265:
1447:
242:. While its exact function and importance in the physiology of the brain are still not entirely clear, it has been demonstrated in humans that surgical transection—the cutting of the fornix along its body—can cause memory loss. There is some debate over what type of memory is affected by this damage, but it has been found to most closely correlate with
596:
584:
620:
608:
637:
273:
52:
40:
385:
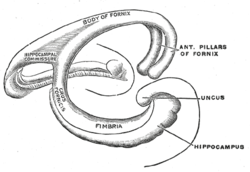
The terminal lamina creates the commissure plate. This structure gives existence to the corpus callosum, the septum pellucidum, and the fornix. The fornix splits into two columns at the front (anterior pillars), and then splits into two posterior crura. These two crura are joined together through
507:
have shown that the monkeys were strongly impaired on object-in-scene learning, which is a type of recall memory, specifically episodic-like memory (integrating what and where, although not when). Fornix transection in rodents impairs performance on tasks that require the encoding and retrieval of
571:
which are transmitted through the fornix to the hippocampus. In the absence of these external modulators, the hippocampus is radically dysfunctional. In addition, the fornix transmits mnemonic information from the hippocampus to deep brain structures, which potentially allows us to use stored
523:
that is indistinguishable from the anterograde amnesia observed after focal hippocampal lesions. Deficits in recall are greater than for recognition, and the deficit is found across all types of material (e.g. visual and verbal). This supports the idea that damage to any part of the extended
1467:
250:. This means that damage to the fornix can cause difficulty in recalling long-term information such as details of past events, but it has little effect on the ability to recognize objects or familiar situations.
508:
spatiotemporal context and, therefore, serves as a proxy for human episodic memory. For instance, fornix transection consistently leads to robust impairments in learning new routes and spatial locations.
1141:
531:. This literature has shown that fractional anisotropy (FA) in the fornix decreases with advanced age, correlates with age-related memory impairments, and is relatively decreased in
390:. The latter name is used because the structure resembles a lyra (or triangular harp): The two crura are the "chassis" of the lyra, and the commissure connections are the fibers.
524:
hippocampal memory system causes similar memory deficits. Other aspects of cognition, such as social cognition and language ability, remain intact after fornix damage.
167:
774:
Aggleton, J. P.; McMackin, D.; Carpenter, K.; Hornak, J.; Kapur, N.; Halpin, S.; Wiles, C. M.; Kamel, H.; Brennan, P.; Carton, S.; Gaffan, D. (2000-04-01).
1134:
415:
1324:
1127:
1022:"The fimbria-fornix/cingular bundle pathways: A review of neurochemical and behavioral approaches using lesions and transplantation techniques"
143:
139:
1217:
465:
1379:
668:
Gaffan, D. (1994). "Scene-specific memory for objects: a model of episodic memory impairment in monkeys with fornix transection".
174:
162:
73:
1437:
1477:
1360:
1356:
1317:
1170:
327:
264:
1067:
Rawlins, J. N. P.; Feldon, J.; Gray, J. A. (1979). "Septo-hippocampal connections and the hippocampal theta rhythm".
511:
Fornix damage in humans is rare; a few individuals have had their fornix transected inadvertently during removal of
1185:
1180:
1275:
871:"Fornix as an imaging marker for episodic memory deficits in healthy aging and in various neurological disorders"
532:
528:
97:
453:
They are flattened bands, and, at their commencement, are intimately connected with the under surface of the
776:"Differential cognitive effects of colloid cysts in the third ventricle that spare or compromise the fornix"
1446:
1482:
1310:
560:
540:
536:
480:
331:
284:
150:
134:
1407:
1391:
1263:
646:
488:
476:
1291:
1114:
114:
1423:
1222:
520:
419:
307:
205:
1415:
1411:
1092:
1049:
1002:
850:
701:
358:
The lateral portions of the body of the fornix are joined by a thin triangular lamina, named the
300:
247:
1472:
1395:
1268:
1250:
1209:
1150:
1084:
1041:
994:
952:
902:
842:
803:
795:
756:
693:
685:
651:
595:
367:
346:
323:
296:
583:
1387:
1383:
1197:
1076:
1033:
984:
942:
934:
923:"Anatomy and function of the fornix in the context of its potential as a therapeutic target"
892:
882:
834:
787:
746:
738:
677:
822:
543:
to stimulate the fornix as some evidence has shown that doing so improves episodic memory.
