40:
279:
223:
210:(GAPs). The mutation of exon 6 of the sequence can eliminate the critical chain that is responsible for recognizing guanine. This strips the GTPase of its capability to hydrolyze GTP, its hallmark trait. This overall affects the ability of Sar1B GTPase to control chylomicron release. A third mutant allele containing a
118:. For this reason, the disease is likely to be underdiagnosed by physicians. Fat-soluble nutrients are essential for growth, development, and normal bodily function. Vitamin E deficiency is especially serious, as the vitamin is necessary for proper neurological function and development. Without Vitamin E,
269:
and one of the five proteins of the COPll coatomer. A mutation in the sar1B gene and subsequently the sar1B protein are the common genetic origins of chylomicron retention disorder. Without the fully functional sar1B protein, the COPll coatomer proteins engulf pre-chylomicrons exiting the ER but are
201:
Chylomicron retention disease is an autosomal homozygous recessive disorder arising from mutations in the gene encoding the Sar1B GTPase. The Sar1B gene is located at position 5q31.1 in the fifth chromosome and is composed of eight exons. Alternative splicing of the second exon results into two
319:
Clinical manifestation of CMRD symptoms begin during infancy and early childhood but may go undetected due to the non-specific symptoms associated with the disease. Many of these symptoms can be attributed to malnutrition and nonspecific postnatal diarrhea, confounding early diagnosis. Careful
997:
Jones, Bethan; Jones, Emma L.; Bonney, Stephanie A.; Patel, Hetal N.; Mensenkamp, Arjen R.; Eichenbaum-Voline, Sophie; Rudling, Mats; Myrdal, Urban; Annesi, Grazia; Naik, Sandhia; Meadows, Nigel; Quattrone, Aldo; Islam, Suhail A.; Naoumova, Rossitza P.; Angelin, Bo; Infante, Recaredo; Levy, Emile;
348:
Early diagnosis is important for improving patient outcomes. Patients with delayed diagnoses experienced decreased growth compared to those diagnosed earlier in life. Long-term treatment plans center around dietary management, but because long term results have not been documented due to a lack of
513:
Charlotte
Anderson first published a description of the disorder in 1961, where she observed a seven month old girl who developed intestinal mucosa filled with fat droplets. In 2003, Jones and colleagues identified mutations in the SAR1B gene, which transcripts the SAR1B protein involved in COPII
125:
Symptoms that manifest in the GI tract are likely to be a consequence of both reduced absorption of fats and physiological stress imposed on enterocytes that can not shuttle fats into circulation. Additional symptoms that occur throughout the body can be attributed to the lack of sufficient lipid
315:
As of March 2020, only 50 cases of CMRD have been documented in the medical literature. This small number speaks to the rarity of the disease as well as the lack of thorough research and documentation. As a result, the full course of the disease, life expectancy, and mortality are also poorly
290:
relies chiefly on blood lipid analysis following a 12-hr fasting period. Lipids analyzed are LDL (low-density lipoproteins), triglyceride, and apolipoprotein B levels. A patient could be diagnosed with CMRD should they lack sufficient apolipoprotein B levels in the blood. Furthermore, a
812:
Georges, Amandine; Bonneau, Jessica; Bonnefont-Rousselot, Dominique; Champigneulle, Jacqueline; Rabès, Jean P.; Abifadel, Marianne; Aparicio, Thomas; Guenedet, Jean C.; Bruckert, Eric; Boileau, Catherine; Morali, Alain; Varret, Mathilde; Aggerbeck, Lawrence P.; Samson-Bouma, Marie E. (2011).
760:
Georges, Amandine; Bonneau, Jessica; Bonnefont-Rousselot, Dominique; Champigneulle, Jacqueline; Rabès, Jean P.; Abifadel, Marianne; Aparicio, Thomas; Guenedet, Jean C.; Bruckert, Eric; Boileau, Catherine; Morali, Alain; Varret, Mathilde; Aggerbeck, Lawrence P.; Samson-Bouma, Marie E. (2011).
689:
Simone, Maria Luisa; Rabacchi, Claudio; Kuloglu, Zarife; Kansu, Aydan; Ensari, Arzu; Demir, Arzu Meltem; Hizal, Gulin; Di Leo, Enza; Bertolini, Stefano; Calandra, Sebastiano; Tarugi, Patrizia (July 2019). "Novel mutations of SAR1B gene in four children with chylomicron retention disease".
