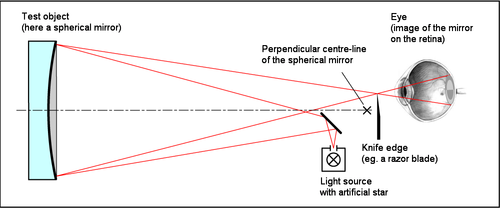
107:. The mirror to be tested is placed vertically in a stand. The Foucault tester is set up at the distance of the mirror's radius of curvature (radius R is twice the focal length.) with the pinhole to one side of the centre of curvature (a short vertical slit parallel to the knife edge can be used instead of the pinhole). The tester is adjusted so that the returning beam from the pinhole light source is interrupted by the knife edge.
89:
531:
555:
507:
543:
17:
519:
161:
accuracy on small and medium-sized mirrors. The
Caustic test is capable of measuring larger mirrors and achieving a (λ/20) wave peak to valley accuracy by using a testing stage which is adjusted from side to side so as to measure each zone of each side of the mirror from the center of its curvature.
110:
Viewing the mirror from behind the knife edge shows a pattern on the mirror surface. If the mirror surface is part of a perfect sphere, the mirror appears evenly lighted across the entire surface. If the mirror is spherical but with defects such as bumps or depressions, the defects appear greatly
122:
mask, Everest pin stick (after A. W. Everest) or other zone marker over the mirror. A series of measurements with the tester, finding the radii of curvature of the zones along the optical axis of the mirror (Y-axis). These data are then reduced and graphed against an ideal parabolic curve.
55:
as a way to measure conic shapes of optical mirrors. It measures mirror surface dimensions by reflecting light into a knife edge at or near the mirror's centre of curvature. In doing so, it only needs a tester which in its most basic 19th century form consists of a
169:
uses a plano-convex lens placed a short distance in front of the pinhole. With the correct positioning of the lens, a parabolic mirror appears flat under testing instead of doughnut-shaped so testing is much easier and zonal measurements are not
141:
A number of other tests are used which measure the mirror at the center of curvature. Some telescope makers use a variant of the
Foucault test called a Ronchi test that replaces the knife edge with a grating (similar to a very coarse
146:) comprising fine parallel wires, an etching on a glass plate, a photograph negative or computer printed transparency. Ronchi test patterns are matched to those of standard mirrors or generated by computer.
64:), and is usually equipped with measurable adjustment to 0.001 inch (25 μm) or better along lines parallel to the optical axis. The test can measure errors in a mirror's curvature to fractions of
191:
method. Interferometric testing has been made more affordable in recent years by affordable lasers, digital cameras (such as webcams), and computers, but remains primarily an industrial methodology.
60:, a piece of tinfoil with a pinhole in it, and a razor blade to create the knife edge. The testing device is adjustable along the X-axis (knife cut direction) across the Y-axis (
235:
429:
92:
From top: Parabolic mirror showing
Foucault shadow patterns made by knife edge inside radius of curvature R (red X), at R and outside R.
391:
115:, the mirror usually looks like a doughnut or lozenge although the exact appearance depends on the exact position of the knife edge.
448:
353:
180:
580:
230:
497:
575:
225:
590:
210:
184:
481:
L. Foucault, "Description des procedees employes pour reconnaitre la configuration des surfaces optiques,"
200:
188:
118:
It is possible to calculate how closely the mirror surface resembles a perfect parabola by placing a
104:
40:
595:
559:
143:
150:
547:
535:
219:
215:
463:
444:
425:
585:
511:
52:
399:
43:. It uses a relatively simple, inexpensive apparatus compared to other testing techniques.
357:
119:
88:
240:
176:
136:
100:
36:
350:
569:
29:
293:
523:
245:
61:
132:
369:
158:
65:
57:
16:
171:
488:
L. Foucault, "Mémoire sur la construction des télescopes en verre argenté,"
329:
205:
77:
69:
483:
Comptes rendus hebdomadaires des séances de l'Académie des
Sciences, Paris
154:
112:
97:
33:
467:
157:
more accurately than the
Foucault test which is limited to about (λ/8)
51:
The
Foucault knife-edge test was described in 1858 by French physicist
518:
96:
Foucault testing is commonly used by amateur telescope makers for
87:
15:
330:"Understanding Foucault: A Primer for Beginners (Second Edition)"
73:
370:
Stellafane ATM Build a Couder Mask; Build an
Everest Pin Stick
28:
is an optical test to accurately measure the shape of concave
351:
Designing and calculating Couder screens for
Foucault testing
187:
method, both published in 1918, the
Lenouvel method and the
149:
Other variants of the
Foucault test include the Gaviola or
443:(second English ed.). Richmond, VA: Willman-Bell.
420:
Harbour, David A (July 2013). William J Welker (ed.).
32:. It is commonly used by amateur telescope makers for
495:
231:Huygens–Fresnel principle#Single slit diffraction
398:. Stockton Astronomical Society. Archived from
422:Understanding Foucault: A primer for beginners
236:Fabrication and testing of optical components
8:
490:Annales de l'Observatoire impériale de Paris
222:for discussion of the Rayleigh criterion)
179:tests which have been used including the
111:magnified in height. If the surface is
502:
424:(2nd ed.). Sapphire Publications.
257:
20:Foucault test setup to measure a mirror
7:
318:Texereau 1984 pp. 55-61 section 2.21
458:Thompson, Allyn J (15 April 1947).
