369:, the ability to read is destroyed by a lesion damaging both the left visual field and the connection between the right visual field and the language areas (Broca's area and Wernicke's area). However, this does not mean one with pure alexia is incapable of comprehending speech—merely that there is no connection between their working visual cortex and language areas—as is demonstrated by the fact that people with pure alexia can still write, speak, and even transcribe letters without understanding their meaning.
826:(GCS) is the most widely used scoring system used to assess the level of severity of a brain injury. This method is based on the objective observations of specific traits to determine the severity of a brain injury. It is based on three traits: eye opening, verbal response, and motor response, gauged as described below. Based on the Glasgow Coma Scale severity is classified as follows, severe brain injuries score 3–8, moderate brain injuries score 9–12 and mild score 13–15.
65:
976:(TBI), physiotherapy treatment during the post-acute phase may include sensory stimulation, serial casting and splinting, fitness and aerobic training, and functional training. Sensory stimulation refers to regaining sensory perception through the use of modalities. There is no evidence to support the efficacy of this intervention. Serial casting and splinting are often used to reduce soft tissue
1106:, consulted on a stroke patient. The patient experienced neither speech nor hearing impairments, but had a few brain deficits. These deficits included: lacking the ability to comprehend what was spoken to him and the words written down. After his death, Wernicke examined his autopsy that found a lesion located in the left temporal region. This area became known as
510:
1122:
1136:
1054:
fully heals from brain damage, but it is possible to have a full recovery. Brain injuries are very hard to predict in outcome. Many tests and specialists are needed to determine the likelihood of the prognosis. People with minor brain damage can have debilitating side effects; not just severe brain damage has debilitating effects.
1150:
3342:
887:-inducing drugs. Diuretics reduce the fluid in tissues lowering the pressure on the brain. In the first week after a traumatic brain injury, a person may have a risk of seizures, which anti-seizure drugs help prevent. Coma-inducing drugs may be used during surgery to reduce impairments and restore blood flow.
492:
There are documented cases of lasting psychological effects as well, such as emotional changes often caused by damage to the various parts of the brain that control human emotions and behavior. Individuals who have experienced emotional changes related to brain damage may have emotions that come very
440:
Headaches and pain can occur as a result of a brain injury, either directly from the damage or due to neurological conditions stemming from the injury. Due to the changes in the brain as well as the issues associated with the change in physical and mental capacity, depression and low self-esteem are
1094:
examined two patients exhibiting impaired speech due to frontal lobe injuries. Broca's first patient lacked productive speech. He saw this as an opportunity to address language localization. It was not until
Leborgne, informally known as "tan", died when Broca confirmed the frontal lobe lesion from
870:
The treatment for emergency traumatic brain injuries focuses on assuring the person has enough oxygen from the brain's blood supply, and on maintaining normal blood pressure to avoid further injuries of the head or neck. The person may need surgery to remove clotted blood or repair skull fractures,
856:
MRI is able to better to detect smaller injuries, detect damage within the brain, diffuse axonal injury, injuries to the brainstem, posterior fossa, and subtemporal and subfrontal regions. However, patients with pacemakers, metallic implants, or other metal within their bodies are unable to have an
760:
Korsakoff psychosis typically follows after the symptoms of
Wernicke's decrease. Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome is typically caused by conditions causing thiamine deficiency, such as chronic heavy alcohol use or by conditions that affect nutritional absorption, including colon cancer, eating disorders
436:
Brain injuries have far-reaching and varied consequences due to the nature of the brain as the main source of bodily control. Brain-injured people commonly experience issues with memory. This can be issues with either long or short-term memories depending on the location and severity of the injury.
1053:
There are many misconceptions that revolve around brain injuries and brain damage. One misconception is that if someone has brain damage then they cannot fully recover. Recovery depends a variety of factors; such as severity and location. Testing is done to note severity and location. Not everyone
987:
Functional training may also be used to treat patients with TBIs. To date, no studies supports the efficacy of sit to stand training, arm ability training and body weight support systems (BWS). Overall, studies suggest that patients with TBIs who participate in more intense rehabilitation programs
500:
The long term psychological and physiological effects will vary by person and injury. For example, perinatal brain damage has been implicated in cases of neurodevelopmental impairments and psychiatric illnesses. If any concerning symptoms, signs, or changes to behaviors are occurring, a healthcare
488:
is a motor disorder caused by damage to the brain, and may be more common in those who have been left brain damaged, with loss of mechanical knowledge critical. Headaches, occasional dizziness, and fatigue—all temporary symptoms of brain trauma—may become permanent, or may not disappear for a long
1086:
and the famous case studies by Paul Broca. The first case study on
Phineas Gage's head injury is one of the most astonishing brain injuries in history. In 1848, Phineas Gage was paving way for a new railroad line when he encountered an accidental explosion of a tamping iron straight through his
734:. The brain damage caused by radiation depends on where the brain tumor is located, the amount of radiation used, and the duration of the treatment. Radiosurgery can also lead to tissue damage that results in about 1 in 20 patients requiring a second operation to remove the damaged tissue.
3306:
1095:
an autopsy. The second patient had similar speech impairments, supporting his findings on language localization. The results of both cases became a vital verification of the relationship between speech and the left cerebral hemisphere. The affected areas are known today as
801:
Unlike some of the more obvious responses to brain damage, the body also has invisible physical responses which can be difficult to notice. These will generally be identified by a healthcare provider, especially as they are normal physical responses to brain damage.
1061:
can have long term effects that may not resolve. Another misconception is that children heal better from brain damage. Children are at greater risk for injury due to lack of maturity. It makes future development hard to predict. This is because different
384:
would eliminate the enhanced activation seen in occipital and fusiform visual areas in response to fear with the area intact. Amygdala lesions change the functional pattern of activation to emotional stimuli in regions that are distant from the amygdala.
792:
on the brain leading to lesions in the white matter tracts of the brain. These shearing forces are seen in cases where the brain had a sharp rotational acceleration, and is caused by the difference in density between white matter and grey matter.
532:
occurs when the force impacting the head is not only strong enough to cause a contusion at the site of impact, but also able to move the brain and cause it to displace rapidly into the opposite side of the skull, causing an additional contusion.
437:
Sometimes memory can be improved through rehabilitation, although it can be permanent. Behavioral and personality changes are also commonly observed due to changes of the brain structure in areas controlling hormones or major emotions.
1046:, areas of the brain can learn to compensate for other damaged areas, and may increase in size and complexity and even change function, just as someone who loses a sense may gain increased acuity in another sense—a process termed
730:. Radiation and chemotherapy can lead to brain tissue damage by disrupting or stopping blood flow to the affected areas of the brain. This damage can cause long term effects such as but not limited to; memory loss, confusion, and
2831:
Canning, C; Shepherd, R.; Carr, J.; Alison, J.; Wade, L.; White, A. (2003). "A randomized controlled trial of the effects of intensive sit-to-stand training after recent traumatic brain injury on sit-to-stand performance".
806:
are known to be induced in response to brain injury. These have diverse actions that can cause, exacerbate, mediate and/or inhibit cellular injury and repair. TGFβ seems to exert primarily neuroprotective actions, whereas
441:
common side effects that can be treated with psychological help. Antidepressants must be used with caution in brain injury people due to the potential for undesired effects because of the already altered brain chemistry.
2219:
493:
quickly and are very intense, but have very little lasting effect. Emotional changes may not be triggered by a specific event, and can be a cause of stress to the injured party and their family and friends. Often,
191:
Symptoms of brain injuries vary based on the severity of the injury or how much of the brain is affected. The four categories used for classifying the severity of brain injuries are mild, moderate, or severe.
853:. CT scans and MRI are the two techniques widely used and are most effective. CT scans can show brain bleeds, fractures of the skull, fluid build up in the brain that will lead to increased cranial pressure.
815:, probably through multiple actions on glia, neurons, and the vasculature. Cytokines may be useful in order to discover novel therapeutic strategies. At the current time, they are already in clinical trials.
457:, nerve tracts, or sections of the brain can be affected by damage. The immediate response can take many forms. Initially, there may be symptoms such as swelling, pain, bruising, or loss of consciousness.
2032:
365:
An impairment following damage to a region of the brain does not necessarily imply that the damaged area is wholly responsible for the cognitive process which is impaired, however. For example, in
2184:
2053:
Pamies, David; Block, Katharina; Lau, Pierre; Gribaldo, Laura; Pardo, Carlos A.; Barreras, Paula; Smirnova, Lena; Wiersma, Daphne; Zhao, Liang; Harris, Georgina; Hartung, Thomas (2018-09-01).
