58:
204:
118:
255:
Disease onset is typically in early infancy but may occur later in life. Children who have the classic form of Farber disease develop symptoms within the first few weeks to months of life. Individuals with moderate or attenuated forms may develop symptoms at any time in childhood. Sometimes it is
534:
Elsea, SH; Solyom, A; Martin, K; Harmatz, P; Mitchell, J; Lampe, C; Grant, C; Selim, L; Mungan, NO; Guelbert, N; Magnusson, B; Sundberg, E; Puri, R; Kapoor, S; Arslan, N; DiRocco, M; Zaki, M; Ozen, S; Mahmoud, IG; Ehlert, K; Hahn, A; Gokcay, G; Torcoletti, M; Ferreira, CR (September 2020).
233:
and has one copy of the gene that is functioning properly and one that is not. Siblings of individuals with Farber disease have a 25% chance to also have Farber disease, a 50% chance to be a carrier like the parents, and a 25% chance of being unaffected and not a carrier.
247:(SMA-PME). Farber disease and SMA-PME have been classified as separate disorders, however more recent case reports have identified some individuals with overlapping symptoms of both disorders. Some individuals with SMA symptoms without seizures have also been described.
221:
enzyme. Individuals with Farber disease have two copies of this gene that are not functioning properly leading to the enzyme deficiency. Over 73 different gene variants have been reported to cause Farber disease. No definitive genotype-phenotype correlations are known.
288:
Studies in cells and mice have shown proof-of-concept for enzyme replacement therapy for Farber disease. Aceragen, a biopharmaceutical company, is currently developing an investigational enzyme replacement therapy with a clinical study planned for late 2022.
297:
Children with the most severe forms of Farber disease generally die by age 2–3 years. The life expectancy of individuals with moderate or attenuated forms is unknown. The oldest reported individuals living with Farber disease were in their 50s and 60s.
1084:
1064:
921:
Bonafé, L; Kariminejad, A; Li, J; Royer-Bertrand, B; Garcia, V; Mahdavi, S; Bozorgmehr, B; Lachman, RL; Mittaz-Crettol, L; Campos-Xavier, B; Nampoothiri, S; Unger, S; Rivolta, C; Levade, T; Superti-Furga, A (September 2016).
285:(small masses of inflamed tissue) and inflammation in patients with little or no lung or nervous system complications. Supportive therapies such as physical therapy, respiratory support, and mobility aids may be required.
801:
Mitchell, John; Solyom, Alexander; Makay, Balahan; Arslan, Nur; Batu, Ezgi Deniz; Ozen, Seza; Hügle, Boris; Schuchman, Edward; Magnusson, Bo (February 2016). "Farber disease: Implications of anti-inflammatory treatment".
276:
There is no disease specific treatment for Farber disease. Anti-inflammatory medications, specifically tocilizumab (an interleukin-6 receptor inhibitor), has been shown to improve inflammation and pain in some patients.
1510:
829:
Ehlert, K; Levade, T; Di Rocco, M; Lanino, E; Albert, MH; Führer, M; Jarisch, A; Güngör, T; Ayuk, F; Vormoor, J (March 2019). "Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation in Farber disease".
988:
Farber S (1952). "A lipid metabolic disorder: disseminated lipogranulomatosis; a syndrome with similarity to, and important difference from, Niemann-Pick and Hand-Schüller-Christian disease".
244:
306:
To date, there have been approximately 200 reported cases of Farber disease and SMA-PME in the literature. The disorders are ultra-rare and estimated to occur in fewer than one per million.
676:
Filosto, M; Aureli, M; Castellotti, B; Rinaldi, F; Schiumarini, D; Valsecchi, M; Lualdi, S; Mazzotti, R; Pensato, V; Rota, S; Gellera, C; Filocamo, M; Padovani, A (November 2016).
633:
Lee, BH; Mongiovi, P; Levade, T; Marston, B; Mountain, J; Ciafaloni, E (October 2020). "Spinal muscular atrophy and Farber disease due to ASAH1 variants: A case report".
