66:
807:
should invest in maximizing these learning and experience effects and that market share is underestimated as an enabler of this investment. The reasoning is that increased activity leads to increased learning, which leads to lower costs, which can lead to lower prices, which can lead to increased market share, which can lead to increased profitability and market dominance. This was particularly true when a firm had an early leadership in market share. It was suggested that if a company cannot get enough market share to be competitive, it should exit that business and concentrate resources where it was possible to take advantage of experience effects and gain (preferably dominant) market share. The BCG strategists developed
677:: As the manufacturers and consumers have more experience with the product, they can usually find improvements. This filters through to the manufacturing process. A good example of this is Cadillac's testing of various "bells and whistles" specialty accessories. The ones that did not break became mass-produced in other General Motors products; the ones that didn't stand the test of user "beatings" were discontinued, saving the car company money. As General Motors produced more cars, they learned how to best produce products that work for the least money.
142:
percentage and did not vary at different scales of operation. The learning curve model posits that for each doubling of the total quantity of items produced, costs decrease by a fixed proportion. Generally, the production of any good or service shows the learning curve or experience curve effect. Each time cumulative volume doubles, value-added costs (including administration, marketing, distribution, and manufacturing) fall by a constant percentage.
835:(efficiencies arising from an increased scale of production) that it is impossible to separate the two. In practice, this view suggests, economies of scale coincide with experience effects (efficiencies arising from the learning and experience gained over repeated activities). The approach, however, accepts the existence of both as underlying causes. Economies of scale afford experience and experience may afford economies of scale.
687:): As a product enters more widespread use, the consumer uses it more efficiently because they're familiar with it. One fax machine in the world can do nothing, but if everyone has one, they build an increasingly efficient network of communications. Another example is email accounts; the more there are, the more efficient the network is, the lower everyone's cost per utility of using it.
32:
802:"In one pattern, prices, in current dollars, remained constant for long periods and then began a relatively steep and long continued decline in constant dollars. In the other pattern, prices, in constant dollars, declined steadily at a constant rate of about 25 percent each time accumulated experience doubled. That was the experience curve."
818:
One consequence of experience curve strategy is that it predicts that cost savings should be passed on as price decreases rather than kept as profit margin increases. The BCG strategists felt that maintaining a relatively high price, although very profitable in the short run, spelled disaster for the
797:
Henderson wrote on the development of the experience curve. According to
Henderson, BCG's first "attempt to explain cost behavior over time in a process industry" began in 1966. The datum he focused on was the striking correlation between competitive profitability and market share. Using price data
621:
These effects are often expressed graphically. The curve is plotted with the cumulative units produced on the horizontal axis and unit cost on the vertical axis. The BCG group used the value of b to name a given industry curve. Thus a curve showing a 15% cost reduction for every doubling of output
141:
production doubled, the required labor time for a new aircraft fell by 20%. This has become known as "Wright's law". Studies in other industries have yielded different percentage values (ranging from only a couple of percent up to 30%), but in most cases, the value in each industry was a constant
647:: Workers become physically more dexterous. They become mentally more confident and spend less time hesitating, learning, experimenting, or making mistakes. Over time they learn short-cuts and improvements. This applies to all employees and managers, not just those directly involved in production.
806:
The suggestion was that failure of production to show the learning curve effect was a risk indicator. The BCG strategists examined the consequences of the experience effect for businesses. They concluded that because relatively low cost of operations is a very powerful strategic advantage, firms
161:, suggesting that "the two are related, but quite different." In 1968, Henderson and BCG began to emphasize the implications of the experience curve for strategy. Research by BCG in the 1960s and 70s observed experience curve effects for various industries that ranged from 10% to 25%.
499:
637:, learning generally begins with making successively larger finds and then successively smaller ones. The equations for these effects come from the usefulness of mathematical models for certain somewhat predictable aspects of those generally non-deterministic processes.
112:. Ebbinghaus was investigating the difficulty of memorizing verbal stimuli. He found that performance increased in proportion to experience (practice and testing) on memorizing the word set. (More detail about the complex processes of learning are discussed in the
124:
This was later more generalized to: the more times a task has been performed, the less time is required on each subsequent iteration. This relationship was probably first quantified in the industrial setting in 1936 by
759:
Graphically, the curve is truncated. Existing processes become obsolete and the firm must upgrade to remain competitive. The upgrade will mean the old experience curve will be replaced by a new one. This occurs when:
653:: As processes, parts, and products become more standardized, efficiency tends to increase. When employees specialize in a limited set of tasks, they gain more experience with these tasks and operate at a faster rate.
