272:(typically, 120 ohms for twisted pairs). The termination also includes pull up and pull down resistors to establish bias for each data wire for the case when the lines are not being driven by any device. This way, the lines will be biased to known voltages and nodes will not interpret the noise from undriven lines as actual data; without biasing resistors, the data lines float in such a way that electrical noise sensitivity is greatest when all device stations are silent or unpowered.
446:
249:
2221:
303:
points (signal lines); A, B and C. The data is transmitted on A and B. C is a ground reference. This section also defines the logic states 1 (off) and 0 (on), by the polarity between A and B terminals. If A is negative with respect to B, the state is binary 1. The reversed polarity (A positive with respect to B) is binary 0. The standard does not assign any logic function to the two states.
653:
245:, or multiply connected network. Star and ring topologies are not recommended because of signal reflections or excessively low or high termination impedance. If a star configuration is unavoidable, special RS-485 repeaters are available which bidirectionally listen for data on each span and then retransmit the data onto all other spans.
284:), but the EIA-TIA officially replaced "RS" with "EIA/TIA" to help identify the origin of its standards. The EIA has officially disbanded and the standard is now maintained by the TIA as TIA-485, but engineers and applications guides continue to use the RS-485 designation. The initial edition of EIA RS-485 was dated April 1983.
437:; merely an electrical interface. Although many applications use RS-485 signal levels, the speed, format, and protocol of the data transmission are not specified by RS-485. Interoperability of even similar devices from different manufacturers is not assured by compliance with the signal levels alone.
302:
Section 4 defines the electrical characteristics of the generator (transmitter or driver), receiver, transceiver, and system. These characteristics include: definition of a unit load, voltage ranges, open-circuit voltages, thresholds, and transient tolerance. It also defines three generator interface
581:
RS-485 standard conformant drivers provide a differential output of a minimum 1.5 V across a 54-Ω load, whereas standard conformant receivers detect a differential input down to 200 mV. The two values provide a sufficient margin for a reliable data transmission even under severe signal degradation
610:
that can be impressed on the receiver inputs. The allowable common-mode voltage is in the range −7 V to +12 V, i.e. ±7 V on top of the 0–5 V signal range. Failure to stay within this range will result in, at best, signal corruption, and, at worst, damage to connected devices.
569:
These manufacturers all agree on the meaning of the standard, and their practice is in widespread use. The issue also exists in programmable logic controller applications. Care must be taken when using A/B naming. Alternate nomenclature is often used to avoid confusion surrounding the A/B naming:
390:
in their line of industrial control units. Utilizing a series of dedicated interface devices, it allows PCs and industrial controllers to communicate. Since it is differential, it resists electromagnetic interference from motors and welding equipment.
232:
using only two wires. The equipment located along a set of RS-485 wires are interchangeably called nodes, stations or devices. The recommended arrangement of the wires is as a connected series of point-to-point (multidropped) nodes, i.e. a line or
966:"EIA Standard RS 485 Electrical Characteristics of Generators and Receivers for Use in Balanced Digital Multipoint Systems", reproduced in " Data Communications Standards LibraryÈ, Telebyte Technology Inc., Greenlawn, New York 1985.
409:
as the simple bus wiring and long cable length is ideal for joining remote devices. It may be used to control video surveillance systems or to interconnect security control panels and devices such as access control card readers.
618:
to the SC connection. Grounds between buildings may vary by a small voltage, but with very low impedance and hence the possibility of catastrophic currents – enough to melt signal cables, PCB traces, and transceiver devices.
533:
The truth tables of most popular devices, starting with the SN75176, show the output signals inverted. This is in accordance with the A/B naming used by most differential transceiver manufacturers, including:
252:
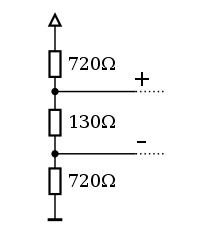
Typical bias network together with termination. Biasing and termination values are not specified in the RS-485 standard. However, bias resistors are commonly not recommended any more by component suppliers.
746:
wire, in the definition of the D-sub connector and M12 circular connector, as can be seen in
Profibus guides. As long as standard excludes logic function of the generator or receiver, it would make sense
593:
connections, an optional, third connection may be present (the TIA standard requires the presence of a common return path between all circuit grounds along the balanced line for proper operation) called
1397:
2248:
315:
by using four wires. Since RS-485 is a multi-point specification, however, this is not necessary or desirable in many cases. RS-485 and RS-422 can interoperate with certain restrictions.
1105:
633:
The standard does not discuss cable shielding but makes some recommendations on preferred methods of interconnecting the signal reference common and equipment case grounds.
