377:
487:
develops as follows: The early embryo is turned onto its left side, such that its left is turned to the yolk and its right is turned away from the yolk. This asymmetric orientation is compensated by asymmetric growth, to regain superficial bilateral symmetry. The anterior head region turns to the left, as shown in the schema. The forebrain is not a superficial structure, but it is so intimately associated with superficial body structures that it turns along with the anterior head. These structures will later form the eyes, nostrils and mouth.
20:
474:
385:
396:(1898). According to this theory, the function of the optic chiasm is to repair the retinal field image on the visual cortex. The pupil in the vertebrates’ eyes inverts the image on the retina, so that the visual periphery projects to the medial side of the retina. By the chiasmatic crossing, the visual periphery is again on the outside, if one assumes that the retinal map is faithfully maintained throughout the optic tract.
3149:
3159:
94:
619:
who are born with two faces, one on either side of the head. These twins have two brains and two spinal cords, but these are located on the left and the right side of the body. According to the axial twist hypothesis, the two nervous systems could not turn due to the complex configuration of the body
1328:
Ramón y Cajal, Santiago (1898). "Estructura del quiasma óptico y teoría general de los entrecruzamientos de las vías nerviosas. (Structure of the
Chiasma opticum and general theory of the crossing of nerve tracks)" [Die Structur des Chiasma opticum nebst einer allgemeine Theorie der Kreuzung der
477:
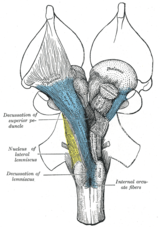
Schema of the developmental twist, according to the axial twist hypothesis. A, B: The early embryo turns onto its left side; B, C: Symmetry is retained by a further left turn in the anterior head region and a compensating right turn in the rest of the body. D, E: Growth of the optic tract leading to
53:
represent mainly the contralateral side of the body. Consequently, the left side of the forebrain mostly represents the right side of the body, and the right side of the brain primarily represents the left side of the body. The contralateral organization involves both executive and sensory functions
535:
The somatic twist hypothesis was proposed as an improvement to the inversion hypothesis, and thus has a much wider explanatory power than its predecessor, but is also more complicated. It not only explains the inversion of the body but additionally the contralateral forebrain. It does not explain,
494:
The optic tract grows from the retina to the optic tectum. Because dorsal and ventral are inverted in the anterior head region, the tracts grow at first toward the ventral side, to meet in the midline to form a chiasma. Since the optic tectum lies on the dorsal midbrain, each tract then continues
486:
was designed to explain how the pattern of contralateral organization, decussations and chiasmas develops, and why this pattern is so evolutionarily stable, having no known exceptions throughout the 500 million years of vertebrate evolution. According to the theory, the contralateral organization
352:
Other hypotheses tend to explain specific aspects of the phenomenon. One proposes that crossing generally provides better geometrical mapping. According to another view, the crossing is a coincidence that has been conserved by parcellation. A third hypothesis proposes that the crossing results
564:
show the presence of an optic chiasma: this idea was worked out by
Kinsbourne. There is molecular evidence for the inversion hypothesis in almost all groups of deuterostomes. It is not known, however, what exactly was the selective pressure that caused the inversion. Twisting and asymmetric
547:
was proposed independently. In addition to providing rationale for the inverted body and the contralateral forebrain, it explains why the heart and bowels are asymmetric. It is the only one of the three theories that is supported by evidence from embryological growth.
605:, the hemispheres of the cerebrum or part of it are not aligned on the left and right side but only on the frontal and occipital sides of the skull, and the head usually remains very small. According to the axial twist hypothesis, this represents an extreme case of
490:
The body behind the head compensates the asymmetric body orientation in the opposite direction, by turning to the right. (See schema.) Due to these oppositely directed compensations of the anterior head and the rest of the body, the animal becomes twisted.
498:
The heart and bowels are internal organs with no strong integration in external body structures, so there is no evolutionary pressure to make them turn in a similar way. Rather, these organs retain their original asymmetric orientation in the body.
407:.) As a result, the retinal map shows the visual periphery on the medial side. However, the central objective of the theory was to obtain a precise, faithful visual map with the medial field projecting to the medial sides of the visual cortex.
102:
310:
connections of the forebrain have bilateral components, especially outside the primary sensory and motor regions. As a result, a hemiplegia that is acquired at very young age can sometimes be completely compensated over
531:
have a ventral one. According to the somatic twist hypothesis, not the entire animal turned on its back but just the somatic part—i.e., everything behind the eyes, mouth and nostrils, including the forebrain.
862:
Flinker, Adeen; Korzeniewska, Anna; Shestyuk, Avgusta Y.; Franaszczuk, Piotr J.; Dronkers, Nina F.; Knight, Robert T.; Crone, Nathan E. (2015). "Redefining the role of Broca's area in speech".
884:
Ebbesson, Sven O. E. (1980). "The parcellation theory and its relation to interspecific variability in brain organization, evolutionary and ontogenetic development, and neuronal plasticity".
2881:
659:"The neural pathway midline crossing theory: a historical analysis of Santiago Rámon y Cajal's contribution on cerebral localization and on contralateral forebrain organization"
234:
Although the forebrain of all vertebrates shows a contralateral organization, this contralaterality is by no means complete. Some of these exceptions are worth mentioning:
753:
Burgess, Robert W.; Jucius, Thomas J.; Ackerman, Susan L. (206). "Motor axon guidance of the mammalian
Trochlear and Phrenic nerves: Dependence on the Netrin receptor
465:
has been used on the axial twist theory to generate empirically testable predictions, all of which were confirmed, albeit in a work by the first author of the theory.
502:
The axial twist hypothesis predicts that small asymmetries of the face and brain—as well as those found in the opposite direction in the trunk—remain into adulthood.
438:
part of the head, including the forebrain, is in fact effectively completely turned around. As a consequence, the left and right in the brain are reversed, but also
1252:
Banihani, S. M. (2010), "Crossing of neuronal pathways: is it a response to the occurrence of separated parts for the body (limbs, eyes, etc.) during evolution?",
819:
Luiten, P.G.M. (1981). "Two visual pathways to the telencephalon in the nurse shark (Ginglymostoma cirratum). II. ascending thalamo-telencephalic connections".
