152:
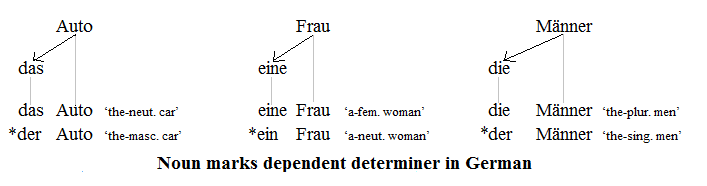
The noun marks the dependent determiner in gender (masculine, feminine, or neuter) and number (singular or plural). In other words, the gender and number of the noun determine the form of the determiner that must appear. Nouns in German also mark their dependent adjectives in gender and number, but
59:
in 1986, and has since become a central criterion in language typology in which languages are classified according to whether they are more head-marking or dependent-marking. Many languages employ both head and dependent-marking, but some employ
79:
has few inflectional markers of agreement and so can be construed as zero-marking much of the time. Dependent-marking, however, occurs when a singular or plural noun demands the singular or plural form of the demonstrative determiner
230:Ágel, V., L. Eichinger, H.-W. Eroms, P. Hellwig, H. Heringer, and H. Lobin (eds.) 2003/6. Dependency and valency: An international handbook of contemporary research. Berlin: Walter de Gruyter.
144:
118:
124:
Plural nouns in
English require the plural form of a dependent demonstrative determiner, and prepositions require the object form of a dependent personal pronoun.
132:
Such instances of dependent-marking are a relatively rare occurrence in
English, but dependent-marking occurs much more frequently in related languages, such as
68:. However, it is not clear that the head of a clause has anything to do with the head of a noun phrase, or even what the head of a clause is.
153:
the markings vary across determiners and adjectives. Also, a head noun in German can mark a dependent noun with the genitive case.
249:
143:
163:
136:. There, for instance, dependent-marking is present in most noun phrases. A noun marks its dependent determiner:
117:
217:
Dependency grammar trees similar to the ones that appear here can be found en masse in Ágel et al. (2003/6).
173:
61:
32:
188:
183:
65:
52:
44:
178:
168:
109:
48:
236:
Nichols, J. 1992. Linguistic diversity in space and time. Chicago: University of
Chicago Press.
76:
133:
56:
36:
88:
and when a verb or preposition demands the subject or object form of a personal pronoun:
243:
233:
Nichols, J. 1986. Head-marking and dependent-marking grammar. Language 62, 1, 56-119.
17:
40:
8:
55:and dependent-marking was first explored by
201:
7:
108:. The following representations of
25:
142:
116:
1:
43:that tend to appear more on
31:has grammatical markers of
266:
51:. The distinction between
29:dependent-marking language
208:See Nichols (1986, 1992).
164:Constituent (linguistics)
112:illustrate some cases:
64:, and yet others employ
174:Double-marking language
189:Zero-marking language
184:Head-marking language
39:between the words of
250:Linguistic typology
179:Head (linguistics)
169:Dependency grammar
110:dependency grammar
18:Dependent-marking
16:(Redirected from
257:
218:
215:
209:
206:
146:
120:
21:
265:
264:
260:
259:
258:
256:
255:
254:
240:
239:
227:
222:
221:
216:
212:
207:
203:
198:
193:
159:
130:
74:
57:Johanna Nichols
37:case government
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
263:
261:
253:
252:
242:
241:
238:
237:
234:
231:
226:
223:
220:
219:
210:
200:
199:
197:
194:
192:
191:
186:
181:
176:
171:
166:
160:
158:
155:
150:
149:
148:
147:
129:
126:
122:
121:
73:
70:
62:double-marking
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
262:
251:
248:
247:
245:
235:
232:
229:
228:
224:
214:
211:
205:
202:
195:
190:
187:
185:
182:
180:
177:
175:
172:
170:
167:
165:
162:
161:
156:
154:
145:
141:
140:
139:
138:
137:
135:
127:
125:
119:
115:
114:
113:
111:
107:
103:
99:
95:
91:
87:
83:
78:
71:
69:
67:
63:
58:
54:
50:
46:
42:
38:
34:
30:
19:
213:
204:
151:
131:
123:
105:
101:
97:
93:
89:
85:
81:
75:
66:zero-marking
53:head-marking
28:
26:
196:References
86:that/those
82:this/these
72:In English
45:dependents
128:In German
102:they/them
33:agreement
244:Category
157:See also
106:who/whom
47:than on
225:Sources
98:she/her
77:English
41:phrases
134:German
94:he/him
49:heads
90:I/me
35:and
84:or
246::
104:,
100:,
96:,
92:,
27:A
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.