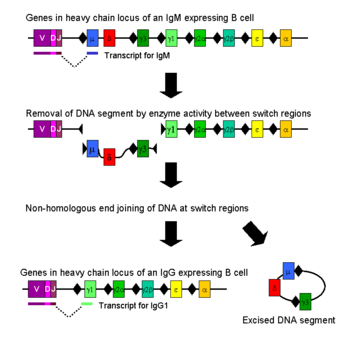
281:. AID begins the process of class switching by deaminating (removing an amino group from) cytosines within the S regions, converting the original C bases into deoxyuridine and allowing the uracil glycosylase to excise the base. This allows AP-endonucleases to cut the newly-formed abasic site, creating the initial SSBs that spontaneously form DSBs. The intervening DNA between the S-regions is subsequently deleted from the chromosome, removing unwanted μ or δ heavy chain constant region
31:
147:), they undergo antibody class switching to produce IgG, IgA or IgE antibodies. During class switching, the constant region of the immunoglobulin heavy chain changes but the variable regions do not, and therefore antigenic specificity, remains the same. This allows different daughter cells from the same activated B cell to produce antibodies of different isotypes or subtypes (e.g. IgG1, IgG2 etc.).
664:
and synapsis of broken S regions are under the control of a large super-enhancer, located downstream the more distal Calpha gene, the 3' regulatory region (3'RR). In some occasions, the 3'RR super-enhancer can itself be targeted by AID and undergo DNA breaks and junction with Sμ, which then deletes the Ig heavy chain locus and defines
663:
In addition to the highly repetitive structure of the target S regions, the process of class switching needs S regions to be first transcribed and spliced out of the immunoglobulin heavy chain transcripts (where they lie within introns). Chromatin remodeling, accessibility to transcription and to AID
293:
to the desired downstream constant domain exon of the antibody heavy chain. In the absence of non-homologous end joining, free ends of DNA may be rejoined by an alternative pathway biased toward microhomology joins. With the exception of the μ and δ genes, only one antibody class is expressed by a B
294:
cell at any point in time. While class switch recombination is mostly a deletional process, rearranging a chromosome in "cis", it can also occur (in 10 to 20% of cases, depending upon the Ig class) as an inter-chromosomal translocation mixing immunoglobulin heavy chain genes from both alleles.
1006:
Yan CT, Boboila C, Souza EK, Franco S, Hickernell TR, Murphy M, Gumaste S, Geyer M, Zarrin AA, Manis JP, Rajewsky K, Alt FW (2007). "IgH class switching and translocations use a robust non-classical end-joining pathway".
1388:
Péron S, Laffleur B, Denis-Lagache N, Cook-Moreau J, Tinguely A, Delpy L, Denizot Y, Pinaud E, Cogné M (May 2012). "AID-driven deletion causes immunoglobulin heavy chain locus suicide recombination in B cells".
1474:
226:
Class switching occurs by a mechanism called class switch recombination (CSR) binding. Class switch recombination is a biological mechanism that allows the class of
116:) to generate the different classes of antibody, all with the same variable domains as the original antibody generated in the immature B cell during the process of
971:
Lieber MR, Yu K, Raghavan SC (2006). "Roles of nonhomologous DNA end-joining, V(D)J recombination, and class switch recombination in chromosomal translocations".
713:"The variability of the serological response to SARS-corona virus-2: Potential resolution of ambiguity through determination of avidity (functional affinity)"
302:
T cell cytokines modulate class switching in mouse (Table 1) and human (Table 2). These cytokines may have suppressive effect on production of IgM.
1467:
267:
242:, and the gene segments surrounding the deleted portion are rejoined to retain a functional antibody gene that produces antibody of a different
1364:
1181:
1153:
1194:
Shparago, N.; Zelazowski, P.; Jin, L.; McIntyre, T. M.; Stuber, E.; Peçanha, L. M.; Kehry, M. R.; Mond, J. J.; Max, E. E. (1996-05-01).