1468:
Knowledge (XXG) articles incorporating text from the 20th edition of Gray's
Anatomy (1918)
1352:
1162:
775:
516:
500:
454:
431:
427:
411:
310:. The left and right parts separate, but there is also an anterior/posterior divergence.
243:
234:. The fornix also carries some afferent fibers to the hippocampus from structures in the
1119:
1021:
727:"Dissecting the fornix in basic memory processes and neuropsychiatric disease: A review"
386:
the hippocampal commissure. The beginning of the splitting is called the psalterium or
1451:
1399:
1336:
947:
922:
897:
870:
751:
277:
196:
1037:
989:
972:
1461:
1333:
1258:
642:
568:
556:
552:
342:
239:
1096:
1053:
1006:
854:
705:
527:
Lesion findings have been extended by work using the non-invasive in vivo technique
1344:
619:
607:
512:
319:
287:; the separate left and right sides are each called the crus of the fornix (plural
235:
102:
1403:
1192:
1154:
472:
423:
371:
291:). The bundles of fibers come together in the midline of the brain, forming the
231:
227:
127:
17:
838:
791:
681:
379:
259:
109:
938:
887:
799:
689:
572:
memories to guide us to rewarding people, places, and sources of sustenance.
155:
1419:
742:
519:. Nevertheless this small literature has consistently reported a persistent
998:
956:
906:
846:
807:
760:
697:
1045:
1371:
1175:
1088:
461:
121:
1302:
475:, on the surface of which some of its fibers are spread out to form the
460:
Diverging from one another, each curves around the posterior end of the
180:
1080:
504:
823:"Episodic memory, amnesia, and the hippocampal–anterior thalamic axis"
306:
The body of the fornix travels anteriorly and divides again near the
67:
272:
39:
484:
271:
263:
223:
85:
51:
283:
The fibers begin in the hippocampus on each side of the brain as
564:
219:
1306:
1123:
479:, while the remainder is continued as a narrow white band, the
726:
499:
The fornix is essential for acquiring and consolidating new
921:
Senova, S; Fomenko, A.; Gondard, E.; Lozano, A. M. (2020).
555:– which is crucial for memory encoding – is sent from the
973:"Neuromodulation: acetylcholine and memory consolidation"
551:
The fornix is the conduit by which the neurotransmitter
450:) of the fornix are prolonged backward from the body.
1435:
303:) is attached to the upper face of the fornix body.
1370:
1343:
1284:
1249:
1231:
1208:
1161:
927:
Journal of
Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry
161:
149:
133:
120:
108:
96:
84:
79:
66:
61:
32:
725:Benear, Susan; Ngo, Chi; Olson, Ingrid R. (2019).
567:-producing neurons in the septal nuclei generate
430:to the base of the brain, where it ends in the
238:and basal forebrain. The fornix is part of the
1318:
1135:
8:
464:, and passes downward and forward into the
1325:
1311:
1303:
1142:
1128:
1120:
374:across the middle line and constitute the
50:
38:
988:
946:
896:
886:
750:
471:Here, it lies along the concavity of the
719:
717:
715:
495:Functional consequences of fornix damage
1442:
660:
579:
268:Fornix as one of the limbic structures.
821:Aggleton, J. P.; Brown, M. W. (1999).
641:This article incorporates text in the
178:
44:Diagram of the fornix. Right=anterior
29:
563:to the hippocampus. In addition, the
295:of the fornix. The lower edge of the
72:Small medial central branches of the
7:
318:) of each side continue through the
1218:Vascular organ of lamina terminalis
211:
27:Bundle of nerve fibers in the brain
466:temporal horn of lateral ventricle
25:
1380:Anterior limb of internal capsule
670:Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience
539:. New research studies are using
314:The posterior fibers (called the
299:(the membrane that separates the
1445:
635:
618:
606:
594:
582:
503:. Fornix transection studies in
422:, and each descends through the
175:Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy
875:Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience
483:, which is prolonged into the
414:arch downward in front of the
226:that acts as the major output
1:
1038:10.1016/S0301-0082(97)00009-9
990:10.1016/S1364-6613(99)01365-0
827:Behavioral and Brain Sciences
378:(also called the hippocampal
366:). This lamina contains some
74:anterior communicating artery
977:Trends in Cognitive Sciences
1361:Anterior nuclei of thalamus
1069:Experimental Brain Research
869:Douet, V; Chang, L (2015).