3450:
3424:
777:
and other brain disorders. These lesions are induced by excision or by electric shocks (electrolytic lesions) to the exposed brain or commonly by infusion of excitotoxins to specific areas.
468:
As time progresses, and the severity of injury becomes clear, there are further responses that may become apparent. Due to loss of blood flow or damaged tissue, sustained during the injury,
1066:
areas mature at different stages, with some major cell populations and their corresponding cognitive faculties remaining unrefined until early adulthood. In the case of a child with
3042:
2875:
Wilson, D; Powell, M.; Gorham, J.; Childers, M. (2006). "Ambulation training with or without partial weightbearing after traumatic brain injury: Results of a controlled trial".
1356:
3656:
2227:
2611:
An, Shuo; Jia, Ying; Tian, Ye; Sun, Jian; Wei, Yingsheng; Yue, Shuyuan; Lin, Lijuan; Wei, Yongyue; Li, Ying; Lei, Ping; Zhang, Jianning; Jiang, Rongcai (November 2020).
1793:
2205:
1322:
2285:
137:. Brain injuries occur due to a wide range of internal and external factors. In general, brain damage refers to significant, undiscriminating trauma-induced damage.
1516:
1934:
958:, are able to maintain the health of the severely brain-injured with constant administration of medication and neurological monitoring, including the use of the
1978:
1728:
Denny-Brown, D., and Betty Q. Banker. "Amorphosynthesis from Left
Parietal Lesion". A.M.A. Archives of Neurology and Psychiatry 71, no. 3 (March 1954): 302–13.
289:
Symptoms of brain injuries can also be influenced by the location of the injury and as a result impairments are specific to the part of the brain affected.
2024:
2540:
2176:
1678:
Jaeger, W.; Krastel, H.; Braun, St. (1988-12-01). "Cerebrale
Achromatopsie (Symptomatik, Verlauf, Differentialdiagnose und Strategie der Untersuchung)".
1436:
850:
546:
penetrating: when a sharp object enters the brain, causing a large damage area. Penetrating injuries caused by bullets have a 91 percent mortality rate.
281:
Symptoms observed in children include changes in eating habits, persistent irritability or sadness, changes in attention, or disrupted sleeping habits.
1999:
1377:
Stefaniak, James D.; Halai, Ajay D.; Lambon Ralph, Matthew A. (2019). "The neural and neurocomputational bases of recovery from post-stroke aphasia".
331:
Studies show there is a correlation between brain lesion and language, speech, and category-specific disorders. Wernicke's aphasia is associated with
891:
has been licensed in China since 2003 and is used to promote neurological recovery in a range of brain injuries, including intracerebral hemorrhage.
1554:
Purves, Dale; Augustine, George J.; Fitzpatrick, David; Katz, Lawrence C.; LaMantia, Anthony-Samuel; McNamara, James O.; Williams, S. Mark (2001).
812:
2648:
362:, and problems with comprehension and production. Broca's aphasia is indicative of damage to the posterior inferior frontal gyrus of the brain.
3690:
988:
will see greater benefits in functional skills. More research is required to better understand the efficacy of the treatments mentioned above.
731:
3455:
3118:
3491:
3429:
3150:
2595:
2570:
1738:
Vakil, Eli (2005-11-01). "The Effect of
Moderate to Severe Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) on Different Aspects of Memory: A Selective Review".
753:. Typically Wernicke's encephalopathy precedes symptoms of Korsakoff psychosis. Wernicke's encephalopathy results from focal accumulation of
2750:
Hellweg, Stephanie; Johannes, Stonke (February 2008). "Physiotherapy after traumatic brain injury: A systematic review of the literature".
1465:
923:
1494:
3034:
2721:
2317:
1087:
frontal lobe. Gage observed to be intellectually unaffected but was claimed by some to have exemplified post-injury behavioral deficits.
980:
and muscle tone. Evidence based research reveals that serial casting can be used to increase passive range of motion (PROM) and decrease
513:
A coup injury occurs under the site of impact with an object, and a contrecoup injury occurs on the side opposite the area that was hit.
3376:
3288:
1236:
1024:
169:
118:
2613:"Mouse nerve growth factor promotes neurological recovery in patients with acute intracerebral hemorrhage: A proof-of-concept study"
2398:
1348:
3369:
The Tale of the
Dueling Neurosurgeons: The History of the Human Brain as Revealed by True Stories of Trauma, Madness, and Recovery
3591:
1242:
1000:
943:
525:
1282:
742:
3738:
3626:
1851:
1182:
857:
MRI done. Typically the other imaging techniques are not used in a clinical setting because of the cost, lack of availability.
842:
2796:
Watson, Martin (2001). "Do patients with severe traumatic brain injury benefit from physiotherapy? A review of the evidence".
1789:
497:
is suggested for those who experience this effect after their injury, and may be available as an individual or group session.
1020:
692:
173:
1314:
339:), and problems with comprehension. The symptoms of Wernicke's aphasia are caused by damage to the posterior section of the
245:. Mental fatigue is a common debilitating experience and may not be linked by the patient to the original (minor) incident.
2257:
2258:"Effects of Thiamine Deficiency on Brain Metabolism: Implications for the Pathogenesis of the Wernicke-Korsakoff Syndrome"
1563:
31:
1822:
1524:
1043:
846:
1926:
3529:
3524:
808:
325:
1015:
Prognosis, or the likely progress of a disorder, depends on the nature, location, and cause of the brain damage (see
1970:
950:
may be involved in running rehabilitation programs to help restore lost function or help re-learn essential skills.
942:
specialising in understanding the effects of brain injury and may be involved in assessing the severity or creating
834:
654:
258:
238:
114:
829:
There are several imaging techniques that can aid in diagnosing and assessing the extent of brain damage, such as
3672:
3631:
3484:
1035:
1110:. Wernicke later hypothesized the relationship between Wernicke's area and Broca's area, which was proven fact.
3743:
3702:
3576:
2536:
935:
838:
703:
1428:
3685:
3651:
3608:
3549:
3516:
811:
might contribute to neuronal injury and exert protective effects. IL-1 mediates ischaemic, excitotoxic, and
340:
317:
2003:
1070:
injury, for example, the impact of the damage may be undetectable until that child fails to develop normal
3707:
3697:
3581:
3508:
1315:"Traumatic Brain Injury Information Page: National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS)"
1254:
1039:
1016:
973:
895:
645:
634:
529:
521:
458:
305:
141:
110:
73:
38:
293:
size is correlated with severity, recovery, and comprehension. Brain injuries often create impairment or
3641:
3636:
3598:
3307:"The Disappearing Lesion: Sigmund Freud, Sensory-Motor Physiology, and the Beginnings of Psychoanalysis"
785:
626:
494:
480:
has been documented in patients. Amnesia is a condition in which a person is unable to remember things.
313:
153:
106:
3733:
3586:
3477:
2066:
1057:
The side-effects of a brain injury depend on location and the body's response to injury. Even a mild
947:
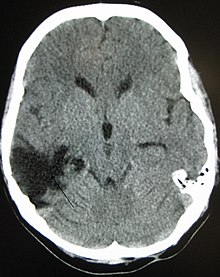
622:
2671:"Corticosteroids in acute traumatic brain injury: systematic review of randomised controlled trials"
3603:
3566:
3126:
1188:
1071:
955:
888:
830:
750:
165:
3158:
3065:"Static and Dynamic Factors Promoting Resilience following Traumatic Brain Injury: A Brief Review"
1082:
The foundation for understanding human behavior and brain injury can be attributed to the case of
3618:
3561:
3334:
2900:
2857:
2813:
2775:
1771:
1711:
1410:
959:
823:
688:
541:
400:
in different areas of the brain depending on the size of the lesion and location relative to the
93:
1457:
1107:
2918:
Turner-Stokes, Lynne; Pick, Anton; Nair, Ajoy; Disler, Peter B.; Wade, Derick T. (2015-12-22).