1101:"Immunoglobulin genes undergo legitimate repair in human B cells not only after cis- but also frequent trans-class switch recombination"
1460:
762:
139:. After activation by antigen, these B cells proliferate. If these activated B cells encounter specific signaling molecules via their
1806:
285:
and allowing substitution of a γ, α or ε constant region gene segment. The free ends of the DNA are rejoined by a process called
92:). Since the variable region does not change, class switching does not affect antigen specificity. Instead, the antibody retains
830:
Durandy A (2003). "Activation-induced cytidine deaminase: a dual role in class-switch recombination and somatic hypermutation".
1913:
1908:
1744:
717:
665:
1630:
286:
255:
121:
77:
1300:"Interleukin-10 induces immunoglobulin G isotype switch recombination in human CD40-activated naive B lymphocytes"
234:
to change during a process known as isotype or class switching. During CSR, portions of the antibody heavy chain
1298:
Malisan F, Brière F, Bridon JM, Harindranath N, Mills FC, Max EE, Banchereau J, Martinez-Valdez H (March 1996).
1446:
1200:
1810:
1568:
93:
1903:
1832:
1550:
1486:
1442:
258:; these occur adjacent to all heavy chain constant region genes with the exception of the δ-chain. DNA is
1779:
1635:
1613:
682:
1251:"Human interleukin 10 induces naive surface immunoglobulin D+ (sIgD+) B cells to secrete IgG1 and IgG3"
1060:"Interallelic class switch recombination contributes significantly to class switching in mouse B cells"
1796:
1729:
1640:
1564:
1398:
1016:
243:
66:
1452:
1918:
1856:
1791:
1774:
1608:
1526:
117:
1676:
1422:
1246:
1159:
1040:
855:
97:
1724:
1490:
1414:
1370:
1360:
1329:
1280:
1227:
1219:
1177:
1149:
1122:
1081:
1032:
988:
953:
904:
847:
797:
744:
687:
608:
434:
939:
1844:
1784:
1756:
1751:
1719:
1706:
1696:
1406:
1352:
1319:
1311:
1270:
1262:
1209:
1112:
1071:
1024:
980:
943:
935:
894:
886:
839:
789:
734:
726:
278:
235:
175:
136:
73:
69:
30:
34:
Mechanism of class-switch recombination that allows isotype switching in activated B cells.
1739:
274:
113:
1402:
1347:
Pinaud E, Marquet M, Fiancette R, Péron S, Vincent-Fabert C, Denizot Y, Cogné M (2011).
1020:
1766:
1711:
1652:
1572:
1545:
1356:
1324:
1299:
1275:
1250:
948:
923:
899:
874:
739:
712:
692:
144:
1897:
1734:
1623:
577:
521:
398:
342:
859:
1701:
1686:
1681:
1618:
1516:
1426:
1044:
767:
1142:
1076:
1059:
984:
80:
is changed, but the variable region of the heavy chain stays the same (the terms
793:
17:
1824:
1577:
1483:
259:
247:
239:
1223:
1214:
1195:
1882:
1587:
1410:
1418:
1374:
1126:
1085:
1036:
992:
957:
908:
851:
801:
748:
1333:
1315:
1284:
1266:
1231:
843:
88:
refer to changes or lack thereof between antibodies that target different
1872:
1657:
1645:
1603:
1557:
1521:
1117:
1100:
677:
227:
89:
62:
1028:
890:
1877:
1691:
1540:
1511:
1058:
Reynaud S, Delpy L, Fleury L, Dougier HL, Sirac C, Cogné M (May 2005).
730:
1849:
1837:
1582:
1533:
1099:
Laffleur B, Bardet SM, Garot A, Brousse M, Baylet A, Cogné M (2014).
271:
263:
231:
135:, which are the first two heavy chain segments in the immunoglobulin
109:
58:
262:
and broken at two selected S-regions by the activity of a series of
1349:
The IgH locus 3' regulatory region: pulling the strings from behind
764:
V(D)J Recombination and the
Evolution of the Adaptive Immune System
76:. During this process, the constant-region portion of the antibody
780:
Stavnezer J, Amemiya CT (2004). "Evolution of isotype switching".
151:
29:
290:
282:
251:
140:
1456:
213:
192:
165:
159:
132:
128:
875:"Class switching and Myc translocation: how does DNA break?"