508:
is a statistical parameter and thus does not exactly predict the unit cost of producing any future unit. However, it has been found to be useful in many contexts. Across numerous industries (see below), estimates of
693:: Experience curve effects are reinforced when two or more products share a common activity or resource. Any efficiency learned from one product can be applied to the other products. (This is related to the
665:: As total production has increased, manufacturing equipment will have been more fully exploited, lowering fully accounted unit costs. In addition, purchase of more productive equipment can be justifiable.
93:
of that production, specifically, efficiency gains that follow investment in the effort. The effect has large implications for costs and market share, which can increase competitive advantage over time.
285:
823:. If prices were reduced as unit costs fell (due to experience curve effects), then competitive entry would be discouraged while market share increases should increase overall profitability.
253:
1310:
625:
A third formulation of Wright's Law is used by a group of innovation investment analysts, working with cumulative average cost per unit and cumulative numbers of units produced.
574:
1395:
Sterman, John D.; Henderson, Rebecca; Beinhocker, Eric D.; Newman, Lee I. (2007). "Getting Big Too Fast: Strategic
Dynamics with Increasing Returns and Bounded Rationality".
659:: Automated production technology and information technology can introduce efficiencies as they are implemented and people learn how to use them efficiently and effectively.
1038:
65:
1508:
157:(BCG), based on analyses of overall cost behavior in the 1960s. While accepting that the learning curve formed an attractive explanation, he used the name
169:
Mathematically, Wright's law takes the form of a power function. Empirical research has validated the following mathematical form for the unit cost
958:
767:
Key suppliers have much bigger customers that determine the price of products and services, and that becomes the main cost driver for the product
1673:
1424:
1146:
819:
strategy in the long run. High profits would encourage competitors to enter the market, triggering a steep price decline and a competitive
633:
The primary reason for why experience and learning curve effects apply is the complex processes of learning involved. As discussed in the
798:
in the semiconductor industry supplied by the
Electronic Industries Association, he suggested that not one but two patterns emerged.
1689:
1617:
1599:
1379:
1259:
494:{\displaystyle C_{2x}=C_{1}(2x)^{\log _{2}(b)}=C_{1}x^{\log _{2}(b)}\cdot 2^{\log _{2}(b)}=C_{x}\cdot 2^{\log _{2}(b)}=C_{x}\cdot b}
694:
17:
1693:
1109:
1173:
897:
839:
1719:
1714:
931:
50:
1331:
1699:
963:
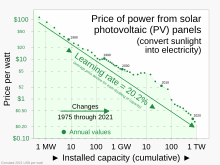
OWID credits source data to: Nemet (2009); Farmer & Lafond (2016); International
Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA).
1443:
865:
1366:
Berndt, Ernst R. (1991). "Costs, Learning Curves, and Scale
Economies : From Simple to Multiple Regression".
1297:
189:
1536:
973:
701:
For some examples, NASA quotes the following progress ratios in experience curves from different industries:
1490:
950:
843:
154:
854:
1197:
Hax, Arnoldo C.; Majluf, Nicolas S. (October 1982), "Competitive cost dynamics: the experience curve",
526:
831:
Ernst R. Berndt claims that in most organizations, experience effects are so closely intertwined with
1455:
892:
671:: As a company acquires experience, it can alter its mix of inputs and thereby become more efficient.
126:
108:
An early empirical demonstration of learning curves was produced in 1885 by the German psychologist
40:
858:
847:
808:
850:
have been proposed as alternative strategies for leadership that do not rely on lower unit costs.
23:
Express the relationship between experience producing a good and the efficiency of that production
1556:
1214:
1126:
902:
882:
832:
590:
150:
109:
16:
This article is about fall in costs with increased experience in production. For other uses, see
857:, for instance by pre-emptively expanding production have been criticized, with factors such as
1438:
73:
states that solar module prices have dropped about 20% for each doubling of installed capacity.