1184:
361:
725:
Schuchman, Edward H.; Mitchell, John; Solyom, Alex (2 September 2017). "Morbidity and mortality associated with Farber disease and prospects for therapy".
1321:
1515:
537:"ASAH1 pathogenic variants associated with acid ceramidase deficiency: Farber disease and spinal muscular atrophy with progressive myoclonic epilepsy"
1429:
1500:
1177:
505:
384:
1162:
471:
Dyment, DA; Bennett, SAL; Medin, JA; Levade, T; Adam, MP; Ardinger, HH; Pagon, RA; Wallace, SE; Bean, LJH; Mirzaa, G; Amemiya, A (2018).
1099:
229:
manner. Affected individuals inherit one copy of the gene that is not functioning properly from each parent. Each parent is a called a
1460:
1326:
924:"Brief Report: Peripheral Osteolysis in Adults Linked to ASAH1 (Acid Ceramidase) Mutations: A New Presentation of Farber's Disease"
125:
The symptoms of Farber disease develop over time. The onset of symptoms and how quickly they progress vary from person to person.
1505:
1464:
1201:
1170:
1434:
1455:
1421:
1267:
132:
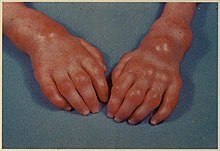
Bumps under the skin located at pressure points and joints, also called subcutaneous nodules, lipogranulomas, or granulomas
1376:
257:
1371:
678:"ASAH1 variant causing a mild SMA phenotype with no myoclonic epilepsy: a clinical, biochemical and molecular study"
1197:
1193:
90:
1317:
1110:
156:
1495:
1474:
1205:
278:
1262:
1287:
1150:
872:
He, X; Dworski, S; Zhu, C; DeAngelis, V; Solyom, A; Medin, JA; Simonaro, CM; Schuchman, EH (June 2017).
336:
762:"Farber disease: report of three cases with joint involvement mimicking juvenile idiopathic arthritis"
105:
and fatty acid. When the enzyme is deficient, this leads to an accumulation of fatty material (called
1336:
150:
57:
1088:
226:
87:
513:
1381:
1253:
1248:
953:
854:
742:
658:
615:
584:
Teoh, HL; Solyom, A; Schuchman, EH; Mowat, D; Roscioli, T; Farrar, M; Sampaio, H (October 2016).
566:
230:
1121:
997:
945:
903:
846:
783:
707:
650:
607:
558:
484:
438:
380:
355:
168:
46:
1332:
1257:
1214:
935:
893:
885:
838:
811:
773:
734:
697:
689:
642:
597:
548:
428:
418:
874:"Enzyme replacement therapy for Farber disease: Proof-of-concept studies in cells and mice"
1018:
261:
203:
191:
1038:
976:
512:. Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center (GARD) – an NCATS Program. Archived from
1468:
1439:
1385:
1357:
1235:
898:
873:
778:
761:
702:
677:
433:
406:
1093:
1489:
1310:
1302:
1291:
662:
570:
315:
109:) in the lysosomes of the cells, leading to the signs and symptoms of this disorder.
51:
17:
957:
858:
746:
135:
Swollen, painful joints with progressive limitation of range of motion resulting in
117:
1352:
619:
586:"Polyarticular Arthritis and Spinal Muscular Atrophy in Acid Ceramidase Deficiency"
184:
174:
738:
1115:
889:
256:
difficult to diagnose Farber disease because the symptoms can be misdiagnosed as
1395:
1244:
1230:
1023:
815:
472:
136:
102:
1126:
1073:
971:
423:
218:
178:
98:
94:
77:
1367:
1347:
1279:
282:
1001:
949:
907:
850:
787:
711:
654:
611:
602:
585:
562:
488:
442:
1403:
1219:
1145:
1033:
693:
646:
160:
145:
Other symptoms observed in some individuals with Farber disease include:
106:
1056:
1019:
National
Organization for Rare Disorders (NORD): ASAH1-Related Disorders
842:
553:
536:
940:
923:
1068:
760:
Moghadam, SH; Tavasoli, AR; Modaresi, M; Ziaee, V (1 December 2019).