1140:
Janeway CA Jr.; Travers P; Walport M; Shlomchik MJ (2001).
250:
motifs, called switch (S) regions, which are upstream from
246:. Double-stranded breaks are generated in DNA at conserved
1351:. Advances in Immunology. Vol. 110. pp. 27–70.
1196:"IL-10 selectively regulates murine Ig isotype switching"
659:
Gene regulatory sequences responsible for class switching
924:"Mechanism and Regulation of Class Switch Recombination"
96:
for the same antigens, but can interact with different
1245:
Brière F, Servet-Delprat C, Bridon JM, Saint-Remy JM,
254:
segments that encode the constant regions of antibody
120:, but possessing distinct constant domains in their
108:
Class switching occurs after activation of a mature
1865:
1823:
1765:
1666:
1596:
1504:
1497:
1141:
1468:
1172:Male D, Brostoff J, Roth DB, Roitt I (2006).
922:Stavnezer J, Guikema JE, Schrader CE (2008).
761:Eleonora Market, F. Nina Papavasiliou (2003)
112:via its membrane-bound antibody molecule (or
8:
57:), is a biological mechanism that changes a
65:from one type to another, such as from the
1501:
1475:
1461:
1453:
143:and cytokine receptors (both modulated by
1445:at the U.S. National Library of Medicine
1323:
1274:
1213:
1116:
1075:
947:
898:
738:
298:Cytokines responsible for class switching
940:10.1146/annurev.immunol.26.021607.090248
483:
304:
150:In humans, the order of the heavy chain
703:
268:activation-induced (cytidine) deaminase
279:apyrimidic/apurinic (AP)-endonucleases
7:
1304:The Journal of Experimental Medicine
1255:The Journal of Experimental Medicine
1148:(5th ed.). Garland Publishing.
485:Table 2. Class switching in humans
289:(NHEJ) to link the variable domain
1357:10.1016/B978-0-12-387663-8.00002-8
127:Naïve mature B cells produce both
25:
306:Table 1. Class switching in mice
819:(4th ed.). Garland Science.
1802:Immunoglobulin class switching
1443:Immunoglobulin+class+switching
1176:Philadelphia: Mosby Elsevier,
39:Immunoglobulin class switching
1:
1077:10.4049/jimmunol.174.10.6176
985:10.1016/j.dnarep.2006.05.013
643:
636:
624:
619:
602:
593:
588:
567:
549:
542:
539:
532:
471:
453:
450:
445:
428:
425:
420:
417:
412:
409:
388:
370:
367:
364:
361:
358:
353:
718:Journal of Medical Virology
666:locus suicide recombination
1935:
1631:Polyclonal B cell response
794:10.1016/j.smim.2004.08.005
287:non-homologous end joining
51:class-switch recombination
607:
520:
495:
492:
489:
433:
341:
316:
313:
310:
230:produced by an activated
1447:Medical Subject Headings
1201:International Immunology
873:Casali P, Zan H (2004).
1411:10.1126/science.1218692
496:Immunoglobulin classes
317:Immunoglobulin classes
1745:Tolerance in pregnancy
1487:adaptive immune system
1215:10.1093/intimm/8.5.781
815:Parham, Peter (2015).
35:
1914:Immune system process
1780:Somatic hypermutation
1614:Polyclonal antibodies
1609:Monoclonal antibodies
1316:10.1084/jem.183.3.937
1267:10.1084/jem.179.2.757
1064:Journal of Immunology
844:10.1002/eji.200324133
683:Genetic recombination
238:are removed from the
33:
1909:Biological processes
1797:Junctional diversity
1565:Antigen presentation
1160:(via NCBI Bookshelf)
1118:10.1038/gene.2014.25
47:isotypic commutation
27:Biological mechanism
1792:V(D)J recombination
1775:Affinity maturation
1527:Antigenic variation
1403:2012Sci...336..931P
1174:Immunology, 7th ed.
1029:10.1038/nature06020
1021:2007Natur.449..478Y
891:10.1038/ni1104-1101
486:
307:
118:V(D)J recombination
1105:Genes and Immunity
973:DNA Repair (Amst.)