352:
Evaluations tracking liver function that involve the use of ultrasounds to monitor liver growth, are recommended to be administered every three years. At about ten years of age (pre-puberty), neurological and ophthalmological exams may be required every three years to track muscle and eye
245:
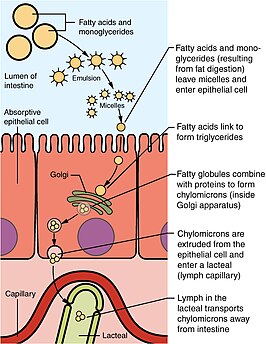
Once transported to the ER the triglycerides are incorporated into pre-chylomicrons which are made up of TGs, cholesterol, and phospholipids. The pre-chylomicrons are then packaged into PCTV to be transported to the Golgi apparatus for additional maturation prior to exocytosis into the
1402:
250:. From the lymphatic system, they enter general circulation, where they are produced in various forms that can be absorbed by bodily tissues and metabolized or stored by adipose tissue. Before the PCTV leaves the ER, it is incorporated into a
1085:
294:
Because patient outcomes rely on early diagnosis, it is recommended that candidates for the disorder should receive lipid panel testing prior to 6 months of age. In patients with only CMRD, lipid panels are expected to display normal
1395:
353:
activity/strength. In adulthood, past eighteen years of age, echocardiograms are recommended to track heart activity. Thorough and vigorous testing warrant themselves to the treatment of a disease of which we know so little.
937:
Peretti, Noel; Sassolas, Agnès; Roy, Claude C.; Deslandres, Colette; Charcosset, Mathilde; Castagnetti, Justine; Pugnet-Chardon, Laurence; Moulin, Philippe; Labarge, Sylvie; Bouthillier, Lise; Lachaux, Alain (2010-09-29).
877:
Peretti, Noel; Sassolas, Agnès; Roy, Claude C.; Deslandres, Colette; Charcosset, Mathilde; Castagnetti, Justine; Pugnet-Chardon, Laurence; Moulin, Philippe; Labarge, Sylvie; Bouthillier, Lise; Lachaux, Alain (2010-09-29).
340:. People with CMRD are at an increased risk for essential fatty acid deficiency, so dietary counseling is required to maintain the low-fat diet, while attaining sufficient caloric intake and essential fatty acid intake.
1388:
514:
transport and proposed this was the molecular defect of the disorder. To present day, 16 mutations of the SAR1B gene have been discovered. This disease is rare, with only 55 cases diagnosed worldwide.
94:
cannot be absorbed. Chylomicrons have a crucial role in fat absorption and transport, thus a deficiency in chylomicron functioning reduces available levels of dietary fats and fat-soluble vitamins.
262:
and fusion with the cis-golgi network. In chylomicron retention disease, the PCTV vesicles are competent for budding from the ER membrane but are defective for fusion with the cis-golgi body.
286:
There is no medical consensus on methodology of diagnosis for CMRD itself. There are, however, protocols used to diagnose the family of genetic disorders to which CMRD belongs. Assessment of
2157:
214:
mutation has also been reported to cause CMRD. All three of these alleles display recessive inheritance, suggesting that they loss-of-function mutations cause the symptoms of CMRD.
1182:
1283:
254:
of five proteins. The PCTV undergoes a similar mechanism for budding as normal COPII transport vesicles. Though PCTV does not require COPII coatomer proteins for
39:
202:
different splice isoforms for the Sar1B transcript RNA. In CMRD, a mutation of this genomic sequence affects the Sar1B enzyme's ability to interact with
198:
The Sar1B GTPase is an enzyme located in epithelial cells of the gastrointestinal tract. These proteins are critical for release of chylomicrons in the body.
349:
thorough research, careful monitoring of the disease is required. Yearly check-ups are recommended to track the growth of children affected by the disease.
1935:
572:
Jones B, Jones EL, Bonney SA, et al. (May 2003). "Mutations in a Sar1 GTPase of COPII vesicles are associated with lipid absorption disorders".
1787:
1175:
940:"Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of chylomicron retention disease based on a review of the literature and the experience of two centers"
880:"Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of chylomicron retention disease based on a review of the literature and the experience of two centers"
2114:
1533:
320:
regulation of diet and nutrition are required for management of CMRD since the disease results from the poor absorption of nutrients from food.
1866:
2142:
1650:
1605:
1543:
122:
cannot operate correctly and signals from the brain are weakened. This leads to reduced muscle development and reduced muscle contraction.
2177:
1168:
1097:
2004:
1474:
1454:
1229:
533:"Malabsorption, hypocholesterolemia, and fat-filled enterocytes with increased intestinal apoprotein B. Chylomicron retention disease"
203:
1464:
2019:
1714:
1523:
1479:
1195:
1244:
815:"Molecular analysis and intestinal expression of SAR1 genes and proteins in Anderson's disease (Chylomicron retention disease)"
763:"Molecular analysis and intestinal expression of SAR1 genes and proteins in Anderson's disease (Chylomicron retention disease)"
328:
It is recommended that patients with CMRD follow a strict low-fat diet in addition to fat-soluble vitamin supplementation. The
1518:
1417:
1338:
291:
minimally invasive endoscopic procedure can be used to examine the bowel. A pale intestine can also be indicative of CMRD.
