175:; second language teaching and learning; and second language assessment. This helped inform the choice and treatment of test topics and tasks. For example, tasks involving scanning were rejected since children only demonstrated search and stop strategies from around age 11. The research also recognized that children are motivated by and perform best on tasks directly related to their experiences of teaching and learning; a wide range of course books and teaching materials were reviewed to identify the main content areas (topics, vocabulary, etc.)
194:. The trial feedback was used to construct the live tests. The trials also identified issues of practicality. For example, schools enter children when ready, that could be at any time in the year. Instead of a fixed exam timetable, a flexible system was adopted so that tests could be taken in familiar surroundings in a child's school and administered to fit within regional/local conditions (e.g. school term periods).
226:). A total of 4,000 trial tests were taken. Following analysis of the results, the Young Learners tests were revised and went live in January 2007. Teacher feedback indicated: “an appreciation of the clearer test focus for each task and the new words in the vocabulary lists. In addition, the new task types have led to clearer guidelines for markers and this enhances marker standardization”.
540:
25:
84:
792:
327:
The
Speaking test has five parts. In the computer-based test, the learner responds to audio and visual prompts and will answer a few warm-up questions to get them used to interact with an animated character. In the paper-based test, the learner takes the test with an examiner. (Someone they know will
493:
Part 4 has a text with some missing words (gaps). The missing words may be nouns, adjectives or verbs. Next to the text is a box with words in it. Children decide which word goes in each gap and copy the word in the gap. In the last question, children choose the best title for the text from a choice
489:
Part 3 has a short conversation between two people. Everything the first speaker says is printed on the question paper, with gaps for the second speaker's answers. Children decide what the second speaker says, choosing from a list of options (A to H). Part 3 tests reading a conversation and choosing
461:
Part 3 has a two sets of pictures. On the left are pictures of some people and their names (or named places / objects). On the right are pictures with letters, but no words. Children listen to a conversation between two people and match each of the pictures on the right to one of the pictures on the
377:
Part 5 has a big picture which shows different objects. Children listen to a conversation between an adult and a child. The adult asks the child to colour different objects in the picture and write a simple word or draw an object. Children have to follow the instructions given in the recording. Part
369:
Part 3 has a conversation between an adult and a child. In the conversation, the child talks about what they did on different days of the week. Children listen to the information in the recording and draw a line from the day of the week to the picture which shows what the child did on that day. Part
309:
Part 3 has five pictures of objects. Children have to find the right word for the object. After each picture, there are some dashes (- - - -) that show how many letters are in the word. There are also some jumbled letters (e.g. B O K O). Children have to put the jumbled letters in the right order to
197:
In 2003, 10 years after the initial development work, the tests were reviewed again. This involved further consultation with test centres, teachers and examiners. The consultation indicated high levels of satisfaction with the tests in general but identified several tasks where changes might be made
576:
Cambridge
English: Young Learners tests are used to celebrate children's achievement, build their confidence and show parents the progress they are making. Millions of children have taken the tests and the tests are recognized as one of the most authoritative international testing systems for young
519:
In Part 1 the examiner greets the child and asks them their name. The examiner gives the child a picture. The examiner keeps another picture, which is similar but has some differences. The examiner reads some sentences about the picture they have and the child must look at their picture and say how
515:
The
Speaking test has four parts. In the computer-based test, the learner responds to audio and visual prompts, and will answer a few warm up questions to get them used to interacting with an animated character. In the paper-based test the learner takes the test with an examiner. (Someone they know
453:
Part 1 has a big picture. The picture shows people doing different things. Above and below the picture are some names. Children listen carefully to a conversation between an adult and a child. They draw a line from each name to the correct person in the big picture. Part 1 tests listening for names
398:
Part 3 has a short conversation between two people. Everything the first speaker says is printed on the question paper, with gaps for the second speaker's answers. Children decide what the second speaker says, choosing from three options (A, B or C). Part 3 tests reading a conversation and choosing
361:
Part 1 has a big picture. The picture shows people doing different things. Above and below the picture are some names. Children listen carefully to a conversation between an adult and a child. They draw a line from each name to the correct person in the big picture. Part 1 tests listening for names
550:
Results are reported using shields as an indication of how well the candidate has done in each paper (Reading and
Writing paper, Listening paper, and Speaking paper). The certificate shows how many shields the candidate has received for each paper, with a maximum of five shields available for each
469:
Part 5 has a big picture which shows different objects. Children listen to a conversation between an adult and a child. Children then colour in objects in the picture using the colour they hear in the conversation. Children also have to draw and colour a simple object somewhere on the big picture.
