26:
345:
Morse AT, Murphy KD, Nigoghossian E, Okach L, Oommachen S, Reyes R, Rife CL, Schimmel P, Trout CV, van den Bedem H, Weekes D, White A, Xu Q, Hodgson KO, Wooley J, Deacon AM, Godzik A, Lesley SA, Wilson IA (November 2007). "Identification and structural characterization of heme binding in a novel dye-decolorizing peroxidase, TyrA".
301:
AT, Nigoghossian E, Okach L, Oommachen S, Reyes R, Rife CL, Schimmel P, van den Bedem H, Weekes D, White A, Xu Q, Hodgson KO, Wooley J, Deacon AM, Godzik A, Lesley SA, Wilson IA (November 2007). "Crystal structures of two novel dye-decolorizing peroxidases reveal a beta-barrel fold with a conserved heme-binding motif".
344:
Zubieta C, Joseph R, Krishna SS, McMullan D, Kapoor M, Axelrod HL, Miller MD, Abdubek P, Acosta C, Astakhova T, Carlton D, Chiu HJ, Clayton T, Deller MC, Duan L, Elias Y, Elsliger MA, Feuerhelm J, Grzechnik SK, Hale J, Han GW, Jaroszewski L, Jin KK, Klock HE, Knuth MW, Kozbial P, Kumar A, Marciano D,
300:
Zubieta C, Krishna SS, Kapoor M, Kozbial P, McMullan D, Axelrod HL, Miller MD, Abdubek P, Ambing E, Astakhova T, Carlton D, Chiu HJ, Clayton T, Deller MC, Duan L, Elsliger MA, Feuerhelm J, Grzechnik SK, Hale J, Hampton E, Han GW, Jaroszewski L, Jin KK, Klock HE, Knuth MW, Kumar A, Marciano D, Morse
223:
conditions compared with the other plant peroxidases. In terms of substrate specificity, DyP degrades the typical peroxidase substrates, but also degrades hydroxyl-free
118:
390:"DyP, a unique dye-decolorizing peroxidase, represents a novel heme peroxidase family: ASP171 replaces the distal histidine of classical peroxidases"
181:
peroxidases. The DyP (for dye de-colourising peroxidase) family constitutes a novel class of haem peroxidase. Because these
138:
198:
194:
30:
crystal structure of a dye-decolorizing peroxidase (dyp) from bacteroides thetaiotaomicron vpi-5482 at 1.6 a resolution
253:
domain likely to be related by a duplication of an ancestral gene, as inferred from the conserved topology of the
449:
283:
histidine used by plant peroxidases. This Asp substitution helps explain why the DyP family is active at low pH.
126:
219:
specificity, a lack of homology to most other peroxidases, and the ability to function well under much lower
215:
have several characteristics that distinguish them from all other peroxidases, including a particularly wide
122:
193:
similarity to classical fungal peroxidases, such as LiP and MnP, and does not contain the conserved
370:
326:
265:
190:
189:
related to the class II secretory fungal peroxidases. However, the DyP family exhibits only low
411:
362:
318:
230:
113:
401:
354:
310:
216:
105:
238:
234:
155:
254:
443:
224:
374:
54:
330:
276:
186:
101:
67:
435:
79:
272:
250:
246:
201:
162:
280:
268:
415:
406:
389:
366:
322:
173:
peroxidases (which are subdivided into class I, II and III), which include
25:
431:
205:
178:
74:
358:
314:
242:
212:
158:
388:
Sugano Y, Muramatsu R, Ichiyanagi A, Sato T, Shoda M (December 2007).
182:
174:
166:
133:
185:
were derived from fungal sources, the DyP family was thought to be
170:
427:
261:
258:
95:
61:
49:
165:
were originally divided into two superfamilies, namely, the
220:
426:
This article incorporates text from the public domain
264:
is penta-coordinated, with the protein contributing a
227:(many dyes are derived from anthraquinone compounds).
208:
found in other plant peroxidase superfamily members.