1722:
1588:
1249:
1234:
1224:
1940:
1538:
1964:
1918:
1746:
150:- Low levels of Vitamin E due to the malabsorption of fats in the diet, causes poor brain, muscle, and eye development.
1761:
1311:
83:
with around 40 cases reported worldwide. Since the disease allele is recessive, parents usually do not show symptoms.
1846:
1755:
1469:
303:
levels may >50% below normal range. The test should also reveal low levels of
Vitamin E and heightened levels of
1369:
1191:
1804:
1698:
1364:
2072:
1633:
1426:
207:
156:- A class of diseases that affects heart muscle, causing shortness of breath, tiredness, and swelling of the legs
110:
typically manifest between infancy and adolescence. The symptoms of CmRD are similar to the physical symptoms of
1818:
1380:
2128:
1528:
1502:
1434:
1275:
1108:
300:
465:
Ultrasonography (steatosis, portal hypertension, yearly), Elastometry
Fibroscan? (further studies are needed)
1906:
1853:
1659:
1298:
1239:
741:
287:
1832:
1510:
665:
103:
1950:
1148:
1045:
1306:
1219:
1215:
270:
unable to disassemble upon arrival at the cis-Golgi, preventing membrane fusion with this organelle.
147:
80:
238:
into two fatty acids and a monoglyceride molecule. Those components are then transported across the
1266:
278:
259:
174:
168:
638:
1988:
1858:
1619:
1514:
1444:
1160:
1027:
854:
723:
620:
597:
76:
114:, as the disease arises due to the poor absorption of lipids and fat-soluble nutrients such as
1569:
1359:
1119:
1019:
979:
961:
919:
901:
846:
794:
715:
707:
589:
554:
332:
are A, D, E, and K. A combination of vitamin A and vitamin E are effective for combating
211:
162:
47:
1000:"Mutations in a Sar1 GTPase of COPII vesicles are associated with lipid absorption disorders"
2066:
1983:
1880:
1775:
1684:
1011:
969:
951:
909:
891:
836:
826:
784:
774:
699:
581:
544:
247:
177:- Excessive fat buildup in the liver, a result of the abnormal lipid panels of CMRD patients
1978:
1945:
1872:
1583:
1439:
1288:
304:
400:
Sufficient caloric intake, low fat diet (fat <30% total energy), EFA supplementation?
139:- Abnormal stools, often foul smelling, due to the increased presence of undigested fats
2100:
1958:
1886:
1207:
974:
939:
914:
879:
841:
814:
789:
762:
389:
153:
107:
222:
2171:
1330:
727:
549:
532:
333:
52:
1031:
601:
1553:
1199:
296:
231:
180:
111:
858:
1113:
1929:
1737:
1354:
136:
72:
1124:
703:
242:
membrane as micelles and reformed into triglycerides once across the membrane.
2047:
337:
239:
186:
998:
Roy, Claude C.; Freemont, Paul S.; Scott, James; Shoulders, Carol C. (2003).
965:
905:
711:
2033:
1493:
115:
91:
87:
1023:
983:
956:
923:
896:
850:
798:
719:
593:
336:
complications. When vitamin D is administered early, it aids in preventing
831:
779:
558:
1256:
1143:
142:
130:
165:- Insufficient weight gain, or drastic levels of weight loss in children
102:
Physical symptoms of CMRD involving the development and function of the
2094:
2086:
2080:
2013:
1798:
329:
1077:
86:
Without functional chylomicrons, certain fat-soluble vitamins such as
2122:
2108:
2027:
1972:
1733:
1678:
1089:
266:
235:
119:
481:
Fundus, color vision, visual evoked potentials, electroretinography
79:
which leads to nutritional and developmental problems. It is a rare
1015:
660:
658:
585:
1840:
1826:
1812:
1769:
1664:
1627:
1613:
1599:
429:
Plasma levels of vitamins A, D, E and K or INR (vit K deficiency)
380:
Appetite, diarrhea, abdominal distension, vomiting, hepatic size?
277:
255:
251:
68:
64:
999:
742:"Lipid — Digestion of dietary fatty acids | Britannica"
2136:
2041:
1900:
1894:
1692:
1644:
1577:
1563:
1102:
1384:
1164:
388:
Developmental retardation, areflexia, ataxia, dysarthria, deep
1411:
Deficiencies of intracellular signaling peptides and proteins
258:
from the ER, association with the coatomer is necessary for
755:
753:
751:
133:- Diarrhea that results from the poor absorption of fats
531:
Roy CC, Levy E, Green PH, et al. (February 1987).
