:
1110:
1108:
1105:
1104:
1100:
1098:
1095:
1094:
1090:
1088:
1085:
1084:
1081:190 BC–428 AD
1080:
1078:
1075:
1074:
1071:247 BC–224 AD
1070:
1068:
1065:
1064:
1060:
1058:
1055:
1054:
1050:
1048:
1045:
1044:
1040:
1038:
1035:
1034:
1030:
1028:
1025:
1024:
1020:
1018:
1015:
1014:
1010:
1008:
1005:
1004:
1000:
998:
995:
994:
990:
988:
985:
984:
980:
978:
975:
974:
970:
968:
965:
964:
958:
955:
953:
950:
949:
945:
944:Classical Age
940:
939:
929:
927:
924:
923:
919:
917:
916:Median Empire
914:
913:
909:
907:
904:
903:
899:
897:
894:
893:
889:
887:
884:
883:
879:
877:
874:
873:
869:
867:
864:
863:
859:
857:
854:
853:
849:
847:
844:
843:
839:
837:
834:
833:
829:
827:
824:
823:
818:
813:
812:
802:
800:
797:
796:
792:
790:
787:
786:
782:
780:
777:
776:
772:
770:
767:
766:
762:
760:
757:
756:
752:
750:
747:
746:
742:
740:
737:
736:
732:
730:
727:
726:
722:
720:
717:
716:
712:
710:
707:
706:
702:
700:
697:
696:
692:
690:
687:
686:
682:
680:
677:
676:
672:
670:
667:
666:
662:
660:
657:
656:
652:
650:
647:
646:
642:
640:
637:
636:
632:
630:
627:
626:
622:
620:
617:
616:
612:
610:
607:
606:
602:
600:
597:
596:
591:
586:
585:
573:
571:
568:
567:
561:
559:
556:
555:
546:
544:
541:
540:
534:
531:
530:
526:
521:
520:
516:
512:
511:
508:
501:
496:
490:
480:
475:
473:
468:
466:
461:
460:
458:
457:
454:
444:
443:
436:
433:
431:
428:
426:
423:
421:
418:
416:
413:
411:
408:
406:
403:
401:
398:
396:
393:
392:
386:
385:
378:
375:
373:
370:
368:
365:
362:
358:
354:
351:
349:
346:
344:
341:
339:
336:
334:
331:
329:
326:
324:
321:
319:
316:
315:
312:
311:Modern Greece
307:
306:
299:
296:
293:
290:
287:
284:
283:
280:
275:
274:
267:
264:
261:
258:
257:
254:
249:
248:
238:
235:
229:
226:
220:
217:
211:
208:
202:
199:
198:
195:
190:
189:
172:
169:
156:
153:
140:
137:
134:
131:
130:
127:
122:
121:
114:
111:
110:
107:
102:
101:
97:
93:
92:
89:
82:
77:
71:
62:
52:
48:
43:
39:
35:
32:This article
30:
26:
21:
20:
4274:
4244:Vatican City
4197:Saudi Arabia
4169:North Africa
3832:
3823:
3814:
3805:
3796:
3787:
3778:
3769:
3760:
3751:
3742:
3733:
3724:
3715:
3706:
3700:
3689:
3680:
3671:
3662:
3653:
3644:
3625:
3619:
3610:
3601:
3551:
3534:
3501:
3487:
3470:
3453:
3433:
3397:
3358:
3345:
3296:
3273:Seljuk Turks
3266:
3257:
3246:
3238:
3206:
3190:
3174:
3130:
3099:
3076:
3073:
3066:
3057:
3047:
3021:
2999:
2996:Anatolia 842
2961:
2943:
2935:
2920:
2890:
2877:
2866:
2850:
2847:Nikephoros I
2823:
2800:
2793:
2786:
2769:
2763:
2758:
2749:
2720:
2708:
2687:
2681:
2673:
2648:
2624:
2605:
2595:
2584:
2570:
2566:
2483:Thessalonica
2324:
2273:
2269:Tiberios III
2266:
2255:
2241:
2237:Justinian II
2232:
2226:
2216:threat, the
2212:. Now a new
2174:
2150:
2124:
2117:
2107:
2085:
2060:
2033:
1973:
1932:
1878:Martyropolis
1851:
1832:
1827:Nicene Creed
1724:
1673:
1621:
1620:
1559:LGBT history
1517:Christianity
1287:Kara Koyunlu
1257:Latin Empire
1135:Medieval Age
1107:Ancient Rome
1101:163 BC–72 AD
836:Neo-Hittites
749:Neo-Hittites
733:1300–1250 BC
713:1500–1290 BC
703:1500–1300 BC
693:1500–1320 BC
683:1680–1220 BC
673:1650–1450 BC
663:1700–1300 BC
653:1780–1680 BC
643:1950–1750 BC
633:2300–1400 BC
623:2400–2150 BC
613:2500–2000 BC
415:Constitution
237:Roman Greece
59:January 2013
56:
47:You can help
33:
4234:Switzerland
4200:(Classical)
4182:(Classical)
4104:(Classical)
4084:(Classical)
3328:Michael VII
3166:Mesopotamia
3133:Michael III
3091:Kievan Rus'
3044:Michael III
3034:(842–867).
