877:
915:
1085:
891:
965:
1107:
989:
941:
903:
977:
928:
40:
953:
654:
60:
1061:
1073:
1049:
1025:
663:
1013:
1001:
554:
269:
1037:
1145:
631:. However, the cervical spine is comparatively mobile, and some component of this movement is due to flexion and extension of the vertebral column itself. This movement between the atlas and occipital bone is often referred to as the "yes joint", owing to its nature of being able to move the head in an up-and-down fashion.
261:
292:
are numbered, with the first one (C1) closest to the skull and higher numbered vertebrae (C2–C7) proceeding away from the skull and down the spine. The general characteristics of the third through sixth cervical vertebrae are described here. The first, second, and seventh vertebrae are extraordinary,
599:
The transverse processes are of considerable size; their posterior roots are large and prominent, while the anterior are small and faintly marked. The upper surface of each usually has a shallow sulcus for the eighth spinal nerve, and its extremity seldom presents more than a trace of bifurcation.
2582:
606:
On the left side, it occasionally gives passage to the vertebral artery; more frequently, the vertebral vein traverses it on both sides, but the usual arrangement is for both artery and vein to pass in front of the transverse process, not through the foramen.
767:
A common practice is to immobilize a patient's cervical spine to prevent further damage during transport to hospital. This practice has come under review recently as incidence rates of unstable spinal trauma can be as low as 2% in immobilized patients. In
638:. A small amount of rotation of the vertebral column itself contributes to the movement. This movement between the atlas and axis is often referred to as the "no joint", owing to its nature of being able to rotate the head in a side-to-side fashion.
545:(dens) that rises perpendicularly from the upper surface of the body and articulates with C1. The body is deeper in front than behind, and prolonged downward anteriorly so as to overlap the upper and front part of the third vertebra.
1084:
876:
418:. Each process consists of an anterior and a posterior part. These two parts are joined, outside the foramen, by a bar of bone that exhibits a deep sulcus on its upper surface for the passage of the corresponding
1493:
331:
are directed laterally and backward, and attach to the body midway between its upper and lower borders, so that the superior vertebral notch is as deep as the inferior, but it is, at the same time, narrower.
1585:
737:
Injuries to the cervical spine are common at the level of the second cervical vertebrae, but neurological injury is uncommon. C4 and C5 are the areas that see the highest amount of cervical spine trauma.
723:, which are used in a grading system from 0–4 ranging from no changes (0) to early with minimal development of osteophytes (1) to mild with definite osteophytes (2) to moderate with additional disc space
882:
565:, or C7, has a distinctive long and prominent spinous process, which is palpable from the skin surface. Sometimes, the seventh cervical vertebra is associated with an abnormal extra rib, known as a
308:
are flattened and of equal depth; the former is placed on a lower level than the latter, and its inferior border is prolonged downward, so as to overlap the upper and forepart of the vertebra below.
914:
603:
The transverse foramen may be as large as that in the other cervical vertebrae, but it is generally smaller on one or both sides; occasionally, it is double, and sometimes it is absent.
448:
The posterior part, the true transverse process, springs from the vertebral arch behind the foramen and is directed forward and laterally; it ends in a flattened vertical tubercle, the
534:. It lacks a vertebral body, spinous process, and discs either superior or inferior to it. It is ring-like and consists of an anterior arch, posterior arch, and two lateral masses.
322:
is concave from front to back, convex from side to side, and presents laterally shallow concavities that receive the corresponding projecting lips of the underlying vertebra.
1490:
890:
236:
In humans, cervical vertebrae are the smallest of the true vertebrae and can be readily distinguished from those of the thoracic or lumbar regions by the presence of a
1419:
940:
1060:
1363:"Cervical degenerative index: a new quantitative radiographic scoring system for cervical spondylosis with interobserver and intraobserver reliability testing"
133:
1361:
Ofiram, Elisha; Garvey, Timothy A; Schwender, James D; Denis, Francis; Perra, Joseph H; Transfeldt, Ensor E; Winter, Robert B; Wroblewski, Jill M (2009).
569:, which develops from the anterior root of the transverse process. These ribs are usually small, but may occasionally compress blood vessels (such as the
988:
361:
rather than directly to the vertebrae; the nuchal ligament itself attaching to the spinous processes of C2–C7 and to the posterior tubercle of the atlas.
1575:
1613:
217:, they are small and completely fused to the vertebrae. The vertebral transverse processes of mammals are homologous to the cervical ribs of other
2448:
2157:
1746:
1580:
1072:
349:
is short and bifid, the two divisions being often of unequal size. Because the spinous processes are so short, certain superficial muscles (the
2597:
1736:
2379:
2250:
1341:
109:
1048:
1347:
1024:
2587:
2559:
2517:
1308:
902:
634:
The movement of shaking or rotating the head left and right happens almost entirely at the joint between the atlas and the axis, the
772:, Canadian studies have developed the Canadian C-Spine Rule (CCR) for physicians to decide who should receive radiological imaging.