63:
is a disorder of fat absorption. It is associated with
421:
AST, ALT, GGT, total bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase?
621:"Chylomicron retention disease: MedlinePlus Genetics"
1067:
189:- Muscle tissue "wasting," the loss of muscle tissue
2058:
2003:
1917:
1786:
1745:
1731:
1713:
1552:
1501:
1492:
1453:
1425:
1416:
1347:
1329:
1297:
1274:
1265:
1206:
1134:
1071:
46:
29:
24:
1284:Lecithin cholesterol acyltransferase deficiency
2158:intracellular signaling peptides and proteins
1396:
1176:
872:
870:
868:
8:
473:Clinical, creatine kinase, electromyography
632:
630:
1742:
1498:
1422:
1403:
1389:
1381:
1271:
1230:Familial apoprotein CII deficiency/Type Ib
1183:
1169:
1161:
1068:
38:
21:
2020:EDARADD Hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia
1046:"Orphanet: Chylomicron retention disease"
973:
955:
913:
895:
840:
830:
788:
778:
548:
392:loss, muscular weakness or pain, cramps?
183:- Absent or low levels of muscle reflexes
1245:Familial dysbetalipoproteinemia/Type III
355:
234:(TGs), are enzymatically catabolized by
221:
523:
372:Weight and height to draw growth curve
1235:Familial hypercholesterolemia/Type IIa
1250:Familial hypertriglyceridemia/Type IV
1225:Lipoprotein lipase deficiency/Type Ia
615:
613:
611:
413:Total and LDL cholesterol, HDL-C, TG
7:
1651:Neutrophil immunodeficiency syndrome
1534:Albright's hereditary osteodystrophy
489:Bone mineral content for whole body
437:Deficiency induced by low fat diet?
282:Abetalipoproteinemia – high mag
2005:Signal transducing adaptor proteins
666:"Orphanet: Hypobetalipoproteinemia"
1589:KRAS Cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome
1480:X-linked intellectual disability 1
1475:Juvenile primary lateral sclerosis
450:Delayed Follow-Up (every 3 years)
14:
1936:Bannayan–Riley–Ruvalcaba syndrome
944:Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases
884:Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases
819:Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases
767:Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases
1524:Progressive osseous heteroplasia
1370:APOA1 familial renal amyloidosis
1240:Combined hyperlipidemia/Type IIb
2129:PRKCSH Polycystic liver disease
639:"Chylomicron retention disease"
175:Hepatic Steatosis (Fatty Liver)
2115:Wolff–Parkinson–White syndrome
1519:Pseudopseudohypoparathyroidism
1418:GTP-binding protein regulators
692:Journal of Clinical Lipidology
171:- Low blood cholesterol levels
131:Chronic Malabsorptive Diarrhea
1:
1723:Cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome
1671:Chylomicron retention disease
1317:Chylomicron retention disease
61:Chylomicron retention disease
25:Chylomicron retention disease
1965:X-linked myotubular myopathy
1276:Hypoalphalipoproteinemia/HDL
550:10.1016/0016-5085(87)90133-8
81:autosomal recessive disorder
1762:X-linked agammaglobulinemia
1606:Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease
1312:Apolipoprotein B deficiency
1299:Hypobetalipoproteinemia/LDL
230:During digestion, fats, or
2194:
2178:Lipid metabolism disorders
1465:Marinesco–Sjögren syndrome
704:10.1016/j.jacl.2019.05.013
637:Reference, Genetics Home.