1669:
1653:
1613:
1595:
1502:
1375:
1255:
1089:
1000:
275:
is the proportion reduction in the unit cost with each doubling in the cumulative production (
1643:
1635:
1548:
1471:
1404:
1206:
1155:
1118:
1079:
1071:
919:
877:
78:
70:
1626:
Le Morvan, Pierre; Stock, Barbara (2005), "Medical
Learning Curves and the Kantian Ideal",
1567:
812:
992:
925:
913:
1581:
The
Learning Curve Deskbook: A Reference Guide to Theory, Calculations, and Applications
1648:
1233:
1084:
907:
684:
634:
130:
113:
103:
45:
1708:
1666:
Technological
Learning in the Energy Sector, Lessons for Policy, Industry and Science
1589:
1532:
1368:
1239:
783:
134:
1218:
1516:
Abernathy, William; Wayne, Kenneth (Sep–Oct 1974), "Limits to the
Learning Curve",
1107:
Swift, Edgar James (1903). "Studies in the
Psychology and Physiology of Learning".
744:
718:
711:
90:
1075:
1059:
1524:
Kiechel, Walter III (October 5, 1981), "The Decline of the Experience Curve",
887:
777:
520:
The unit curve was expressed in slightly different nomenclature by Henderson:
1610:
Economia: New Economic Systems to Empower People and Support the Living World
1342:
1004:
1639:
1247:
728:
705:
1657:
1408:
1093:
1459:
1210:
820:
770:
Technological change requires a change in processes to remain competitive
138:
98:
History: from psychological learning curves to the learning curve effect
1560:
1251:
1130:
738:
1274:
764:
Competitors introduce new products or processes that demand a response
1552:
1122:
868:
may lead people to overestimate the effect of the experience curve.
1475:
1159:
119:
86:
64:
1570:(March–April 1985), "Building Strategy on the Experience Curve",
1482:
Hirschmann, W. (Jan–Feb 1964), "Profit from the Learning Curve",
1144:
Wright, T. P. (1936). "Factors Affecting the Cost of Airplanes".
25:
773:
The experience curve strategies must be re-evaluated because
1664:
Junginger, Martin; van Sark, Wilfried; Faaij, André (2010),
1243:
951:"Solar (photovoltaic) panel prices vs. cumulative capacity"
120:
Wright's law and the discovery of the learning curve effect
651:
Standardization, specialization, and methods improvements
85:
express the relationship between experience producing a
1370:
The Practice of Econometrics: Classic and Contemporary
1311:"The Experience Curve – Reviewed I: The Concept, 1974"
974:"Swanson's Law and Making US Solar Scale Like Germany"
1275:"What Is Wright's Law | Learning Curve of Innovation"
928:
of simultaneous wireless conversation capacity growth
853:
Attempts to use the learning curve effect to improve
529:
288:
192:
1298:
Cost Estimating Web Site - Learning Curve Calculator
1332:"The Experience Curve Reviewed: V. Price Stability"
1060:"Memory: A Contribution to Experimental Psychology"
1039:"The Experience Curve – Reviewed II: History, 1973"
1367:
916:of magnetic disk storage growth in the early 2000s
568:
493:
247:
183:, for a wide variety of products and services:
861:and durable products cited as reasons for this.
617:is the elasticity of cost with regard to output
1341:. The Boston Consulting Group. Archived from
8:
724:Repetitive electronics manufacturing: 90–95%
176:of producing the x unit, starting with unit
1539:(1983), "Diagnosing the Experience Curve",
1032:
1030:
1028:
1026:
1024:
1022:
1020:
248:{\displaystyle C_{x}=C_{1}x^{\log _{2}(b)}}
39:It has been suggested that this article be
1507:: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (
910:of affordable computing performance growth
1647:
1460:"Factors Affecting the Cost of Airplanes"
1083:
557:
547:
534:
528:
479:
452:
447:
434:
407:
402:
375:
370:
360:
333:
328:
309:
293:
287:
225:
220:
210:
197:
191:
734:Repetitive electrical operations: 75–85%
681:Network-building and use-cost reductions
69:An example of experience curve effects:
1694:Cost Models - Learning Curve Calculator
1668:, Cheltenham: Edward Elgar Publishing,
961:from the original on 29 September 2023.
942:
1500:
622:was called an "85% experience curve".