649:of the 20th edition of
426:in the lateral wall of the
345:of the basal forebrain and
328:anterior nuclei of thalamus
56:Tractography showing fornix
1499:
529:diffusion-weighted imaging
349:of each half of the brain.
257:
218:) is a C-shaped bundle of
1276:Cave of septum pellucidum
839:10.1017/S0140525X99002034
682:10.1162/jocn.1994.6.4.305
533:mild cognitive impairment
416:interventricular foramina
173:
49:
37:
1026:Progress in Neurobiology
971:Hasselmo, M. E. (1999).
939:10.1136/jnnp-2019-322375
888:10.3389/fnagi.2014.00343
792:10.1093/brain/123.4.800
1357:Mammillothalamic tract
1020:Cassel, J. C. (1997).
561:Diagonal band of Broca
541:deep brain stimulation
481:fimbria of hippocampus
332:mammillothalamic tract
316:postcommissural fornix
280:
269:
200:
1408:Hippocampal formation
1392:Parahippocampal gyrus
1264:Medial septal nucleus
743:10.31234/osf.io/bnfmu
489:parahippocampal gyrus
370:that connect the two
339:precommissural fornix
337:The anterior fibers (
275:
267:
258:Further information:
1292:Posterior commissure
376:commissure of fornix
1478:Hippocampus (brain)
1223:Anterior commissure
601:Velum interpositum
537:Alzheimer's disease
521:anterograde amnesia
420:anterior commissure
308:anterior commissure
1151:Commissural fibers
1081:10.1007/BF01474253
731:Brain Connectivity
589:Fornix (animation)
368:commissural fibers
301:lateral ventricles
281:
270:
248:recognition memory
1433:
1432:
1396:Entorhinal cortex
1300:
1299:
1269:Subfornical organ
1251:Septum pellucidum
1210:Lamina terminalis
576:Additional images
501:episodic memories
448:posterior pillars
432:mammillary bodies
347:nucleus accumbens
324:mammillary bodies
297:septum pellucidum
209:
189:
188:
184:
16:(Redirected from
1490:
1450:
1449:
1441:
1327:
1320:
1313:
1304:
1198:Indusium griseum
1144:
1137:
1130:
1121:
1101:
1100:
1064:
1058:
1057:
1017:
1011:
1010:
992:
967:
961:
960:
950:
917:
911:
910:
900:
890:
865:
859:
858:
818:
812:
811:
771:
765:
764:
754:
721:
710:
709:
665:
639:
638:
622:
610:
598:
586:
517:third ventricles
404:anterior pillars
213:
210:'arch';
204:
181:edit on Wikidata
54:
42:
30:
21:
1498:
1497:
1493:
1492:
1491:
1489:
1488:
1487:
1458:
1457:
1456:
1444:
1436:
1434:
1429:
1384:Cingulate gyrus
1366:
1353:Mammillary body
1339:
1331:
1301:
1296:
1280:
1245:
1227:
1204:
1163:Corpus callosum
1157:
1148:
1110:
1105:
1104:
1066:
1065:
1061:
1019:
1018:
1014:
970:
968:
964:
920:
918:
914:
868:
866:
862:
820:
819:
815:
773:
772:
768:
724:
722:
713:
667:
666:
662:
636:
633:
626:
623:
614:
611:
602:
599:
590:
587:
578:
549:
497:
455:corpus callosum
440:
428:third ventricle
418:and behind the
396:
356:
262:
256:
185:
142:
57:
45:
28:
23:
22:
18:Fornix of brain
15:
12:
11:
5:
1496:
1494:
1486:
1485:
1480:
1475:
1470:
1460:
1459:
1455:
1454:
1431:
1430:
1428:
1427:
1400:Perforant path
1376:
1374:
1368:
1367:
1365:
1364:
1349:
1347:
1341:
1340:
1332:
1330:
1329:
1322:
1315:
1307:
1298:
1297:
1295:
1294:
1288:
1286:
1282:
1281:
1279:
1278:
1273:
1272:
1271:
1266:
1255:
1253:
1247:
1246:
1244:
1243:
1237:
1235:
1229:
1228:
1226:
1225:
1220:
1214:
1212:
1206:
1205:
1203:
1202:
1201:
1200:
1189:
1188:
1183:
1178:
1173:
1167:
1165:
1159:
1158:
1149:
1147:
1146:
1139:
1132:
1124:
1118:
1117:
1109:
1108:External links
1106:
1103:
1102:
1059:
1032:(6): 663–716.
