215:. The Duilong has hydro-electrical power generation capacity of 4,000 KW. The non-monsoon season lasts from October to May each year, and the monsoon season from June to October. 80% of the precipitation is in the monsoon season, when warm and moist air is transported to the Tibet Plateau from the south Indian Ocean.
29:
275:
A 1995 paper concluded that proposed
Yangjinshi Reservoir would provide a good balance between the conflicting demands for irrigation and hydroelectric power generation. It could not be built in the lower reaches, where the river is paralleled by the Qinghai-Xizang Road, or in the middle reach where
254:
The southern
Tibetan Plateau is tectonically active, and contains many geothermal springs. Although rivers in Tibet are generally considered to be clean, the water of the Duilong is affected by these springs. A 2015 study reported that during the non-monsoon season the levels of
210:
The
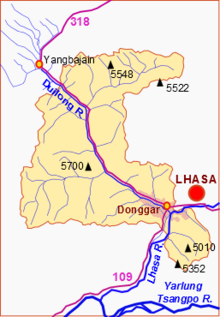
Duilong is the largest tributary of the Lhasa River, with a length of 137 kilometres (85 mi) and a basin area of 4,988 square kilometres (1,926 sq mi). The valley of the Duilong River leads south to the Lhasa River, and is contained by two ridges of the
276:
it would cover the
Yangbajain geothermal field. The chosen location was therefore upstream, controlling a catchment area of 1,580 square kilometres (610 sq mi) with an annual normal runoff of 394,000,000 cubic metres (1.39
406:
202:, Tibet, China. The river is about 137 kilometres (85 mi) in length. Water quality may be compromised by dissolved substances including arsenic from geothermal springs.
280:
10 cu ft). If the water level were maintained at 4,360 metres (14,300 ft) above sea level, the reservoir would have a capacity of 81,000,000 cubic metres (2.9
284:
10 cu ft) including available storage of 19,000,000 cubic metres (670,000,000 cu ft). The project would include a 4500 kW power station.
538:
543:
500:
94:
187:
390:
264:
212:
64:
34:
219:
533:
465:
Modelling and
Management of Sustainable Basin-scale Water Resource Systems (Proceedings of a Boulder Symposium)
246:
river to link the station in Liuwu township on the south side of the river to central Lhasa on the north side.
432:
Li, Chaoliu; Kang, Shichang; Chen, Pengfei; Zhang, Qianggong; Mi, Jue; Gao, Shaopeng; Sillanpää, Mika (2013).
548:
263:
guideline of 10 μg/L for drinking water. The source of the pollution seems to be untreated water from the
179:
434:"Geothermal spring causes arsenic contamination in river waters of the southern Tibetan Plateau, China"
433:
28:
508:
501:"Pollution of Geothermal Wastewater Produced by Tibet Yangbajin Geothermal Power Station"
457:
267:
power station. It can be detected 90 kilometres (56 mi) downstream from this site.
239:
171:
148:
60:
407:"Rural Urbanization in China's Tibetan Region: Duilongdeq County as a Typical Example"
527:
472:
Ye, Aizhong; Duan, Qingyun; Zeng, Hongjuan; Li, Lin; Wang, Caiyun (September 2010).
473:
223:
195:
154:
77:
235:
336:
109:
96:
474:"A Distributed Time-Variant Gain Hydrological Model Based on Remote Sensing"
458:"Research on the rational use of water resources on the Lhasa River, Tibet"
231:
256:
227:
243:
199:
50:
242:
county into west Lhasa. A new railway bridge was built over the
260:
391:"China Strives to Complete Gormo-Lhasa railroad by October"
222:
approaches Lhasa from the northwest. It descends from the
146:
141:
133:
125:
86:
76:
71:
56:
46:
41:
21:
259:in the river, at 205.6 μg/L were higher than the
337:China Strives to Complete Gormo-Lhasa railroad..
348:
324:
8:
393:. Central Tibetan Administration. 2005-04-16
300:
499:Zhang, Tianhua; Huang, Qiongzhong (1997).
360:
234:, and then follows the Toelung River from
27:
198:, which it enters just below the city of
293:
18:
137:4,988 km (1,926 sq mi)
7:
539:Tributaries of the Brahmaputra River
372:
312:
33:Sketch map of the Duilong River and
414:Chinese Sociology and Anthropology
14:
481:Journal of Resources and Ecology
194:), is a right tributary of the
191:
88: • coordinates
1:
505:Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae
72:Physical characteristics
438:Environmental Earth Sciences
265:Yangbajain Geothermal Field
213:Nianqing Tanggula Mountains
565:
456:Shen, Dajun (July 1995).
175:
26:
405:Ge, Le; Li, Tao (1996).