614:
Care must be taken that an SC connection, especially over long cable runs, does not result in an attempt to connect disparate grounds together – it is wise to add some
1020:
421:. The external interface to the DCC command station is often RS-485 used by hand-held controllers or for controlling the layout in a networked PC environment.
1231:
645:
of the A (blue) and B (red) pins of an RS-485 line before, during, and after transmission of one byte (0xD3, least significant bit first) of data using an
1661:
2189:
1044:
1818:
1127:"Data Sheet FN6074.3: ±15kV ESD Protected, 1/8 Unit Load, 5V, Low Power, High Speed and Slew Rate Limited, Full Duplex, RS-485/RS-422 Transceivers"
1681:
158:
582:
across the cable and connectors. This robustness is the main reason why RS-485 is well suited for long-distance networking in noisy environment.
1488:
351:
for data transmission between a controller and a disk drive. RS-485 is used for low-speed data communications in commercial aircraft cabins'
1869:
1540:
264:
off the unterminated end of the cable can cause data corruption. Termination resistors also reduce electrical noise sensitivity due to the
2216:
Interfaces are listed by their speed in the (roughly) ascending order, so the interface at the end of each section should be the fastest.
70:
1922:
1761:
1691:
998:
2258:
1751:
606:, the common signal reference ground used by the receiver to measure the A and B voltages. This connection may be used to limit the
335:
very large RS-485 networks can be formed. TSB-89A, Application
Guidelines for TIA/EIA-485-A does not recommend using star topology.
782:
in drivers and line labeling as can be read in a section of an application bulletin: "Design
Consideration #3: Sometimes Bus Node
1849:
1175:
770:
at a higher voltage in
Profibus guidelines. That so-called 'Pesky Polarity' problem raised confusion which made authors think
1353:
1077:
976:
1641:
162:
835:
145:, is a standard, originally introduced in 1983, defining the electrical characteristics of drivers and receivers for use in
2193:
1844:
1813:
1261:
1203:
1182:
1155:"Data Sheet 19-0122 – MAX481/MAX483/MAX485/MAX487–MAX491/MAX1487: Low-Power, Slew-Rate-Limited RS-485/RS-422 Transceivers"
359:
166:
1791:
1126:
363:
299:
which contains application guidelines, including data signaling rate vs. cable length, stub length, and configurations.
165:(TIA/EIA). Digital communications networks implementing the standard can be used effectively over long distances and in
2117:
2056:
1911:
1575:
1224:
312:
295:; Other standards define the protocols for communication over an RS-485 link. The foreword to the standard references
547:, as seen in their data sheet for the MAX483 transceiver and for the new generation 3.3v micro controller the MAX3485
1716:
1481:
709:. It is clear in the figure that follows that the off state corresponds to binary 1 and on corresponds to binary 0.
367:
1771:
174:
269:
190:
2224:
2199:
2091:
1746:
1466:
879:
Soltero, Manny; Zhang, Jing; Cockril, Chris; Zhang, Kevin; Kinnaird, Clark; Kugelstadt, Thomas (May 2010) .
646:
414:
394:
In theatre and performance venues, RS-485 networks are used to control lighting and other systems using the
292:
154:
1452:
1052:
2253:
1781:
790:". It is now a common design decision to make this inversion which involves the following polarity chain:
434:
422:
194:
2243:
2045:
1998:
1854:
1626:
1474:
668:
2041:
1894:
1776:
1210:
1133:
795:
281:
257:
146:
1953:
1508:
1048:
406:
229:
224:
In contrast to RS-422, which has a driver circuit which cannot be switched off, RS-485 drivers use
529:
For an on, space or logic 0 state, the driver's A terminal is positive relative to the B terminal.
526:
For an off, mark or logic 1 state, the driver's A terminal is negative relative to the B terminal.
343:
RS-485 signals are used in a wide range of computer and automation systems. In a computer system,
1497:
861:
642:
607:
1308:
514:(logic 1) condition is traditionally represented (e.g. in RS-232) with a negative voltage; and
1943:
1565:
1501:
1112:
935:
910:
890:
693:
550:
328:
261:
225:
907:
Electrical
Characteristics of Generators and Receivers for Use in Balanced Multipoint Systems
1676:
1418:
1414:
1161:
615:
544:
355:. It requires minimal wiring and can share the wiring among several seats, reducing weight.
