1924:
2343:
1261:
2331:
2355:
604:
1755:
73:
53:
1148:
1406:
1474:
650:
1095:
612:
1137:. The anterior cerebral artery supplies the anterior portions of the brain, including most of the frontal lobe. The middle cerebral artery supplies the parietal lobes, temporal lobes, and parts of the occipital lobes. The middle cerebral artery splits into two branches to supply the left and right hemisphere, where they branch further. The posterior cerebral artery supplies the occipital lobes.
2013:
1632:, for example, which serves critical functions such as regulation of heart and respiration rates, many areas of the cerebral cortex are not strictly necessary for survival. Thus, the evolution of the cerebral cortex has seen the advent and modification of new functional areas—particularly association areas that do not directly receive input from outside the cortex.
411:
1672:
673:
1449:. These cells will form the deep layers of the mature cortex, layers five and six. Later born neurons migrate radially into the cortical plate past the deep layer neurons, and become the upper layers (two to four). Thus, the layers of the cortex are created in an inside-out order. The only exception to this inside-out sequence of
2315:. Mushroom bodies are structures in the brains of many types of worms and arthropods that are known to play important roles in learning and memory; the genetic evidence indicates a common evolutionary origin, and therefore indicates that the origins of the earliest precursors of the cerebral cortex date back to the
574:(MRI) makes it possible to get a measure for the thickness of the human cerebral cortex and relate it to other measures. The thickness of different cortical areas varies but in general, sensory cortex is thinner than motor cortex. One study has found some positive association between the cortical thickness and
1883:(or nuclei). The basal ganglia receive input from the substantia nigra of the midbrain and motor areas of the cerebral cortex, and send signals back to both of these locations. They are involved in motor control. They are found lateral to the thalamus. The main components of the basal ganglia are the
586:
patients, though it is not known if this is the result of migraine attacks, the cause of them or if both are the result of a shared cause. A later study using a larger patient population reports no change in the cortical thickness in patients with migraine. A genetic disorder of the cerebral cortex,
2020:
over the brain cortex. Pictures are dynamically subtracted to a reference picture 40 s before. First we see the initial area of change at the exact moment where the middle cerebral artery group (left) is occluded. The area is highlighted with a white line. Later we appreciate the signal produced by
970:
showed that the functional properties of the cortex change abruptly between laterally adjacent points; however, they are continuous in the direction perpendicular to the surface. Later works have provided evidence of the presence of functionally distinct cortical columns in the visual cortex (Hubel
924:
to the thalamus, establishing a very precise reciprocal interconnection between the cortex and the thalamus. That is, layer VI neurons from one cortical column connect with thalamus neurons that provide input to the same cortical column. These connections are both excitatory and inhibitory. Neurons
3568:
Bhagwandin, Adhil; Molnár, Zoltán; Bertelsen, Mads F.; Karlsson, Karl Æ.; Alagaili, Abdulaziz N.; Bennett, Nigel C.; Hof, Patrick R.; Kaswera‐Kyamakya, Consolate; Gilissen, Emmanuel; Jayakumar, Jaikishan; Manger, Paul R. (2024). "Where Do Core
Thalamocortical Axons Terminate in Mammalian Neocortex
1951:
or prefrontal association complex is involved in planning actions and movement, as well as abstract thought. Globally, the association areas are organized as distributed networks. Each network connects areas distributed across widely spaced regions of the cortex. Distinct networks are positioned
1829:
The motor areas are located in both hemispheres of the cortex. The motor areas are very closely related to the control of voluntary movements, especially fine fragmented movements performed by the hand. The right half of the motor area controls the left side of the body, and vice versa.
5670:
Smigiel, R; Cabala, M; Jakubiak, A; Kodera, H; Sasiadek, MJ; Matsumoto, N; Sasiadek, MM; Saitsu, H (April 2016). "Novel COL4A1 mutation in an infant with severe dysmorphic syndrome with schizencephaly, periventricular calcifications, and cataract resembling congenital infection".
5413:
Kentar, Modar; Mann, Martina; Sahm, Felix; Olivares-Rivera, Arturo; Sanchez-Porras, Renan; Zerelles, Roland; Sakowitz, Oliver W.; Unterberg, Andreas W.; Santos, Edgar (15 January 2020). "Detection of spreading depolarizations in a middle cerebral artery occlusion model in swine".
1586:
shift in the cortical region occurs. This ultimately causes an expansion of the rostral regions. Therefore, Fgf8 and other FGFs play a role in the regulation of expression of Emx2 and Pax6 and represent how the cerebral cortex can become specialized for different functions.
859:
from thalamus type C neurons (core-type) as well as intra-hemispheric corticocortical afferents. The layers above layer IV are also referred to as supragranular layers (layers I-III), whereas the layers below are referred to as infragranular layers (layers V and VI).
787:
interactions in the cerebral cortex involved in associative learning and attention. While it was once thought that the input to layer I came from the cortex itself, it is now realized that layer I across the cerebral cortex mantle receives substantial input from
1712:
and Schüz (1998) claim that in primary sensory areas, at the cortical level where the input fibers terminate, up to 20% of the synapses are supplied by extracortical afferents but that in other areas and other layers the percentage is likely to be much lower.
699:. Each cortical layer has a characteristic distribution of different neurons and their connections with other cortical and subcortical regions. There are direct connections between different cortical areas and indirect connections via the thalamus.
2260:. The basic form of the pallium is a cylindrical layer enclosing fluid-filled ventricles. Around the circumference of the cylinder are four zones, the dorsal pallium, medial pallium, ventral pallium, and lateral pallium, which are thought to be
1293:
in order to give a fine distinction between the different cortical layers. Laminar differentiation is not fully complete until after birth since during development laminar neurons are still sensitive to extrinsic signals and environmental cues.
1477:
Depicted in blue, Emx2 is highly expressed at the caudomedial pole and dissipates outward. Pax6 expression is represented in purple and is highly expressed at the rostral lateral pole. (Adapted from Sanes, D., Reh, T., & Harris, W. (2012).
2796:
Functional columns were first defined in the cortex by
Mountcastle (1957), who proposed the columnar hypothesis, which states that the cortex is composed of discrete, modular columns of neurons, characterized by a consistent connectivity
957:
The cortical layers are not simply stacked one over the other; there exist characteristic connections between different layers and neuronal types, which span all the thickness of the cortex. These cortical microcircuits are grouped into
1952:
adjacent to one another yielding a complex series of interwoven networks. The specific organization of the association networks is debated with evidence for interactions, hierarchical relationships, and competition between networks.
1821:, where the size of different body parts reflects the relative density of their innervation. Areas with much sensory innervation, such as the fingertips and the lips, require more cortical area to process finer sensation.
1284:
of superficial layers. This differential cell fate creates an inside-out topography in the cortex with younger neurons in superficial layers and older neurons in deeper layers. In addition, laminar neurons are stopped in
1325:
are excitatory during development. This excitation is primarily driven by the flux of chloride ions through the GABA receptor, however in adults chloride concentrations shift causing an inward flux of chloride that
1352:
present on the cortical neuron's cell body, and the axon is undeveloped. During the first year of life the dendrites become dramatically increased in number, such that they can accommodate up to a hundred thousand
982:. Cortical areas that have only a rudimentary layer IV are called dysgranular. Information processing within each layer is determined by different temporal dynamics with that in layers II/III having a slow 2
487:
cortex has a total surface area of about 0.12 square metres (1.3 sq ft). The folding is inward away from the surface of the brain, and is also present on the medial surface of each hemisphere within the
2354:
1537:
in Pax6 can cause expression levels of Emx2 to expand out of its normal expression domain, which would ultimately lead to an expansion of the areas normally derived from the caudal medial cortex, such as the
3310:
Meyer, Gundela; Goffinet, André M.; Fairén, Alfonso (1999). "Feature
Article: What is a Cajal–Retzius cell? A Reassessment of a Classical Cell Type Based on Recent Observations in the Developing Neocortex".
1276:. Similarly, the process of neurogenesis regulates lamination to form the different layers of the cortex. During this process there is an increase in the restriction of cell fate that begins with earlier
736:
cross-sections of the cortex to reveal the position of neuronal cell bodies and the intracortical axon tracts allowed neuroanatomists in the early 20th century to produce a detailed description of the
1060:, where layers 2, 3 and 4 are merged. This area incorporates the proisocortex of the neocortex and the periallocortex of the allocortex. In addition, the cerebral cortex may be classified into four
6015:
826:, contains predominantly small and medium-size pyramidal neurons, as well as non-pyramidal neurons with vertically oriented intracortical axons; layers I through III are the main target of
4901:
Stahl, Ronny; Walcher, Tessa; De Juan Romero, Camino; Pilz, Gregor
Alexander; Cappello, Silvia; Irmler, Martin; Sanz-Aquela, José Miguel; Beckers, Johannes; Blum, Robert (25 April 2013).
2127:
directly onto the exposed brain in order to localise the functions of specific areas of the cortex. It is used in clinical and therapeutic applications including pre-surgical mapping.
1013:
The neocortex is also known as the isocortex or neopallium and is the part of the mature cerebral cortex with six distinct layers. Examples of neocortical areas include the granular
1628:
Of all the different brain regions, the cerebral cortex shows the largest evolutionary variation and has evolved most recently. In contrast to the highly conserved circuitry of the
1497:
early in embryonic development. These signals regulate the size, shape, and position of cortical areas on the surface of the cortical primordium, in part by regulating gradients of
2342:
1389:
is elongated, in what is seen as selective cell-cycle lengthening, the newly born neurons migrate to more superficial layers of the cortex. The migrating daughter cells become the
1923:
566:, have a neocortical thickness of about 0.5 mm; the ones with the largest brains, such as humans and fin whales, have thicknesses of 2–4 mm. There is an approximately
492:. Most mammals have a cerebral cortex that is convoluted with the peaks known as gyri and the troughs or grooves known as sulci. Some small mammals including some small
1782:. For example, the right primary somatosensory cortex receives information from the left limbs, and the right visual cortex receives information from the left visual
5565:"Preoperative multimodal motor mapping: a comparison of magnetoencephalography imaging, navigated transcranial magnetic stimulation, and direct cortical stimulation"
2330:
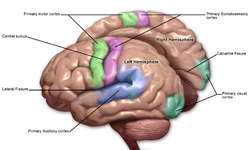
343:, the majority of the cerebral cortex is not visible from the outside, but buried in the sulci. The major sulci and gyri mark the divisions of the cerebrum into the
1978:, for language reception. However, the processes of language expression and reception have been shown to occur in areas other than just those structures around the
5741:
308:. In most mammals, apart from small mammals that have small brains, the cerebral cortex is folded, providing a greater surface area in the confined volume of the
3083:
Katherine L. Narr; Roger P. Woods; Paul M. Thompson; Philip
Szeszko; Dilbert Robinson; Teodora Dimtcheva; Mala Gurbani; Arthur W. Toga; Robert M. Bilder (2007).
2089:
1554:
next to the cortex could contribute to the regional expression of these transcription factors. Two very well studied patterning signals for the cortex include
189:
1647:
level. The protomap hypothesis states that the cellular and molecular identity and characteristics of neurons in each cortical area are specified by cortical
4415:
Kostović, Ivica (1990). "Developmental history of the transient subplate zone in the visual and somatosensory cortex of the macaque monkey and human brain".
1643:
hypothesis, first proposed by Rakic. This theory states that new cortical areas are formed by the addition of new radial units, which is accomplished at the
3292:
2016:
Hemodynamic changes observed on gyrencephalic brain cortex after an arterial vessel occlusion in IOS. The video has a speed of 50x to better appreciate the
1268:
The cerebral cortex is composed of a heterogenous population of cells that give rise to different cell types. The majority of these cells are derived from
5315:
Yeo BT, Krienen FM, Sepulcre J, Sabuncu MR, Lashkari D, Hollinshead M, Roffman JL, Smoller JW, Zöllei L, Polimeni JR, Fischl B, Liu H, Buckner RL (2011).
562:
For species of mammals, larger brains (in absolute terms, not just in relation to body size) tend to have thicker cortices. The smallest mammals, such as
5259:
Braitenberg, V and Schüz, A 1998. "Cortex: Statistics and
Geometry of Neuronal Connectivity. Second thoroughly revised edition" New York: Springer-Verlag
2291:'s neuroarchitecture to be reminiscent of the mammalian cerebral cortex. The avian pallium has also been suggested to be an equivalent neural basis for
1955:
In humans, association networks are particularly important to language function. In the past it was theorized that language abilities are localized in
7375:
7370:
6170:
6042:
1369:. Then, some progenitor cells begin to divide asymmetrically, producing one postmitotic cell that migrates along the radial glial fibers, leaving the
946:
806:
6161:
1171:
571:
4204:
Rakic, P (November 1972). "Extrinsic cytological determinants of basket and stellate cell dendritic pattern in the cerebellar molecular layer".
1333:. The glial fibers produced in the first divisions of the progenitor cells are radially oriented, spanning the thickness of the cortex from the
7295:
6147:
2012:
542:
is a rim of cortex on the medial side of each hemisphere and is also often included. There are also three lobules of the brain described: the
4139:
3018:
2957:
2517:
1394:
1297:
Although the majority of the cells that compose the cortex are derived locally from radial glia there is a subset population of neurons that
161:
157:
1931:
The association areas are the parts of the cerebral cortex that do not belong to the primary regions. They function to produce a meaningful
4458:
Rakic, P (1 February 1974). "Neurons in rhesus monkey visual cortex: systematic relation between time of origin and eventual disposition".
4660:
Garel, S; Huffman, KJ; Rubenstein, JL (May 2003). "Molecular regionalization of the neocortex is disrupted in Fgf8 hypomorphic mutants".
3814:
4795:
Rajagopalan, V; Scott, J; Habas, PA; Kim, K; Corbett-Detig, J; Rousseau, F; Barkovich, AJ; Glenn, OA; Studholme, C (23 February 2011).
4029:; Ryan S. Dammerman & Arnold R. Kriegstein (2001). "Neurons derived from radial glial cells establish radial units in neocortex".
3671:"Neocortical neurogenesis is not really "neo": a new evolutionary model derived from a comparative study of chick pallial development"
2875:
2710:
2411:
1161:
2298:
Until recently no counterpart to the cerebral cortex had been recognized in invertebrates. However, a study published in the journal
5759:
Stacho, Martin; Herold, Christina; Rook, Noemi; Wagner, Hermann; Axer, Markus; Amunts, Katrin; Güntürkün, Onur (25 September 2020).
5717:
5617:
Walsh, Christopher A.; Mochida, Ganeshwaran H. (1 May 2004). "Genetic Basis of
Developmental Malformations of the Cerebral Cortex".
5296:
Saladin, Kenneth. Anatomy and
Physiology: The Unity of Form and Function, 5th Ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Companies Inc., 2010. Print.
4256:
4013:
3952:
2990:
2740:
2481:
934:
926:
6009:
4274:"Selective lengthening of the cell cycle in the neurogenic subpopulation of neural progenitor cells during mouse brain development"
5174:
Bishop, KM; Goudreau, G; O'Leary, DD (14 April 2000). "Regulation of area identity in the mammalian neocortex by Emx2 and Pax6".
4703:
Bishop, KM; Goudreau, G; O'Leary, DD (14 April 2000). "Regulation of area identity in the mammalian neocortex by Emx2 and Pax6".