420:
The
Speaking test has four parts. In the computer-based test the learner responds to audio and visual prompts, and will answer a few warm up questions to get them used to interacting with an animated character. In the paper-based test the learner takes the test with an examiner. (Someone they know
178:
Draft specifications and sample materials were developed, covering all four skills – speaking, listening, reading and writing – with a greater focus on oral skills because of the emphasis on spoken language over written language among young children. Tasks were designed to be brief and ‘active’ or
814:
The placement test uses the same task types as
Cambridge English: Young Learners and covers listening, reading and writing skills. The placement test is computer adaptive. It becomes progressively easier or more difficult based on the student's responses, assessing the entire spectrum of language
457:
Part 2 has a short conversation between two people. There is a form or notebook page with some missing words (gaps). Children listen to the information in the recording and fill in each gap. The answer might be a word or a number. Part 2 tests listening for names, spellings and other information.
365:
Part 2 has a short conversation between two people. There is a form or notebook page with some missing words (gaps). Children listen to the information in the recording and fill in each gap. The answer might be a word or a number. Part 2 tests listening for names, spellings and other information.
390:
Part 1 has eight pictures of things, with the
English word under them. On the right-hand side there are six definitions. Children choose which picture matches each definition and copy the correct word underneath the definition. Part 1 tests reading short sentences, matching to words and copying
523:
In Part 2 the child and the examiner each have two similar pictures (e.g. two different classrooms). The examiner has information about one of the pictures. The child has information about the other pictures. The examiner asks the child questions about one picture. Then, the child asks similar
402:
Part 4 has a text with some missing words (gaps). Next to the text are some small pictures and words. Children decide which word goes in each gap and copy the word in the gap. In the last question, children choose the best title for the text from a choice of three possible titles. Part 4 tests
288:
Part 4 has a big picture with seven examples of the same object (e.g. seven balls, seven books). Children listen to a conversation between an adult and a child and colour in each object using the colour mentioned in the conversation. Part 4 tests listening for words, colours, and prepositions.
276:
Part 1 has a big picture and pictures of seven small objects. Children listen to five short conversations between a man and a woman. Children listen to the information in the conversations and draw a line from each of the objects to the place where it should be on the big picture. Part 1 tests
424:
In Part 1 the examiner greets the child and asks them their name. Then, they look at two pictures, which are similar but have some differences. The examiner asks the child to describe four differences in the pictures. Part 1 tests describing differences, talking about colours, sizes, numbers,
301:
Part 1 has five pictures of objects. There is a sentence underneath each picture, e.g. ‘This is a ball.’ If the sentence is true, children should put a tick next to the picture. If the sentence is false, children should put a cross next to the picture. Part 1 tests reading short sentences and
258:
in some countries. This provides learners with a wider availability of test dates and faster results. Both formats of the exams have the same task types, topics, number of questions, timings and marks. And both formats lead to the same certificate. Where the computer-based test differs is the
334:
In Part 2 the examiner shows the child small pictures of some objects. The examiner names three objects and asks the child to point to them. The examiner then asks the child to put each object card somewhere on the big picture used in Part 1 (e.g. ‘Put the ball under the tree’). Part 2 tests
170:
Development work began in 1993. The planning phase involved extensive research and consultation since relatively little research had been carried out into assessing second language learning in children. The research is focused on three related fields: children's socio-psychological and
810:
The placement test helps teachers to understand a learner's
English language level and ensure that they are working at the correct level. Teachers can use the results to decide which language class and exam is most appropriate, and choose suitable teaching and learning materials.
428:
In Part 2 the examiner shows four pictures which tell a story, and tells the child about the first picture. The child has to continue the story and describe the other three pictures. Part 2 tests understanding the beginning of a story, continuing a story and describing pictures.
551:
paper and 15 shields available in total. A result of one shield (out of five) for a test paper means a child can improve a lot in that skill. A result of five shields (out of five) for a test paper means a child did very well in that skill and answered most questions correctly.
527:
In Part 3 the examiner shows five pictures which tell a story, and tells the child about the first picture. The child has to continue the story and describe the other four pictures. Part 3 tests understanding the beginning of a story, continuing a story and describing pictures.
229:
Twenty years after the initial development work, the tests have been updated again. Since
January 2014, the paper-based tests have new graphics designed to motivate and engage young learners. In addition, computer-based tests are being launched on a country-by-country basis.