497:
The cervical spinal nerves emerge from above the cervical vertebrae. For example, the cervical spinal nerve 3 (C3) passes above C3.
964:
592:
attaches to. This process is not always the most prominent of the spinous processes, being found only about 70% of the time, C6 or
588:
The long spinous process of C7 is thick and nearly horizontal in direction. It is not bifurcated, and ends in a tubercle that the
1012:
2244:
1226:
Varela-Lasheras, Irma; Bakker, Alexander J; Van Der Mije, Steven D; Metz, Johan AJ; Van Alphen, Joris; Galis, Frietson (2011).
2225:
976:
1411:
128:
1550:
2592:
1825:
1726:
1664:
1606:
479:
2150:
1518:
769:
2105:
620:
616:
415:
249:
441:. It arises from the side of the body, is directed laterally in front of the foramen, and ends in a tubercle, the
1919:
1890:
1659:
741:
If it does occur, however, it may cause death or profound disability, including paralysis of the arms, legs, and
2362:
2357:
2340:
2335:
2330:
1914:
1907:
1902:
952:
679:
582:
140:
92:
1291:
Galis, Frietson (1999). "Why do almost all mammals have seven cervical vertebrae? Developmental constraints,
727:
or narrowing (3) to the stage of many large osteophytes, severe narrowing of the disc space, and more severe
2453:
2325:
2320:
2315:
2310:
2305:
2300:
2295:
2290:
2285:
2260:
2217:
2212:
2207:
2202:
2197:
2192:
2187:
2182:
1818:
1766:
1599:
1090:
Anterior view of cervical spine showing the vertebral arteries along with the spinal nerves. See this in 3d
1000:
624:
354:
1106:
2143:
1761:
1681:
1564:
1228:"Breaking evolutionary and pleiotropic constraints in mammals: On sloths, manatees and homeotic mutations"
1120:
467:
116:
104:
927:
2522:
2493:
2488:
2483:
2478:
2473:
2419:
2414:
2409:
2404:
2399:
2265:
1813:
1808:
1756:
826:
281:
1443:"Degeneration of the cervical disc: histology compared with radiography and magnetic resonance imaging"
1441:
Christie, A; Läubli, R; Guzman, R; Berlemann, U; Moore, R J; Schroth, G; Vock, P; Lövblad, K O (2005).
1154:
753:
1272:"Sticking their necks out for evolution: Why sloths and manatees have unusually long (or short) necks"
1177:"Evolution of the axial system in craniates: morphology and function of the perivertebral musculature"
537:
The axis (C2) forms the pivot on which the atlas rotates. The most distinctive characteristic of this
1936:
1691:
731:
297:
The bodies of these four vertebrae are small, and broader from side to side than from front to back.
1036:
1931:
1926:
1696:
1570:
1442:
781:
746:
712:
635:
365:
276:(left) and giraffe (right) both have seven cervical vertebrae. The giraffe's neck is elongated by
2352:
2255:
2120:
2082:
2062:
1873:
1853:
1795:
1785:
1731:
1473:
1271:
742:
593:
237:
186:
44:
Position of human cervical vertebrae (shown in red). It consists of 7 bones, from top to bottom,
1091:
526:
The atlas (C1) is the topmost vertebra, and along with the axis forms the joint connecting the
2436:
2110:
1895:
1878:
1848:
1676:
1465:
1392:
1337:
1331:
1312:
1259:
1208:
1159:
1132:
839:
833:
691:
687:
589:
570:
339:
39:
221:. Most mammals have seven cervical vertebrae, with the only three known exceptions being the
2547:
1835:
1741:
1649:
1457:
1382:
1374:
1304:
1249:
1239:
1198:
1188:
1127:
787:
542:
531:
475:
407:
241:
230:
190:
59:
2583:
Knowledge (XXG) articles incorporating text from the 20th edition of Gray's
Anatomy (1918)
2534:
2367:
2277:
2236:
2231:
2174:
2087:
2077:
1751:
1701:
1669:
1511:"Canadian C-Spine Rule - Emergency Medicine Research - Ottawa Hospital Research Institute"
1497:
757:
675:
653:
578:
574:
516:
506:
491:
487:
358:
245:
45:
581:, causing pain, numbness, tingling, and weakness in the upper limb, a condition known as
478:
and the carotid artery can be massaged against this tubercle to relieve the symptoms of
2027:
1778:
1773:
1654:
1387:
1362:
1254:
1227:
1203:
1176:
1112:
849:
628:
520:
510:
471:
411:
226:
49:
2576:
2505:
2465:
2431:
2391:
2115:
2097:
2072:
2054:
2032:
2010:
1946:
1885:
1150:
1066:
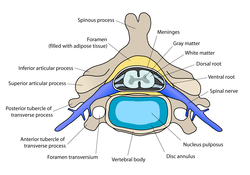
Median sagittal section through the occipital bone and first three cervical vertebrae
372:, columns of bone that project laterally from the junction of the pedicle and lamina.