1700:. Most sensory information is routed to the cerebral cortex via the thalamus. Olfactory information, however, passes through the
196:
3188:
7046:
2085:
1579:
827:
2891:
Toro, Roberto; Perron, Michel; Pike, Bruce; Richer, Louis; Veillette, Suzanne; Pausova, Zdenka; Paus, Tomáš (1 October 2008).
1260:
6634:
6326:
6003:
2036:
2003:
1875:, which decides which voluntary movements to make according to higher-order instructions, rules, and self-generated thoughts.
1872:
1790:
1770:
are called primary sensory areas. The senses of vision, hearing, and touch are served by the primary visual cortex, primary
884:, contains large pyramidal neurons. Axons from these leave the cortex and connect with subcortical structures including the
7249:
6035:
3970:"The transcription factor, Pax6, is required for cell proliferation and differentiation in the developing cerebral cortex"
2017:
1746:
In more general terms the cortex is typically described as comprising three parts: sensory, motor, and association areas.
184:
5652:
2376:
1606:, which generates the characteristic folds of the cerebral cortex. Gyrification is regulated by a DNA-associated protein
1365:
The first divisions of the progenitor cells are symmetric, which duplicates the total number of progenitor cells at each
430:, it is between 2 and 3-4 mm. thick, and makes up 40% of the brain's mass. 90% of the cerebral cortex is the six-layered
6622:
5465:
Nakazawa T, Ohara T, Hirabayashi N, Furuta Y, Hata J, Shibata M, Honda T, Kitazono T, Nakao T, Ninomiya T (March 2022).
2120:
1947:– all located in the posterior part of the cortex – integrate sensory information and information stored in memory. The
1775:
1575:
1530:
1522:
1437:. Next, a cohort of neurons migrating into the middle of the preplate divides this transient layer into the superficial
1302:
5467:"Multiple-region grey matter atrophy as a predictor for the development of dementia in a community: the Hisayama Study"
1789:
The organization of sensory maps in the cortex reflects that of the corresponding sensing organ, in what is known as a
6714:
4515:
2234:, identified more than 40 different types of cortical neurons based on the distribution of their dendrites and axons.
2156:
1327:
967:
418:
The cerebral cortex is the outer covering of the surfaces of the cerebral hemispheres and is folded into peaks called
1417:
of the mature cerebral cortex is formed during development. The first pyramidal neurons generated migrate out of the
937:
these same thalamus neurons or ones adjacent to them. One theory is that because the inhibitory output is reduced by
2811:"Gene-environment interactions in cortical interneuron development and dysfunction: A review of preclinical studies"
7288:
7126:
6682:
5745:
2190:
1542:. On the contrary, if mutations in Emx2 occur, it can cause the Pax6-expressing domain to expand and result in the
1314:
930:
920:, contains few large pyramidal neurons and many small spindle-like pyramidal and multiform neurons; layer VI sends
856:
1911:, because together they form a lens-shaped body. The putamen and caudate nucleus are also collectively called the
7085:
6783:
6646:
6627:
3089:
2025:
1866:
1373:, and one progenitor cell, which continues to divide until the end of development, when it differentiates into a
1134:
31:
1778:
respectively. In general, the two hemispheres receive information from the opposite (contralateral) side of the
1272:
migration that form the different cell types of the neocortex and it is a period associated with an increase in
7422:
6957:
6904:
6825:
6792:
6692:
6508:
6491:
6431:
6028:
5985:
1847:
1708:). The majority of connections are from one area of the cortex to another, rather than from subcortical areas;
1595:
1583:
1555:
1491:
1126:
551:
547:
115:
2220:
distinguished 52 different regions of the cerebral cortex based on their cytoarchitecture. These are known as
2066:
603:
6853:
5283:
5269:
872:
do not have a layer IV with axons which would terminate there going instead to the inner part of layer III.
461:
is completely hidden. The cortex is thickest over the top of a gyrus and thinnest at the bottom of a sulcus.
449:
The neocortex is separable into different regions of cortex known in the plural as cortices, and include the
320:
and its functional organisation. In mammals with small brains, there is no folding and the cortex is smooth.
6909:
6799:
6443:
6184:
6179:
2401:
2227:
1814:
1640:
1599:
1487:
1310:
847:
5284:"Behavioral Planning: Neurophysiological Approach of the Frontal Lobe Function in Primates - ScienceDirect"
2302:
in 2010, based on gene expression profiles, reported strong affinities between the cerebral cortex and the
1602:. During the period of cortical neurogenesis and layer formation, many higher mammals begin the process of
1430:
776:
7170:
6236:
6134:
6088:
3825:
11: 975–988. "...they either lack (agranular) or have only a rudimentary granular layer IV (dysgranular)."
2249:
2231:
2152:
2029:
2007:
1960:
1636:
1623:
1130:
616:
246:
168:
152:
5934:"Profiling by image registration reveals common origin of annelid mushroom bodies and vertebrate pallium"
5932:
Tomer, R; Denes, AS; Tessmar-Raible, K; Arendt, D; Tomer R; Denes AS; Tessmar-Raible K; Arendt D (2010).
4082:
Sur, Mriganka; Leamey, Catherine A. (2001). "Development and
Plasticity of Cortical Areas and Networks".
3034:
Frithjof
Kruggel; Martina K. Brückner; Thomas Arendt; Christopher J. Wiggins; D. Yves von Cramon (2003).
2021:
Spreading Depolarizations. We see markedly the front of waves. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-019-04132-8
1032:
The allocortex is the part of the cerebral cortex with three or four layers, and has three subtypes, the
7281:
7157:
7016:
6930:
6830:
4903:"Trnp1 regulates expansion and folding of the mammalian cerebral cortex by control of radial glial fate"
2311:
2062:
2040:
1709:
1486:
The map of functional cortical areas, which include primary motor and visual cortex, originates from a '
1018:
423:
328:
58:
1754:
1393:
of the cerebral cortex. The development process is time ordered and regulated by hundreds of genes and
72:
2104:. Infections can also affect the development of the cortex. A viral infection is one of the causes of
7130:
6978:
6870:
6547:
6407:
6304:
6253:
6110:
5882:
5819:
5183:
5130:
5083:
4712:
4616:
4569:
4467:
4332:
4040:
3848:
3763:
2822:
2549:
2292:
2116:
2077:
1837:
1697:
1693:
1660:
1514:
1498:
1414:
1231:
1199:
1167:
1107:
1089:
1014:
998:
921:
834:
830:
703:
623:-stained visual cortex of a human adult. Middle: Nissl-stained motor cortex of a human adult. Right:
579:
489:
399:
382:
in the human cerebral cortex. These are organised into horizontal cortical layers, and radially into
332:
297:
6020:
4962:"Hedgehog signaling promotes basal progenitor expansion and the growth and folding of the neocortex"
3670:
7107:
6517:
4797:"Local tissue growth patterns underlying normal fetal human brain gyrification quantified in utero"
3483:"Thalamic input to distal apical dendrites in neocortical layer 1 is massive and highly convergent"
3438:
Cauller L (1995). "Layer I of primary sensory neocortex: where top-down converges upon bottom-up".
3132:
2386:
1904:
1818:
1567:
1502:
1422:
1330:
1318:
966:. It has been proposed that the minicolumns are the basic functional units of the cortex. In 1957,
963:
901:
484:
443:
301:
132:
5017:
Rash, Brian G.; Tomasi, Simone; Lim, H. David; Suh, Carol Y.; Vaccarino, Flora M. (26 June 2013).
4748:"FGF signaling expands embryonic cortical surface area by regulating Notch-dependent neurogenesis"
7165:
6988:
6962:
6563:
6533:
6455:
6387:
6375:
6276:
6272:
6006:, Webvision: Comprehensive article about the structure and function of the primary visual cortex.
5965:
5914:
5851:
5735:
5447:
5242:
5156:
4685:
4642:
4491:
4440:
4229:
4107:
4064:
3703:
3550:
3463:
3369:
3183:
2381:
2261:
2217:
2160:
1935:
of the world, enable us to interact effectively, and support abstract thinking and language. The
1728:
1727:
The whole of the cerebral cortex was divided into 52 different areas in an early presentation by
1563:
1313:
as their main neurotransmitter. These GABAergic neurons are generated by progenitor cells in the
1241:
1195:
1061:
986:
888:. In the primary motor cortex of the frontal lobe, layer V contains giant pyramidal cells called
741:
543:
515:
509:
438:. There are between 14 and 16 billion neurons in the cortex, and these are organized radially in
344:
6813:
1972:
1879:
Just underneath the cerebral cortex are interconnected subcortical masses of grey matter called
1147:
1122:
drain the deoxygenated blood, and metabolic wastes including carbon dioxide, back to the heart.
7244:
7073:
7039:
7034:
7029:
6618:
6228:
6207:
6080:
5957:
5906:
5898:
5843:
5835:
5788:
5780:
5723:
5713:
5688:
5634:
5594:
5545:
5496:
5439:
5431:
5395:
5346:
5317:"The organization of the human cerebral cortex estimated by intrinsic functional connectivity"
5234:
5199:
5148:
5099:
5056:
5038:
4999:
4981:
4942:
4934:
4883:
4865:
4826:
4777:
4728:
4677:
4634:
4585:
4542:
4483:
4432:
4397:
4348:
4323:
4303:
4252:
4221:
4186:
4135:
4099:
4056:
4009:
3991:
3948:
3925:
3876:
3811:
3793:
3744:
3695:
3651:
3586:
3542:
3504:
3455:
3420:
3328:
3274:
3233:
3159:
3108:
3065:
3014:
2986:
2963:
2953:
2922:
2914:
2871:
2848:
2787:
2736:
2706:
2680:
2624:
2575:
2513:
2477:
2048:
1908:
1900:
1652:
1629:
1591:
1269:
1249:
1118:
the cerebrum. This arterial blood carries oxygen, glucose, and other nutrients to the cortex.
1111:
1099:
1057:
676:
641:
month-old infant. The Nissl stain shows the cell bodies of neurons; the Golgi stain shows the
3968:
Warren N, Caric D, Pratt T, Clausen JA, Asavaritikrai P, Mason JO, Hill RE, Price DJ (1999).
7196:
7145:
7140:
7135:
7117:
7112:
7100:
7095:
7090:
7078:
7061:
7051:
6983:
6914:
6895:
6890:
6885:
6880:
6875:
6863:
6835:
6817:
6809:
6804:
6754:
6735:
6702:
6697:
6538:
6522:
6513:
6367:
6352:
6343:
6338:
6331:
6319:
6314:
6309:
6293:
6281:
6202:
6194:
6166:
6157:
6143:
6138:
6125:
6120:
5947:
5890:
5827:
5772:
5680:
5626:
5584:
5576:
5535:
5527:
5486:
5478:
5423:
5385:
5377:
5336:
5328:
5226:
5191:
5138:
5091:
5046:
5030:
4989:
4973:
4924:
4914:
4873:
4857:
4816:
4808:
4767:
4759:
4720:
4669:
4624:
4577:
4532:
4524:
4475:
4424:
4387:
4379:
4340:
4293:
4285:
4213:
4176:
4168:
4091:
4048:
4031:
3981:
3915:
3907:
3866:
3856:
3837:"Layer-specific network oscillation and spatiotemporal receptive field in the visual cortex"
3783:
3775:
3734:
3685:
3641:
3633:
3578:
3534:
3494:
3447:
3410:
3400:
3359:
3320:
3264:
3223:
3215:
3149:
3141:
3098:
3055:
3047:
2945:
2904:
2838:
2830:
2777:
2769:
2670:
2662:
2614:
2606:
2565:
2557:
2505:
2136:
1968:
1964:
1896:
1736:
1418:
1405:
1370:
1342:
1334:
1306:
1264:
Neurogenesis is shown in red and lamination is shown in blue. Adapted from (Sur et al. 2001)
1245:
1237:
1141:
1045:
979:
893:
861:
715:
289:
52:
5230:
1590:
Rapid expansion of the cortical surface area is regulated by the amount of self-renewal of
1533:
pole. The establishment of this gradient is important for proper development. For example,
1210:
of the nervous system. The most anterior (front, or cranial) part of the neural plate, the
1144:
is the main blood system that deals with blood supply in the cerebrum and cerebral cortex.
1029:
which is a transitional region between the isocortex and the regions of the periallocortex.
7354:
7065:
6993:
6787:
6651:
6639:
6602:
6595:
6583:
6578:
6573:
6568:
6501:
6496:
6460:
6448:
6436:
6424:
6419:
6412:
6380:
6263:
6258:
6246:
6241:
6115:
6103:
6098:
6093:
4026:
3896:"Temporal Specification and Bilaterality of Human Neocortical Topographic Gene Expression"
3818:
3060:
2773:
2391:
2303:
2277:
1912:
1892:
1884:
1851:
1783:
1771:
1705:
1473:
1277:
959:
707:
619:, each showing a vertical cross-section, with the surface of the cortex at the top. Left:
439:
383:
305:
6152:
2069:
that serves to protect the brain from infection can become compromised allowing entry to
1956:
1301:
from other regions. Radial glia give rise to neurons that are pyramidal in shape and use
744:(1909) established that the mammalian neocortex is consistently divided into six layers.
591:, where there are four layers instead of six, is in some instances seen to be related to
5886:
5823:
5381:
5187:
5134:
5087:
4716:
4620:
4573:
4471:
4336:
4044:
3852:
3812:
Quantitative Architecture Distinguishes Prefrontal Cortical Systems in the Rhesus Monkey
3622:"Functional Organization of the Somatosensory Cortical Layer 6 Feedback to the Thalamus"
3085:"Relationships between IQ and Regional Cortical Grey Matter Thickness in Healthy Adults"
2826:
2553:
649:
7396:
7228:
7220:
6952:
6947:
6858:
6687:
6667:
6357:
6288:
5938:
5589:
5564:
5540:
5515:
5491:
5466:
5390:
5365:
5341:
5316:
5051:
5018:
4994:
4961:
4878:
4845:
4821:
4796:
4772:
4747:
4537:
4528:
4510:
4392:
4367:
4298:
4273:
4181:
4156:
3920:
3895:
3871:
3836:
3788:
3646:
3621:
3228:
3203:
3154:
3145:
3127:
2949:
2843:
2810:
2782:
2757:
2675:
2650:
2619:
2594:
2570:
2537:
2500:
Strominger, Norman L.; Demarest, Robert J.; Laemle, Lois B. (2012). "Cerebral Cortex".
2416:
2253:
2205:
2144:
1979:
1944:
1762:
The sensory areas are the cortical areas that receive and process information from the
1701:
1611:
1551:
1462:
1390:
1298:
1211:
1182:
The cerebral cortex develops from the most anterior part, the forebrain region, of the
1119:
1094:
1077:
1041:
972:
811:
780:
768:
760:
535:
531:
476:
458:
368:
356:
317:
5870:
5807:
5760:
3538:
3253:"The neurological basis of developmental dyslexia: an overview and working hypothesis"
3051:
2084:
and problems in later development. Maternal alcohol consumption for example can cause
611:
7416:
7401:
7262:
7180:
7175:
6768:
6747:
6730:
6709:
6526:
6476:
5994:
5918:
5855:
5451:
5217:
Grove, EA; Fukuchi-Shimogori, T (2003). "Generating the cerebral cortical area map".
3451:
3373:
3178:
3126:
Alexandre F.M. DaSilva; Cristina Granziera; Josh Snyder; Nouchine Hadjikhani (2007).