1012:
983:(9): 351–359.
962:
933:(5): 547–559.
912:
860:
833:(3): 425–489.
813:
786:(4): 800–815.
766:
737:(7): 331–354.
711:
676:(4): 305–320.
659:
658:
652:Gray's Anatomy
632:
629:
628:
627:
624:
617:
615:
612:
605:
603:
600:
593:
591:
588:
581:
577:
574:
548:
545:
496:
493:
439:
436:
395:
392:
355:
352:
351:
350:
335:
326:; then to the
278:rhinencephalon
255:
252:
187:
186:
177:
171:
170:
165:
159:
158:
153:
147:
146:
137:
131:
130:
125:
118:
117:
112:
106:
105:
100:
94:
93:
88:
82:
81:
77:
76:
70:
64:
63:
59:
58:
55:
47:
46:
43:
35:
34:
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1495:
1484:
1483:Limbic system
1481:
1479:
1476:
1474:
1471:
1469:
1466:
1465:
1463:
1453:
1448:
1443:
1439:
1425:
1421:
1417:
1413:
1409:
1405:
1401:
1397:
1393:
1389:
1385:
1381:
1378:
1377:
1375:
1373:
1372:Telencephalon
1369:
1362:
1358:
1354:
1351:
1350:
1348:
1346:
1342:
1338:
1335:
1334:Papez circuit
1328:
1323:
1321:
1316:
1314:
1309:
1308:
1305:
1293:
1290:
1289:
1287:
1283:
1277:
1274:
1270:
1267:
1265:
1262:
1261:
1260:
1259:Septal nuclei
1257:
1256:
1254:
1252:
1248:
1242:
1239:
1238:
1236:
1234:
1230:
1224:
1221:
1219:
1216:
1215:
1213:
1211:
1207:
1199:
1196:
1195:
1194:
1191:
1190:
1187:
1184:
1182:
1179:
1177:
1174:
1172:
1169:
1168:
1166:
1164:
1160:
1156:
1152:
1145:
1140:
1138:
1133:
1131:
1126:
1125:
1122:
1116:
1113:More info at
1112:
1111:
1107:
1098:
1094:
1090:
1086:
1082:
1078:
1074:
1070:
1063:
1060:
1055:
1051:
1047:
1043:
1039:
1035:
1031:
1027:
1023:
1016:
1013:
1008:
1004:
1000:
996:
991:
986:
982:
978:
974:
966:
963:
958:
954:
949:
944:
940:
936:
932:
928:
924:
916:
913:
908:
904:
899:
894:
889:
884:
880:
876:
872:
864:
861:
856:
852:
848:
844:
840:
836:
832:
828:
824:
817:
814:
809:
805:
801:
797:
793:
789:
785:
781:
777:
770:
767:
762:
758:
753:
748:
744:
740:
736:
732:
728:
720:
718:
716:
712:
707:
703:
699:
695:
691:
687:
683:
679:
675:
671:
664:
661:
657:
656:
653:
650:
648:
644:
643:public domain
630:
621:
616:
609:
604:
597:
592:
585:
580:
575:
573:
570:
569:theta rhythms
566:
562:
558:
557:medial septum
554:
553:acetylcholine
546:
544:
542:
538:
534:
530:
525:
522:
518:
514:
513:colloid cysts
509:
506:
502:
494:
492:
490:
486:
482:
478:
474:
469:
467:
463:
458:
456:
451:
449:
445:
437:
435:
433:
429:
425:
421:
417:
413:
409:
405:
401:
393:
391:
389:
383:
381:
377:
373:
369:
365:
361:
353:
348:
344:
343:septal nuclei
341:) end at the
340:
336:
333:
329:
325:
321:
317:
313:
312:
311:
309:
304:
302:
298:
294:
290:
286:
279:
274:
266:
261:
253:
251:
249:
245:
244:recall memory
241:
240:limbic system
237:
233:
229:
225:
221:
217:
207:
202:
198:
194:
182:
176:
172:
169:
166:
164:
160:
157:
154:
152:
148:
145:
141:
138:
136:
132:
129:
126:
123:
119:
116:
113:
111:
107:
104:
101:
99:
95:
92:
89:
87:
83:
78:
75:
71:
69:
65:
60:
53:
48:
41:
36:
31:
19:
1345:Diencephalon
1240:
1232:
1075:(1): 49–63.