501:
Part 6 has a text with some missing words (gaps). For each gap there is a choice of three possible answers. Children decide which answer is correct and copy the word into the gap. Part 6 tests reading and understanding a factual text, simple grammar and copying words.
410:
Part 6 has a text with some missing words (gaps). For each gap there is a choice of three possible answers. Children decide which answer is correct and copy the word into the gap. Part 6 tests reading and understanding a factual text, simple grammar and copying words.
317:
Part 5 has three pictures that tell a story. Each picture has one or two questions. Children answer each question based on what they can see in the pictures. They only have to write one word for each answer. Part 5 tests reading questions and writing one-word answers.
313:
Part 4 has a text with some missing words (gaps). Below the text, there is a box with some pictures and some words. Children have to choose the right word from the box and copy it into the right gap. Part 4 tests reading a text and writing missing words (nouns).
284:
Part 3 has five short conversations between different pairs of people. There are a question and three pictures for each conversation. Children listen to each conversation and choose the right picture (A, B, or C). Part 3 tests listening for specific information.
280:
Part 2 has a set of questions and a short conversation between a child and an adult. Children listen to the information in the conversation to answer each of the questions. The answer will be a name or a number. Part 2 tests listening for numbers and spelling.
143:
was first introduced in 1997, following extensive test development and piloting during the mid-1990s. There was immediate interest in the tests and by 2001, worldwide candidature had reached nearly 200,000, with large numbers of candidates in countries such as
505:
Part 7 has a text from a letter or diary. There are five gaps in the text. Children have to write the missing word in each gap. There is no list of words to choose from. Part 7 tests reading and understanding a short text and supplying correct words.
497:
Part 5 has a complete story and seven sentences about the story. Each of the seven sentences has a gap. Children complete the sentences about the story using one, two, three or four words. Part 5 tests reading a story and completing sentences.
305:
Part 2 has a big picture and some sentences about the picture. If the sentence is true, children should write ‘yes’. If the sentence is false, children should write ‘no’. Part 2 tests reading short sentences and writing one-word answers.
485:
Part 2 has a big picture and seven sentences about the picture. If the sentence is true, children should write ‘yes’. If the sentence is false, children should write ‘no’. Part 2 tests reading sentences and writing one-word answers.
394:
Part 2 has a big picture and six sentences about the picture. If the sentence is true, children should write ‘yes’. If the sentence is false, children should write ‘no’. Part 2 tests reading sentences and writing one-word answers.
465:
Part 4 has five short conversations. There is a question and three pictures for each conversation. Children listen to each conversation and choose the right picture (A, B or C). Part 3 tests listening for specific information.
373:
Part 4 has five short conversations. There is a question and three pictures for each conversation. Children listen to each conversation and choose the right picture (A, B or C). Part 3 tests listening for specific information.
259:
speaking paper – in the computer-based
Speaking test, children respond to audio and visual prompts rather than to an examiner. Children answer a few warm-up questions to get them used to interacting with an animated character.
432:
In Part 3 the examiner shows the child four sets of four pictures. In each set one picture is different from the other three. The child has to say which picture is different and explain why. Part 3 tests explaining reasons.
580:
The skills covered in the tests aim to support children to access English-language books, songs, television, films, internet and other media, use English as a common international language, and get ready for future study.
406:
Part 5 has three pictures which tell a story. After each picture/part of the story, children complete sentences about the story using one, two or three words. Part 5 tests reading a story and completing sentences.
815:
ability from CEFR level pre A1 to level A2. The test is accessed online and can be taken anytime. Most learners take between 30 and 40 minutes to complete the test, and the results are available instantly.
244:
Results are reported using shields as an indication of how well the candidate has done in each skill. A maximum of five shields are available per paper, and a maximum of 15 shields are available in total.
799:
A comprehensive list of test centres can be found on the Cambridge English Language Assessment website. Free test preparation materials, such as sample tests, are available from the official website.
338:
In Part 3 the examiner asks the child some questions about the big picture used in Part 1 (e.g. ‘What is this?’ ‘What colour is the …?’). Part 3 tests understanding and answering spoken questions.
1134:
531:
In Part 4 the examiner asks the child some questions about themselves (e.g. school, family, birthday, hobbies or holidays). Part 4 tests understanding and responding to personal questions.
479:
The Reading and Writing paper has seven sections and 50 questions in total. Each part begins with one or two examples. Children must spell their answers correctly in all parts of the test.