3032:Michael III
3008:(829–842).
2835:Charlemagne
2808:Charlemagne
2736:Michael III
2712:iconolaters
2695:(741–775).
2582:(713–715).
2525:Longobardia
2513:Dyrrhachium
2501:Cephallenia
2495:Peloponnese
2400:Mesopotamia
2388:Paphlagonia
2244:Justinian I
2114:Constans II
1890:Lazican War
1886:Iberian War
1480:Oghuz Turks
1445:(1930–1945)
1443:(1923–1930)
1433:(1920–1923)
1423:(1919–1922)
1387:(1908–1922)
1377:(1789–1908)
1367:(1703–1789)
1357:(1566–1703)
1347:(1453–1566)
1337:(1299–1453)
1315:Ottoman Era
1301:(1378–1501)
1291:(1375–1468)
1281:(1256–1335)
1271:(1250–1487)
1261:(1204–1261)
1251:(1204–1461)
1241:(1101–1409)
1231:(1098–1150)
1221:(1081–1423)
1211:(1078–1375)
1201:(1077–1307)
1191:(1071–1178)
1187:Danishmends
1181:(1037–1194)
900:1000–545 BC
890:1000–700 BC
880:1000–560 BC
870:1100–560 BC
860:1150–547 BC
850:1200–700 BC
840:1200–800 BC
830:1200–800 BC
793:1000–545 BC
783:1000–700 BC
773:1150–547 BC
763:1200–700 BC
753:1200–800 BC
743:1200–800 BC
723:1450–350 BC
709:Hayasa-Azzi
603:3000–700 BC
504:History of
395:Agriculture
361:Free Greece
85:History of
4247:(Classical
4192:San Marino
4154:Montenegro
4129:Luxembourg
4092:(Classical
4041:(Classical
3919:Azerbaijan
3593:References
3445:laid siege
3338:Alp Arslan
3315:Alp Arslan
3277:Alp Arslan
3164:and upper
3162:Germanicea
3146:Paulicians
3018:Theophilos
3006:Theophilos
2988:Michael II
2964:Michael II
2869:Staurakios
2852:Nikephoros
2827:Nikephoros
2755:Artabasdos
2716:iconodules
2616:Armeniakon
2612:Anatolikon
2572:Philipikos
2535:(omitted:
2448:Aegean Sea
2357:Charsianon
2353:Cappadocia
2149:The seven
2076:Cappadocia
2068:Mu'awiya I
2064:Nile River
1988:Cappadocia
1956:Shahrbaraz
1943:Khosrow II
1758:Asia Minor
1754:Aegean Sea
1734:Asia Minor
1721:Background
1363:Old Regime
1297:Ak Koyunlu
1267:Karamanids
1051:282–129 BC
1001:306–168 BC
997:Antigonids
991:322–130 BC
981:334–301 BC
971:559–331 BC
930:685–547 BC
920:678–549 BC
669:Kizzuwatna
590:Bronze Age
525:Prehistory
113:Pelasgians
4283:Medieval)
4275:Medieval)
4139:Macedonia
4067:Medieval)
4059:Medieval)
4045:Medieval)
4022:Medieval)
4014:Medieval)
3976:Medieval)
3962:Medieval)
3895:Medieval)
3587:Mehmet II
3575:Bayezid I
3449:Jerusalem
3437:Dorylaeum
3403:into the
3401:Pechenegs
3382:Artuk Bey
3342:Boccaccio
3311:Manzikert
3293:Manzikert
2873:Michael I
2658:Isaurians
2507:Nicopolis
2471:Macedonia
2412:Sebasteia
2376:Optimates
2185:Chalcedon
2119:strategos
1968:Chalcedon
1954:generals
1947:Heraclius
1918:(620–630)
1762:Black Sea
1649:Heraclius
1277:Ilkhanate
1171:(637–656)
1097:Commagene
1091:133–27 BC
1061:281–64 BC
1041:297–74 BC
1031:302–64 BC
1021:305–30 BC
1011:305–64 BC
552:10,000 BC
425:Ethnonyms
367:Civil War
51:talk page
4304:Category
4220:Slovenia
4215:Slovakia
4205:Scotland
4179:Portugal
4028:Guernsey
3579:John VII
3540:and the
3441:Tatikios
3417:Normandy
3409:Urban II
3370:Caesarea
3366:Melitene
3323:Valerian
3197:Melitene
3170:Melitene
3150:Tephrike
3097:of 860.
3050:Theodora
2941:in 815.
