697:
522:
685:
756:
31:
1527:
Although metal centers (e.g., Li, Zn, Sc, etc.) are most commonly cationic and electrophilic (Lewis acidic) in nature, certain metal centers (particularly ones in a low oxidation state and/or carrying a negative charge) are among the strongest recorded nucleophiles and are sometimes referred to as
1892:
Mayr, Herbert; Bug, Thorsten; Gotta, Matthias F; Hering, Nicole; Irrgang, Bernhard; Janker, Brigitte; Kempf, Bernhard; Loos, Robert; Ofial, Armin R; Remennikov, Grigoriy; Schimmel, Holger (2001). "Reference Scales for the
Characterization of Cationic Electrophiles and Neutral Nucleophiles".
193:
of the conjugate acid) the more reactive it is as a nucleophile. Within a series of nucleophiles with the same attacking element (e.g. oxygen), the order of nucleophilicity will follow basicity. Sulfur is in general a better nucleophile than oxygen.
2051:
Dessy, Raymond E.; Pohl, Rudolph L.; King, R. Bruce (November 1966). "Organometallic
Electrochemistry. VII. 1 The Nucleophilicities of Metallic and Metalloidal Anions Derived from Metals of Groups IV, V, VI, VII, and VIII".
469:
287:
493:
in the Swain–Scott equation is absent. The equation states that two nucleophiles react with the same relative reactivity regardless of the nature of the electrophile, which is in violation of the
1328:
is not a nucleophile), their anions are good nucleophiles. In polar, protic solvents, F is the weakest nucleophile, and I the strongest; this order is reversed in polar, aprotic solvents.
965:
1251:
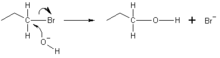
2 reaction occurs by backside attack. This means that the hydroxide ion attacks the carbon atom from the other side, exactly opposite the bromine ion. Because of this backside attack, S
1046:
1192:
862:
1277:
696:
1116:
633:
735:
to 1-phenyl-2-propene (2), and 0.96 (1) for addition to 2-methyl-1-pentene (3), −0.13 (1.21) for reaction with triphenylallylsilane (4), 3.61 (1.11) for reaction with
1738:
Quantitative
Correlation of Relative Rates. Comparison of Hydroxide Ion with Other Nucleophilic Reagents toward Alkyl Halides, Esters, Epoxides and Acyl Halides
99:. Nucleophilicity, sometimes referred to as nucleophile strength, refers to a substance's nucleophilic character and is often used to compare the affinity of
1865:
Mayr, Herbert; Patz, Matthias (1994). "Scales of
Nucleophilicity and Electrophilicity: A System for Ordering Polar Organic and Organometallic Reactions".
684:
1694:
Ingold, C. K. (1933). "266. Significance of tautomerism and of the reactions of aromatic compounds in the electronic theory of organic reactions".
1543:) is about 10 times more nucleophilic. Other supernucleophilic metal centers include low oxidation state carbonyl metalate anions (e.g., CpFe(CO)
494:
1460:(RSH), thiolate anions (RS), anions of thiolcarboxylic acids (RC(O)-S), and anions of dithiocarbonates (RO-C(S)-S) and dithiocarbamates (R
521:
2120:
724:
406:
228:
1276:
755:
297:
504:
In the original publication the data were obtained by reactions of selected nucleophiles with selected electrophilic
900:
381:
116:
978:
1648:
1343:
1127:
293:
797:
563:
anion. The values for the relative cation reactivities are −0.4 for the malachite green cation, +2.6 for the
2008:
Schrauzer, G. N.; Deutsch, E.; Windgassen, R. J. (April 1968). "The nucleophilicity of vitamin B(sub 12s)".
1309:
1256:
564:
158:
739:(5), +7.48 (0.89) for reaction with isobutenyltributylstannane (6) and +13.36 (0.81) for reaction with the
1960:
1654:
1268:
732:
642:
486:
300:
1951:
Phan, Thanh Binh; Breugst, Martin; Mayr, Herbert (2006). "Towards a
General Scale of Nucleophilicity?".