2406:
2288:
2243:
2221:
2174:
2164:
2148:
2105:
1983:
1975:
1940:
1936:
1880:
1794:
1740:
1732:
1689:
1559:
1539:
1322:
1280:
giving rise to any cell type in the cortex and later progenitors giving rise only to
1073:
1069:
885:
852:
727:
711:
657:
527:
523:
454:
395:
360:
352:
274:
222:
5246:
5160:
4646:
4495:
4444:
4233:
3707:
3554:
2436:
1309:, however these migrating cells contribute neurons that are stellate-shaped and use
1098:
Arterial supply showing the regions supplied by the posterior, middle, and anterior
691:
is formed of six layers, numbered I to VI, from the outermost layer I – near to the
514:
The larger sulci and gyri mark the divisions of the cortex of the cerebrum into the
7328:
6300:
6064:
5034:
4812:
4763:
4689:
4289:
4068:
3779:
3467:
2140:
2109:
2081:
2058:
1948:
1739:
but also relate to various functions. An example is Brodmann area 17, which is the
1722:
1603:
1547:
1543:
1450:
1273:
1227:
1187:
1065:
1026:
869:
696:
661:
575:
519:
497:
480:
470:
450:
391:
348:
336:
313:
309:
5969:
4111:
1357:
with other neurons. The axon can develop to extend a long way from the cell body.
410:
17:
5195:
4724:
4479:
3911:
3405:
3388:
2699:
2509:
1056:
There is a transitional area between the neocortex and the allocortex called the
714:. This is a band of whiter tissue that can be observed with the naked eye in the
145:
120:
7345:
7340:
7007:
6056:
5019:"Cortical gyrification induced by fibroblast growth factor 2 in the mouse brain"
3269:
3252:
2834:
2316:
2284:
2269:
2208:, a condition marked by the absence of large parts of the cerebral hemispheres.
2178:
1341:
surface, and provide scaffolding for the migration of neurons outwards from the
1215:
1191:
1183:
1049:
1040:
which has four or five, and a transitional area adjacent to the allocortex, the
1037:
1033:
938:
783:
can be found here. Inputs to the apical tufts are thought to be crucial for the
772:
624:
620:
539:
427:
364:
340:
296:
making up the remainder. The cortex is divided into left and right parts by the
5952:
5933:
5531:
5427:
4919:
4902:
4861:
1684:
The cerebral cortex is connected to various subcortical structures such as the
7335:
5989:
5653:"EMX2 empty spiracles homeobox 2 [Homo sapiens (human)] – Gene – NCBI"
5630:
4383:
3739:
3722:
3364:
3347:
2561:
2307:
2257:
1987:
1932:
1813:
in the primary sensory cortex. This last topographic map of the body onto the
1810:
1802:
1779:
1286:
1006:
897:
653:
588:
435:
387:
293:
254:
127:
35:
5902:
5839:
5784:
5727:
5580:
5482:
5435:
5042:
4985:
4938:
4869:
3986:
3969:
3590:
3324:
3219:
2918:
1550:
regions enlarging. Therefore, researchers believe that similar gradients and
779:
and subpial granular layer cells are present in this layer. Also, some spiny
177:
173:
7391:
7323:
6590:
5998:
5894:
5831:
5776:
5143:
5118:
5095:
4629:
4604:
4581:
4344:
3861:
3637:
3525:
Jones EG (1998). "Viewpoint: the core and matrix of thalamic organization".
3499:
3482:
3103:
3084:
2909:
2892:
2610:
2265:
2124:
2097:
1648:
1644:
1374:
1338:
1207:
1115:
1002:
942:
889:
757:
692:
688:
665:
567:
431:
285:
278:
258:
250:
7273:
5961:
5910:
5847:
5792:
5692:
5638:
5598:
5549:
5500:
5443:
5399:
5350:
5238:
5203:
5152:
5060:
5003:
4946:
4887:
4830:
4781:
4732:
4681:
4638:
4546:
4401:
4307:
4190:
4103:
4060:
3995:
3929:
3880:
3797:
3699:
3655:
3508:
3424:
3332:
3278:
3237:
3163:
3112:
3069:
2967:
2926:
2852:
2791:
2684:
2628:
2579:
1817:
has been illustrated as a deformed human representation, the somatosensory
475:
The cerebral cortex is folded in a way that allows a large surface area of
5332:
5103:
4589:
4487:
4436:
4428:
4352:
4225:
4217:
3748:
3546:
3481:
Rubio-Garrido P, Pérez-de-Manzo F, Porrero C, Galazo MJ, Clascá F (2009).
3459:
3348:"The discovery of the subpial granular layer in the human cerebral cortex"
2705:(4th ed.). McGraw-Hill, Health Professions Division. 5 January 2000.
2032:, show as a marker, an atrophy of the grey matter of the cerebral cortex.
457:. About two thirds of the cortical surface is buried in the sulci and the
7206:
6012:, Webvision: Image of the basic cell types of the monkey cerebral cortex.
2273:
2070:
2061:
from disease or trauma, can involve damage to a specific lobe such as in
2044:
1806:
1767:
1685:
1534:
1442:
1382:
1378:
1349:
1290:
764:
733:
723:
642:
607:
Diagram of layers pattern. Cells grouped on left, axonal layers on right.
592:
583:
270:
226:
139:
91:
4929:
1671:
1001:
the cerebral cortex can be classified into two types, the large area of
672:
5684:
3415:
2361:
2135:
There are a number of genetic mutations that can cause a wide range of
2052:
1888:
1656:
1454:
1386:
1366:
1354:
865:
680:
262:
4673:
4157:"Evolution of the neocortex: a perspective from developmental biology"
3690:
3582:
2651:"Evolution of the neocortex: a perspective from developmental biology"
1321:. This migration of GABAergic neurons is particularly important since
6742:
5806:
Nieder, Andreas; Wagener, Lysann; Rinnert, Paul (25 September 2020).
5366:"The anatomy of language: contributions from functional neuroimaging"
4095:
4052:
2201:
2186:
1907:. The putamen and globus pallidus are also collectively known as the
1798:
1763:
1458:
1426:
1281:
1203:
493:
379:
266:
242:
238:
234:
5712:. Kandel, Eric R. (5th ed.). New York. 2013. pp. 347–348.
5074:
Rakic, P (8 July 1988). "Specification of cerebral cortical areas".
4977:
4844:
Lui, Jan H.; Hansen, David V.; Kriegstein, Arnold R. (8 July 2011).
4560:
Rakic, P (8 July 1988). "Specification of cerebral cortical areas".
4172:
3204:"Absence of changes in cortical thickness in patients with migraine"
2666:
1655:, in a primordial map. This map is controlled by secreted signaling
1252:–progenitor cells, which divide to produce glial cells and neurons.
1170:
of the cerebral cortex is a complex and finely tuned process called
202:
3894:
Pletikos, Mihovil; Sousa, Andre MM; et al. (22 January 2014).
929:
fibers to neurons in the thalamus and also send collaterals to the
7201:
3128:"Thickening in the somatosensory cortex of patients with migraine"
2170:
2101:
2080:
is susceptible to a range of environmental factors that can cause
1922:
1753:
1670:
1607:
1472:
1404:
1259:
1146:
1093:
983:
671:
648:
610:
602:
563:
419:
409:
324:
230:
103:
62:
5673:
Birth Defects Research. Part A, Clinical and Molecular Teratology
4746:
Rash, BG; Lim, HD; Breunig, JJ; Vaccarino, FM (26 October 2011).
4251:(8th ed.). Sinauer Associates Publishers. pp. 394–395.
3764:"Receptive fields of single neurones in the cat's striate cortex"
1409:
Human cortical development between 26 and 39 week gestational age
1218:
begins, gives rise to the cerebral hemispheres and later cortex.
1174:, influenced by the interplay between genes and the environment.
390:. Cortical areas have specific functions such as movement in the
2758:"Generating Neuronal Diversity in the Mammalian Cerebral Cortex"
2396:
2197:
2182:
2093:
1991:
1571:
1526:
1518:
1510:
1506:
1494:
719:
7277:
6024:
4511:"Development of layer I neurons in the primate cerebral cortex"
277:. The cerebral cortex is the part of the brain responsible for
5995:
Stained brain slice images which include the "cerebral cortex"
5808:"A neural correlate of sensory consciousness in a corvid bird"
5119:"Neocortex patterning by the secreted signaling molecule FGF8"
4605:"Neocortex patterning by the secreted signaling molecule FGF8"
2944:. Progress in Brain Research. Vol. 195. pp. 123–63.
2595:"Cerebral cortex expansion and folding: what have we learned?"
2593:
Fernández, V; Llinares-Benadero, C; Borrell, V (17 May 2016).
2088:. Other factors that can cause neurodevelopment disorders are
4368:"Epigenetic control on cell fate choice in neural stem cells"
4321:
P. Rakic (1988). "Specification of cerebral cortical areas".
1441:, which will become layer I of the mature neocortex, and the
3947:(Fifth ed.). UK: Oxford University Press. p. 533.
3035:
989:
while that in layer V has a fast 10–15 Hz oscillation.
4008:
Larsen, W J. Human Embryology 3rd edition 2001. pp 421-422
1833:
Two areas of the cortex are commonly referred to as motor:
1766:. Parts of the cortex that receive sensory inputs from the
1505:. Examples of such transcription factors include the genes
833:, and layer III is the principal source of corticocortical
4130:
Sanes, Dan H.; Reh, Thomas A.; Harris, William A. (2012).
2870:(3rd ed.). Williams & Wilkins. pp. 348–358.
718:
of the occipital lobe. The line of Gennari is composed of
570:
relationship between brain weight and cortical thickness.
402:, and the visual cortex is located in the occipital lobe.
335:
and continue to mature after birth through the process of
4272:
Calegari, F; Haubensack W; Haffner C; Huttner WB (2005).
3569:
When There Is No Cytoarchitecturally Distinct Layer 4?".
3389:"Brain states: top-down influences in sensory processing"
1461:, neurogenesis continues throughout the entire period of
904:, which is the main pathway for voluntary motor control.
664:(predominantly blue) is seen at the bottom of the image.
331:(plural sulci). These surface convolutions appear during
5761:"A cortex-like canonical circuit in the avian forebrain"
5305:
Dorland's Medical Dictionary for Health Consumers, 2008.
2364:
monkey. The cerebral cortex is depicted in dark violet.
2181:
are associated with microcephaly. Mutations in the gene
1005:
which has six cell layers, and the much smaller area of
587:
whereby decreased folding in certain areas results in a
1797:, for example, correspond to neighboring points in the
4960:
Wang, Lei; Hou, Shirui; Han, Young-Goo (23 May 2016).
2055:(difficulties in speech expression or comprehension).
1862:
In addition, motor functions have been described for:
1635:
A key theory of cortical evolution is embodied in the
1317:(MGE) that migrate tangentially to the cortex via the
1194:. From the cavity inside the neural tube develops the
446:, in the horizontally organized layers of the cortex.
2893:"Brain Size and Folding of the Human Cerebral Cortex"
695:, to the innermost layer VI – near to the underlying
3293:"Scientists identify a new kind of human brain cell"
7384:
7363:
7312:
7237:
7219:
7189:
7156:
7060:
7015:
7006:
6971:
6940:
6929:
6846:
6776:
6767:
6723:
6675:
6666:
6611:
6556:
6484:
6475:
6400:
6366:
6227:
6220:
6193:
6079:
6072:
6063:
5117:Fukuchi-Shimogori, T; Grove, EA (2 November 2001).
4603:Fukuchi-Shimogori, T; Grove, EA (2 November 2001).
3011:
The central nervous system of vertebrates, Volume 1
2756:Lodato, Simona; Arlotta, Paola (13 November 2015).
1490:', which is regulated by molecular signals such as
1106:Blood supply to the cerebral cortex is part of the
763:. Layer I consists largely of extensions of apical
434:whilst the other 10% made up of three/four-layered
183:
167:
151:
138:
126:
114:
102:
97:
87:
82:
45:
7261:Some categorizations are approximations, and some
4846:"Development and evolution of the human neocortex"
2698:
975:, 1959), auditory cortex, and associative cortex.
754:molecular layer of cerebral cortex|molecular layer
312:. Apart from minimising brain and cranial volume,
27:Outer layer of the cerebrum of the mammalian brain
3009:Nieuwenhuys R, Donkelaar HJ, Nicholson C (1998).
2735:(3rd ed.). Springer-Verlag. pp. 86–92.
2065:, and associated functions will be affected. The
1080:, named from their overlying bones of the skull.
414:Lateral view of cerebrum showing several cortices
1758:Motor and sensory regions of the cerebral cortex
941:input to the cerebral cortex, this provides the
756:, and contains few scattered neurons, including
3810:S.M. Dombrowski, C.C. Hilgetag, and H. Barbas.
3202:Datte R, Detre JA, et al. (October 2011).
2809:Ansen-Wilson, LJ; Lipinski, RJ (January 2017).
2762:Annual Review of Cell and Developmental Biology
2538:"Structure and function of the cerebral cortex"
2476:(3rd ed.). McGraw-Hill. pp. 416–422.
2123:is an invasive procedure that involves placing
1125:The main arteries supplying the cortex are the
978:Cortical areas that lack a layer IV are called
945:with adjustable "gain control for the relay of
855:and pyramidal cells, and is the main target of
398:. The motor cortex is primarily located in the
5869:Herculano-Houzel, Suzana (25 September 2020).
5516:"Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder: An Overview"
5514:Mukherjee, Raja A.S.; Hollins, Sheila (2006).
3179:"Migraine Sufferers Have Thicker Brain Cortex"
2502:Noback's Human Nervous System, Seventh Edition
77:Motor and sensory areas of the cerebral cortex
7289:
6036:
2940:Nieuwenhuys, R (2012). "The insular cortex".
1927:Cortical areas involved in speech processing.
1566:in different areas of the developing cortex,
8:
3723:"The columnar organization of the neocortex"
2644:
2642:
2640:
2638:
2531:
2529:
2495:
2493:
2336:Lateral surface of the human cerebral cortex
771:and horizontally oriented axons, as well as
2348:Medial surface of the human cerebral cortex
2108:, which results in a smooth cortex without
1869:, which guides voluntary movements in space
538:is often included as the insular lobe. The
7296:
7282:
7274:
7012:
6937:
6773:
6672:
6481:
6224:
6076:
6069:
6043:
6029:
6021:
5740:: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (
3036:"Analyzing the neocortical fine-structure"
3004:
3002:
1236:Cortical neurons are generated within the
323:A fold or ridge in the cortex is termed a
304:that are joined beneath the cortex by the
71:
51:
5951:
5588:
5563:Tarapore, PE; et al. (August 2012).
5539:
5490:
5389:
5340:
5142:
5050:
4993:
4928:
4918:
4877:
4820:
4771:
4628:
4536:
4391:
4297:
4180:
3985:
3919:
3870:
3860:
3787:
3738:
3689:
3678:Development, Growth & Differentiation
3645:
3498:
3414:
3404:
3363:
3268:
3227:
3153:
3102:
3059:
2908:
2842:
2781:
2726:
2724:
2722:
2674:
2618:
2569:
2467:
2465:
2463:
2461:
2459:
2457:
1517:form an opposing gradient of expression.
792:or M-type thalamus cells (in contrast to
615:Three drawings of cortical lamination by
6016:Cerebral Cortex – Cell Centered Database
5871:"Birds do have a brain cortex—and think"
5612:
5610:
5608:
5520:Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine
3520:
3518:
3346:Judaš, Miloš; Pletikos, Mihovil (2010).