611:is the cumulative volume of production
279:). To see this, note the following:
991:Hirschmann, Winfred B. (1964-01-01).
137:. Wright found that every time total
7:
1464:Journal of the Aeronautical Sciences
1147:Journal of the Aeronautical Sciences
793:Strategic consequences of the effect
815:(in part) to manage this strategy.
164:
14:
1698:Federal Aviation Administration,
1690:Federation of American Scientists
731:or punch-press operations: 90–95%
569:{\displaystyle C_{n}=C_{1}n^{-a}}
993:"Profit from the Learning Curve"
755:Experience curve discontinuities
513:range from 0.75 to 0.9 (i.e., 1-
30:
1594:(3rd ed.), Prentice Hall,
695:principle of least astonishment
18:Learning curve (disambiguation)
1235:Contemporary strategy analysis
1110:American Journal of Psychology
467:
461:
422:
416:
390:
384:
348:
342:
325:
315:
240:
234:
1:
1608:Davies, Geoffrey F. (2004),
1588:Ostwald, Phillip F. (1992),
1444:Resources in other libraries
1076:10.5214/ans.0972.7531.200408
1058:Ebbinghaus, Hermann (1885).
809:product portfolio techniques
165:Wright's law unit cost curve
81:, models of the learning or
1591:Engineering Cost Estimating
1579:Teplitz, C.J., ed. (1991),
1374:. Reading: Addison-Wesley.
898:Porter's generic strategies
840:Porter's generic strategies
669:Changes in the resource mix
1736:
1495:Perspectives on Experience
866:well travelled road effect
657:Technology-driven learning
517:ranges from 0.1 to 0.25).
101:
56:Proposed since April 2024.
15:
1628:Journal of Medical Ethics
1537:Montgomery, David Bernard
1439:Resources in your library
1330:Henderson, Bruce (1974).
1232:Grant, Robert M. (2004),
999:. No. January 1964.
922:of wired bandwidth growth
782:they are not producing a
691:Shared experience effects
589:is the cost of the first
1583:, New York: Quorum Books
1430:Experience curve effects
1254:: Blackwell publishing,
1640:10.1136/jme.2004.009316
1572:Harvard Business Review
1518:Harvard Business Review
1484:Harvard Business Review
1178:Boston Consulting Group
1064:Annals of Neurosciences
997:Harvard Business Review
844:product differentiation
750:Purchased parts: 85–88%
663:Better use of equipment
155:Boston Consulting Group
83:experience curve effect
1700:18. The Learning Curve
1409:10.1287/mnsc.1060.0673
1174:"The Experience Curve"
804:
786:that the market values
721:for new models: 75–85%
635:Learning curve article
629:Reasons for the effect
605:-th unit of production
570:
495:
249:
74:
1456:Wright, Theodore Paul
855:competitive advantage
800:
571:
496:
250:
153:, the founder of the
68:
1720:Production economics
1715:Strategic management
1541:Journal of Marketing
1309:Henderson, Bruce D.
1211:10.1287/inte.12.5.50
1037:Henderson, Bruce D.