1642:
1397:
1393:
1371:
1363:
665:
210:
for many reactions involving many nucleophiles and electrophiles. Nucleophiles displaying the so-called
120:
1071:
672:
1401:
1355:
1965:
1292:
is one that can attack from two or more places, resulting in two or more products. For example, the
585:
202:
Many schemes attempting to quantify relative nucleophilic strength have been devised. The following
2088:
1429:
1240:
108:
51:
1838:
Cation–anion combination reactions. XIII. Correlation of the reactions of nucleophiles with esters
1304:
of an alkyl halide with SCN often leads to a mixture of an alkyl thiocyanate (R-SCN) and an alkyl
1918:
1405:
2069:
2033:
2025:
1978:
1910:
1841:
1741:
1555:
The following table shows the nucleophilicity of some molecules with methanol as the solvent:
1471:, which makes it readily polarizable, and its lone pairs of electrons are readily accessible.
1437:
1347:
136:
2061:
2017:
1970:
1935:
An internet database for reactivity parameters maintained by the Mayr group is available at
1902:
1874:
1849:
1822:
1795:
1770:
1749:
1719:
1699:
1678:
1453:
1385:
1359:
568:
374:
66:
876:
the nucleophile-dependent slope parameter. This equation can be rewritten in several ways:
189:
In general, in a group across the periodic table, the more basic the ion (the higher the pK
1508:
1351:
529:
385:
370:
1528:"supernucleophiles." For instance, using methyl iodide as the reference electrophile, Ph
322:
that depends on the sensitivity of a substrate to nucleophilic attack (defined as 1 for
1381:
1305:
884:= 1 for carbocations this equation is equal to the original Mayr–Patz equation of 1994,
790:
In an effort to unify the above described equations the Mayr equation is rewritten as:
323:
174:
170:
96:
2114:
1512:
1496:
736:
717:
207:
132:
70:
119:, whereby a nucleophile becomes attracted to a full or partial positive charge, and
1922:
1636:
1297:
1232:
1227:
of the hydroxide ion donates an electron pair to form a new chemical bond with the
747:
676:
314:, of a standard reaction with water as the nucleophile, to a nucleophilic constant
211:
153:
39:
1444:. Nucleophilic attack does not take place during intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
1296:
ion (SCN) may attack from either the sulfur or the nitrogen. For this reason, the
17:
1998:. Thompson, Alison and Pincock, James, Dalhousie University Chemistry Department
1533:
1441:
1293:
505:
354:
329:
This treatment results in the following values for typical nucleophilic anions:
767:
560:
112:
86:
47:
2073:
2029:
222:
The first such attempt is found in the Swain–Scott equation derived in 1953:
1800:
1775:
1504:
1500:
1425:
1389:
1367:
1337:
1205:
771:
552:
513:
509:
400:
The
Ritchie equation, derived in 1972, is another free-energy relationship:
342:
203:
58:
35:
1982:
1974:
1914:
1878:
1682:
1677:
Nucleophilicity—Periodic Trends and
Connection to Basicity. Einar Uggerud.
1639: – A chemical species that accepts an electron pair from a nucleophile
2037:
1936:
1717:
Lapworth, A. (1925). "Replaceability of
Halogen Atoms by Hydrogen Atoms".
1532:
Sn is about 10000 times more nucleophilic than I, while the Co(I) form of
135:
property (i.e. relates to an equilibrium state), but nucleophilicity is a
30:
1703:
1433:
1321:
709:
705:
639:
544:
540:
358:
334:
128:
124:
85:
can act as nucleophiles. Because nucleophiles donate electrons, they are
74:
2065:
2021:
1853:
1826:
1753:
95:
describes the affinity of a nucleophile to bond with positively charged
1492:
1480:
1380:
are also carbon nucleophiles. The formation of an enol is catalyzed by
1244:
1236:
1213:
740:
728:
713:
648:
at 20 °C for a reaction is related to a nucleophilicity parameter
548:
366:
362:
346:
330:
104:
82:
1906:
1260:
1243:, with the bromine atom taking the donated electron and becoming the
1228:
1224:
1204:
Examples of nucleophiles are anions such as Cl, or a compound with a
350:
178:
774:, and 5.20 (0.89) for water. In short, nucleophilicities towards sp
671:
Many of the constants have been derived from reaction of so-called
1516:
1488:
1484:
1457:
1417:
556:
489:
for water. In this equation, a substrate-dependent parameter like
389:
338:
29:
1377:
139:
property, which relates to rates of certain chemical reactions.
