491:
1067:
455:
479:
503:
467:
36:
533:
59:
410:
arising from the falx cerebri and completely concealed by the overlying cortex. Falcine meningioma tends to grow predominantly into one cerebral hemisphere but is often bilateral, and in some patients the tumor grows into the inferior edge of the sagittal sinus. However, although much information is
312:
Lymphatic drainage of the falx cerebri occurs mostly via meningeal lymphatic vessels that run parallel to the dural sinuses and that eventually exit the cranial vault through the jugular foramen to empty into deep cervical lymph nodes. A minority of lymph from the falx cerebri is drained anteriorly
321:
The falx cerebri receives innervaton from all three branches of the trigeminal nerve. It receives symphatetic innervation predominantly from the superior cervical ganglia. It may receive additional innervation from dorsal rami of CN 1 and CN 2, the hypoglossal nerve, and recurrent branches of the
308:
The falx cerebri receives its blood supply primarily from two vessels; the anterior portion receives blood supply from the anterior meningeal artery (a.k.a. anterior falx artery, or anterior falcine artery) (a branch of the anterior ethmoidal artery), and the posterior portion from the posterior
1087:
376:
of the falx cerebri may occur, and may result in adherence of the cerebral hemispheres across the midline. Agenesis is usually associated with other developmental complications; falx cerebri agenesis in absence of other neural symptoms is exceedingly rare.
490:
297:(the latter representing its posterior-most point of attachment); the superior sagittal sinus runs in the cranial groove between the falx cerebri's two attachments.
689:
423:(complete or partial) of the falx cerebri results in the adherence of the cerebral hemispheres, blocking midline transcallosal surgical access to the ventricles.
63:
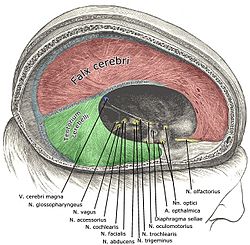
Diagrammatic representation of a section across the top of the skull, showing the membranes of the brain, etc. (Falx cerebri is yellow line running down center.)
142:
723:
Daghighi MH, Rezaei V, Zarrintan S, Pourfathi H (2007). "Intracranial physiological calcifications in adults on computed tomography in Tabriz, Iran."
293:
Its convex superior margin is attached to the internal surface of the skull on either side of the midline. This attachment runs as far back as the
665:
118:
398:
Calcification of the falx cerebri is more prevalent in older patients, often without a determinable cause, and without pathogenic symptoms.
478:
419:
The falx cerebri is a significant surgical landmark for access of the lateral ventricles via the interhemispheric transcallosal approach;
808:
934:
149:
294:
780:
746:
Chung SB, Kim CY, Park CK, Kim DG, Jung HW (2007). "Falx
Meningiomas: Surgical Results and Lessons Learned from 68 Cases."
454:
137:
1057:
572:
Saladin K. "Anatomy & Physiology: The Unity of Form and
Function. New York: McGraw Hill, 2014. Print. pp 512, 770-773
944:
259:
Anteriorly, the falx cerebri is narrower, thinner, and may have a number of perforations. It is broader posteriorly.
776:
949:
924:
350:
346:
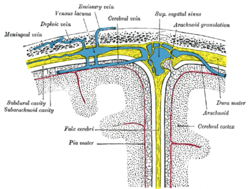
is contained in the superior margin of the falx cerebri and overlies the longitudinal fissure of the brain.
343:
1066:
703:
801:
440:
125:
113:
971:
905:
890:
542:
519:
466:
895:
287:
253:
183:
179:
106:
1042:
853:
770:
330:
The falx cerebri is situated in the longitudinal fissure, in between the cerebral hemispheres. The
245:
233:
213:
The falx cerebri is often subject to age-related calcification, and a site of falcine meningiomas.