239:
213:
202:
116:
1104:
1077:
1166:
1028:
149:
Respiratory disease, e.g. lung infections, labored breathing,
207:
This condition is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner
375:
James, William D.; Berger, Timothy G.; et al. (2006).
245:
spinal muscular atrophy with progressive myoclonic epilepsy
405:
Yu, FPS; Amintas, S; Levade, T; Medin, JA (20 July 2018).
407:"Acid ceramidase deficiency: Farber disease and SMA-PME"
86:-related disorders) is an extremely rare, progressive,
766:
268:
gene or by measuring acid ceramidase enzyme activity.
1046:
1511:
Skin conditions resulting from errors in metabolism
1448:
1420:
1393:
1345:
1300:
1277:
1228:
1213:
1136:
1050:
377:
45:
37:
32:
1029:Thank Farber: Farber disease educational website
173:Bone disease, e.g. erosion of bone near joints,
243:gene is also known to cause a condition called
101:is responsible for breaking down ceramide into
1178:
8:
635:American Journal of Medical Genetics. Part A
211:Farber disease is caused by variants in the
360:: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (
260:(JIA). Diagnosis is confirmed by molecular
1225:
1185:
1171:
1163:
1047:
56:
29:
939:
897:
777:
701:
601:
552:
432:
422:
400:
398:
396:
990:American Journal of Diseases of Children
466:
464:
462:
460:
458:
456:
454:
452:
327:
831:Journal of Inherited Metabolic Disease
500:
498:
353:
155:Central nervous system disease, e.g.
7:
1024:GeneReviews: ASAH1-Related Disorders
335:RESERVED, INSERM US14-- ALL RIGHTS.
217:gene. This gene codes for the acid
93:caused by a deficiency of the acid
682:European Journal of Human Genetics
225:Farber disease is inherited in an
128:The most common symptoms include:
25:
1461:Cholesteryl ester storage disease
804:Molecular Genetics and Metabolism
411:Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases
1516:Diseases named after discoverers
1465:Lysosomal acid lipase deficiency
1456:Cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis
727:Expert Opinion on Orphan Drugs
1:
1501:Autosomal recessive disorders
1377:Multiple sulfatase deficiency
1034:Aceragen Pipeline with Farber
739:10.1080/21678707.2017.1359086
258:Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
1372:Metachromatic leukodystrophy
928:Arthritis & Rheumatology
890:10.1016/j.bbacli.2017.02.001
82:, "Lipogranulomatosis", and
1435:Jansky–Bielschowsky disease
816:10.1016/j.ymgme.2015.12.364
72:Farber's lipogranulomatosis
1532:
1194:Lysosomal storage diseases
337:"Orphanet: Farber disease"
41:Acid ceramidase deficiency
1039:Free Genetic Testing for
510:rarediseases.info.nih.gov
424:10.1186/s13023-018-0845-z
91:lysosomal storage disease
1506:Lipid storage disorders
1206:Lipid storage disorders
121:Hands in Farber disease
1475:Sea-blue histiocytosis
603:10.1542/peds.2016-1068
279:Bone marrow transplant
208:
122:
1288:Globotriaosylceramide
379:. Saunders Elsevier.
206:
165:Systemic inflammation
120:
18:Farber's disease
1318:Niemann–Pick disease
694:10.1038/ejhg.2016.28
647:10.1002/ajmg.a.61764
151:respiratory distress
477:-Related Disorders"
227:autosomal recessive
194:, corneal opacities
159:, muscle weakness,
157:developmental delay
88:autosomal recessive
1382:Galactocerebroside
1254:GM2 gangliosidoses
1249:GM1 gangliosidoses
1137:External resources
843:10.1002/jimd.12043
554:10.1002/humu.24056
209:
190:Eye disease, e.g.