2360:Tissue slice from the brain of an adult
2248:The cerebral cortex is derived from the
2131:Genes associated with cortical disorders
2011:
1696:and receiving information from them via
1482:(3rd ed.). Burlington: Elsevier Science)
645:and axons of a random subset of neurons.
4025:Stephen C. Noctor; Alexander C. Flint;
2428:
2326:
1624:Pallium (neuroanatomy) § Evolution
572:Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain
327:(plural gyri) and a groove is termed a
5733:
5231:10.1146/annurev.neuro.26.041002.131137
3669:Suzuki, IK; Hirata, T (January 2013).
3615:
3613:
3177:Catharine Paddock (20 November 2007).
2985:(13th. ed.). Wiley. p. 549.
2983:Principles of anatomy & physiology
2037:diseases of the central nervous system
1021:. The neocortex has two subtypes, the
496:have smooth cerebral surfaces without
200:
42:
5704:
5702:
4366:Hu, X.L.; Wang, Y.; Shen, Q. (2012).
4125:
4123:
4121:
2774:10.1146/annurev-cellbio-100814-125353
1809:in the primary auditory cortex and a
1501:expression, through a process called
722:bringing visual information from the
7:
4206:The Journal of Comparative Neurology
3762:Hubel DH, Wiesel TN (October 1959).
2155:can also result causing a number of
1793:. Neighboring points in the primary
1692:, sending information to them along
1445:, forming a middle layer called the
378:There are between 14 and 16 billion
6953:Lateral (frontal+parietal+temporal)
5382:10.1046/j.1469-7580.2000.19730335.x
2252:, a layered structure found in the
1801:. This topographic map is called a
578:. Another study has found that the
483:. When unfolded in the human, each
4529:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-15-05607.2001
3146:10.1212/01.wnl.0000291618.32247.2d
2981:Tortora, G; Derrickson, B (2011).
2950:10.1016/B978-0-444-53860-4.00007-6
2504:. Humana Press. pp. 429–451.
2412:List of regions in the human brain
2139:of the cerebral cortex, including
1805:. In the same way, there exists a
1162:Development of the cerebral cortex
900:, and the spinal cord forming the
740:in different species. The work of
660:(predominantly pink). Subcortical
479:to fit within the confines of the
288:makes up approximately 90% of the
25:
5270:"Cerebral cortex - ScienceDirect"
4132:Development of the Nervous System
3191:from the original on 11 May 2008.
2193:, characterised by microcephaly.
1971:, for language expression and in
1570:is disrupted. Specifically, when
1480:Development of the Nervous System
1044:. Examples of allocortex are the
1036:with three cortical laminae, the
892:, whose axons travel through the
518:. There are four main lobes: the
34:. For the cerebellar cortex, see
4417:Journal of Comparative Neurology
3571:Journal of Comparative Neurology
3013:. Springer. pp. 2011–2012.
2353:
2341:
2329:
1915:after their striped appearance.
1395:epigenetic regulatory mechanisms
828:interhemispheric corticocortical
796:or C-type that go to layer IV).
702:One of the clearest examples of
197:Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy
65:(folds and ridges) of the cortex
30:For the scientific journal, see
7047:Posterior parahippocampal gyrus
6989:Collateral (temporal+occipital)
2536:Shipp, Stewart (17 June 2007).
2177:, and disorders in this and in
2086:fetal alcohol spectrum disorder
1675:Some functional areas of cortex
1244:. At first, this zone contains
1009:that has three or four layers:
814:and numerous stellate neurons.
738:laminar structure of the cortex
347:. The four major lobes are the
36:Cerebellum § Gross anatomy
6635:Secondary somatosensory cortex
6327:Ventromedial prefrontal cortex
5035:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3621-12.2013
4813:10.1523/jneurosci.5458-10.2011
4764:10.1523/jneurosci.4439-11.2011
4290:10.1523/jneurosci.0778-05.2005
3780:10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006308
3061:11858/00-001M-0000-0010-9C60-3
2942:Evolution of the Primate Brain
2004:Central nervous system disease
1982:, including the frontal lobe,
1873:Dorsolateral prefrontal cortex
851:, contains different types of
1:
7250:Poles of cerebral hemispheres
6984:Cingulate (frontal+cingulate)
5471:J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry
5219:Annual Review of Neuroscience
3539:10.1016/S0306-4522(97)00581-2
3387:Gilbert CD, Sigman M (2007).
3052:10.1016/S1361-8415(03)00006-9
1190:folds and closes to form the
6623:Primary somatosensory cortex
5710:Principles of neural science
5196:10.1126/science.288.5464.344
4725:10.1126/science.288.5464.344
4480:10.1126/science.183.4123.425
3912:10.1016/j.neuron.2013.11.018
3452:10.1016/0166-4328(95)00032-1
3406:10.1016/j.neuron.2007.05.019
2701:Principles of neural science
2510:10.1007/978-1-61779-779-8_25
2157:neurodevelopmental disorders
2121:cortical stimulation mapping
1776:primary somatosensory cortex
1348:At birth there are very few
997:Based on the differences in
241:. It is the largest site of
6715:Transverse occipital sulcus
6004:"The primary visual cortex"
5023:The Journal of Neuroscience
4801:The Journal of Neuroscience
4752:The Journal of Neuroscience
4516:The Journal of Neuroscience
4509:Zecevic N, Rakic P (2001).
4278:The Journal of Neuroscience
4161:Nature Reviews Neuroscience
4084:Nature Reviews Neuroscience
3620:Lam YW, Sherman SM (2010).
2835:10.1016/j.neuro.2016.12.002
2655:Nature Reviews Neuroscience
1594:and is partly regulated by
1529:is highly expressed in the
1521:is highly expressed at the
1457:, in which, in contrast to
1222:Cortical neuron development
363:lobes. Other lobes are the
7439:
7127:Isthmus of cingulate gyrus
6948:Central (frontal+parietal)
6683:Occipital pole of cerebrum
5953:10.1016/j.cell.2010.07.043
5532:10.1177/014107680609900616
5428:10.1007/s00701-019-04132-8
5321:Journal of Neurophysiology
4920:10.1016/j.cell.2013.03.027
4862:10.1016/j.cell.2011.06.030
3352:Translational Neuroscience
2241:
2191:Nijmegen breakage syndrome
2053:different types of aphasia
2026:Neurodegenerative diseases
2001:
1720:
1621:
1315:medial ganglionic eminence
1225:
1214:, which is evident before
1159:
1087:
931:thalamic reticular nucleus
507:
468:
300:, which separates the two
249:, and plays a key role in
29:
7258:
6784:Transverse temporal gyrus
6647:Posterior parietal cortex
5631:10.1001/archneur.61.5.637
4384:10.1007/s13238-012-2916-6
4155:Rakic, P (October 2009).
3945:Principles of development
3768:The Journal of Physiology
3365:10.2478/v10134-010-0037-4
3270:10.1093/brain/123.12.2373
2868:Core text of neuroanatomy
2649:Rakic, P (October 2009).
2562:10.1016/j.cub.2007.03.044
2472:Saladin, Kenneth (2011).
1867:Posterior parietal cortex
1848:Supplementary motor areas
1704:to the olfactory cortex (
1453:occurs in the layer I of
1135:posterior cerebral artery
1084:Blood supply and drainage
857:thalamocortical afferents
371:often referred to as the
195:
70:
50:
32:Cerebral Cortex (journal)
6905:Inferior temporal sulcus
6826:Superior temporal sulcus
6509:Inferior parietal lobule
6492:Superior parietal lobule
6432:Supplementary motor area
5581:10.3171/2012.5.JNS112124
5483:10.1136/jnnp-2021-326611
3841:Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A
3220:10.1177/0333102411421025
2377:Brain–computer interface
2287:, evidence suggests the
2153:Chromosome abnormalities
2018:spreading depolarization
1731:. These areas, known as
1492:fibroblast growth factor
1127:anterior cerebral artery
882:internal pyramidal layer
824:external pyramidal layer
552:inferior parietal lobule
548:superior parietal lobule
221:, is the outer layer of
7376:External granular layer
7371:Internal granular layer
6910:Inferior temporal gyrus
6854:Occipitotemporal sulcus
6800:Superior temporal gyrus
6693:Lateral occipital gyrus
6444:Supplementary eye field
6185:Inferior frontal sulcus
6180:Superior frontal sulcus
5895:10.1126/science.abe0536
5832:10.1126/science.abb1447
5777:10.1126/science.abc5534
5569:Journal of Neurosurgery
5364:Cathy J. Price (2000).
5144:10.1126/science.1064252
5096:10.1126/science.3291116
4630:10.1126/science.1064252
4582:10.1126/science.3291116
4345:10.1126/science.3291116
4247:Gilbert, Scott (2006).
3943:Wolpert, Lewis (2015).
3862:10.1073/pnas.0903962106
3740:10.1093/brain/120.4.701
2611:10.15252/embj.201593701
2402:Gray matter heterotopia
1815:posterior central gyrus
848:internal granular layer
807:external granular layer
679:neurons in the cortex (
7171:Fimbria of hippocampus
6237:Superior frontal gyrus
6135:Inferior frontal gyrus
6089:Superior frontal gyrus
3987:10.1093/cercor/9.6.627
3721:Mountcastle V (1997).
3603:Creutzfeldt, O. 1995.
3325:10.1093/cercor/9.8.765
3040:Medical Image Analysis
2232:Santiago Ramon y Cajal
2041:neurological disorders
2022:
2008:Developmental toxicity
1961:inferior frontal gyrus
1928:
1759:
1676:
1637:radial unit hypothesis
1483:
1410:
1265:
1152:
1131:middle cerebral artery
1114:supply the blood that
1103:
775:. During development,
684:
669:
646:
617:Santiago Ramon y Cajal
608:
415:
247:central nervous system
7158:Hippocampal formation
7017:Parahippocampal gyrus
6831:Middle temporal gyrus
5744:) CS1 maint: others (
5619:Archives of Neurology
5333:10.1152/jn.00338.2011
4429:10.1002/cne.902970309
4249:Developmental biology
4218:10.1002/cne.901460304
3835:Sun W, Dan Y (2009).
3638:10.1093/cercor/bhp077
3500:10.1093/cercor/bhn259
3104:10.1093/cercor/bhl125
2910:10.1093/cercor/bhm261
2441:TheFreeDictionary.com
2312:Platynereis dumerilii
2063:frontal lobe disorder
2015:
2002:Further information:
1998:Clinical significance
1959:in areas of the left
1933:perceptual experience
1926:
1757:
1741:primary visual cortex
1735:, are based on their
1674:
1661:transcription factors
1515:transcription factors
1476:
1431:Cajal–Retzius neurons
1408:
1263:
1248:, that transition to
1226:Further information:
1200:neuroepithelial cells
1151:Cortical blood supply
1150:
1097:
1019:primary visual cortex
726:into layer IV of the
712:primary visual cortex
675:
652:
627:-stained cortex of a
614:
606:
469:Further information:
422:, and grooves called
413:
7131:Retrosplenial cortex
6979:Longitudinal fissure
6871:Medial temporal lobe
6548:Intraparietal sulcus
6408:Primary motor cortex
6305:Orbitofrontal cortex
6254:Medial frontal gyrus
6111:Middle frontal gyrus
5657:www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
5416:Acta Neurochirurgica
2228:Rafael Lorente de Nó
2204:are associated with
2117:electrocorticography
1858:voluntary movements.
1844:voluntary movements
1838:Primary motor cortex
1698:afferent connections
1694:efferent connections
1574:is increased in the
1499:transcription factor
1355:synaptic connections
1331:postsynaptic neurons
1232:Neuroepithelial cell
1168:prenatal development
1108:cerebral circulation
1090:Cerebral circulation
1015:primary motor cortex
999:laminar organization
580:somatosensory cortex
490:longitudinal fissure
302:cerebral hemispheres
298:longitudinal fissure
217:, also known as the
7108:Posterior cingulate
6518:Supramarginal gyrus
5887:2020Sci...369.1567H
5881:(6511): 1567–1568.
5824:2020Sci...369.1626N
5818:(6511): 1626–1629.
5188:2000Sci...288..344B
5135:2001Sci...294.1071F
5088:1988Sci...241..170R
5029:(26): 10802–10814.
4966:Nature Neuroscience
4717:2000Sci...288..344B
4621:2001Sci...294.1071F
4574:1988Sci...241..170R
4472:1974Sci...183..425R
4337:1988Sci...241..170R
4045:2001Natur.409..714N
3853:2009PNAS..10617986S
3847:(42): 17986–17991.
2827:2017NeuTx..58..120A
2731:Roberts, P (1992).
2554:2007CBio...17.R443S
2387:Cortical homunculus
2067:blood–brain barrier
2030:Alzheimer's disease
1905:subthalamic nucleus
1568:cortical patterning
1503:cortical patterning
1469:Cortical patterning
1423:subventricular zone
1361:Asymmetric division
1319:subventricular zone
902:corticospinal tract
777:Cajal–Retzius cells
599:Layers of neocortex
394:, and sight in the
316:is crucial for the
7322:True isocortex or
7166:Hippocampal sulcus
7086:Anterior cingulate
6963:Preoccipital notch
6564:Paracentral lobule
6534:Parietal operculum
6456:Frontal eye fields
6388:Paracentral sulcus
6376:Paracentral lobule
6277:Paraolfactory area
6273:Paraterminal gyrus
6010:"Basic cell types"
5685:10.1002/bdra.23488
5370:Journal of Anatomy
4372:Protein & Cell
4027:Tamily A. Weissman
3817:2008-08-29 at the
3607:. Springer-Verlag.
3184:Medical News Today
2866:Carpenter (1985).
2382:Cortical dysplasia
2218:Korbinian Brodmann
2161:fragile X syndrome
2096:, and exposure to
2049:movement disorders
2023:
1929:
1760:
1729:Korbinian Brodmann
1677:
1653:radial glial cells
1592:radial glial cells
1484:
1411:
1401:Layer organization
1266:
1250:radial glial cells
1202:of its walls, the
1196:ventricular system
1153:
1104:
1017:, and the striate
968:Vernon Mountcastle
742:Korbinian Brodmann
685:
670:
647:
609:
544:paracentral lobule
516:lobes of the brain
510:Lobes of the brain
416:
345:lobes of the brain
243:neural integration
18:Cortical thickness
7410:
7409:
7271:
7270:
7215:
7214:
7040:Postrhinal cortex
7035:Perirhinal cortex
7030:Entorhinal cortex
7002:
7001:
6958:Parieto-occipital
6925:
6924:
6763:
6762:
6662:
6661:
6619:Postcentral gyrus
6471:
6470:
6396:
6395:
6216:
6215:
6208:Precentral sulcus
6171:Pars triangularis
5999:BrainMaps project
4674:10.1242/dev.00416
4331:(4862): 170–176.
4141:978-0-12-374539-2
4039:(6821): 714–720.
3691:10.1111/dgd.12020
3583:10.1002/cne.25652
3299:. 27 August 2018.
3140:(21): 1990–1995.
3020:978-3-540-56013-5
2959:978-0-444-53860-4
2903:(10): 2352–2357.