928:Annu. Rev. Immunol
484:
305:
36:
1891:
1890:
1819:
1818:
1569:professional APCs
1366:978-0-12-387663-8
1249:(February 1994).
1182:978-0-323-03399-2
1155:978-0-8153-3642-6
979:(9–10): 1234–45.
817:The Immune System
731:10.1002/jmv.26262
688:Immune checkpoint
656:
655:
482:
481:
61:'s production of
43:isotype switching
16:(Redirected from
1926:
1785:Clonal selection
1757:Immune privilege
1752:Immunodeficiency
1707:Cross-reactivity
1697:Hypersensitivity
1502:
1477:
1470:
1463:
1454:
1431:
1430:
1385:
1379:
1378:
1344:
1338:
1337:
1327:
1295:
1289:
1288:
1278:
1242:
1236:
1235:
1217:
1191:
1185:
1170:
1164:
1163:
1147:
1137:
1131:
1130:
1120:
1096:
1090:
1089:
1079:
1055:
1049:
1048:
1015:(7161): 478–82.
1003:
997:
996:
968:
962:
961:
951:
919:
913:
912:
902:
870:
864:
863:
827:
821:
820:
812:
806:
805:
777:
771:
759:
753:
752:
742:
711:Bauer G (2020).
708:
646:
639:
627:
596:
570:
552:
545:
535:
487:
474:
456:
448:
423:
415:
391:
373:
356:
308:
41:, also known as
21:
1934:
1933:
1929:
1928:
1927:
1925:
1924:
1923:
1894:
1893:
1892:
1887:
1861:
1815:
1761:
1740:Clonal deletion
1668:
1662:
1592:
1493:
1481:
1439:
1434:
1397:(6083): 931–4.
1387:
1386:
1382:
1367:
1346:
1345:
1341:
1297:
1296:
1292:
1244:
1243:
1239:
1193:
1192:
1188:
1171:
1167:
1156:
1139:
1138:
1134:
1098:
1097:
1093:
1070:(10): 6176–83.
1057:
1056:
1052:
1005:
1004:
1000:
970:
969:
965:
921:
920:
916:
872:
871:
867:
832:Eur. J. Immunol
829:
828:
824:
814:
813:
809:
779:
778:
774:
760:
756:
710:
709:
705:
701:
674:
661:
644:
637:
625:
594:
581:
568:
550:
543:
533:
525:
472:
454:
446:
421:
413:
402:
389:
371:
354:
346:
300:
275:DNA glycosylase
221:
208:
201:
190:
183:
173:
154:is as follows:
114:B cell receptor
106:
72:to the isotype
28:
23:
22:
18:Class switching
15:
12:
11:
5:
1932:
1930:
1922:
1921:
1916:
1911:
1906:
1896:
1895:
1889:
1888:
1886:
1885:
1880:
1875:
1869:
1867:
1863:
1862:
1860:
1859:
1854:
1853:
1852:
1842:
1841:
1840:
1829:
1827:
1821:
1820:
1817:
1816:
1814:
1813:
1804:
1799:
1794:
1789:
1788:
1787:
1782:
1771:
1769:
1767:Immunogenetics
1763:
1762:
1760:
1759:
1754:
1749:
1748:
1747:
1742:
1737:
1732:
1727:
1715:
1714:
1712:Co-stimulation
1709:
1704:
1699:
1694:
1689:
1684:
1679:
1672:
1670:
1664:
1663:
1661:
1660:
1655:
1653:Immune complex
1649:
1648:
1643:
1638:
1633:
1628:
1627:
1626:
1621:
1616:
1611:
1600:
1598:
1594:
1593:
1591:
1590:
1585:
1580:
1575:
1573:Dendritic cell
1561:
1560:
1555:
1554:
1553:
1551:Conformational
1548:
1537:
1536:
1531:
1530:
1529:
1524:
1519:
1508:
1506:
1499:
1495:
1494:
1482:
1480:
1479:
1472:
1465:
1457:
1451:
1450:
1438:
1437:External links
1435:
1433:
1432:
1380:
1365:
1339:
1290:
1237:
1208:(5): 781–790.
