331:
280:
293:
184:
252:
343:
319:
216:
release. Consequently, DR2 uses different source identification numbers than DR1. A number of issues have been identified with the DR2 data, including small systematic errors in astrometry and significant contamination of radial velocity values in crowded star fields, which may affect some one percent of the radial velocity values. Ongoing work should resolve these issues in future releases. A guide for researchers using Gaia DR2, which collected "all information, tips and tricks, pitfalls, caveats and recommendations relevant to" DR2, was prepared by the Gaia
Helpdesk in December 2019.
31:
268:
279:
292:
240:
The full DR3, published on 13 June 2022, includes the EDR3 data plus Solar System data; variability information; results for non-single stars, for quasars, and for extended objects; astrophysical parameters; and a special data set, the Gaia
Andromeda Photometric Survey (GAPS), providing a photometric
224:
Due to uncertainties in the data pipeline, the third data release, based on 34 months of observations, has been split into two parts so that data that was ready first, was released first. The first part, EDR3 (Early Data
Release 3), consisting of improved positions, parallaxes and proper motions, was
191:
The second data release (DR2), which occurred on 25 April 2018, is based on 22 months of observations made between 25 July 2014 and 23 May 2016. It includes positions, parallaxes and proper motions for about 1.3 billion stars and positions of an additional 300 million stars in the magnitude range g =
140:
The GEPC v3.0 catalogue contains 612,946 objects from a field of one square degree each at the north and south poles. The north pole is relatively sparse and contains 164,468 objects, while the south pole is still in the region of the Large
Magellanic Cloud and contains 448,478 objects. The GEPC data
659:
Mignard, F.; Klioner, S.; Lindegren, L.; Bastian, U.; Bombrun, A.; Hernández, J.; Hobbs, D.; Lammers, U.; Michalik, D.; Ramos-Lerate, M.; Biermann, M.; Butkevich, A.; Comoretto, G.; Joliet, E.; Holl, B.; Hutton, A.; Parsons, P.; Steidelmüller, H.; Andrei, A.; Bourda, G.; Charlot, P. (November 2016).
358:
The full data release for the five-year nominal mission, DR4, will include full astrometric, photometric and radial-velocity catalogues, variable-star and non-single-star solutions, source classifications plus multiple astrophysical parameters for stars, unresolved binaries, galaxies and quasars, an
96:
data. A first version was created in 2013, a more refined version in April 2014. In total, the
Attitude Star Catalog contains 8,173,331 entries with information on position, proper motion and magnitude. Starting with Gaia DR2, the Attitude Star Catalog was replaced with a new list generated from the
215:
shows a global agreement of 20 to 30 μas, although individual sources may differ by several mas. Since the data processing procedure links individual Gaia observations with particular sources on the sky, in some cases the association of observations with sources will be different in the second data
119:
A list of quasars based on the Large Quasar
Astrometric Catalog was prepared for IGSL. This in turn goes back to the Sloan Digital Sky Survey. From the more than one million objects, a selection of 150,000 quasars was made, which are in the region of Gaia's magnitude limit. The selected objects are
110:
to detect. It was anticipated that some of the stars selected may be previously unrecognized doubles or variable stars that would need to be deleted from the catalogue; for this reason the list contains more stars than necessary. For Gaia EDR3 (Early Data
Release 3), a selection was made from more
105:
IGSL contains a list of about 200 stars of different spectral classes and magnitudes needed for calibration of the photometric measurements. It is the result of the Gaia
Spectrophotometric Standard Stars Survey (SPSS), a selection of stars using Earth-based data in advance of the Gaia mission.
83:
mission. The mission should have delivered a catalogue based entirely on its own data. For the first catalogue, Gaia DR1, a way was needed to be able to assign the observations to an object and to compare them with the objects from other star catalogues. For this purpose, a separate catalog of
192:
3–20, red and blue photometric data for about 1.1 billion stars and single colour photometry for an additional 400 million stars, and median radial velocities for about 7 million stars between magnitude 4 and 13. It also contains data for over 14,000 selected Solar System objects.
362:
The last catalogue, DR5, will consist of all data collected during the lifespan of the mission. It will be 1.4 times more precise than DR4, while proper motions will be 2.8 times more precise than DR4. It will be published no earlier than the end of 2030.
359:
exo-planet list and epoch and transit data for all sources. Most measurements in DR4 are expected to be 1.7 times more precise than DR2; proper motions will be 4.5 times more precise. DR4 is expected to be released no earlier than mid-2026.
