399:
76:
66:
976:
1348:
1321:
79:
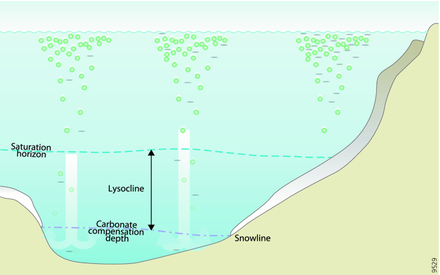
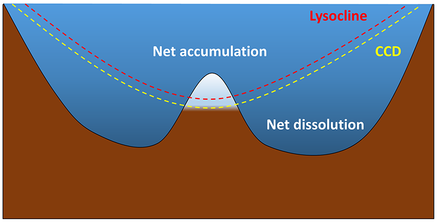
Calcareous sediment can only accumulate in depths shallower than the calcium carbonate compensation depth (CCD). Below the CCD, calcareous sediments dissolve and will not accumulate. The lysocline represents the depth range in which the rate of dissolution increases
1088:
it is intermediate between the
Atlantic and the Pacific at approximately 4300 meters. The variation in the depth of the CCD largely results from the length of time since the bottom water has been exposed to the surface; this is called the "age" of the
100:
of the oceans (green circles). Upon death, those tests escaping dissolution near the surface settle, along with clay materials. In seawater, a dissolution boundary is formed as a result of temperature, pressure, and depth, and is known as the
317:
1203:, which is also caused by increasing carbon dioxide concentrations in the atmosphere, will increase such dissolution and shallow the carbonate compensation depth on timescales of tens to hundreds of years.
1101:, sink from the surface waters into deeper water, deep water masses tend to accumulate dissolved carbon dioxide as they age. The oldest water masses have the highest concentrations of CO
1160:
in the ocean mixed surface layer. This effect was somewhat moderated by the deep oceans' elevated temperatures during this period. In the late Eocene the transition from a
366:, may bring the carbonate layer below the CCD; the carbonate layer may be prevented from chemically interacting with the sea water by overlying sediments such as a layer of
57:
carbonates. Aragonite is more soluble than calcite, and the aragonite compensation depth is generally shallower than both the calcite compensation depth and the CCD.
1035:
in the water. Calcium carbonate is more soluble at lower temperatures and at higher pressures. It is also more soluble if the concentration of dissolved CO
486:
771:
444:
1121:
occurs. This downwelling brings young, surface water with relatively low concentrations of carbon dioxide into the deep ocean, depressing the CCD.
158:
944:
1185:
471:
1007:
825:
35:. That is, solvation 'compensates' supply. Below the CCD solvation is faster, so that carbonate particles dissolve and the carbonate shells (
1470:
1304:
949:
1170:
investigated and experimented on the dissolution of calcium carbonate and was first to identify the carbonate compensation depth in oceans.
109:
tests are largely preserved. Below it, waters are undersaturated, because of both the increasing solubility with depth and the release of CO
1179:
414:
124:
from above. At steady state this depth, the CCD, is similar to the snowline (the first depth where carbonate-poor sediments occur). The
117:
will dissolve. The sinking velocity of debris is rapid (broad pale arrows), so dissolution occurs primarily at the sediment surface.
39:) of animals are not preserved. Carbonate particles cannot accumulate in the sediments where the sea floor is below this depth.
1039:
is higher. Adding a reactant to the above chemical equation pushes the equilibrium towards the right producing more products:
1161:
874:
1136:
the CCD was much shallower globally than it is today; due to intense volcanic activity during this period atmospheric CO
864:
544:
1383:
Boudreau, Bernard P.; Middelburg, Jack J.; Luo, Yiming (2018). "The role of calcification in carbonate compensation".
