201:
208:
739:— Dharavarsha let Ghurid army into the pass and closed the enemy retreat behind them. In front of Ghurids, facing them was the main Chaulukya army along with Chauhans of Nadol and Jalore. After a sanguinary battle, Ghurid army was signally defeated with great slaughter. Muhammad who got wounded in action, fled from the battlefield; after much trouble in the flight he finally reached
46:
414:
forces at Gāḍarāraghaṭṭa pass and secured for her son title of "vanquisher of the king of Ghazni". However, Ashoke Kumar
Majumdar criticised the writing of Merutunga who used mythical stories to fascinate his readers. In any case, Merutunga is dismissed as "completely unreliable" by modern scholars .
532:
inscription, issued during Bhima's reign, records repairs to a temple damaged by the
Turushkas. The proponents of this theory argue that Mularaja's forces defeated another king, or that Muhammad of Ghor invaded the Chaulukya territory twice around 1178 CE.
702:
mentioned that by time the Turks reached the
Chahamana kingdom, they were so parched by marching through the desert that they had to drink the blood of their own horses. After crossing the
495:
also states that the ruler of
Gujarat defeated the Muslim army "with great slaughter", and the remnant of the defeated army faced many hardships during its return journey to
221:
1399:
410:
The 14th century account of
Merutunga states that Naiki devi took her son Mularaja in her lap and marched at the head of the Chaulukya army and defeated the
450:, Muhammad of Ghor had captured Naddula during his invasion of India. Kelhanadeva managed to regain control of Naddula after the victory at Kasahrada.
1384:
200:
1389:
1369:
1315:
1144:
879:
484:. In the ensuing battle, "the army of Islam was defeated and put to rout", and the invading ruler had to return without any accomplishment.
528:. This theory is based on some Muslim chronicles, which state that "Bhim Dev" was the one who defeated Muhammad of Ghor. Moreover, an 1178
37:
1275:
1175:
751:
The
Catastrophe did not dampen Muhammad's aspirations, who thenceforth opted for northern routes into mainland India through the
1379:
1339:
487:
Nizam-ud-din gives a similar account and states that
Muhammad of Ghor marched to Gujarat via desert. The 16th century writer
355:
The later
Chaulukya (Solanki) inscriptions, as well as the chroniclers of Gujarat, greatly praise Mularaja for this victory:
386:, states that Naikidevi gave Mularaja an army to play with. With this army, Mularaja defeated the Hammira (Sanskrit form of
1364:
798:
and sacked his capital, thereby avenging the humiliation of
Muhammad at the same battlefield twenty years later in 1197.
82:
767:
in 1186, deposing them from their last bastion, which heralded a series of lucrative forays into the fertile plains of
1394:
1359:
787:
488:
20:
1331:
Al-Hind the Making of the Indo-Islamic World: The Slave Kings and the
Islamic Conquest : 11Th-13th Centuries
616:
rulers in the same year. During the course of these incursions, Muhammad avoided a direct confrontation with the
507:
None of the Chaulukya inscriptions and chroniclers mentions the invading king's name, simply describing him as a
524:
According to an alternative theory, the Battle of Kasahrada took place during the reign of Mularaja's successor
718:
656:
163:
550:
1136:
The Paramāras: (c. 800 - 1305 A.D.) ; a Study in the Political and Cultural History of Their Kingdoms
302:
from there before he attempted to penetrate into mainland India, approaching it through the territory of
1374:
1206:"Expanding the Ghurid Architectural Corpus East of the Indus: The Jāgeśvara Temple at Sādaḍi, Rajasthan"
722:
648:
652:
566:
717:
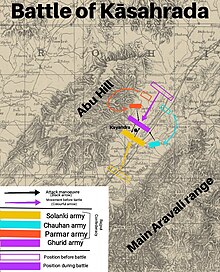
At the foot of Mount Abu, the Ghurid army confronted the combined army of Chaulukya feudatories —
491:
also mentions the invader's defeat, and states that he retreated to Ghazni with great difficulty.
1233:
699:
446:
419:
1335:
1311:
1292:
1271:
1252:
1225:
1192:
1171:
1140:
875:
783:
637:
303:
172:
771:. After a series of gains and reverses, Muhammad and his lieutenants, swiftly swept down the
1217:
869:
562:
554:
542:
379:
283:
268:
168:
735:
248:
72:
1246:
1161:
772:
692:
633:
529:
514:
460:
360:
139:
1353:
481:
865:
776:
628:. Hence, to bypass the Ghaznawids, Muhammad turned south towards coastal plains of
625:
586:
396:
army, whose soldiers were covered from head to toe in order to protect themselves.
