293:
457:
262:
242:
277:
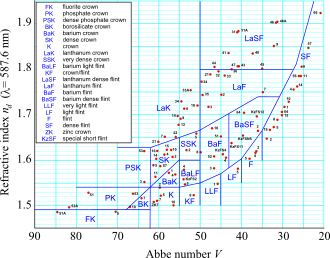
230:, showing refractive index (y-axis) as a function of Abbe number (x-axis). Most classical crown and flint glasses follow a gentle curve on the right side of the chart, which demonstrates these classical glasses have an inverse dependence between refractive index and Abbe number. Lens materials to the left of those have a higher Abbe number for a given refractive index, and may be considered to be low-dispersion types, including many of the lanthanum-doped glasses.
96:
402:
used in binocular objective lenses to help focus the light waves of the color spectrum on the human eye, and to deliver bright, sharp images. ED lenses are composed of a specific formulation that contains rare-earth elements. However, there is no ED standard that dictates the materials that must be used in ED lenses. Therefore, the quality of ED glass can vary.
31:
411:
292:
320:. The positive element is made of a low-dispersion glass, the negative element from a high-dispersion glass. To counteract the effect of the negative lens, the positive lens has to be thicker. Achromatic doublets therefore have higher thickness and weight than the equivalent non-chromatic-corrected single lenses.
401:
In binoculars, ED glass, also sometimes referred to as a high density (HD) glass, is a high quality optical glass that increases light transmission, decreases light dispersion, and so cuts down on chromatic aberration, or "color fringing", which is due to the splitting of the light spectrum. It is
221:
There are no industry-wide standards which determine whether a given material may be considered LD glass; these designations should be seen as manufacturer-specific, i.e., special glasses with LD / ED / UD labels have lower dispersion than conventional glasses from the same manufacturer.
587:
Lenses which incorporate low-dispersion glass element(s) can be more expensive than equivalent lenses using classical glass elements. This is because several of the mentioned high-performance glasses require the production of high-purity chemicals in substantial quantities.
261:
241:
456:
276:
445:, resulting in a lens material with high refractive index and low dispersion, suitable for apochromatic designs. Thoriated glass was in use before World War II, but not widely used until the 1950s. Because
572:, and weather factors. However borate glass with more than 20 mol.% of lanthanum oxide is very durable under ambient conditions. Another high-performance glass contains a high proportion of
833:
829:
453:, optical engineers and designers sought a replacement using different doping elements, and lens designs using thoriated glass been discontinued by the late 1980s.
1004:
974:
370:
also has benefits to CCTV cameras. The low chromatic aberration of SLD glass allows the lens to always stay in focus, from visible light to infrared.
1204:
106:
with LD glass have been branded and marketed with different names to indicate the use of low-dispersion elements in the optical design, including:
430:
lenses; in contrast to the achromatic doublets, which converge blue and red wavelengths, apochromats converge focus of three or more wavelengths.
618:
were used starting in the 1960s for lens elements requiring low dispersion; however, there were significant drawbacks to using fluorite: the low
1151:
1098:
958:
931:
492:
is also radioactive, it has far less activity than thorium. Borate glasses have lower wavelength-refraction dependence in the blue region of
218:
Some glasses may include a "Super" modifier (e.g., "Super ED") to designate materials with even lower wavelength dispersion characteristics.
71:
does not change as strongly with different wavelengths of light. In other words, the light passing through the glass has a smaller spread or
1304:
821:
1187:
1134:
1081:
1029:
626:. In addition, fluorite has poor shape retention and is very fragile, requiring special handling to process into lens elements.
670:
508:
manufactured high-performance thorium-free optical glass for aerial photography, but it was yellow-tinted. In combination with
796:
1279:
1319:
363:
provided by a telephoto lens also allows the subject of the photography to stand out better against the background.
665:
539:
could be used as a suitable replacement for thorium. However, additional elements had to be added to preserve the
423:
390:
898:
270:
from inadequate correction to converge different wavelengths, giving a "rainbow effect" at high-contrast edges.
690:
286:: crown and flint glasses are used together to converge the red and blue wavelengths at a single focal point.