1477:
2166:
1941:
1803:
1708:
566:
419:
277:
202:
553:
268:
97:
17:
2042:
2037:
2022:
803:
704:
527:
483:
2005:
1461:
1378:
1102:
820:
791:
720:
716:
662:
210:
198:
121:
2067:
2000:
845:
761:
350:
1510:
1469:
1396:
1316:
1263:
1244:
1212:
1309:
10.1002/(SICI)1097-010X(19990415)285:1<19::AID-JEZ3>3.0.CO;2-Z
1193:
1987:
1634:
1544:
864:
pulse can be palpated against the transverse process of the C6 vertebrae.
816:
728:
724:
708:
449:
442:
403:
399:
346:
335:
328:
289:
174:
158:
861:
857:
683:
222:
218:
315:
is concave transversely, and presents a projecting lip on either side.
146:
1978:
1958:
1865:
1591:
1078:
Section of the neck at about the level of the sixth cervical vertebra
853:
458:
The anterior tubercle of the sixth cervical vertebra is known as the
430:
206:
194:
615:
The movement of nodding the head takes place predominantly through
1626:
920:
Shape of cervical vertebrae (shown in blue and yellow). Animation.
883:
Scrollable computed tomography images of normal cervical vertebrae
809:
552:
376:
273:
267:
260:
182:
80:
368:
of cervical vertebrae have fused on either or both sides to form
2135:
1622:
799:
752:
Common patterns of injury include the odontoid fracture and the
538:
252:
pass. The remainder of this article focuses upon human anatomy.
214:
178:
2139:
1595:
1995:
1054:
Posterior atlanto-occipital membrane and atlantoaxial ligament
1030:
Second cervical vertebra, epistropheus, or axis, from the side
426:
946:
Cervical vertebrae, lateral view (shown in blue and yellow)
756:, both of which are often treated with immobilization in a
1588:- BlueLink Anatomy - University of Michigan Medical School
406:, which, in the upper six vertebrae, gives passage to the
896:
Position of cervical vertebrae (shown in red). Animation.
197:) lie caudal (toward the tail) of cervical vertebrae. In
482:. The carotid tubercle is also used as a landmark for
1018:
Second cervical vertebra, or epistropheus, from above
240:(hole) in each transverse process, through which the
2533:
2464:
2390:
2276:
2173:
2096:
2053:
1986:
1977:
1957:
1864:
1834:
1794:
1717:
1642:
1633:
127:
115:
103:
91:
79:
74:
69:
32:
994:X-ray of cervical spine in flexion and extension
393:face forward, downward, and slightly laterally.
2151:
1607:
425:The anterior portion is the homologue of the
386:face backward, upward, and slightly medially.
338:are narrow and thinner above than below; the
8:
213:dinosaurs, the cervical ribs are large; in
2158:
2144:
2136:
1983:
1639:
1614:
1600:
1592:
585:. Very rarely, this rib occurs in a pair.
58:
38:
1386:
1253:
1243:
1202:
1192:
1367:Journal of Orthopaedics and Traumatology
686:, respectively. Incongruencies indicate
678:of the cervical vertebrae, here seen on
272:Despite greatly differing neck lengths,
264:Side view of a typical cervical vertebra
259:
2449:Posterior branches of the lumbar nerves
1412:"Degenerative Cervical Spine Disorders"
1410:Garfin, Steven R; Bono, Christopher M.
1167:
872:
1149:This article incorporates text in the
144:
29:
2380:Posterior branches of thoracic nerves
2251:Posterior branches of cervical nerves
1538:
1536:
1336:. Palgrave Macmillan. pp. 280–.
596:can sometimes be the most prominent.
201:species, the cervical vertebrae bear
166:
7:
1422:from the original on 28 October 2016
523:(C2) are the two topmost vertebrae.
2560:Posterior branch of coccygeal nerve
2518:Posterior branches of sacral nerves
433:region, and is therefore named the
908:Illustration of cervical vertebrae
342:is large and of a triangular form.
185:. Truncal vertebrae (divided into
25:
2363:Thoraco-abdominal nerves – T7–T11
1175:Schilling, N (10 February 2011).
1006:First cervical vertebra, or atlas
860:. It is also the level where the
1521:from the original on 14 May 2017
1350:from the original on 2018-05-06.
1143:
1105:
1083:
1071:
1059:
1047:
1035:
1023:
1011:
999:
987:
975:
963:
951:
939:
925:
913:
901:
889:
875:
661:
652:
280:, extension of the time for the
703:arise from conditions such as
379:are flat and of an oval form:
1:
2598:Bones of the vertebral column
1330:Hillis, David M. (May 2011).
1278:(Press release). May 6, 2011.