1186:
1165:
1154:
1132:
1091:
1050:
998:
963:
914:
885:(11): 1101–3.
865:
838:(8): 2069–73.
822:
807:
782:Semin. Immunol
772:
754:
725:(1): 311–322.
702:
700:
697:
696:
695:
693:Immunogenetics
690:
685:
680:
673:
670:
660:
657:
654:
653:
651:
649:
647:
642:
640:
635:
631:
630:
628:
623:
621:
618:
616:
614:
611:
605:
604:
601:
599:
597:
592:
590:
587:
584:
579:
574:
573:
571:
566:
564:
562:
560:
558:
554:
553:
548:
546:
541:
538:
536:
531:
528:
523:
518:
517:
514:
511:
508:
505:
502:
498:
497:
494:
491:
480:
479:
477:
475:
470:
468:
466:
464:
460:
459:
457:
452:
449:
444:
442:
440:
437:
431:
430:
427:
424:
419:
416:
411:
408:
405:
400:
395:
394:
392:
387:
385:
383:
381:
379:
375:
374:
369:
366:
363:
360:
357:
352:
349:
344:
339:
338:
335:
332:
329:
326:
323:
319:
318:
315:
312:
299:
296:
224:
223:
219:
216:
210:
206:
203:
199:
196:
188:
185:
181:
178:
171:
168:
162:
145:T helper cells
105:
102:
63:immunoglobulin
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1931:
1920:
1917:
1915:
1912:
1910:
1907:
1905:
1904:Immune system
1902:
1901:
1899:
1884:
1881:
1879:
1876:
1874:
1871:
1870:
1868:
1864:
1858:
1855:
1851:
1848:
1847:
1846:
1843:
1839:
1836:
1835:
1834:
1831:
1830:
1828:
1826:
1822:
1812:
1808:
1805:
1803:
1800:
1798:
1795:
1793:
1790:
1786:
1783:
1781:
1778:
1777:
1776:
1773:
1772:
1770:
1768:
1764:
1758:
1755:
1753:
1750:
1746:
1743:
1741:
1738:
1736:
1735:Clonal anergy
1733:
1731:
1728:
1726:
1723:
1722:
1721:
1717:
1716:
1713:
1710:
1708:
1705:
1703:
1700:
1698:
1695:
1693:
1690:
1688:
1685:
1683:
1680:
1678:
1674:
1673:
1671:
1665:
1659:
1656:
1654:
1651:
1650:
1647:
1644:
1642:
1639:
1637:
1634:
1632:
1629:
1625:
1624:Microantibody
1622:
1620:
1617:
1615:
1612:
1610:
1607:
1606:
1605:
1602:
1601:
1599:
1595:
1589:
1586:
1584:
1581:
1579:
1576:
1574:
1570:
1566:
1563:
1562:
1559:
1556:
1552:
1549:
1547:
1544:
1543:
1542:
1539:
1538:
1535:
1532:
1528:
1525:
1523:
1520:
1518:
1515:
1514:
1513:
1510:
1509:
1507:
1503:
1500:
1496:
1492:
1488:
1485:
1478:
1473:
1471:
1466:
1464:
1459:
1458:
1455:
1448:
1444:
1441:
1440:
1436:
1428:
1424:
1420:
1416:
1412:
1408:
1404:
1400:
1396:
1392:
1384:
1381:
1376:
1372:
1368:
1362:
1358:
1354:
1350:
1343:
1340:
1335:
1331:
1326:
1321:
1317:
1313:
1310:(3): 937–47.
1309:
1305:
1301:
1294:
1291:
1286:
1282:
1277:
1272:
1268:
1264:
1261:(2): 757–62.