1930:
380:
Cajal's schema of the visual map theory. O=Optic chiasm; C=Visual (and motor) cortex; M, S=Decussating pathways; R, G: Sensory nerves, motor ganglia.
3134:
2589:
1940:
956:
de
Lussanet, M.H.E.; Osse, J.W.M. (2012). "An ancestral axial twist explains the contralateral forebrain and the optic chiasm in vertebrates".
3183:
2897:
2657:
2254:
1286:
Whitehead, L.; Banihani, S. M. (2014), "The evolution of contralateral control of the body by the brain: is it a protective mechanism?",
2980:
1900:
214:(i.e., cranial nerve IV), which originates in the ventral midbrain and innervates one of the six muscles that rotate the eye (i.e., the
776:
Luiten, P.G.M. (1981). "Two visual pathways to the telencephalon in the nurse shark (Ginglymostoma cirratum). I. retinal projections".
2642:
2302:
1666:
69:
A number of theories have been put forward to explain this phenomenon, but none are generally accepted. These include, among others,
714:
2714:
2312:
634:
516:
284:
556:
A remarkable property of the contralateral organization is that it is present in every vertebrate. Even the most distant clades—
2959:
2949:
2873:
2148:
2276:
1081:
Loosemore, Guy (2011). "Translocation of progenitor retinal cells on bifurcation of the optic primordium: a contrarian view".
593:
which buries obliquely with its mouth turned up, or many fish which tend to turn around when feeding from the water surface).
388:
Transformations of the visual field toward the visual map on the primary visual cortex. U=up; D=down; L=left; R=right; F=fovea
3087:
2954:
2734:
2478:
2180:
2069:
2222:
3188:
3152:
2483:
3092:
2594:
458:
phenomenon of the inversions of the forebrain, the axial twist theory also addresses the development and the evolution.
447:
3162:
2756:
1391:
Vulliemoz, S.; Raineteau, O.; Jabaudon, D. (2005). "Reaching beyond the midline: why are human brains cross wired?".
912:
2858:
2032:
1492:
3198:
2652:
2449:
2259:
2027:
1920:
393:
70:
3075:
2939:
2911:
2886:
2843:
2746:
2739:
2679:
2427:
2395:
2368:
2358:
1554:"Opposite asymmetries of face and trunk and of kissing and hugging, as predicted by the axial twist hypothesis"
1218:
Kashalikar, S. J. (1988), "An explanation for the development of decussations in the central nervous system.",
658:
478:
the optic chiasma. Colors refer to early embryo: Red=right side, blue=left side, black=dorsal, white=ventral.
3080:
3010:
2919:
2647:
2529:
2297:
1893:
589:
which turn their mouth downwards after the larva has briefly settled with the mouth turned up, or the adult
215:
3119:
2768:
2709:
2637:
2599:
2500:
2471:
2444:
2439:
2037:
1175:
1132:
187:, and visual primary regions in the forebrain predominantly represent the contralateral side of the body.
152:
399:
The theory has a number of weaknesses. For example, the visual tracts spiral their way from the thalamic
3060:
2934:
2853:
2848:
2833:
2818:
2808:
2724:
2699:
2630:
2534:
2490:
2454:
2422:
2363:
2341:
2322:
2138:
2089:
2084:
2042:
1148:
361:
2185:
360:, is that the contralateral organisation might have an advantage for motor control, but simulations by
345:
The Visual Map Theory and the Axial Twist Theory have been formulated in detail and can be regarded as
3034:
2929:
2863:
2664:
2579:
2495:
2407:
2390:
2317:
2307:
2017:
1925:
1909:
1752:
1695:
455:
307:
303:
172:
156:
1180:
3097:
3055:
3005:
2924:
2772:
2764:
2694:
2674:
2620:
2554:
2464:
2217:
2160:
2022:
2005:
1983:
346:
42:
3158:
367:
Further studies have asked if there is a topological or functional advantage of the decussations.
3070:
3022:
3015:
2612:
2524:
2385:
2346:
2170:
2114:
2104:
2064:
1978:
1973:
1968:
1886:
1864:
1821:
1778:
1721:
1624:
1466:
1416:
1373:
1311:
1201:
1090:
1063:
1037:
983:
965:
844:
801:
606:
483:
417:
321:
82:
1839:
Viggiano, D.; Pirolo, L. (2002). "Testing the model of optic chiasm formation in human beings".
296:
260:), the thalamus does not retrieve a branch from the optic tract but only from the contralateral
3193:
3112:
2838:
2786:
2380:
2281:
2244:
2239:
2195:
2190:
2143:
2109:
1856:
1813:
1770:
1713:
1662:
1585:
1515:
1458:
1408:
1365:
1348:
Llinás, R.R. (2003). "The contribution of
Santiago Ramón y Cajal to functional neuroscience".
1303:
1269:
1235:
1193:
1055:
836:
793:
710:
678:
602:
462:
435:
431:
364:
have shown that both ipsi- and contralateral connections are of major importance for control.
2704:
2271:
2249:
2057:
1848:
1805:
1760:
1703:
1616:
1575:
1565:
1507:
1450:
1400:
1357:
1295:
1261:
1227:
1185:
1047:
975:
893:
828:
785:
670:
219:
132:
1028:
Shinbrot, Troy; Young, Wise (2008). "Why decussate? Topological constraints on 3D wiring".
222:(cranial nerve III) crosses the midline before leaving the central nervous system (i.e. it
3065:
2516:
2505:
2459:
2402:
2351:
2131:
1935:
629:
612:
578:
404:
339:
249:
211:
184:
292:
1756:
1699:
1166:
Shinbrot, T.; Young, W. (2008), "Why decussate? Topological constraints on 3D wiring.",
560:—possess an optic chiasma, and even the skull impressions of early vertebrates from the
384:
334:). A number of other explanations have been published, the most popular of which is the
2905:
2777:
2079:
2074:
2012:
1990:
1580:
1553:
616:
451:
242:
191:
137:
1852:
1708:
1683:
1404:
585:. Turning toward the side or upside-down also occurs frequently in these clades (e.g.
473:
3177:
3107:
2985:
2944:
2790:
2684:
2559:
2544:
2212:
2207:
1231:
703:
Nieuwenhuys, R.; Donkelaar, H.J.; Nicholson, C.; Smeets, W.J.A.J.; Wicht, H. (1998).