207:
195:
1037:
986:
929:
683:
502:
1092:
863:
794:
731:
671:
661:
614:
547:
249:
939:
751:
432:
272:
1088:
Knowledge (XXG) articles incorporating text from the 20th edition of Gray's
Anatomy (1918)
1002:
919:
878:
868:
436:
354:
331:
786:
755:
1071:
1032:
1027:
981:
976:
914:
858:
361:
241:
20:
1081:
1007:
538:
280:
276:
187:
268:
203:
353:
is contained in the inferior free margin of the falx cerebri and arches over the
825:
821:
44:
606:
840:
675:
407:
237:
229:
175:
101:
40:
130:
963:
411:
available regarding meningiomas, little is known about falcine meningiomas.
735:
655:
618:
817:
420:
373:
364:
courses along the juncture of the falx cerebri and cerebellar tentorium.
77:
155:
35:
334:
lies immediately inferior to the lower (free) margin of falx cerebri.
313:
through the cribiform plate into the lymphatics of the nasal mucosa.
217:
191:
43:
and its processes exposed by removing part of the right half of the
58:
199:
89:
48:
309:
meningeal artery (a branch of the ascending pharyngeal artery).
790:
484:
Sagittal section of the skull, showing the sinuses of the dura.
252:; it is formed through invagination of the dura mater into the
300:
The (concave) inferior margin of the falx cerebri is free.
657:
Gray's
Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice
522:, other parts of the anatomy with names including "falx"
228:
The falx cerebri is a strong, crescent-shaped sheet of
1055:
385:
The falx cerebri contains blood vessels, and nerves.
286:
Posteriorly, it blends into the upper surface of the
1020:
995:
962:
904:
877:
839:
832:
136:
124:
112:
100:
88:
83:
73:
68:
28:
781:grossanatomy/dissector/labs/h_n/cranium/cn1_1a.htm
613:, Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing,
802:
8:
267:The falx cerebri attaches anteriorly at the
232:lying in the sagittal plane between the two
883:
836:
809:
795:
787:
688:: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (
605:Bair, Michael M.; Munakomi, Sunil (2022),
57:
34:
660:(42th ed.). New York. p. 398.
357:, deep within the longitudinal fissure.
1062:
556:
450:
681:
649:
647:
645:
643:
641:
639:
637:
635:
633:
537:This article incorporates text in the
460:Falx cerebri in relation to the skull.
174:) is a large, crescent-shaped fold of
153:
25:
600:
598:
7:
773:at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center
596:
594:
592:
590:
588:
586:
584:
582:
580:
578:
568:
566:
564:
562:
560:
496:Human brain dura mater (reflections)
256:between the cerebral hemispheres.
216:The falx cerebri is named for its
178:that descends vertically into the
14:
16:Anatomical structure of the brain
1065:
531:
501:
489:
477:
465:
453:
206:anteriorly, and blends with the
150:Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy
295:internal occipital protuberance
1:
607:"Neuroanatomy, Falx Cerebri"
472:Frontal bone. Inner surface.
240:of the brain along with the
545:of the 20th edition of
427:Subfalcine brain herniation
1109:
18:
935:Of lateral cerebral fossa
886:
654:Standring, Susan (2020).
148:
56:
33:
950:Cerebellopontine cistern
771:Anatomy photo:28:st-1602
406:Falcine meningioma is a
202:. It is attached to the
19:Not to be confused with
925:Interpeduncular cistern
748:J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
351:inferior sagittal sinus
344:superior sagittal sinus
725:Folia Morphol (Warsz).
441:traumatic brain injury
972:Denticulate ligaments
906:Subarachnoid cisterns
891:Arachnoid granulation
520:Falx (disambiguation)
389:Clinical significance
945:Of lamina terminalis
896:Arachnoid trabeculae
439:may occur following
368:Anatomical variation
338:Dural venous sinuses
326:Anatomical relations
288:cerebellar tentorium
254:longitudinal fissure
236:. It is one of four
234:cerebral hemispheres
184:cerebral hemispheres
180:longitudinal fissure
1043:Cerebrospinal fluid
854:Tentorium cerebelli
271:(proximally to the
246:tentorium cerebelli
208:tentorium cerebelli
170:(also known as the
1038:Subarachnoid space
987:Perivascular space
930:Chiasmatic cistern
198:drainage from the
186:. It supports the
1053:
1052:
1016:
1015:
958:
957:
864:Diaphragma sellae
750:42 (4): 276-280.