790:is often used as a marker of
701:Cervical degenerative changes
1826:Uncinate process of vertebra
1727:Uncinate process of vertebra
856:becomes continuous with the
848:becomes continuous with the
557:Position of C7 shown in red.
480:supraventricular tachycardia
288:By convention, the cervical
1157:of the 20th edition of
982:X-ray of cervical vertebrae
770:clearing the cervical spine
2614:
2588:Bones of the head and neck
2106:Superior thoracic aperture
1118:
779:
719:. The changes are seen on
627:between the atlas and the
504:
364:The superior and inferior
250:inferior cervical ganglion
229:with five or six, and the
1920:posterior sacral foramina
1462:10.1007/s00234-005-1412-6
1379:10.1007/s10195-008-0041-3
1042:Seventh cervical vertebra
414:, as well as a plexus of
139:
64:A human cervical vertebra
57:
52:, C3, C4, C5, C6, and C7.
37:
1908:anterior sacral foramina
674:are annotations used in
583:thoracic outlet syndrome
402:are each pierced by the
293:and are detailed later.
181:, immediately below the
141:Anatomical terms of bone
2358:Intercostobrachial – T2
715:, and the formation of
694:and/or ligament injury.
625:atlanto-occipital joint
2454:Superior cluneal L1–L3
2261:Greater occipital – C2
1682:Intervertebral foramen
1581:Cervical vertebra quiz
1576:Mnemonic for Landmarks
1571:Cervical Spine Anatomy
1245:10.1186/2041-9139-2-11
1121:anatomical terminology
558:
470:). This separates the
404:foramen transversarium
285:
265:
2523:Medial cluneal nerves
1194:10.1186/1742-9994-8-4
827:common carotid artery
642:Clinical significance
556:
282:embryonic development
271:
263:
27:Vertebrae of the neck
2266:Third occipital – C3
1937:Lateral sacral crest
1295:genes, and cancer".
1181:Frontiers in Zoology
713:intervertebral discs
464:Chassaignac tubercle
400:transverse processes
86:vertebrae cervicales
2593:Bones of the thorax
1932:Medial sacral crest
1927:Median sacral crest
1500:, Table 64, page 66
852:and also where the
798:At C1, base of the
782:Anatomical landmark
747:respiratory failure
729:vertebral end plate
636:atlanto-axial joint
577:) or nerves in the
468:Édouard Chassaignac
366:articular processes
2121:Infrasternal angle
2083:Xiphisternal joint
2063:Suprasternal notch
1796:Thoracic vertebrae
1786:Vertebra prominens
1747:Posterior tubercle
1732:Transverse foramen
1719:Cervical vertebrae
1586:Cervical vertebrae
1496:2014-02-22 at the
1491:2012 Annual Report
1333:Principles of Life
1119:This article uses
754:hangman's fracture
563:vertebra prominens
559:
549:Vertebra prominens
450:posterior tubercle
416:sympathetic nerves
306:posterior surfaces
286:
266:
163:cervical vertebrae
33:Cervical vertebrae
2570:
2569:
2437:Lumbosacral trunk
2256:Suboccipital – C1
2133:
2132:
2129:
2128:
2111:Intercostal space
1973:
1972:
1896:sacral tuberosity
1879:sacral promontory
1737:Anterior tubercle
1677:Vertebral foramen
1643:General structure
1343:978-1-4641-6298-5
1133:Cervical fracture
869:Additional images
840:cricoid cartilage
834:thyroid cartilage
812:of a closed mouth
794:. This includes:
745:, which leads to
692:spondylolisthesis
688:cervical fracture
590:ligamentum nuchae
571:subclavian artery
443:anterior tubercle
370:articular pillars
340:vertebral foramen
155:
154:
150:
18:Cervical vertebra
16:(Redirected from
2605:
2548:Coccygeal plexus
2160:
2153:
2146:
2137:
1984:
1836:Lumbar vertebrae
1742:Carotid tubercle
1640:
1616:
1609:
1602:
1593:
1553:
1540:
1531:
1530:
1528:
1526:
1507:
1501:
1488:
1482:
1481:
1447:
1438:
1432:
1431:
1429:
1427:
1407:
1401:
1400:
1390:
1358:
1352:
1351:
1327:
1321:
1320:
1288:
1282:
1279:
1267:
1257:
1247:
1223:
1217:
1216:
1206:
1196:
1172:
1147:
1146:
1128:Vertebral column
1115:
1110:
1109:
1087:
1075:
1063:
1051:
1039:
1027:
1015:
1003:
991:
979:
970:Vertebral column
967:
958:Vertebral column
955:
943:
931:
930:
917:
905:
893:
879:
788:vertebral column
665:
656:
543:odontoid process
476:vertebral artery
460:carotid tubercle
408:vertebral artery
377:articular facets
357:) attach to the
355:splenius capitis
242:vertebral artery
231:three-toed sloth
191:lumbar vertebrae
168:
147:edit on Wikidata
62:
42:
30:
21:
2613:
2612:
2608:
2607:
2606:
2604:
2603:
2602:
2573:
2572:
2571:
2566:
2529:
2460:
2386:
2368:Subcostal – T12
2272:
2237:Brachial plexus
2232:Cervical plexus
2169:
2164:
2134:
2125:
2092:
2088:Xiphoid process
2078:Body of sternum
2049:
1969:
1953:
1891:Lateral surface
1860:
1830:
1790:
1713:
1629:
1620:
1561:
1556:
1541:
1534:
1524:
1522:
1509:
1508:
1504:
1498:Wayback Machine
1489:
1485:
1456:(10): 721–729.