66:
The catalogues are released in stages that will contain increasing amounts of information; the early releases also miss some stars, especially fainter stars located in dense star fields. Data from every data release can be accessed at the
285:
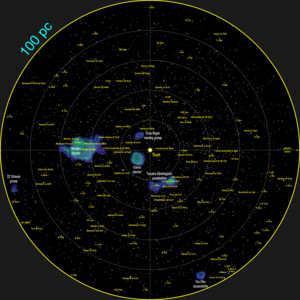
Star density maps of the Gaia
Catalogue of Nearby Stars. The Sun is located at the centre of both maps. The regions with higher density of stars are shown; these correspond with known star clusters (Hyades and Coma Berenices) and moving
161:
Gaia DR1, the first data release based on 14 months of observations made through
September 2015, took place on 13 September 2016. It includes "positions and magnitudes in a single photometric band for 1.1 billion stars using only
174:
data for those objects in both catalogues, "light curves and characteristics for about 3000 variable stars, and positions and magnitudes for more than 2000 extragalactic sources used to define the celestial reference frame".
330:
342:
132:
at the Max Planck Institute for Astronomy in La Silla, Chile. It contains precise positions, UBV I photometry for the southern field and the corresponding magnitudes. The northern part was created with the
251:
298:
This image shows the orbits of the more than 150 000 asteroids in DR3, from the inner parts of the Solar System to the Trojan asteroids at the distance of Jupiter, with different colour codes.
241:
time series for about 1 million sources located in a 5.5-degree radius field centered on the Andromeda galaxy. The release dates of EDR3 and DR3 were delayed by the effects of the
149:
was operated in Ecliptic Poles Scan Law mode (EPSL), in which the two poles were measured twice during each revolution. The initial catalogue was used for Gaia DR1 to match
42:
in each portion of the sky. Brighter regions indicate denser concentrations of stars, while darker regions correspond to patches of the sky where fewer stars are observed.
111:
than 100,000 objects that were used for the calibration. These are well-observed objects selected according to Stetson Secondary Standards, but only Gaia data were used.
1448:
1335:
917:
145:
space probe ended on July 18, 2014. This was followed by a calibration phase of 28 days, during which the ecliptic poles were measured intensively. During this time,
939:
203:–CRF2), which is based on observations of 492,006 sources believed to be quasars and has been described as "the first full-fledged optical realisation of the
583:
318:
183:
128:
Gaia Ecliptic Pole Catalogue (GEPC) was created for measuring the poles. The southern part of the catalogue was compiled from observations made with the
713:
Michalik, Daniel; Lindegren, Lennart (February 2016). "Quasars can be used to verify the parallax zero-point of the Tycho - Gaia Astrometric Solution".
84:
objects from several other catalogues was compiled, which roughly represents the state of knowledge of astronomy at the beginning of the Gaia mission.
1595:
204:
401:
234:
212:
134:
120:
already well observed and documented. In most cases, quasars are very far away, so that their proper motions and parallaxes are negligibly small.
1501:
568:
233:–CRF3), based on observations of 1,614,173 extragalactic sources, 2,269 of which were common to radio sources in the third revision of the
987:
237:. Included is the Gaia Catalogue of Nearby Stars (GCNS), containing 331,312 stars within (nominally) 100 parsecs (330 light-years).
106:
Previous catalogues for calibrating magnitudes could not be used for the mission because many of these objects are too bright for
1600:
406:
92:
The Attitude Star Catalog is a subset of the IGSL, required for the first approximation in the iterative evaluation of the
767:
267:
817:
1605:
34:
An all-sky view of stars in the Milky Way and neighbouring galaxies, based on the first year of observations by
141:
was needed right at the beginning of the mission for the initial calibration. The commissioning phase of the
30:
1401:
1271:
79:
The Initial Gaia Source List (IGSL) is a star catalogue of 1.2 billion objects created in support of the
1329:
562:
166:
data, positions, parallaxes and proper motions for more than 2 million stars" based on a combination of
941:
Gaia DR2 primer: Everything you wish you had known before you started working with Gaia Data Release 2
773:. Gaia Data Release 1 (Report). European Space Agency and Gaia Data Processing and Analysis Consortium
1293:
1218:
1088:
1031:
890:
732:
679:
534:
1349:
1590:
1555:
1565:
1560:
1550:
1317:
1283:
1234:
1208:
1104:
1078:
1047:
1021:
895:
748:
722:
695:
669:
641:
613:
550:
524:
494:
207:... built only on extragalactic sources." Comparison of the positions of 2,843 sources common to
1309:
633:
242:
171:
129:
59:
479:
1483:
1301:
1297:
1226:
1222:
1096:
1092:
1039:
1035:
740:
736:
687:
683:
623:
542:
1375:
793:
538:
1526:
1145:
886:
480:"The Initial Gaia Source List and the Attitude Star Catalog GAIA-C3-TN-OATO-RLS-004-02"
309:
54:
1584:
1426:
1321:
1238:
752:
645:
546:
1123:
1108:
1051:
699:
554:
1305:
1230:
1100:
1043:
744:
691:
628:
601:
1252:
864:
375:
Archive is a catalogue that contains positions and brightnesses for 1.7 billion
1170:
660:"Gaia Data Release 1: Reference frame and optical properties of ICRF sources".