574:
566:
180:
160:
29:
1825:
1782:
1628:
1470:
1420:
1377:
1315:
1205:
1094:
1067:
848:
805:
3102:
3050:
2995:
2828:
2823:
2564:
2175:
1868:
1725:
1605:"Why are the great motor and sensory tracts of the central nervous system crossed?"
1128:
987:
570:
527:
turned on its back. As a result, vertebrates have a dorsal nervous system, whereas
524:
443:
357:
261:
257:
203:
195:
144:
109:
55:
19:
1441:
Kinsbourne, M. (2013). "Somatic twist: a model for the evolution of decussation".
338:(explained below). A short review of existing hypotheses is given by reference. A
1299:
704:
3129:
3000:
2781:
2729:
2264:
2094:
2000:
1958:
528:
376:
326:
According to current understanding, the contralateral organization is due to an
199:
168:
114:
63:
1265:
2990:
2891:
2813:
2800:
2689:
2549:
2234:
2121:
2099:
2052:
2047:
1995:
1963:
1001:
674:
561:
265:
164:
59:
979:
682:
392:
The visual map theory was published by the famous neuroscientist and pioneer
3124:
2975:
2719:
2539:
2202:
1950:
586:
557:
276:
238:
202:(i.e., cranial nerve II), which originates from the eyes and inserts on the
140:
127:
33:
1860:
1817:
1589:
1519:
1462:
1412:
1369:
1307:
1273:
1197:
1059:
1774:
1717:
1239:
840:
832:
797:
789:
734:: Localization, morphology and ultrastructure of identified motoneurons".
3027:
2375:
2229:
1109:
609:, and may occur when the cerebrum does not turn during early embryology.
590:
582:
439:
288:
207:
50:
46:
41:: contra‚ against; latus‚ side; lateral‚ sided) is the property that the
1523:
245:
connects to the ipsilateral (same-side) centers of the frontal cerebrum.
2669:
2569:
2417:
2412:
2126:
1878:
1620:
1570:
1511:
1006:
897:
78:
1765:
1740:
1454:
1189:
1111:
Natural smartness in hypothetical animals: Of paddlers and glow balls
1051:
537:
280:
272:
253:
148:
1809:
1604:
1361:
268:
twice, and the forebrain represents the ipsilateral (same-side) eye.
1042:
730:
Muñoz, M.; González, A. (1995). "The trochlear nucleus of the frog
101:
93:
16:
Each side of the forebrain represents the opposite side of the body
2625:
2434:
2333:
970:
472:
375:
119:
92:
38:
523:
According to the dorsoventral inversion hypothesis, an ancestral
2584:
176:
1882:
1493:"Decussation as an axial twist: A comment on Kinsbourne (2013)"
1796:
Toga, A.W.; Thompson, P.M. (2003). "Mapping brain asymmetry".
454:). Whereas the somatic twist hypothesis focuses purely on the
400:
403:
to the visual cortex. (See figure; this path is known as the
657:
Mora, Carla; Velásquez, Carlos; Martino, Juan (2019-09-01).
422:
Two twist hypotheses have been proposed independently: the
123:
353:
directly from optical inversion on the retina of the eye.
1329:
Nervenbahnen (German, 1899, Verlag Joh. A. Barth)].
112:, the contralateral organization is manifested by major
536:
however, how the twist might develop in the vertebrate
241:(i.e., smelling sense) is a noteworthy exception. Each
1661:. New York: Clarendon Press, Oxford University Press.
62:). The contralateral organization is only present in
299:) are situated in the left hemisphere of most humans.
3043:
2968:
2872:
2799:
2755:
2610:
2514:
2331:
2290:
2159:
1949:
1646:. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. p. 5.
1137:. Philadelphia and London: Lippincott. p. 209.
175:connections from the spine, the cerebellum and the
506:Comparing inversion, somatic twist and axial twist
147:). A decussation denotes a crossing of bundles of
698:
696:
694:
692:
1739:Arendt, Detlev; Nübler-Jung, Katharina (1994).
1682:Nübler-Jung, Katharina; Arendt, Detlev (1996).
1547:
1545:
1543:
1486:
1484:
1482:
1480:
1436:
1434:
1432:
1430:
951:
949:
947:
945:
943:
941:
939:
937:
935:
933:
74:
879:
877:
540:, nor does it address the possible evolution.
1894:
1134:Forced movements, tropisms and animal conduct
8:
1153:Vehicles-experiments in synthetic psychology
495:dorsally to the contralateral optic tectum.
230:The contralateral organization is incomplete
1901:
1887:
1879:
1491:de Lussanet, M.H.E.; Osse, J.W.M. (2015).
1117:(PhD thesis). Utrecht: Utrecht University.
179:to the thalamus are crossed. Thus, motor,
1764:
1707:
1579:
1569:
1179:
1041:
969:
706:The central nervous system of vertebrates
520:; and was proposed by Marcel Kinsbourne.
426:by de Marc Lussanet and Jan Osse and the
3135:Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance
383:
342:video explains these theories in brief.
100:
77:, different topological approaches, the
18:
911:Poinsett, Pierrette Mimi (9 Jan 2024).
646:
620:and therefore remained on either side.
1684:"Enteropneusts and chordate evolution"
565:development are well known from other
283:), some functions tend to be strongly
2898:Dialogues Concerning Natural Religion
1609:The Dublin Journal of Medical Science
349:, and are explained in detail below.
7:
652:
650:
356:An old notion, first worked out by
2303:Evolutionary developmental biology
1644:Asymmetrical function of the brain
14:
1741:"Inversion of dorsoventral axis?"
517:dorsoventral inversion hypothesis
3157:
3148:
3147:
1002:"Your head might be on sideways"
635:Lateralization of brain function
434:. Both of them propose that the
331:
2960:Extended evolutionary synthesis
2149:Gene-centered view of evolution
913:"Infant Brain Damage Prognosis"
3088:Hologenome theory of evolution
2955:History of molecular evolution
2181:Evolutionarily stable strategy
2070:Last universal common ancestor
613:Cephalopagus or janiceps twins
1:
2882:Renaissance and Enlightenment
1853:10.1016/S0361-9230(02)00846-8
1709:10.1016/S0960-9822(02)00491-8
1405:10.1016/S1474-4422(05)00990-7
917:www.cerebralpalsyguidance.com
3184:Animal developmental biology
3093:Missing heritability problem
2720:Gamete differentiation/sexes
1552:de Lussanet, M.H.E. (2019).