1329:
1305:
1286:
1265:
1186:
1165:
1134:
849:
752:
703:
644:
601:
593:
585:, Muhammad utilized the city as a spring-board for carrying attacks down to the
578:
574:
465:
427:
327:
323:
299:
260:
155:
151:
1325:
668:
617:
613:
597:
557:, with Ghiyath al-Din overseeing the westward expansion of the Sultanate from
287:
1229:
97:
84:
1296:
1256:
795:
756:
730:
711:
680:
676:
509:
423:
365:
338:
army was routed and wounded Muhammad of Ghor, retreated back to his capital
319:
252:
159:
76:
1196:
675:
to penetrate into northern territory of the Chaulukyas through westernmost
480:
of Nahrwala" (the Chaulukya king) was young but commanded a huge army with
406:
states that even a woman could defeat Hammira during the reign of Mularaja.
624:
and instead focused on lands bordering the middle and lower course of the
791:
558:
525:
492:
403:
1237:
1205:
1221:
726:
629:
546:
441:
426:
routed the Turushka army at Kasahrada. It also states that his brother
307:
45:
782:
The Chaulukya kingdom was raided by Muhammad's elite slave commander
764:
760:
740:
707:
621:
605:
582:
570:
496:
473:
432:
411:
339:
335:
331:
311:
291:
275:
264:
256:
134:
117:
464:, Muhammad of Ghor marched towards Nahrwala (the Chaulukya capital
768:
688:
684:
672:
659:, mustered a powerful army to confront the advancing Ghurid army.
437:
279:
521:. However, modern historians identify him with Muhammad of Ghor.
518:
477:
388:
710:, Muhammad's exhausted army eventually reached at foothills of
874:. Vol. VI: The Art of Storytelling. Motilal Banarsidass.
609:
469:
359:
The poet Someshvara writes that Mularaja defeated the lord of
315:
295:
440:
after destroying the Turushkas. Kelhanadeva was the ruler of
399:
Arisimha also mentions that Mularaja defeated the Muslims.
271:, during which the Ghurid forces were signally defeated.
907:
905:
903:
819:
817:
815:
813:
811:
643:
Meanwhile, the Chaulukyas led by their stripling monarch
565:
endeavoured for eastward expansion towards the plains of
775:
and eventually extended the Ghurid power as far as the
322:
in state of exhaustion after a long march through the
755:. Therefore, Muhammad of Ghor attacked the truncated
326:, where they confronted the forces of Chaulukya king
698:The 12th century Kashmiri-historian Jayanka in his
342:, through the desert with considerable difficulty.
458:According to the 13th century Persian chronicler
541:During the last quarter of twelfth century, the
422:inscription of the Jalor Chahamanas boasts that
372:Balachandra mentions that Mularaja defeated the
30:
632:in order to open an alternative route to the
334:allies. In the decisive battle, the famished
8:
282:during the last quarter of twelfth century,
894:
247:was fought in 1178 at modern Kasahrada in
44:
27:
310:. The Ghurid army marching by the way of
173:
1115:
1079:
1055:
995:
947:
935:
911:
851:Studies in the Cultural History of India
835:
823:
679:. Before reaching the site of battle in
581:by 1173. Subsequently after taking over
807:
444:; according to the legendary chronicle
1067:
1043:
983:
592:In 1175, Muhammad of Ghor crossed the
1307:The Ebb and Flow of the Ghūrid Empire
1007:
923:
667:Muhammad of Ghor persisting with the
7:
1400:Battles involving the Ghurid dynasty
1103:
1091:
1031:
1019:
971:
959:
38:Indian campaigns of Muhammad of Ghor
636:through the wealthy kingdom of the
225:Location of the Battle of Kasahrada
19:For later battle at same site, see
1270:. S. Chand / Motilal Banarsidass.
647:along with their feudatories from
14:
1245:Srivastava, Ashoke Kumar (1979).
854:, Shiva Lal Agarwala, p. 237
363:(Turkic people), and crushed the
207:
1385:Battles involving Turkic peoples
206:
199:
1185:Majumdar, Ashoke Kumar (1956).
671:, marched by the way of lower
318:reached Kasahrada, at foot of
251:near Mount Abu in present-day
1:
1390:12th-century military history
1370:Battles involving the Rajputs
436:) at the shrine of the deity
376:king despite being an infant.
1251:. Sahitya Sansar Prakashan.
306:situated in the present-day
255:. It was fought between the
16:12th century battle in India
1310:. Sydney University Press.
1264:Sharma, Dasharatha (1959).