287:
RS-485 only specifies the electrical characteristics of the generator and the receiver: the
1806:
1656:
1636:
1511:
1154:
1081:
949:
705:
There is an apparent typo in this statement as both states in the standard are designated
445:
1426:
2107:
1801:
1726:
1651:
1555:
1530:
1459:
627:
623:
556:
515:
511:
348:
288:
265:
248:
2237:
2179:
2066:
1958:
1906:
1889:
1671:
1570:
1560:
1535:
418:
387:
213:, the speed in bit/s multiplied by the length in meters should not exceed 10. Thus a
210:
186:
170:
74:
60:
1186:
228:
allowing individual transmitters to be deactivated. This allows RS-485 to implement
1916:
1859:
1711:
1616:
1434:
1073:
880:
242:
238:
198:
1367:
882:
RS-422 and RS-485 Standards
Overview and System Configurations, Application Report
1415:"Tutorial 763: Guidelines for Proper Wiring of an RS-485 (TIA/EIA-485-A) Network"
1092:
844:
205:. It is generally accepted that RS-485 can be used with data rates up to 10
2184:
2163:
2086:
2081:
1926:
1864:
1839:
1766:
1550:
1545:
559:, as seen in their datasheet for the ADM3483, ADM3485, ADM3488, ADM3490, ADM3491
352:
234:
78:
1322:
928:
622:
RS-485 does not specify any connector or pinout. Circuits may be terminated on
2037:
1736:
1525:
774:
is inverting within the TIA-485-A standard itself and advise to swap what is
652:
1278:
1137:
2061:
2051:
2018:
2013:
1948:
1823:
1611:
1596:
1591:
914:
1000:
What is the difference between RS422 communication and RS485 communication?
1337:"Application Bulletin AB-19, Profibus Compliance: A Hardware Design Guide"
2071:
2008:
1741:
1601:
953:
862:"How Far and How Fast Can You Go with RS-485? - Application Note – Maxim"
727:
538:
375:
332:
150:
1336:
1095:, "BiDiBus, a Highspeed-Bus for model-railways", accessed July 26, 2015.
209:
or, at lower speeds, distances up to 1,200 m (4,000 ft). As a
2204:
2158:
2142:
1968:
1786:
1731:
1666:
1621:
362:
and on factory floors. RS-485 is used as the physical layer underlying
206:
268:. The value of each termination resistor should be equal to the cable
17:
2137:
2028:
2003:
1988:
1983:
1978:
1796:
1686:
1646:
1606:
1453:"Application Note AN-960: RS-485/RS-422 Circuit Implementation Guide"
723:
719:
522:
signal and B as inverting. The RS-485 standard states (paraphrased):
395:
371:
324:
202:
169:. Multiple receivers may be connected to such a network in a linear,
2122:
2033:
1293:
1246:
518:(logic 0) represented with a positive one, A may be considered the
2132:
2023:
1963:
1901:
1874:
1756:
1706:
1631:
651:
444:
247:
755:(red, positive). However this contradicts the facts that an idle
2127:
2112:
1973:
1884:
1879:
1721:
791:
673:
562:
399:
344:
157:
systems are supported. The standard is jointly published by the
1470:
260:
connected across the two wires. Without termination resistors,
2076:
1701:
1696:
1176:"LTC2850/LTC2851/LTC2852 3.3V 20Mbps RS485/RS422 Transceivers"
553:, as seen in their datasheet for the LTC2850, LTC2851, LTC2852
929:"Application Note 847 FAILSAFE Biasing of Differential Buses"
280:
The EIA once labeled all its standards with the prefix "RS" (
574:
TX+/RX+ or D+ as alternative for B (high for mark i.e. idle)
577:
TX−/RX− or D− as alternative for A (low for mark i.e. idle)
347:-2 and SCSI-3 may use this specification to implement the
565:, as seen in their datasheet for the USB-RS485-WE-1800-BT
541:, as seen in their data sheet for the ISL4489 transceiver
1354:"White paper: Polarities for Differential Pair Signals"
493:
The RS-485 differential line consists of two signals:
810:, the green wire, is indeed connected to the driver
500:, which is low for logic 1 and high for logic 0 and,
398:
protocol. RS-485 serves as a physical layer for the
2172:
2151:
2100:
1936:
1832:
1584:
1518:
1410:- The Standard for sale from the current publisher.
124:
116:
100:
92:
84:
66:
56:
51:
39:
32:
1292:
1245:
1204:"ADM3483/ADM3485/ADM3488/ADM3490/ADM3491 (Rev. E)"
364:many standard and proprietary automation protocols
1022:TSB-89A, Application Guidelines for TIA/EIA-485-A
386:is a proprietary communications protocol used by
2249:Telecommunications-related introductions in 1998
1447:– Practical information about implementing RS485
1297:. 1.4. P International. January 2007. p. 8.
1250:. 1.4. P International. January 2007. p. 7.
506:, which is high for logic 1 and low for logic 0.