1300:10.1080/1357650X.2013.824461
1232:10.1016/0306-9877(88)90103-X
1155:. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
1108:Bertin, René J. V. (1994).
597:Developmental malformations
97:Some afferent decussations.
3215:
2725:Life cycles/nuclear phases
2277:Trivers–Willard hypothesis
1603:Dixon, A. Francis (1907).
1266:10.1016/j.mehy.2009.10.037
864:Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA
415:
371:Visual map theory by Cajal
319:
155:. Due to decussations the
3143:
2223:Parent–offspring conflict
2028:Earliest known life forms
1916:
675:10.3171/2019.6.FOCUS19341
264:, so that the optic path
226:rather than chiasmates).
3076:Cultural group selection
2940:The eclipse of Darwinism
2912:On the Origin of Species
2887:Transmutation of species
980:10.1163/157075611X617102
58:may cause a right-sided
3081:Dual inheritance theory
2920:History of paleontology
1642:Kinsbourne, M. (1978).
1331:Rev. Trim. Micrográfica
271:In large brains (e.g.,
216:superior oblique muscle
194:show chiasmas: (1) the
159:of the cerebrum to the
105:Pyramidal decussations.
2769:Punctuated equilibrium
2090:Non-adaptive radiation
2038:Evolutionary arms race
1149:Braitenberg, Valentino
709:. New York: Springer.
479:
409:
394:Santiago Ramón y Cajal
389:
381:
153:central nervous system
106:
98:
24:
3061:Evolutionary medicine
2935:Mendelian inheritance
2643:Biological complexity
2631:Programmed cell death
2323:Phenotypic plasticity
2043:Evolutionary pressure
2033:Evidence of evolution
1931:Timeline of evolution
833:10.1002/cne.901960403
790:10.1002/cne.901960402
476:
387:
379:
374:
362:Valentino Braitenberg
171:are crossed; and the
104:
96:
22:
3189:Evolutionary biology
3035:Teleology in biology
2930:Blending inheritance
2308:Genetic assimilation
2171:Artificial selection
1910:Evolutionary biology
1657:Janvier, P. (1996).
1393:The Lancet Neurology
757:and modifier loci".
514:was inspired by the
287:. For example, the
157:efferent connections
79:somatic twist theory
54:(e.g., a left-sided
32:organization of the
3098:Molecular evolution
3056:Ecological genetics
2925:Transitional fossil
2715:Sexual reproduction
2555:endomembrane system
2484:pollinator-mediated
2440:dolphins and whales
2218:Parental investment
1757:1994Natur.371...26A
1700:1996CBio....6..352N
663:Neurosurgical Focus
347:scientific theories
23:Contralateral brain
3071:Cultural evolution
2186:Fisher's principle
2115:Handicap principle
2105:Parallel evolution
1969:Adaptive radiation
1798:Nat. Rev. Neurosci
1621:10.1007/BF02972358
1571:10.7717/peerj.7096
1512:10.1037/neu0000163
1350:Nat. Rev. Neurosci
1254:Medical Hypotheses
1220:Medical Hypotheses
898:10.1007/BF00234781
607:Yakovlevian torque
545:axial twist theory
484:axial twist theory
480:
469:Axial twist theory
418:Axial twist theory
390:
382:
322:Axial Twist theory
151:fibres inside the
107:
99:
83:axial twist theory
25:
3171:
3170:
2787:Uniformitarianism
2740:Sex-determination
2245:Sexual dimorphism
2240:Natural selection
2144:Unit of selection
2110:Signalling theory
1659:Early vertebrates
1174:(10): 1278–1292,
1168:Anatomical Record
1036:(10): 1278–1292.
603:holoprosencephaly
463:scientific method
432:Marcel Kinsbourne
336:visual map theory
75:visual map theory
3206:
3199:Biology theories
3161:
3151:
3150:
2950:Modern synthesis
2710:Multicellularity
2705:Mosaic evolution
2590:auditory ossicle
2272:Social selection
2255:Flowering plants
2250:Sexual selection
1903:
1896:
1889:
1880:
1873:
1872:
1836:
1830:
1829:
1793:
1787:
1786:
1768:
1766:10.1038/371026a0
1736:
1730:
1729:
1711:
1679:
1673:
1672:
1654:
1648:
1647:
1639:
1633:
1632:
1600:
1594:
1593:
1583:
1573:
1549:
1538:
1537:
1535:
1534:
1528:
1522:. Archived from
1497:
1488:
1475:
1474:
1455:10.1037/a0033662
1438:
1425:
1424:
1388:
1382:
1381:
1345:
1339:
1338:
1325:
1319:
1318:
1283:
1277:
1276:
1249:
1243:
1242:
1215:
1209:
1208:
1190:10.1002/ar.20731
1183:
1163:
1157:
1156:
1145:
1139:
1138:
1125:
1119:
1118:
1116:
1105:
1099:
1098:
1078:
1072:
1071:
1052:10.1002/ar.20731
1045:
1025:
1019:
1018:
1016:
1015:
998:
992:
991:
973:
953:
928:
927:
925:
923:
908:
902:
901:
881:
872:
871:
859:
853:
852:
816:
810:
809:
773:
767:
766:
765:(21): 5756–5766.
750:
744:
743:
727:
721:
720:
700:
687:
686:
654:
220:oculomotor nerve
126:, 'deca,' as an
3214:
3213:
3209:
3208:
3207:
3205:
3204:
3203:
3174:
3173:
3172:
3167:
3139:
3066:Group selection
3039:
2964:
2868:
2795:
2757:Tempo and modes
2751:
2606:
2510:
2327:
2286:
2162:
2155:
2132:Species complex
1945:
1936:History of life
1912:
1907:
1877:
1876:
1841:Brain Res. Bull
1838:
1837:
1833:
1810:10.1038/nrn1009
1795:
1794:
1790:
1738:
1737:
1733:
1688:Current Biology
1681:
1680:
1676:
1669:
1656:
1655:
1651:
1641:
1640:
1636:
1602:
1601:
1597:
1551:
1550:
1541:
1532:
1530:
1526:
1500:Neuropsychology
1495:
1490:
1489:
1478:
1443:Neuropsychology
1440:
1439:
1428:
1390:
1389:
1385:
1362:10.1038/nrn1011
1347:
1346:
1342:
1327:
1326:
1322:
1285:
1284:
1280:
1251:
1250:
1246:
1217:
1216:
1212:
1181:10.1.1.694.3088
1165:
1164:
1160:
1147:
1146:
1142:
1127:
1126:
1122:
1114:
1107:
1106:
1102:
1080:
1079:
1075:
1027:
1026:
1022:
1013:
1011:
1000:
999:
995:
955:
954:
931:
921:
919:
910:
909:
905:
886:Cell Tissue Res
883:
882:
875:
870:(9): 2871–2875.