264:Texereau 1984 pp.68-70 section 2.25
153:which can measure mirrors of fast
14:
462:. Cambridge, MA: Sky Publishing.
298:Notes on AMATEUR TELESCOPE OPTICS
553:
541:
529:
517:
505:
485:, vol. 47, pages 958-959 (1858).
390:Baldwin, Jeff (September 2000).
292:Sacek, Vladimir (14 July 2006).
492:, vol. 5, pages 197-237 (1859).
360:Ken Slater and Nils Olof Carlin
282:Texereau 1984 p.70 section 2.26
328:Harbour, David A (July 2001).
220:Angular resolution#Explanation
1:
612:
226:Diffraction-limited system
130:
460:Making Your Own Telescope
211:Amateur telescope making
127:Other testing techniques
26:Foucault knife-edge test
441:How to Make a Telescope
439:Texereau, Jean (1984).
294:"4.5.2. Foucault test"
175:There are a number of
93:
21:
581:Measuring instruments
380:Harbour 2008 pp 49-51
201:Schlieren photography
105:reflecting telescopes
91:
41:reflecting telescopes
19:
332:. The ATM's Workshop
84:Foucault test basics
144:diffraction grating
72:, millionths of an
392:"The Caustic Test"
356:2021-02-23 at the
216:Angular resolution
94:
22:
576:Amateur astronomy
431:978-1-62374-003-0
273:Harbour 2008 p 39
603:
558:
557:
556:
546:
545:
544:
534:
533:
532:
522:
521:
510:
509:
508:
501:
471:
454:
435:
412:
411:
409:
407:
402:on July 28, 2011
387:
381:
378:
372:
367:
361:
348:
342:
341:
339:
337:
325:
319:
316:
310:
309:
307:
305:
300:. Vladimir Sacek
289:
283:
280:
274:
271:
265:
262:
181:Michelson-Twyman
611:
610:
606:
605:
604:
602:
601:
600:
591:Optical devices
566:
565:
564:
554:
552:
542:
540:
530:
528:
516:
506:
504:
496:
478:
476:Further reading
457:
451:
438:
432:
419:
416:
415:
405:
403:
389:
388:
384:
379:
375:
368:
364:
358:Wayback Machine
349:
345:
335:
333:
327:
326:
322:
317:
313:
303:
301:
291:
290:
286:
281:
277:
272:
268:
263:
259:
254:
197:
177:interferometric
139:
131:Main articles:
129:
101:primary mirrors
86:
49:
37:primary mirrors
12:
11:
5:
609:
607:
599:
598:
593:
588:
583:
578:
568:
567:
563:
562:
550:
538:
526:
514:
494:
493:
486:
477:
474:
473:
472:
455:
449:
436:
430:
414:
413:
382:
373:
362:
343:
320:
311:
284:
275:
266:
256:
255:
253:
250:
249:
248:
243:
241:Null corrector
238:
233:
228:
223:
213:
208:
203:
196:
193:
167:Dall null test
137:Interferometry
128:
125:
85:
82:
48:
45:
30:curved mirrors
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
608:
597:
594:
592:
589:
587:
584:
582:
579:
577:
574:
573:
571:
561:
551:
549:
539:
537:
527:
525:
520:
515:
513:
503:
499:
491:
487:
484:
480:
479:
475:
469:
465:
461:
456:
452:
450:0-943396-04-2
446:
442:
437:
433:
427:
423:
418:
417:
401:
397:
393:
386:
383:
377:
374:
371:
366:
363:
359:
355:
352:
347:
344:
331:
324:
321:
315:
312:
299:
295:
288:
285:
279:
276:
270:
267:
261:
258:
251:
247:
244:
242:
239:
237:
234:
232:
229:
227:
224:
221:
217:
214:
212:
209:
207:
204:
202:
199:
198:
194:
192:
190:
186:
182:
178:
173:
172:
168:
163:
160:
156:
152:
147:
145:
138:
134:
126:
124:
121:
116:
114:
108:
106:
102:
99:
90:
83:
81:
79:
75:
71:
68:of light (or
67:
63:
59:
54:
53:Léon Foucault
46:
44:
42:
38:
35:
31:
27:
18:
560:Solar System
489:
482:
459:
440:
421:
404:. Retrieved
400:the original
396:Valley Skies
395:
385:
376:
365:
346:
334:. Retrieved
323:
314:
302:. Retrieved
297:
287:
278:
269:
260:
246:Strehl ratio
174:
166:
164:
151:Caustic test
148:
140:
117:
113:paraboloidal
109:
95:
62:optical axis
50:
25:
23:
548:Outer space
536:Spaceflight
336:18 December
304:18 December
133:Ronchi test
66:wavelengths
596:Telescopes
570:Categories
468:B0007DK32U
406:January 9,
252:References
159:wavelength
78:nanometers
58:light bulb
512:Astronomy
206:Airy disk
185:Michelson
70:Angstroms
354:Archived
195:See also
183:and the
98:figuring
47:Overview
34:figuring
586:Mirrors
498:Portals
170:needed.
155:f/ratio
466:
447:
428:
189:Fizeau
120:Couder
524:Stars
218:(see
76:, or
464:ASIN
445:ISBN
426:ISBN
408:2011
338:2010
306:2010
165:The
135:and
74:inch
24:The
103:in
80:).
39:in
572::
394:.
296:.
500::
470:.
453:.
434:.
410:.
340:.
308:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.