2519:978-1-61779-778-1
2437:"cerebral mantle"
2323:Additional images
2137:genetic disorders
1919:Association areas
1909:lentiform nucleus
1901:nucleus accumbens
1630:medulla oblongata
1552:signaling centers
1513:. Together, both
1415:layered structure
1246:neural stem cells
1112:Cerebral arteries
1100:cerebral arteries
1058:paralimbic cortex
914:polymorphic layer
862:African elephants
812:pyramidal neurons
810:, contains small
769:pyramidal neurons
704:cortical layering
333:fetal development
211:
210:
206:
16:(Redirected from
7430:
7298:
7291:
7284:
7275:
7197:Indusium griseum
7062:Cingulate cortex
7052:Prepyriform area
7013:
6938:
6818:Planum temporale
6774:
6755:Calcarine sulcus
6673:
6482:
6353:Olfactory sulcus
6339:Subcallosal area
6225:
6203:Precentral gyrus
6162:Pars opercularis
6077:
6070:
6045:
6038:
6031:
6022:
5974:
5973:
5955:
5929:
5923:
5922:
5866:
5860:
5859:
5803:
5797:
5796:
5756:
5750:
5749:
5739:
5731:
5706:
5697:
5696:
5667:
5661:
5660:
5649:
5643:
5642:
5614:
5603:
5602:
5592:
5560:
5554:
5553:
5543:
5511:
5505:
5504:
5494:
5462:
5456:
5455:
5410:
5404:
5403:
5393:
5361:
5355:
5354:
5344:
5327:(3): 1125–1165.
5312:
5306:
5303:
5297:
5294:
5288:
5287:
5280:
5274:
5273:
5266:
5260:
5257:
5251:
5250:
5214:
5208:
5207:
5171:
5165:
5164:
5146:
5129:(5544): 1071–4.
5114:
5108:
5107:
5071:
5065:
5064:
5054:
5014:
5008:
5007:
4997:
4957:
4951:
4950:
4932:
4922:
4898:
4892:
4891:
4881:
4841:
4835:
4834:
4824:
4792:
4786:
4785:
4775:
4758:(43): 15604–17.
4743:
4737:
4736:
4700:
4694:
4693:
4657:
4651:
4650:
4632:
4615:(5544): 1071–4.
4600:
4594:
4593:
4557:
4551:
4550:
4540:
4506:
4500:
4499:
4455:
4449:
4448:
4412:
4406:
4405:
4395:
4363:
4357:
4356:
4318:
4312:
4311:
4301:
4269:
4263:
4262:
4244:
4238:
4237:
4201:
4195:
4194:
4184:
4152:
4146:
4145:
4134:. Elsevier Inc.
4127:
4116:
4115:
4096:10.1038/35067562
4079:
4073:
4072:
4053:10.1038/35055553
4022:
4016:
4006:
4000:
3999:
3989:
3965:
3959:
3958:
3940:
3934:
3933:
3923:
3891:
3885:
3884:
3874:
3864:
3832:
3826:
3808:
3802:
3801:
3791:
3759:
3753:
3752:
3742:
3718:
3712:
3711:
3693:
3675:
3666:
3660:
3659:
3649:
3617:
3608:
3601:
3595:
3594:
3565:
3559:
3558:
3522:
3513:
3512:
3502:
3478:
3472:
3471:
3435:
3429:
3428:
3418:
3408:
3384:
3378:
3377:
3367:
3343:
3337:
3336:
3307:
3301:
3300:
3289:
3283:
3282:
3272:
3251:Habib M (2000).
3248:
3242:
3241:
3231:
3199:
3193:
3192:
3174:
3168:
3167:
3157:
3123:
3117:
3116:
3106:
3097:(9): 2163–2171.
3080:
3074:
3073:
3063:
3031:
3025:
3024:
3006:
2997:
2996:
2978:
2972:
2971:
2937:
2931:
2930:
2912:
2888:
2882:
2881:
2863:
2857:
2856:
2846:
2806:
2800:
2799:
2785:
2753:
2747:
2746:
2728:
2717:
2716:
2704:
2695:
2689:
2688:
2678:
2646:
2633:
2632:
2622:
2599:The EMBO Journal
2590:
2584:
2583:
2573:
2533:
2524:
2523:
2497:
2488:
2487:
2469:
2452:
2451:
2449:
2447:
2433:
2357:
2345:
2333:
2280:, respectively.
2278:olfactory cortex
2078:developing fetus
1897:substantia nigra
1737:cytoarchitecture
1425:, together with
1419:ventricular zone
1371:ventricular zone
1343:ventricular zone
1335:ventricular zone
1307:neurotransmitter
1238:ventricular zone
1198:, and, from the
1142:circle of Willis
1046:olfactory cortex
960:cortical columns
894:internal capsule
716:calcarine sulcus
640:
639:
635:
632:
440:cortical columns
400:precentral gyrus
384:cortical columns
314:cortical folding
284:The six-layered
203:edit on Wikidata
75:
55:
43:
21:
7438:
7437:
7433:
7432:
7431:
7429:
7428:
7427:
7423:Cerebral cortex
7413:
7412:
7411:
7406:
7380:
7359:
7355:Line of Gennari
7313:Structure types
7308:
7306:cerebral cortex
7302:
7272:
7267:
7254:
7233:
7211:
7185:
7152:
7056:
6998:
6994:Callosal sulcus
6972:Medial/inferior
6967:
6932:
6921:
6847:Medial/inferior
6842:
6814:Wernicke's area
6788:Auditory cortex
6759:
6724:Medial/inferior
6719:
6658:
6607:
6603:Marginal sulcus
6557:Medial/inferior
6552:
6467:
6420:Premotor cortex
6392:
6362:
6221:Medial/inferior
6212:
6189:
6059:
6053:cerebral cortex
6051:Anatomy of the
6049:
5982:
5977:
5931:
5930:
5926:
5868:
5867:
5863:
5805:
5804:
5800:
5758:
5757:
5753:
5732:
5720:
5708:
5707:
5700:
5669:
5668:
5664:
5651:
5650:
5646:
5616:
5615:
5606:
5562:
5561:
5557:
5513:
5512:
5508:
5464:
5463:
5459:
5412:
5411:
5407:
5363:
5362:
5358:
5314:
5313:
5309:
5304:
5300:
5295:
5291:
5282:
5281:
5277:
5268:
5267:
5263:
5258:
5254:
5216:
5215:
5211:
5182:(5464): 344–9.
5173:
5172:
5168:
5116:
5115:
5111:
5082:(4862): 170–6.
5073:
5072:
5068:
5016:
5015:
5011:
4978:10.1038/nn.4307
4959:
4958:
4954:
4900:
4899:
4895:
4843:
4842:
4838:
4794:
4793:
4789:
4745:
4744:
4740:
4711:(5464): 344–9.
4702:
4701:
4697:
4659:
4658:
4654:
4602:
4601:
4597:
4568:(4862): 170–6.
4559:
4558:
4554:
4523:(15): 5607–19.
4508:
4507:
4503:
4466:(4123): 425–7.
4457:
4456:
4452:
4414:
4413:
4409:
4365:
4364:
4360:
4320:
4319:
4315:
4271:
4270:
4266:
4259:
4246:
4245:
4241:
4203:
4202:
4198:
4173:10.1038/nrn2719
4154:
4153:
4149:
4142:
4129:
4128:
4119:
4081:
4080:
4076:
4024:
4023:
4019:
4007:
4003:
3974:Cerebral Cortex
3967:
3966:
3962:
3955:
3942:
3941:
3937:
3893:
3892:
3888:
3834:
3833:
3829:
3819:Wayback Machine
3809:
3805:
3761:
3760:
3756:
3720:
3719:
3715:
3673:
3668:
3667:
3663:
3619:
3618:
3611:
3602:
3598:
3567:
3566:
3562:
3524:
3523:
3516:
3493:(10): 2380–95.
3480:
3479:
3475:
3446:(1–2): 163–70.
3440:Behav Brain Res
3437:
3436:
3432:
3386:
3385:
3381:
3345:
3344:
3340:
3313:Cerebral Cortex
3309:
3308:
3304:
3297:Allen Institute
3291:
3290:
3286:
3263:(12): 2373–99.
3250:
3249:
3245:
3201:
3200:
3196:
3176:
3175:
3171:
3125:
3124:
3120:
3090:Cerebral Cortex
3082:
3081:
3077:
3033:
3032:
3028:
3021:
3008:
3007:
3000:
2993:
2980:
2979:
2975:
2960:
2939:
2938:
2934:
2897:Cerebral Cortex
2890:
2889:
2885:
2878:
2865:
2864:
2860:
2815:Neurotoxicology
2808:
2807:
2803:
2755:
2754:
2750:
2743:
2730:
2729:
2720:
2713:
2697:
2696:
2692:
2667:10.1038/nrn2719
2648:
2647:
2636:
2605:(10): 1021–44.
2592:
2591:
2587:
2542:Current Biology
2535:
2534:
2527:
2520:
2499:
2498:
2491:
2484:
2471:
2470:
2455:
2445:
2443:
2435:
2434:
2430:
2426:
2421:
2392:Eloquent cortex
2372:
2365:
2358:
2349:
2346:
2337:
2334:
2325:
2304:mushroom bodies
2246:
2240:
2230:, a student of
2214:
2185:that codes for
2133:
2010:
2000:
1973:Wernicke's area
1945:occipital lobes
1921:
1913:corpus striatum
1893:globus pallidus
1885:caudate nucleus
1852:premotor cortex
1827:
1811:somatotopic map
1803:retinotopic map
1791:topographic map
1772:auditory cortex
1752:
1725:
1719:
1706:piriform cortex
1682:
1669:
1659:and downstream
1626:
1620:
1610:and by FGF and
1523:rostral lateral
1471:
1403:
1391:pyramidal cells
1363:
1258:
1234:
1224:
1180:
1164:
1158:
1092:
1086:
995:
993:Types of cortex
955:
922:efferent fibers
918:multiform layer
910:
878:
843:
822:Layer III, the
820:
802:
761:rosehip neurons
752:Layer I is the
750:
708:line of Gennari
637:
633:
630:
628:
601:
560:
512:
506:
473:
467:
408:
318:brain circuitry
306:corpus callosum
219:cerebral mantle
215:cerebral cortex
207:
160:
78:
66:
46:Cerebral cortex
39:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
7436:
7434:
7426:
7425:
7415:
7414:
7408:
7407:
7405:
7404:
7399:
7397:Pyramidal cell
7394:
7388:
7386:
7382:
7381:
7379:
7378:
7373:
7367:
7365:
7361:
7360:
7358:
7357:
7351:
7350:
7349:
7348:
7343:
7333:
7332:
7331:
7326:
7316:
7314:
7310:
7309:
7303:
7301:
7300:
7293:
7286:
7278:
7269:
7268:
7263:Brodmann areas
7259:
7256:
7255:
7253:
7252:
7247:
7241:
7239:
7235:
7234:
7232:
7231:
7229:Insular cortex
7225:
7223:
7221:Insular cortex
7217:
7216:
7213:
7212:
7210:
7209:
7204:
7199:
7193:
7191:
7187:
7186:
7184:
7183:
7178:
7173:
7168:
7162:
7160:
7154:
7153:
7151:
7150:
7149:
7148:
7143:
7138:
7123:
7122:
7121:
7120:
7115:
7105:
7104:
7103:
7098:
7093:
7083:
7082:
7081:
7074:Subgenual area
7070:
7068:
7058:
7057:
7055:
7054:
7049:
7044:
7043:
7042:
7037:
7032:
7021:
7019:
7010:
7004:
7003:
7000:
6999:
6997:
6996:
6991:
6986:
6981:
6975:
6973:
6969:
6968:
6966:
6965:
6960:
6955:
6950:
6944:
6942:
6935:
6933:sulci/fissures
6927:
6926:
6923:
6922:
6920:
6919:
6918:
6917:
6907:
6901:
6900:
6899:
6898:
6893:
6888:
6883:
6878:
6868:
6867:
6866:
6859:Fusiform gyrus
6856:
6850:
6848:
6844:
6843:
6841:
6840:
6839:
6838:
6828:
6823:
6822:
6821:
6807:
6797:
6796:
6795:
6780:
6778:
6771:
6765:
6764:
6761:
6760:
6758:
6757:
6751:
6750:
6745:
6740:
6739:
6738:
6727:
6725:
6721:
6720:
6718:
6717:
6712:
6707:
6706:
6705:
6700:
6690:
6688:Occipital gyri
6685:
6679:
6677:
6670:
6668:Occipital lobe
6664:
6663:
6660:
6659:
6657:
6656:
6655:
6654:
6644:
6643:
6642:
6632:
6631:
6630:
6615:
6613:
6609:
6608:
6606:
6605:
6600:
6599:
6598:
6588:
6587:
6586:
6581:
6576:
6571:
6560:
6558:
6554:
6553:
6551:
6550:
6544:
6543:
6542:
6541:
6531:
6530:
6529:
6520:
6506:
6505:
6504:
6499:
6488:
6486:
6479:
6473:
6472:
6469:
6468:
6466:
6465:
6464:
6463:
6453:
6452:
6451:
6441:
6440:
6439:
6429:
6428:
6427:
6417:
6416:
6415:
6404:
6402:
6398:
6397:
6394:
6393:
6391:
6390:
6385:
6384:
6383:
6372:
6370:
6364:
6363:
6361:
6360:
6358:Orbital sulcus
6355:
6349:
6348:
6347:
6346:
6336:
6335:
6334:
6324:
6323:
6322:
6317:
6312:
6298:
6297:
6296:
6289:Straight gyrus
6286:
6285:
6284:
6269:
6268:
6267:
6266:
6261:
6251:
6250:
6249:
6244:
6233:
6231:
6222:
6218:
6217:
6214:
6213:
6211:
6210:
6205:
6199:
6197:
6191:
6190:
6188:
6187:
6182:
6176:
6175:
6174:
6173:
6164:
6150:
6148:Pars orbitalis
6141:
6131:
6130:
6129:
6128:
6123:
6118:
6108:
6107:
6106:
6101:
6096:
6085:
6083:
6074:
6067:
6061:
6060:
6050:
6048:
6047:
6040:
6033:
6025:
6019:
6018:
6013:
6007:
6001:
5992:
5981:
5980:External links
5978:
5976:
5975:
5946:(5): 800–809.
5924:
5861:
5798:
5751:
5718:
5698:
5662:
5644:
5625:(5): 637–640.
5604:
5555:
5526:(6): 298–302.
5506:
5477:(3): 263–271.
5457:
5422:(3): 581–592.
5405:
5376:(3): 335–359.
5356:
5307:
5298:
5289:
5275:
5261:
5252:
5209:
5166:
5109:
5066:
5009:
4952:
4913:(3): 535–549.
4893:
4836:
4807:(8): 2878–87.
4787:
4738:
4695:
4668:(9): 1903–14.
4652:
4595:
4552:
4501:
4450:
4423:(3): 441–470.
4407:
4378:(4): 278–290.
4358:
4313:
4284:(28): 6533–8.
4264:
4257:
4239:
4196:
4167:(10): 724–35.
4147:
4140:
4117:
4090:(4): 251–262.
4074:
4017:
4001:
3960:
3953:
3935:
3906:(2): 321–332.
3886:
3827:
3803:
3754:
3733:(4): 701–722.
3713:
3661:
3609:
3605:Cortex Cerebri
3596:
3560:
3514:
3473:
3430:
3379:
3358:(3): 255–260.
3338:
3319:(8): 765–775.
3302:
3284:
3243:
3214:(14): 1452–8.
3194:
3169:
3118:
3075:
3046:(3): 251–264.