1819:Coherent Accelerator Processor Interface (CAPI)
1225:"USB to RS485 Serial Converter Cable Datasheet"
1045:"DH-485 Industrial Local Area Network Overview"
256:Ideally, the two ends of the cable will have a
1309:"RS-485 Technical Manual, That Pesky Polarity"
297:The Telecommunications Systems Bulletin TSB-89
173:. These characteristics make RS-485 useful in
1482:
331:to communicate with remote devices. By using
8:
1262:"SIMATIC NET Profibus Network Manual (PDF)"
1232:Future Technology Devices International Ltd
692:Under some conditions it can be used up to
1489:
1475:
1467:
1294:"Profibus Interconnection Guideline (PDF)"
1279:"RS-485 Technical Manual, TIA-485 section"
1247:"Profibus Interconnection Guideline (PDF)"
905:Electronic Industries Association (1983).
658:A (U−, non-inverting) signal shown in blue
630:connectors, or other types of connectors.
29:
1398:"TIA Standards Store: TIA-485 Revision A"
1076:, XpressNET FAQ, accessed July 26, 2015
452:
370:, including the most common versions of
827:
685:
319:Converters, repeaters and star topology
291:. It does not specify or recommend any
159:Telecommunications Industry Association
27:Multidrop serial communication standard
656:B (U+, inverting) signal shown in red,
7:
217:cable should not signal faster than
1267:. Siemens. April 2009. p. 157.
798:idle → TTL/CMOS = +5 V → Line
1383:ANSI/TIA/EIA-485-A, page 15, A.4.1
766:the termination polarization puts
25:
950:"Trim-the-fat-off-RS-485-designs"
751:(green, negative) is higher than
311:RS-485, like RS-422, can be made
149:systems. Electrical signaling is
2220:
2219:
814:signal, as seen in a whitepaper.
1136:. 28 April 2006. Archived from
167:electrically noisy environments
1325:. Chipkins Automation Systems.
360:programmable logic controllers
323:Converters between RS-485 and
163:Electronic Industries Alliance
61:Balanced interconnecting cable
1:
1814:Intel Ultra Path Interconnect
1429:. Pinouts.ru. 7 October 2012.
1427:"RS232 to RS485 cable pinout"
1183:Linear Technology Corporation
894:(Technical report). SLLA070D.
1792:Intel QuickPath Interconnect
1782:Direct Media Interface (DMI)
402:digital audio interconnect.
185:RS-485 supports inexpensive
47:Reaffirmed: December 7, 2012
1437:. Lammert Bies. August 2012
112:(Voa–Vob > +200 mV)
108:(Voa–Vob < −200 mV)
104:Different receiver levels:
2275:
1777:Compute Express Link (CXL)
1435:"RS485 serial information"
1356:. Advantech B+B SmartWorx.
1080:November 17, 2017, at the
368:industrial control systems
177:and similar applications.
175:industrial control systems
2213:
2014:IEEE-1284 (parallel port)
1929:logical device interface)
1368:"The RS-485 Design Guide"
981:, Advantech B+B SmartWorx
696:speeds of 64 Mbit/s.
433:RS-485 does not define a
327:are available to allow a
2259:Serial digital interface
1342:. NVE Corporation. 2010.
641:The diagram below shows
449:RS-485 3 wire connection
270:characteristic impedance
191:multidrop communications
45:Approved: March 3, 1998
43:ANSI/TIA/EIA-485-A-1998
1323:"RS485 Polarity Issues"
909:. EIA Standard RS-485.
866:www.maximintegrated.com
647:asynchronous start-stop
425:are used in this case.
423:8P8C modular connectors
415:Digital Command Control
405:RS-485 is also used in
293:communications protocol
1576:List of bus bandwidths
1400:. TIA. 7 December 2012
1185:. 2007. Archived from
1106:"Polarity conventions"
978:RS-485 CONNECTIONS FAQ
837:RS-485 Reference Guide
786:Isn’t Really Bus Node
730:, A/B labeling refers
659:
450:
435:communication protocol
253:
195:differential signaling
193:links, using the same
88:At least 32 unit loads
1451:Marais, Hein (2008).
669:List of network buses
655:
454:RS-485 signal states
448:
307:Full duplex operation
251:
230:linear bus topologies
147:serial communications
35:(Revision of EIA-485)
2019:IEEE-1394 (FireWire)
1757:PCI Extended (PCI-X)
1373:. Texas Instruments.
1211:Analog Devices, Inc.
1134:Intersil Corporation
282:Recommended Standard
258:termination resistor
52:Protocol information
1860:Parallel ATA (PATA)
1421:. 19 November 2001.
1049:Rockwell Automation
759:state is a logical
585:In addition to the
455:
413:It is also used in
407:building automation
1767:PCI Express (PCIe)
806:voltage, implying
802:voltage > Line
660:
608:common-mode signal
453:
451:
366:used to implement
358:These are used in
262:signal reflections
254:
2231:
2230:
2217:
1944:Apple Desktop Bus
1921:PCI Express (via
1880:Serial ATA (SATA)
1566:Network on a chip
1213:22 November 2011.