1416:
1191:. Bharatiya Vidya Bhavan.
848:Crouzet, François (1965),
687:, desecrating the idol of
430:erected a golden gateway (
50:Map of Battle of Kasahrada
21:Battle of Kasahrada (1197)
18:
1288:History of the Chāhamānas
733:from Jalor. According to
729:of Nadol and his brother
194:
181:
145:
128:
54:
43:
35:
1139:. Munshiram Manoharlal.
245:Battle of Gadararaghatta
1267:Early Chauhān Dynasties
1248:The Chahamanas of Jalor
1170:. Motilal Banarsidass.
871:Indian Kāvya Literature
551:Ghiyath al-Din Muhammad
384:Sukrita-Kirti-Kallolini
31:1st Battle of Kasahrada
1304:Thomas, David (2018).
561:, his younger partner
503:Alternative chronology
146:Commanders and leaders
1380:12th century in India
1285:Singh, R. B. (1964).
1210:Archives of Asian Art
1188:Chaulukyas of Gujarat
182:Casualties and losses
1365:History of Rajasthan
1204:Patel, Alka (2009).
721:Dharavarsha of Abu,
589:and further ahead.
569:. Muhammad captured
222:class=notpageimage|
1133:Bhatia, P. (1970).
786:in course of which
763:and finally seized
286:, marched down the
237:Battle of Kasahrada
94: /
71:Kayandra in modern
1395:History of Gujarat
1222:10.1353/aaa.0.0008
1106:, p. 144-149.
1094:, p. 143-144.
1058:, p. 131-137.
1046:, p. 138-139.
1034:, p. 108-109.
998:, p. 135-136.
962:, p. 140-141.
950:, p. 132-133.
700:Prithviraja Vijaya
683:, Muhammad sacked
447:Prithviraja Vijaya
402:An inscription of
278:expansion east of
257:Rajput Confederacy
241:Battle of Kayadara
135:Rajput Confederacy
118:Rajput confederacy
1360:Conflicts in 1178
1317:978-1-74332-542-1
1146:978-81-215-0410-2
881:978-81-208-0615-3
784:Qutb al-Din Aybeg
263:and the invading
233:
232:
124:
123:
98:24.571°N 72.838°E
1407:
1345:
1321:
1300:
1281:
1260:
1241:
1200:
1181:
1157:
1155:
1153:
1119:
1113:
1107:
1101:
1095:
1089:
1083:
1077:
1071:
1065:
1059:
1053:
1047:
1041:
1035:
1029:
1023:
1017:
1011:
1005:
999:
993:
987:
981:
975:
969:
963:
957:
951:
945:
939:
933:
927:
921:
915:
909:
898:
892:
886:
885:
862:
856:
855:
845:
839:
833:
827:
821:
790:Chaulukya ruler
759:principality in
563:Muhammad of Ghor
555:Muhammad of Ghor
543:Ghurid Sultanate
380:Udayaprabha Suri
284:Muhammad of Ghor
274:Endeavoring for
269:Muhammad of Ghor
239:, also known as
210:
209:
203:
175:
169:Muhammad of Ghur
109:
108:
106:
105:
104:
99:
95:
92:
91:
90:
87:
56:
55:
48:
28:
1415:
1414:
1410:
1409:
1408:
1406:
1405:
1404:
1350:
1349:
1348:
1342:
1324:
1318:
1303:
1284:
1278:
1263:
1244:
1203:
1184:
1178:
1162:Majumdar, R. C.
1160:
1151:
1149:
1147:
1132:
1128:
1123:
1122:
1114:
1110:
1102:
1098:
1090:
1086:
1078:
1074:
1066:
1062:
1054:
1050:
1042:
1038:
1030:
1026:
1018:
1014:
1006:
1002:
994:
990:
982:
978:
970:
966:
958:
954:
946:
942:
934:
930:
922:
918:
910:
901:
897:, pp. 4–5.
895:Srivastava 1979
893:
889:
882:
864:
863:
859:
847:
846:
842:
834:
830:
822:
809:
804:
749:
736:Prabandha Kosha
665:
545:was ruled in a
539:
505:
456:
454:Muslim accounts
369:(foreign) army.
353:
351:Native accounts
348:
249:Sirohi district
229:
228:
227:
226:
224:
218:
217:
216:
215:
211:
162:
158:
154:
102:
100:
96:
93:
88:
85:
83:
81:
80:
79:
73:Sirohi district
49:
24:
17:
12:
11:
5:
1413:
1411:
1403:
1402:
1397:
1392:
1387:
1382:
1377:
1372:
1367:
1362:
1352:
1351:
1347:
1346:
1340:
1322:
1316:
1301:
1291:. N. Kishore.