3026:
3019:
2998:
2991:
2973:
2958:
2932:
2883:
2877:978-0683014556
2876:
2858:
2801:
2768:(1): 699–720.
2748:
2741:
2718:
2712:978-0838577011
2711:
2690:
2661:(10): 724–35.
2634:
2585:
2548:(12): R443–9.
2525:
2518:
2489:
2482:
2453:
2427:
2425:
2422:
2420:
2419:
2417:Insular cortex
2414:
2409:
2404:
2399:
2394:
2389:
2384:
2379:
2373:
2371:
2368:
2367:
2366:
2359:
2352:
2350:
2347:
2340:
2338:
2335:
2328:
2324:
2321:
2239:
2236:
2222:Brodmann areas
2213:
2210:
2206:schizencephaly
2145:schizencephaly
2132:
2129:
1999:
1996:
1980:lateral sulcus
1920:
1917:
1877:
1876:
1870:
1860:
1859:
1845:
1826:
1823:
1751:
1748:
1733:Brodmann areas
1718:
1717:Cortical areas
1715:
1702:olfactory bulb
1681:
1678:
1668:
1665:
1619:
1616:
1578:pole, Emx2 is
1562:. If FGFs are
1548:motor cortical
1470:
1467:
1463:corticogenesis
1447:cortical plate
1402:
1399:
1379:ependymal cell
1362:
1359:
1337:to the outer,
1328:hyperpolarizes
1323:GABA receptors
1257:
1254:
1240:, next to the
1223:
1220:
1212:prosencephalon
1179:
1176:
1172:corticogenesis
1157:
1154:
1120:Cerebral veins
1088:Main article:
1085:
1082:
1078:occipital lobe
1054:
1053:
1042:periallocortex
1030:
1023:true isocortex
994:
991:
954:
951:
912:Layer VI, the
909:
906:
877:
874:
845:Layer IV, the
842:
839:
819:
816:
804:Layer II, the
801:
798:
781:stellate cells
749:
746:
600:
597:
582:is thicker in
559:
556:
536:insular cortex
532:occipital lobe
505:
502:
466:
463:
459:insular cortex
407:
404:
369:insular cortex
209:
208:
199:
193:
192:
187:
181:
180:
171:
165:
164:
155:
149:
148:
143:
136:
135:
130:
124:
123:
118:
112:
111:
109:cortex cerebri
106:
100:
99:
95:
94:
89:
85:
84:
80:
79:
76:
68:
67:
56:
48:
47:
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
7435:
7424:
7421:
7420:
7418:
7403:
7402:Stellate cell
7400:
7398:
7395:
7393:
7390:
7389:
7387:
7383:
7377:
7374:
7372:
7369:
7368:
7366:
7362:
7356:
7353:
7352:
7347:
7344:
7342:
7339:
7338:
7337:
7334:
7330:
7327:
7325:
7321:
7320:
7318:
7317:
7315:
7311:
7307:
7299:
7294:
7292:
7287:
7285:
7280:
7279:
7276:
7266:
7264:
7257:
7251:
7248:
7246:
7243:
7242:
7240:
7236:
7230:
7227:
7226:
7224:
7222:
7218:
7208:
7205:
7203:
7200:
7198:
7195:
7194:
7192:
7188:
7182:
7181:Rhinal sulcus
7179:
7177:
7176:Dentate gyrus
7174:
7172:
7169:
7167:
7164:
7163:
7161:
7159:
7155:
7147:
7144:
7142:
7139:
7137:
7134:
7133:
7132:
7128:
7125:
7124:
7119:
7116:
7114:
7111:
7110:
7109:
7106:
7102:
7099:
7097:
7094:
7092:
7089:
7088:
7087:
7084:
7080:
7077:
7076:
7075:
7072:
7071:
7069:
7067:
7063:
7059:
7053:
7050:
7048:
7045:
7041:
7038:
7036:
7033:
7031:
7028:
7027:
7026:
7023:
7022:
7020:
7018:
7014:
7011:
7009:
7005:
6995:
6992:
6990:
6987:
6985:
6982:
6980:
6977:
6976:
6974:
6970:
6964:
6961:
6959:
6956:
6954:
6951:
6949:
6946:
6945:
6943:
6941:Superolateral
6939:
6936:
6934:
6928:
6916:
6913:
6912:
6911:
6908:
6906:
6903:
6902:
6897:
6894:
6892:
6889:
6887:
6884:
6882:
6879:
6877:
6874:
6873:
6872:
6869:
6865:
6862:
6861:
6860:
6857:
6855:
6852:
6851:
6849:
6845:
6837:
6834:
6833:
6832:
6829:
6827:
6824:
6819:
6815:
6811:
6808:
6806:
6803:
6802:
6801:
6798:
6794:
6791:
6790:
6789:
6785:
6782:
6781:
6779:
6777:Superolateral
6775:
6772:
6770:
6769:Temporal lobe
6766:
6756:
6753:
6752:
6749:
6748:Lingual gyrus
6746:
6744:
6741:
6737:
6734:
6733:
6732:
6731:Visual cortex
6729:
6728:
6726:
6722:
6716:
6713:
6711:
6710:Lunate sulcus
6708:
6704:
6701:
6699:
6696:
6695:
6694:
6691:
6689:
6686:
6684:
6681:
6680:
6678:
6676:Superolateral
6674:
6671:
6669:
6665:
6653:
6650:
6649:
6648:
6645:
6641:
6638:
6637:
6636:
6633:
6629:
6626:
6625:
6624:
6620:
6617:
6616:
6614:
6610:
6604:
6601:
6597:
6594:
6593:
6592:
6589:
6585:
6582:
6580:
6577:
6575:
6572:
6570:
6567:
6566:
6565:
6562:
6561:
6559:
6555:
6549:
6546:
6545:
6540:
6537:
6536:
6535:
6532:
6528:
6527:Angular gyrus
6524:
6521:
6519:
6515:
6512:
6511:
6510:
6507:
6503:
6500:
6498:
6495:
6494:
6493:
6490:
6489:
6487:
6485:Superolateral
6483:
6480:
6478:
6477:Parietal lobe
6474:
6462:
6459:
6458:
6457:
6454:
6450:
6447:
6446:
6445:
6442:
6438:
6435:
6434:
6433:
6430:
6426:
6423:
6422:
6421:
6418:
6414:
6411:
6410:
6409:
6406:
6405:
6403:
6399:
6389:
6386:
6382:
6379:
6378:
6377:
6374:
6373:
6371:
6369:
6365:
6359:
6356:
6354:
6351:
6350:
6345:
6342:
6341:
6340:
6337:
6333:
6330:
6329:
6328:
6325:
6321:
6318:
6316:
6313:
6311:
6308:
6307:
6306:
6302:
6299:
6295:
6292:
6291:
6290:
6287:
6283:
6280:
6279:
6278:
6274:
6271:
6270:
6265:
6262:
6260:
6257:
6256:
6255:
6252:
6248:
6245:
6243:
6240:
6239:
6238:
6235:
6234:
6232:
6230:
6226:
6223:
6219:
6209:
6206:
6204:
6201:
6200:
6198:
6196:
6192:
6186:
6183:
6181:
6178:
6177:
6172:
6168:
6165:
6163:
6159:
6156:
6155:
6154:
6151:
6149:
6145:
6142:
6140:
6136:
6133:
6132:
6127:
6124:
6122:
6119:
6117:
6114:
6113:
6112:
6109:
6105:
6102:
6100:
6097:
6095:
6092:
6091:
6090:
6087:
6086:
6084:
6082:
6078:
6075:
6073:Superolateral
6071:
6068:
6066:
6062:
6058:
6054:
6046:
6041:
6039:
6034:
6032:
6027:
6026:
6023:
6017:
6014:
6011:
6008:
6005:
6002:
6000:
5996:
5993:
5991:
5987:
5984:
5983:
5979:
5971:
5967:
5963:
5959:
5954:
5949:
5945:
5941:
5940:
5935:
5928:
5925:
5920:
5916:
5912:
5908:
5904:
5900:
5896:
5892:
5888:
5884:
5880:
5876:
5872:
5865:
5862:
5857:
5853:
5849:
5845:
5841:
5837:
5833:
5829:
5825:
5821:
5817:
5813:
5809:
5802:
5799:
5794:
5790:
5786:
5782:
5778:
5774:
5770:
5766:
5762:
5755:
5752:
5747:
5743:
5737:
5729:
5725:
5721:
5719:9780071390118
5715:
5711:
5705:
5703:
5699:
5694:
5690:
5686:
5682:
5678:
5674:
5666:
5663:
5658:
5654:
5648:
5645:
5640:
5636:
5632:
5628:
5624:
5620:
5613:
5611:
5609:
5605:
5600:
5596:
5591:
5586:
5582:
5578:
5575:(2): 354–62.
5574:
5570:
5566:
5559:
5556:
5551:
5547:
5542:
5537:
5533:
5529:
5525:
5521:
5517:
5510:
5507:
5502:
5498:
5493:
5488:
5484:
5480:
5476:
5472:
5468:
5461:
5458:
5453:
5449:
5445:
5441:
5437:
5433:
5429:
5425:
5421:
5417:
5409:
5406:
5401:
5397:
5392:
5387:
5383:
5379:
5375:
5371:
5367:
5360:
5357:
5352:
5348:
5343:
5338:
5334:
5330:
5326:
5322:
5318:
5311:
5308:
5302:
5299:
5293:
5290:
5285:
5279:
5276:
5271:
5265:
5262:
5256:
5253:
5248:
5244:
5240:
5236:
5232:
5228:
5224:
5220:
5213:
5210:
5205:
5201:
5197:
5193:
5189:
5185:
5181:
5177:
5170:
5167:
5162:
5158:
5154:
5150:
5145:
5140:
5136:
5132:
5128:
5124:
5120:
5113:
5110:
5105:
5101:
5097:
5093:
5089:
5085:
5081:
5077:
5070:
5067:
5062:
5058:
5053:
5048:
5044:
5040:
5036:
5032:
5028:
5024:
5020:
5013:
5010:
5005:
5001:
4996:
4991:
4987:
4983:
4979:
4975:
4972:(7): 888–96.
4971:
4967:
4963:
4956:
4953:
4948:
4944:
4940:
4936:
4931:
4926:
4921:
4916:
4912:
4908:
4904:
4897:
4894:
4889:
4885:
4880:
4875:
4871:
4867:
4863:
4859:
4855:
4851:
4847:
4840:
4837:
4832:
4828:
4823:
4818:
4814:
4810:
4806:
4802:
4798:
4791:
4788:
4783:
4779:
4774:
4769:
4765:
4761:
4757:
4753:
4749:
4742:
4739:
4734:
4730:
4726:
4722:
4718:
4714:
4710:
4706:
4699:
4696:
4691:
4687:
4683:
4679:
4675:
4671:
4667:
4663:
4656:
4653:
4648:
4644:
4640:
4636:
4631:
4626:
4622:
4618:
4614:
4610:
4606:
4599:
4596:
4591:
4587:
4583:
4579:
4575:
4571:
4567:
4563:
4556:
4553:
4548:
4544:
4539:
4534:
4530:
4526:
4522:
4518:
4517:
4512:
4505:
4502:
4497:
4493:
4489:
4485:
4481:
4477:
4473:
4469:
4465:
4461:
4454:
4451:
4446:
4442:
4438:
4434:
4430:
4426:
4422:
4418:
4411:
4408:
4403:
4399:
4394:
4389:
4385:
4381:
4377:
4373:
4369:
4362:
4359:
4354:
4350:
4346:
4342:
4338:
4334:
4330:
4326:
4325:
4317:
4314:
4309:
4305:
4300:
4295:
4291:
4287:
4283:
4279:
4275:
4268:
4265:
4260:
4258:9780878932504
4254:
4250:
4243:
4240:
4235:
4231:
4227:
4223:
4219:
4215:
4212:(3): 335–54.
4211:
4207:
4200:
4197:
4192:
4188:
4183:
4178:
4174:
4170:
4166:
4162:
4158:
4151:
4148:
4143:
4137:
4133:
4126:
4124:
4122:
4118:
4113:
4109:
4105:
4101:
4097:
4093:
4089:
4085:
4078:
4075:
4070:
4066:
4062:
4058:
4054:
4050:
4046:
4042:
4038:
4034:
4033:
4028:
4021:
4018:
4015:
4014:0-443-06583-7
4011:
4005:
4002:
3997:
3993:
3988:
3983:
3980:(6): 627–35.
3979:
3975:
3971:
3964:
3961:
3956:
3954:9780199678143
3950:
3946:
3939:
3936:
3931:
3927:
3922:
3917:
3913:
3909:
3905:
3901:
3897:
3890:
3887:
3882:
3878:
3873:
3868:
3863:
3858:
3854:
3850:
3846:
3842:
3838:
3831:
3828:
3824:
3820:
3816:
3813:
3807:
3804:
3799:
3795:
3790:
3785:
3781:
3777:
3774:(3): 574–91.
3773:
3769:
3765:
3758:
3755:
3750:
3746:
3741:
3736:
3732:
3728:
3724:
3717:
3714:
3709:
3705:
3701:
3697:
3692:
3687:
3684:(1): 173–87.
3683:
3679:
3672:
3665:
3662:
3657:
3653:
3648:
3643:
3639:
3635:
3631:
3627:
3623:
3616:
3614:
3610:
3606:
3600:
3597:
3592:
3588:
3584:
3580:
3576:
3572:
3564:
3561:
3556:
3552:
3548:
3544:
3540:
3536:
3533:(2): 331–45.
3532:
3528:
3521:
3519:
3515:
3510:
3506:
3501:
3496:
3492:
3488:
3484:
3477:
3474:
3469:
3465:
3461:
3457:
3453:
3449:
3445:
3441:
3434:
3431:
3426:
3422:
3417:
3412:
3407:
3402:
3399:(5): 677–96.