453:, occurring at different times after the initial occurrence of damage, as the functions of the
380:, the inability to distinguish faces and other complex objects from each other. Lesions in the
3712:
3544:
3539:
3372:
3326:
3267:
3218:
3200:
3096:
3016:
2998:
2957:
2939:
2892:
2849:
2767:
2729:
2702:
2640:
2632:
2591:
2566:
2515:
2497:
2458:
2440:
2371:
2277:
2199:
2157:
2139:
2100:
2082:
1905:
1763:
1755:
1703:
1695:
1660:
1625:
1607:
1486:
1402:
1394:
1155:
1141:
1031:
576:
562:
401:
226:
81:
1245: – Therapy to regain or improve neurocognitive function that has been lost or diminished
3556:
3318:
3286:
Paul Broca's
Historic Cases: High Resolution MR Imaging of the Brains of Leborgne and Lelong
3257:
3249:
3208:
3192:
3181:"The effect of pediatric traumatic brain injury on behavioral outcomes: a systematic review"
3086:
3076:
3006:
2988:
2947:
2931:
2884:
2841:
2805:
2759:
2692:
2682:
2624:
2505:
2489:
2448:
2432:
2361:
2351:
2269:
2147:
2131:
2090:
2074:
1895:
1885:
1747:
1687:
1652:
1615:
1597:
1386:
965:
951:
911:
616:
571:
536:
425:
161:
3285:
2338:
Vieira RC, Paiva WS, de
Oliveira DV, Teixeira MJ, de Andrade AF, de Sousa RM (2016-10-20).
2175:
Prevention, Cancer
Resources from OncoLink | Treatment, Research, Coping, Clinical Trials.
328:. Even a mild incident can have long-term effects or cause symptoms to appear years later.
3445:
3419:
3292:
2273:
2120:"Impact of Sleep Disturbances on Neurodegeneration: Insight from Studies in Animal Models"
1127:
1063:
1047:
931:
723:
684:
674:
409:
180:
145:
64:
2390:
1096:
745:
can cause brain damage and results from a Vitamin B deficiency (specifically vitamin B1,
347:
261:. Physical symptoms include headaches that worsen or do not go away, vomiting or nausea,
2070:
1185: – Group of conditions resulting from maternal alcohol consumption during pregnancy
3262:
3237:
3213:
3180:
3091:
3064:
3011:
2976:
2952:
2919:
2888:
2697:
2670:
2510:
2477:
2453:
2420:
2366:
2339:
2152:
2119:
2095:
2054:
1900:
1873:
1620:
1585:
1248:
1224:
1170:
1164:
789:
630:
417:
373:
332:
230:
222:
2920:"Multi-disciplinary rehabilitation for acquired brain injury in adults of working age"
1872:
Baumard, Josselin; Osiurak, François; Lesourd, Mathieu; Le Gall, Didier (2014-01-01).
3727:
3440:
3414:
3196:
1715:
1586:"Amygdala Response to Emotional Stimuli without Awareness: Facts and Interpretations"
1414:
1289:
1200:
1103:
996:
413:
405:
393:
389:
377:
156:(ABI) is used in appropriate circles to differentiate brain injuries occurring after
3338:
2904:
2861:
2817:
2779:
1843:
1775:
3680:
2935:
1218:
1083:
1067:
977:
939:
919:
880:
770:
715:
582:
558:
2309:
2977:"Cognitive Impairment and Rehabilitation Strategies After Traumatic Brain Injury"
2493:
3661:
1957:
Assessment & Management of Emotional Reactions to Brain Damage & Aphasia
1656:
1260:
1194:
915:
754:
670:
650:
366:
351:
149:
134:
2078:
1555:
1215: – Formation of muscular tissue, particularly during embryonic development
3646:
3571:
3322:
2845:
2763:
2687:
2628:
2436:
2135:
1814:
1751:
1390:
1212:
1117:
1091:
1058:
992:
981:
719:
678:
662:
658:
600:
397:
359:
336:
301:
294:
262:
254:
3330:
3204:
3002:
2993:
2943:
2809:
2636:
2501:
2444:
2356:
2143:
2086:
2055:"Rotenone exerts developmental neurotoxicity in a human brain spheroid model"
1890:
1759:
1699:
1664:
1611:
1602:
1398:
749:). This syndrome presents with two conditions, Wernicke's encephalopathy and
17:
2612:
1230:
927:
803:
612:
604:
587:
266:
210:
86:
3271:
3222:
3100:
3020:
2961:
2896:
2853:
2771:
2644:
2519:
2462:
2375:
2161:
2104:
1909:
1767:
1691:
1629:
1584:
Diano, Matteo; Celeghin, Alessia; Bagnis, Arianna; Tamietto, Marco (2017).
1406:
392:
have different effects depending on the location of the damage. Lesions to
3295:." Brain: A Journal of Neurology 130.5 (2007): 1432–41. Web. 31 Oct. 2016.
3253:
3081:
2706:
2340:"Diffuse Axonal Injury: Epidemiology, Outcome and Associated Risk Factors"
2281:
2177:"Possible Side Effects of Radiation Treatment for Brain Tumors | OncoLink"
1707:
300:
In cases of severe brain injuries, the likelihood of areas with permanent
2588:
Current Diagnosis & Treatment: Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation
2563:
Current Diagnosis & Treatment: Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation
2025:"Overview of Brain Dysfunction – Brain, Spinal Cord, and Nerve Disorders"
1206:
1176:
899:
876:
774:
746:
666:
608:
381:
355:
320:. There may also be personality changes. The most severe cases result in
309:
253:
Cognitive symptoms include confusion, aggressiveness, abnormal behavior,
214:
206:
509:
1004:
696:
640:
596:
485:
481:
477:
473:
469:
462:
421:
242:
218:
3400:
1233: – Medical specialty dealing with disorders of the nervous system
962:
used by other health professionals to quantify extent of orientation.
3464:
3459:
3433:
1643:
Celesia, Gastone G. (2010-01-01). "Visual Perception and Awareness".
1556:"Lesions of the Temporal Association Cortex: Deficits of Recognition"
727:
592:
554:
454:
416:
can cause the loss of the ability to perceive motion. Lesions to the
290:
270:
234:
76:
showing an empty space where the damage occurred, marked by the arrow
1203: – Therapeutic method for progressively developing coordination
3284:
Dronkers, N. F., O. Plaisant, M. T. Iba-Zizen, and E. A. Cabanis. "
424:, an inability to recognize complex objects, smells, or shapes, or
1167: – Group of movement disorders that appear in early childhood
872:
517:
Brain injuries can result from a number of conditions, including:
157:
884:
566:
321:
3473:
2310:"Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia"
269:, inability to awaken from sleep, weakness in extremities, and
179:
Impaired function of affected areas can be compensated through
3469:
3145:
3143:
1251: – Formation of neuronal junctions in the nervous system
910:
Various professions may be involved in the medical care and
875:
may be necessary. Medicines used for traumatic injuries are
757:, causing problems with vision, coordination, and balance.
350:
typically produces symptoms like omitting functional words (
769:
Brain lesions are sometimes intentionally inflicted during
2877:
American Journal of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation
773:, such as the carefully placed brain lesion used to treat
140:
A common category with the greatest number of injuries is
428:, a loss of perception on the opposite side of the body.
2975:
Barman, Apurba; Chatterjee, Ahana; Bhide, Rohit (2016).
1179: – Group of neurological disorders causing seizures
484:
is the loss or impairment of word comprehension or use.
968:
also play a significant role in rehabilitation after a
1038:
but is much rarer and more difficult to assist in the
2220:"Long Term Side Effects of Brain Tumour Radiotherapy"
1458:"Superior Temporal Gyrus :: DNA Learning Center"
1227: – Cognitive functions related to a brain region
3390:
3238:"Phineas Gage and the Science of Brain Localisation"
1740:
Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology
914:
of someone with an impairment after a brain injury.
3671:
3657:
Spinal cord injury without radiographic abnormality
3617:
3507:
3394:
1257: – Injury of the brain from an external source
102:
92:
80:
54:
49:
30:"Brain damage" redirects here. For other uses, see
3242:Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry
3035:"Traumatic brain injury - Diagnosis and treatment"
2722:"Glasgow Coma Scale: Technique and Interpretation"
461:is also common with brain damage, as is temporary
37:For the scientific journal on brain injuries, see
1927:"Emotional Problems After Traumatic Brain Injury"
445:Long term psychological and physiological effects
1349:"Traumatic brain injury Symptoms – Mayo Clinic"
3063:Schmidt, Adam T.; Holland, Jessica N. (2015).
2118:Owen, Jessica E.; Veasey, Sigrid (June 2020).
991:Other treatments for brain injury can include
695:, and even on rare occasion getting shot by a
3485:
2476:Zhang, Jun-Ming; An, Jianxiong (2007-01-01).