667:978-0-7020-7707-4
447:Additional images
415:Surgical landmark
372:Total or partial
250:diaphragma sellae
164:
163:
159:
1100:
1070:
1069:
1061:
940:Superior cistern
884:
837:
811:
804:
797:
788:
758:
744:
738:
721:
715:
714:
712:
710:
700:
694:
693:
687:
679:
651:
628:
627:
626:
625:
602:
573:
570:
535:
534:
505:
493:
481:
469:
457:
273:cribriform plate
238:dural partitions
182:to separate the
156:edit on Wikidata
61:
38:
26:
1108:
1107:
1103:
1102:
1101:
1099:
1098:
1097:
1078:
1077:
1076:
1064:
1056:
1054:
1049:
1012:
1003:Filum terminale
991:
954:
920:Pontine cistern
900:
879:Arachnoid mater
873:
869:Trigeminal cave
828:
815:
777:MedEd at Loyola
767:
762:
761:
745:
741:
722:
718:
708:
706:
702:
701:
697:
680:
668:
653:
652:
631:
623:
621:
604:
603:
576:
571:
558:
532:
529:
516:
509:
506:
497:
494:
485:
482:
473:
470:
461:
458:
449:
437:cingulate gyrus
429:
417:
404:
396:
391:
383:
370:
355:corpus callosum
340:
332:corpus callosum
328:
319:
306:
304:Vascular supply
281:ethmoid sinuses
265:
226:
160:
64:
52:
24:
17:
12:
11:
5:
1106:
1104:
1096:
1095:
1090:
1080:
1079:
1075:
1074:
1051:
1050:
1048:
1047:
1046:
1045:
1035:
1033:Subdural space
1030:
1028:Epidural space
1024:
1022:
1018:
1017:
1014:
1013:
1011:
1010:
1005:
999:
997:
993:
992:
990:
989:
984:
982:Choroid plexus
979:
977:Tela choroidea
974:
968:
966:
960:
959:
956:
955:
953:
952:
947:
942:
937:
932:
927:
922:
917:
915:Cisterna magna
911:
909:
902:
901:
899:
898:
893:
887:
881:
875:
874:
872:
871:
866:
861:
859:Falx cerebelli
856:
851:
845:
843:
834:
830:
829:
816:
814:
813:
806:
799:
791:
785:
784:
774:
766:
765:External links
763:
760:
759:
739:
716:
695:
666:
629:
574:
555:
554:
548:Gray's Anatomy
528:
525:
524:
523:
515:
512:
511:
510:
507:
500:
498:
495:
488:
486:
483:
476:
474:
471:
464:
462:
459:
452:
448:
445:
428:
425:
416:
413:
403:
400:
395:
392:
390:
387:
382:
379:
369:
366:
362:straight sinus
339:
336:
327:
324:
318:
315:
305:
302:
264:
261:
242:falx cerebelli
225:
222:
162:
161:
152:
146:
145:
140:
134:
133:
128:
122:
121:
116:
110:
109:
104:
98:
97:
92:
86:
85:
81:
80:
75:
71:
70:
66:
65:
62:
54:
53:
39:
31:
30:
21:falx cerebelli
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1105:
1094:
1091:
1089:
1086:
1085:
1083:
1073:
1068:
1063:
1059:
1044:
1041:
1040:
1039:
1036:
1034:
1031:
1029:
1026:
1025:
1023:
1019:
1009:
1008:Leptomeninges
1006:
1004:
1001:
1000:
998:
994:
988:
985:
983:
980:
978:
975:
973:
970:
969:
967:
965:
961:
951:
948:
946:
943:
941:
938:
936:
933:
931:
928:
926:
923:
921:
918:
916:
913:
912:
910:
907:
903:
897:
894:
892:
889:
888:
885:
882:
880:
876:
870:
867:
865:
862:
860:
857:
855:
852:
850:
847:
846:
844:
842:
838:
835:
831:
827:
823:
819:
812:
807:
805:
800:
798:
793:
792:
789:
783:
782:
778:
775:
772:
769:
768:
764:
757:
753:
749:
743:
740:
737:
733:
729:
726:
720:
717:
705:
699:
696:
691:
685:
677:
673:
669:
663:
659:
658:
650:
648:
646:
644:
642:
640:
638:
636:
634:
630:
620:
616:
612:
608:
601:
599:
597:
595:
593:
591:
589:
587:
585:
583:
581:
579:
575:
569:
567:
565:
563:
561:
557:
553:
552:
549:
546:
544:
540:
539:public domain
526:
521:
518:
517:
513:
504:
499:
492:
487:
480:
475:
468:
463:
456:
451:
446:
444:
442:
438:
434:
426:
424:
422:
414:
412:
409:
401:
399:
394:Calcification
393:
388:
386:
380:
378:
375:
367:
365:
363:
358:
356:
352:
347:
345:
337:
335:
333:
325:
323:
322:vagus nerve.
316:
314:
310:
303:
301:
298:
296:
291:
289:
284:
282:
278:
274:
270:
262:
260:
257:
255:
251:
247:
243:
239:
235:
231:
223:
221:
220:-like shape.
219:
214:
211:
210:posteriorly.
209:
205:
201:
197:
193:
190:that provide
189:
188:dural sinuses
185:
181:
177:
173:
172:cerebral falx
169:
157:
151:
147:
144:
141:
139:
135:
132:
129:
127:
123:
120:
117:
115:
111:
108:
105:
103:
99:
96:
93:
91:
87:
82:
79:
76:
72:
67:
60:
55:
50:
46:
42:
37:
32:
27:
22:
849:Falx cerebri
848:
779:
747:
742:
727:
724:
719:
707:. Retrieved
698:
656:
622:, retrieved
610:
550:
536:
530:
508:Falx cerebri
430:
418:
405:
397:
384:
381:Microanatomy
371:
359:
348:
341:
329:
320:
311:
307:
299:
292:
285:
269:crista galli
266:
258:
227:
215:
212:
204:crista galli
171:
168:falx cerebri
167:
165:
119:A14.1.01.103
95:falx cerebri
94:
29:Falx cerebri
826:spinal cord
730:(2):115-9.
431:Subfalcine
317:Innervation
275:and to the
263:Attachments
84:Identifiers
1082:Categories
841:Dura mater
676:1201341621
624:2022-04-26
611:StatPearls
527:References
433:herniation
408:meningioma
402:Meningioma
230:dura mater
176:dura mater
102:NeuroNames
41:Dura mater
964:Pia mater
709:10 August
684:cite book
1093:Meninges
996:Combined
818:Meninges
736:17594669
619:31424888
543:page 873
514:See also
421:agenesis
374:agenesis
78:Meninges
47:and the
1072:Anatomy
820:of the
756:2588203
435:of the
277:frontal
224:Anatomy
74:Part of
69:Details
1058:Portal
1021:Spaces
833:Layers
754:
734:
704:"Falx"
674:
664:
617:
551:(1918)
248:, and
218:sickle
192:venous
822:brain
541:from
200:brain
154:[
143:83967
90:Latin
49:brain
45:skull
824:and
732:PMID
711:2024
690:link
672:OCLC
662:ISBN
615:PMID
360:The
349:The
342:The
279:and
194:and
166:The
131:5374
114:TA98
107:1237
752:PMC
283:).
196:CSF
138:FMA
126:TA2
1084::
728:66
686:}}
682:{{
670:.
632:^
609:,
577:^
559:^
443:.
290:.
244:,
1060::
908::
810:e
803:t
796:v
713:.
692:)
678:.
158:]
51:.
23:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.