387:
The Reading and Writing paper has six sections and 40 questions in total. Each part begins with one or two examples. Children must spell their answers correctly in all parts of the test.
341:
In Part 4 the examiner asks the child some questions about the small pictures of objects used in Part 2 (e.g. ‘What is this?’). Part 4 tests understanding and answering spoken questions.
298:
The Reading and Writing paper has five parts and 25 questions in total. Each part begins with one or two examples. Children must spell their answers correctly in all parts of the test.
539:
179:
game-like, e.g. colouring activities, and aimed to test the use of language in relevant contexts in a bid to close the gap between children's experiences of learning and testing.
436:
In Part 4 the examiner asks the child some questions about themselves (e.g. school, weekends, friends, hobbies). Part 4 tests understanding and responding to personal questions.
132:
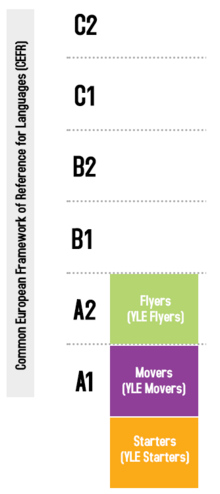
at CEFR Level B2. A2 Flyers is roughly equivalent to A2 Key for Schools regarding difficulty, but the words and contexts covered in A2 Flyers are suitable for younger children.
600:
331:
In Part 1 the examiner greets the child, asks them their name, and asks them to point to things in a big picture. Part 1 tests understanding and following spoken instructions.
114:
482:
Part 1 has 15 words and 10 definitions. Children write the correct word next to each definition. Part 1 tests reading short sentences, matching to words and copying words.
344:
In Part 5 the examiner asks the child some questions about themselves (e.g. their age, family, friends). Part 5 tests understanding and responding to personal questions.
167:
was whether it was possible to create an international English language test for children that was accurate, fair and had a positive impact on future language learning.
1326:
977:
248:
The tests are available in pen-and-paper format. Since January 2014, there have been updated paper-based tests with new graphics designed to motivate young learners.
1235:
1209:
1164:
1007:
1279:
584:
The tests can be used to prepare and motivate children for future English-language learning. Children who have taken A2 Flyers can begin to aim for tests such as
520:
it is different. Part 1 tests understanding differences, talking about colours, sizes, numbers, positions, how people or things look, what people are doing, etc.
1331:
763:
Understand longer texts about everyday topics, even if they do not know all the words, and can use a dictionary to help them understand words they do not know.
791:
241:
Each of the tests has three papers: a Listening paper, a Reading and Writing paper, and a Speaking paper. Each paper is worth a third of the total marks.
163:
The increase in teaching English to young learners (aged approximately 7 to 12 years old) has led to growing demands for assessment. The key question for
117:(CEFR). Pre A1 Starters (YLE Starters) is targeted at pre-A1 Level, A1 Movers (YLE Movers) at CEFR Level A1, and A2 Flyers (YLE Flyers) at CEFR Level A2.
1142:
450:
The Listening paper has five parts and 25 questions in total. Each part begins with one or two examples. The children will hear each recording twice.
358:
The Listening paper has five parts and 25 questions in total. Each part begins with one or two examples. The children will hear each recording twice.
273:
The Listening paper has four parts and 20 questions in total. Each part begins with one or two examples. The children will hear each recording twice.
102:), is a suite of English language tests that is specially designed for children in primary and lower-secondary school. The tests are provided by the
562:
Candidates take all their test papers within a period of five days, with the Listening paper is always taken before the Reading and Writing paper.
752:
Say they do not understand something / cannot do something and ask for help using expressions such as: ‘Could you say that again, please?’
565:
Different test centres offer different dates to take the test. Candidates contact their local test centre to find out their test dates.
603:(CEFR). Pre A1 Starters is focused on the pre A1 level, A1 Movers is focused on the A1 level and A2 Flyers is focused on the A2 level.
743:
Make and respond to invitations, suggestions, apologies and requests, such as arranging with friends to do something / play together.
68:
50:
39:
35:
524:
questions about the other picture. Part 2 tests answering questions with short answers and asking questions to get informations.
238:
All three tests in the suite are designed to test the four core language skills (reading, writing, speaking and listening).
87:
Comparison between the exams Cambridge English: Young Learners and the Common European Framework of Reference for Languages.
981:
568:
All candidates receive a certificate. Candidates receive their certificate three to four weeks after the test or earlier.
