271:
237:
29:
192:
bud, regions where enamel formation is completed, the enamel organ gives rise to
Hertwig's epithelial root sheath, composed of two epithelial layers derived from the external and internal epithelia. The sheath is irregularly fragmented in time and space as it promotes cementum deposition on the newly
246:
The shape and location of the cementoenamel junction (CEJ) on each tooth surface should be considered. CEJs differ from tooth to tooth in terms of their anatomy. The curvature of the CEJ is greatest on anterior teeth due to the narrow profile of these teeth. On the anteriors, the distal aspect's
175:
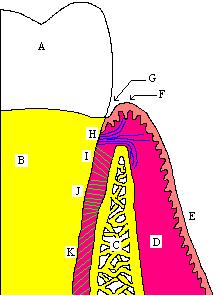
There exists a normal variation in the relationship of the cementum and the enamel at the cementoenamel junction. In about 60–65% of teeth, the cementum overlaps the enamel at the CEJ, while in about 30% of teeth, the cementum and enamel abut each other with no overlap. In only 5–10% of teeth,
201:
epithelial root sheath yields an equally irregular limit of cervical enamel and an irregular onset of formation and deposition of cementum. Consequently, the relationship between cementum and enamel at the CEJ presents an irregular contour, as observed during scanning electron microscope (SEM)
168:. A significant proportion of tooth loss is caused by tooth resorption, which occurs in 5 to 10 percent of the population. The clinical location of CEJ which is a static landmark, serves as a crucial anatomical site for the measurement of
149:, which covers the anatomical root of a tooth, meet. Informally it is known as the neck of the tooth. The border created by these two dental tissues has much significance as it is usually the location where the
160:
Active recession of the gingiva reveals the cementoenamel junction in the mouth and is usually a sign of an unhealthy condition. The loss of attachment is considered a more reliable indicator of
212:. If Hertwig's epithelial root sheath is not fragmented, there will be enamel deposition and it will be transformed into reduced epithelium, thus preventing cementum deposition on its surface.
224:
Abutment - It is also known as vis a vis relation, where the cement and enamel meet at the butt joint, occurring in 30% of sections, and the least common, occurring in 10% of sections.
97:
259:
Root resorption often starts at cementoenamel junction (CEJ) in teeth. Types of tooth resorption include internal resorption and external resorption.
606:
283:
External resorption can be classified into four categories by its clinical and histologic manifestations: external surface resorption, external
526:
427:
402:
377:
208:
of
Hertwig's epithelial root sheath and exposure of dentin covered by a thin layer of intermediate cementum are fundamental for the onset of
41:
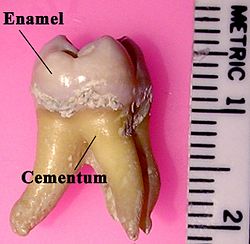
198:
172:
pocket depth (PPD) and clinical attachment level (CAL). The CEJ varies between subjects, but also between teeth from the same person.
892:
193:
formed dentin. After this fragmentation, Hertwig's epithelial root sheath also participates in cementogenesis and formation of the
267:
There are two types of internal resorption - root canal (internal) replacement resorption and internal inflammatory resorption.
92:
241:
Comparison of the cementoenamel junction on the mesial surfaces of the maxillary central, first bicuspid, and first molar
1011:
205:
599:
291:. External inflammatory root resorption can be further categorized into cervical resorption with or without a vital
823:
797:
792:
634:
251:
aspect. Posterior teeth have flatter CEJ curvatures on the inter-proximal surfaces in comparison to the anteriors.
818:
736:
710:
705:
731:
393:
Carranza FA, Bernard GW (2002). "The Tooth-Supporting
Structures". In Newman MG, Takei HH, Carranza FA (eds.).
68:
1006:
844:
1001:
940:
839:
757:
592:
104:
80:
752:
629:
492:
194:
963:
161:
579:
474:
885:
802:
558:
522:
466:
423:
398:
373:
348:
169:
715:
456:
338:
328:
165:
976:
679:
652:
288:
154:
950:
915:
880:
615:
343:
316:
209:
122:
995:
872:
672:
478:
138:
367:
935:
905:
849:
762:
662:
292:
284:
270:
197:, giving rise to the epithelial rests of Malassez. This irregular fragmentation of
134:
461:
444:
73:
863:
644:
236:
40:
910:
333:
176:
there is a space between the enamel and the cementum at which the underlying
49:
is the more or less horizontal demarcation line that distinguishes the crown
546:
85:
562:
470:
352:
445:"Teeth resorption at cement - enamel junction (CEJ) - Microscopy analysis"
28:
776:
667:
295:(invasive cervical root resorption) and external apical root resorption.
146:
689:
657:
150:
110:
945:
248:
177:
189:
142:
584:
372:. Internet Archive. Baltimore : Urban & Schwarzenberg.