1445:
1440:
1439:
1435:
1425:
1423:
1409:
1408:
1404:
1360:
1359:
1355:
1344:
1329:
1328:
1324:
1290:
1289:
1285:
1270:
1225:
1224:
1220:
1174:
1173:
1169:
1144:
1141:
1124:
1111:
1104:
1101:
1094:
1088:
1079:
1076:
1067:
1064:
1055:
1052:
1043:
1040:
1031:
1028:
1019:
1016:
1007:
1004:
995:
992:
983:
980:
971:
968:
959:
956:
947:
944:
935:
932:
926:
921:
918:
909:
906:
897:
894:
885:
880:
871:
838:From C6–7, the
832:From C4–5, the
784:
778:
758:cervical collar
698:
697:
696:
695:
676:medical imaging
668:
667:
666:
658:
657:
644:
613:
579:brachial plexus
575:subclavian vein
551:
513:
507:Atlas (anatomy)
505:Main articles:
503:
492:cervical plexus
488:brachial plexus
359:nuchal ligament
347:spinous process
284:of these bones.
258:
246:vertebral veins
151:
65:
53:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
2611:
2609:
2601:
2600:
2595:
2590:
2585:
2575:
2574:
2568:
2567:
2565:
2564:
2563:
2562:
2552:
2551:
2550:
2539:
2537:
2531:
2530:
2528:
2527:
2526:
2525:
2520:
2510:
2509:
2508:
2497:
2496:
2491:
2486:
2481:
2476:
2470:
2468:
2462:
2461:
2459:
2458:
2457:
2456:
2451:
2441:
2440:
2439:
2434:
2423:
2422:
2417:
2412:
2407:
2402:
2396:
2394:
2388:
2387:
2385:
2384:
2383:
2382:
2372:
2371:
2370:
2365:
2360:
2355:
2344:
2343:
2338:
2333:
2328:
2323:
2318:
2313:
2308:
2303:
2298:
2293:
2288:
2282:
2280:
2274:
2273:
2271:
2270:
2269:
2268:
2263:
2258:
2253:
2241:
2240:
2239:
2234:
2221:
2220:
2215:
2210:
2205:
2200:
2195:
2190:
2185:
2179:
2177:
2171:
2170:
2165:
2163:
2162:
2155:
2148:
2140:
2131:
2130:
2127:
2126:
2124:
2123:
2118:
2113:
2108:
2102:
2100:
2094:
2093:
2091:
2090:
2085:
2080:
2075:
2070:
2065:
2059:
2057:
2051:
2050:
2048:
2047:
2046:
2045:
2040:
2035:
2030:
2025:
2015:
2014:
2013:
2008:
2003:
1992:
1990:
1981:
1975:
1974:
1971:
1970:
1968:
1967:
1963:
1961:
1955:
1954:
1952:
1951:
1950:
1949:
1939:
1934:
1929:
1924:
1923:
1922:
1915:Dorsal surface
1912:
1911:
1910:
1903:Pelvic surface
1900:
1899:
1898:
1888:
1883:
1882:
1881:
1870:
1868:
1862:
1861:
1859:
1858:
1857:
1856:
1851:
1840:
1838:
1832:
1831:
1829:
1828:
1823:
1822:
1821:
1816:
1811:
1800:
1798:
1792:
1791:
1789:
1788:
1783:
1782:
1781:
1771:
1770:
1769:
1767:posterior arch
1764:
1759:
1749:
1744:
1739:
1734:
1729:
1723:
1721:
1715:
1714:
1712:
1711:
1706:
1705:
1704:
1699:
1694:
1684:
1679:
1674:
1673:
1672:
1667:
1662:
1652:
1646:
1644:
1637:
1631:
1630:
1621:
1619:
1618:
1611:
1604:
1596:
1590:
1589:
1583:
1578:
1573:
1568:
1560:
1559:External links
1557:
1555:
1554:
1532:
1502:
1483:
1450:Neuroradiology
1433:
1402:
1353:
1342:
1322:
1283:
1281:
1280:
1218:
1166:
1160:Gray's Anatomy
1140:
1137:
1136:
1135:
1130:
1117:
1116:
1113:Anatomy portal
1100:
1097:
1096:
1095:
1089:
1082:
1080:
1077:
1070:
1068:
1065:
1058:
1056:
1053:
1046:
1044:
1041:
1034:
1032:
1029:
1022:
1020:
1017:
1010:
1008:
1005:
998:
996:
993:
986:
984:
981:
974:
972:
969:
962:
960:
957:
950:
948:
945:
938:
936:
933:
924:
922:
919:
912:
910:
907:
900:
898:
895:
888:
886:
881:
874:
870:
867:
866:
865:
850:laryngopharynx
842:
836:
830:
823:
813:
806:
777:
774:
672:Cervical lines
670:
669:
660:
659:
651:
650:
649:
648:
647:
643:
640:
629:occipital bone
612:
609:
550:
547:
541:is the strong
511:Axis (anatomy)
502:
501:Atlas and axis
499:
472:carotid artery
456:
455:
454:
453:
446:
439:costal element
435:costal process
396:
395:
394:
387:
373:
362:
343:
332:
325:
324:
323:
316:
309:
257:
254:
227:two-toed sloth
225:with six, the
153:
152:
143:
137:
136:
131:
125:
124:
119:
113:
112:
107:
101:
100:
95:
89:
88:
83:
77:
76:
72:
71:
67:
66:
63:
55:
54:
43:
35:
34:
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2610:
2599:
2596:
2594:
2591:
2589:
2586:
2584:
2581:
2580:
2578:
2561:
2558:
2557:
2556:
2553:
2549:
2546:
2545:
2544:
2541:
2540:
2538:
2536:
2532:
2524:
2521:
2519:
2516:
2515:
2514:
2511:
2507:
2506:Sacral plexus
2504:
2503:
2502:
2499:
2498:
2495:
2492:
2490:
2487:
2485:
2482:
2480:
2477:
2475:
2472:
2471:
2469:
2467:
2463:
2455:
2452:
2450:
2447:
2446:
2445:
2442:
2438:
2435:
2433:
2432:Lumbar plexus
2430:
2429:
2428:
2425:
2424:
2421:
2418:
2416:
2413:
2411:
2408:
2406:
2403:
2401:
2398:
2397:
2395:
2393:
2389:
2381:
2378:
2377:
2376:
2373:
2369:
2366:
2364:
2361:
2359:
2356:
2354:
2351:
2350:
2349:
2346:
2345:
2342:
2339:
2337:
2334:
2332:
2329:
2327:
2324:
2322:
2319:
2317:
2314:
2312:
2309:
2307:
2304:
2302:
2299:
2297:
2294:
2292:
2289:
2287:
2284:
2283:
2281:
2279:
2275:
2267:
2264:
2262:
2259:
2257:
2254:
2252:
2249:
2248:
2247:
2246:
2242:
2238:
2235:
2233:
2230:
2229:
2228:
2227:
2223:
2222:
2219:
2216:
2214:
2211:
2209:
2206:
2204:
2201:
2199:
2196:
2194:
2191:
2189:
2186:
2184:
2181:
2180:
2178:
2176:
2172:
2168:
2167:Spinal nerves
2161:
2156:
2154:
2149:
2147:
2142:
2141:
2138:
2122:
2119:
2117:
2116:Costal margin
2114:
2112:
2109:
2107:
2104:
2103:
2101:
2099:
2098:Thoracic cage
2095:
2089:
2086:
2084:
2081:
2079:
2076:
2074:
2073:Sternal angle
2071:
2069:
2066:
2064:
2061:
2060:
2058:
2056:
2052:
2044:
2041:
2039:
2036:
2034:
2033:costal groove
2031:
2029:
2026:
2024:
2021:
2020:
2019:
2016:
2012:
2011:floating ribs
2009:
2007:
2004:
2002:
1999:
1998:
1997:
1994:
1993:
1991:
1989:
1985:
1982:
1980:
1976:
1965:
1964:
1962:
1960:
1956:
1948:
1947:sacral hiatus
1945:
1944:
1943:
1940:
1938:
1935:
1933:
1930:
1928:
1925:
1921:
1918:
1917:
1916:
1913:
1909:
1906:
1905:
1904:
1901:
1897:
1894:
1893:
1892:
1889:
1887:
1886:Ala of sacrum
1884:
1880:
1877:
1876:
1875:
1872:
1871:
1869:
1867:
1863:
1855:
1852:
1850:
1847:
1846:
1845:
1842:
1841:
1839:
1837:
1833:
1827:
1824:
1820:
1817:
1815:
1812:
1810:
1807:
1806:
1805:
1804:Costal facets
1802:
1801:
1799:
1797:
1793:
1787:
1784:
1780:
1777:
1776:
1775:
1772:
1768:
1765:
1763:
1762:anterior arch
1760:
1758:
1755:
1754:
1753:
1750:
1748:
1745:
1743:
1740:
1738:
1735:
1733:
1730:
1728:
1725:
1724:
1722:
1720:
1716:
1710:
1707:
1703:
1700:
1698:
1695:
1693:
1690:
1689:
1688:
1685:
1683:
1680:
1678:
1675:
1671:
1668:
1666:
1663:
1661:
1658:
1657:
1656:
1653:
1651:
1648:
1647:
1645:
1641:
1638:
1636:
1632:
1628:
1624:
1617:
1612:
1610:
1605:
1603:
1598:
1597:
1594:
1587:
1584:
1582:
1579:
1577:
1574:
1572:
1569:
1567:at kenyon.edu
1566:
1563:
1562:
1558:
1552:
1548:
1546:
1539:
1537:
1533:
1520:
1516:
1512:
1506:
1503:
1499:
1495:
1492:
1487:
1484:
1479:
1475:
1471:
1467:
1463:
1459:
1455:
1451:
1444:
1437:
1434:
1421:
1417:
1416:spineuniverse
1413:
1406:
1403:
1398:
1394:
1389:
1384:
1380:
1376:
1372:
1368:
1364:
1357:
1354:
1349:
1345:
1339:
1335:
1334:
1326:
1323:
1318:
1314:
1310:
1306:
1302:
1298:
1294:
1287:
1284:
1277:
1273:
1269:
1268:
1265:
1261:
1256:
1251:
1246:
1241:
1237:
1233:
1229:
1222:
1219:
1214:
1210:
1205:
1200:
1195:
1190:
1186:
1182:
1178:
1171:
1168:
1165:
1164:
1161:
1158:
1156:
1152:
1151:public domain
1138:
1134:
1131:
1129:
1126:
1125:
1122:
1114:
1108:
1103:
1098:
1093:
1086:
1081:
1074:
1069:
1062:
1057:
1050:
1045:
1038:
1033:
1026:
1021:
1014:
1009:
1002:
997:
990:
985:
978:
973:
966:
961:
954:
949:
942:
937:
929:
923:
916:
911:
904:
899:
892:
887:
884:
878:
873:
868:
863:
859:
855:
851:
847:
843:
841:
837:
835:
831:
828:
824:
822:
818:
814:
811:
807:
805:
801:
797:
796:
795:
793:
792:human anatomy
789:
783:
775:
773:
771:
765:
763:
759:
755:
750:
748:
744:
739:
735:
733:
730:
726:
722:
718:
714:
710:
706:
702:
693:
689:
685:
681:
677:
673:
664:
655:
646:
641:
639:
637:
632:
630:
626:
622:
618:
610:
608:
604:
601:
597:
595:
591:
586:
584:
580:
576:
572:
568:
564:
555:
548:
546:
544:
540:
535:
533:
529:
524:
522:
518:
512:
508:
500:
498:
495:
493:
489:
485:
481:
477:
473:
469:
465:
461:
451:
447:
444:
440:
436:
432:
428:
424:
423:
421:
417:
413:
409:
405:
401:
397:
392:
388:
385:
381:
380:
378:
374:
371:
367:
363:
360:
356:
352:
348:
344:
341:
337:
333:
330:
326:
321:
320:lower surface
317:
314:
313:upper surface
310:
307:
303:
299:
298:
296:
295:
294:
291:
283:
279:
275:
270:
262:
255:
253:
251:
247:
243:
239:
234:
232:
228:
224:
220:
216:
212:
208:
204:
203:cervical ribs
200:
196:
192:
188:
184:
180:
176:
172:
164:
160:
148:
142:
138:
135:
132:
130:
126:
123:
120:
118:
114:
111:
108:
106:
102:
99:
96:
94:
90:
87:
84:
82:
78:
73:
68:
61:
56:
51:
47:
41:
36:
31:
19:
2554:
2542:
2512:
2500:
2443:
2426:
2374:
2347:
2243:
2224:
2017:
1942:Sacral canal
1843:
1757:lateral mass
1718:
1709:Spinal canal
1686:
1542:
1523:. Retrieved
1514:
1505:
1486:
1453:
1449:
1436:
1424:. Retrieved
1415:
1405:
1373:(1): 21–26.
1370:
1366:
1356:
1332:
1325:
1303:(1): 19–26.
1300:
1297:J. Exp. Zool
1296:
1292:
1286:
1276:ScienceDaily
1275:
1235:
1231:
1221:
1184:
1180:
1170:
1162:
1148:
1142:
785:
766:
751:
740:
736:
700:
699:
671:
645:
633:
614:
605:
602:
598:
587:
567:cervical rib
562:
560:
536:
525:
514:
496:
463:
459:
457:
438:
434:
420:spinal nerve
390:
383:
369:
319:
312:
305:
301:
287:
278:heterochrony
235:
233:with nine.
170:
162:
156:
110:A02.2.02.001
85:
2353:Intercostal
1515:www.ohri.ca
844:At C6, the
829:bifurcates.