100:
464:{\displaystyle \log _{10}\left({\frac {k}{k_{0}}}\right)=N^{+}}
78:
1271:
is flipped as compared to that of the original electrophile.
723:
Typical N values with s in parentheses are −4.47 (1.32) for
282:{\displaystyle \log _{10}\left({\frac {k}{k_{0}}}\right)=sn}
766:, typical nucleophile values N (s) are 15.63 (0.64) for
1659:
Pages displaying short descriptions of redirect targets
532:. Many other reaction types have since been described.
1469:
sulfur is very nucleophilic because of its large size
1130:
1074:
981:
903:
800:
588:
409:
231:
1263:, it typically maintains its chirality, though the S
497:. For this reason, this equation is also called the
1392:nucleophiles, but, in general, nucleophilic at the
1324:
are not nucleophilic in their diatomic form (e.g. I
1867:Angewandte Chemie International Edition in English
1186:
1110:
1040:
959:
891:= 0.6 for most n nucleophiles the equation becomes
856:
627:
463:
307:, of a reaction, normalized to the reaction rate,
281:
318:for a given nucleophile and a substrate constant
972:or the original Scott–Swain equation written as:
872:the electrophile-dependent slope parameter and s
214:are usually omitted in this type of treatment.
1235:molecule. The bond between the carbon and the
656:, and a nucleophile-dependent slope parameter
357:6.4. Typical substrate constants are 0.66 for
173:in 1925. The word nucleophile is derived from
81:with a free pair of electrons or at least one
27:Chemical species that donates an electron pair
1308:(R-NCS). Similar considerations apply in the
1122:or the original Ritchie equation written as:
8:
1792:The IUPAC Compendium of Chemical Terminology
1767:The IUPAC Compendium of Chemical Terminology
1259:of the electrophile. If the electrophile is
746:The range of organic reactions also include
691:and a diverse collection of π-nucleophiles:
1946:
1944:
1370:. These reagents are often used to perform
960:{\displaystyle \log(k)=0.6s_{E}N+0.6s_{E}E}
478:is the nucleophile dependent parameter and
392:anion reacts 3000 times faster than water.
1041:{\displaystyle \log(k)=\log(k_{0})+s_{E}N}
127:. The difference between the two is, that
1964:
1799:
1774:
1696:Journal of the Chemical Society (Resumed)
1255:2 reactions result in a inversion of the
1187:{\displaystyle \log(k)-\log(k_{0})=N^{+}}
1178:
1162:
1129:
1073:
1029:
1013:
980:
948:
929:
902:
833:
823:
799:
587:
455:
436:
427:
414:
408:
258:
249:
236:
230:
2054:Journal of the American Chemical Society
2010:Journal of the American Chemical Society
1895:Journal of the American Chemical Society
1815:Nucleophilic reactivities toward cations
1557:
123:. Nucleophilicity is closely related to
1953:Angewandte Chemie International Edition
1937:http://www.cup.uni-muenchen.de/oc/mayr/
1670:
1651: – Type of organometallic reaction
857:{\displaystyle \log(k)=s_{E}s_{N}(N+E)}
103:. Neutral nucleophilic reactions with
1657: – Organometallic chemistry rule
206:data have been obtained by measuring
7:
1740:C. Gardner Swain, Carleton B. Scott
1416:Examples of oxygen nucleophiles are
1817:Calvin D. Ritchie Acc. Chem. Res.;
725:electrophilic aromatic substitution
704:Typical E values are +6.2 for R =
579:In the Mayr–Patz equation (1994):
38:ion acting as a nucleophile in an
25:
1396:atom. Enols are commonly used in
1111:{\displaystyle \log(k)=0.6N+0.6E}
782:centers follow the same pattern.
528:or (not displayed) ions based on
499:constant selectivity relationship
380:The equation predicts that, in a
1275:
754:
695:
683:
652:, an electrophilicity parameter
520:
495:reactivity–selectivity principle
115:. Nucleophiles may take part in
69:that forms bonds by donating an
1464:N-C(S)-S) are used most often.