123:
113:Signs and symptoms
1483:
1482:
1416:
1415:
1337:Gaucher's disease
1263:Tay–Sachs disease
1160:
1159:
941:10.1002/art.39659
688:(11): 1578–1583.
641:(10): 2369–2371.
386:978-0-7216-2921-6
169:Failure to thrive
65:
64:
27:Medical condition
16:(Redirected from
1523:
1333:Glucocerebroside
1322:SMPD1-associated
1258:Sandhoff disease
1226:
1215:Sphingolipidoses
1202:lipid metabolism
1187:
1180:
1173:
1164:
1048:
1006:
1005:
985:
979:
968:
962:
961:
943:
918:
912:
911:
901:
869:
863:
862:
826:
820:
819:
798:
792:
791:
781:
757:
751:
750:
722:
716:
715:
705:
673:
667:
666:
630:
624:
623:
605:
596:(4): e20161068.
581:
575:
574:
556:
547:(9): 1469–1487.
531:
525:
524:
522:
521:
506:"Farber disease"
502:
493:
492:
468:
447:
446:
436:
426:
402:
391:
390:
372:
366:
365:
359:
351:
349:
347:
332:
314:It is named for
183:Enlarged liver (
141:Hoarse voice/cry
61:
60:
30:
21:
1531:
1530:
1526:
1525:
1524:
1522:
1521:
1520:
1486:
1485:
1484:
1479:
1444:
1412:
1389:
1350:
1341:
1296:
1292:Fabry's disease
1273:
1233:
1217:
1209:
1191:
1161:
1156:
1155:
1132:
1131:
1059:
1015:
1010:
1009:
987:
986:
982:
969:
965:
920:
919:
915:
871:
870:
866:
828:
827:
823:
800:
799:
795:
759:
758:
754:
724:
723:
719:
675:
674:
670:
632:
631:
627:
583:
582:
578:
533:
532:
528:
519:
517:
504:
503:
496:
470:
469:
450:
404:
403:
394:
387:
374:
373:
369:
352:
345:
343:
334:
333:
329:
324:
312:
304:
295:
274:
262:genetic testing
253:
201:
192:cherry-red spot
115:
70:(also known as
55:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
1529:
1527:
1519:
1518:
1513:
1508:
1503:
1498:
1488:
1487:
1481:
1480:
1478:
1477:
1472:
1469:Wolman disease
1458:
1452:
1450:
1446:
1445:
1443:
1442:
1440:Batten disease
1437:
1432:
1426:
1424:
1418:
1417:
1414:
1413:
1411:
1410:
1408:Farber disease
1400:
1398:
1391:
1390:
1388:
1386:Krabbe disease
1379:
1374:
1365:
1363:
1362:
1361:
1358:leukodystrophy
1343:
1342:
1340:
1339:
1330:
1324:
1307:
1305:
1298:
1297:
1295:
1294:
1284:
1282:
1275:
1274:
1272:
1271:
1265:
1260:
1251:
1241:
1239:
1236:gangliosidoses
1223:
1211:
1210:
1192:
1190:
1189:
1182:
1175:
1167:
1158:
1157:
1154:
1153:
1141:
1140:
1138:
1134:
1133:
1130:
1129:
1118:
1107:
1096:
1081:
1060:
1055:
1054:
1052:
1051:Classification
1045:
1044:
1036:
1031:
1026:
1021:
1014:
1013:External links
1011:
1008:
1007:
996:(4): 499–500.
980:
963:
913:
864:
837:(2): 286–294.
821:
810:(2): S81–S82.
793:
772:(4): 521–525.
752:
733:(9): 717–726.