1164:. September 2009.
1113:Texas Instruments
936:Texas Instruments
891:Texas Instruments
694:data transmission
551:Linear Technology
491:
490:
329:personal computer
226:three-state logic
132:
131:
117:Available signals
101:Mode of operation
16:(Redirected from
2266:
2223:
2222:
2215:
1677:HP Precision Bus
1491:
1484:
1477:
1468:
1463:
1457:
1446:
1444:
1442:
1430:
1422:
1419:Maxim Integrated
1409:
1407:
1405:
1384:
1381:
1375:
1374:
1372:
1364:
1358:
1357:
1350:
1344:
1343:
1341:
1333:
1327:
1326:
1319:
1313:
1312:
1305:
1299:
1298:
1296:
1289:
1283:
1282:
1275:
1269:
1268:
1266:
1258:
1252:
1251:
1249:
1242:
1236:
1235:
1229:
1221:
1215:
1214:
1208:
1200:
1194:
1193:
1191:
1180:
1172:
1166:
1165:
1162:Maxim Integrated
1159:
1151:
1145:
1144:
1142:
1131:
1123:
1117:
1116:
1110:
1102:
1096:
1090:
1084:
1071:
1065:
1064:
1062:
1060:
1051:. Archived from
1041:
1035:
1034:
1033:
1032:
1027:
1017:
1011:
1010:
1009:
1008:
1003:, Brainboxes LLC
995:
989:
988:
987:
986:
973:
967:
964:
958:
957:
946:
940:
939:
933:
925:
919:
918:
902:
896:
895:
887:
876:
870:
869:
858:
852:
851:
849:
843:, archived from
842:
832:
815:
716:
710:
703:
697:
690:
637:Waveform example
616:current limiting
465:Space (logic 0)
456:
384:
383:
220:
216:
137:, also known as
93:Maximum distance
67:Network topology
30:
21:
2274:
2273:
2269:
2268:
2267:
2265:
2264:
2263:
2234:
2233:
2232:
2227:
2218:
2209:
2168:
2147:
2096:
2009:IEEE-488 (GPIB)
1932:
1828:
1807:Infinity Fabric
1637:Europe Card Bus
1580:
1514:
1495:
1455:
1450:
1440:
1438:
1433:
1425:
1413:
1403:
1401:
1396:
1393:
1388:
1387:
1382:
1378:
1370:
1366:
1365:
1361:
1352:
1351:
1347:
1339:
1335:
1334:
1330:
1321:
1320:
1316:
1307:
1306:
1302:
1291:
1290:
1286:
1277:
1276:
1272:
1264:
1260:
1259:
1255:
1244:
1243:
1239:
1227:
1223:
1222:
1218:
1206:
1202:
1201:
1197:
1189:
1178:
1174:
1173:
1169:
1157:
1153:
1152:
1148:
1140:
1129:
1125:
1124:
1120:
1108:
1104:
1103:
1099:
1091:
1087:
1082:Wayback Machine
1072:
1068:
1058:
1056:
1043:
1042:
1038:
1030:
1028:
1025:
1019:
1018:
1014:
1006:
1004:
997:
996:
992:
984:
982:
975:
974:
970:
965:
961:
948:
947:
943:
931:
927:
926:
922:
904:
903:
899:
885:
878:
877:
873:
860:
859:
855:
847:
840:
834:
833:
829:
824:
819:
818:
717:
713:
704:
700:
691:
687:
682:
665:
657:
639:
624:screw terminals
462:Mark (logic 1)
443:
431:
381:
380:
341:
321:
309:
278:
266:lower impedance
218:
214:
183:
125:Connector types
111:
109:
107:
105:
85:Maximum devices
46:
44:
34:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
2272:
2270:
2262:
2261:
2256:
2251:
2246:
2236:
2235:
2229:
2228:
2214:
2211:
2210:
2208:
2207:
2202:
2197:
2187:
2182:
2176:
2174:
2170:
2169:
2167:
2166:
2161:
2155:
2153:
2149:
2148:
2146:
2145:
2140:
2135:
2130:
2125:
2120:
2118:Intel HD Audio
2115:
2110:
2108:ADAT Lightpipe
2104:
2102:
2098:
2097:
2095:
2094:
2089:
2084:
2079:
2074:
2069:
2064:
2059:
2054:
2049:
2031:
2026:
2021:
2016:
2011:
2006:
2001:
1996:
1991:
1986:
1981:
1976:
1971:
1966:
1961:
1956:
1951:
1946:
1940:
1938:
1934:
1933:
1931:
1930:
1919:
1914:
1909:
1904:
1899:
1898:
1897:
1892:
1882:
1877:
1872:
1867:
1862:
1857:
1852:
1847:
1842:
1836:
1834:
1830:
1829:
1827:
1826:
1821:
1816:
1811:
1810:
1809:
1802:HyperTransport
1799:
1794:
1789:
1784:
1779:
1774:
1769:
1764:
1759:
1754:
1749:
1744:
1739:
1734:
1729:
1724:
1719:
1714:
1709:
1704:
1699:
1694:
1689:
1684:
1679:
1674:
1669:
1664:
1659:
1654:
1649:
1644:
1639:
1634:
1629:
1624:
1619:
1614:
1609:
1604:
1599:
1594:
1588:
1586:
1582:
1581:
1579:
1578:
1573:
1568:
1563:
1558:
1556:Bus contention
1553:
1548:
1543:
1538:
1533:
1531:Front-side bus
1528:
1522:
1520:
1516:
1515:
1512:computer buses
1496:
1494:
1493:
1486:
1479:
1471:
1465:
1464:
1460:Analog Devices
1448:
1431:
1423:
1411:
1392:
1391:External links
1389:
1386:
1385:
1376:
1359:
1345:
1328:
1314:
1300:
1284:
1270:
1253:
1237:
1234:. 27 May 2010.
