31:
372:
71:
40:
256:
398:, the maturation protein is called the A protein, as it belongs to the first open reading frame in the viral RNA. In Qβ the A protein was initially thought to be A1, as it is more abundant within the virion and is also required for infection. However, once the sequence of Qβ was determined, A1 was revealed to be a readthrough of the leaky stop codon.
362:
for both the replicase and the RNA product. In fact, pure Qbeta polymerase is not soluble enough to be produced in large quantities, and a fusion protein constructed from the replicase and the two EF subunits is usually used instead. The fusion can function independently of ribosomal protein S1.
272:, depending on the source which sequenced the virus. Qβ has been isolated all over the world, multiple times, with various subspecies that code for nearly identical proteins but can have very different nucleotide sequences.
430:
in experiments that favored faster replication, and thus shorter strands of RNA. He ended up with
Spiegelman's Monster, a minimal RNA chain of only 218 nucleotides that can be replicated by Qβ replicase.
636:
Kita H, Cho J, Matsuura T, Nakaishi T, Taniguchi I, Ichikawa T, Shima Y, Urabe I, Yomo T (May 2006). "Functional Qbeta replicase genetically fusing essential subunits EF-Ts and EF-Tu with beta-subunit".
940:
323:
The RNA-dependent RNA polymerase that replicates both the positive and negative RNA strands is a complex of four proteins: the catalytic beta subunit (replicase,
1009:
329:) is encoded by the phage, while the other three subunits are encoded by the bacterial genome: alpha subunit (ribosomal protein S1), gamma subunit (
391:, the maturation protein was shown to be taken up by the host along with the viral RNA and the maturation protein was subsequently cleaved.
748:
Moore CH, Farron F, Bohnert D, Weissmann C (September 1971). "Possible origin of a minor virus specific protein (A1) in Q-beta particles".
713:
Paranchych W, Ainsworth SK, Dick AJ, Krahn PM (September 1971). "Stages in phage R17 infection. V. Phage eclipse and the role of F pili".
828:"Structures of Qβ virions, virus-like particles, and the Qβ-MurA complex reveal internal coat proteins and the mechanism of host lysis"
891:
569:
689:
449:"Asymmetric cryo-EM structure of the canonical Allolevivirus Qβ reveals a single maturation protein and the genomic ssRNA in situ"
30:
47:
672:
Rūmnieks J, Tārs K (2018). "Protein-RNA Interactions in the Single-Stranded RNA Bacteriophages". In Harris RJ, Bhella D (eds.).
296:
987:
783:
Winter RB, Gold L (July 1983). "Overproduction of bacteriophage Q beta maturation (A2) protein leads to cell lysis".
1014:
70:
503:"Ongoing phenotypic and genomic changes in experimental coevolution of RNA bacteriophage Qβ and Escherichia coli"
224:
1037:
421:
908:
882:
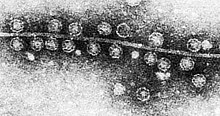
1042:
412:
by binding to MurA, which catalyzes the first enzymatically committed step in cell wall biosynthesis.
387:
in the maturation protein are unable to infect their host, or are 'immature.' For the related +ssRNA
65:
587:"Assembly of Q{beta} viral RNA polymerase with host translational elongation factors EF-Tu and -Ts"
359:
371:
808:
276:
945:
561:
379:
All positive-strand RNA phages encode a maturation protein, whose function is to bind the host
996:
887:
859:
800:
765:
730:
695:
685:
654:
618:
565:
552:
van Duin J, Tsareva N (2006). "Single-stranded RNA phages. Chapter 15". In
Calendar RL (ed.).
534:
480:
395:
388:
346:
849:
839:
792:
757:
722:
677:
646:
608:
598:
553:
524:
514:
470:
460:
237:
401:
A2 is the maturation protein for Qβ and has an additional role of being the lysis protein.
877:
300:
39:
854:
827:
613:
586:
529:
502:
475:
448:
427:
384:
826:
Cui Z, Gorzelnik KV, Chang JY, Langlais C, Jakana J, Young R, Zhang J (October 2017).
223:), commonly referred to as Qbeta or Qβ, is a species consisting of several strains of
1031:
796:
726:
554:
409:
341:
249:
131:
119:
107:
812:
1001:
972:
155:
143:
255:
681:
519:
981:
676:. Subcellular Biochemistry. Vol. 88. Springer Singapore. pp. 281–303.
315:
There are approximately 178 copies of the coat protein and/or A1 in the capsid.
242:
931:
832:
Proceedings of the
National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
591:
Proceedings of the
National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
453:
Proceedings of the
National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
405:
292:
269:
844:
603:
465:
167:
95:
863:
761:
699:
658:
622:
538:
484:
804:
769:
734:
966:
925:
447:
Gorzelnik KV, Cui Z, Reed CA, Jakana J, Young R, Zhang J (October 2016).
325:
299:(RdRp) termed the replicase. The genome is highly structured, regulating
228:
650:
280:
56:
354:
350:
288:
259:
Schematic drawing of a levivirus virion (cross section and side view)
245:
902:
380:
370:
334:
330:
304:
284:
254:
252:
Qβ enters its host cell after binding to the side of the F-pilus.