38:, from July 2014 to September 2015. Map shows the density of stars observed by
433:
225:
released on 3 December 2020. The coordinates in EDR3 use a new version of the
1313:
1195:
Lindegren, L.; Klioner, S.; Hernandez, J.; Bombrun, A.; et al. (2021). "
1065:
Lindegren, L.; Hernandez, J.; Bombrun, A.; Klioner, S.; et al. (2018). "
637:
1449:"New Gaia release reveals rare lenses, cluster cores and unforeseen science"
1487:
1529:. Heidelberg: Astronomisches Rechen-Institut (ZAH), Universität Heidelberg
965:
918:"You Are Here: Scientists Unveil Precise Map Of More Than A Billion Stars"
379:, including distances and proper motions for more than 1.3 billion stars.
842:
384:
17:
348:
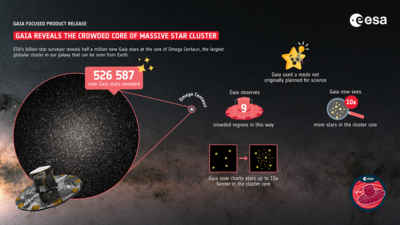
Gaia view of Omega Centauri from Gaia’s Focused Product Release in 2023
1270:
Richard Smart, L. M. Sarro, J. Rybizki, C. Reyle, A. C. Robin (2021).
988:"Selected asteroids detected by Gaia between August 2014 and May 2016"
388:, has been developed to explore the galaxy in three dimensions using
1575:
1477:
460:
1288:
1213:
1083:
1026:
891:"Gaia's Map of 1.3 Billion Stars Makes for a Milky Way in a Bottle"
727:
674:
618:
529:
182:
29:
1570:
376:
1272:"Gaia Early Data Release 3: The Gaia Catalogue of Nearby Stars"
602:"Gaia Early Data Release 3: Photometric content and validation"
312:
and contained more that half a million stars from that region.
821:
438:
336:
Gaia view of Omega Centauri from Gaia’s Data Release 3 in 2022
1012:
Data Release 2 – The celestial reference frame (Gaia-CRF2)".
1253:"Gaia EDR3 - Gaia Catalogue of Nearby Stars - Gaia - Cosmos"
308:
Gaia Focused Product Release from October 2023 focused on
1008:
Gaia Collaboration; Mignard, F.; et al. (2018). "
600:
Marco Riello; F. De Angeli; D. W. Evans (2020-12-03).
482:. Gaia DPAC Data Processing & Analysis Consortium.
245:
on the Gaia Data Processing and Analysis Consortium.
818:"Gaia's billion-star map hints at treasures to come"
97:
Gaia Main Data Base (MDB), using the same criteria.
27:
Catalogues consisting of data from the Gaia misson.
1199:Early Data Release 3 – The astrometric solution".
517:Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society
515:standard stars survey - I. Preliminary results".
428:
426:
424:
422:
1122:Prusti, Timo; Brown, Anthony (3 February 2017).
1471:
1469:
235:International Celestial Reference Frame (ICRF3)
101:Gaia Spectrophotometric Standard Star Catalogue
766:Altmann, M.; Bastian, Uli (17 February 2017).
933:
931:
768:"2.2.4 The Gaia Ecliptic Pole Catalog (GEPC)"
8:
1482:. 53rd ESLAB symposium "the Gaia universe".
1334:: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (
1069:Data Release 2 – The astrometric solution".
794:"Gaia space telescope plots a billion stars"
584:"The Gaia Spectrophotometric Standard Stars"
153:-found objects to previous star catalogues.
1376:"Update to the Gaia data release scenario"
1350:"Gaia Data Release 3 split into two parts"
1287:
1212:
1082:
1025:
726:
673:
627:
617:
528:
1171:"Gaia Early Data Release 3 (Gaia EDR3)"
1165:
1163:
418:
402:Data Processing and Analysis Consortium
314:
247:
211:–CRF2 and a preliminary version of the
1327:
560:
195:The coordinates in DR2 use the second
57:created using the results obtained by
1476:Brown, Anthony G.A. (12 April 2019).