1216:
1195:
1192:on 2011-03-02.
1167:
1146:
1143:on 2004-12-04.
1118:
1097:
1085:
1066:
1036:
1012:
990:
968:
959:
941:
920:
897:
871:
853:
826:
825:
823:
820:
817:
816:
736:negative green
711:
698:
684:
683:
681:
678:
677:
676:
671:
664:
661:
638:
635:
628:D-subminiature
579:
578:
575:
567:
566:
560:
557:Analog Devices
554:
548:
542:
531:
530:
527:
508:
507:
501:
489:
488:
485:
482:
478:
477:
474:
471:
467:
466:
463:
460:
442:
439:
430:
427:
419:model railways
349:physical layer
340:
337:
320:
317:
308:
305:
289:physical layer
277:
274:
187:local networks
182:
179:
130:
129:
126:
122:
121:
118:
114:
113:
106:binary 1 (OFF)
102:
98:
97:
94:
90:
89:
86:
82:
81:
71:Point-to-point
68:
64:
63:
58:
57:Physical media
54:
53:
49:
48:
41:
37:
36:
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2271:
2260:
2257:
2255:
2254:EIA standards
2252:
2250:
2247:
2245:
2242:
2241:
2239:
2226:
2212:
2206:
2203:
2201:
2198:
2195:
2191:
2188:
2186:
2183:
2181:
2180:Multidrop bus
2178:
2177:
2175:
2171:
2165:
2162:
2160:
2157:
2156:
2154:
2150:
2144:
2141:
2139:
2136:
2134:
2131:
2129:
2126:
2124:
2121:
2119:
2116:
2114:
2111:
2109:
2106:
2105:
2103:
2099:
2093:
2090:
2088:
2087:External PCIe
2085:
2083:
2080:
2078:
2075:
2073:
2070:
2068:
2067:Parallel SCSI
2065:
2063:
2060:
2058:
2055:
2053:
2050:
2047:
2043:
2039:
2035:
2032:
2030:
2027:
2025:
2022:
2020:
2017:
2015:
2012:
2010:
2007:
2005:
2002:
2000:
1997:
1995:
1992:
1990:
1987:
1985:
1982:
1980:
1977:
1975:
1972:
1970:
1967:
1965:
1962:
1960:
1959:Commodore bus
1957:
1955:
1952:
1950:
1947:
1945:
1942:
1941:
1939:
1935:
1928:
1924:
1920:
1918:
1915:
1913:
1910:
1908:
1907:Fibre Channel
1905:
1903:
1900:
1896:
1893:
1891:
1888:
1887:
1886:
1883:
1881:
1878:
1876:
1873:
1871:
1868:
1866:
1863:
1861:
1858:
1856:
1853:
1851:
1848:
1846:
1843:
1841:
1838:
1837:
1835:
1831:
1825:
1822:
1820:
1817:
1815:
1812:
1808:
1805:
1804:
1803:
1800:
1798:
1795:
1793:
1790:
1788:
1785:
1783:
1780:
1778:
1775:
1773:
1770:
1768:
1765:
1763:
1760:
1758:
1755:
1753:
1750:
1748:
1745:
1743:
1740:
1738:
1735:
1733:
1730:
1728:
1725:
1723:
1720:
1718:
1715:
1713:
1710:
1708:
1705:
1703:
1700:
1698:
1695:
1693:
1690:
1688:
1685:
1683:
1680:
1678:
1675:
1673:
1670:
1668:
1665:
1663:
1660:
1658:
1655:
1653:
1650:
1648:
1645:
1643:
1640:
1638:
1635:
1633:
1630:
1628:
1625:
1623:
1620:
1618:
1615:
1613:
1610:
1608:
1605:
1603:
1600:
1598:
1595:
1593:
1590:
1589:
1587:
1583:
1577:
1574:
1572:
1571:Plug and play
1569:
1567:
1564:
1562:
1561:Bus mastering
1559:
1557:
1554:
1552:
1549:
1547:
1544:
1542:
1539:
1537:
1536:Back-side bus
1534:
1532:
1529:
1527:
1524:
1523:
1521:
1517:
1513:
1510:
1506:
1504:
1499:
1492:
1487:
1485:
1480:
1478:
1473:
1472:
1469:
1461:
1454:
1449:
1436:
1432:
1428:
1424:
1420:
1416:
1412:
1399:
1395:
1394:
1390:
1380:
1377:
1369:
1363:
1360:
1355:
1349:
1346:
1338:
1332:
1329:
1324:
1318:
1315:
1310:
1304:
1301:
1295:
1288:
1285:
1280:
1274:
1271:
1263:
1257:
1254:
1248:
1241:
1238:
1233:
1226:
1220:
1217:
1212:
1205:
1199:
1196:
1188:
1184:
1177:
1171:
1168:
1163:
1156:
1150:
1147:
1139:
1135:
1128:
1122:
1119:
1114:
1107:
1101:
1098:
1094:
1089:
1086:
1083:
1079:
1075:
1070:
1067:
1055:on 2012-03-10
1054:
1050:
1046:
1040:
1037:
1024:
1023:
1016:
1013:
1002:
1001:
994:
991:
980:
979:
972:
969:
963:
960:
955:
951:
945:
942:
937:
930:
924:
921:
916:
912:
908:
901:
898:
893:
892:
884:
883:
875:
872:
867:
863:
857:
854:
850:on 2018-05-17
846:
839:
838:
831:
828:
821:
813:
809:
805:
801:
797:
793:
789:
785:
781:
777:
773:
769:
765:
762:
758:
754:
750:
745:
741:
737:
733:
729:
725:
721:
715:
712:
708:
702:
699:
695:
689:
686:
679:
675:
672:
670:
667:
666:
662:
654:
650:
648:
644:
636:
634:
631:
629:
625:
620:
617:
612:
609:
605:
601:
597:
592:
588:
583:
576:
573:
572:
571:
564:
561:
558:
555:
552:
549:
546:
543:
540:
537:
536:
535:
528:
525:
524:
523:
521:
520:non-inverting
517:
513:
505:
502:
499:
496:
495:
494:
486:
483:
480:
479:
475:
472:
469:
468:
464:
461:
458:
457:
447:
440:
438:
436:
428:
426:
424:
420:
416:
411:
408:
403:
401:
397:
392:
389:
388:Allen-Bradley
385:
377:
373:
369:
365:
361:
356:
354:
350:
346:
338:
336:
334:
330:
326:
318:
316:
314:
306:
304:
300:
298:
294:
290:
285:
283:
275:
273:
271:
267:
263:
259:
250:
246:
244:
240:
236:
231:
227:
222:
212:
211:rule of thumb
208:
204:
200:
196:
192:
188:
180:
178:
176:
172:
171:multidrop bus
168:
164:
160:
156:
152:
148:
144:
140:
136:
128:Not specified
127:
123:
119:
115:
110:binary 0 (ON)
103:
99:
96:Not specified
95:
91:
87:
83:
80:
76:
75:multi-dropped
72:
69:
65:
62:
59:
55:
50:
42:
38:
31:
19:
2244:Serial buses
1993:
1712:TURBOchannel
1502:
1439:. Retrieved
1402:. Retrieved
1379:
1362:
1348:
1331:
1317:
1311:. Wikibooks.
1303:
1287:
1281:. Wikibooks.