232:
82:
51:
906:
383:
and the viral RNA. The maturation protein is named thus, as
295:
in the coat protein, called A1; and the β-subunit of an
560:(Second ed.). Oxford University Press. pp.
956:
915:
496:
494:
404:The mechanism of lysis is similar to that of
8:
903:
38:
29:
18:
853:
843:
674:Virus Protein and Nucleoprotein Complexes
612:
602:
528:
518:
474:
464:
358:). The two EF proteins serve as a
639:Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering
585:Takeshita D, Tomita K (September 2010).
268:The genome of Qβ is approximately 4,217
241:. Its linear genome is packaged into an
439:
426:RNA from Bacteriophage Qβ was used by
7:
50:of bacteriophage Qβ attached to the
501:Kashiwagi A, Yomo T (August 2011).
291:protein; a readthrough of a leaky
14:
303:and protecting itself from host
69:
408:; A2 inhibits the formation of
248:with a diameter of 28 nm.
375:Life cycle of bacteriophage Qβ
1:
886:. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt.
797:10.1016/0092-8674(83)90030-2
727:10.1016/0042-6822(71)90176-0
682:10.1007/978-981-10-8456-0_13
520:10.1371/journal.pgen.1002188
297:RNA-dependent RNA-polymerase
367:Maturation/lysis protein A2
340:The structure of the Qbeta
1059:
917:Enterobacteria phage Qbeta
419:
225:positive-strand RNA virus
194:
189:
64:
46:
37:
28:
21:
200:Enterobacteria phage MX1
197:Enterobacteria phage M11
988:Escherichia virus Qbeta
845:10.1073/pnas.1707102114
604:10.1073/pnas.1006559107
466:10.1073/pnas.1609482113
206:Enterobacteria phage VK
203:Enterobacteria phage ST
762:10.1038/newbio234204a0
376:
333:), and delta subunit (
260:
374:
275:The genome has three
258:
880:; Wong, Yan (2016).
422:Spiegelman's monster
66:Virus classification
883:The Ancestor's Tale
838:(44): 11697–11702.
651:10.1263/jbb.101.421
459:(41): 11519–11524.
277:open reading frames
215:Bacteriophage Qbeta
556:The Bacteriophages
377:
261:
1025:
1024:
909:Taxon identifiers
396:bacteriophage MS2
389:bacteriophage MS2
344:has been solved (
283:: the maturation/
279:that encode four
212:
211:
1050:
1018:
1017:
1005:
1004:
992:
991:
990:
977:
976:
975:
949:
948:
936:
935:
934:
904:
898:
897:
878:Dawkins, Richard
874:
868:
867:
857:
847:
823:
817:
816:
780:
774:
773:
745:
739:
738:
710:
704:
703:
669:
663:
662:
633:
627:
626:
616:
606:
582:
576:
575:
559:
549:
543:
542:
532:
522:
498:
489:
488:
478:
468:
444:
357:
328:
287:protein A2; the
238:Escherichia coli
235:, most commonly
74:
73:
42:
33:
19:
16:Species of virus
1058:
1057:
1053:
1052:
1051:
1049:
1048:
1047:
1028:
1027:
1026:
1021:
1013:
1008:
1000:
995:
986:
985:
980:
971:
970:
965:
958:Qubevirus durum
952:
944:
939:
930:
929:
924:
911:
901:
894:
876:
875:
871:
825:
824:
820:
782:
781:
777:
747:
746:
742:
712:
711:
707:
692:
671:
670:
666:
635:
634:
630:
597:(36): 15733–8.
584:
583:
579:
572:
551:
550:
546:
513:(8): e1002188.
500:
499:
492:
446:
445:
441:
437:
424:
418:
369:
345:
324:
321:
313:
311:Coat protein A1
301:gene expression
266:
220:Qubevirus durum
190:Member viruses
185:
182:Qubevirus durum
68:
60:and its genome
23:Qubevirus durum
17:
12:
11:
5:
1056:
1054:
1046:
1045:
1040:
1038:Bacteriophages
1030:
1029:
1023:
1022:
1020:
1019:
1006:
993:
978:
962:
960:
954:
953:
951:
950:
937:
921:
919:
913:
912:
907:
900:
899:
893:978-0544859937
892:
869:
818:
775:
740:
705:
690:
664:
628:
577:
571:978-0195148503
570:
544:
490:
438:
436:
433:
428:Sol Spiegelman
420:Main article:
417:
414:
368:
365:
320:
319:Replicase/RdRp
317:
312:
309:
265:
262:
227:which infects
210:
209:
208:
207:
204:
201:
198:
192:
191:
187:
186:
179:
177:
173:
172:
165:
161:
160:
153:
149:
148:
141:
137:
136:
129:
125:
124:
117:
113:
112:
105:
101:
100:
93:
86:
85:
80:
76:
75:
62:
61:
44:
43:
35:
34:
26:
25:
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1055:
1044:
1041:
1039:
1036:
1035:
1033:
1016:
1011:
1007:
1003:
998:
994:
989:
983:
979:
974:
968:
964:
963:
961:
959:
955:
947:
942:
938:
933:
927:
923:
922:
920:
918:
914:
910:
905:
895:
889:
885:
884:
879:
873:
870:
865:
861:
856:
851:
846:
841:
837:
833:
829:
822:
819:
814:
810:
806:
802:
798:
794:
791:(3): 877–85.