861:
860:
856:
821:J. Comp. Neurol
818:
817:
813:
778:J. Comp. Neurol
775:
774:
770:
752:
751:
747:
736:Brain Res. Bull
729:
728:
724:
717:
702:
701:
690:
656:
655:
648:
643:
630:Brain asymmetry
626:
617:conjoined twins
599:
579:Cephalochordata
554:
508:
471:
420:
414:
405:optic radiation
373:
340:popular-science
324:
318:
297:Wernicke's area
291:regions (i.e.,
250:chondrichthyans
232:
212:trochlear nerve
91:
17:
12:
11:
5:
3212:
3210:
3202:
3201:
3196:
3191:
3186:
3176:
3175:
3169:
3168:
3166:
3165:
3155:
3144:
3141:
3140:
3138:
3137:
3132:
3127:
3122:
3117:
3116:
3115:
3105:
3100:
3095:
3090:
3085:
3084:
3083:
3078:
3073:
3063:
3058:
3053:
3047:
3045:
3041:
3040:
3038:
3037:
3032:
3031:
3030:
3025:
3020:
3019:
3018:
3008:
3003:
2998:
2993:
2988:
2978:
2972:
2970:
2966:
2965:
2963:
2962:
2957:
2952:
2947:
2942:
2937:
2932:
2927:
2922:
2917:
2916:
2915:
2906:Charles Darwin
2903:
2902:
2901:
2889:
2884:
2878:
2876:
2870:
2869:
2867:
2866:
2861:
2856:
2851:
2846:
2844:Non-ecological
2841:
2836:
2831:
2826:
2821:
2816:
2811:
2805:
2803:
2797:
2796:
2794:
2793:
2784:
2775:
2761:
2759:
2753:
2752:
2750:
2749:
2744:
2743:
2742:
2737:
2732:
2727:
2722:
2712:
2707:
2702:
2697:
2692:
2687:
2682:
2677:
2672:
2667:
2662:
2661:
2660:
2650:
2645:
2640:
2635:
2634:
2633:
2628:
2617:
2615:
2608:
2607:
2605:
2604:
2603:
2602:
2597:
2595:nervous system
2592:
2587:
2582:
2574:
2573:
2572:
2567:
2562:
2557:
2552:
2547:
2537:
2532:
2527:
2521:
2519:
2512:
2511:
2509:
2508:
2503:
2498:
2493:
2488:
2487:
2486:
2476:
2475:
2474:
2469:
2468:
2467:
2462:
2452:
2447:
2442:
2437:
2432:
2431:
2430:
2425:
2415:
2405:
2400:
2399:
2398:
2388:
2383:
2378:
2373:
2372:
2371:
2361:
2356:
2355:
2354:
2344:
2338:
2336:
2329:
2328:
2326:
2325:
2320:
2315:
2310:
2305:
2300:
2294:
2292:
2288:
2287:
2285:
2284:
2279:
2274:
2269:
2268:
2267:
2262:
2257:
2247:
2242:
2237:
2232:
2227:
2226:
2225:
2220:
2210:
2205:
2200:
2199:
2198:
2188:
2183:
2178:
2173:
2167:
2165:
2157:
2156:
2154:
2153:
2152:
2151:
2141:
2136:
2135:
2134:
2129:
2119:
2118:
2117:
2107:
2102:
2097:
2095:Origin of life
2092:
2087:
2082:
2080:Microevolution
2077:
2075:Macroevolution
2072:
2067:
2062:
2061:
2060:
2050:
2045:
2040:
2035:
2030:
2025:
2020:
2015:
2013:Common descent
2010:
2009:
2008:
1998:
1993:
1991:Baldwin effect
1988:
1987:
1986:
1981:
1971:
1966:
1961:
1955:
1953:
1947:
1946:
1944:
1943:
1938:
1933:
1928:
1923:
1917:
1914:
1913:
1908:
1906:
1905:
1898:
1891:
1883:
1875:
1874:
1847:(2): 111–115.
1831:
1788:
1731:
1694:(4): 352–353.
1674:
1668:978-0198540472
1667:
1649:
1634:
1595:
1539:
1506:(5): 713–714.
1476:
1449:(5): 511–515.
1426:
1383:
1340:
1333:(in Spanish).
1320:
1294:(3): 325–339,
1278:
1260:(4): 741–745,
1244:
1210:
1158:
1140:
1120:
1100:
1073:
1020:
993:
964:(2): 193–216.
958:Animal Biology
929:
903:
892:(2): 179–212.
873:
854:
827:(4): 539–548.
811:
784:(4): 531–538.