588:
397:(9th ed.). Philadelphia: W. B. Saunders. p. 43.
16:
Region on a tooth's surface where cementum and enamel join
221:
Coronal cementum - where the enamel overlaps the cement.
153:(gums) attaches to a healthy tooth by fibers called the
521:(9th ed.). Philadelphia, Pa., London: Saunders.
227:
Gap between cementum and enamel exposing the dentin.
871:
862:
832:
811:
785:
775:
745:
724:
698:
688:
643:
622:
519:
Wheeler's dental anatomy, physiology, and occlusion
422:(7th ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
91:
79:
67:
62:
21:
545:Ne RF, Witherspoon DE, Gutmann JL (January 1999).
310:
308:
600:
287:root resorption, replacement resorption, and
8:
369:Anatomy, a regional atlas of the human body
321:Journal of Indian Society of Periodontology
247:curvature is usually one mm lower than the
868:
782:
695:
607:
593:
585:
39:
27:
540:
538:
460:
443:Metwally S, Stachewicz U (October 2020).
342:
332:
315:Vandana KL, Haneet RK (September 2014).
269:
235:
497:Dimensions of Dental Hygiene | Magazine
304:
108:
18:
7:
317:"Cementoenamel junction: An insight"
395:Carranza's Clinical Periodontology
14:
202:analysis of the primary teeth.
164:. The CEJ is the site of major
137:, which covers the anatomical
1:
462:10.1016/j.micron.2020.102913
1028:
635:Universal Numbering System
551:Quintessence International
517:Nelson SJ, Ash MM (2010).
133:is the location where the
972:
959:
926:
901:
103:
38:
26:
493:"Remembering Your Roots"
420:Woelfel's Dental Anatomy
334:10.4103/0972-124X.142437
53:of the tooth from root
941:Dental-enamel junction
931:Cementoenamel junction
893:Zuckerkandl's tubercle
275:
243:
127:cementoenamel junction
105:Anatomical terminology
22:Cementoenamel junction
630:Glossary of dentistry
273:
239:
366:Clemente CD (1987).
195:periodontal ligament
1012:Human mouth anatomy
274:Types of Resorption
162:periodontal disease
547:"Tooth resorption"
418:Scheid RC (2012).
276:
244:
989:
988:
985:
984:
886:Cusp of Carabelli
858:
857:
771:
770:
528:978-1-4160-6209-7
429:978-1-60831-746-2
404:978-0-7216-8331-7
379:978-0-8067-0323-7
119:
118:
114:
1019:
869:
783:
696:
609:
602:
595:
586:
567:
566:
542:
533:
532:
514:
508:
507:
505:
504:
489:
483:
482:
464:
440:
434:
433:
415:
409:
408:
390:
384:
383:
363:
357:
356:
346:
336:
312:
255:Teeth resorption
166:tooth resorption
111:edit on Wikidata
43:
31:
19:
1027:
1026:
1022:
1021:
1020:
1018:
1017:
1016:
992:
991:
990:
981:
977:Dental alveolus
968:
955:
922:
897:
854:
828:
824:Second premolar
807:
798:Lateral incisor
793:Central incisor
767:
741:
737:Second premolar
720:
711:Lateral incisor
706:Central incisor
684:
639:
618:
613:
576:
571:
570:
544:
543:
536:
529:
516:
515:
511:
502:
500:
491:
490:
486:
442:
441:
437:
430:
417:
416:
412:
405:
392:
391:
387:
380:
365:
364:
360:
314:
313:
306:
301:
281:
265:
257:
234:
218:
186:
155:gingival fibers
115:
58:
34:
17:
12:
11:
5:
1025:
1023:
1015:
1014:
1009:
1007:Parts of tooth
1004:
994:
993:
987:
986:
983:
982:
980:
979:
973:
970:
969:
967:
966:
960:
957:
956:
954:
953:
951:Dental papilla
948:
943:
938:
933:
927:
924:
923:
921:
920:
919:
918:
916:Apical foramen
908:
902:
899:
898:
896:
895:
890:
889:
888:
877:
875:
866:
860:
859:
856:
855:
853:
852:
847:
842:
836:
834:
830:
829:
827:
826:
821:
819:First premolar
815:
813:
809:
808:
806:
805:
800:
795:
789:
787:
780:
773:
772:
769:
768:
766:
765:
760:
755:
749:
747:
743:
742:
740:
739:
734:
732:First premolar
728:
726:
722:
721:
719:
718:
713:
708:
702:
700:
693:
686:
685:
683:
682:
677:
676:
675:
670:
665:
660:
649:
647:
641:
640:
638:
637:
632:
626:
624:
620:
619:
616:Dental anatomy
614:
612:
611:
604:
597:
589:
583:
582:
580:Biology-Online
575:
574:External links
572:
569:
568:
534:
527:
509:
484:
435:
428:
410:
403:
385:
378:
358:
327:(5): 549–554.
