750:
27:
502:
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0
484:
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
753:
Example of erosion on a grayscale image using a 5x5 flat structuring element. The top figure demonstrates the application of the structuring element window to the individual pixels of the original image. The bottom figure shows the resulting eroded
1351:
1025:
In other words the erosion of a point is the minimum of the points in its neighborhood, with that neighborhood defined by the structuring element. In this way it is similar to many other kinds of image filters like the
704:
246:
485:
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
151:
The basic idea in binary morphology is to probe an image with a simple, pre-defined shape, drawing conclusions on how this shape fits or misses the shapes in the image. This simple "probe" is called
818:
449:
1010:
592:
1266:
320:
639:
1388:
142:
107:
382:. For example, the erosion of a square of side 10, centered at the origin, by a disc of radius 2, also centered at the origin, is a square of side 6 centered at the origin.
349:
840:
554:
1162:
1234:
1195:
1098:
887:
1118:
864:
724:
1274:
1138:
1477:
1463:
1449:
1435:
1505:
647:
188:
46:
780:
396:
916:
559:
1500:
1239:
520:
20:
268:
1400:
612:
763:
1405:
1046:
734:
727:
42:
1358:
118:
83:
1415:
1410:
470:
325:
749:
152:
62:
823:
533:
1147:
1207:
1167:
1071:
1473:
1459:
1445:
1431:
1346:{\displaystyle \bigwedge _{i}\varepsilon (X_{i})=\varepsilon \left(\bigwedge _{i}X_{i}\right)}
869:
1103:
849:
709:
1062:
1042:
738:
58:
1123:
1031:
767:
78:
492:
the origin of B, if B is completely contained by A the pixel is retained, else deleted.
503:
0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
49:
from which all other morphological operations are based. It was originally defined for
1494:
1058:
1027:
771:
358:
has a center (e.g., a disk or a square), and this center is located on the origin of
113:
843:
510:
inside A that the pixels values are retained, otherwise it gets deleted or eroded.
50:
30:
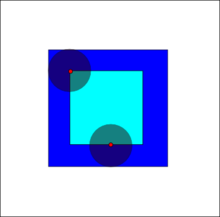
The erosion of the dark-blue square by a disk, resulting in the light-blue square.
527:
759:
54:
1442:
Image
Analysis and Mathematical Morphology, Volume 2: Theoretical Advances
1054:
1050:
1019:
110:
900:, where B is the space that b(x) is defined, the grayscale erosion of
155:, and is itself a binary image (i.e., a subset of the space or grid).
1268:
that distributes over the infimum, and preserves the universe. I.e.:
74:
26:
748:
370:
can be understood as the locus of points reached by the center of
65:
for probing and reducing the shapes contained in the input image.
25:
1140:, respectively. Its universe and least element are symbolized by
488:
Assuming that the origin B is at its center, for each pixel in A
1100:
be a complete lattice, with infimum and supremum symbolized by
699:{\displaystyle (A\ominus B)\ominus C=A\ominus (B\oplus C)}
241:{\displaystyle A\ominus B=\{z\in E\mid B_{z}\subseteq A\}}
1470:
Morphological Image
Analysis; Principles and Applications
1487:, 2nd ed. Upper Saddle River, N.J.: Prentice Hall, 2002.
41:) is one of two fundamental operations (the other being
481:
Suppose A is a 13 x 13 matrix and B is a 3 x 3 matrix:
1361:
1277:
1242:
1210:
1170:
1150:
1126:
1106:
1074:
919:
872:
852:
826:
813:{\displaystyle \mathbb {R} \cup \{\infty ,-\infty \}}
783:
712:
650:
615:
562:
536:
399:
328:
271:
191:
121:
86:
1382:
1345:
1260:
1228:
1189:
1156:
1132:
1112:
1092:
1004:
881:
858:
834:
812:
718:
698:
633:
586:
548:
444:{\displaystyle A\ominus B=\bigcap _{b\in B}A_{-b}}
443:
343:
314:
240:
136:
101:
1456:An Introduction to Morphological Image Processing
948:
866:is an element larger than any real number, and
1005:{\displaystyle (f\ominus b)(x)=\inf _{y\in B}}
587:{\displaystyle A\ominus B\subseteq C\ominus B}
73:In binary morphology, an image is viewed as a
162:be a Euclidean space or an integer grid, and
8:
1184:
1171:
889:is an element smaller than any real number.
807:
792:
309:
285:
235:
204:
1261:{\displaystyle \varepsilon :L\rightarrow L}
499:of A by B is given by this 13 x 13 matrix.