2419:Dammann, Olaf; O'Shea, Michael (2016-11-12).
1074:in his or her late teens and early twenties.
8:
3185:Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology
2791:
2789:
2204:: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (
2000:"Birth Hypoxia and Brain Damage to Newborns"
1921:
1919:
1874:"Tool use disorders after left brain damage"
1790:"What Happens Immediately After the Injury?"
1102:A few years later, a German neuroscientist,
449:There are multiple responses of the body to
2924:The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews
1429:"Traumatic Brain Injury Signs and Symptoms"
706:sleep deprivation lasting longer than a day
3492:
3478:
3470:
3391:
2586:Watanabe, Thomas; Marino, Michael (2014).
2561:Watanabe, Thomas; Marino, Michael (2014).
1680:Klinische Monatsblätter für Augenheilkunde
524:; multiple traumatic injuries can lead to
285:Location of brain damage predicts symptoms
63:
46:
27:Destruction or degeneration of brain cells
3261:
3212:
3090:
3080:
3010:
2992:
2951:
2696:
2686:
2509:
2452:
2365:
2355:
2251:
2249:
2247:
2245:
2151:
2094:
1899:
1889:
1619:
1601:
851:single-photon emission tomography (SPECT)
3449:) is being considered for deletion. See
3423:) is being considered for deletion. See
3112:
3110:
2981:Indian Journal of Psychological Medicine
1173: – Disorder or disease of the brain
796:
508:
205:Symptoms of a mild brain injury include
176:describe the severity and localization.
133:) is the destruction or degeneration of
3119:"10 Myths About Traumatic Brain Injury"
1971:"TBI: Causes of Traumatic Brain Injury"
1274:
930:specialising in treating brain injury.
172:identify the processes involved, while
3465:International Brain Injury Association
2421:"Cytokines and Perinatal Brain Damage"
2304:
2302:
2197:
1544:More Brain Lesions, Kathleen V. Wilkes
233:. Other symptoms include trouble with
2531:
2529:
2274:10.1093/oxfordjournals.alcalc.a044913
1263: – Serious trauma to the cranium
1197: – Serious trauma to the cranium
718:can cause brain damage to the neural
152:from an outside source, and the term
7:
2617:Journal of the Neurological Sciences
2482:International Anesthesiology Clinics
1343:
1341:
1339:
1042:(brain or spinal cord). However, in
954:, such as those working in hospital
316:), speech or movement problems, and
170:Primary and secondary brain injuries
2256:Butterworth, Roger F (1981-07-01).
2059:Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology
1283:"What is an Acquired Brain Injury?"
297:that can vary greatly in severity.
183:by forming new neural connections.
3179:Li, Linda; Liu, Jianghong (2013).
2889:10.1097/01.phm.0000193507.28759.37
2669:Alderson, P.; Roberts, I. (1997).
2478:"Cytokines, Inflammation and Pain"
2226:. October 22, 2015. Archived from
2002:. Michael E. Duffy. Archived from
1237:Primary and secondary brain injury
1025:Primary and secondary brain injury
25:
3453:to help reach a consensus. ›
3427:to help reach a consensus. ›
2537:"What Is the Glasgow Coma Scale?"
1001:neuropsychological rehabilitation
894:In the case of brain damage from
3592:Chronic traumatic encephalopathy
3197:10.1111/j.1469-8749.2012.04414.x
1517:"Broca's and Wernicke's Aphasia"
1243:Rehabilitation (neuropsychology)
1221: – Damage to nervous tissue
1148:
1134:
1120:
871:for which cutting a hole in the
526:chronic traumatic encephalopathy
3627:Anterior spinal artery syndrome
3345:from the original on 2019-11-01
3045:from the original on 2023-03-17
2651:from the original on 2024-07-26
2543:from the original on 2016-11-15
2401:from the original on 2018-01-08
2320:from the original on 2016-07-04
2288:from the original on 2024-07-26
2187:from the original on 2016-09-23
2035:from the original on 2018-07-30
1981:from the original on 2016-11-15
1937:from the original on 2016-11-11
1854:from the original on 2016-11-12
1825:from the original on 2016-11-09
1796:from the original on 2016-11-12
1566:from the original on 2022-05-15
1497:from the original on 2020-05-22
1468:from the original on 2016-12-20
1439:from the original on 2020-04-26
1359:from the original on 2016-11-15
1325:from the original on 2018-11-10
1209: – Neurosurgical operation
1183:Fetal alcohol spectrum disorder
843:magnetic resonance spectroscopy
797:Body's response to brain injury
335:, unknowingly making up words (
98:Depending on brain area injured
72:A CT of the head years after a
3305:Guenther, Katja (2013-11-01).
2936:10.1002/14651858.CD004170.pub3
2029:Merck Manuals Consumer Version
1021:Focal and diffuse brain injury
501:provider should be consulted.
249:Moderate/severe brain injuries
174:focal and diffuse brain injury
1:
3151:"Myths & Facts About TBI"
465:, or impairment of language.
354:), sound production changes,
32:Brain damage (disambiguation)
3117:Holtz, Pamela (2015-06-09).
2600:– via Access Medicine.
2575:– via Access Medicine.
2494:10.1097/AIA.0b013e318034194e
1975:www.traumaticbraininjury.com
1819:National Aphasia Association
1491:National Aphasia Association
1191: – Type of brain injury
1044:neural development in humans
847:positron emission tomography
265:, brain pulsation, abnormal
3530:Intraventricular hemorrhage
3525:Intraparenchymal hemorrhage
3311:Modern Intellectual History
1645:Journal of Psychophysiology
936:clinical neuropsychologists
743:Wernicke–Korsakoff syndrome
738:Wernicke–Korsakoff syndrome
412:, and bilateral lesions to
326:persistent vegetative state
3760:
2079:10.1016/j.taap.2018.02.003
835:magnetic resonance imaging
732:loss of cognitive function
476:may become permanent, and
259:disorders of consciousness
36:
29:
3703:Injury of accessory nerve
3323:10.1017/S147924431300022X
2846:10.1191/0269215503cr620oa
2764:10.1080/02699050801998250
2688:10.1136/bmj.314.7098.1855
2629:10.1016/j.jns.2020.117069
2590:. McGraw-Hill Education.
2565:. McGraw-Hill Education.
2437:10.1016/j.clp.2008.07.011
2136:10.1016/j.nbd.2020.104820
1959:. Far Communications Ltd.
1752:10.1080/13803390490919245
1657:10.1027/0269-8803/a000014
1560:Neuroscience. 2nd Edition
1391:10.1038/s41582-019-0282-1
1288:. Headway. Archived from
1239: – Medical condition
1036:peripheral nervous system
579:, including birth hypoxia
396:, for example, can cause
71:
62:
58:Brain damage, neurotrauma
3577:Post-concussion syndrome
3451:templates for discussion
3425:templates for discussion
2994:10.4103/0253-7176.183086
2810:10.1179/ptr.2001.6.4.233
2798:Physical Therapy Reviews
2720:Bhaskar S (3 Aug 2017).
2357:10.3389/fneur.2016.00178
1955:Währborg, Peter (1991).
1891:10.3389/fpsyg.2014.00473
1603:10.3389/fpsyg.2016.02029
1379:Nature Reviews Neurology
839:diffusion tensor imaging
312:(often, to be specific,
3686:Peripheral nerve injury
3652:Posterior cord syndrome
3609:Penetrating head injury
3550:Subarachnoid hemorrhage
3517:Intracranial hemorrhage
2834:Clinical Rehabilitation
2425:Clinics in Perinatology
2391:"Diffuse axonal injury"
2124:Neurobiology of Disease
1878:Frontiers in Psychology
1848:www.merriam-webster.com
1844:"Definition of Amnesia"
1590:Frontiers in Psychology
948:Occupational therapists
898:, dexamethasone and/or
693:falling off from height
432:Non-localizing features
341:superior temporal gyrus
318:intellectual disability
306:neurocognitive deficits
3739:Neurological disorders
3708:Brachial plexus injury
3698:Wallerian degeneration
3632:Brown-Séquard syndrome
3582:Second-impact syndrome
3509:Traumatic brain injury
2344:Frontiers in Neurology
2262:Alcohol and Alcoholism
1692:10.1055/s-2008-1050309
1255:Traumatic brain injury
1040:central nervous system
1017:Traumatic brain injury
974:traumatic brain injury
896:traumatic brain injury
813:traumatic brain injury
646:Substance use disorder
530:coup-contrecoup injury
514:
459:Post-traumatic amnesia
314:monothematic delusions
142:traumatic brain injury
111:traumatic brain injury
74:traumatic brain injury
39:Brain Injury (journal)
3642:Central cord syndrome
3637:Cauda equina syndrome
3599:Diffuse axonal injury
3254:10.1136/jnnp.71.6.761
2230:on September 23, 2016
1815:"Aphasia Definitions"
1099:and Broca's Aphasia.