1072:
1068:
1062:
1029:
1025:
1015:
980:
976:
969:Reviewed in
965:
930:
926:
919:Reviewed by
915:
878:
874:
867:Reviewed by
863:
830:
826:
816:
783:
779:
769:
734:
730:
723:Reviewed by
673:
669:
663:
654:
640:
634:
550:
526:
510:
498:
470:
459:
452:
447:
443:
441:
408:fornicolumns
407:
403:
399:
397:
388:Lyra Davidis
387:
384:
375:
363:
359:
357:
338:
320:hypothalamus
315:
305:
292:
288:
282:
246:rather than
236:diencephalon
220:nerve fibers
215:
192:
190:
144:A14.1.09.255
140:A14.1.08.949
90:
1404:Hippocampus
1193:Archicortex
1155:human brain
515:from their
473:hippocampus
424:grey matter
232:hippocampus
128:birnlex_705
80:Identifiers
1462:Categories
631:References
380:commissure
372:hippocampi
360:psalterium
354:Commissure
276:Scheme of
260:Commissure
110:NeuroNames
1420:Subiculum
1115:BrainInfo
800:0006-8950
690:0898-929X
410:) of the
254:Structure
1473:Cerebrum
1388:Cingulum
1176:Splenium
1097:19459725
1054:24914572
1007:14725160
999:10461198
957:32132227
907:25642186
855:11258997
847:11301518
808:10734011
761:32567331
706:11731649
698:23961727
647:page 837
547:Function
505:macaques
462:thalamus
330:via the
285:fimbriae
216:fornices
122:NeuroLex
1452:Anatomy
1337:pathway
1186:Rostrum
1181:Tapetum
1153:in the
1046:9175161
948:7231447
898:4294158
881:: 343.
752:7495920
535:and in
487:of the
400:columns
394:Columns
322:to the
230:of the
222:in the
208:
103:D020712
62:Details
1438:Portal
1424:Fornix
1241:Fornix
1233:Fornix
1095:
1089:385334
1087:
1052:
1044:
1005:
997:
955:
945:
905:
895:
853:
845:
806:
798:
759:
749:
704:
696:
688:
655:(1918)
625:Fornix
613:Fornix
477:alveus
412:fornix
201:fornix
195:(from
193:fornix
91:fornix
68:Artery
33:Fornix
1285:Other
1093:S2CID
1050:S2CID
1003:S2CID
851:S2CID
780:Brain
702:S2CID
645:from
485:uncus
444:crura
289:crura
228:tract
224:brain
197:Latin
179:[
168:61965
86:Latin
1422:) →
1171:Genu
1085:PMID
1042:PMID
995:PMID
953:PMID
903:PMID
843:PMID
804:PMID
796:ISSN
757:PMID
694:PMID
686:ISSN
565:GABA
442:The
438:Crus
398:The
364:lyra
293:body
206:lit.
191:The
156:5633
135:TA98
98:MeSH
1416:CA1
1412:CA3
1077:doi
1034:doi
985:doi
981:101
943:PMC
935:doi
893:PMC
883:doi
835:doi
788:doi
784:123
747:PMC
739:doi
678:doi
382:).
212:pl.
163:FMA
151:TA2
115:268
1464::
1418:→
1414:→
1402:→
1398:→
1394:→
1390:→
1386:→
1382:→
1359:→
1355:→
1091:.
1083:.
1073:37
1071:.
1048:.
1040:.
1030:51
1028:.
1024:.
1001:.
993:.
979:.
975:.
951:.
941:.
931:91
929:.
925:.
901:.
891:.
877:.
873:.
849:.
841:.
831:22
829:.
825:.
802:.
794:.
782:.
778:.
755:.
745:.
735:10
733:.
729:.
714:^
700:.
692:.
684:.
672:.
491:.
468:.
457:.
434:.
406:;
214::
203:,
199::
124:ID
1440::
1426:→
1410:(
1406:/
1363:→
1326:e
1319:t
1312:v
1143:e
1136:t
1129:v
1099:.
1079::
1056:.
1036::
1009:.
987::
959:.
937::
909:.
885::
879:6
857:.
837::
810:.
790::
763:.
741::
708:.
680::
674:6
559:/
446:(
402:(
362:(
334:.
183:]
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.