1239:
1213:
1168:
1011:
824:
251:
164:
103:
120:
Cambridge English: Young Learners leads to Cambridge English examinations designed for school-aged learners, including
624:
Respond to simple expressions of communication with expressions such as: ‘Yes, please’, ‘Sorry’, ‘I don’t understand’.
627:
Understand simple sentences about things around them such as: ‘This is a chair’, ‘I like my school’, ‘That’s my pen’.
1093:
737:
Communicate in familiar situations and interact with English speakers who talk slowly and clearly. E.g. they can:
699:
Understand instructions given by the teacher in the classroom such as: ‘Take off your coat’, ‘You must do this’.
554:
Children who achieve a total of 10 or 11 shields or above are ready to start preparing for the next exam level.
879:
922:"Juliet Wilson, 2007, Reviewing the Cambridge Young Learners English (YLE) tests in Research Notes, Issue 28"
107:
1309:
941:
713:
Read and write simple texts and notes, including information about times, dates and places. E.g. they can:
1261:
1106:
679:
Ask questions and use fixed expressions such as: ‘How much is/are?’, ‘What’s the matter?’, ‘I’m good at’.
172:
1076:
1058:
858:
921:
892:
635:
Follow simple classroom instructions such as: ‘Open your book’, ‘Read the question’, ‘Listen to me’.
494:
of three possible titles. Part 4 tests reading for specific information and gist and copying words.
1037:
638:
Understand simple written instructions such as how they should do an exercise in their course book.
255:
661:
Recognise and copy words, phrases and short sentences from a text, book or board in the classroom.
802:
Free learning materials, including games and apps, are also available from the official website.
696:
Understand basic notices, instructions and information and complete basic forms. E.g. they can:
621:
Understand simple expressions of communication such as: ‘Hello’, ‘How are you?’, ‘Thank you’.
599:
Cambridge English: Young Learners demonstrates language proficiency at various levels of the
516:
will introduce them to the examiner and explain what is going to happen in their language.)
421:
will introduce them to the examiner and explain what is going to happen in their language.)
641:
Listen to and repeat words and phrases after appropriate to the level after their teacher.
1191:
834:
757:
Understand simple written English, short notices and spoken directions. E.g. they can:
691:
Ask somebody about how they are and what they like doing, and answer similar questions.
589:
328:
introduce them to the examiner and explain what is going to happen in their language.)
223:
191:
125:
596:, which lead to internationally recognised certificates, accepted for study and work.
1320:
682:
Ask questions about school activities such as classroom tasks, homework and holidays.
611:
Pre A1 Starters indicates that typical candidates at this level have the ability to:
187:
978:"Test format of Cambridge English: Starters (YLE Starters) | Cambridge English"
685:
Agree or disagree with someone using phrases such as: ‘I think so’, ‘You are right’.
83:
113:
The suite includes three qualifications, each targeted at a different level of the
688:
Understand when somebody talks about their family and friends in simple sentences.
777:
Make up a story in English using ideas, pictures or words the teacher gives them.
1008:"Test format of Cambridge English: Flyers (YLE Flyers) | Cambridge English"
198:
to improve the tests. These new tasks were trialed in centres across the world (
733:
A2 Flyers indicates that typical candidates at this level have the ability to:
716:
Write about what they like doing in their free time, using words given to them.
672:
A1 Movers indicates that typical candidates at this level have the ability to:
959:
768:
Write short, simple notes using basic phrases and expressions. E.g. they can:
676:
Take part in a basic factual conversation on a familiar topic. E.g. they can:
722:
Continue a story or text that has been started or add words that are missing.
655:
Read short, simple words and names of objects such as animals, toys, clothes.
199:
153:
1236:"Why take Cambridge English: Flyers (YLE Flyers)? | Cambridge English"
1210:"Why take Cambridge English: Movers (YLE Movers)? | Cambridge English"
1165:"Why take Cambridge English: Flyers (YLE Flyers)? | Cambridge English"
780:
Write short dialogues such as in speech bubbles, picture stories or comics.
618:
Respond to personal questions on topics such as age, family and their home.
746:
Talk briefly about things they have done, such as their favourite holiday.
839:
593:
219:
215:
129:
462:
left. Part 3 tests listening for words, names and detailed information.
702:
Understand simple sentences if they read them slowly and several times.
615:
Understand and use simple expressions of communication. E.g. they can:
719:
Understand simple stories and shorter texts with the help of pictures.
829:
774:
Write about how they feel, and give reasons why, in simple sentences.
585:
470:
Part 5 tests listening for words, colours and specific informations.