786:Diffuse axonal injury
551:Deceleration injuries
512:
388:Other lesions to the
154:acquired brain injury
119:primary and secondary
107:Acquired brain injury
3587:Dementia pugilistica
1487:"Wernicke's Aphasia"
956:intensive care units
761:and gastric bypass.
623:Neurological illness
557:; for example, from
304:is great, including
277:Symptoms in children
271:loss of coordination
267:dilation of the eyes
257:, and coma or other
196:Severity of injuries
160:from injury, from a
3604:Abusive head trauma
3567:Cerebral laceration
3236:Haas L. F. (2001).
3082:10.1155/2015/902802
2071:2018ToxAP.354..101P
1515:Kean, Mary Louise.
1189:Frontal lobe injury
1072:executive functions
972:. In the case of a
831:computed tomography
751:Korsakoff psychosis
726:cells that produce
635:Parkinson's disease
599:, which may follow
201:Mild brain injuries
166:congenital disorder
3619:Spinal cord injury
3562:Cerebral contusion
3371:. Back Bay Books.
3291:2021-11-18 at the
3123:Task & Purpose
2726:Clinics in Surgery
2224:Cancer Research UK
1521:www-rohan.sdsu.edu
1353:www.mayoclinic.org
960:Glasgow Coma Scale
932:Neuropsychologists
824:Glasgow Coma Scale
542:closed head injury
515:
187:Signs and symptoms
3721:
3720:
3713:Traumatic neuroma
3673:Peripheral nerves
3545:Epidural hematoma
3540:Subdural hematoma
3408:
3407:
3367:Sam Kean (2015).
3069:Neural Plasticity
2681:(7098): 1855–59.
2597:978-0-07-179329-2
2572:978-0-07-179329-2
1319:www.ninds.nih.gov
1156:Psychology portal
1142:Philosophy portal
1090:Ten years later,
1034:can occur in the
1032:neuroregeneration
952:Registered nurses
565:and compounds of
402:calcarine fissure
164:(GBI), or from a
124:
123:
44:Medical condition
16:(Redirected from
3751:
3557:Brain herniation
3494:
3487:
3480:
3471:
3392:
3382:
3354:
3353:
3351:
3350:
3302:
3296:
3282:
3276:
3275:
3265:
3233:
3227:
3226:
3216:
3176:
3170:
3169:
3167:
3166:
3157:. Archived from
3147:
3138:
3137:
3135:
3134:
3125:. Archived from
3114:
3105:
3104:
3094:
3084:
3060:
3054:
3053:
3051:
3050:
3031:
3025:
3024:
3014:
2996:
2972:
2966:
2965:
2955:
2930:(12): CD004170.
2915:
2909:
2908:
2872:
2866:
2865:
2828:
2822:
2821:
2793:
2784:
2783:
2747:
2741:
2740:
2738:
2737:
2728:. Archived from
2717:
2711:
2710:
2700:
2690:
2666:
2660:
2659:
2657:
2656:
2608:
2602:
2601:
2583:
2577:
2576:
2558:
2552:
2551:
2549:
2548:
2533:
2524:
2523:
2513:
2473:
2467:
2466:
2456:
2416:
2410:
2409:
2407:
2406:
2386:
2380:
2379:
2369:
2359:
2335:
2329:
2328:
2326:
2325:
2306:
2297:
2296:
2294:
2293:
2253:
2240:
2239:
2237:
2235:
2216:
2210:
2209:
2203:
2195:
2193:
2192:
2181:www.oncolink.org
2172:
2166:
2165:
2155:
2115:
2109:
2108:
2098:
2050:
2044:
2043:
2041:
2040:
2021:
2015:
2014:
2012:
2011:
1996:
1990:
1989:
1987:
1986:
1967:
1961:
1960:
1952:
1946:
1945:
1943:
1942:
1923:
1914:
1913:
1903:
1893:
1869:
1863:
1862:
1860:
1859:
1840:
1834:
1833:
1831:
1830:
1811:
1805:
1804:
1802:
1801:
1786:
1780:
1779:
1735:
1729:
1726:
1720:
1719:
1675:
1669:
1668:
1640:
1634:
1633:
1623:
1605:
1581:
1575:
1574:
1572:
1571:
1551:
1545:
1542:
1536:
1535:
1533:
1532:
1523:. Archived from
1512:
1506:
1505:
1503:
1502:
1483:
1477:
1476:
1474:
1473:
1454:
1448:
1447:
1445:
1444:
1425:
1419:
1418:
1374:
1368:
1367:
1365:
1364:
1345:
1334:
1333:
1331:
1330:
1311:
1305:
1304:
1302:
1300:
1294:
1287:
1279:
1158:
1153:
1152:
1151:
1144:
1139:
1138:
1137:
1130:
1125:
1124:
1123:
966:Physiotherapists
617:arteriosclerosis
572:Genetic disorder
537:open head injury
426:amorphosynthesis
376:often result in
162:genetic disorder
144:(TBI) following
115:focal or diffuse
67:
47:
21:
3759:
3758:
3754:
3753:
3752:
3750:
3749:
3748:
3744:Causes of death
3724:
3723:
3722:
3717:
3667:
3613:
3503:
3498:
3454:
3428:
3409:
3404:
3403:
3389:
3379:
3366:
3363:
3361:Further reading
3358:
3357:
3348:
3346:
3304:
3303:
3299:
3293:Wayback Machine
3283:
3279:
3235:
3234:
3230:
3178:
3177:
3173:
3164:
3162:
3149:
3148:
3141:
3132:
3130:
3116:
3115:
3108:
3062:
3061:
3057:
3048:
3046:
3033:
3032:
3028:
2974:
2973:
2969:
2917:
2916:
2912:
2874:
2873:
2869:
2830:
2829:
2825:
2795:
2794:
2787:
2749:
2748:
2744:
2735:
2733:
2719:
2718:
2714:
2668:
2667:
2663:
2654:
2652:
2610:
2609:
2605:
2598:
2585:
2584:
2580:
2573:
2560:
2559:
2555:
2546:
2544:
2535:
2534:
2527:
2475:
2474:
2470:
2418:
2417:
2413:
2404:
2402:
2397:. Radiopaedia.
2395:radiopaedia.org
2388:
2387:
2383:
2337:
2336:
2332:
2323:
2321:
2314:medlineplus.gov
2308:
2307:
2300:
2291:
2289:
2255:
2254:
2243:
2233:
2231:
2218:
2217:
2213:
2196:
2190:
2188:
2174:
2173:
2169:
2117:
2116:
2112:
2052:
2051:
2047:
2038:
2036:
2023:
2022:
2018:
2009:
2007:
1998:
1997:
1993:
1984:
1982:
1969:
1968:
1964:
1954:
1953:
1949:
1940:
1938:
1925:
1924:
1917:
1871:
1870:
1866:
1857:
1855:
1842:
1841:
1837:
1828:
1826:
1813:
1812:
1808:
1799:
1797:
1788:
1787:
1783:
1746:(8): 977–1021.