768:
745:
732:Rana ridibunda
722:
715:
688:
645:
644:
642:
639:
638:
637:
632:
625:
622:
598:
595:
553:
550:
510:The idea of a
507:
504:
470:
467:
416:Main article:
413:
410:
372:
369:
320:Main article:
317:
314:
313:
312:
300:
269:
246:
243:olfactory lobe
231:
228:
210:; and (2) the
192:cranial nerves
118:(based on the
90:
87:
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
3211:
3200:
3197:
3195:
3192:
3190:
3187:
3185:
3182:
3181:
3179:
3164:
3160:
3156:
3154:
3146:
3145:
3142:
3136:
3133:
3131:
3128:
3126:
3123:
3121:
3118:
3114:
3111:
3110:
3109:
3108:Phylogenetics
3106:
3104:
3101:
3099:
3096:
3094:
3091:
3089:
3086:
3082:
3079:
3077:
3074:
3072:
3069:
3068:
3067:
3064:
3062:
3059:
3057:
3054:
3052:
3049:
3048:
3046:
3042:
3036:
3033:
3029:
3026:
3024:
3021:
3017:
3014:
3013:
3012:
3011:Structuralism
3009:
3007:
3004:
3002:
2999:
2997:
2994:
2992:
2989:
2987:
2986:Catastrophism
2984:
2983:
2982:
2979:
2977:
2974:
2973:
2971:
2967:
2961:
2958:
2956:
2953:
2951:
2948:
2946:
2945:Neo-Darwinism
2943:
2941:
2938:
2936:
2933:
2931:
2928:
2926:
2923:
2921:
2918:
2914:
2913:
2909:
2908:
2907:
2904:
2900:
2899:
2895:
2894:
2893:
2890:
2888:
2885:
2883:
2880:
2879:
2877:
2875:
2871:
2865:
2862:
2860:
2859:Reinforcement
2857:
2855:
2852:
2850:
2847:
2845:
2842:
2840:
2837:
2835:
2832:
2830:
2827:
2825:
2822:
2820:
2817:
2815:
2812:
2810:
2807:
2806:
2804:
2802:
2798:
2792:
2791:Catastrophism
2788:
2785:
2783:
2782:Macromutation
2779:
2778:Micromutation
2776:
2774:
2770:
2766:
2763:
2762:
2760:
2758:
2754:
2748:
2745:
2741:
2738:
2736:
2733:
2731:
2728:
2726:
2723:
2721:
2718:
2717:
2716:
2713:
2711:
2708:
2706:
2703:
2701:
2698:
2696:
2693:
2691:
2688:
2686:
2685:Immune system
2683:
2681:
2678:
2676:
2673:
2671:
2668:
2666:
2663:
2659:
2656:
2655:
2654:
2651:
2649:
2646:
2644:
2641:
2639:
2636:
2632:
2629:
2627:
2624:
2623:
2622:
2619:
2618:
2616:
2614:
2609:
2601:
2598:
2596:
2593:
2591:
2588:
2586:
2583:
2581:
2578:
2577:
2575:
2571:
2568:
2566:
2563:
2561:
2558:
2556:
2553:
2551:
2548:
2546:
2545:symbiogenesis
2543:
2542:
2541:
2538:
2536:
2533:
2531:
2528:
2526:
2523:
2522:
2520:
2518:
2513:
2507:
2504:
2502:
2499:
2497:
2494:
2492:
2489:
2485:
2482:
2481:
2480:
2477:
2473:
2470:
2466:
2463:
2461:
2458:
2457:
2456:
2453:
2451:
2448:
2446:
2443:
2441:
2438:
2436:
2433:
2429:
2426:
2424:
2421:
2420:
2419:
2416:
2414:
2411:
2410:
2409:
2406:
2404:
2401:
2397:
2394:
2393:
2392:
2389:
2387:
2384:
2382:
2379:
2377:
2374:
2370:
2367:
2366:
2365:
2362:
2360:
2357:
2353:
2350:
2349:
2348:
2345:
2343:
2340:
2339:
2337:
2335:
2330:
2324:
2321:
2319:
2316:
2314:
2311:
2309:
2306:
2304:
2301:
2299:
2296:
2295:
2293:
2289:
2283:
2280:
2278:
2275:
2273:
2270:
2266:
2263:
2261:
2258:
2256:
2253:
2252:
2251:
2248:
2246:
2243:
2241:
2238:
2236:
2233:
2231:
2228:
2224:
2221:
2219:
2216:
2215:
2214:
2213:Kin selection
2211:
2209:
2208:Genetic drift
2206:
2204:
2201:
2197:
2194:
2193:
2192:
2189:
2187:
2184:
2182:
2179:
2177:
2174:
2172:
2169:
2168:
2166:
2164:
2158:
2150:
2147:
2146:
2145:
2142:
2140:
2137:
2133:
2130:
2128:
2125:
2124:
2123:
2120:
2116:
2113:
2112:
2111:
2108:
2106:
2103:
2101:
2098:
2096:
2093:
2091:
2088:
2086:
2083:
2081:
2078:
2076:
2073:
2071:
2068:
2066:
2063:
2059:
2056:
2055:
2054:
2051:
2049:
2046:
2044:
2041:
2039:
2036:
2034:
2031:
2029:
2026:
2024:
2021:
2019:
2016:
2014:
2011:
2007:
2004:
2003:
2002:
1999:
1997:
1994:
1992:
1989:
1985:
1982:
1980:
1977:
1976:
1975:
1972:
1970:
1967:
1965:
1962:
1960:
1957:
1956:
1954:
1952:
1948:
1942:
1939:
1937:
1934:
1932:
1929:
1927:
1924:
1922:
1919:
1918:
1915:
1911:
1904:
1899:
1897:
1892:
1890:
1885:
1884:
1881:
1870:
1866:
1862:
1858:
1854:
1850:
1846:
1842:
1835:
1832:
1827:
1823:
1819:
1815:
1811:
1807:
1803:
1799:
1792:
1789:
1784:
1780:
1776:
1772:
1767:
1762:
1758:
1754:
1750:
1746:
1742:
1735:
1732:
1727:
1723:
1719:
1715:
1710:
1705:
1701:
1697:
1693:
1689:
1685:
1678:
1675:
1670:
1664:
1660:
1653:
1650:
1645:
1638:
1635:
1630:
1626:
1622:
1618:
1614:
1610:
1606:
1599:
1596:
1591:
1587:
1582:
1577:
1572:
1567:
1563:
1559:
1555:
1548:
1546:
1544:
1540:
1529:on 2021-07-14
1525:
1521:
1517:
1513:
1509:
1505:
1501:
1494:
1487:
1485:
1483:
1481:
1477:
1472:
1468:
1464:
1460:
1456:
1452:
1448:
1444:
1437:
1435:
1433:
1431:
1427:
1422:
1418:
1414:
1410:
1406:
1402:
1398:
1394:
1387:
1384:
1379:
1375:
1371:
1367:
1363:
1359:
1355:
1351:
1344:
1341:
1336:
1332:
1324:
1321:
1317:
1313:
1309:
1305:
1301:
1297:
1293:
1289:
1282:
1279:
1275:
1271:
1267:
1263:
1259:
1255:
1248:
1245:
1241:
1237:
1233:
1229:
1225:
1221:
1214:
1211:
1207:
1203:
1199:
1195:
1191:
1187:
1182:
1177:
1173:
1169:
1162:
1159:
1154:
1150:
1144:
1141:
1136:
1135:
1130:
1129:Loeb, Jacques
1124:
1121:
1113:
1112:
1104:
1101:
1096:
1092:
1088:
1084:
1083:Hyp. Life Sci
1077:
1074:
1069:
1065:
1061:
1057:
1053:
1049:
1044:
1039:
1035:
1031:
1024:
1021:
1009:
1008:
1003:
997:
994:
989:
985:
981:
977:
972:
967:
963:
959:
952:
950:
948:
946:
944:
942:
940:
938:
936:
934:
930:
918:
914:
907:
904:
899:
895:
891:
887:
880:
878:
874:
869:
865:
858:
855:
850:
846:
842:
838:
834:
830:
826:
822:
815:
812:
807:
803:
799:
795:
791:
787:
783:
779:
772:
769:
764:
760:
756:
749:
746:
742:(5): 433–441.