457:After the age of 10 years
2153:
2073:Neurofibromatosis type II
1907:Pseudohypoaldosteronism 2
1634:Griscelli syndrome type 2
1427:GTPase-activating protein
1339:Barraquer–Simons syndrome
493:
456:
404:
363:
358:
37:
1941:Lhermitte–Duclos disease
1539:McCune–Albright syndrome
1529:Pseudohypoparathyroidism
1435:Neurofibromatosis type I
359:Early Follow-Up(Annual)
204:Guanine Exchange Factors
1699:Bardet–Biedl syndrome 3
643:Genetics Home Reference
486:Total body composition
344:Proposed Treatment Plan
288:hypobetalipoproteinemia
208:GTP-Activating Proteins
71:prevent the release of
1847:Peutz–Jeghers syndrome
1833:Incontinentia pigmenti
1819:Li–Fraumeni syndrome 2
1470:Aarskog–Scott syndrome
1257:Xanthoma/Xanthomatosis
957:10.1186/1750-1172-5-24
897:10.1186/1750-1172-5-24
434:Essential Fatty Acids
283:
227:
104:gastrointestinal tract
1951:Proteus-like syndrome
1805:Coffin-Lowry syndrome
832:10.1186/1750-1172-6-1
780:10.1186/1750-1172-6-1
281:
226:2431 Lipid Absorption
225:
1859:Myotonic dystrophy 1
1307:Abetalipoproteinemia
1220:Hypertriglyceridemia
1216:Hypercholesterolemia
478:Ophthalmologic exam
330:fat soluble vitamins
299:levels, but LDL and
148:Vitamin E deficiency
1267:Hypolipoproteinemia
397:Dietary counseling
169:Hypocholesterolemia
1989:Metachondromatosis
1685:Joubert syndrome 8
1620:Carpenter syndrome
1455:Guanine nucleotide
1445:Tuberous sclerosis
1365:Lipoid proteinosis
1135:External resources
1052:. October 13, 2023
502:Ejection fraction
470:Neurological exam
284:
228:
98:Signs and symptoms
33:Anderson's Disease
2165:
2164:
1999:
1998:
1979:Noonan syndrome 1
1873:Seckel syndrome 1
1709:
1708:
1584:Noonan syndrome 3
1570:Costello syndrome
1488:
1487:
1378:
1377:
1360:Adiposis dolorosa
1325:
1324:
1158:
1157:
506:
505:
499:Echocardiography
442:Blood cell count
163:Failure to thrive
58:
57:
19:Medical condition
16:Medical condition
2185:
1984:LEOPARD syndrome
1887:Oguchi disease 2
1788:Serine/threonine
1776:ZAP70 deficiency
1743:
1499:
1423:
1405:
1398:
1391:
1382:
1272:
1196:lipid metabolism
1185:
1178:
1171:
1162:
1069:
1062:
1061:
1059:
1057:
1042:
1036:
1035:
994:
988:
987:
977:
959:
934:
928:
927:
917:
899:
874:
863:
862:
844:
834:
809:
803:
802:
792:
782:
757:
746:
745:
738:
732:
731:
686:
680:
679:
677:
676:
662:
653:
652:
650:
649:
634:
625:
624:
617:
606:
605:
569:
563:
562:
552:
537:Gastroenterology
528:
356:
248:lymphatic system
42:
22:
2193:
2192:
2188:
2187:
2186:
2184:
2183:
2182:
2168:
2167:
2166:
2161:
2149:
2054:
1995:
1946:Cowden syndrome
1920:
1913:
1789:
1782:
1747:Tyrosine kinase
1727:
1705:
1548:
1484:
1457:exchange factor
1456:
1449:
1440:Watson syndrome
1412:
1409:
1379:
1374:
1343:
1321:
1293:
1289:Tangier disease
1261:
1202:
1189:
1159:
1154:
1153:
1130:
1129:
1080:
1066:
1065:
1055:
1053:
1044:
1043:
1039:
1004:Nature Genetics
996:
995:
991:
936:
935:
931:
876:
875:
866:
811:
810:
806:
759:
758:
749:
740:
739:
735:
688:
687:
683:
674:
672:
664:
663:
656:
647:
645:
636:
635:
628:
619:
618:
609:
571:
570:
566:
530:
529:
525:
520:
511:
346:
326:
313:
305:creatine kinase
276:
220:
196:
100:
67:. Mutations in
20:
17:
12:
11:
5:
2191:
2189:
2181:
2180:
2170:
2169:
2163:
2162:
2154:
2151:
2150:
2148:
2147:
2146:
2145:
2133:
2132:
2131:
2119:
2118:
2117:
2105:
2104:
2103:
2101:Carney complex
2091:
2090:
2089:
2077:
2076:
2075:
2062:
2060:
2056:
2055:
2053:
2052:
2051:
2050:
2038:
2037:
2036:
2024:
2023:
2022:
2009:
2007:
2001:
2000:
1997:
1996:
1994:
1993:
1992:
1991:
1986:
1981:
1969:
1968:
1967:
1955:
1954:
1953:
1948:
1943:
1938:
1925:
1923:
1915:
1914:
1912:
1911:
1910:
1909:
1891:
1890:
1889:
1877:
1876:
1875:
1863:
1862:
1861:
1851:
1850:
1849:
1837:
1836:
1835:
1823:
1822:
1821:
1809:
1808:
1807:
1794:
1792:
1784:
1783:
1781:
1780:
1779:
1778:
1766:
1765:
1764:
1751:
1749:
1740:
1729:
1728:
1726:
1725:
1719:
1717:
1711:
1710:
1707:
1706:
1704:
1703:
1702:
1701:
1689:
1688:
1687:
1675:
1674:
1673:
1656:
1655:
1654:
1653:
1639:
1638:
1637:
1636:
1624:
1623:
1622:
1610:
1609:
1608:
1594:
1593:
1592:
1591:
1586:
1574:
1573:
1572:
1558:
1556:
1550:
1549:
1547:
1546:
1541:
1536:
1531:
1526:
1521:
1507:
1505:
1496:
1490:
1489:
1486:
1485:
1483:
1482:
1477:
1472:
1467:
1461:
1459:
1451:
1450:
1448:
1447:
1442:
1437:
1431:
1429:
1420:
1414:
1413:
1410:
1408:
1407:
1400:
1393:
1385:
1376:
1375:
1373:
1372:
1367:
1362:
1357:
1351:
1349:
1345:
1344:
1342:
1341:
1335:
1333:
1327:
1326:
1323:
1322:
1320:
1319:
1314:
1309:
1303:
1301:
1295:
1294:
1292:
1291:
1286:
1280:
1278:
1269:
1263:
1262:
1260:
1259:
1254:
1253:
1252:
1247:
1242:
1237:
1232:
1227:
1212:
1210:
1208:Hyperlipidemia
1204:
1203:
1190:
1188:
1187:
1180:
1173:
1165:
1156:
1155:
1152:
1151:
1139:
1138:
1136:
1132:
1131:
1128:
1127:
1116:
1105:
1094:
1081:
1076:
1075:
1073:
1072:Classification
1064:
1063:
1037:
1016:10.1038/ng1145
989:
929:
864:
804:
747:
733:
698:(4): 554–562.
681:
654:
626:
607:
586:10.1038/ng1145
564:
522:
521:
519:
516:
510:
507:
504:
503:
500:
496:
495:
491:
490:
487:
483:
482:
479:
475:
474:
471:
467:
466:
463:
459:
458:
454:
453:
451:
447:
446:
443:
439:
438:
435:
431:
430:
427:
423:
422:
419:
415:
414:
411:
407:
406:
402:
401:
398:
394:
393:
390:proprioception
386:
382:
381:
378:
374:
373:
370:
369:Anthropometry
366:
365:
361:
360:
345:
342:
334:ophthalmologic
325:
322:
312:
309:
307:in the blood.
275:
272:
252:COPII coatomer
219:
216:
195:
192:
191:
190:
184:
178:
172:
166:
160:
157:
154:Cardiomyopathy
151:
145:
140:
134:
108:nervous system
99:
96:
56:
55:
50:
44:
43:
35:
34:
31:
27:
26:
18:
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2190:
2179:
2176:
2175:
2173:
2160:
2159:
2152:
2144:
2141:
2140:
2139:
2138:
2134:
2130:
2127:
2126:
2125:
2124:
2120:
2116:
2113:
2112:
2111:
2110:
2106:
2102:
2099:
2098:
2097:
2096:
2092:
2088:
2085:
2084:
2083:
2082:
2078:
2074:
2071:
2070:
2069:
2068:
2064:
2063:
2061:
2057:
2049:
2046:
2045:
2044:
2043:
2039:
2035:
2032:
2031:
2030:
2029:
2025:
2021:
2018:
2017:
2016:
2015:
2011:
2010:
2008:
2006:
2002:
1990:
1987:
1985:
1982:
1980:
1977:
1976:
1975:
1974:
1970:
1966:
1963:
1962:
1961:
1960:
1956:
1952:
1949:
1947:
1944:
1942:
1939:
1937:
1934:
1933:
1932:
1931:
1927:
1926:
1924:
1922:
1916:
1908:
1905:
1904:
1903:
1902:
1897:
1896:
1892:
1888:
1885:
1884:
1883:
1882:
1878:
1874:
1871:
1870:
1869:
1868:
1864:
1860:
1857:
1856:
1855:
1852:
1848:
1845:
1844:
1843:
1842:
1838:
1834:
1831:
1830:
1829:
1828:
1824:
1820:
1817:
1816:
1815:
1814:
1810:
1806:
1803:
1802:
1801:
1800:
1796:
1795:
1793:
1791:
1785:
1777:
1774:
1773:
1772:
1771:
1767:
1763:
1760:
1759:
1758:
1757:
1753:
1752:
1750:
1748:
1744:
1741:
1739:
1735:
1730:
1724:
1721:
1720:
1718:
1716:
1712:
1700:
1697:
1696:
1695:
1694:
1690:
1686:
1683:
1682:
1681:
1680:
1676:
1672:
1669:
1668:
1667:
1666:
1661:
1658:
1657:
1652:
1649:
1648:
1647:
1646:
1641:
1640:
1635:
1632:
1631:
1630:
1629:
1625:
1621:
1618:
1617:
1616:
1615:
1611:
1607:
1604:
1603:
1602:
1601:
1596:
1595:
1590:
1587:
1585:
1582:
1581:
1580:
1579:
1575:
1571:
1568:
1567:
1566:
1565:
1560:
1559:
1557:
1555:
1551:
1545:
1542:
1540:
1537:
1535:
1532:
1530:
1527:
1525:
1522:
1520:
1516:
1512:
1509:
1508:
1506:
1504:
1503:Heterotrimeic
1500:
1497:
1495:
1491:
1481:
1478:
1476:
1473:
1471:
1468:
1466:
1463:
1462:
1460:
1458:
1452:
1446:
1443:
1441:
1438:
1436:
1433:
1432:
1430:
1428:
1424:
1421:
1419:
1415:
1406:
1401:
1399:
1394:
1392:
1387:
1386:
1383:
1371:
1368:
1366:
1363:
1361:
1358:
1356:
1353:
1352:
1350:
1346:
1340:
1337:
1336:
1334:
1332:
1331:Lipodystrophy
1328:
1318:
1315:
1313:
1310:
1308:
1305:
1304:
1302:
1300:
1296:
1290:
1287:
1285:
1282:
1281:
1279:
1277:
1273:
1270:
1268:
1264:
1258:
1255:
1251:
1248:
1246:
1243:
1241:
1238:
1236:
1233:
1231:
1228:
1226:
1223:
1222:
1221:
1217:
1214:
1213:
1211:
1209:
1205:
1201:
1197:
1193:
1186:
1181:
1179:
1174:
1172:
1167:
1166:
1163:
1150:
1146:
1145:
1141:
1140:
1137:
1133:
1126:
1122:
1121:
1117:
1115:
1111:
1110:
1106:
1104:
1100:
1099:
1095:
1092:
1091:
1087:
1083:
1082:
1079:
1074:
1070:
1051:
1047:
1041:
1038:
1033:
1029:
1025:
1021:
1017:
1013:
1009:
1005:
1001:
993:
990:
985:
981:
976:
971:
967:
963:
958:
953:
949:
945:
941:
933:
930:
925:
921:
916:
911:
907:
903:
898:
893:
889:
885:
881:
873:
871:
869:
865:
860:
856:
852:
848:
843:
838:
833:
828:
824:
820:
816:
808:
805:
800:
796:
791:
786:
781:
776:
772:
768:
764:
756:
754:
752:
748:
743:
737:
734:
729:
725:
721:
717:
713:
709:
705:
701:
697:
693:
685:
682:
671:
667:
661:
659:
655:
644:
640:
633:
631:
627:
622:
616:
614:
612:
608:
603:
599:
595:
591:
587:
583:
579:
575:
568:
565:
560:
556:
551:
546:
542:
538:
534:
527:
524:
517:
515:
508:
501:
498:
497:
492:
488:
485:
484:
480:
477:
476:
472:
469:
468:
464:
461:
460:
455:
452:
449:
448:
444:
441:
440:
436:
433:
432:
428:
425:
424:
420:
417:
416:
412:
409:
408:
403:
399:
396:
395:
391:
387:
385:Neurological
384:
383:
379:
376:
375:
371:
368:
367:
362:
357:
354:
350:
343:
341:
339:
335:
331:
323:
321:
317:
310:
308:
306:
302:
298:
292:
289:
280:
273:
271:
268:
263:
261:
257:
253:
249:
243:
241:
237:
233:
232:triglycerides
224:
217:
215:
213:
209:
205:
199:
193:
188:
185:
182:
179:
176:
173:
170:
167:
164:
161:
159:Slowed Growth
158:
155:
152:
149:
146:
144:
141:
138:
135:
132:
129:
128:
127:
123:
121:
117:
113:
109:
105:
97:
95:
93:
89:
84:
82:
78:
74:
70:
66:
62:
54:
53:Endocrinology
51:
49:
45:
41:
36:
32:
28:
23:
2155:
2135:
2121:
2107:
2093:
2079:
2065:
2040:
2026:
2012:
1971:
1957:
1928:
1899:
1893:
1879:
1865:
1839:
1825:
1811:
1797:
1768:
1754:
1691:
1677:
1670:
1663:
1643:
1626:
1612:
1598:
1576:
1562:
1316:
1200:dyslipidemia
1192:Inborn error
1142:
1118:
1107:
1096:
1084:
1054:. Retrieved
1049:
1040:
1010:(1): 29–31.