1479:Nitrogen nucleophiles include
1342:Carbon nucleophiles are often
1168:
1155:
1143:
1137:
1087:
1081:
1019:
1006:
994:
988:
916:
910:
851:
839:
813:
807:
764:S-methyldibenzothiophenium ion
628:{\displaystyle \log(k)=s(N+E)}
622:
610:
601:
595:
1:
1996:Chem 2401 Supplementary Notes
161:in 1933, replacing the terms
1645: – Chemical bond theory
1346:such as those found in the
1062:= 0.6 the equation becomes:
2137:
2121:Physical organic chemistry
1335:
1223:In the example below, the
1058:= 1 for carbocations and s
303:(in water at 25 °C),
2089:"Chapter 8: Nucleophiles"
1561:Relative nucleophilicity
382:nucleophilic displacement
117:nucleophilic substitution
1765:"Swain–Scott equation".
1649:Nucleophilic abstraction
1452:Of sulfur nucleophiles,
559:anion, and 10.7 for the
294:free-energy relationship
2095:. University of Calgary
1801:10.1351/goldbook.R05402
1776:10.1351/goldbook.S06201
1362:or reactions involving
1344:organometallic reagents
1310:Kolbe nitrile synthesis
1208:of electrons such as NH
762:With E = −9.15 for the
565:benzenediazonium cation
159:Christopher Kelk Ingold
1975:10.1002/anie.200600542
1879:10.1002/anie.199409381
1683:10.1002/chem.200500639
1655:Addition to pi ligands
1398:condensation reactions
1372:nucleophilic additions
1364:organolithium reagents
1269:absolute configuration
1188:
1112:
1042:
961:
858:
733:electrophilic addition
731:(1), −0.41 (1.12) for
643:reaction rate constant
629:
487:reaction rate constant
465:
301:reaction rate constant
283:
54:
1643:Lewis acids and bases
1580:Br⁻, OH⁻, RO⁻, CN⁻, N
1247:ion (Br), because a S
1189:
1113:
1043:
962:
859:
664:is defined as 1 with
630:
466:
284:
143:History and Etymology
121:nucleophilic addition
33:
1848:; 97(5); 1170–1179.
1790:"Ritchie equation".
1704:10.1039/jr9330001120
1402:Claisen condensation
1356:Reformatsky reaction
1290:ambident nucleophile
1284:Ambident Nucleophile
1128:
1072:
979:
901:
798:
668:as the nucleophile.
586:
407:
229:
218:Swain–Scott equation
169:proposed earlier by
111:and water are named
2066:10.1021/ja00974a015
2022:10.1021/ja01011a054
1854:10.1021/ja00838a035
1827:10.1021/ar50058a005
1754:10.1021/ja01097a041
1241:heterolytic fission
770:, 10.49 (0.68) for
567:, and +4.5 for the
555:anion, 8.5 for the
551:anion, 7.5 for the
177:and the Greek word
157:were introduced by
1840:Calvin D. Ritchie
1821:; 5(10); 348-354.
1748:; 75(1); 141-147.
1442:carboxylate anions
1406:aldol condensation
1231:at the end of the
1184:
1108:
1038:
957:
854:
716:and −7.02 for R =
673:benzhydrylium ions
666:2-methyl-1-pentene
625:
575:Mayr–Patz equation
461:
298:pseudo first order
279:
181:, meaning friend.
55:
18:Carbon nucleophile
2060:(22): 5121–5124.
1907:10.1021/ja010890y
1842:J. Am. Chem. Soc.
1742:J. Am. Chem. Soc.
1628:
1627:
1438:hydrogen peroxide
1348:Grignard reaction
442:
367:2,3-epoxypropanol
264:
16:(Redirected from
2128:
2105:
2104:
2102:
2100:
2093:chem.ucalgary.ca
2084:
2078:
2077:
2048:
2042:
2041:
2016:(9): 2441–2442.