741:
737:
733:
726:
723:
718:
716:9783642621277
712:
708:
707:
699:
697:
695:
693:
689:
684:
680:
676:
672:
668:
664:
660:
653:
651:
647:
640:
636:
633:
631:
628:
627:
623:
621:
618:
614:
610:
608:
604:
596:
594:
592:
588:
584:
580:
576:
575:Echinodermata
572:
568:
567:deuterostomes
563:
559:
551:
549:
546:
541:
539:
533:
530:
526:
521:
519:
518:
513:
512:somatic twist
505:
503:
500:
496:
492:
488:
485:
475:
468:
466:
464:
459:
457:
456:morphological
453:
449:
445:
441:
437:
433:
429:
428:somatic twist
425:
419:
411:
408:
406:
402:
397:
395:
386:
378:
370:
368:
365:
363:
359:
354:
350:
348:
343:
341:
337:
333:
329:
323:
315:
309:
305:
301:
298:
294:
290:
286:
282:
278:
274:
270:
267:
263:
259:
255:
251:
247:
244:
240:
237:
236:
235:
229:
227:
225:
221:
217:
213:
209:
205:
201:
197:
193:
188:
186:
182:
181:somatosensory
178:
174:
170:
166:
162:
161:basal ganglia
158:
154:
150:
146:
142:
139:
135:
134:
129:
125:
122:notation for
121:
117:
116:
111:
103:
95:
88:
86:
84:
80:
76:
72:
67:
65:
61:
57:
52:
48:
44:
40:
36:
35:
31:
30:contralateral
21:
3120:Polymorphism
3103:Astrobiology
3051:Biogeography
3006:Saltationism
2996:Orthogenesis
2981:Alternatives
2910:
2896:
2829:Cospeciation
2824:Cladogenesis
2773:Saltationism
2730:Mating types
2653:Color vision
2638:Avian flight
2560:mitochondria
2298:Canalisation
2176:Biodiversity
1921:Introduction
1844:
1840:
1834:
1804:(1): 37–48.
1801:
1797:
1791:
1751:(6492): 26.
1748:
1744:
1734:
1691:
1687:
1677:
1658:
1652:
1643:
1637:
1612:
1608:
1598:
1561:
1557:
1531:. Retrieved
1524:the original
1503:
1499:
1446:
1442:
1399:(2): 87–99.
1396:
1392:
1386:
1356:(1): 77–80.
1353:
1349:
1343:
1334:
1330:
1323:
1291:
1287:
1281:
1257:
1253:
1247:
1223:
1219:
1213:
1171:
1167:
1161:
1152:
1143:
1133:
1123:
1110:
1103:
1086:
1082:
1076:
1033:
1029:
1023:
1012:. Retrieved
1005:
996:
961:
957:
920:. Retrieved
916:
906:
889:
885:
867:
863:
857:
824:
820:
814:
781:
777:
771:
762:
758:
754:
748:
739:
735:
731:
725:
705:
666:
662:
611:
600:
571:Hemichordata
555:
544:
542:
534:
525:deuterostome
522:
515:
511:
509:
501:
497:
493:
489:
481:
460:
427:
423:
421:
398:
391:
366:
358:Jacques Loeb
355:
351:
344:
335:
327:
325:
262:optic tectum
233:
223:
204:optic tectum
189:
143:letter 'Χ,'
131:
115:decussations
113:
110:Anatomically
108:
68:
56:brain lesion
28:
26:
3130:Systematics
3001:Mutationism
2819:Catagenesis
2747:Snake venom
2680:Eusociality
2658:in primates
2648:Cooperation
2576:In animals
2396:butterflies
2369:Cephalopods
2359:Brachiopods
2291:Development
2265:Mate choice
2018:Convergence
2001:Coevolution
1959:Abiogenesis
759:J. Neurosci
529:protostomes
424:axial twist
412:Axial twist
330:(explained
328:axial twist
285:lateralized
200:optic tract
190:Two of the
136:(after the
64:vertebrates
43:hemispheres
3178:Categories
2991:Lamarckism
2969:Philosophy
2892:David Hume
2854:Peripatric
2849:Parapatric
2834:Ecological
2814:Anagenesis
2809:Allopatric
2801:Speciation
2765:Gradualism
2690:Metabolism
2550:chromosome
2540:Eukaryotes
2318:Modularity
2235:Population
2161:Population
2122:Speciation
2100:Panspermia
2053:Extinction
2048:Exaptation
2023:Divergence
1996:Cladistics
1984:Reciprocal
1964:Adaptation
1615:(1): 1–4.
1533:2017-08-28
1288:Laterality
1226:(1): 1–8,
1043:2405.07837
1014:2020-02-09
669:(3): E10.
641:References
562:Ordovician
266:decussates
224:decussates
165:cerebellum
60:hemiplegia
3125:Protocell
2976:Darwinism
2864:Sympatric
2613:processes
2501:Tetrapods
2450:Kangaroos
2376:Dinosaurs
2313:Inversion
2282:Variation
2203:Gene flow
2196:Inclusive
2006:Mutualism
1951:Evolution
1564:: e7096.
1176:CiteSeerX
1089:: 46–51.