183:
121:
942:"Cambridge English Qualifications Schools | Cambridge English"
1135:"New oriental to administer Cambridge Young Learners English Exam"
425:
positions, how people or things look, what people are doing, etc.
211:
207:
203:
157:
149:
145:
82:
740:
Introduce themselves and answer basic questions about themselves.
547:
All candidates receive a certificate. There is no pass or fail.
310:
make the word (e.g. BOOK). Part 3 tests simple words' spelling.
378:
5 tests listening for words, colours and specific information.
182:
The tests were trialed in 1995–96 with over 3,000 children in
18:
403:
reading for specific information and gist and copying words.
790:
760:
Understand audio and video clips used in the English lesson.
538:
646:
Read and write simple words and sentences. E.g. they can:
658:
Write simple sentences about themselves and their family.
370:
3 tests listening for specific information (past tense).
649:
Recognise and write the letters of the English alphabet.
46:
543:
Sample Cambridge English: Young Learners certificates
601:
Common European Framework of Reference for Languages
115:
Common European Framework of Reference for Languages
806:
Cambridge English Placement Test for Young Learners
705:Write simple sentences, using words given to them.
335:understanding and following spoken instructions.
1096:cambridgeenglish.org Retrieved 25 February 2015
1262:"Parents and children | Cambridge English"
882:cambridgeenglish.org Retrieved 25 February 2015
16:English language proficiency tests for children
632:Understand basic instructions. E.g. they can:
771:Write a short message on a postcard or email.
8:
1038:"A2 Flyers results | Cambridge English"
861:britishcouncil.hk Retrieved 25 February 2015
69:Learn how and when to remove this message
1192:"Young Learners (YLE) - Exams Catalunya"
1053:
1051:
1327:Standardized tests for English language
1032:
1030:
1002:
1000:
936:
934:
851:
875:
873:
871:
869:
867:
749:Talk about a problem in simple terms.
277:listening to words and prepositions.
7:
1332:University of Cambridge examinations
1077:"A2 Flyers | Cambridge English"
708:Understand signs and simple notices.
1280:"Cambridge English Placement Test"
652:Spell their name and simple words.
577:learners of the English language.
40:integrate it into the encyclopedia
14:
141:Cambridge English: Young Learners
92:Cambridge English: Young Learners
51:that are relevant to the context
23:
1094:YLE Information for Candidates
1:
825:Cambridge Assessment English
474:Paper 2. Reading and Writing
382:Paper 2. Reading and Writing
293:Paper 2. Reading and Writing
252:Cambridge Assessment English
165:Cambridge Assessment English
104:Cambridge Assessment English
96:Young Learners English Tests
1348:
1181:Retrieved 25 February 2015
835:B1 Preliminary for Schools
795:Free preparation materials
590:B1 Preliminary for Schools
126:B1 Preliminary for Schools
1107:"Brief guide for schools"
1024:Accessed 25 February 2015
994:Accessed 25 February 2015
880:YLE Handbook for Teachers
106:(previously known as the
53:within the existing text.
1266:www.cambridgeenglish.org
1081:www.cambridgeenglish.org
1063:www.cambridgeenglish.org
1042:www.cambridgeenglish.org
946:www.cambridgeenglish.org
108:University of Cambridge
36:links to other articles
796:
544:
88:
1059:"Find an exam centre"
794:
542:
173:cognitive development
128:at CEFR Level B1 and
86:
1114:cambridgeenglish.org
900:cambridgeenglish.org
840:B2 First for Schools
594:B2 First for Schools
256:computer-based tests
130:B2 First for Schools
110:ESOL Examinations).
94:, formerly known as
47:improve this article
1196:exams-catalunya.com
984:on 16 February 2015
490:correct responses.
399:correct responses.
302:recognizing words.
1014:on 17 January 2015
830:A2 Key for Schools
797:
586:A2 Key for Schools
558:Timing and results
545:
454:and descriptions.
445:Paper 1. Listening
362:and descriptions.