1282:
1276:
1261:
1242:
1201:
1182:
1176:
1158:
1145:
1129:
1127:
1124:
1121:
1120:
1118:, p. 143.
1108:
1096:
1084:
1082:, p. 136.
1072:
1070:, p. 176.
1060:
1048:
1036:
1024:
1022:, p. 143.
1012:
1000:
988:
976:
974:, p. 142.
964:
952:
940:
938:, p. 132.
928:
926:, p. 259.
916:
914:, p. 135.
899:
887:
880:
857:
840:
838:, p. 137.
828:
826:, p. 131.
806:
805:
803:
800:
773:Gangetic Plain
748:
745:
719:Paramara ruler
706:southwards to
664:
661:
634:Gangetic Plain
579:Oghuz Turkmens
538:
535:
504:
501:
461:Minhaj-i-Siraj
455:
452:
408:
407:
400:
397:
377:
370:
352:
349:
347:
344:
231:
230:
220:
219:
213:
212:
205:
204:
198:
197:
196:
195:
192:
191:
188:
184:
183:
179:
178:
166:
148:
147:
143:
142:
137:
131:
130:
126:
125:
122:
121:
115:
111:
110:
103:24.571; 72.838
70:
68:
64:
63:
60:
52:
51:
41:
40:
33:
32:
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1412:
1401:
1398:
1396:
1393:
1391:
1388:
1386:
1383:
1381:
1378:
1376:
1373:
1371:
1368:
1366:
1363:
1361:
1358:
1357:
1355:
1343:
1337:
1333:
1332:
1327:
1323:
1319:
1313:
1309:
1308:
1302:
1298:
1294:
1290:
1289:
1283:
1279:
1277:9780842606189
1273:
1269:
1268:
1262:
1258:
1254:
1250:
1249:
1243:
1239:
1235:
1231:
1227:
1223:
1219:
1215:
1211:
1207:
1202:
1198:
1194:
1190:
1189:
1183:
1179:
1177:9788120804364
1173:
1169:
1168:
1167:Ancient India
1163:
1159:
1148:
1142:
1138:
1137:
1131:
1130:
1125:
1117:
1116:Majumdar 1956
1112:
1109:
1105:
1100:
1097:
1093:
1088:
1085:
1081:
1080:Majumdar 1956
1076:
1073:
1069:
1064:
1061:
1057:
1056:Majumdar 1956
1052:
1049:
1045:
1040:
1037:
1033:
1028:
1025:
1021:
1016:
1013:
1010:, p. 40.
1009:
1004:
1001:
997:
996:Majumdar 1956
992:
989:
986:, p. 65.
985:
980:
977:
973:
968:
965:
961:
956:
953:
949:
948:Majumdar 1956
944:
941:
937:
936:Majumdar 1956
932:
929:
925:
920:
917:
913:
912:Majumdar 1956
908:
906:
904:
900:
896:
891:
888:
883:
877:
873:
872:
867:
861:
858:
853:
852:
844:
841:
837:
836:Majumdar 1956
832:
829:
825:
824:Majumdar 1956
820:
818:
816:
814:
812:
808:
801:
799:
797:
793:
789:
785:
780:
778:
774:
770:
766:
762:
758:
754:
746:
744:
742:
738:
737:
732:
728:
724:
720:
715:
713:
709:
705:
701:
696:
694:
690:
686:
682:
678:
674:
670:
662:
660:
658:
654:
650:
646:
641:
639:
635:
631:
627:
623:
619:
615:
611:
607:
603:
599:
595:
590:
588:
584:
580:
577:ejecting the
576:
572:
568:
564:
560:
556:
552:
548:
544:
536:
534:
531:
527:
522:
520:
516:
512:
511:
502:
500:
498:
494:
490:
485:
483:
479:
475:
471:
467:
463:
462:
453:
451:
449:
448:
443:
439:
435:
434:
429:
425:
421:
416:
413:
405:
401:
398:
395:
391:
390:
385:
381:
378:
375:
371:
368:
367:
362:
358:
357:
356:
350:
345:
343:
341:
337:
333:
330:aided by his
329:
325:
321:
317:
313:
309:
305:
301:
298:ejecting the
297:
293:
289:
285:
281:
277:
272:
270:
266:
265:Ghurid forces
262:
258:
254:
250:
246:
242:
238:
223:
202:
193:
189:
186:
185:
180:
176:
170:
167:
165:
161:
157:
153:
150:
149:
144:
141:
140:Ghurid Empire
138:
136:
133:
132:
127:
119:
116:
113:
112:
107:
78:
74:
69:
66:
65:
61:
58:
57:
53:
47:
42:
39:
34:
29:
26:
22:
1375:1178 in Asia
1330:
1306:
1287:
1266:
1247:
1213:
1209:
1187:
1166:
1150:. Retrieved
1135:
1126:Bibliography
1111:
1099:
1087:
1075:
1063:
1051:
1039:
1027:
1015:
1003:
991:
979:
967:
955:
943:
931:
919:
890:
870:
866:A. K. Warder
860:
850:
843:
831:
781:
777:Bengal Delta
750:
734:
716:
697:
666:
642:
626:Indus Valley
604:, capturing
596:through the
591:
587:Indus Valley
573:and eastern
540:
523:
508:
506:
486:
459:
457:
445:
431:
417:
409:
393:
387:
383:
373:
364:
354:
273:
244:
240:
236:
234:
129:Belligerents
25:
1326:Wink, Andre
1068:Bhatia 1970
1044:Sharma 1959
984:Thomas 2018
788:he defeated
753:Khyber Pass
704:Thar desert
645:Mularaja II
602:Khyber Pass
600:instead of
594:Indus River
575:Afghanistan
466:Anahilavada
428:Kelhanadeva
420:Sundha Hill
324:Thar Desert
300:Carmathians
290:and seized
261:Mularaja II
164:Dharavarsha
156:Kelhanadeva
152:Mularaja II
101: /
1354:Categories
1341:9004102361
1008:Patel 2009
924:Singh 1964
802:References
669:Gumal Pass
638:Chaulukyas
618:Ghaznawids
614:Carmathian
598:Gumal Pass
537:Background
392:) and his
304:Chaulukyas
288:Gumal Pass
89:72°50′17″E
86:24°34′16″N
1334:. BRILL.
1230:0066-6637
1216:: 33–56.
1104:Wink 1991
1092:Wink 1991
1032:Wink 1991
1020:Wink 1991
972:Wink 1991
960:Wink 1991
796:Mount Abu
779:in east.
757:Ghaznawid
747:Aftermath
731:Kirtipala
723:Chahamana
712:Mount Abu
681:Mount Abu
677:Rajasthan
612:from the
510:mlechchha
482:elephants
424:Kirtipala
394:mlechchha
382:, in his
374:mlechchha
366:mlechchha
361:Turushkas
320:Mount Abu
253:Rajasthan
214:Kasahrada
160:Kirtipala
77:Rajasthan
1328:(1991).
1297:11038728
1257:12737199
1238:40863700
1164:(1977).
868:(1992).
792:Bhima II
559:Firuzkuh
526:Bhima II
515:Turushka
493:Firishta
404:Bhima II
328:Mularaja
67:Location
36:Part of
1197:4413150
727:Kelhana
649:Naddula
630:Gujarat
547:dyarchy
519:Hammira
489:Badauni
476:. The "
470:Uchchha
442:Naddula
438:Somesha
346:Sources
308:Gujarat
267:led by
259:led by
187:Unknown
171: (
120:victory
1338:
1314:
1295:
1274:
1255:
1236:
1228:
1195:
1174:
1143:
878:
765:Lahore
761:Panjab
741:Ghazna
725:ruler
708:Marwar
693:Kiradu
663:Battle
622:Punjab
606:Multan
583:Ghazna
571:Ghazna
530:Kiradu
497:Ghazni
474:Multan
468:) via
433:torana
412:Ghurid
340:Ghazna
336:Ghurid
332:Rajput
312:Multan
292:Multan
276:Ghurid
114:Result
1234:JSTOR
1152:1 May
794:near
769:India
689:Shiva
685:Nadol
673:Sindh
653:Jalor
567:India
280:Indus
190:Heavy
1336:ISBN
1312:ISBN
1293:OCLC
1272:ISBN
1253:OCLC
1226:ISSN
1193:OCLC
1172:ISBN
1154:2022
1141:ISBN
876:ISBN
655:and
608:and
553:and
472:and
418:The
389:Emir
314:and
294:and
235:The
62:1178
59:Date
1218:doi
714:.
691:in
657:Abu
640:.
620:in
610:Uch
549:by
517:or
478:Rae
316:Uch
296:Uch
243:or
174:WIA
75:of
1356::
1232:.
1224:.
1214:59
1212:.
1208:.
902:^
810:^
743:.
695:.
651:,
513:,
499:.
1344:.
1320:.
1299:.
1280:.
1259:.
1240:.
1220::
1199:.
1180:.
1156:.
884:.
177:)
23:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.