1167:
1059:
934:
832:
538:
532:
1634:
1342:
939:
559:
358:
will dissolve before reaching this level, preventing deposition of carbonate sediment. As the sea floor spreads,
1365:
1097:
determines the relative ages of the water in these basins. Because organic material, such as fecal pellets from
1000:
1094:
914:
842:
837:
820:
665:
526:
424:
924:
439:
744:
520:
481:
449:
45:
is the least soluble of these carbonates, so the CCD is normally the compensation depth for calcite. The
1664:
993:
980:
929:
660:
120:
At the carbonate compensation depth, the rate of dissolution exactly matches the rate of supply of CaCO
1599:
1499:
1392:
856:
758:
514:
419:
75:
1265:
1200:
805:
621:
476:
136:
Calcium carbonate is essentially insoluble in sea surface waters today. Shells of dead calcareous
65:
1568:
1408:
1310:
1255:
1020:
The exact value of the CCD depends on the solubility of calcium carbonate which is determined by
884:
652:
636:
631:
554:
359:
1615:
1527:
1466:
1300:
1055:
815:
594:
429:
339:
149:
85:
28:
1545:
Boudreau, Bernard P.; Middelburg, Jack J.; Hofmann, Andreas F.; Meysman, Filip J. R. (2010).
1607:
1558:
1517:
1507:
1458:
1400:
1292:
1225:; on the sea floors below the carbonate compensation depth, the most commonly found ooze is
1212:
1145:
781:
675:
670:
398:
1222:
909:
776:
709:
697:
626:
500:
1603:
1503:
1396:
1522:
1487:
1250:
1226:
1114:
1110:
1081:
1029:
919:
889:
869:
810:
724:
607:
602:
463:
367:
93:
36:
1587:
1287:
Middelburg, Jack J. (2019). "Biogeochemical
Processes and Inorganic Carbon Dynamics".
1658:
1611:
1412:
1314:
1125:
1066:
16:
Depth in the oceans below which no calcium carbonate sediment particles are preserved
1572:
1192:
1085:
702:
616:
570:
508:
390:
371:
327:
148:
increases dramatically with depth and pressure. By the time the CCD is reached all
1028:
and the chemical composition of the water – in particular the amount of dissolved
1462:
1296:
1218:
1196:
1118:
1044:
1021:
766:
739:
734:
729:
719:
689:
575:
434:
128:
is the depth interval between the saturation and carbonate compensation depths.
97:
1492:
Proceedings of the
National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
1457:. Encyclopedia of Earth Sciences Series. Springer Netherlands. pp. 71–73.
1352:
1325:
1404:
1234:
1129:
1090:
714:
363:
312:{\displaystyle {\ce {CaCO3 + CO2 + H2O <=> Ca^2+ (aq) + 2HCO_3^- (aq)}}}
145:
1619:
1453:
Berger, Wolfgang H.; et al. (2016). "Calcite
Compensation Depth (CCD)".
1512:
1440:"Warmer than a Hot Tub: Atlantic Ocean Temperatures Much Higher in the Past"
1260:
1074:
1070:
351:
343:
141:
125:
54:
32:
1531:
1586:
Johnson, Thomas C.; Hamilton, Edwin L.; Berger, Wolfgang H. (1977-08-01).
1324:
Modified material was copied from this source, which is available under a
1588:"Physical properties of calcareous ooze: Control by dissolution at depth"
1563:
1546:
1230:
1106:
1098:
1078:
1025:
335:
323:
137:
1439:
1221:
above the carbonate compensation depth, the most commonly found ooze is
1105:
and therefore the shallowest CCD. The CCD is relatively shallow in high
1547:"Ongoing transients in carbonate compensation: COMPENSATION TRANSIENTS"
1488:"Current CaCO3 dissolution at the seafloor caused by anthropogenic CO2"
1347:
1320:
1040:
797:
580:
331:
42:
1351:
Modified text was copied from this source, which is available under a
140:
sinking to deeper waters are practically unaltered until reaching the
1238:
1133:
959:
1366:"Ocean acidification due to increasing atmospheric carbon dioxide"
954:
347:
74:
64:
27:) is the depth, in the oceans, at which the rate of supply of
1128:
the depth of the CCD has shown significant variation. In the
1291:. SpringerBriefs in Earth System Sciences. pp. 77–105.
1140:
concentrations were much higher. Higher concentrations of CO
205:
189:
173:
1069:
is about 4200–4500 metres except beneath the equatorial
105:. Above this horizon, waters are supersaturated and CaCO
1152:
over the ocean. This greater pressure of atmospheric CO
1353:
Creative
Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
1326:
Creative
Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
232:
161:
311:
1486:Sulpis, Olivier; et al. (October 29, 2018).