2005:
1999:
1993:
1987:
1986:
1968:
1948:
1939:
1933:
1927:
1926:
1889:
1883:
1882:
1862:
1856:
1835:
1829:
1812:
1806:
1805:
1803:
1787:
1781:
1780:
1778:
1762:
1756:
1735:
1729:
1728:
1714:
1708:
1707:
1691:
1685:
1675:
1660:
1558:
1454:hydrogen sulfide
1400:, including the
1360:Barbier reaction
1279:
1193:
1191:
1190:
1185:
1183:
1182:
1167:
1166:
1117:
1115:
1114:
1109:
1047:
1045:
1044:
1039:
1034:
1033:
1018:
1017:
966:
964:
963:
958:
953:
952:
934:
933:
863:
861:
860:
855:
838:
837:
828:
827:
786:Unified equation
758:
708:, +5.90 for R =
699:
687:
634:
632:
631:
626:
569:tropylium cation
535:Typical Ritchie
524:
470:
468:
467:
462:
460:
459:
447:
443:
441:
440:
428:
419:
418:
396:Ritchie equation
375:benzoyl chloride
288:
286:
285:
280:
269:
265:
263:
262:
250:
241:
240:
67:chemical species
21:
2136:
2135:
2131:
2130:
2129:
2127:
2126:
2125:
2111:
2110:
2109:
2108:
2098:
2096:
2086:
2085:
2081:
2050:
2049:
2045:
2007:
2006:
2002:
1994:
1990:
1966:10.1.1.617.3287
1959:(23): 3869–74.
1950:
1949:
1942:
1934:
1930:
1901:(39): 9500–12.
1891:
1890:
1886:
1864:
1863:
1859:
1836:
1832:
1813:
1809:
1789:
1788:
1784:
1764:
1763:
1759:
1736:
1732:
1716:
1715:
1711:
1693:
1692:
1688:
1676:
1672:
1667:
1658:
1633:
1623:
1611:
1599:
1595:
1583:
1553:
1546:
1542:
1537:
1531:
1525:
1509:phenylhydrazine
1477:
1463:
1456:and its salts,
1450:
1423:
1414:
1352:Blaise reaction
1340:
1334:
1327:
1318:
1301:
1286:
1266:
1254:
1250:
1239:then undergoes
1219:
1211:
1202:
1174:
1158:
1126:
1125:
1070:
1069:
1061:
1057:
1025:
1009:
977:
976:
944:
925:
899:
898:
890:
883:
875:
871:
829:
819:
796:
795:
788:
781:
777:
660:. The constant
584:
583:
577:
543:) are: 0.5 for
530:malachite green
484:
451:
432:
423:
410:
405:
404:
398:
386:benzyl chloride
373:, and 1.43 for
371:benzyl chloride
363:β-propiolactone
313:
254:
245:
232:
227:
226:
220:
200:
198:Nucleophilicity
192:
187:
145:
46:, converting a
43:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
2134:
2132:
2124:
2123:
2113:
2112:
2107:
2106:
2079:
2043:
2000:
1988:
1940:
1928:
1884:
1857:
1830:
1807:
1782:
1757:
1730:
1709:
1686:
1669:
1668:
1666:
1663:
1662:
1661:
1652:
1646:
1640:
1632:
1629:
1626:
1625:
1621:
1618:
1614:
1613:
1609:
1606:
1602:
1601:
1597:
1596:, Cl⁻, F⁻, RCO
1593:
1590:
1586:
1585:
1581:
1578:
1574:
1573:
1570:
1566:
1565:
1562:
1552:
1549:
1544:
1540:
1535:
1529:
1524:
1521:
1476:
1473:
1461:
1449:
1446:
1421:
1413:
1410:
1333:
1330:
1325:
1317:
1314:
1306:isothiocyanate
1299:
1285:
1282:
1281:
1280:
1264:
1252:
1248:
1217:
1209:
1201:
1198:
1197:
1196:
1195:
1194:
1181:
1177:
1173:
1170:
1165:
1161:
1157:
1154:
1151:
1148:
1145:
1142:
1139:
1136:
1133:
1120:
1119:
1118:
1107:
1104:
1101:
1098:
1095:
1092:
1089:
1086:
1083:
1080:
1077:
1064:
1063:
1059:
1055:
1051:
1050:
1049:
1048:
1037:
1032:
1028:
1024:
1021:
1016:
1012:
1008:
1005:
1002:
999:
996:
993:
990:
987:
984:
969:
968:
967:
956:
951:
947:
943:
940:
937:
932:
928:
924:
921:
918:
915:
912:
909:
906:
893:
892:
888:
885:
881:
873:
869:
866:
865:
853:
850:
847:
844:
841:
836:
832:
826:
822:
818:
815:
812:
809:
806:
803:
787:
784:
779:
775:
760:
759:
702:
701:
689:
688:
636:
635:
624:
621:
618:
615:
612:
609:
606:
603:
600:
597:
594:
591:
576:
573:
547:, 5.9 for the
526:
525:
482:
472:
471:
458:
454:
450:
446:
439:
435:
431:
426:
422:
417:
413:
397:
394:
359:ethyl tosylate
324:methyl bromide
311:
290:
289:
278:
275:
272:
268:
261:
257:
253:
248:
244:
239:
235:
219:
216:
208:reaction rates
199:
196:
190:
186:
183:
171:A. J. Lapworth
144:
141:
41:
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2133:
2122:
2119:
2118:
2116:
2094:
2090:
2083:
2080:
2075:
2071:
2067:
2063:
2059:
2055:
2047:
2044:
2039:
2035:
2031:
2027:
2023:
2019:
2015:
2011:
2004:
2001:
1997:
1992:
1989:
1984:
1980:
1976:
1972:
1967:
1962:
1958:
1954:
1947:
1945:
1941:
1938:
1932:
1929:
1924:
1920:
1916:
1912:
1908:
1904:
1900:
1896:
1888:
1885:
1880:
1876:
1872:
1868:
1861:
1858:
1855:
1851:
1847:
1843:
1839:
1834:
1831:
1828:
1824:
1820:
1816:
1811:
1808:
1802:
1797:
1793:
1786:
1783:
1777:
1772:
1768:
1761:
1758:
1755:
1751:
1747:
1743:
1739:
1734:
1731:
1726:
1722:
1721:
1713:
1710:
1705:
1701:
1697:
1690:
1687:
1684:
1680:
1674:
1671:
1664:
1656:
1653:
1650:
1647:
1644:
1641:
1638:
1635:
1634:
1630:
1619:
1616:
1615:
1607:
1604:
1603:
1591:
1588:
1587:
1579:
1576:
1575:
1572:I⁻, HS⁻, RS⁻
1571:
1568:
1567:
1563:
1560:
1559:
1556:
1550:
1548:
1538:
1523:Metal centers
1522:
1520:
1518:
1514:
1513:semicarbazide
1510:
1506:
1502:
1498:
1497:hydroxylamine
1494:
1490:
1486:
1482:
1474:
1472:
1470:
1465:
1459:
1455:
1447:
1445:
1443:
1439:
1435:
1431:
1427:
1419:
1411:
1409:
1407:
1403:
1399:
1395:
1391:
1387:
1383:
1379:
1375:
1373:
1369:
1365:
1361:
1357:
1353:
1349:
1345:
1339:
1331:
1329:
1323:
1315:
1313:
1311:
1307:
1303:
1295:
1291:
1283:
1278:
1274:
1273:
1272:
1270:
1262:
1258:
1257:configuration
1246:
1242:
1238:
1234:
1230:
1226:
1221:
1215:
1207:
1199:
1179:
1175:
1171:
1163:
1159:
1152:
1149:
1146:
1140:
1134:
1131:
1124:
1123:
1121:
1105:
1102:
1099:
1096:
1093:
1090:
1084:
1078:
1075:
1068:
1067:
1066:
1065:
1053:
1052:
1035:
1030:
1026:
1022:
1014:
1010:
1003:
1000:
997:
991:
985:
982:
975:
974:
973:
970:
954:
949:
945:
941:
938:
935:
930:
926:
922:
919:
913:
907:
904:
897:
896:
895:
894:
886:
879:
878:
877:
864:
848:
845:
842:
834:
830:
824:
820:
816:
810:
804:
801:
793:
792:
791:
785:
783:
773:
769:
765:
757:
753:
752:
751:
749:
748:SN2 reactions
744:
742:
738:
737:2-methylfuran
734:
730:
726:
721:
719:
718:dimethylamine
715:
711:
707:
698:
694:
693:
692:
686:
682:
681:
680:
678:
677:electrophiles
674:
669:
667:
663:
659:
655:
651:
647:
644:
641:
619:
616:
613:
607:
604:
598:
592:
589:
582:
581:
580:
574:
572:
570:
566:
562:
558:
554:
550:
546:
542:
538:
533:
531:
523:
519:
518:
517:
515:
511:
507:
502:
500:
496:
492:
488:
481:
477:
456:
452:
448:
444:
437:
433:
429:
424:
420:
415:
411:
403:
402:
401:
395:
393:
391:
387:
383:
378:
376:
372:
368:
364:
360:
356:
352:
348:
344:
340:
336:
332:
327:
325:
321:
317:
310:
306:
302:
299:
295:
276:
273:
270:
266:
259:
255:
251:
246:
242:
237:
233:
225:
224:
223:
217:
215:
213:
209:
205:
197:
195:
184:
182:
180:
179:φιλος, philos
176:
172:
168:
164:
160:
156:
155:
150:
142:
140:
138:
134:
133:thermodynamic
130:
126:
122:
118:
114:
110:
106:
102:
98:
97:atomic nuclei
94:
90:
88:
84:
80:
76:
72:
71:electron pair
68:
64:
60:
53:
49:
45:
37:
32:
19:
2097:. Retrieved
2092:
2082:
2057:
2053:
2046:
2013:
2009:
2003:
1995:
1991:
1956:
1952:
1931:
1898:
1894:
1887:
1870:
1866:
1860:
1845:
1837:
1833:
1818:
1814:
1810:
1791:
1785:
1766:
1760:
1745:
1737:
1733:
1724:
1718:
1712:
1695:
1689:
1673:
1637:Electrophile
1554:
1526:
1478:
1468:
1467:In general,
1466:
1451:
1415:
1394:alpha carbon
1388:. Enols are
1376:
1341:
1319:
1289:
1287:
1267:2 product's
1233:bromopropane
1222:
1203:
971:
867:
794:
789:
763:
761:
745:
722:
712:, 0 for R =
703:
690:
670:
661:
657:
653:
649:
645:
640:second order
637:
578:
536:
534:
527:
506:carbocations
503:
498:
490:
479:
475:
473:
399:
379:
328:
319:
315:
308:
304:
296:relates the
291:
221:
212:alpha effect
201:
188:
166:
162:
154:electrophile
152:
148:
146:
93:Nucleophilic
92:
91:
62:
56:
1408:reactions.
1294:thiocyanate
539:values (in
369:, 0.87 for
365:, 1.00 for
361:, 0.77 for
355:thiosulfate
149:nucleophile
87:Lewis bases
63:nucleophile
2087:Ian Hunt.
1873:(9): 938.
1665:References
1617:Very Weak
1569:Very Good
1564:Molecules
1539:(vitamin B
1368:acetylides
1336:See also:
1320:While the
1302:2 reaction
768:piperidine
561:thiophenol
185:Properties
147:The terms
113:solvolysis
48:haloalkane
44:2 reaction
2074:0002-7863
2030:0002-7863
1961:CiteSeerX
1534:vitamin B
1505:carbazide
1501:hydrazine
1426:hydroxide
1338:Carbanion
1206:lone pair
1153:
1147:−
1135:
1079:
1004:
986:
908:
805:
772:methoxide
593:
553:methoxide
516:cations:
514:diazonium
510:tropylium
421:
353:5.0, and
343:hydroxide
243:
204:empirical
167:cationoid
75:molecules
59:chemistry
36:hydroxide
2115:Category
2099:15 April
1983:16646102
1915:11572670
1794:. 2014.
1769:. 2014.
1698:: 1120.