825:At C4, the
815:At C3, the
808:At C2, the
804:hard palate
721:radiographs
717:osteophytes
705:spondylosis
484:anaesthesia
211:saurischian
75:Identifiers
2577:Categories
2006:false ribs
1854:mammillary
1819:transverse
1692:transverse
1426:25 October
1187:(4): 3–4.
1139:References
846:oesophagus
821:hyoid bone
780:See also:
762:halo brace
173:) are the
2555:posterior
2535:Coccygeal
2513:posterior
2444:posterior
2375:posterior
2245:posterior
2068:Manubrium
2001:true ribs
1849:accessory
1844:Processes
1697:articular
1687:Processes
1635:Vertebrae
1545:Mnemonics
776:Landmarks
743:diaphragm
732:sclerosis
621:extension
519:(C1) and
474:from the
351:trapezius
290:vertebrae
256:Structure
199:sauropsid
175:vertebrae
159:tetrapods
2543:anterior
2501:anterior
2427:anterior
2348:anterior
2278:Thoracic
2226:anterior
2175:Cervical
2028:tubercle
1988:Rib cage
1814:inferior
1809:superior
1519:Archived
1494:Archived
1478:10970503
1470:16136264
1420:Archived
1397:19384631
1348:Archived
1317:10327647
1264:21548920
1213:21306656
1099:See also
934:3D image
817:mandible
802:and the
725:stenosis
709:stenosis
611:Function
431:thoracic
391:inferior
384:superior
329:pedicles
302:anterior
219:amniotes
187:thoracic
171:vertebra
2055:Sternum
1702:spinous
1660:pedicle
1625:of the
1565:Diagram
1551:3548
1543:Medical
1388:2657349
1255:3120709
1232:EvoDevo
1204:3041741
1155:page 97
862:carotid
858:trachea
623:at the
617:flexion
486:of the
429:in the
336:laminae
238:foramen
223:manatee
207:lizards
195:mammals
177:of the
98:D002574
70:Details
2466:Sacral
2392:Lumbar
1979:Thorax
1959:Coccyx
1866:Sacrum
1665:lamina
1476:
1468:
1395:
1385:
1340:
1315:
1262:
1252:
1238:: 11.
1211:
1201:
1163:(1918)
854:larynx
248:, and
2023:angle
2018:Parts
1752:Atlas
1670:notch
1627:torso
1623:Bones
1525:6 May
1474:S2CID
1446:(PDF)
1153:from
1092:here.
810:teeth
734:(4).
680:X-ray
532:spine
528:skull
517:atlas
466:(for
274:okapi
215:birds
205:. In
183:skull
145:[
81:Latin
2043:head
2038:neck
1996:Ribs
1966:none
1874:Base
1779:dens
1774:Axis
1655:Arch
1650:Body
1547:.com
1527:2018
1466:PMID
1428:2016
1393:PMID
1338:ISBN
1313:PMID
1260:PMID
1209:PMID
819:and
800:nose
786:The
682:and
619:and
561:The
539:bone
530:and
521:axis
515:The
509:and
490:and
412:vein
410:and
398:The
389:the
382:the
375:The
353:and
345:The
334:The
327:The
318:The
311:The
304:and
300:The
209:and
189:and
179:neck
134:9915
122:1032
105:TA98
93:MeSH
2341:T12
2336:T11
2331:T10
1458:doi
1383:PMC
1375:doi
1305:doi
1301:285
1293:Hox
1250:PMC
1240:doi
1199:PMC
1189:doi
760:or
711:of
573:or
462:or
437:or
427:rib
193:in
167:sg.
157:In
129:FMA
117:TA2
2579::
2494:S5
2489:S4
2484:S3
2479:S2
2474:S1
2420:L5
2415:L4
2410:L3
2405:L2
2400:L1
2326:T9
2321:T8
2316:T7
2311:T6
2306:T5
2301:T4
2296:T3
2291:T2
2286:T1
2218:C8
2213:C7
2208:C6
2203:C5
2198:C4
2193:C3
2188:C2
2183:C1
1549::
1535:^
1517:.
1513:.
1472:.
1464:.
1454:47
1452:.
1448:.
1418:.
1414:.
1391:.
1381:.
1371:10
1369:.
1365:.
1346:.
1311:.
1299:.
1274:.
1258:.
1248:.
1234:.
1230:.
1207:.
1197:.
1183:.
1179:.
764:.
749:.
707:,
690:,
684:CT
594:T1
494:.
422:.
244:,
169::
161:,
50:C2
48:,
46:C1
2159:e
2152:t
2145:v
1615:e
1608:t
1601:v
1529:.
1480:.
1460::
1430:.
1399:.
1377::
1319:.
1307::
1266:.
1242::
1236:2
1215:.
1191::
1185:8
1123:.
452:.
445:.
165:(
149:]
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.