982:
742:
509:
630:
465:
623:
536:
521:
356:
336:
332:
313:
267:
84:
64:
39:
79:
effect" at high-contrast edges. Wavelength dispersion in a certain material is characterized by its
517:
139:
72:
35:
551:
485:
352:
317:
283:
1045:
1183:
1130:
1077:
1025:
998:
954:
927:
573:
513:
199:
156:
103:
948:
921:
1254:
717:
638:
619:
602:
532:
379:
252:
68:
655:
544:
520:. The use of rare earths allowed development of high-index low-dispersion glasses of both
481:
473:
442:
438:
46:
837:
497:
488:, greatly expanding the available range of high-index low-dispersion glasses; although
360:
324:
299:
1255:"Fluorite lenses: Corrective capabilities beyond the limits of ordinary optical glass"
1229:
873:
851:
768:
531:
The use of low-dispersion glass in long-focal-length lens assemblies was pioneered by
1313:
650:
634:
348:
340:
629:
A good high-refraction replacement for calcium fluoride as a lens material can be a
477:
383:
328:
1177:
1124:
1071:
1019:
247:
White light passing through a prism using conventional glass is dispersed into a
1287:
660:
525:
501:
450:
331:
objectives benefit less from low-dispersion elements, as their chief problem is
80:
43:
339:. The spherical aberration introduced by the LD elements can be corrected with
427:
415:
343:
elements. The increased sharpness provided by SLD elements allows using lower
227:
212:
581:
561:
540:
489:
223:
95:
547:
which would cause striae defects in images captured through those lenses.
622:
of fluorite required high curvatures of the lenses, therefore increasing
597:
577:
493:
344:
17:
615:
446:
410:
248:
118:
76:
30:
27:
Lens glass material with reduced refractive index shift with wavelength
1205:"Asahi Pentax Ultra Achromatic Takumar 85mm lens - achromatic imaging"
569:
182:
169:
143:
797:"Groundbreaking 06: Bringing Special Low Dispersion Glass to Life"
505:
455:
409:
386:
135:
94:
60:
29:
718:"NIKKOR - The Thousand and One Nights No.11: NIKKOR-H 300mm F2.8"
565:
87:
is an example of a relatively inexpensive low-dispersion glass.
596:
In parallel to the development of LD glass, artificially-grown
535:(Leitz) after World War II. Leitz laboratories discovered that
226:
publishes a diagram of the glasses it manufactures, grouped by
83:; LD glass has a higher Abbe number than conventional types.
1152:"Rare Earth Glass Leica Lenses: A Quick and Quirky Overview"
99:
Abbe number versus refractive index for glass lens materials
1046:"Binocular Lens and Prism Glass - Helpful Facts for 2022"
75:
between its constituent colors, resulting in a reduced "
633:. Here, a proportion of fluorides is stabilized with a
312:
Low-dispersion glasses are particularly used to reduce
38:(i.e., the distance between foci for blue and red) of
378:
Low-dispersion glasses are also employed in handling
555:
782:– via Pacific Rim Camera, Reference Library.
743:"Make Your First Interchangeable Lens a Telephoto"
584:to prevent contamination with crucible material.
576:; however its high melting point requires use of
512:, the tint was actually beneficial, improving
422:Some glasses have a peculiar property called
8:
791:
789:
426:. Abnormal dispersion is required to design
418:triplet converges three wavelengths of light
554:" glasses, which Schott classifies as KzF (
1103:ORAU Museum of Radiation and Radioactivity
1073:Camera Lenses: From box camera to digital
682:
237:
1150:Schneider, Jason (September 5, 2018).
1003:: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (
996:
1179:History of Astronomy: An encyclopedia
1126:The Art and Science of Optical Design
1070:Smith, Gregory Hallock (2006-01-01).
691:"Minolta announce two new SSM lenses"
560:), are however highly susceptible to
7:
592:Calcium fluoride (fluorite) crystals
302:often incorporate LD glass elements.
1099:"Thoriated Camera Lens (ca. 1970s)"
920:Gerald F. Marshall (19 July 1991).
543:structure of the glass and prevent
749:. No. 3. 1985. pp. 13–16
25:
1123:Shannon, Robert R. (1997-06-13).
434:Rare earth and radioactive lenses
389:, to prevent pulse broadening by
34:Comparison of visible wavelength
291:
275:
260:
240:
953:. Amherst Media. pp. 19–.