132:
112:
94:
89:
73:
60:
48:
40:
35:
18:
8:
86:
24:
405:
292:
271:ligand to the iron centre. A conserved
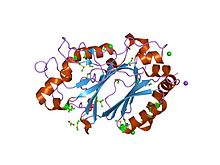
237:, each one adopting a ferredoxin-like
15:
279:/acceptor and takes the place of the
7:
14:
233:of DyP family members reveal two
1:
90:Available protein structures:
466:
425:
150:In molecular biology, the
19:Dyp-type peroxidase family
85:
23:
407:10.1074/jbc.M706996200
275:most likely acts as a
154:family is a family of
169:peroxidases and the
152:DyP-type peroxidase
359:10.1002/prot.21673
315:10.1002/prot.21550
231:Crystal structures
204:and an essential
148:
147:
144:
143:
139:structure summary
457:
450:Protein families
420:
419:
409:
385:
379:
378:
341:
335:
334:
297:
87:
28:
16:
465:
464:
460:
459:
458:
456:
455:
454:
440:
439:
438:
424:
423:
400:(50): 36652–8.
387:
386:
382:
343:
342:
338:
299:
298:
294:
289:
177:(class II) and
156:haem peroxidase
31:
12:
11:
5:
463:
461:
453:
452:
442:
441:
422:
421:
380:
336:
291:
290:
288:
285:
245:consist of an
146:
145:
142:
141:
136:
130:
129:
116:
110:
109:
99:
92:
91:
83:
82:
77:
71:
70:
65:
58:
57:
52:
46:
45:
42:
38:
37:
33:
32:
29:
21:
20:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
462:
451:
448:
447:
445:
437:
433:
429:
417:
413:
408:
403:
399:
395:
394:J. Biol. Chem
391:
384:
381:
376:
372:
368:
364:
360:
356:
353:(2): 234–43.
352:
348:
340:
337:
332:
328:
324:
320:
316:
312:
309:(2): 223–33.
308:
304:
296:
293:
286:
284:
282:
278:
274:
270:
267:
263:
260:
256:
252:
249:domain and a
248:
244:
240:
236:
232:
228:
226:
225:anthraquinone
222:
218:
214:
209:
207:
203:
200:
196:
192:
188:
184:
180:
176:
172:
168:
164:
160:
157:
153:
140:
137:
135:
131:
128:
124:
120:
117:
115:
111:
107:
103:
100:
97:
93:
88:
84:
81:
78:
76:
72:
69:
66:
63:
59:
56:
53:
51:
47:
43:
39:
34:
27:
22:
17:
397:
393:
383:
350:
346:
339:
306:
302:
295:
277:proton donor
229:
210:
187:structurally
151:
149:
163:peroxidases
36:Identifiers
287:References
251:C-terminal
247:N-terminal
202:histidines
102:structures
436:IPR006314
281:catalytic
269:histidine
266:conserved
217:substrate
179:bacterial
80:IPR006314
44:Dyp_perox
444:Category
432:InterPro
416:17928290
375:24489389
367:17654547
347:Proteins
323:17654545
303:Proteins
243:proteins
213:proteins
206:arginine
195:proximal
191:sequence
119:RCSB PDB
75:InterPro
331:2845167
255:domains
235:domains
183:enzymes
161:. Haem
159:enzymes
55:PF04261
414:
373:
365:
329:
321:
257:. The
241:. The
199:distal
175:fungal
167:animal
134:PDBsum
108:
98:
68:CL0032
41:Symbol
371:S2CID
327:S2CID
171:plant
430:and
428:Pfam
412:PMID
363:PMID
319:PMID
262:iron
259:haem
239:fold
211:DyP
197:and
127:PDBj
123:PDBe
106:ECOD
96:Pfam
64:clan
62:Pfam
50:Pfam
402:doi
398:282
355:doi
311:doi
273:Asp
114:PDB
446::
434::
410:.
396:.
392:.
369:.
361:.
351:69
349:.
325:.
317:.
307:69
305:.
221:pH
125:;
121:;
104:/
418:.
404::
377:.
357::
333:.
313::
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.