1428:Image Analysis and Mathematical Morphology
16:Basic operation in mathematical morphology
1360:
1332:
1322:
1298:
1282:
1276:
1241:
1209:
1178:
1169:
1149:
1125:
1105:
1073:
951:
918:
896:and the grayscale structuring element by
871:
851:
828:
827:
825:
785:
784:
782:
711:
649:
614:
561:
535:
432:
416:
398:
327:
276:
270:
223:
190:
128:
124:
123:
120:
93:
89:
88:
85:
315:{\displaystyle B_{z}=\{b+z\mid b\in B\}}
469:This is more generally also known as a
61:. The erosion operation usually uses a
634:{\displaystyle A\ominus B\subseteq A}
7:
601:belongs to the structuring element
1151:
876:
853:
804:
795:
329:
14:
1383:{\displaystyle \varepsilon (U)=U}
1197:be a collection of elements from
393:is also given by the expression:
1483:R. C. Gonzalez and R. E. Woods,
137:{\displaystyle \mathbb {Z} ^{d}}
102:{\displaystyle \mathbb {R} ^{d}}
1057:. In particular, it contains a
506:This means that only when B is
1371:
1365:
1304:
1291:
1252:
1223:
1211:
1164:, respectively. Moreover, let
1087:
1075:
999:
996:
990:
981:
969:
963:
941:
935:
932:
920:
693:
681:
663:
651:
344:{\displaystyle \forall z\in E}
47:morphological image processing
1:
1038:Erosions on complete lattices
354:When the structuring element
1049:, where every subset has an
835:{\displaystyle \mathbb {R} }
549:{\displaystyle A\subseteq C}
57:images, and subsequently to
1065:(also denoted "universe").
458:denotes the translation of
178:by the structuring element
1522:
1157:{\displaystyle \emptyset }
53:, later being extended to
18:
1229:{\displaystyle (L,\leq )}
1190:{\displaystyle \{X_{i}\}}
1093:{\displaystyle (L,\leq )}
1485:Digital image processing
1458:by Edward R. Dougherty,
1018:where "inf" denotes the
882:{\displaystyle -\infty }
37:(usually represented by
21:Erosion (disambiguation)
1506:Mathematical morphology
1401:Mathematical morphology
1113:{\displaystyle \wedge }
859:{\displaystyle \infty }
762:morphology, images are
719:{\displaystyle \oplus }
265:by the vector z, i.e.,
1384:
1347:
1262:
1230:
1191:
1158:
1134:
1114:
1094:
1047:partially ordered sets
1006:
883:
860:
836:
814:
755:
728:morphological dilation
720:
700:
644:The erosion satisfies
635:
605:, then the erosion is
588:
550:
445:
362:, then the erosion of
345:
316:
261:is the translation of
242:
138:
103:
31:
1385:
1348:
1263:
1231:
1192:
1159:
1135:
1133:{\displaystyle \vee }
1115:
1095:
1007:
892:Denoting an image by
884:
861:
837:
815:
752:
721:
701:
636:
589:
551:
521:translation invariant
446:
346:
317:
243:
144:, for some dimension
139:
104:
29:
1359:
1275:
1240:
1208:
1168:
1148:
1124:
1104:
1072:
917:
870:
850:
824:
781:
710:
648:
613:
560:
534:
508:completely contained
471:Minkowski difference
397:
326:
269:
189:
174:of the binary image
119:
84:
19:For other uses, see
153:structuring element
63:structuring element
1472:by Pierre Soille,
1380:
1343:
1327:
1287:
1258:
1226:
1187:
1154:
1130:
1110:
1090:
1002:
962:
879:
856:
832:
810:
756:
716:
696:
631:
584:
546:
441:
427:
341:
312:
238:
166:a binary image in
134:
99:
32:
1318:
1278:
1043:Complete lattices
947:
745:Grayscale erosion
597:If the origin of
412:
59:complete lattices
1513:
1501:Digital geometry
1389:
1387:
1386:
1381:
1352:
1350:
1349:
1344:
1342:
1338:
1337:
1336:
1326:
1303:
1302:
1286:
1267:
1265:
1264:
1259:
1236:is any operator
1235:
1233:
1232:
1227:
1196:
1194:
1193:
1188:
1183:
1182:
1163:
1161:
1160:
1155:
1139:
1137:
1136:
1131:
1119:
1117:
1116:
1111:
1099:
1097:
1096:
1091:
1063:greatest element
1011:
1009:
1008:
1003:
961:
888:
886:
885:
880:
865:
863:
862:
857:
841:
839:
838:
833:
831:
819:
817:
816:
811:
788:
739:set intersection
725:
723:
722:
717:
705:
703:
702:
697:
640:
638:
637:
632:
593:
591:
590:
585:
555:
553:
552:
547:
450:
448:
447:
442:
440:
439:
426:
350:
348:
347:
342:
321:
319:
318:
313:
281:
280:
247:
245:
244:
239:
228:
227:
143:
141:
140:
135:
133:
132:
127:
108:
106:
105:
100:
98:
97:
92:
1521:
1520:
1516:
1515:
1514:
1512:
1511:
1510:
1491:
1490:
1444:by Jean Serra,
1430:by Jean Serra,
1424:
1397:
1357:
1356:
1328:
1317:
1313:
1294:
1273:
1272:
1238:
1237:
1206:
1205:
1174:
1166:
1165:
1146:
1145:
1122:
1121:
1102:
1101:
1070:
1069:
1040:
1032:gaussian filter
915:
914:
868:
867:
848:
847:
822:
821:
779:
778:
768:Euclidean space
747:
733:The erosion is
708:
707:
646:
645:
611:
610:
558:
557:
532:
531:
519:The erosion is
516:
504:
486:
479:
456:
428:
395:
394:
385:The erosion of
324:
323:
272:
267:
266:
260:
219:
187:
186:
182:is defined by:
122:
117:
116:
87:
82:
81:
79:Euclidean space
71:
24:
17:
12:
11:
5:
1519:
1517:
1509:
1508:
1503:
1493:
1492:
1489:
1488:
1481:
1467:
1453:
1439:
1423:
1420:
1419:
1418:
1413:
1408:
1403:
1396:
1393:
1392:
1391:
1379:
1376:
1373:
1370:
1367:
1364:
1354:
1341:
1335:
1331:
1325:
1321:
1316:
1312:
1309:
1306:
1301:
1297:
1293:
1290:
1285:
1281:
1257:
1254:
1251:
1248:
1245:
1225:
1222:
1219:
1216:
1213:
1204:An erosion in
1186:
1181:
1177:
1173:
1153:
1129:
1109:
1089:
1086:
1083:
1080:
1077:
1039:
1036:
1016:
1015:
1014:
1013:
1001:
998:
995:
992:
989:
986:
983:
980:
977:
974:
971:
968:
965:
960:
957:
954:
950:
946:
943:
940:
937:
934:
931:
928:
925:
922:
878:
875:
855:
842:is the set of
830:
809:
806:
803:
800:
797:
794:
791:
787:
746:
743:
742:
741:
731:
715:
695:
692:
689:
686:
683:
680:
677:
674:
671:
668:
665:
662:
659:
656:
653:
642:
630:
627:
624:
621:
618:
607:anti-extensive
595:
583:
580:
577:
574:
571:
568:
565:
545:
542:
539:
530:, that is, if
524:
515:
512:
501:
495:Therefore the
483:
478:
475:
454:
438:
435:
431:
425:
422:
419:
415:
411:
408:
405:
402:
340:
337:
334:
331:
311:
308:
305:
302:
299:
296:
293:
290:
287:
284:
279:
275:
256:
250:
249:
237:
234:
231:
226:
222:
218:
215:
212:
209:
206:
203:
200:
197:
194:
131:
126:
96:
91:
70:
69:Binary erosion
67:
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1518:
1507:
1504:
1502:
1499:
1498:
1496:
1486:
1482:
1479:
1478:3-540-65671-5
1475:
1471:
1468:
1465:
1464:0-8194-0845-X
1461:
1457:
1454:
1451:
1450:0-12-637241-1
1447:
1443:
1440:
1437:
1436:0-12-637240-3
1433:
1429:
1426:
1425:
1421:
1417:
1414:
1412:
1409:
1407:
1404:
1402:
1399:
1398:
1394:
1377:
1374:
1368:
1362:
1355:
1339:
1333:
1329:
1323:
1319:
1314:
1310:
1307:
1299:
1295:
1288:
1283:
1279:
1271:
1270:
1269:
1255:
1249:
1246:
1243:
1220:
1217:
1214:
1202:
1200:
1179:
1175:
1143:
1127:
1107:
1084:
1081:
1078:
1066:
1064:
1060:
1059:least element
1056:
1052:
1048:
1044:
1037:
1035:
1033:
1029:
1028:median filter
1023:
1021:
993:
987:
984:
978:
975:
972:
966:
958:
955:
952:
944:
938:
929:
926:
923:
913:
912:
911:
910:
909:
907:
903:
899:
895:
890:
873:
845:
801:
798:
789:
776:
773:
769:
765:
761:
751:
744:
740:
736:
732:
729:
713:
690:
687:
684:
678:
675:
672:
669:
666:
660:
657:
654:
643:
628:
625:
622:
619:
616:
608:
604:
600:
596:
581:
578:
575:
572:
569:
566:
563:
543:
540:
537:
529:
525:
522:
518:
517:
513:
511:
509:
500:
498:
493:
491:
482:
476:
474:
472:
467:
465:
461:
457:
436:
433:
429:
423:
420:
417:
413:
409:
406:
403:
400:
392:
388:
383:
381:
378:moves inside
377:
373:
369:
365:
361:
357:
352:
338:
335:
332:
306:
303:
300:
297:
294:
291:
288:
282:
277:
273:
264:
259:
255:
232:
229:
224:
220:
216:
213:
210:
207:
201:
198:
195:
192:
185:
184:
183:
181:
177:
173:
169:
165:
161:
156:
154:
149:
147:
129:
115:
112:
94:
80:
76:
68:
66:
64:
60:
56:
52:
51:binary images
48:
44:
40:
36:
28:
22:
1484:
1469:
1455:
1441:
1427:
1203:
1198:
1141:
1067:
1041:
1024:
1017:
908:is given by
905:
901:
897:
893:
891:
774:
757:
735:distributive
726:denotes the
606:
602:
598:
507:
505:
496:
494:
489:
487:
480:
468:
463:
459:
452:
390:
386:
384:
379:
375:
371:
367:
363:
359:
355:
353:
262:
257:
253:
251:
179:
175:
171:
167:
163:
159:
157:
150:
145:
72:
38:
34:
33:
490:superimpose
1495:Categories
1422:References
766:mapping a
528:increasing
514:Properties
1363:ε
1320:⋀
1311:ε
1289:ε
1280:⋀
1253:→
1244:ε
1221:≤
1152:∅
1128:∨
1108:∧
1085:≤
985:−
956:∈
927:⊖
877:∞
874:−
854:∞
805:∞
802:−
796:∞
790:∪
764:functions
760:grayscale
714:⊕
688:⊕
679:⊖
667:⊖
658:⊖
626:⊆
620:⊖
579:⊖
573:⊆
567:⊖
541:⊆
434:−
421:∈
414:⋂
404:⊖
336:∈
330:∀
304:∈
298:∣
230:⊆
217:∣
211:∈
196:⊖
55:grayscale
1406:Dilation
1395:See also
1055:supremum
1030:and the
820:, where
706:, where
609:, i.e.,
451:, where
43:dilation
1416:Closing
1411:Opening
1051:infimum
1020:infimum
556:, then
497:Erosion
477:Example
172:erosion
111:integer
109:or the
35:Erosion
1480:(1999)
1476:
1466:(1992)
1462:
1452:(1988)
1448:
1438:(1982)
1434:
1061:and a
1053:and a
754:image.
526:It is
252:where
170:. The
75:subset
844:reals
777:into
737:over
374:when
77:of a
45:) in
1474:ISBN
1460:ISBN
1446:ISBN
1432:ISBN
1144:and
1120:and
1068:Let
1045:are
898:b(x)
894:f(x)
772:grid
158:Let
114:grid
949:inf
904:by
770:or
758:In
462:by
389:by
366:by
1497::
1201:.
1034:.
1022:.
846:,
473:.
466:.
464:-b
455:−b
351:.
322:,
148:.
1390:.
1378:U
1375:=
1372:)
1369:U
1366:(
1353:,
1340:)
1334:i
1330:X
1324:i
1315:(
1308:=
1305:)
1300:i
1296:X
1292:(
1284:i
1256:L
1250:L
1247::
1224:)
1218:,
1215:L
1212:(
1199:L
1185:}
1180:i
1176:X
1172:{
1142:U
1088:)
1082:,
1079:L
1076:(
1012:,
1000:]
997:)
994:y
991:(
988:b
982:)
979:y
976:+
973:x
970:(
967:f
964:[
959:B
953:y
945:=
942:)
939:x
936:(
933:)
930:b
924:f
921:(
906:b
902:f
829:R
808:}
799:,
793:{
786:R
775:E
730:.
694:)
691:C
685:B
682:(
676:A
673:=
670:C
664:)
661:B
655:A
652:(
641:.
629:A
623:B
617:A
603:B
599:E
594:.
582:B
576:C
570:B
564:A
544:C
538:A
523:.
460:A
453:A
437:b
430:A
424:B
418:b
410:=
407:B
401:A
391:B
387:A
380:A
376:B
372:B
368:B
364:A
360:E
356:B
339:E
333:z
310:}
307:B
301:b
295:z
292:+
289:b
286:{
283:=
278:z
274:B
263:B
258:z
254:B
248:,
236:}
233:A
225:z
221:B
214:E
208:z
205:{
202:=
199:B
193:A
180:B
176:A
168:E
164:A
160:E
146:d
130:d
125:Z
95:d
90:R
39:⊖
23:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.