2740:Theodora
2726:and the
2591:Opsikion
2537:Dalmatia
2424:Seleucia
2418:Lykandos
2406:Koloneia
2329:(c. 950)
2262:Leontios
2189:Bithynia
2157:Anatolia
2096:Lombards
2013:Kavad II
1978:such as
1951:Carthage
1843:Licinius
1808:Orthodox
1760:and the
1750:hegemony
1696:Trapezus
1626:Anatolia
1571:Timeline
1507:Religion
1468:By topic
1237:Artuqids
1037:Bithynia
886:Tuwanuwa
817:Iron Age
779:Tuwanuwa
679:Hittites
609:Hattians
576:5,500 BC
564:9,000 BC
495:a series
493:Part of
435:Military
430:Language
400:Alphabet
171:Mycenean
139:Cycladic
76:a series
74:Part of
4261:Tunisia
4256:Ukraine
4187:Romania
4159:Morocco
4144:Moldova
4033:Hungary
4005:Germany
4000:Georgia
3967:Croatia
3934:Belgium
3929:Balkans
3924:Austria
3905:Andorra
3900:Algeria
3559:Osman I
3405:Balkans
3241:Fatimid
3230:Cilicia
3137:Basil I
2972:Phrygia
2968:Amorium
2770:themata
2759:themata
2670:Leo III
2654:Isauria
2650:Leo III
2645:invaded
2620:Leo III
2607:themata
2587:Galatia
2477:Strymon
2394:Chaldia
2351:(incl.
2319:of the
2257:themata
2233:themata
2228:themata
2218:Bulgars
2193:Cyzicus
2181:Amorium
2152:themata
2109:themata
2098:in the
2088:Bulgars
2072:Amorium
2000:Armenia
1964:Cilicia
1935:Maurice
1882:Armenia
1870:Kavad I
1845:at the
1752:in the
1706:History
1657:Antioch
1522:Judaism
1057:Galatia
876:Aeolis
846:Phrygia
826:Diauehi
759:Phrygia
739:Diauehi
699:Mitanni
649:Kussara
639:Assyria
629:Luwians
420:Economy
4210:Serbia
4149:Monaco
4109:Kuwait
4101:Kosovo
4089:Jordan
4081:Jersey
3986:France
3632:
3557:under
3419:, and
3413:France
3216:, one
3214:Aleppo
3154:Tarsus
3058:Caesar
3054:Bardas
2923:Thrace
2833:under
2774:Leo IV
2688:Corpus
2683:Ecloga
2519:Sicily
2489:Hellas
2465:Thrace
2436:Cyprus
2317:Themes
2281:consul
2214:Turkic
2210:Thrace
2206:Danube
1996:Thrace
1960:Shahin
1939:Phocas
1868:under
1774:Pompey
1665:Aleppo
1663:, and
1661:Tarsus
1630:Turkey
906:Urartu
866:Doris
799:Urartu
729:Assuwa
689:Arzawa
506:Turkey
497:on the
410:Church
155:Minoan
87:Greece
78:on the
49:. The
4289:Wales
4134:Malta
4119:Libya
3875:Roman
3474:Syria
3421:Italy
3181:Çorum
3158:Adana
3069:Irene
2917:Leo V
2893:Leo V
2789:Irene
2732:Leo V
2724:Irene
2442:Samos
2197:Mysia
1980:Egypt
1874:Amida
1819:saint
1817:as a
1736:" in
1642:Egypt
1512:Islam
926:Lydia
896:Ionia
856:Caria
789:Ionia
769:Caria
719:Lycia
4038:Iraq
3877:and
3630:ISBN
3583:fell
2880:Krum
2614:and
2529:12.
2523:11.
2517:10.
2446:17.
2440:16.
2434:15.
2428:14.
2422:13.
2416:12.
2410:11.
2404:10.
2355:and
2129:and
2090:and
2074:and
2028:and
1958:and
1914:and
1876:and
1837:and
1811:icon
1714:and
1686:and
1640:and
1333:Rise
599:Troy
3609:",
3344:'s
3281:Ani
3179:at
2511:9.
2505:8.
2499:7.
2493:6.
2487:5.
2481:4.
2475:3.
2469:2.
2463:1.
2398:9.
2392:8.
2386:7.
2380:6.
2374:5.
2368:4.
2362:3.
2347:2.
2341:1.
2195:in
2187:in
2155:in
1888:or
1806:An
405:Art
181:BC)
165:BC)
149:BC)
4306::
4281:-
4273:-
4249:-
4227:-
4094:-
4073:-
4069:,
4065:-
4057:-
4043:-
4020:-
4012:-
3992:-
3974:-
3960:-
3946:-
3912:-
3893:-
3527:.
3480:.
3415:,
3199:.
3064:.
2978:.
2933:.
2859:.
2776:.
2742:.
2610:,
2161:c.
1746:BC
1702:.
1659:,
1653:AD
548:c.
359:,
176:c.
160:c.
144:c.
4285:)
4277:(
4267:)
4263:(
4077:)
4061:(
4024:)
4016:(
3996:)
3988:(
3866:e
3859:t
3852:v
3638:.
3605:"
3350:.
2970:(
2539:)
2359:)
2309:e
2302:t
2295:v
2221:(
2166:)
2159:(
1829:.
1610:e
1603:t
1596:v
1161:)
478:e
471:t
464:v
363:)
355:(
174:(
158:(
142:(
61:)
57:(
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.