893:Marketing strategies
776:they are leading to
527:
286:
190:
127:Theodore Paul Wright
859:bounded rationality
848:market segmentation
838:Approaches such as
601:is the cost of the
1491:Consulting, Boston
1397:Management Science
955:OurWorldInData.org
903:Strategic planning
883:Hermann Ebbinghaus
878:Economies of scale
833:economies of scale
591:unit of production
566:
491:
245:
151:Bruce D. Henderson
110:Hermann Ebbinghaus
75:
1675:978-1-84844-834-6
1458:(February 1936),
1425:Library resources
932:Learning-by-doing
129:, an engineer at
63:
62:
58:
1727:
1678:
1660:
1651:
1622:
1604:
1584:
1575:
1568:Ghemawat, Pankaj
1563:
1528:
1520:
1512:
1506:
1498:
1486:
1478:
1413:
1412:
1392:
1386:
1385:
1373:
1363:
1357:
1356:
1354:
1353:
1347:
1336:
1327:
1321:
1320:
1318:
1317:
1306:
1300:
1295:
1289:
1288:
1286:
1285:
1271:
1265:
1264:
1229:
1223:
1222:
1194:
1188:
1187:
1185:
1184:
1170:
1164:
1163:
1141:
1135:
1134:
1104:
1098:
1097:
1087:
1055:
1049:
1048:
1046:
1045:
1034:
1015:
1014:
1012:
1011:
988:
982:
981:
970:
964:
962:
947:
675:Product redesign
645:Labor efficiency
575:
573:
572:
567:
565:
564:
552:
551:
539:
538:
500:
498:
497:
492:
484:
483:
471:
470:
457:
456:
439:
438:
426:
425:
412:
411:
394:
393:
380:
379:
365:
364:
352:
351:
338:
337:
314:
313:
301:
300:
254:
252:
251:
246:
244:
243:
230:
229:
215:
214:
202:
201:
159:experience curve
149:was proposed by
147:experience curve
54:
34:
33:
26:
1735:
1734:
1730:
1729:
1728:
1726:
1725:
1724:
1705:
1704:
1686:
1681:
1676:
1663:
1625:
1620:
1607:
1602:
1587:
1578:
1566:
1553:10.2307/1251492
1531:
1523:
1515:
1499:
1489:
1481:
1454:
1450:
1449:
1448:
1433:
1432:
1428:
1421:
1419:Further reading
1416:
1394:
1393:
1389:
1382:
1365:
1364:
1360:
1351:
1349:
1345:
1334:
1329:
1328:
1324:
1315:
1313:
1308:
1307:
1303:
1296:
1292:
1283:
1281:
1273:
1272:
1268:
1262:
1231:
1230:
1226:
1196:
1195:
1191:
1182:
1180:
1172:
1171:
1167:
1143:
1142:
1138:
1123:10.2307/1412713
1106:
1105:
1101:
1057:
1056:
1052:
1043:
1041:
1036:
1035:
1018:
1009:
1007:
990:
989:
985:
978:Greentech Media
972:
971:
967:
949:
948:
944:
940:
874:
829:
795:
757:
741:operations: 90%
685:network effects
631:
599:
588:
553:
543:
530:
525:
524:
475:
448:
443:
430:
403:
398:
371:
366:
356:
329:
324:
305:
289:
284:
283:
221:
216:
206:
193:
188:
187:
181:
174:
167:
122:
106:
100:
59:
35:
31:
24:
21:
12:
11:
5:
1733:
1731:
1723:
1722:
1717:
1707:
1706:
1703:
1702:
1696:
1685:
1684:External links
1682:
1680:
1679:
1674:
1661:
1634:(9): 513–518,
1623:
1618:
1605:
1600:
1585:
1576:
1574:, vol. 42
1564:
1547:(Spring): 44,
1533:Day, George S.
1529:
1521:
1513:
1497:, Boston, Mass
1487:
1479:
1470:(4): 122–128,
1451:
1447:
1446:
1441:
1435:
1434:
1423:
1422:
1420:
1417:
1415:
1414:
1403:(4): 683–696.
1387:
1380:
1358:
1322:
1301:
1290:
1266:
1260:
1224:
1189:
1165:
1154:(4): 122–128.
1136:
1117:(2): 201–251.