1007:
1003:
992:
947:
943:
932:
887:
883:
822:
818:
807:
770:
766:
736:
695:
691:
684:
673:. Retrieved
669:
646:. Retrieved
642:
580:(1): 29–31.
577:
573:
567:
543:(2): 390–9.
540:
536:
526:
512:
351:
347:
327:
318:
316:documented.
314:
297:triglyceride
293:
285:
264:
244:
229:
200:
197:
181:Hyporeflexia
124:
112:malnutrition
101:
85:
73:chylomicrons
60:
59:
1921:phosphatase
1738:phosphatase
1355:Lipomatosis
1056:October 14,
405:Biological
265:Sar1B is a
206:(GEFs) and
137:Steatorrhea
77:circulation
30:Other names
2048:Zaspopathy
1715:MAP kinase
1120:DiseasesDB
675:2020-05-07
648:2020-05-04
574:Nat. Genet
518:References
494:Adult age
377:Digestive
338:osteopenia
240:enterocyte
218:Physiology
187:Amyotrophy
2156:See also
2034:Cherubism
1554:Monomeric
1494:G protein
966:1750-1172
950:(1): 24.
906:1750-1172
890:(1): 24.
728:190892043
712:1933-2874
670:orpha.net
426:Vitamins
364:Clinical
324:Treatment
311:Prognosis
274:Diagnosis
126:sources.
116:vitamin E
92:vitamin E
88:vitamin D
48:Specialty
2172:Category
1919:Tyrosine
1144:Orphanet
1050:Orphanet
1032:10543077
1024:12692552
984:20920215
924:20920215
851:21235735
799:21235735
720:31253576
602:10543077
594:12692552
462:Hepatic
445:Anemia?
418:Hepatic
212:missense
194:Genetics
143:Vomiting
2095:PRKAR1A
2087:CADASIL
2081:Notch 3
2014:EDARADD
1799:RPS6KA3
1114:C535460
1093:: E78.6
975:2956717
915:2956717
842:3029219
790:3029219
559:3792776
509:History
410:Lipids
260:docking
256:budding
236:lipases
120:neurons
75:in the
2123:PRKCSH
2109:PRKAG2
2028:SH3BP2
1973:PTPN11
1790:kinase
1734:kinase
1732:Other
1679:ARL13B
1103:246700
1030:
1022:
982:
972:
964:
922:
912:
904:
859:927898
857:
849:
839:
797:
787:
726:
718:
710:
600:
592:
557:
267:GTPase
2143:XIAP2
2059:Other
1841:STK11
1827:IKBKG
1813:CHEK2
1770:ZAP70
1665:SAR1B
1642:RHO:
1628:RAB27
1614:RAB23
1597:RAB:
1561:RAS:
1544:CGL 2
1515:GNAS1
1348:Other
1125:33188
1028:S2CID
855:S2CID
825:: 1.
773:: 1.
724:S2CID
598:S2CID
69:SAR1B
65:SAR1B
2137:XIAP
2042:LDB3
1959:MTM1
1930:PTEN
1901:WNK1
1895:WNK4
1881:GRK1
1854:DMPK
1693:ARL6
1645:RAC2
1600:RAB7
1578:KRAS
1564:HRAS
1511:cAMP
1194:of
1109:MeSH
1098:OMIM
1058:2023
1020:PMID
980:PMID
962:ISSN
920:PMID
902:ISSN
847:PMID
795:PMID
716:PMID
708:ISSN
590:PMID
555:PMID
106:and
90:and
2067:NF2
1867:ATR
1756:BTK
1660:ARF
1086:ICD
1012:doi
970:PMC
952:doi
910:PMC
892:doi
837:PMC
827:doi
785:PMC
775:doi
700:doi
582:doi
545:doi
301:HDL
2174::
1662::
1517::
1198::
1149:71
1147::
1123::
1112::
1101::
1090:10
1048:.
1026:.
1018:.
1008:34
1006:.
1002:.
978:.
968:.
960:.
946:.
942:.
918:.
908:.
900:.
886:.
882:.
867:^
853:.
845:.
835:.
821:.
817:.
793:.
783:.
769:.
765:.
750:^
722:.
714:.
706:.
696:13
694:.
668:.
657:^
641:.
629:^
610:^
596:.
588:.
578:34
576:.
553:.
541:92
539:.
535:.
1898:/
1736:/
1513:/
1404:e
1397:t
1390:v
1218:/
1184:e
1177:t
1170:v
1088:-
1078:D
1060:.
1034:.
1014::
986:.
954::
948:5
926:.
894::
888:5
861:.
829::
823:6
801:.
777::
771:6
744:.
730:.
702::
678:.
651:.
623:.
604:.
584::
561:.
547::
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.