717:
668:
625:
576:
541:Human Mutation
526:
494:
448:
392:
385:
367:
326:
325:
323:
320:
311:
308:
303:
300:
294:
291:
273:
270:
252:
249:
200:
197:
196:
195:
188:
181:
171:
166:
163:
153:
143:
142:
139:
133:
114:
111:
68:Farber disease
63:
62:
49:
43:
42:
39:
35:
34:
33:Farber disease
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1528:
1517:
1514:
1512:
1509:
1507:
1504:
1502:
1499:
1497:
1496:Rare diseases
1494:
1493:
1491:
1476:
1473:
1470:
1466:
1462:
1459:
1457:
1454:
1453:
1451:
1447:
1441:
1438:
1436:
1433:
1431:
1428:
1427:
1425:
1423:
1419:
1409:
1405:
1402:
1401:
1399:
1397:
1392:
1387:
1383:
1380:
1378:
1375:
1373:
1369:
1366:
1364:
1359:
1356:
1355:
1354:
1349:
1344:
1338:
1334:
1331:
1328:
1325:
1323:
1319:
1316:
1315:phospholipid:
1312:
1311:Sphingomyelin
1309:
1308:
1306:
1304:
1303:sphingomyelin
1299:
1293:
1289:
1286:
1285:
1283:
1281:
1276:
1269:
1266:
1264:
1261:
1259:
1255:
1252:
1250:
1246:
1243:
1242:
1240:
1237:
1232:
1227:
1224:
1221:
1216:
1212:
1207:
1203:
1199:
1198:Inborn errors
1195:
1188:
1183:
1181:
1176:
1174:
1169:
1168:
1165:
1152:
1148:
1147:
1143:
1142:
1139:
1135:
1128:
1124:
1123:
1119:
1117:
1113:
1112:
1108:
1106:
1102:
1101:
1097:
1095:
1091:
1090:
1086:
1082:
1079:
1075:
1071:
1070:
1066:
1062:
1061:
1058:
1053:
1049:
1043:
1042:
1037:
1035:
1032:
1030:
1027:
1025:
1022:
1020:
1017:
1016:
1012:
1003:
999:
995:
991:
984:
981:
978:
977:Who Named It?
974:
973:
967:
964:
959:
955:
951:
947:
942:
937:
934:(9): 2323–7.
933:
929:
925:
917:
914:
909:
905:
900:
895:
891:
887:
883:
879:
875:
868:
865:
860:
856:
852:
848:
844:
840:
836:
832:
825:
822:
817:
813:
809:
805:
797:
794:
789:
785:
780:
775:
771:
767:
763:
756:
753:
748:
744:
740:
736:
732:
728:
721:
718:
713:
709:
704:
699:
695:
691:
687:
683:
679:
672:
669:
664:
660:
656:
652:
648:
644:
640:
636:
629:
626:
621:
617:
613:
609:
604:
599:
595:
591:
587:
580:
577:
572:
568:
564:
560:
555:
550:
546:
542:
538:
530:
527:
516:on 2021-08-23
515:
511:
507:
501:
499:
495:
490:
486:
482:
478:
476:
467:
465:
463:
461:
459:
457:
455:
453:
449:
444:
440:
435:
430:
425:
420:
416:
412:
408:
401:
399:
397:
393:
388:
382:
378:
371:
368:
363:
357:
342:
341:www.orpha.net
338:
331:
328:
321:
319:
317:
316:Sidney Farber
309:
307:
301:
299:
292:
290:
286:
284:
280:
271:
269:
267:
263:
259:
250:
248:
246:
242:
241:
235:
232:
228:
223:
220:
216:
215:
205:
198:
193:
189:
186:
182:
180:
177:, peripheral
176:
172:
170:
167:
164:
162:
158:
154:
152:
148:
147:
146:
140:
138:
134:
131:
130:
129:
126:
119:
112:
110:
108:
104:
100:
97:enzyme. Acid
96:
92:
89:
85:
81:
79:
73:
69:
59:
53:
52:Endocrinology
50:
48:
44:
40:
36:
31:
19:
1407:
1353:sulfatidoses
1314:
1144:
1120:
1109:
1098:
1083:
1063:
1040:
993:
989:
983:
970:
966:
931:
927:
916:
881:
878:BBA Clinical
877:
867:
834:
830:
824:
807:
803:
796:
769:
765:
755:
730:
726:
720:
685:
681:
671:
638:
634:
628:
593:
589:
579:
544:
540:
529:
518:. Retrieved
514:the original
509:
480:
474:
414:
410:
376:
370:
344:. Retrieved
340:
330:
313:
305:
296:
287:
281:may improve
275:
265:
254:
238:
236:
224:
212:
210:
185:hepatomegaly
175:osteoporosis
144:
127:
124:
83:
75:
71:
67:
66:
1396:sphingosine
1245:Ganglioside
1231:ganglioside
481:GeneReviews
417:(121): 20.