1737:
1736:
1732:
1727:
1723:
1677:
1676:
1672:
1642:
1641:
1637:
1583:
1582:
1578:
1569:
1567:
1553:
1552:
1548:
1543:
1539:
1530:
1528:
1514:
1513:
1509:
1500:
1498:
1485:
1484:
1480:
1471:
1469:
1456:
1455:
1451:
1442:
1440:
1427:
1426:
1422:
1376:
1375:
1371:
1362:
1360:
1347:
1346:
1337:
1328:
1326:
1313:
1312:
1308:
1298:
1296:
1292:
1285:
1281:
1280:
1276:
1271:
1266:
1154:
1149:
1147:
1140:
1135:
1133:
1128:Medicine portal
1126:
1121:
1119:
1116:
1108:Wernicke's area
1080:
1048:neuroplasticity
1013:
908:
868:
863:
821:
799:
790:shearing forces
783:
767:
740:
724:oligodendrocyte
713:
702:Acute total or
685:Suicide attempt
675:West Nile fever
615:, and cerebral
507:
447:
434:
410:color-blindness
372:Lesions to the
287:
279:
251:
241:, attention or
203:
198:
189:
181:neuroplasticity
146:physical trauma
45:
42:
35:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
3757:
3755:
3747:
3746:
3741:
3736:
3726:
3725:
3719:
3718:
3716:
3715:
3710:
3705:
3700:
3695:
3694:
3693:
3691:classification
3688:
3677:
3675:
3669:
3668:
3666:
3665:
3664:(Quadriplegia)
3659:
3654:
3649:
3644:
3639:
3634:
3629:
3623:
3621:
3615:
3614:
3612:
3611:
3606:
3601:
3596:
3595:
3594:
3589:
3584:
3579:
3569:
3564:
3559:
3554:
3553:
3552:
3547:
3542:
3534:
3533:
3532:
3527:
3519:
3513:
3511:
3505:
3504:
3499:
3497:
3496:
3489:
3482:
3474:
3468:
3467:
3462:
3438:
3436:
3412:
3406:
3405:
3399:
3398:
3396:
3395:Classification
3388:
3387:External links
3385:
3384:
3383:
3378:978-0316182355
3377:
3362:
3359:
3356:
3355:
3317:(3): 569–601.
3297:
3277:
3228:
3171:
3139:
3106:
3055:
3026:
2967:
2910:
2867:
2823:
2785:
2742:
2712:
2661:
2603:
2596:
2578:
2571:
2553:
2525:
2468:
2411:
2381:
2330:
2298:
2268:(4): 271–279.
2241:
2211:
2167:
2110:
2045:
2016:
1991:
1962:
1947:
1915:
1864:
1835:
1806:
1792:. 2008-07-25.
1781:
1730:
1721:
1686:(12): 627–34.
1670:
1635:
1576:
1546:
1537:
1507:
1478:
1449:
1435:. 2017-12-01.
1420:
1369:
1335:
1306:
1273:
1272:
1270:
1267:
1265:
1264:
1258:
1252:
1249:Synaptogenesis
1246:
1240:
1234:
1228:
1225:Neurocognition
1222:
1216:
1210:
1204:
1198:
1192:
1186:
1180:
1174:
1171:Encephalopathy
1168:
1165:Cerebral palsy
1161:
1160:
1159:
1145:
1131:
1115:
1112:
1079:
1076:
1012:
1009:
944:rehabilitation
912:rehabilitation
907:
904:
867:
864:
862:
859:
820:
817:
798:
795:
782:
781:Diffuse axonal
779:
766:
763:
739:
736:
712:
709:
708:
707:
700:
682:
648:
643:
638:
631:cerebral palsy
620:
590:
585:
580:
574:
569:
552:
549:
548:
547:
544:
539:
506:
503:
446:
443:
433:
430:
420:may result in
418:parietal lobes
374:fusiform gyrus
346:Damage to the
286:
283:
278:
275:
255:slurred speech
250:
247:
223:sleep patterns
202:
199:
197:
194:
188:
185:
122:
121:
104:
100:
99:
96:
90:
89:
84:
78:
77:
69:
68:
60:
59:
56:
52:
51:
43:
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
3756:
3745:
3742:
3740:
3737:
3735:
3732:
3731:
3729:
3714:
3711:
3709:
3706:
3704:
3701:
3699:
3696:
3692:
3689:
3687:
3684:
3683:
3682:
3679:
3678:
3676:
3674:
3670:
3663:
3660:
3658:
3655:
3653:
3650:
3648:
3645:
3643:
3640:
3638:
3635:
3633:
3630:
3628:
3625:
3624:
3622:
3620:
3616:
3610:
3607:
3605:
3602:
3600:
3597:
3593:
3590:
3588:
3585:
3583:
3580:
3578:
3575:
3574:
3573:
3570:
3568:
3565:
3563:
3560:
3558:
3555:
3551:
3548:
3546:
3543:
3541:
3538:
3537:
3535:
3531:
3528:
3526:
3523:
3522:
3520:
3518:
3515:
3514:
3512:
3510:
3506:
3502:
3495:
3490:
3488:
3483:
3481:
3476:
3475:
3472:
3466:
3463:
3461:
3457:
3452:
3448:
3447:
3442:
3437:
3435:
3431:
3426:
3422:
3421:
3416:
3411:
3410:
3402:
3397:
3393:
3386:
3380:
3374:
3370:
3365:
3364:
3360:
3344:
3340:
3336:
3332:
3328:
3324:
3320:
3316:
3312:
3308:
3301:
3298:
3294:
3290:
3287:
3281:
3278:
3273:
3269:
3264:
3259:
3255:
3251:
3247:
3243:
3239:
3232:
3229:
3224:
3220:
3215:
3210:
3206:
3202:
3198:
3194:
3190:
3186:
3182:
3175:
3172:
3161:on 2016-11-27
3160:
3156:
3152:
3146:
3144:
3140:
3129:on 2016-08-02
3128:
3124:
3120:
3113:
3111:
3107:
3102:
3098:
3093:
3088:
3083:
3078:
3074:
3070:
3066:
3059:
3056:
3044:
3040:
3036:
3030:
3027:
3022:
3018:
3013:
3008:
3004:
3000:
2995:
2990:
2987:(3): 172–81.
2986:
2982:
2978:
2971:
2968:
2963:
2959:
2954:
2949:
2945:
2941:
2937:
2933:
2929:
2925:
2921:
2914:
2911:
2906:
2902:
2898:
2894:
2890:
2886:
2882:
2878:
2871:
2868:
2863:
2859:
2855:
2851:
2847:
2843:
2840:(4): 355–62.
2839:
2835:
2827:
2824:
2819:
2815:
2811:
2807:
2804:(4): 233–49.
2803:
2799:
2792:
2790:
2786:
2781:
2777:
2773:
2769:
2765:
2761:
2758:(5): 365–73.
2757:
2753:
2746:
2743:
2732:on 2020-01-16
2731:
2727:
2723:
2716:
2713:
2708:
2704:
2699:
2694:
2689:
2684:
2680:
2676:
2672:
2665:
2662:
2650:
2646:
2642:
2638:
2634:
2630:
2626:
2622:
2618:
2614:
2607:
2604:
2599:
2593:
2589:
2582:
2579:
2574:
2568:
2564:
2557:
2554:
2542:
2538:
2532:
2530:
2526:
2521:
2517:
2512:
2507:
2503:
2499:
2495:
2491:
2487:
2483:
2479:
2472:
2469:
2464:
2460:
2455:
2450:
2446:
2442:
2438:
2434:
2430:
2426:
2422:
2415:
2412:
2400:
2396:
2392:
2385:
2382:
2377:
2373:
2368:
2363:
2358:
2353:
2349:
2345:
2341:
2334:
2331:
2319:
2315:
2311:
2305:
2303:
2299:
2287:
2283:
2279:
2275:
2271:
2267:
2263:
2259:
2252:
2250:
2248:
2246:
2242:
2234:September 22,
2229:
2225:
2221:
2215:
2212:
2207:
2201:
2186:
2182:
2178:
2171:
2168:
2163:
2159:
2154:
2149:
2145:
2141:
2137:
2133:
2129:
2125:
2121:
2114:
2111:
2106:
2102:
2097:
2092:
2088:
2084:
2080:
2076:
2072:
2068:
2064:
2060:
2056:
2049:
2046:
2034:
2030:
2026:
2020:
2017:
2006:on 2013-08-05
2005:
2001:
1995:
1992:
1980:
1976:
1972:
1966:
1963:
1958:
1951:
1948:
1936:
1932:
1931:www.msktc.org
1928:
1922:
1920:
1916:
1911:
1907:
1902:
1897:
1892:
1887:
1883:
1879:
1875:
1868:
1865:
1853:
1849:
1845:
1839:
1836:
1824:
1820:
1816:
1810:
1807:
1795:
1791:
1785:
1782:
1777:
1773:
1769:
1765:
1761:
1757:
1753:
1749:
1745:
1741:
1734:
1731:
1725:
1722:
1717:
1713:
1709:
1705:
1701:
1697:
1693:
1689:
1685:
1682:(in German).