3398:
3394:
3390:
3383:
3380:
3375:
3371:
3366:
3361:
3357:
3353:
3349:
3342:
3339:
3334:
3330:
3326:
3322:
3318:
3314:
3306:
3303:
3298:
3294:
3288:
3285:
3280:
3276:
3271:
3266:
3262:
3258:
3254:
3247:
3244:
3239:
3235:
3230:
3225:
3221:
3217:
3213:
3209:
3205:
3198:
3195:
3190:
3186:
3185:
3180:
3173:
3170:
3165:
3161:
3156:
3151:
3147:
3143:
3139:
3135:
3134:
3129:
3122:
3119:
3114:
3110:
3105:
3100:
3096:
3092:
3091:
3086:
3079:
3076:
3071:
3067:
3062:
3057:
3053:
3049:
3045:
3041:
3037:
3030:
3027:
3022:
3016:
3012:
3005:
3003:
2999:
2994:
2992:9780470646083
2988:
2984:
2977:
2974:
2969:
2965:
2961:
2955:
2951:
2947:
2943:
2936:
2933:
2928:
2924:
2920:
2916:
2911:
2906:
2902:
2898:
2894:
2887:
2884:
2879:
2873:
2869:
2862:
2859:
2854:
2850:
2845:
2840:
2836:
2832:
2828:
2824:
2820:
2816:
2812:
2805:
2802:
2798:
2793:
2789:
2784:
2779:
2775:
2771:
2767:
2763:
2759:
2752:
2749:
2744:
2742:9780387977775
2738:
2734:
2727:
2725:
2723:
2719:
2714:
2708:
2703:
2702:
2694:
2691:
2686:
2682:
2677:
2672:
2668:
2664:
2660:
2656:
2652:
2645:
2643:
2641:
2639:
2635:
2630:
2626:
2621:
2616:
2612:
2608:
2604:
2600:
2596:
2589:
2586:
2581:
2577:
2572:
2567:
2563:
2559:
2555:
2551:
2547:
2543:
2539:
2532:
2530:
2526:
2521:
2515:
2511:
2507:
2503:
2496:
2494:
2490:
2485:
2483:9780071222075
2479:
2475:
2474:Human anatomy
2468:
2466:
2464:
2462:
2460:
2458:
2454:
2442:
2438:
2432:
2429:
2423:
2418:
2415:
2413:
2410:
2408:
2407:Limbic system
2405:
2403:
2400:
2398:
2395:
2393:
2390:
2388:
2385:
2383:
2380:
2378:
2375:
2374:
2369:
2363:
2356:
2351:
2344:
2339:
2332:
2327:
2322:
2320:
2318:
2314:
2313:
2309:
2305:
2301:
2296:
2294:
2293:consciousness
2290:
2289:avian pallium
2286:
2281:
2279:
2275:
2271:
2267:
2263:
2259:
2255:
2251:
2245:
2244:Barrel cortex
2238:Other animals
2237:
2235:
2233:
2229:
2225:
2223:
2219:
2211:
2209:
2207:
2203:
2199:
2196:Mutations in
2194:
2192:
2188:
2184:
2180:
2176:
2175:microcephalin
2172:
2168:
2166:
2165:Rett syndrome
2162:
2158:
2154:
2150:
2149:lissencephaly
2147:and types of
2146:
2142:
2138:
2130:
2128:
2126:
2122:
2118:
2113:
2111:
2107:
2106:lissencephaly
2103:
2099:
2095:
2091:
2087:
2083:
2082:birth defects
2079:
2074:
2072:
2068:
2064:
2060:
2056:
2054:
2050:
2046:
2042:
2038:
2033:
2031:
2027:
2019:
2014:
2009:
2005:
1997:
1995:
1993:
1989:
1985:
1984:basal ganglia
1981:
1977:
1974:
1970:
1966:
1962:
1958:
1953:
1950:
1946:
1942:
1938:
1934:
1925:
1918:
1916:
1914:
1910:
1906:
1902:
1898:
1894:
1890:
1886:
1882:
1881:basal ganglia
1874:
1871:
1868:
1865:
1864:
1863:
1857:
1853:
1849:
1846:
1843:
1839:
1836:
1835:
1834:
1831:
1824:
1822:
1820:
1816:
1812:
1808:
1807:tonotopic map
1804:
1800:
1796:
1795:visual cortex
1792:
1787:
1785:
1781:
1777:
1773:
1769:
1765:
1756:
1750:Sensory areas
1749:
1747:
1744:
1742:
1738:
1734:
1730:
1724:
1716:
1714:
1711:
1707:
1703:
1699:
1695:
1691:
1690:basal ganglia
1687:
1679:
1673:
1666:
1664:
1662:
1658:
1654:
1650:
1646:
1642:
1638:
1633:
1631:
1625:
1617:
1615:
1613:
1609:
1605:
1601:
1597:
1593:
1588:
1585:
1581:
1580:downregulated
1577:
1573:
1569:
1565:
1561:
1560:retinoic acid
1557:
1553:
1549:
1545:
1541:
1540:visual cortex
1536:
1532:
1528:
1524:
1520:
1516:
1512:
1508:
1504:
1500:
1496:
1493:
1489:
1481:
1475:
1468:
1466:
1464:
1460:
1456:
1452:
1448:
1444:
1440:
1439:marginal zone
1436:
1432:
1428:
1424:
1420:
1416:
1407:
1400:
1398:
1396:
1392:
1388:
1384:
1380:
1376:
1372:
1368:
1367:mitotic cycle
1360:
1358:
1356:
1351:
1346:
1344:
1340:
1336:
1332:
1329:
1324:
1320:
1316:
1312:
1308:
1304:
1300:
1295:
1292:
1288:
1283:
1279:
1275:
1271:
1262:
1255:
1253:
1251:
1247:
1243:
1239:
1233:
1229:
1221:
1219:
1217:
1213:
1209:
1205:
1201:
1197:
1193:
1189:
1185:
1177:
1175:
1173:
1169:
1163:
1155:
1149:
1145:
1143:
1138:
1136:
1132:
1128:
1123:
1121:
1117:
1113:
1109:
1101:
1096:
1091:
1083:
1081:
1079:
1075:
1074:parietal lobe
1071:
1070:temporal lobe
1067:
1063:
1059:
1051:
1047:
1043:
1039:
1035:
1031:
1028:
1024:
1020:
1016:
1012:
1011:
1010:
1008:
1004:
1000:
992:
990:
988:
985:
981:
976:
974:
969:
965:
961:
952:
950:
948:
944:
940:
936:
932:
928:
923:
919:
915:
907:
905:
903:
899:
895:
891:
887:
886:basal ganglia
883:
880:Layer V, the
875:
873:
871:
867:
863:
858:
854:
850:
849:
840:
838:
836:
832:
829:
825:
817:
815:
813:
809:
808:
799:
797:
795:
791:
786:
782:
778:
774:
770:
766:
762:
759:
755:
747:
745:
743:
739:
735:
731:
729:
728:visual cortex
725:
721:
717:
713:
709:
705:
700:
698:
694:
690:
682:
678:
677:Golgi-stained
674:
667:
663:
659:
658:visual cortex
655:
651:
644:
626:
622:
618:
613:
605:
598:
596:
594:
590:
585:
581:
577:
573:
569:
565:
557:
555:
553:
549:
545:
541:
537:
533:
529:
528:temporal lobe
525:
524:parietal lobe
521:
517:
511:
503:
501:
499:
495:
491:
486:
482:
478:
477:neural tissue
472:
464:
462:
460:
456:
455:visual cortex
452:
447:
445:
441:
437:
433:
429:
425:
421:
412:
405:
403:
401:
397:
396:visual cortex
393:
389:
385:
381:
376:
374:
370:
366:
362:
358:
354:
350:
346:
342:
338:
334:
330:
326:
321:
319:
315:
311:
307:
303:
299:
295:
291:
287:
282:
280:
276:
275:consciousness
272:
268:
264:
260:
256:
252:
248:
244:
240:
236:
232:
228:
224:
223:neural tissue
220:
216:
204:
198:
194:
191:
188:
186:
182:
179:
175:
172:
170:
166:
163:
159:
156:
154:
150:
147:
144:
141:
137:
134:
131:
129:
125:
122:
119:
117:
113:
110:
107:
105:
101:
96:
93:
90:
86:
81:
74:
69:
64:
60:
54:
49:
44:
41:
37:
33:
19:
7329:Proisocortex
7305:
7260:
7024:
6301:Orbital gyri
6153:Broca's area
6065:Frontal lobe
6052:
5943:
5937:
5927:
5878:
5874:
5864:
5815:
5811:
5801:
5768:
5764:
5754:
5709:
5679:(4): 304–7.
5676:
5672:
5665:
5656:
5647:
5622:
5618:
5572:
5568:
5558:
5523:
5519:
5509:
5474:
5470:
5460:
5419:
5415:
5408:
5373:
5369:
5359:
5324:
5320:
5310:
5301:
5292:
5278:
5264:
5255:
5222:
5218:
5212:
5179:
5175:
5169:
5126:
5122:
5112:
5079:
5075:
5069:
5026:
5022:
5012:
4969:
4965:
4955:
4930:10261/338716
4910:
4906:
4896:
4856:(1): 18–36.
4853:
4849:
4839:
4804:
4800:
4790:
4755:
4751:
4741:
4708:
4704:
4698:
4665:
4661:
4655:
4612:
4608:
4598:
4565:
4561:
4555:
4520:
4514:
4504:
4463:
4459:
4453:
4420:
4416:
4410:
4375:
4371:
4361:
4328:
4322:
4316:
4281:
4277:
4267:
4248:
4242:
4209:
4205:
4199:
4164:
4160:
4150:
4131:
4087:
4083:
4077:
4036:
4030:
4020:
4004:
3977:
3973:
3963:
3944:
3938:
3903:
3899:
3889:
3844:
3840:
3830:
3822:
3806:
3771:
3767:
3757:
3730:
3726:
3716:
3681:
3677:
3664:
3632:(1): 13–24.
3629:
3626:Cereb Cortex
3625:
3604:
3599:
3574:
3570:
3563:
3530:
3527:Neuroscience
3526:
3490:
3487:Cereb Cortex
3486:
3476:
3443:
3439:
3433:
3396:
3392:
3382:
3355:
3351:
3341:
3316:
3312:
3305:
3296:
3287:
3260:
3256:
3246:
3211:
3207:
3197:
3182:
3172:
3137:
3131:
3121:
3094:
3088:
3078:
3043:
3039:
3029:
3010:
2982:
2976:
2941:
2935:
2900:
2896:
2886:
2867:
2861:
2818:
2814:
2804:
2795:
2765:
2761:
2751:
2733:Neuroanatomy
2732:
2700:
2693:
2658:
2654:
2602:
2598:
2588:
2545:
2541:
2501:
2473:
2444:. Retrieved
2440:
2431:
2310:
2299:
2297:
2285:avian brains
2282:
2247:
2226:
2215:
2195:
2169:
2141:microcephaly
2134:
2114:
2110:gyrification
2075:
2059:Brain damage
2057:
2034:
2024:
1957:Broca's area
1954:
1949:frontal lobe
1930:
1878:
1861:
1855:
1841:
1832:
1828:
1788:
1761:
1745:
1726:
1723:Cortical map
1683:
1639:and related
1634:
1627:
1604:gyrification
1589:
1564:misexpressed
1525:pole, while
1485:
1479:
1451:neurogenesis
1446:
1438:
1434:
1412:
1364:
1347:
1296:
1274:neurogenesis
1267:
1235:
1228:Neurogenesis
1188:neural plate
1181:
1165:
1139:
1124:
1105:
1066:frontal lobe
1055:
1027:proisocortex
1022:
996:
977:
956:
917:
913:
911:
881:
879:
870:hippopotamus
846:
844:
823:
821:
805:
803:
793:
789:
784:
753:
751:
737:
732:
701:
697:white matter
686:
666:HE-LFB stain
662:white matter
656:showing the
576:intelligence
561:
520:frontal lobe
513:
498:gyrification
481:neurocranium
474:
471:Gyrification
451:motor cortex
448:
417:
392:motor cortex
377:
373:insular lobe
372:
337:gyrification
322:
283:
218:
214:
212:
162:A14.1.09.301
158:A14.1.09.003
146:birnlex_1494
108:
40:
7346:Archicortex
7341:Paleocortex
7008:Limbic lobe
6057:human brain
4662:Development
3416:11336/67502
3208:Cephalalgia
2821:: 120–129.
2317:Precambrian
2270:hippocampus
2258:vertebrates
1825:Motor areas
1710:Braitenberg
1680:Connections
1651:, known as
1600:Notch genes
1531:caudomedial
1433:, from the
1429:-producing
1278:progenitors
1270:radial glia
1256:Radial glia
1216:neurulation
1192:neural tube
1184:neural tube
1178:Neural tube
1156:Development
1050:hippocampus
1038:archicortex
1034:paleocortex
987:oscillation
964:minicolumns
939:cholinergic
773:glial cells
568:logarithmic
540:limbic lobe
485:hemispheric
444:minicolumns
428:human brain
388:minicolumns
365:limbic lobe
341:human brain
292:, with the
98:Identifiers
7336:Allocortex
7319:Isocortex
7265:span gyri.
6931:Interlobar
6628:3, 1 and 2
6368:Precentral
6229:Prefrontal
6195:Precentral
6081:Prefrontal
5990:NeuroNames
5225:: 355–80.
2424:References
2262:homologous
2242:See also:
2189:can cause
2173:codes for
2125:electrodes
2115:A type of
1988:cerebellum
1903:, and the
1819:homunculus
1721:See also:
1649:stem cells
1622:See also:
1614:signaling
1375:glial cell
1242:ventricles
1160:See also:
1133:, and the
1076:, and the
1007:allocortex
927:excitatory
898:brain stem
890:Betz cells
654:Micrograph
589:microgyrus
550:, and the
508:See also:
436:allocortex
367:, and the
294:allocortex
255:perception
237:and other
128:NeuroNames
7392:Betz cell
7324:Neocortex
7304:Types of
7245:Operculum
6793:41 and 42
6591:Precuneus
5919:221882004
5903:0036-8075
5856:221881862
5840:0036-8075
5785:0036-8075
5736:cite book
5728:795553723
5452:210196036
5436:0942-0940
5043:1529-2401
4986:1546-1726
4939:1097-4172
4870:1097-4172
3591:0021-9967
3374:143409890
3133:Neurology
2919:1047-3211
2266:neocortex
2254:forebrain
2216:In 1909,
2098:radiation
2090:toxicants
2071:pathogens
1645:stem cell
1618:Evolution
1535:mutations
1381:. As the
1350:dendrites
1303:glutamate
1003:neocortex
980:agranular
949:inputs".
947:lemniscal
943:brainstem
866:cetaceans
835:efferents
831:afferents
818:Layer III
767:tufts of
765:dendritic
758:GABAergic
693:pia mater
689:neocortex
643:dendrites
558:Thickness
432:neocortex
426:. In the
406:Structure
357:occipital
339:. In the
286:neocortex
279:cognition
259:awareness
251:attention
7417:Category
7207:Amygdala
7025:anterior
5962:20813265
5911:32973020
5848:32973028
5793:32973004
5771:(6511).
5693:26879631
5639:15148137
5599:22702484
5550:16738372
5501:34670843
5444:31940093
5400:11117622
5351:21653723
5247:12282525
5239:14527269
5204:10764649
5161:14807054
5153:11567107
5061:23804101
5004:27214567
4947:23622239
4888:21729779
4831:21414909
4782:22031906
4733:10764649
4682:12642494
4647:14807054
4639:11567107
4547:11466432
4496:10881759
4445:21371568
4402:22549586
4308:16014714
4234:31900267
4191:19763105
4104:11283748
4061:11217860
3996:10498281
3930:24373884
3881:19805197
3821:.Cereb.
3815:Archived
3798:14403679
3708:36706690
3700:23230908
3656:19447861
3555:17846130
3509:19188274
3425:17553419
3333:10600995
3279:11099442
3238:21911412
3189:Archived
3164:18025393
3113:17118969
3070:12946467
2968:22230626
2927:18267953
2853:27932026
2797:profile.