769:"Pentax 6×7 [brochure]"
671:Material dispersion coefficient
472:As an alternative, after 1930,
1129:. Cambridge University Press.
1018:Horn, Alexander (2009-11-09).
1:
1209:JMC Scientific Consulting Ltd
1176:Lankford, John (1997-01-01).
1021:Ultra-fast Material Metrology
351:. This is critical, e.g., in
424:anomalous partial dispersion
368:special-low-dispersion glass
255:is a function of wavelength.
149:Extraordinary Low Dispersion
1203:Crowther, Jonathan (2017).
1156:Leica Society International
926:. CRC Press. pp. 65–.
556:
464:fitted to K-19B camera for
1336:
950:Telephoto Lens Photography
899:"Interactive Abbe diagram"
822:"Tamron Product Brochures"
774:. Pentax Corporation. 1976
666:Diffraction-limited system
1192:– via Google Books.
1139:– via Google Books.
1086:– via Google Books.
1024:. John Wiley & Sons.
393:in the optical elements.
391:group velocity dispersion
1182:. Taylor & Francis.
128:Extraordinary Dispersion
469:
419:
188:Special Low Dispersion
100:
49:
947:Rob Sheppard (1997).
852:"Tokina Lens Catalog"
631:fluorophosphate glass
466:aerial reconnaissance
459:
413:
347:and therefore faster
316:, most often used in
98:
33:
1050:Birds At First Sight
840:on November 6, 2007.
624:spherical aberration
537:lanthanum(III) oxide
510:black and white film
484:and oxides of other
357:wildlife photography
337:chromatic aberration
333:spherical aberration
314:chromatic aberration
268:Chromatic aberration
205:Ultra-low Dispersion
192:Super Low Dispersion
175:Super Low Dispersion
124:Extra-low Dispersion
111:Anomalous Dispersion
65:chromatic aberration
53:Low-dispersion glass
1305:Lens Specifications
1259:Canon Camera Museum
1234:Canon Camera Museum
878:Canon Camera Museum
637:, with addition of
486:rare-earth elements
366:Infrared corrected
318:achromatic doublets
104:Photographic lenses
1320:Glass compositions
1230:"FL-F 300mm f/5.6"
979:www.oemcameras.com
518:ultraviolet filter
470:
420:
382:of light, in e.g.
353:sports photography
284:achromatic doublet
101:
50:
1280:"Optical glasses"
960:978-0-936262-53-6
933:978-0-8247-8473-7
874:"FD 500mm f/4.5L"
854:. Tokina Co., Ltd
574:zirconium dioxide
550:These so-called "
380:ultrashort pulses
323:In comparison to
298:High-performance
47:converging lenses
16:(Redirected from
1327:
1292:
1291:
1286:. Archived from
1276:
1270:
1269:
1267:
1265:
1251:
1245:
1244:
1242:
1240:
1226:
1220:
1219:
1217:
1215:
1200:
1194:
1193:
1173:
1167:
1166:
1164:
1162:
1147:
1141:
1140:
1120:
1114:
1113:
1111:
1109:
1094:
1088:
1087:
1067:
1061:
1060:
1058:
1057:
1042:
1036:
1035:
1015:
1009:
1008:
1002:
994:
992:
990:
981:. Archived from
971:
965:
964:
944:
938:
937:
923:Optical Scanning
917:
911:
910:
908:
906:
895:
889:
888:
886:
884:
870:
864:
863:
861:
859:
848:
842:
841:
836:. Archived from
818:
812:
811:
809:
807:
793:
784:
783:
781:
779:
773:
765:
759:
758:
756:
754:
739:
733:
732:
730:
728:
713:
707:
706:
704:
702:
687:
639:titanium dioxide
620:refraction index
613:
611:
610:
559:
533:Ernst Leitz GmbH
516:by acting as an
498:silicate glasses
325:telephoto lenses
300:telephoto lenses
295:
279:
264:
253:refractive index
244:
69:refractive index
21:
1335:
1334:
1330:
1329:
1328:
1326:
1325:
1324:
1310:
1309:
1301:
1296:
1295:
1278:
1277:
1273:
1263:
1261:
1253:
1252:
1248:
1238:
1236:
1228:
1227:
1223:
1213:
1211:
1202:
1201:
1197:
1190:
1175:
1174:
1170:
1160:
1158:
1149:
1148:
1144:
1137:
1122:
1121:
1117:
1107:
1105:
1096:
1095:
1091:
1084:
1069:
1068:
1064:
1055:
1053:
1044:
1043:
1039:
1032:
1017:
1016:
1012:
995:
988:
986:
985:on 3 March 2016
975:"Archived copy"
973:
972:
968:
961:
946:
945:
941:
934:
919:
918:
914:
904:
902:
897:
896:
892:
882:
880:
872:
871:
867:
857:
855:
850:
849:
845:
820:
819:
815:
805:
803:
795:
794:
787:
777:
775:
771:
767:
766:
762:
752:
750:
741:
740:
736:
726:
724:
715:
714:
710:
700:
698:
689:
688:
684:
679:
656:Achromatic lens
647:
609:
606:
605:
604:
601:
594:
545:crystallization
504:. During WWII,
482:lanthanum oxide
474:George W. Morey
443:thorium dioxide
439:Thoriated glass
436:
408:
399:
376:
310:
303:
296:
287:
280:
271:
265:
256:
245:
236:
93:
59:) is a type of
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
1333:
1331:
1323:
1322:
1312:
1311:
1308:
1307:
1300:
1299:External links
1297:
1294:
1293:
1290:on 2016-11-30.