1631:See also
1551:Examples
1493:nitrites
1475:Nitrogen
1436:anions,
1434:alkoxide
1430:alcohols
1404:and the
1390:ambident
1322:halogens
1316:Halogens
1216:) and PR
710:hydrogen
706:chlorine
545:methanol
541:methanol
508:such as
335:chloride
163:anionoid
129:basicity
125:basicity
109:alcohols
107:such as
105:solvents
50:into an
2038:5642073
1923:8392147
1612:O, ROH
1481:ammonia
1428:anion,
1245:bromide
1237:bromine
1214:ammonia
741:enamine
729:toluene
714:methoxy
675:as the
549:cyanide
347:aniline
331:acetate
175:nucleus
137:kinetic
83:pi bond
52:alcohol
2072:
2036:
2028:
1981:
1963:
1921:
1913:
1727:: 625.
1720:Nature
1515:, and
1489:amines
1458:thiols
1448:Sulfur
1440:, and
1412:Oxygen
1358:, and
1332:Carbon
1261:chiral
1229:carbon
1225:oxygen
1054:with s
887:with s
880:with s
868:with s
474:where
388:, the
351:iodide
73:. All
1919:S2CID
1605:Weak
1589:Fair
1577:Good
1517:amide
1485:azide
1418:water
1378:Enols
1200:Types
778:or sp
557:azide
390:azide
349:4.5,
345:4.2,
341:4.0,
339:azide
337:3.0,
333:2.7,
292:This
131:is a
101:atoms
65:is a
2101:2024
2070:ISSN
2034:PMID
2026:ISSN
1979:PMID
1911:PMID
1846:1975
1819:1972
1746:1953
1424:O),
1386:base
1382:acid
1366:and
638:The
485:the
165:and
151:and
79:ions
77:and
61:, a
2062:doi
2018:doi
1971:doi
1903:doi
1899:123
1875:doi
1850:doi
1823:doi
1796:doi
1771:doi
1750:doi
1725:115
1700:doi
1679:doi
1620:RCO
1547:).
1541:12s
1384:or
1288:An
1150:log
1132:log
1103:0.6
1094:0.6
1076:log
1001:log
983:log
942:0.6
923:0.6
905:log
802:log
743:7.
727:to
590:log
512:or
412:log
384:on
326:).
234:log
89:.
57:In
2117::
2091:.
2068:.
2058:88
2056:.
2032:.
2024:.
2014:90
2012:.
1977:.
1969:.
1957:45
1955:.
1943:^
1917:.
1909:.
1897:.
1871:33
1869:.
1844:;
1744:;
1723:.
1624:H
1600:⁻
1592:NH
1584:⁻
1536:12
1519:.
1511:,
1507:,
1503:,
1499:,
1495:,
1491:,
1487:,
1483:,
1432:,
1420:(H
1374:.
1354:,
1350:,
1312:.
1220:.
750::
720:.
679::
571:.
501:.
416:10
377:.
238:10
34:A
2103:.
2076:.
2064::
2040:.
2020::
1985:.
1973::
1925:.
1905::
1881:.
1877::
1852::
1825::
1804:.
1798::
1779:.
1773::
1752::
1706:.
1702::
1681::
1622:2
1610:2
1608:H
1598:2
1594:3
1582:3
1545:2
1530:3
1462:2
1422:2
1326:2
1300:N
1298:S
1265:N
1253:N
1249:N
1218:3
1212:(
1210:3
1180:+
1176:N
1172:=
1169:)
1164:0
1160:k
1156:(
1144:)
1141:k
1138:(
1106:E
1100:+
1097:N
1091:=
1088:)
1085:k
1082:(
1060:N
1056:E
1036:N
1031:E
1027:s
1023:+
1020:)
1015:0
1011:k
1007:(
998:=
995:)
992:k
989:(
955:E
950:E
946:s
939:+
936:N
931:E
927:s
920:=
917:)
914:k
911:(
889:N
882:E
874:N
870:E
852:)
849:E
846:+
843:N
840:(
835:N
831:s
825:E
821:s
817:=
814:)
811:k
808:(
780:3
776:2
700:.
662:s
658:s
654:E
650:N
646:k
623:)
620:E
617:+
614:N
611:(
608:s
605:=
602:)
599:k
596:(
537:N
491:s
483:0
480:k
476:N
457:+
453:N
449:=
445:)
438:0
434:k
430:k
425:(
320:s
316:n
312:0
309:k
305:k
277:n
274:s
271:=
267:)
260:0
256:k
252:k
247:(
191:a
42:N
40:S
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.