1073:zone, where the CCD is about 5000 m. In the
362:of the plate, which has the effect of increasing
240:
239:
222:
221:
1282:
1280:
1084:the CCD is at approximately 5000 m. In the
1345:, page 273–297, Rebus Community. Updated 2020.
350:. If the exposed sea bed is below the CCD tiny
374:clay deposited on top of the carbonate layer.
1001:
144:, the point about 3.5 km deep past which the
8:
1229:. While calcareous ooze mostly consists of
1195:are causing the CCD to rise, with zones of
338:can consist of calcareous sediments called
1008:
994:
381:
152:has dissolved according to this equation:
1562:
1521:
1511:
297:
291:
286:
281:
264:
255:
241:
234:
233:
231:
223:
216:
214:
213:
211:
204:
199:
188:
183:
172:
167:
162:
160:
1276:
945:Territorialisation of carbon governance
389:
215:
1648:– via Roger Williams University.
950:Total Carbon Column Observing Network
70:Carbonate compensation concept
7:
1233:, siliceous ooze mostly consists of
1180:Effects of climate change on oceans
1065:At the present time the CCD in the
113:from organic matter decay, and CaCO
1455:Encyclopedia of Marine Geosciences
84:As shown in the diagram, biogenic
14:
1442:. Physorg.com. February 17, 2006.
1425:Thurman, Harold., Alan Trujillo.
1050:, and consuming more reactants CO
342:, which is essentially a type of
1346:
1319:
975:
974:
397:
53:) is the compensation depth for
1186:atmospheric concentration of CO
1164:coincided with a deepened CCD.
1162:greenhouse to an icehouse Earth
1156:leads to increased dissolved CO
910:Climate reconstruction proxies
378:Variations in value of the CCD
326:particles can be found in the
304:
298:
271:
265:
242:
217:
1:
1289:Marine Carbon Biogeochemistry
1639:Introduction to Oceanography
1635:"12.6 Sediment Distribution"
1612:10.1016/0025-3227(77)90071-8
1551:Global Biogeochemical Cycles
1463:10.1007/978-94-007-6238-1_47
1339:Introduction to Oceanography
880:Carbonate compensation depth
545:Particulate inorganic carbon
47:aragonite compensation depth
21:carbonate compensation depth
1343:Chapter 12: Ocean Sediments
1297:10.1007/978-3-030-10822-9_5
1681:
1633:Webb, Paul (August 2023).
1210:
1177:
1109:with the exception of the
935:Carbon capture and storage
539:Particulate organic carbon
533:Dissolved inorganic carbon
1427:Introductory Oceanography
1405:10.1038/s41561-018-0259-5
940:Carbon cycle re-balancing
334:is above the CCD, bottom
1095:Thermohaline circulation
1060:Le Chatelier's principle
915:Carbon-to-nitrogen ratio
875:Carbonate–silicate cycle
843:Carbon dioxide clathrate
838:Clathrate gun hypothesis
666:Net ecosystem production
527:Dissolved organic carbon
322:Calcareous plankton and
1513:10.1073/pnas.1804250115
925:Deep Carbon Observatory
385:Part of a series on the
132:Solubility of carbonate
1199:first being affected.
1174:Climate change impacts
745:Continental shelf pump
521:Total inorganic carbon
487:Satellite measurements
330:above the CCD. If the
313:
81:
72:
1144:resulted in a higher
930:Global Carbon Project
661:Ecosystem respiration
314:
78:
68:
1564:10.1029/2009GB003654
759:Carbon sequestration
515:Total organic carbon
159:
96:are produced in the
31:matches the rate of
1604:1977MGeol..24..259J
1504:2018PNAS..11511700S
1498:(46): 11700–11705.