303:
302:
300:
297:
280:
277:
264:
261:
256:
253:
233:
230:
229:
228:
225:
222:
217:
214:
210:cementogenesis
185:
182:
123:dental anatomy
117:
116:
107:
101:
100:
95:
89:
88:
83:
77:
76:
71:
65:
64:
60:
59:
44:
36:
35:
32:
24:
23:
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1024:
1013:
1010:
1008:
1005:
1003:
1002:Dental enamel
1000:
999:
997:
978:
975:
974:
971:
965:
962:
961:
958:
952:
949:
947:
944:
942:
939:
937:
934:
932:
929:
928:
925:
917:
914:
913:
912:
909:
907:
904:
903:
900:
894:
891:
887:
884:
883:
882:
879:
878:
876:
874:
870:
867:
865:
861:
851:
848:
846:
843:
841:
838:
837:
835:
831:
825:
822:
820:
817:
816:
814:
810:
804:
801:
799:
796:
794:
791:
790:
788:
784:
781:
778:
774:
764:
761:
759:
756:
754:
751:
750:
748:
744:
738:
735:
733:
730:
729:
727:
723:
717:
714:
712:
709:
707:
704:
703:
701:
697:
694:
691:
687:
681:
678:
674:
671:
669:
666:
664:
661:
659:
656:
655:
654:
651:
650:
648:
646:
642:
636:
633:
631:
628:
627:
625:
621:
617:
610:
605:
603:
598:
596:
591:
590:
587:
581:
578:
577:
573:
564:
560:
556:
552:
548:
541:
539:
535:
530:
524:
520:
513:
510:
498:
494:
488:
485:
480:
476:
472:
468:
463:
458:
454:
450:
446:
439:
436:
431:
425:
421:
414:
411:
406:
400:
396:
389:
386:
381:
375:
371:
370:
362:
359:
354:
350:
345:
340:
335:
330:
326:
322:
318:
311:
309:
305:
298:
296:
294:
290:
286:
278:
272:
268:
262:
260:
254:
252:
250:
242:
238:
231:
226:
223:
220:
219:
215:
213:
211:
207:
206:Fragmentation
203:
200:
196:
191:
183:
181:
179:
173:
171:
167:
163:
158:
156:
152:
148:
144:
140:
136:
132:
128:
124:
112:
106:
102:
99:
96:
94:
90:
87:
84:
82:
78:
75:
72:
70:
66:
61:
57:of the tooth.
56:
52:
48:
42:
37:
33:Labeled molar
30:
25:
20:
930:
845:Second molar
758:Second molar
623:Nomenclature
554:
550:
518:
512:
501:. Retrieved
499:. 2021-09-22
496:
487:
452:
448:
438:
419:
413:
394:
388:
368:
361:
324:
320:
285:inflammatory
282:
266:
258:
245:
240:
204:
187:
180:is exposed.
174:
159:
130:
126:
120:
54:
50:
46:
850:Third molar
840:First molar
763:Third molar
753:First molar
557:(1): 9–25.
63:Identifiers
996:Categories
911:Root canal
777:Mandibular
503:2023-08-07
455:: 102913.
299:References
145:, and the
690:Maxillary
680:Deciduous
653:Permanent
479:220120744
289:ankylosis
232:Curvature
199:Hertwig's
184:Formation
812:Premolar
725:Premolar
668:premolar
563:10323155
471:32590194
353:25425813
279:External
263:Internal
147:cementum
964:Mamelon
786:Incisor
699:Incisor
658:incisor
344:4239741
188:In the
170:probing
151:gingiva
74:D019237
946:Dentin
936:Enamel
803:Canine
716:Canine
663:canine
561:
525:
477:
469:
449:Micron
426:
401:
376:
351:
341:
249:mesial
178:dentin
135:enamel
125:, the
873:Crown
864:Parts
833:Molar
779:teeth
746:Molar
692:teeth
673:molar
645:Teeth
475:S2CID
216:Types
190:tooth
143:tooth
141:of a
139:crown
109:[
98:55627
906:Pulp
881:Cusp
559:PMID
523:ISBN
467:PMID
424:ISBN
399:ISBN
374:ISBN
349:PMID
293:pulp
131:CEJ)
69:MeSH
45:The
457:doi
453:137
339:PMC
329:doi
121:In
93:FMA
86:926
81:TA2
55:(B)
51:(A)
47:CEJ
998::
555:30
553:.
549:.
537:^
495:.
473:.
465:.
451:.
447:.
347:.
337:.
325:18
323:.
319:.
307:^
157:.
608:e
601:t
594:v
565:.
531:.
506:.
481:.
459::
432:.
407:.
382:.
355:.
331::
129:(
113:]
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.