137:contracture
103:sphingosine
38:Other names
1490:Categories
1268:AB variant
1122:DiseasesDB
590:Pediatrics
520:2021-08-17
322:References
302:Prevalence
283:granulomas
219:ceramidase
179:osteolysis
99:ceramidase
95:ceramidase
80:deficiency
78:ceramidase
1430:Infantile
1368:Sulfatide
1348:sulfatide
1280:globoside
884:: 85–96.
663:220369745
571:218895424
293:Prognosis
272:Treatment
251:Diagnosis
47:Specialty
1404:Ceramide
1220:ceramide
1146:Orphanet
1002:12975849
972:synd/453
958:37749661
950:26945816
908:28275553
859:73478264
851:30815900
788:31789304
747:79980666
712:27026573
655:32627310
612:27650050
563:32449975
489:29595935
443:30029679
356:cite web
346:17 April
199:Genetics
161:seizures
107:ceramide
1116:D055577
1080:E75.29)
899:5338723
779:6944811
703:5110045
620:2152446
434:6053731
264:of the
231:carrier
1327:type C
1105:228000
1000:
956:
948:
906:
896:
857:
849:
786:
776:
745:
710:
700:
661:
653:
618:
610:
569:
561:
487:
441:
431:
383:
310:Eponym
54:
1449:Other
1346:From
1301:From
1278:From
1229:From
1127:29174
1094:272.8
1074:E75.2
1041:ASAH1
954:S2CID
855:S2CID
743:S2CID
659:S2CID
616:S2CID
567:S2CID
475:ASAH1
266:ASAH1
240:ASAH1
214:ASAH1
84:ASAH1
76:acid
1218:(to
1111:MeSH
1100:OMIM
1089:9-CM
1078:ILDS
998:PMID
946:PMID
904:PMID
847:PMID
784:PMID
708:PMID
651:PMID
608:PMID
559:PMID
485:PMID
439:PMID
381:ISBN
362:link
348:2019
237:The
1422:NCL
1394:To
1200:of
1151:333
1085:ICD
1065:ICD
975:at
936:doi
894:PMC
886:doi
839:doi
812:doi
808:117
774:PMC
735:doi
698:PMC
690:doi
643:doi
639:182
598:doi
594:138
549:doi
429:PMC
419:doi
1492::
1406::
1384::
1370::
1335::
1313::
1290::
1247::
1196::
1149::
1125::
1114::
1103::
1092::
1072::
1069:10
994:84
992:.
952:.
944:.
932:68
930:.
926:.
902:.
892:.
880:.
876:.
853:.
845:.
835:42
833:.
806:.
782:.
770:19
768:.
764:.
741:.
729:.
706:.
696:.
686:24
684:.
680:.
657:.
649:.
637:.
614:.
606:.
592:.
588:.
565:.
557:.
545:41
543:.
539:.
508:.
497:^
483:.
479:.
451:^
437:.
427:.
415:13
413:.
409:.
395:^
358:}}
354:{{
339:.
318:.
74:,
1471:)
1467:/
1463:(
1360:)
1351:(
1329:)
1320:(
1270:)
1256:(
1238:)
1234:(
1222:)
1208:)
1204:(
1186:e
1179:t
1172:v
1087:-
1076:(
1067:-
1057:D
1004:.
960:.
938::
910:.
888::
882:7
861:.
841::
818:.
814::
790:.
749:.
737::
731:5
714:.
692::
665:.
645::
622:.
600::
573:.
551::
523:.
491:.
473:"
445:.
421::
389:.
364:)
350:.
187:)
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.