353:Paper 1. Listening
268:Paper 1. Listening
254:has also launched
124:at CEFR Level A2,
122:A2 Key for Schools
89:
512:(7 to 9 minutes)
510:Paper 3. Speaking
417:(5 to 7 minutes)
415:Paper 3. Speaking
324:(3 to 5 minutes)
322:Paper 3. Speaking
79:
78:
71:
1339:
1313:
1312:
1310:Official website
1295:
1294:
1292:
1290:
1284:cambridge.org.br
1276:
1270:
1269:
1258:
1252:
1251:
1249:
1247:
1242:on 31 March 2015
1238:. Archived from
1232:
1226:
1225:
1223:
1221:
1216:on 20 March 2015
1212:. Archived from
1206:
1200:
1199:
1188:
1182:
1180:
1178:
1176:
1171:on 31 March 2015
1167:. Archived from
1161:
1155:
1154:
1152:
1150:
1141:. Archived from
1131:
1125:
1124:
1122:
1120:
1111:
1103:
1097:
1091:
1085:
1084:
1073:
1067:
1066:
1055:
1046:
1045:
1034:
1025:
1023:
1021:
1019:
1010:. Archived from
1004:
995:
993:
991:
989:
980:. Archived from
974:
968:
967:
956:
950:
949:
938:
929:
928:
926:
918:
912:
911:
909:
907:
897:
893:"Research notes"
889:
883:
877:
862:
856:
74:
67:
63:
60:
54:
49:by adding links
27:
26:
19:
1347:
1346:
1342:
1341:
1340:
1338:
1337:
1336:
1317:
1316:
1308:
1307:
1304:
1299:
1298:
1288:
1286:
1278:
1277:
1273:
1260:
1259:
1255:
1245:
1243:
1234:
1233:
1229:
1219:
1217:
1208:
1207:
1203:
1190:
1189:
1185:
1174:
1172:
1163:
1162:
1158:
1148:
1146:
1145:on 3 March 2016
1133:
1132:
1128:
1118:
1116:
1109:
1105:
1104:
1100:
1092:
1088:
1075:
1074:
1070:
1057:
1056:
1049:
1036:
1035:
1028:
1017:
1015:
1006:
1005:
998:
987:
985:
976:
975:
971:
964:www.youtube.com
958:
957:
953:
940:
939:
932:
924:
920:
919:
915:
905:
903:
902:. February 2002
895:
891:
890:
886:
878:
865:
857:
853:
848:
821:
808:
789:
731:
670:
609:
607:Pre A1 Starters
574:
560:
537:
442:
350:
265:
263:Pre A1 Starters
236:
192:South East Asia
138:
75:
64:
58:
55:
44:
28:
24:
17:
12:
11:
5:
1345:
1343:
1335:
1334:
1329:
1319:
1318:
1315:
1314:
1303:
1302:External links
1300:
1297:
1296:
1271:
1253:
1227:
1201:
1183:
1156:
1139:prnewswire.com
1126:
1098:
1086:
1068:
1047:
1026:
996:
969:
951:
930:
913:
884:
863:
859:Young Learners
850:
849:
847:
844:
843:
842:
837:
832:
827:
820:
817:
807:
804:
788:
785:
784:
783:
782:
781:
778:
775:
772:
766:
765:
764:
761:
755:
754:
753:
750:
747:
744:
741:
730:
727:
726:
725:
724:
723:
720:
717:
711:
710:
709:
706:
703:
700:
694:
693:
692:
689:
686:
683:
680:
669:
666:
665:
664:
663:
662:
659:
656:
653:
650:
644:
643:
642:
639:
636:
630:
629:
628:
625:
622:
619:
608:
605:
573:
570:
559:
556:
536:
533:
441:
438:
349:
346:
264:
261:
235:
232:
137:
134:
77:
76:
59:September 2024
31:
29:
22:
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1344:
1333:
1330:
1328:
1325:
1324:
1322:
1311:
1306:
1305:
1301:
1285:
1281:
1275:
1272:
1267:
1263:
1257:
1254:
1241:
1237:
1231:
1228:
1215:
1211:
1205:
1202:
1197:
1193:
1187:
1184:
1170:
1166:
1160:
1157:
1144:
1140:
1136:
1130:
1127:
1115:
1108:
1102:
1099:
1095:
1090:
1087:
1082:
1078:
1072:
1069:
1064:
1060:
1054:
1052:
1048:
1043:
1039:
1033:
1031:
1027:
1013:
1009:
1003:
1001:
997:
983:
979:
973:
970:
965:
961:
955:
952:
947:
943:
937:
935:
931:
923:
917:
914:
901:
894:
888:
885:
881:
876:
874:
872:
870:
868:
864:
860:
855:
852:
845:
841:
838:
836:
833:
831:
828:
826:
823:
822:
818:
816:
812:
805:
803:
800:
793:
786:
779:
776:
773:
770:
769:
767:
762:
759:
758:
756:
751:
748:
745:
742:
739:
738:
736:
735:
734:
728:
721:
718:
715:
714:
712:
707:
704:
701:
698:
697:
695:
690:
687:
684:
681:
678:
677:
675:
674:
673:
667:
660:
657:
654:
651:
648:
647:
645:
640:
637:
634:
633:
631:
626:
623:
620:
617:
616:
614:
613:
612:
606:
604:
602:
597:
595:
591:
587:
582:
578:
571:
569:
566:
563:
557:
555:
552:
548:
541:
534:
532:
529:
525:
521:
517:
513:
511:
507:
503:
499:
495:
491:
487:
483:
480:
477:
476:(40 minutes)
475:
471:
467:
463:
459:
455:
451:
448:
447:(25 minutes)
446:
439:
437:
434:
430:
426:
422:
418:
416:
412:
408:
404:
400:
396:
392:
388:
385:
384:(30 minutes)
383:
379:
375:
371:
367:
363:
359:
356:
355:(25 minutes)
354:
347:
345:
342:
339:
336:
332:
329:
325:
323:
319:
315:
311:
307:
303:
299:
296:
295:(20 minutes)
294:
290:
286:
282:
278:
274:
271:
270:(20 minutes)
269:
262:
260:
257:
253:
249:
246:
242:
239:
233:
231:
227:
225:
221:
217:
213:
209:
205:
201:
195:
193:
189:
188:South America
185:
180:
176:
174:
168:
166:
161:
159:
155:
151:
147:
142:
135:
133:
131:
127:
123:
118:
116:
111:
109:
105:
101:
97:
93:
85:
81:
73:
70:
62:
52:
48:
42:
41:
37:
32:This article
30:
21:
20:
1287:. Retrieved
1283:
1274:
1265:
1256:
1244:. Retrieved
1240:the original
1230:
1218:. Retrieved
1214:the original
1204:
1195:
1186:
1173:. Retrieved
1169:the original
1159:
1147:. Retrieved
1143:the original
1138:
1129:
1117:. Retrieved
1113:
1101:
1089:
1080:
1071:
1062:
1041:
1016:. Retrieved
1012:the original
986:. Retrieved
982:the original
972:
963:
954:
945:
916:
904:. Retrieved
899:
887:
854:
813:
809:
801:
798:
732:
671:
610:
598:
583:
579:
575:
567:
564:
561:
553:
549:
546:
530:
526:
522:
518:
514:
509:
508:
504:
500:
496:
492:
488:
484:
481:
478:
473:
472:
468:
464:
460:
456:
452:
449:
444:
443:
435:
431:
427:
423:
419:
414:
413:
409:
405:
401:
397:
393:
389:
386:
381:
380:
376:
372:
368:
364:
360:
357:
352:
351:
343:
340:
337:
333:
330:
326:
321:
320:
316:
312:
308:
304:
300:
297:
292:
291:
287:
283:
279:
275:
272:
267:
266:
250:
247:
243:
240:
237:
228:
196:
181:
177:
169:
162:
140:
139:
119:
112:
99:
95:
91:
90:
80:
65:
56:
45:Please help
33:
1289:25 February
1246:25 February
1220:25 February
1175:25 February
1149:25 February
1119:6 September
1018:25 February
988:25 February
960:"- YouTube"
906:25 February
787:Preparation
34:needs more
1321:Categories
846:References
729:A2 Flyers
668:A1 Movers
440:A2 Flyers
348:A1 Movers
218:, Spain,
200:Argentina
154:Argentina
819:See also
222:and the
220:Thailand
216:Portugal
38:to help
535:Scoring
391:words.
136:History
234:Format
184:Europe
1110:(PDF)
925:(PDF)
896:(PDF)
572:Usage
212:Libya
208:Japan
204:China
158:Italy
150:Spain
146:China
1291:2015
1248:2015
1222:2015
1177:2015
1151:2015
1121:2023
1020:2015
990:2015
908:2015
592:and
190:and
156:and
100:YLE
1323::
1282:.
1264:.
1194:.
1137:.
1112:.
1079:.
1061:.
1050:^
1040:.
1029:^
999:^
962:.
944:.
933:^
898:.
866:^
588:,
224:UK
214:,
210:,
206:,
202:,
186:,
160:.
152:,
148:,
1293:.
1268:.
1250:.
1224:.
1198:.
1179:.
1153:.
1123:.
1083:.
1065:.
1044:.
1022:.
992:.
966:.
948:.
927:.
910:.
98:(
72:)
66:(
61:)
57:(
43:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.