1099:
1050:
1016:
983:
965:
941:
939:
936:
935:
934:
929:
923:
917:
911:
905:
900:
895:
890:
885:
880:
873:
870:
828:
825:
794:
791:
790:
789:
788:
787:
780:
771:
768:
765:
756:
753:
752:
751:
748:
742:
735:
732:
725:
722:
715:
709:
699:
698:
688:
678:
672:
666:
660:
654:
648:
640:They include:
630:
627:
619:
618:
612:
606:
597:
593:
586:
577:
576:
563:
560:
556:
550:
546:
542:
537:
533:
502:
501:
490:
487:
482:
478:
474:
469:
466:
463:
460:
455:
451:
446:
442:
437:
433:
429:
424:
421:
418:
415:
410:
406:
401:
397:
392:
389:
386:
383:
378:
374:
369:
363:
359:
355:
350:
347:
344:
341:
336:
332:
327:
323:
320:
317:
312:
308:
304:
299:
296:
292:
265:progress ratio
257:
256:
242:
239:
236:
233:
228:
224:
219:
213:
209:
205:
200:
196:
179:
172:
166:
163:
131:Curtiss-Wright
121:
118:
114:Learning curve
104:Learning curve
102:Main article:
99:
96:
61:
60:
46:Learning curve
38:
36:
29:
22:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1732:
1721:
1718:
1716:
1713:
1712:
1710:
1701:
1697:
1695:
1691:
1688:
1687:
1683:
1677:
1671:
1667:
1662:
1659:
1655:
1650:
1645:
1641:
1637:
1633:
1629:
1624:
1621:
1619:0-7333-1298-5
1615:
1612:, ABC Books,
1611:
1606:
1603:
1601:0-13-276627-2
1597:
1593:
1592:
1586:
1582:
1577:
1573:
1569:
1565:
1562:
1558:
1554:
1550:
1546:
1542:
1538:
1534:
1530:
1527:
1522:
1519:
1514:
1510:
1504:
1496:
1492:
1488:
1485:
1480:
1477:
1476:10.2514/8.155
1473:
1469:
1465:
1461:
1457:
1453:
1452:
1445:
1442:
1440:
1437:
1436:
1431:
1426:
1418:
1410:
1406:
1402:
1398:
1391:
1388:
1383:
1381:0-201-17628-9
1377:
1372:
1371:
1362:
1359:
1348:on 2018-11-23
1344:
1340:
1333:
1326:
1323:
1312:
1305:
1302:
1299:
1294:
1291:
1280:
1276:
1270:
1267:
1263:
1261:1-4051-1999-3
1257:
1253:
1249:
1245:
1241:
1237:
1236:
1228:
1225:
1220:
1216:
1212:
1208:
1204:
1200:
1193:
1190:
1179:
1175:
1169:
1166:
1161:
1160:10.2514/8.155
1157:
1153:
1149:
1148:
1140:
1137:
1132:
1128:
1124:
1120:
1116:
1112:
1111:
1103:
1100:
1095:
1091:
1086:
1081:
1077:
1073:
1069:
1065:
1061:
1054:
1051:
1040:
1033:
1031:
1029:
1027:
1025:
1023:
1021:
1017:
1006:
1002:
998:
994:
987:
984:
980:. 2014-11-24.
979:
975:
969:
966:
960:
956:
952:
946:
943:
937:
933:
930:
927:
924:
921:
920:Nielsen's law
918:
915:
912:
909:
906:
904:
901:
899:
896:
894:
891:
889:
886:
884:
881:
879:
876:
875:
871:
869:
867:
862:
860:
856:
851:
849:
845:
841:
836:
834:
826:
824:
822:
816:
814:
810:
803:
799:
792:
785:
784:marketing mix
781:
779:
775:
774:
772:
769:
766:
763:
762:
761:
754:
749:
746:
745:Raw materials
743:
740:
736:
733:
730:
726:
723:
720:
719:machine tools
716:
713:
710:
707:
704:
703:
702:
696:
692:
689:
686:
682:
679:
676:
673:
670:
667:
664:
661:
658:
655:
652:
649:
646:
643:
642:
641:
638:
636:
628:
626:
623:
616:
613:
610:
607:
604:
600:
594:
592:
585:
582:
581:
580:
561:
558:
554:
548:
544:
540:
535:
531:
523:
522:
521:
518:
516:
512:
507:
504:The exponent
488:
485:
480:
476:
472:
464:
458:
453:
449:
444:
440:
435:
431:
427:
419:
413:
408:
404:
399:
395:
387:
381:
376:
372:
367:
361:
357:
353:
345:
339:
334:
330:
321:
318:
310:
306:
302:
297:
294:
290:
282:
281:
280:
278:
277:learning rate
274:
270:
266:
262:
237:
231:
226:
222:
217:
211:
207:
203:
198:
194:
186:
185:
184:
182:
175:
162:
160:
156:
152:
148:
143:
140:
136:
135:United States
132:
128:
117:
115:
111:
105:
97:
95:
92:
88:
84:
80:
72:
71:Swanson's law
67:
57:
52:
48:
47:
42:
37:
28:
27:
19:
1665:
1631:
1627:
1609:
1590:
1580:
1571:
1544:
1540:
1525:
1517:
1494:
1483:
1467:
1463:
1429:
1400:
1396:
1390:
1369:
1361:
1350:. Retrieved
1343:the original
1339:Perspectives
1338:
1325:
1314:. Retrieved
1304:
1293:
1282:. Retrieved
1278:
1269:
1234:
1227:
1205:(5): 50–61,
1202:
1198:
1192:
1181:. Retrieved
1177:
1168:
1151:
1145:
1139:
1114:
1108:
1102:
1070:(4): 155–6.