1397:2018NatGe..11..894B
1266:Ocean acidification
1201:Ocean acidification
1191:from combustion of
806:Atmospheric methane
772:Soil carbon storage
622:Reverse Krebs cycle
477:Ocean acidification
296:
228:
207:
191:
175:
1337:Webb, Paul (2019)
1256:Great Calcite Belt
885:Great Calcite Belt
833:Aerobic production
653:Carbon respiration
595:Metabolic pathways
555:Primary production
360:thermal subsidence
309:
282:
247:
195:
179:
163:
103:saturation horizon
82:
73:
29:calcium carbonates
1472:978-94-007-6238-1
1385:Nature Geoscience
1370:The Royal Society
1306:978-3-030-10821-2
1056:calcium carbonate
1018:
1017:
816:Methane emissions
472:In the atmosphere
303:
285:
270:
254:
249:
210:
198:
182:
166:
150:calcium carbonate
86:calcium carbonate
1672:
1650:
1649:
1647:
1645:
1630:
1624:
1623:
1583:
1577:
1576:
1566:
1542:
1536:
1535:
1525:
1515:
1483:
1477:
1476:
1450:
1444:
1443:
1436:
1430:
1423:
1417:
1416:
1380:
1374:
1373:
1362:
1356:
1350:
1335:
1329:
1323:
1318:
1284:
1213:Pelagic sediment
1207:Sedimentary ooze
1146:partial pressure
1010:
1003:
996:
983:
978:
977:
782:pelagic sediment
676:Soil respiration
671:Photorespiration
401:
382:
318:
316:
315:
310:
308:
307:
301:
295:
290:
283:
274:
268:
263:
262:
252:
250:
248:
246:
245:
238:
230:
229:
227:
220:
212:
208:
206:
203:
196:
190:
187:
180:
174:
171:
164:
1680:
1679:
1675:
1674:
1673:
1671:
1670:
1669:
1655:
1654:
1653:
1643:
1641:
1632:
1631:
1627:
1585:
1584:
1580:
1544:
1543:
1539:
1485:
1484:
1480:
1473:
1452:
1451:
1447:
1438:
1437:
1433:
1424:
1420:
1391:(12): 894–900.
1382:
1381:
1377:
1364:
1363:
1359:
1336:
1332:
1307:
1286:
1285:
1278:
1274:
1247:
1223:calcareous ooze
1215:
1209:
1189:
1182:
1176:
1159:
1155:
1151:
1143:
1139:
1132:through to the
1126:geological past
1113:and regions of
1104:
1053:
1048:
1038:
1033:
1014:
973:
966:
965:
964:
904:
896:
895:
894:
859:
849:
848:
847:
800:
790:
789:
788:
777:Marine sediment
761:
751:
750:
749:
710:Solubility pump
698:Biological pump
692:
682:
681:
680:
655:
645:
644:
643:
627:Carbon fixation
612:
597:
587:
586:
585:
566:
550:
503:
501:Forms of carbon
493:
492:
491:
466:
456:
455:
454:
409:
380:
357:
340:calcareous ooze
251:
157:
156:
134:
123:
116:
112:
108:
91:
71:
63:
17:
12:
11:
5:
1678:
1676:
1668:
1667:
1657:
1656:
1652:
1651:
1625:
1598:(4): 259–277.
1592:Marine Geology
1578:
1537:
1478:
1471:
1445:
1431:
1429:.2004.p151-152
1418:
1375:
1357:
1330:
1305:
1275:
1273:
1270:
1269:
1268:
1263:
1258:
1253:
1251:Carbonate pump
1246:
1243:
1227:siliceous ooze
1208:
1205:
1187:
1175:
1172:
1157:
1153:
1149:
1141:
1137:
1115:Southern Ocean
1111:North Atlantic
1102:
1082:Atlantic Ocean
1051:
1046:
1036:
1031:
1016:
1015:
1013:
1012:
1005:
998:
990:
987:
986:
985:
984:
968:
967:
963:
962:
957:
952:
947:
942:
937:
932:
927:
922:
920:Deep biosphere
917:
912:
906:
905:
902:
901:
898:
897:
893:
892:
890:Redfield ratio
887:
882:
877:
872:
870:Nutrient cycle
867:
861:
860:
857:Biogeochemical
855:
854:
851:
850:
846:
845:
840:
835:
830:
829:
828:
823:
813:
811:Methanogenesis
808:
802:
801:
796:
795:
792:
791:
787:
786:
785:
784:
774:
769:
763:
762:
757:
756:
753:
752:
748:
747:
742:
737:
732:
727:
725:Microbial loop
722:
717:
712:
707:
706:
705:
694:
693:
688:
687:
684:
683:
679:
678:
673:
668:
663:
657:
656:
651:
650:
647:
646:
642:
641:
640:
639:
634:
624:
619:
613:
611:
610:
608:Chemosynthesis
605:
603:Photosynthesis
599:
598:
593:
592:
589:
588:
584:
583:
578:
573:
567:
565:
564:
563:
562:
551:
549:
548:
542:
536:
530:
524:
518:
512:
505:
504:
499:
498:
495:
494:
490:
489:
484:
479:
474:
468:
467:
464:Carbon dioxide
462:
461:
458:
457:
453:
452:
447:
442:
437:
432:
427:
422:
417:
411:
410:
407:
406:
403:
402:
394:
393:
387:
386:
379:
376:
368:siliceous ooze
355:
320:
319:
306:
300:
294:
289:
280:
277:
273:
267:
261:
258:
244:
237:
226:
219:
202:
194:
186:
178:
170:
133:
130:
121:
114:
110:
106:
89:
69:
62:
59:
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1677:
1666:
1663:
1662:
1660:
1640:
1636:
1629:
1626:
1621:
1617:
1613:
1609:
1605:
1601:
1597:
1593:
1589:
1582:
1579:
1574:
1570:
1565:
1560:
1556:
1552:
1548:
1541:
1538:
1533:
1529:
1524:
1519:
1514:
1509:
1505:
1501:
1497:
1493:
1489:
1482:
1479:
1474:
1468:
1464:
1460:
1456:
1449:
1446:
1441:
1435:
1432:
1428:
1422:
1419:
1414:
1410:
1406:
1402:
1398:
1394:
1390:
1386:
1379:
1376:
1371:
1367:
1361:
1358:
1354:
1349:
1344:
1340:
1334:
1331:
1327:
1322:
1316:
1312:
1308:
1302:
1298:
1294:
1290:
1283:
1281:
1277:
1271:
1267:
1264:
1262:
1259:
1257:
1254:
1252:
1249:
1248:
1244:
1242:
1240:
1236:
1232:
1228:
1224:
1220:
1214:
1206:
1204:
1202:
1198:
1194:
1190:
1181:
1173:
1171:
1169:
1165:
1163:
1147:
1135:
1131:
1127:
1122:
1120:
1116:
1112:
1108:
1100:
1096:
1092:
1087:
1083:
1080:
1076:
1072:
1068:
1067:Pacific Ocean
1063:
1061:
1058:according to
1057:
1049:
1042:
1034:
1027:
1023:
1011:
1006:
1004:
999:
997:
992:
991:
989:
988:
982:
972:
971:
970:
969:
961:
958:
956:
953:
951:
948:
946:
943:
941:
938:
936:
933:
931:
928:
926:
923:
921:
918:
916:
913:
911:
908:
907:
900:
899:
891:
888:
886:
883:
881:
878:
876:
873:
871:
868:
866:
865:Marine cycles
863:
862:
858:
853:
852:
844:
841:
839:
836:
834:
831:
827:
824:
822:
819:
818:
817:
814:
812:
809:
807:
804:
803:
799:
794:
793:
783:
780:
779:
778:
775:
773:
770:
768:
765:
764:
760:
755:
754:
746:
743:
741:
738:
736:
733:
731:
728:
726:
723:
721:
718:
716:
713:
711:
708:
704:
701:
700:
699:
696:
695:
691:
686:
685:
677:
674:
672:
669:
667:
664:
662:
659:
658:
654:
649:
648:
638:
635:
633:
630:
629:
628:
625:
623:
620:
618:
615:
614:
609:
606:
604:
601:
600:
596:
591:
590:
582:
579:
577:
574:
572:
569:
568:
561:
558:
557:
556:
553:
552:
546:
543:
540:
537:
534:
531:
528:
525:
522:
519:
516:
513:
510:
507:
506:
502:
497:
496:
488:
485:
483:
480:
478:
475:
473:
470:
469:
465:
460:
459:
451:
448:
446:
445:Boreal forest
443:
441:
438:
436:
433:
431:
428:
426:
423:
421:
418:
416:
413:
412:
405:
404:
400:
396:
395:
392:
388:
384:
383:
377:
375:
373:
369:
365:
361:
353:
349:
345:
341:
337:
333:
329:
325:
292:
287:
278:
275:
259:
256:
235:
224:
200:
192:
184:
176:
168:
155:
154:
153:
151:
147:
143:
139:
131:
129:
127:
118:
104:
99:
95:
87:
80:dramatically.