129:137 km (85 mi)
110:29.619711°N 91.010815°E
361:Zhang & Huang 1997
544:Doilungdêqên District
220:Qinghai–Tibet Railway
65:Doilungdêqên District
35:Doilungdêqên District
16:River in Lhasa, Tibet
271:Yangjinshi Reservoir
115:29.619711; 91.010815
142:Basin features
106: /
160:
159:
556:
519:
517:
516:
507:. Archived from
495:
493:
492:
478:
468:
462:
452:
450:
449:
428:
426:
425:
411:
401:
399:
398:
376:
370:
364:
358:
352:
346:
340:
334:
328:
322:
316:
313:Ge & Li 1996
310:
304:
298:
283:
279:
193:
177:
151:
121:
120:
118:
117:
116:
111:
107:
104:
103:
102:
99:
31:
19:
564:
563:
559:
558:
557:
555:
554:
553:
534:Rivers of Lhasa
524:
523:
522:
514:
512:
498:
490:
488:
476:
471:
460:
455:
447:
445:
431:
423:
421:
409:
404:
396:
394:
389:
385:
380:
379:
371:
367:
359:
355:
351:, p. 4143.
347:
343:
335:
331:
327:, p. 4144.
323:
319:
311:
307:
299:
295:
290:
281:
277:
273:
252:
208:
147:
114:
112:
108:
105:
100:
97:
95:
93:
92:
89:
37:
17:
12:
11:
5:
562:
560:
552:
551:
549:Damxung County
546:
541:
536:
526:
525:
521:
520:
496:
469:
453:
429:
402:
386:
384:
381:
378:
377:
375:, p. 155.
365:
353:
349:Li et al. 2013
341:
329:
325:Li et al. 2013
317:
305:
303:, p. 226.
301:Ye et al. 2010
292:
291:
289:
286:
272:
269:
251:
248:
240:Toelung Dechen
226:grasslands to
207:
204:
158:
157:
152:
144:
143:
139:
138:
135:
131:
130:
127:
123:
122:
90:
87:
84:
83:
80:
74:
73:
69:
68:
61:Damxung County
58:
54:
53:
48:
44:
43:
39:
38:
32:
24:
23:
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
561:
550:
547:
545:
542:
540:
537:
535:
532:
531:
529:
511:on 2015-02-10
510:
506:
502:
497:
486:
482:
475:
470:
466:
459:
454:
443:
439:
435:
430:
419:
415:
408:
403:
392:
388:
387:
382:
374:
369:
366:
362:
357:
354:
350:
345:
342:
338:
333:
330:
326:
321:
318:
315:, p. 35.
314:
309:
306:
302:
297:
294:
287:
285:
270:
268:
266:
262:
258:
250:Water quality
249:
247:
245:
241:
237:
233:
229:
225:
221:
216:
214:
205:
203:
201:
197:
189:
185:
184:stod lung chu
181:
173:
169:
165:
164:Duilong River
156:
153:
150:
145:
140:
136:
132:
128:
124:
119:
91:
85:
81:
79:
75:
70:
66:
62:
59:
55:
52:
49:
45:
40:
36:
30:
25:
22:Duilong River
20:
513:. Retrieved
509:the original
504:
489:. Retrieved
484:
480:
464:
446:. Retrieved
441:
437:
422:. Retrieved
417:
413:
395:. Retrieved
368:
356:
344:
332:
320:
308:
296:
274:
253:
217:
209:
183:
167:
163:
161:
149:River system
196:Lhasa River
176:སྟོད་ལུང་ཆུ
155:Lhasa River
113: /
528:Categories
515:2015-02-10
491:2015-02-10
448:2015-02-10
424:2015-02-10
397:2015-02-10
288:References
236:Yangpachen
170:(Toelung,
168:Duilong Qu
134:Basin size
101:91°00′39″E
98:29°37′11″N
373:Shen 1995
238:through
232:Damshung
57:Location
42:Location
467:. IAHS.
383:Sources
257:arsenic
188:Chinese
172:Tibetan
67:, Lhasa
47:Country
228:Nagchu
206:Course
190::
126:Length
82:
477:(PDF)
461:(PDF)
410:(PDF)
244:Lhasa
200:Lhasa
180:Wylie
166:, or
78:Mouth
51:Tibet
230:and
224:Amdo
218:The
162:The
487:(3)
444:(9)
420:(4)
261:WHO
192:堆龙河
530::
503:.
483:.
479:.
463:.
442:71
440:.
436:.
418:28
416:.
412:.
186:;
182::
178:,
174::
63:,
518:.
494:.
485:1
451:.
427:.
400:.
363:.
339:.
282:×
278:×
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.