1030:Anat. Rec
971:1003.1872
683:1092-0684
587:sea stars
569:—such as
558:agnathans
552:Evolution
452:occipital
448:posterior
277:elephants
239:Olfaction
141:uppercase
130:'X') and
128:uppercase
34:forebrain
3194:Cerebrum
3153:Category
3028:Vitalism
3023:Theistic
3016:Spandrel
2700:Morality
2695:Monogamy
2570:plastids
2535:Flagella
2491:Reptiles
2472:sea cows
2455:primates
2364:Molluscs
2342:Bacteria
2230:Mutation
2163:genetics
2139:Taxonomy
2085:Mismatch
2065:Homology
1979:Cheating
1974:Altruism
1861:12379441
1826:15867592
1818:12511860
1783:33780610
1629:76086581
1590:31211022
1520:25528610
1471:11646580
1463:24040928
1421:16367031
1413:15664541
1378:30442863
1370:12511864
1337:: 15–65.
1316:30077243
1308:23931149
1274:19926228
1206:13477741
1198:18780298
1151:(1984).
1131:(1918).
1095:54685340
1068:13477741
1060:18780298
849:13333558
806:36572723
624:See also
591:lancelet
583:Tunicata
450:(back /
440:anterior
316:Theories
308:efferent
304:afferent
289:language
208:midbrain
185:auditory
173:afferent
167:and the
133:chiasmas
81:and the
51:thalamus
49:and the
47:cerebrum
3044:Related
2874:History
2735:Meiosis
2670:Empathy
2665:Emotion
2565:nucleus
2506:Viruses
2496:Spiders
2408:Mammals
2391:Insects
2191:Fitness
2127:Species
1926:Outline
1869:2687785
1775:8072524
1753:Bibcode
1726:8964529
1718:8723329
1696:Bibcode
1581:6557252
1240:3398785
1007:YouTube
988:7399128
841:7204670
798:7204669
444:frontal
436:rostral
293:Broca's
252:(e.g.,
218:). The
206:of the
198:of the
196:chiasma
89:Anatomy
45:of the
3163:Portal
2839:Hybrid
2675:Ethics
2517:organs
2479:Plants
2465:lemurs
2460:humans
2445:horses
2435:hyenas
2423:wolves
2418:canids
2352:origin
1867:
1859:
1824:
1816:
1781:
1773:
1745:Nature
1724:
1716:
1665:
1627:
1588:
1578:
1518:
1469:
1461:
1419:
1411:
1376:
1368:
1314:
1306:
1272:
1238:
1204:
1196:
1178:
1093:
1066:
1058:
1010:. 2020
986:
847:
839:
804:
796:
713:
681:
538:embryo
446:) and
281:whales
273:humans
258:skates
254:sharks
163:, the
149:axonal
2626:Death
2621:Aging
2600:brain
2386:Fungi
2347:Birds
2260:Fungi
2058:Event
1941:Index
1865:S2CID
1822:S2CID
1779:S2CID
1722:S2CID
1625:S2CID
1558:PeerJ
1527:(PDF)
1496:(PDF)
1467:S2CID
1417:S2CID
1374:S2CID
1312:S2CID
1202:S2CID
1115:(PDF)
1091:S2CID
1064:S2CID
1038:arXiv
984:S2CID
966:arXiv
922:6 Aug
845:S2CID
802:S2CID
755:Unc5c
332:below
311:time.
302:Most
169:spine
138:Greek
120:Latin
71:Cajal
39:Latin
3113:Tree
2585:hair
2525:Cell
2428:dogs
2413:cats
2403:Life
2381:Fish
2334:taxa
1857:PMID
1814:PMID
1771:PMID
1714:PMID
1663:ISBN
1586:PMID
1516:PMID
1459:PMID
1409:PMID
1366:PMID
1304:PMID
1270:PMID
1236:PMID
1194:PMID
1056:PMID
924:2024
837:PMID
794:PMID
711:ISBN
679:ISSN
615:are
581:and
543:The
482:The
461:The
306:and
295:and
279:and
256:and
177:pons
27:The
2611:Of
2580:eye
2530:DNA
2515:Of
2332:Of
1849:doi
1806:doi
1761:doi
1749:371
1704:doi
1617:doi
1613:124
1576:PMC
1566:doi
1508:doi
1451:doi
1401:doi
1358:doi
1296:doi
1262:doi
1228:doi
1186:doi
1172:291
1087:1–2
1048:doi
1034:291
976:doi
894:doi
890:213
868:112
829:doi
786:doi
671:doi
601:In
430:by
401:LGN
248:In
145:chi
124:ten
73:'s
3180::
1863:.
1855:.
1845:59
1843:.
1820:.
1812:.
1800:.
1777:.
1769:.
1759:.
1747:.
1743:.
1720:.
1712:.
1702:.
1690:.
1686:.
1623:.
1611:.
1607:.
1584:.
1574:.
1560:.
1556:.
1542:^
1514:.
1504:29
1502:.
1498:.
1479:^
1465:.
1457:.
1447:27
1445:.
1429:^
1415:.
1407:.
1395:.
1372:.
1364:.
1352:.
1310:,
1302:,
1292:19
1290:,
1268:,
1258:74
1256:,
1234:,
1224:26
1222:,
1200:,
1192:,
1184:,
1170:,
1085:.
1062:.
1054:.
1046:.
1032:.
1004:.
982:.
974:.
962:62
960:.
932:^
915:.
888:.
876:^
866:.
843:.
835:.
825:96
823:.
800:.
792:.
782:96
780:.
763:26
761:.
740:36
738:.
691:^
677:.
667:47
665:.
661:.
649:^
577:,
573:,
275:,
183:,
85:.
66:.
2789:/
2780:/
2771:/
2767:/
1902:e
1895:t
1888:v
1871:.
1851::
1828:.
1808::
1802:4
1785:.
1763::
1755::
1728:.
1706::
1698::
1692:6
1671:.
1631:.
1619::
1592:.
1568::
1562:7
1536:.
1510::
1473:.
1453::
1423:.
1403::
1397:4
1380:.
1360::
1354:4
1335:3
1298::
1264::
1230::
1188::
1097:.
1070:.
1050::
1040::
1017:.
990:.
978::
968::
926:.
900:.
896::
851:.
831::
808:.
788::
719:.
685:.
673::
442:(
37:(
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.