77:
67:
60:
58:
56:
52:
48:
44:
40:
38:
34:
30:
26:
22:
1665:Oceanography
1642:. Retrieved
1638:
1628:
1595:
1591:
1581:
1554:
1550:
1540:
1495:
1491:
1481:
1454:
1448:
1434:
1426:
1421:
1388:
1384:
1378:
1369:
1360:
1338:
1333:
1288:
1216:
1193:fossil fuels
1183:
1166:
1123:
1086:Indian Ocean
1064:
1019:
879:
703:Martin curve
690:Carbon pumps
617:Calvin cycle
571:Black carbon
509:Total carbon
450:Geochemistry
391:Carbon cycle
328:water column
321:
135:
119:
102:
83:
50:
46:
41:
24:
20:
18:
1197:downwelling
1184:Increasing
1168:John Murray
1119:downwelling
1022:temperature
767:Carbon sink
730:Viral shunt
720:Marine snow
576:Blue carbon
430:Deep carbon
425:Atmospheric
415:Terrestrial
98:photic zone
1557:(4): n/a.
1272:References
1235:Radiolaria
1219:sea floors
1211:See also:
1178:See also:
1130:Cretaceous
1091:water mass
740:Whale pump
735:Jelly pump
715:Lipid pump
440:Permafrost
408:By regions
146:solubility
55:aragonitic
1620:0025-3227
1413:135284130
1315:104368944
1261:Lysocline
1107:latitudes
1075:temperate
1071:upwelling
344:limestone
336:sediments
293:−
243:⇀
236:−
225:−
218:↽
142:lysocline
126:lysocline
33:solvation
1659:Category
1573:53062358
1532:30373837
1245:See also
1231:Rhizaria
1099:copepods
1079:tropical
1026:pressure
981:Category
324:sediment
138:plankton
61:Overview
1600:Bibcode
1523:6243283
1500:Bibcode
1393:Bibcode
1239:diatoms
1217:On the
1124:In the
826:Wetland
798:Methane
581:Kerogen
482:Removal
372:abyssal
354:of CaCO
332:sea bed
43:Calcite
1644:3 July
1618:
1571:
1530:
1520:
1469:
1411:
1313:
1303:
1134:Eocene
1117:where
979:
960:CO2SYS
821:Arctic
560:marine
420:Marine
352:shells
1569:S2CID
1409:S2CID
1311:S2CID
1148:of CO
955:C4MIP
903:Other
547:(PIC)
541:(POC)
535:(DIC)
529:(DOC)
523:(TIC)
517:(TOC)
364:depth
348:chalk
94:tests
88:(CaCO
37:tests
1646:2024
1616:ISSN
1528:PMID
1467:ISBN
1301:ISBN
1237:and
1077:and
1054:and
1043:and
511:(TC)
435:Soil
165:CaCO
19:The
1608:doi
1559:doi
1518:PMC
1508:doi
1496:115
1459:doi
1401:doi
1293:doi
1045:HCO
370:or
346:or
284:HCO
51:ACD
25:CCD
1661::
1637:.
1614:.
1606:.
1596:24
1594:.
1590:.
1567:.
1555:24
1553:.
1549:.
1526:.
1516:.
1506:.
1494:.
1490:.
1465:.
1407:.
1399:.
1389:11
1387:.
1368:.
1341:,
1309:.
1299:.
1279:^
1241:.
1093:.
1062:.
1041:Ca
1030:CO
1024:,
637:C4
632:C3
302:aq
269:aq
253:Ca
181:CO
92:)
1622:.
1610::
1602::
1575:.
1561::
1534:.
1510::
1502::
1475:.
1461::
1415:.
1403::
1395::
1372:.
1355:.
1328:.
1317:.
1295::
1188:2
1158:2
1154:2
1150:2
1142:2
1138:2
1103:2
1052:2
1047:3
1037:2
1032:2
1009:e
1002:t
995:v
356:3
305:)
299:(
288:3
279:2
276:+
272:)
266:(
260:+
257:2
209:O
201:2
197:H
193:+
185:2
177:+
169:3
122:3
115:3
111:2
107:3
90:3
49:(
23:(
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.