790:
786:
779:
776:
771:
767:
763:
759:
756:(50): 204–6.
755:
751:
744:
741:
736:
732:
728:
724:
721:(3): 615–28.
720:
716:
709:
706:
701:
697:
693:
691:9789811084553
687:
683:
679:
675:
668:
665:
660:
656:
652:
648:
644:
640:
632:
629:
624:
620:
615:
610:
605:
600:
596:
592:
588:
581:
578:
573:
567:
563:
558:
557:
548:
545:
540:
536:
531:
526:
521:
516:
512:
508:
507:PLOS Genetics
504:
497:
495:
491:
486:
482:
477:
472:
467:
462:
458:
454:
450:
443:
440:
434:
432:
429:
423:
415:
413:
411:
410:peptidoglycan
407:
402:
399:
397:
392:
390:
386:
385:amber mutants
382:
373:
366:
364:
361:
356:
352:
348:
343:
342:RNA replicase
338:
336:
332:
327:
318:
316:
310:
308:
306:
302:
298:
294:
290:
286:
282:
278:
273:
271:
263:
257:
253:
251:
250:Bacteriophage
247:
244:
240:
239:
234:
230:
226:
222:
221:
216:
205:
202:
199:
196:
195:
193:
188:
184:
183:
178:
175:
174:
171:
170:
166:
163:
162:
159:
158:
154:
151:
150:
147:
146:
142:
139:
138:
135:
134:
133:Leviviricetes
130:
127:
126:
123:
122:
121:Lenarviricota
118:
115:
114:
111:
110:
109:Orthornavirae
106:
103:
102:
99:
98:
94:
91:
88:
87:
84:
81:
78:
77:
72:
67:
63:
59:
58:
53:
49:
45:
41:
36:
32:
27:
24:
20:
1043:Fiersviridae
957:
916:
881:
872:
835:
831:
821:
788:
784:
778:
753:
749:
743:
718:
714:
708:
673:
667:
645:(5): 421–6.
642:
638:
631:
594:
590:
580:
555:
547:
510:
506:
456:
452:
442:
425:
403:
400:
393:
378:
339:
322:
314:
274:
267:
236:
219:
218:
214:
213:
181:
180:
168:
157:Fiersviridae
156:
145:Norzivirales
144:
132:
120:
108:
96:
89:
79:(unranked):
55:
22:
982:Wikispecies
416:Experiments
270:nucleotides
243:icosahedral
1032:Categories
973:Q106960755
435:References
406:penicillin
293:stop codon
231:that have
360:chaperone
176:Species:
169:Qubevirus
104:Kingdom:
97:Riboviria
967:Wikidata
946:11459720
932:Q4840022
926:Wikidata
864:29078304
813:54345352
715:Virology
700:29900502
659:16781472
623:20798060
539:21829387
485:27671640
281:proteins
264:Genetics
229:bacteria
152:Family:
116:Phylum:
1015:2846023
855:5676892
805:6871998
770:5288806
735:4108185
614:2936634
530:3150450
476:5068298
164:Genus:
140:Order:
128:Class:
57:E. coli
890:
862:
852:
811:
803:
768:
750:Nature
733:
698:
688:
657:
621:
611:
568:
564:–196.
537:
527:
483:
473:
326:P14647
305:RNases
246:capsid
233:F-pili
1002:8TWBL
941:IRMNG
809:S2CID
381:pilus
335:EF-Ts
331:EF-Tu
285:lysis
90:Realm
83:Virus
52:pilus
1010:NCBI
888:ISBN
860:PMID
801:PMID
785:Cell
766:PMID
731:PMID
696:PMID
686:ISBN
655:PMID
619:PMID
566:ISBN
535:PMID
481:PMID
355:3AGQ
351:3AGP
289:coat
997:CoL
850:PMC
840:doi
836:114
793:doi
758:doi
754:234
723:doi
678:doi
647:doi
643:101
609:PMC
599:doi
595:107
562:175
525:PMC
515:doi
471:PMC
461:doi
457:113
394:In
347:PDB
337:).
54:of
48:TEM
1034::
1012::
999::
984::
969::
943::
928::
858:.
848:.
834:.
830:.
807:.
799:.
789:33
787:.
764:.
752:.
729:.
719:45
717:.
694:.
684:.
653:.
641:.
617:.
607:.
593:.
589:.
533:.
523:.
509:.
505:.
493:^
479:.
469:.
455:.
451:.
353:,
349::
307:.
92::
896:.
866:.
842::
815:.
795::
772:.
760::
737:.
725::
702:.
680::
661:.
649::
625:.
601::
574:.
541:.
517::
511:7
487:.
463::
217:(
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.