1271:
1246:
1221:
1195:
1188:
1168:
1142:
1135:
1115:
1089:
1082:
1076:. SPIE Press.
1062:
1037:
1030:
1010:
966:
959:
939:
932:
912:
890:
865:
843:
826:Adaptall-2.com
813:
785:
760:
734:
708:
697:. 3 March 2003
681:
680:
678:
675:
674:
673:
668:
663:
658:
653:
646:
643:
607:
593:
590:
500:with the same
478:borate glasses
441:is doped with
435:
432:
407:
404:
398:
395:
375:
372:
361:depth of field
359:. The shallow
309:
306:
305:
304:
297:
290:
288:
282:Diagram of an
281:
274:
272:
266:
259:
257:
246:
239:
235:
232:
216:
215:
202:
185:
172:
162:Low Dispersion
159:
146:
121:
92:
89:
67:, meaning the
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1332:
1321:
1318:
1317:
1315:
1306:
1303:
1302:
1298:
1289:
1285:
1281:
1275:
1272:
1260:
1256:
1250:
1247:
1235:
1231:
1225:
1222:
1210:
1206:
1199:
1196:
1191:
1189:9780815303220
1185:
1181:
1180:
1172:
1169:
1157:
1153:
1146:
1143:
1138:
1136:9780521588683
1132:
1128:
1127:
1119:
1116:
1104:
1100:
1097:Frame, Paul.
1093:
1090:
1085:
1083:9780819460936
1079:
1075:
1074:
1066:
1063:
1051:
1047:
1041:
1038:
1033:
1031:9783527408870
1027:
1023:
1022:
1014:
1011:
1006:
1000:
984:
980:
976:
970:
967:
962:
956:
952:
951:
943:
940:
935:
929:
925:
924:
916:
913:
900:
894:
891:
879:
875:
869:
866:
853:
847:
844:
839:
835:
831:
827:
823:
817:
814:
802:
798:
792:
790:
786:
770:
764:
761:
748:
744:
738:
735:
723:
722:Nikon Imaging
719:
716:Sato, Haruo.