1067:
1063:
1053:
1042:. Retrieved
1008:. Retrieved
996:
986:
977:
968:
954:
945:
926:Cooper's law
914:Kryder's law
863:
852:
846:and focused
837:
830:
817:
805:
801:
796:
758:
712:Shipbuilding
700:
690:
680:
674:
668:
662:
656:
650:
644:
639:
632:
624:
620:
614:
608:
602:
595:
583:
578:
519:
514:
510:
505:
503:
276:
272:
268:
264:
260:
258:
177:
170:
168:
158:
146:
144:
123:
107:
82:
76:
55:
44:
908:Moore's law
737:Repetitive
727:Repetitive
145:The phrase
116:article.)
1709:Categories
1352:2007-03-24
1316:2013-04-05
1284:2021-11-13
1279:ARK Invest
1199:Interfaces
1183:2020-05-15
1044:2013-04-05
1010:2020-11-17
938:References
888:Management
827:Criticisms
813:BCG Matrix
778:price wars
91:efficiency
1248:Australia
1005:0017-8012
842:based on
811:like the
729:machining
706:Aerospace
559:−
486:⋅
459:
441:⋅
414:
396:⋅
382:
340:
232:
1658:16131552
1503:citation
1493:(1972),
1219:61642172
1094:25206041
959:Archived
957:. 2023.
872:See also
821:shakeout
747:: 93–96%
717:Complex
714:: 80-85%
139:aircraft
89:and the
79:industry
1649:1734219
1561:1251492
1526:Fortune
1252:Germany
1131:1412713
1085:4117135
739:welding
579:where:
263:is the
133:in the
51:Discuss
1672:
1656:
1646:
1616:
1598:
1559:
1427:about
1378:
1258:
1217:
1129:
1092:
1082:
1003:
267:and 1-
259:where
41:merged
1557:JSTOR
1346:(PDF)
1335:(PDF)
1215:S2CID
1127:JSTOR
708:: 85%
43:with
1670:ISBN
1654:PMID
1614:ISBN
1596:ISBN
1509:link
1376:ISBN
1256:ISBN
1240:U.S.
1090:PMID
1001:ISSN
864:The
87:good
1644:PMC
1636:doi
1549:doi
1472:doi
1405:doi
1207:doi
1156:doi
1119:doi
1080:PMC
1072:doi
450:log
405:log
373:log
331:log
223:log
77:In
49:. (
1711::
1692:,
1652:,
1642:,
1632:31
1630:,
1555:,
1545:47
1543:,
1535:;
1505:}}
1501:{{
1466:,
1462:,
1401:53
1399:.
1337:.
1277:.
1250:,
1246:,
1244:UK
1242:,
1238:,
1213:,
1203:12
1201:,
1176:.
1150:.
1125:.
1115:14
1113:.
1088:.
1078:.
1068:20
1066:.
1062:.
1019:^
995:.
976:.
953:.
697:.)
271:=
1638::
1551::
1511:)
1474::
1468:3
1411:.
1407::
1384:.
1355:.
1319:.
1287:.
1221:.
1209::
1186:.
1162:.
1158::
1152:3
1133:.
1121::
1096:.
1074::
1047:.
1013:.
683:(
615:a
609:n
603:n
598:n
596:C
587:1
584:C
562:a
555:n
549:1
545:C
541:=
536:n
532:C
515:b
511:b
506:b
489:b
481:x
477:C
473:=
468:)
465:b
462:(
454:2
445:2
436:x
432:C
428:=
423:)
420:b
417:(
409:2
400:2
391:)
388:b
385:(
377:2
368:x
362:1
358:C
354:=
349:)
346:b
343:(
335:2
326:)
322:x
319:2
316:(
311:1
307:C
303:=
298:x
295:2
291:C
273:l
269:b
261:b
255:,
241:)
238:b
235:(
227:2
218:x
212:1
208:C
204:=
199:x
195:C
180:1
178:C
173:x
171:C
53:)
20:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.