1260:
1256:
1252:
1248:
1241:
1238:
1233:
1229:
1225:
1221:
1216:
1211:
1207:
1203:
1202:
1197:
1190:
1187:
1183:
1179:
1175:
1169:
1166:
1161:
1157:
1151:
1146:
1145:
1144:Immunobiology
1136:
1133:
1128:
1124:
1119:
1114:
1110:
1106:
1102:
1095:
1092:
1087:
1083:
1078:
1073:
1069:
1065:
1061:
1054:
1051:
1046:
1042:
1038:
1034:
1030:
1026:
1022:
1018:
1014:
1010:
1002:
999:
994:
990:
986:
982:
978:
974:
967:
964:
959:
955:
950:
945:
941:
937:
933:
929:
925:
918:
915:
910:
906:
901:
896:
892:
888:
884:
880:
876:
869:
866:
861:
857:
853:
849:
845:
841:
837:
833:
826:
823:
818:
811:
808:
803:
799:
795:
791:
788:(4): 257–75.
787:
783:
776:
773:
769:
766:
765:
758:
755:
750:
746:
741:
736:
732:
728:
724:
720:
719:
714:
707:
704:
698:
694:
691:
689:
686:
684:
681:
679:
676:
675:
671:
669:
667:
658:
652:
650:
648:
641:
633:
632:
629:
622:
617:
615:
612:
610:
606:
600:
598:
591:
585:
583:
576:
575:
572:
565:
563:
561:
559:
556:
555:
547:
537:
529:
527:
519:
515:
512:
509:
506:
503:
500:
499:
488:
478:
476:
469:
467:
465:
462:
461:
458:
443:
441:
438:
436:
432:
406:
404:
397:
396:
393:
386:
384:
382:
380:
377:
376:
350:
348:
340:
336:
333:
330:
327:
324:
321:
320:
309:
303:
297:
295:
292:
288:
284:
280:
276:
273:
269:
265:
261:
257:
253:
249:
245:
241:
237:
233:
229:
217:
215:
211:
204:
197:
194:
186:
179:
177:
169:
167:
163:
161:
157:
156:
155:
153:
148:
146:
142:
138:
134:
130:
125:
123:
119:
115:
111:
103:
101:
99:
95:
91:
87:
83:
79:
75:
71:
68:
64:
60:
56:
52:
48:
44:
40:
32:
19:
1801:
1702:Inflammation
1687:Alloimmunity
1682:Autoimmunity
1667:Immunity vs.
1619:Autoantibody
1517:Superantigen
1394:
1390:
1383:
1348:
1342:
1307:
1303:
1293:
1258:
1254:
1247:Banchereau J
1240:
1205:
1199:
1189:
1173:
1168:
1143:
1135:
1111:(5): 341–6.
1108:
1104:
1094:
1067:
1063:
1053:
1012:
1008:
1001:
976:
972:
966:
931:
927:
917:
882:
879:Nat. Immunol
878:
868:
835:
831:
825:
816:
810:
785:
781:
775:
768:PLoS Biology
763:
757:
722:
716:
706:
662:
301:
266:, including
256:heavy chains
225:
149:
126:
122:heavy chains
107:
85:
81:
54:
50:
46:
42:
38:
37:
1825:Lymphocytes
1484:Lymphocytic
934:: 261–292.
100:molecules.
78:heavy chain
1919:Immunology
1898:Categories
1866:Substances
1730:Peripheral
1718:Inaction:
1597:Antibodies
1578:Macrophage
1491:complement
770:1(1): e16.
699:References
493:Cytokines
314:Cytokines
248:nucleotide
240:chromosome
1883:Cytolysin
1873:Cytokines
1720:Tolerance
1669:tolerance
1588:Immunogen
1224:0953-8178
104:Mechanism
1833:Cellular
1677:Immunity
1675:Action:
1658:Paratope
1646:Idiotype
1636:Allotype
1604:Antibody
1558:Mimotope
1522:Allergen
1505:Antigens
1498:Lymphoid
1419:22539552
1375:21762815
1127:24848929
1086:15879114
1037:17713479
993:16793349
958:18370922
909:15496946
860:32059768
852:12884279
802:15522624
749:32633840
678:Antibody
672:See also
490:T cells
311:T cells
228:antibody
98:effector
94:affinity
90:epitopes
86:constant
82:variable
1878:Opsonin
1857:NK cell
1845:Humoral
1725:Central
1692:Allergy
1641:Isotype
1541:Epitope
1512:Antigen
1427:1513560
1399:Bibcode
1391:Science
1334:8642297
1325:2192363
1285:8294883
1276:2191366
1232:8671667
1045:4341381
1017:Bibcode
949:2707252
900:4625794
740:7361859
668:(LSR).