1681:
1674:
1671:
1666:
1662:
1658:
1654:
1650:
1646:
1639:
1636:
1631:
1627:
1622:
1617:
1613:
1609:
1604:
1599:
1595:
1591:
1587:
1580:
1577:
1565:
1561:
1557:
1550:
1547:
1541:
1538:
1527:on 2017-01-04
1526:
1522:
1518:
1511:
1508:
1496:
1492:
1488:
1482:
1479:
1467:
1463:
1462:www.dnalc.org
1459:
1453:
1450:
1438:
1434:
1430:
1424:
1421:
1416:
1412:
1408:
1404:
1400:
1396:
1392:
1388:
1384:
1380:
1373:
1370:
1358:
1354:
1350:
1344:
1342:
1340:
1336:
1324:
1320:
1316:
1310:
1307:
1295:on 2016-07-05
1291:
1284:
1278:
1275:
1268:
1262:
1259:
1256:
1253:
1250:
1247:
1244:
1241:
1238:
1235:
1232:
1229:
1226:
1223:
1220:
1217:
1214:
1211:
1208:
1205:
1202:
1201:Infinity Walk
1199:
1196:
1193:
1190:
1187:
1184:
1181:
1178:
1175:
1172:
1169:
1166:
1163:
1162:
1157:
1146:
1143:
1132:
1129:
1118:
1113:
1111:
1109:
1105:
1104:Carl Wernicke
1100:
1098:
1093:
1088:
1085:
1077:
1075:
1073:
1069:
1068:frontal brain
1065:
1060:
1055:
1051:
1049:
1045:
1041:
1037:
1033:
1028:
1026:
1022:
1018:
1010:
1008:
1006:
1002:
998:
997:psychotherapy
994:
989:
985:
983:
979:
975:
971:
967:
963:
961:
957:
953:
949:
945:
941:
940:psychologists
937:
933:
929:
925:
921:
920:neurosurgeons
917:
913:
905:
903:
902:may be used.
901:
897:
892:
890:
886:
882:
878:
874:
865:
860:
858:
854:
852:
848:
844:
840:
836:
832:
827:
825:
818:
816:
814:
810:
805:
794:
791:
788:is caused by
787:
780:
778:
776:
772:
764:
762:
758:
756:
752:
748:
744:
737:
735:
733:
729:
725:
721:
717:
710:
705:
701:
698:
694:
690:
686:
683:
680:
676:
672:
668:
664:
660:
656:
652:
649:
647:
644:
642:
639:
636:
632:
628:
624:
621:
618:
614:
610:
606:
602:
598:
594:
591:
589:
586:
584:
581:
578:
575:
573:
570:
568:
564:
560:
556:
553:
550:
545:
543:
540:
538:
535:
534:
531:
527:
523:
520:
519:
518:
511:
504:
502:
498:
496:
490:
487:
483:
479:
475:
471:
466:
464:
460:
456:
452:
444:
442:
438:
431:
429:
427:
423:
419:
415:
411:
407:
404:. Lesions to
403:
399:
395:
391:
390:visual cortex
386:
383:
379:
378:prosopagnosia
375:
370:
368:
363:
361:
357:
353:
349:
344:
342:
338:
334:
329:
327:
323:
319:
315:
311:
307:
303:
298:
296:
292:
284:
282:
276:
274:
272:
268:
264:
260:
256:
248:
246:
244:
240:
239:concentration
236:
232:
228:
224:
221:, changes in
220:
216:
212:
208:
200:
195:
193:
186:
184:
182:
177:
175:
171:
167:
163:
159:
155:
151:
147:
143:
138:
136:
132:
128:
120:
116:
112:
108:
105:
101:
97:
95:
91:
88:
85:
83:
79:
75:
70:
66:
61:
57:
53:
48:
40:
33:
19:
18:Brain-damaged
3681:Nerve injury
3536:Extra-axial
3521:Intra-axial
3500:
3456:Brain injury
3444:
3430:Brain injury
3418:
3368:
3347:. Retrieved
3314:
3310:
3300:
3280:
3245:
3241:
3231:
3191:(1): 37–45.
3188:
3184:
3174:
3163:. Retrieved
3159:the original
3154:
3131:. Retrieved
3127:the original
3122:
3072:
3068:
3058:
3047:. Retrieved
3038:
3029:
2984:
2980:
2970:
2927:
2923:
2913:
2883:(1): 68–74.
2880:
2876:
2870:
2837:
2833:
2826:
2801:
2797:
2755:
2752:Brain Injury
2751:
2745:
2734:. Retrieved
2730:the original
2725:
2715:
2678:
2674:
2664:
2653:. Retrieved
2620:
2616:
2606:
2587:
2581:
2562:
2556:
2545:. Retrieved
2488:(2): 27–37.
2485:
2481:
2471:
2431:(4): 643–v.
2428:
2424:
2414:
2403:. Retrieved
2394:
2389:Gaillard F.
2384:
2347:
2343:
2333:
2322:. Retrieved
2313:
2290:. Retrieved
2265:
2261:
2232:. Retrieved
2228:the original
2223:
2214:
2189:. Retrieved
2180:
2170:
2127:
2123:
2113:
2062:
2058:
2048:
2037:. Retrieved
2028:
2019:
2008:. Retrieved
2004:the original
1994:
1983:. Retrieved
1974:
1965:
1956:
1950:
1939:. Retrieved
1930:
1881:
1877:
1867:
1856:. Retrieved
1847:
1838:
1827:. Retrieved
1818:
1809:
1798:. Retrieved
1784:
1743:
1739:
1733:
1724:
1683:
1679:
1673:
1651:(2): 62–67.
1648:
1644:
1638:
1593:
1589:
1579:
1568:. Retrieved
1559:
1549:
1540:
1529:. Retrieved
1525:the original
1520:
1510:
1499:. Retrieved
1490:
1481:
1470:. Retrieved
1461:
1452:
1441:. Retrieved
1432:
1423:
1385:(1): 43–55.
1382:
1378:
1372:
1361:. Retrieved
1352:
1327:. Retrieved
1318:
1309:
1299:19 September
1297:. Retrieved
1290:the original
1277:
1219:Nerve injury
1101:
1097:Broca's area
1089:
1084:Phineas Gage
1081:
1056:
1052:
1030:In general,
1029:
1014:
990:
986:
978:contractures
970:brain injury
969:
964:
946:strategies.
934:(especially
924:physiatrists
916:Neurologists
909:
893:
881:anti-seizure
869:
855:
828:
822:
800:
784:
771:neurosurgery
768:
759:
741:
716:Chemotherapy
714:
711:Chemotherapy
657:exposure or
559:heavy metals
516:
499:
491:
467:
451:brain injury
450:
448:
439:
435:
387:
371:
364:
348:Broca's area
345:
330:
299:
288:
280:
252:
204:
190:
178:
139:
130:
127:Brain injury
126:
125:
50:Brain injury
3734:Neurotrauma
3662:Tetraplegia
3501:Neurotrauma
3439:‹ The
3413:‹ The
3039:Mayo Clinic
1261:Head injury
1195:Head injury
849:(PET), and
833:(CT) scan,
755:lactic acid
671:Aspergillus
651:Neurotoxins
595:leading to
367:pure alexia
352:agrammatism
263:convulsions
150:head injury
135:brain cells
55:Other names
3728:Categories
3647:Paraplegia
3572:Concussion
3349:2016-12-10
3248:(6): 761.
3165:2016-12-09
3133:2016-12-09
3075:: 902802.
3049:2023-03-17
2736:2020-01-23
2655:2024-06-05
2623:: 117069.
2547:2016-11-15
2405:2018-01-07
2324:2016-11-15
2292:2022-11-26
2191:2016-09-22
2130:: 104820.
2065:: 101–14.