712:
709:
696:
692:
686:
683:
676:
672:
669:
667:
664:
662:
659:
657:
654:
652:
651:Aspheric lens
649:
648:
644:
642:
640:
636:
635:metaphosphate
632:
627:
625:
621:
617:
612:
599:
591:
589:
585:
583:
579:
575:
571:
567:
563:
558:
553:
548:
546:
542:
538:
534:
529:
527:
523:
519:
515:
511:
507:
503:
499:
495:
491:
487:
483:
479:
475:
467:
463:
458:
454:
452:
448:
444:
440:
433:
431:
429:
425:
417:
412:
405:
403:
396:
394:
392:
388:
385:
381:
373:
371:
369:
364:
362:
358:
354:
350:
349:shutter speed
346:
342:
341:aspheric lens
338:
334:
330:
326:
321:
319:
315:
307:
301:
294:
289:
285:
278:
273:
269:
263:
258:
254:
250:
243:
238:
233:
231:
229:
225:
219:
214:
210:
206:
203:
201:
197:
193:
189:
186:
184:
180:
176:
173:
171:
167:
163:
160:
158:
154:
150:
147:
145:
141:
137:
133:
129:
125:
122:
120:
116:
112:
109:
108:
107:
105:
97:
90:
88:
86:
82:
78:
74:
70:
66:
63:with reduced
62:
58:
54:
48:
45:
41:
37:
32:
19:
1288:the original
1283:
1274:
1262:. Retrieved
1258:
1249:
1237:. Retrieved
1233:
1224:
1212:. Retrieved
1208:
1198:
1178:
1171:
1159:. Retrieved
1155:
1145:
1125:
1118:
1106:. Retrieved
1102:
1092:
1072:
1065:
1054:. Retrieved
1052:. 2022-05-16
1049:
1040:
1020:
1013:
987:. Retrieved
983:the original
978:
969:
949:
942:
922:
915:
903:. Retrieved
893:
881:. Retrieved
877:
868:
856:. Retrieved
846:
838:the original
825:
816:
804:. Retrieved
800:
776:. Retrieved
763:
751:. Retrieved
746:
737:
725:. Retrieved
721:
711:
699:. Retrieved
694:
685:
628:
595:
586:
552:borate flint
549:
530:
471:
468:, with puppy
461:
437:
428:apochromatic
421:
416:apochromatic
400:
397:Sport optics
377:
367:
365:
335:rather than
329:focal length
322:
311:
251:because the
234:Applications
220:
217:
208:
204:
195:
191:
187:
178:
174:
165:
161:
152:
148:
131:
127:
123:
114:
110:
102:
56:
52:
51:
901:. Schott AG
828:. pp.
661:Abbe number
502:Abbe number
480:doped with
476:introduced
451:radioactive
384:mode-locked
85:Crown glass
81:Abbe number
44:flint glass
1056:2022-09-28
989:17 January
801:Sigma Sein
695:ePHOTOzine
677:References
462:Aero-Ektar
374:Scientific
327:, shorter
228:glass code
73:dispersion
36:dispersion
1284:GMP Photo
1264:17 August
1239:16 August
1214:16 August
1161:16 August
1108:17 August
905:17 August
883:16 August
858:16 August
806:16 August
778:16 August
753:16 August
747:VisionAge
727:16 August
701:16 August
582:crucibles
562:corrosion
557:kurzflint
541:amorphous
490:lanthanum
345:f-numbers
224:Schott AG
1314:Category
999:cite web
645:See also
616:crystals
598:fluorite
578:platinum
514:contrast
494:spectrum
91:Branding
57:LD glass
18:ED glass
570:alkalis
528:types.
447:thorium
406:History
308:Imaging
249:rainbow
140:Olympus
119:Minolta
77:rainbow
1186:
1133:
1080:
1028:
957:
930:
580:lined
460:Kodak
387:lasers
183:Tokina
170:Tamron
144:Pentax
772:(PDF)
566:acids
526:flint
522:crown
506:Kodak
496:than
414:This
213:Canon
200:Sigma
157:Sigma
136:Nikon
61:glass
40:crown
1266:2024
1241:2024
1216:2024
1184:ISBN
1163:2024
1131:ISBN
1110:2024
1078:ISBN
1026:ISBN
1005:link
991:2022
955:ISBN
928:ISBN
907:2024
885:2024
860:2024
808:2024
780:2024
755:2024
729:2024
703:2024
524:and
355:and
42:and
603:CaF
564:by
449:is
211:):
198:):
196:SLD
190:or
181:):
168:):
155:):
153:ELD
134:):
126:or
117:):
1316::
1282:.
1257:.
1232:.
1207:.
1154:.
1101:.
1048:.
1001:}}
997:{{
977:.
876:.
832:,
824:.
799:.
788:^
745:.
720:.
693:.
641:.
614:)
568:,
209:UD
179:SD
166:LD
142:,
138:,
132:ED
115:AD
1268:.
1243:.
1218:.
1165:.
1112:.
1059:.
1034:.
1007:)
993:.
963:.
936:.
909:.
887:.
862:.
834:2
830:1
810:.
757:.
731:.
705:.
608:2
600:(
207:(
194:(
177:(
164:(
151:(
130:(
113:(
55:(
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.