2792:26359774
2685:19763105
2629:27056680
2580:17580069
2370:See also
2274:amygdala
2159:such as
2100:as from
2092:such as
2045:epilepsy
2043:such as
2039:include
2028:such as
1941:temporal
1937:parietal
1854:, which
1842:executes
1840:, which
1768:thalamus
1688:and the
1686:thalamus
1667:Function
1657:proteins
1641:protomap
1576:anterior
1488:protomap
1455:primates
1443:subplate
1435:preplate
1383:G1 phase
1291:G2 phase
1116:perfuses
1048:and the
1025:and the
908:Layer VI
853:stellate
841:Layer IV
800:Layer II
785:feedback
734:Staining
724:thalamus
593:dyslexia
584:migraine
361:temporal
353:parietal
271:language
227:cerebrum
140:NeuroLex
92:Cerebrum
7238:General
6055:of the
5997:at the
5986:hier-20
5883:Bibcode
5875:Science
5820:Bibcode
5812:Science
5765:Science
5590:4060619
5541:1472723
5492:8862082
5391:1468137
5342:3174820
5184:Bibcode
5176:Science
5131:Bibcode
5123:Science
5104:3291116
5084:Bibcode
5076:Science
5052:3693057
4995:4925239
4879:3610574
4822:3093305
4773:3235689
4713:Bibcode
4705:Science
4690:6533589
4617:Bibcode
4609:Science
4590:3291116
4570:Bibcode
4562:Science
4538:6762645
4488:4203022
4468:Bibcode
4460:Science
4437:2398142
4393:4729703
4353:3291116
4333:Bibcode
4324:Science
4299:6725437
4226:4628749
4182:2913577
4069:3041502
4041:Bibcode
3921:3931000
3872:2764922
3849:Bibcode
3789:1363130
3749:9153131
3647:2792186
3547:9622234
3468:4015532
3460:8747184
3229:3512201
3155:3757544
2844:5328258
2823:Bibcode
2783:4778709
2676:2913577
2620:4868950
2571:1870400
2550:Bibcode
2362:macaque
2308:ragworm
2306:of the
2264:to the
2256:of all
2250:pallium
2212:History
2119:called
1889:putamen
1544:frontal
1459:rodents
1387:mitosis
1299:migrate
1282:neurons
1204:neurons
953:Columns
935:inhibit
876:Layer V
748:Layer I
710:in the
706:is the
681:macaque
636:⁄
494:rodents
380:neurons
349:frontal
310:cranium
263:thought
245:in the
239:mammals
229:of the
225:of the
121:D002540
88:Part of
83:Details
7364:Layers
6743:Cuneus
5970:917306
5968:
5960:
5917:
5909:
5901:
5854:
5846:
5838:
5791:
5783:
5726:
5716:
5691:
5637:
5597:
5587:
5548:
5538:
5499:
5489:
5450:
5442:
5434:
5398:
5388:
5349:
5339:
5245:
5237:
5202:
5159:
5151:
5102:
5059:
5049:
5041:
5002:
4992:
4984:
4945:
4937:
4886:
4876:
4868:
4829:
4819:
4780:
4770:
4731:
4688:
4680:
4645:
4637:
4588:
4545:
4535:
4494:
4486:
4443:
4435:
4400:
4390:
4351:
4306:
4296:
4255:
4232:
4224:
4189:
4179:
4138:
4112:893478
4110:
4102:
4067:
4059:
4032:Nature
4012:
3994:
3951:
3928:
3918:
3900:Neuron
3879:
3869:
3823:Cortex
3796:
3786:
3747:
3706:
3698:
3654:
3644:
3589:
3553:
3545:
3507:
3466:
3458:
3423:
3393:Neuron
3372:
3331:
3277:
3236:
3226:
3162:
3152:
3111:
3068:
3017:
2989:
2966:
2956:
2925:
2917:
2874:
2851:
2841:
2790:
2780:
2739:
2709:
2683:
2673:
2627:
2617:
2578:
2568:
2516:
2480:
2276:, and
2202:COL4A1
2200:, and
2187:nibrin
2102:X-rays
2051:, and
2035:Other
1990:, and
1943:, and
1899:, the
1895:, the
1891:, the
1887:, the
1856:select
1799:retina
1764:senses
1584:caudal
1582:and a
1427:reelin
1377:or an
1186:. The
1129:, the
1072:, the
1064:: the
973:Wiesel
896:, the
868:, and
790:matrix
564:shrews
546:, the
534:. The
530:, and
442:, and
329:sulcus
290:cortex
273:, and
267:memory
235:humans
7385:Cells
7202:Uncus
7190:Other
7066:gyrus
5966:S2CID
5915:S2CID
5852:S2CID
5448:S2CID
5243:S2CID
5157:S2CID
4686:S2CID
4643:S2CID
4492:S2CID
4441:S2CID
4230:S2CID
4108:S2CID
4065:S2CID
3727:Brain
3704:S2CID
3674:(PDF)
3577:(7).
3551:S2CID
3464:S2CID
3370:S2CID
3257:Brain
2446:9 May
2319:era.
2171:MCPH1
2094:drugs
1784:field
1608:Trnp1
1305:as a
1062:lobes
933:that
925:send
720:axons
625:Golgi
621:Nissl
504:Lobes
465:Folds
424:sulci
325:gyrus
231:brain
201:[
190:61830
104:Latin
59:sulci
6612:Both
6401:Both
5958:PMID
5939:Cell
5907:PMID
5899:ISSN
5844:PMID
5836:ISSN
5789:PMID
5781:ISSN
5746:link
5742:link
5724:OCLC
5714:ISBN
5689:PMID
5635:PMID
5595:PMID
5546:PMID
5497:PMID
5440:PMID
5432:ISSN
5396:PMID
5347:PMID
5235:PMID
5200:PMID
5149:PMID
5100:PMID
5057:PMID
5039:ISSN
5000:PMID
4982:ISSN
4943:PMID
4935:ISSN
4907:Cell
4884:PMID
4866:ISSN
4850:Cell
4827:PMID
4778:PMID
4729:PMID
4678:PMID
4635:PMID
4586:PMID
4543:PMID
4484:PMID
4433:PMID
4398:PMID
4349:PMID
4304:PMID
4253:ISBN
4222:PMID
4187:PMID
4136:ISBN
4100:PMID
4057:PMID
4010:ISBN
3992:PMID
3949:ISBN
3926:PMID
3877:PMID
3794:PMID
3745:PMID
3696:PMID
3652:PMID
3587:ISSN
3543:PMID
3505:PMID
3456:PMID
3421:PMID
3329:PMID
3275:PMID
3234:PMID
3160:PMID
3109:PMID
3066:PMID
3015:ISBN
2987:ISBN
2964:PMID
2954:ISBN
2923:PMID
2915:ISSN
2872:ISBN
2849:PMID
2788:PMID
2737:ISBN
2707:ISBN
2681:PMID
2625:PMID
2576:PMID
2514:ISBN
2478:ISBN
2448:2024
2397:EMX1
2300:Cell
2198:EMX2
2183:NBS1
2179:ASPM
2163:and
2076:The
2006:and
1992:pons
1976:BA22
1969:BA45
1967:and
1965:BA44
1850:and
1780:body
1774:and
1598:and
1572:Fgf8
1558:and
1546:and
1527:Emx2
1519:Pax6
1511:PAX6
1509:and
1507:EMX2
1495:FGF8
1421:and
1413:The
1339:pial
1311:GABA
1230:and
1208:glia
1206:and
1166:The
1140:The
971:and
962:and
794:core
687:The
453:and
420:gyri
386:and
359:and
213:The
178:5528
174:5527
153:TA98
116:MeSH
63:gyri
61:and
57:The
5988:at
5948:doi
5944:142
5891:doi
5879:369
5828:doi
5816:369
5773:doi
5769:369
5681:doi
5677:106
5627:doi
5585:PMC
5577:doi
5573:117
5536:PMC
5528:doi
5487:PMC
5479:doi
5424:doi
5420:162
5386:PMC
5378:doi
5374:197
5337:PMC
5329:doi
5325:106
5227:doi
5192:doi
5180:288
5139:doi
5127:294
5092:doi
5080:241
5047:PMC
5031:doi
4990:PMC
4974:doi
4925:hdl
4915:doi
4911:153
4874:PMC
4858:doi
4854:146
4817:PMC
4809:doi
4768:PMC
4760:doi
4721:doi
4709:288
4670:doi
4666:130
4625:doi
4613:294
4578:doi
4566:241
4533:PMC
4525:doi
4476:doi
4464:183
4425:doi
4421:297
4388:PMC
4380:doi
4341:doi
4329:241
4294:PMC
4286:doi
4214:doi
4210:146
4177:PMC
4169:doi
4092:doi
4049:doi
4037:409
3982:doi
3916:PMC
3908:doi
3867:PMC
3857:doi
3845:106
3784:PMC
3776:doi
3772:148
3735:doi
3731:120
3686:doi
3642:PMC
3634:doi
3579:doi
3575:532
3535:doi
3495:doi
3448:doi
3411:hdl
3401:doi
3360:doi
3321:doi
3265:doi
3261:123
3224:PMC
3216:doi
3150:PMC
3142:doi
3099:doi
3056:hdl
3048:doi
2946:doi
2905:doi
2839:PMC
2831:doi
2778:PMC
2770:doi
2671:PMC
2663:doi
2615:PMC
2607:doi
2566:PMC
2558:doi
2506:doi
2283:In
1612:SHH
1596:FGF
1556:FGF
1385:of
1289:or
916:or
233:in
185:FMA
169:TA2
7419::
7146:30
7141:29
7136:26
7129::
7118:31
7113:23
7101:33
7096:32
7091:24
7079:25
6915:20
6896:36
6891:35
6886:34
6881:28
6876:27
6864:37
6836:21
6810:22
6805:38
6736:17
6703:19
6698:18
6539:43
6523:39
6514:40
6344:25
6332:10
6320:12
6315:11
6310:10
6294:11
6282:12
6167:45
6158:44
6144:47
6139:11
6137::
6126:46
6121:10
5964:.
5956:.
5942:.
5936:.
5913:.
5905:.
5897:.
5889:.
5877:.
5873:.
5850:.
5842:.
5834:.
5826:.
5814:.
5810:.
5787:.
5779:.
5767:.
5763:.
5738:}}
5734:{{
5722:.
5701:^
5687:.
5675:.
5655:.
5633:.
5623:61
5621:.
5607:^
5593:.
5583:.
5571:.
5567:.
5544:.
5534:.
5524:99
5522:.
5518:.
5495:.
5485:.
5475:93
5473:.
5469:.
5446:.
5438:.
5430:.
5418:.
5394:.
5384:.
5372:.
5368:.
5345:.
5335:.
5323:.
5319:.
5241:.
5233:.
5223:26
5221:.
5198:.
5190:.
5178:.
5155:.
5147:.
5137:.
5125:.
5121:.
5098:.
5090:.
5078:.
5055:.
5045:.
5037:.
5027:33
5025:.
5021:.
4998:.
4988:.
4980:.
4970:19
4968:.
4964:.
4941:.
4933:.
4923:.
4909:.
4905:.
4882:.
4872:.
4864:.
4852:.
4848:.
4825:.
4815:.
4805:31
4803:.
4799:.
4776:.
4766:.
4756:31
4754:.
4750:.
4727:.
4719:.
4707:.
4684:.
4676:.
4664:.
4641:.
4633:.
4623:.
4611:.
4607:.
4584:.
4576:.
4564:.
4541:.
4531:.
4521:21
4519:.
4513:.
4490:.
4482:.
4474:.
4462:.
4439:.
4431:.
4419:.
4396:.
4386:.
4374:.
4370:.
4347:.
4339:.
4327:.
4302:.
4292:.
4282:25
4280:.
4276:.
4228:.
4220:.
4208:.
4185:.
4175:.
4165:10
4163:.
4159:.
4120:^
4106:.
4098:.
4086:.
4063:.
4055:.
4047:.
4035:.
3990:.
3976:.
3972:.
3924:.
3914:.
3904:81
3902:.
3898:.
3875:.
3865:.
3855:.
3843:.
3839:.
3792:.
3782:.
3770:.
3766:.
3743:.
3729:.
3725:.
3702:.
3694:.
3682:55
3680:.
3676:.
3650:.
3640:.
3630:20
3628:.
3624:.
3612:^
3585:.
3573:.
3549:.
3541:.
3531:85
3529:.
3517:^
3503:.
3491:19
3489:.
3485:.
3462:.
3454:.
3444:71
3442:.
3419:.
3409:.
3397:54
3395:.
3391:.
3368:.
3354:.
3350:.
3327:.
3315:.
3295:.
3273:.
3259:.
3255:.
3232:.
3222:.
3212:31
3210:.
3206:.
3187:.
3181:.
3158:.
3148:.
3138:69
3136:.
3130:.
3107:.
3095:17
3093:.
3087:.
3064:.
3054:.
3042:.
3038:.
3001:^
2962:.
2952:.
2921:.
2913:.
2901:18
2899:.
2895:.
2847:.
2837:.
2829:.
2819:58
2817:.
2813:.
2794:.
2786:.
2776:.
2766:31
2764:.
2760:.
2721:^
2679:.
2669:.
2659:10
2657:.
2653:.
2637:^
2623:.
2613:.
2603:35
2601:.
2597:.
2574:.
2564:.
2556:.
2546:17
2544:.
2540:.
2528:^
2512:.
2492:^
2456:^
2439:.
2295:.
2272:,
2268:,
2224:.
2167:.
2151:.
2143:,
2112:.
2073:.
2047:,
1994:.
1986:,
1963:,
1939:,
1786:.
1743:.
1663:.
1465:.
1397:.
1345:.
1110:.
1068:,
984:Hz
864:,
837:.
730:.
595:.
554:.
526:,
522:,
500:.
375:.
355:,
351:,
281:.
269:,
265:,
261:,
257:,
253:,
176:,
142:ID
133:39
7297:e
7290:t
7283:v
7064:/
6820:)
6816:(
6812:/
6786:/
6652:7
6640:5
6621:/
6596:7
6584:5
6579:3
6574:2
6569:1
6525:-
6516:-
6502:7
6497:5
6461:8
6449:6
6437:6
6425:6
6413:4
6381:4
6303:/
6275:/
6264:9
6259:8
6247:6
6242:4
6169:-
6160:-
6146:-
6116:9
6104:8
6099:6
6094:4
6044:e
6037:t
6030:v
5972:.
5950::
5921:.
5893::
5885::
5858:.
5830::
5822::
5795:.
5775::
5748:)
5730:.
5695:.
5683::
5659:.
5641:.
5629::
5601:.
5579::
5552:.
5530::
5503:.
5481::
5454:.
5426::
5402:.
5380::
5353:.
5331::
5286:.
5272:.
5249:.
5229::
5206:.
5194::
5186::
5163:.
5141::
5133::
5106:.
5094::
5086::
5063:.
5033::
5006:.
4976::
4949:.
4927::
4917::
4890:.
4860::
4833:.
4811::
4784:.
4762::
4735:.
4723::
4715::
4692:.
4672::
4649:.
4627::
4619::
4592:.
4580::
4572::
4549:.
4527::
4498:.
4478::
4470::
4447:.
4427::
4404:.
4382::
4376:3
4355:.
4343::
4335::
4310:.
4288::
4261:.
4236:.
4216::
4193:.
4171::
4144:.
4114:.
4094::
4088:2
4071:.
4051::
4043::
3998:.
3984::
3978:9
3957:.
3932:.
3910::
3883:.
3859::
3851::
3800:.
3778::
3751:.
3737::
3710:.
3688::
3658:.
3636::
3593:.
3581::
3557:.
3537::
3511:.
3497::
3470:.
3450::
3427:.
3413::
3403::
3376:.
3362::
3356:1
3335:.
3323::
3317:9
3281:.
3267::
3240:.
3218::
3166:.
3144::
3115:.
3101::
3072:.
3058::
3050::
3044:7
3023:.
2995:.
2970:.
2948::
2929:.
2907::
2880:.
2855:.
2833::
2825::
2772::
2745:.
2715:.
2687:.
2665::
2631:.
2609::
2582:.
2560::
2552::
2522:.
2508::
2486:.
2450:.
1287:S
1102:.
1052:.
683:)
668:.
638:2
634:1
631:+
629:1
205:]
38:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.