2039:2016-12-09
2010:2013-07-27
1985:2016-11-15
1941:2016-11-12
1858:2016-11-12
1829:2016-11-12
1800:2016-11-12
1570:2020-01-23
1531:2016-12-09
1501:2016-12-09
1472:2016-12-09
1443:2020-01-23
1363:2016-11-15
1329:2018-11-09
1269:References
1213:Myogenesis
1092:Paul Broca
1059:concussion
993:medication
982:spasticity
928:physicians
861:Management
765:Iatrogenic
720:stem cells
679:meningitis
663:Annonaceae
661:exposure (
659:biological
601:thrombosis
588:Infections
561:including
495:counseling
408:can cause
398:blindsight
360:dysgraphia
337:neologisms
302:disability
295:disability
211:confusions
3331:1479-2443
3205:1469-8749
3003:0253-7176
2944:1469-493X
2637:0022-510X
2502:0020-5907
2445:0095-5108
2144:0969-9961
2087:0041-008X
1760:1380-3395
1716:260195187
1700:0023-2165
1665:0269-8803
1612:1664-1078
1433:BrainLine
1415:208302688
1399:1759-4766
1231:Neurology
1011:Prognosis
1003:, and/or
889:Mouse NGF
877:diuretics
819:Diagnosis
804:Cytokines
655:pollution
627:disorders
613:aneurysms
605:embolisms
555:Poisoning
310:delusions
207:headaches
87:Neurology
82:Specialty
3441:template
3415:template
3343:Archived
3339:16372696
3289:Archived
3272:11723197
3223:22998525
3101:26347352
3043:Archived
3021:27335510
2962:26694853
2905:44957954
2897:16357551
2862:36841611
2854:12785242
2818:71247575
2780:13374136
2772:18415716
2649:Archived
2645:32798840
2541:Archived
2520:17426506
2463:19026332
2399:Archived
2376:27812349
2318:Archived
2286:Archived
2200:cite web
2185:Archived
2162:32087293
2105:29428530
2033:Archived
1979:Archived
1935:Archived
1910:24904487
1852:Archived
1823:Archived
1794:Archived
1776:17967490
1768:16207622
1630:28119645
1596:: 2029.
1564:Archived
1495:Archived
1466:Archived
1437:Archived
1407:31772339
1357:Archived
1323:Archived
1207:Lobotomy
1177:Epilepsy
1114:See also
1064:cortical
900:Mannitol
775:epilepsy
747:thiamine
687:such as
677:, Viral
673:spores,
667:rotenone
629:such as
609:angiomas
382:amygdala
356:dyslexia
324:or even
243:thinking
231:behavior
215:tinnitus
94:Symptoms
3443:below (
3417:below (
3263:1737620
3214:3593091
3092:4539485
3012:4904751
2953:8629646
2707:9224126
2698:2126994
2511:2785020
2454:3657129
2367:5071911
2350:: 178.
2282:2675860
2153:7593848
2096:6082736
2067:Bibcode
1901:4033127
1884:: 473.
1708:3265459
1621:5222876
1078:History
1005:surgery
906:Chronic
845:(MRS),
837:(MRI),
697:firearm
689:hanging
641:Surgery
597:infarct
577:Hypoxia
563:mercury
486:Apraxia
482:Aphasia
478:apraxia
474:aphasia
470:amnesia
463:aphasia
455:neurons
422:agnosia
219:fatigue
168:(CBI).
113:(TBI),
109:(ABI),
3460:Curlie
3446:Curlie
3434:Curlie
3420:Curlie
3375:
3337:
3329:
3270:
3260:
3221:
3211:
3203:
3099:
3089:
3019:
3009:
3001:
2960:
2950:
2942:
2903:
2895:
2860:
2852:
2816:
2778:
2770:
2705:
2695:
2643:
2635:
2594:
2569:
2518:
2508:
2500:
2461:
2451:
2443:
2374:
2364:
2280:
2160:
2150:
2142:
2103:
2093:
2085:
1908:
1898:
1774:
1766:
1758:
1714:
1706:
1698:
1663:
1628:
1618:
1610:
1413:
1405:
1397:
938:) are
922:, and
841:(DTI)
728:myelin
699:, etc.
637:, etc.
593:Stroke
583:Tumors
522:Trauma
505:Causes
489:time.
333:anomia
291:Lesion
235:memory
3335:S2CID
3155:CBIRT
2901:S2CID
2858:S2CID
2814:S2CID
2776:S2CID
1772:S2CID
1712:S2CID
1411:S2CID
1293:(PDF)
1286:(PDF)
873:skull
866:Acute
414:MT/V5
158:birth
103:Types
3373:ISBN
3327:ISSN
3268:PMID
3219:PMID
3201:ISSN
3097:PMID
3073:2015
3017:PMID
2999:ISSN
2958:PMID
2940:ISSN
2928:2015
2893:PMID
2850:PMID
2768:PMID
2703:PMID
2641:PMID
2633:ISSN
2592:ISBN
2567:ISBN
2516:PMID
2498:ISSN
2459:PMID
2441:ISSN
2372:PMID
2278:PMID
2236:2016
2206:link
2158:PMID
2140:ISSN
2101:PMID
2083:ISSN
1906:PMID
1764:PMID
1756:ISSN
1704:PMID
1696:ISSN
1661:ISSN
1626:PMID
1608:ISSN
1403:PMID
1395:ISSN
1301:2016
984:.
926:are
885:coma
809:TNFα
722:and
567:lead
528:. A
472:and
322:coma
227:mood
3458:at
3432:at
3319:doi
3258:PMC
3250:doi
3209:PMC
3193:doi
3087:PMC
3077:doi
3007:PMC
2989:doi
2948:PMC
2932:doi
2885:doi
2842:doi
2806:doi
2760:doi
2693:PMC
2683:doi
2679:314
2675:BMJ
2625:doi
2621:418
2506:PMC
2490:doi
2449:PMC
2433:doi
2362:PMC
2352:doi
2270:doi
2148:PMC
2132:doi
2128:139
2091:PMC
2075:doi
2063:354
1896:PMC
1886:doi
1748:doi
1688:doi
1684:193
1653:doi
1616:PMC
1598:doi
1387:doi
1027:).
883:or
704:REM
625:or
229:or
148:or
3730::
3341:.
3333:.
3325:.
3315:10
3313:.
3309:.
3266:.
3256:.
3246:71
3244:.
3240:.
3217:.
3207:.
3199:.
3189:55
3187:.
3183:.
3153:.
3142:^
3121:.
3109:^
3095:.
3085:.
3071:.
3067:.
3041:.
3037:.
3015:.
3005:.
2997:.
2985:38
2983:.
2979:.
2956:.
2946:.
2938:.
2926:.
2922:.
2899:.
2891:.
2881:85
2879:.
2856:.
2848:.
2838:17
2836:.
2812:.
2800:.
2788:^
2774:.
2766:.
2756:22
2754:.
2724:.
2701:.
2691:.
2677:.
2673:.
2647:.
2639:.
2631:.
2619:.
2615:.
2539:.
2528:^
2514:.
2504:.
2496:.
2486:45
2484:.
2480:.
2457:.
2447:.
2439:.
2429:35
2427:.
2423:.
2393:.
2370:.
2360:.
2346:.
2342:.
2316:.
2312:.
2301:^
2284:.
2276:.
2266:24
2264:.
2260:.
2244:^
2222:.
2202:}}
2198:{{
2183:.
2179:.
2156:.
2146:.
2138:.
2126:.
2122:.
2099:.
2089:.
2081:.
2073:.
2061:.
2057:.
2031:.
2027:.
1977:.
1973:.
1933:.
1929:.
1918:^
1904:.
1894:.
1880:.
1876:.
1850:.
1846:.
1821:.
1817:.
1770:.
1762:.
1754:.
1744:27
1742:.
1710:.
1702:.
1694:.
1659:.
1649:24
1647:.
1624:.
1614:.
1606:.
1592:.
1588:.
1562:.
1558:.
1519:.
1493:.
1489:.
1464:.
1460:.
1431:.
1409:.
1401:.
1393:.
1383:16
1381:.
1355:.
1351:.
1338:^
1321:.
1317:.
1050:.
1023:,
1019:,
1007:.
999:,
995:,
918:,
879:,
691:,
669:,
665:,
653:-
633:,
611:,
607:,
603:,
406:V4
394:V1
358:,
343:.
308:,
273:.
237:,
225:,
217:,
213:,
209:,
131:BI
117:,
3493:e
3486:t
3479:v
3401:D
3381:.
3352:.
3321::
3274:.
3252::
3225:.
3195::
3168:.
3136:.
3103:.
3079::
3052:.
3023:.
2991::
2964:.
2934::
2907:.
2887::
2864:.
2844::
2820:.
2808::
2802:6
2782:.
2762::
2739:.
2709:.
2685::
2658:.
2627::
2550:.
2522:.
2492::
2465:.
2435::
2408:.
2378:.
2354::
2348:7
2327:.
2295:.
2272::
2238:.
2208:)
2194:.
2164:.
2134::
2107:.
2077::
2069::
2042:.
2013:.
1988:.
1944:.
1912:.
1888::
1882:5
1861:.
1832:.
1803:.
1778:.
1750::
1718:.
1690::
1667:.
1655::
1632:.
1600::
1594:7
1573:.
1534:.
1504:.
1475:.
1446:.
1417:.
1389::
1366:.
1332:.
1303:.
681:)
619:.
129:(
41:.
34:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.