1273:
1256:
1240:
1219:
1198:
1187:the original
1170:
1149:
1138:the original
1121:
1100:
1088:
1069:
1059:10 September
1057:. Retrieved
1053:the original
1039:
1029:, retrieved
1021:
1015:
1005:, retrieved
999:
993:
983:, retrieved
977:
971:
962:
944:
923:
906:
900:
889:
881:
874:
865:
856:
845:the original
836:
830:
811:
807:
803:
799:
787:
783:
779:
775:
771:
767:
763:
760:
756:
752:
748:
744:positive red
743:
739:
735:
731:
714:
706:
701:
688:
640:
632:
621:
613:
603:
599:
595:
590:
586:
584:
580:
568:
532:
519:
509:
503:
497:
492:
432:
412:
404:
393:
379:
357:
342:
339:Applications
322:
310:
301:
296:
286:
279:
255:
223:
199:twisted pair
184:
142:
138:
134:
133:
2185:CoreConnect
2164:ExpressCard
2092:Thunderbolt
2082:Camera Link
1865:Bus and Tag
1551:Address bus
1546:Control bus
1541:Daisy chain
1441:12 November
1404:2 September
1074:lenzusa.com
353:vehicle bus
313:full-duplex
139:TIA-485(-A)
79:multi-point
2238:Categories
2038:ACCESS.bus
1937:Peripheral
1737:InfiniBand
1732:HP GSC bus
1526:System bus
1031:2019-04-06
1007:2019-03-08
985:2023-09-15
822:References
643:potentials
510:Because a
417:(DCC) for
155:multipoint
1999:Lightning
1949:Atari SIO
1824:SpaceWire
1657:Zorro III
1597:S-100 bus
1592:SS-50 bus
1585:Standards
1505:standards
1498:Technical
1093:bidib.org
812:inverting
738:wire and
604:reference
429:Protocols
333:repeaters
33:TIA-485-A
2225:Category
2200:Wishbone
2173:Embedded
2152:Portable
2072:Profibus
2004:DMX512-A
1890:Parallel
1742:Ethernet
1652:Zorro II
1602:Multibus
1503:de facto
1078:Archived
954:EE Times
915:10728525
728:Profibus
707:binary 1
663:See also
649:method.
539:Intersil
376:Profibus
276:Standard
237:, not a
219:2 Mbit/s
215:50-meter
181:Overview
151:balanced
40:Standard
2205:SLIMbus
2159:PC Card
2143:TOSLINK
1833:Storage
1787:RapidIO
1667:FASTBUS
1622:STD Bus
1519:General
1115:. 2003.
956:. 2000.
938:. 2011.
742:as the
734:as the
459:Signal
441:Signals
143:EIA-485
120:A, B, C
2138:S/PDIF
2029:1-Wire
1994:RS-485
1989:RS-423
1984:RS-422
1979:RS-232
1840:ST-506
1797:NVLink
1647:STEbus
1607:Unibus
913:
724:BACnet
720:Modbus
396:DMX512
382:DH 485
372:Modbus
325:RS-232
207:Mbit/s
203:RS-422
153:, and
135:RS-485
18:DH 485
2133:McASP
2101:Audio
2046:SMBus
2042:PMBus
2024:UNI/O
1964:HP-IL
1917:SATAe
1902:ESCON
1875:HIPPI
1707:NuBus
1662:CAMAC
1632:Q-Bus
1627:SMBus
1612:VAXBI
1509:wired
1456:(PDF)
1371:(PDF)
1340:(PDF)
1265:(PDF)
1228:(PDF)
1207:(PDF)
1190:(PDF)
1179:(PDF)
1158:(PDF)
1141:(PDF)
1130:(PDF)
1109:(PDF)
1026:(PDF)
932:(PDF)
886:(pdf)
848:(PDF)
841:(PDF)
718:With
680:Notes
545:Maxim
516:space
484:High
476:High
197:over
2190:AMBA
2128:MADI
2113:AES3
1974:MIDI
1927:NVMe
1923:AHCI
1885:SCSI
1870:DSSI
1845:ESDI
1722:SBus
1682:EISA
1617:MBus
1507:for
1500:and
1443:2012
1406:2020
1061:2010
911:OCLC
792:UART
778:and
757:mark
726:and
674:UART
589:and
563:FTDI
512:mark
487:Low
473:Low
400:AES3
374:and
345:SCSI
243:ring
239:star
189:and
161:and
2194:AXI
2123:I²S
2077:USB
2062:D²B
2057:SPI
2052:I3C
2034:I²C
1969:HIL
1954:DCB
1925:or
1912:SSA
1895:SAS
1855:SMD
1850:IPI
1772:AGP
1762:PXI
1752:PCI
1747:UPA
1727:VLB
1717:MCA
1702:VPX
1697:VXS
1692:VXI
1687:VME
1672:LPC
1642:ISA
796:MCU
764:and
761:one
602:or
235:bus
201:as
141:or
2240::
2044:,
2040:,
1458:.
1417:.
1230:.
1209:.
1181:.
1160:.
1132:.
1111:.
1047:.
952:.
934:.
888:.
864:.
722:,
626:,
598:,
596:SC
481:B
470:A
378:.
241:,
221:.
77:,
73:,
2196:)
2192:(
2048:)
2036:(
1490:e
1483:t
1476:v
1462:.
1445:.
1408:.
1063:.
917:.
868:.
808:A
804:A
800:B
794:/
788:A
784:A
780:B
776:A
772:A
768:B
753:B
749:A
740:B
732:A
600:G
591:B
587:A
504:B
498:A
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.