270:(AID),
264:enzymes
244:isotype
67:isotype
1850:B cell
1838:T cell
1583:B cell
1546:Linear
1534:Hapten
1449:(MeSH)
1425:
1417:
1373:
1363:
1332:
1322:
1283:
1273:
1230:
1222:
1184:(pbk.)
1180:
1152:
1125:
1084:
1043:
1035:
1009:Nature
991:
956:
946:
907:
897:
858:
850:
800:
747:
737:
634:IL-10
463:IL-10
328:IgG2b
325:IgG2a
272:uracil
260:nicked
232:B cell
222:- IgA2
209:- IgG4
202:- IgG2
184:- IgG1
110:B cell
59:B cell
1423:S2CID
1041:S2CID
856:S2CID
613:TGFβ
586:IFNγ
557:IL-5
530:IL-4
510:IgG4
507:IgG3
504:IgG2
501:IgG1
439:TGFβ
407:IFNγ
378:IL-5
351:IL-4
334:IgG4
331:IgG3
322:IgG1
283:exons
236:locus
152:exons
137:locus
1489:and
1415:PMID
1371:PMID
1361:ISBN
1330:PMID
1281:PMID
1228:PMID
1220:ISSN
1178:ISBN
1150:ISBN
1123:PMID
1082:PMID
1033:PMID
989:PMID
954:PMID
905:PMID
848:PMID
798:PMID
745:PMID
609:Treg
516:IgE
513:IgA
435:Treg
337:IgE
291:exon
277:and
252:gene
212:ε -
176:IgG3
164:δ -
158:μ -
141:CD40
131:and
84:and
1811:HLA
1807:MHC
1407:doi
1395:336
1353:doi
1320:PMC
1312:doi
1308:183
1271:PMC
1263:doi
1259:179
1210:doi
1113:doi
1072:doi
1068:174
1025:doi
1013:449
981:doi
944:PMC
936:doi
895:PMC
887:doi
840:doi
790:doi
735:PMC
727:doi
214:IgE
193:IgA
166:IgD
160:IgM
133:IgD
129:IgM
74:IgG
70:IgM
55:CSR
49:or
1900::
1571::
1421:.
1413:.
1405:.
1393:.
1369:.
1359:.
1328:.
1318:.
1306:.
1302:.
1279:.
1269:.
1257:.
1253:.
1226:.
1218:.
1204:.
1198:.
1158:.
1121:.
1109:15
1107:.
1103:.
1080:.
1066:.
1062:.
1039:.
1031:.
1023:.
1011:.
987:.
975:.
952:.
942:.
932:26
930:.
926:.
903:.
893:.
881:.
877:.
854:.
846:.
836:33
834:.
796:.
786:16
784:.
743:.
733:.
723:93
721:.
715:.
620:↓
603:↓
589:↓
540:↓
451:↓
429:↓
426:↓
418:↓
410:↓
368:↓
365:↓
362:↓
359:↓
191:-
174:-
124:.
45:,
1809:/
1567:/
1476:e
1469:t
1462:v
1429:.
1409::
1401::
1377:.
1355::
1336:.
1314::
1287:.
1265::
1234:.
1212::
1206:8
1162:.
1129:.
1115::
1088:.
1074::
1047:.
1027::
1019::
995:.
983::
977:5
960:.
938::
911:.
889::
883:5
862:.
842::
804:.
792::
751:.
729::
645:↑
638:↑
626:↑
595:↑
582:1
580:h
578:T
569:↑
551:↑
544:↑
534:↑
526:2
524:h
522:T
473:↑
455:↑
447:↑
422:↑
414:↑
403:1
401:h
399:T
390:↑
372:↑
355:↑
347:2
345:h
343:T
220:2
218:α
207:4
205:γ
200:2
198:γ
195:1
189:1
187:α
182:1
180:γ
172:3
170:γ
53:(
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.