1146:"Known issues with the Gaia DR2 data"
511:E. Pancino; et al. (2012). "The
7:
567:: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (
25:
938:Gaia Helpdesk (9 December 2019),
1596:Astronomical catalogues of stars
966:"Gaia Data Release 2 (Gaia DR2)"
843:"Gaia Data Release 1 (Gaia DR1)"
547:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2012.21766.x
341:
329:
317:
291:
278:
266:
250:
1479:The Future of the Gaia Universe
407:List of astronomical catalogues
1525:Sagristà Sellés, Toni (2016).
1427:"Gaia Data Release 3 overview"
792:Jonathan Amos (14 July 2016).
273:Gaia Catalogue of Nearby Stars
135:Canada–France–Hawaii Telescope
1:
1408:, no. #10, 18 March 2020
1276:Astronomy & Astrophysics
1201:Astronomy & Astrophysics
1071:Astronomy & Astrophysics
1014:Astronomy & Astrophysics
715:Astronomy & Astrophysics
662:Astronomy & Astrophysics
606:Astronomy & Astrophysics
434:"Gaia Data Release Scenario"
304:Gaia Focused Product Release
124:Gaia Ecliptic Pole Catalogue
1306:10.1051/0004-6361/202039498
1231:10.1051/0004-6361/202039709
1101:10.1051/0004-6361/201832727
1044:10.1051/0004-6361/201832916
745:10.1051/0004-6361/201527444
692:10.1051/0004-6361/201629534
629:10.1051/0004-6361/202039587
495:"The Attitude Star Catalog"
257:Stars and other objects in
229:celestial reference frame (
199:celestial reference frame (
115:Gaia Initial Quasar Catalog
1622:
493:R. L. Smart (2014-04-28).
478:R. L. Smart (2013-10-17).
382:An outreach application,
75:Initial Gaia Source List
1601:Astronomical catalogues
1556:Gaia EDR3 Documentation
1298:2021A&A...649A...6G
1223:2021A&A...649A...2L
1148:. European Space Agency
1093:2018A&A...616A...2L
1036:2018A&A...616A..14G
737:2016A&A...586A..26M
684:2016A&A...595A...5M
513:Gaia spectrophotometric
324:Focused Product Release
1566:Gaia DR1 Documentation
1561:Gaia DR2 Documentation
1551:Gaia DR3 Documentation
1488:10.5281/zenodo.2637971
1402:"Delay of Gaia (E)DR3"
582:C. Jordi; et al.
188:
137:on Mauna Kea, Hawaii.
43:
1506:irsa.ipac.caltech.edu
186:
88:Attitude Star Catalog
33:
261:Early Data Release 3
1382:. 26 September 2019
1124:"Gaia DR2 Schedule"
867:. 15 September 2016
845:. 14 September 2016
824:. 13 September 2016
539:2012MNRAS.426.1767P
1257:www.cosmos.esa.int
896:The New York Times
189:
44:
1606:Stellar astronomy
1356:. 29 January 2019
820:(Press release).
243:COVID-19 pandemic
187:Stars in Gaia DR2
130:MPG/ESO telescope
63:space telescope.
16:(Redirected from
1613:
1538:
1537:
1535:
1534:
1522:
1516:
1515:
1513:
1512:
1498:
1492:
1491:
1473:
1464:
1463:
1461:
1459:
1445:
1439:
1438:
1436:
1434:
1423:
1417:
1416:
1415:
1413:
1398:
1392:
1391:
1389:
1387:
1372:
1366:
1365:
1363:
1361:
1346:
1340:
1339:
1333:
1325:
1291:
1267:
1261:
1260:
1249:
1243:
1242:
1216:
1192:
1186:
1185:
1183:
1181:
1167:
1158:
1157:
1155:
1153:
1142:
1136:
1135:
1133:
1131:
1119:
1113:
1112:
1086:
1062:
1056:
1055:
1029:
1005:
999:
998:
996:
994:
984:
978:
977:
975:
973:
962:
956:
955:
954:
952:
946:
935:
926:
925:
914:
908:
907:
905:
903:
883:
877:
876:
874:
872:
865:"Data Release 1"
861:
855:
854:
852:
850:
839:
833:
832:
830:
829:
814:
808:
807:
805:
804:
789:
783:
782:
780:
778:
772:
763:
757:
756:
730:
710:
704:
703:
677:
656:
650:
649:
631:
621:
597:
591:
590:
588:
579:
573:
572:
566:
558:
532:
523:(3): 1767–1781.
508:
502:
501:
499:
490:
484:
483:
475:
469:
468:
457:
451:
450:
448:
446:
430:
354:Gaia DR4 and DR5
345:
333:
321:
295:
282:
270:
254:
21:
1621:
1620:
1616:
1615:
1614:
1612:
1611:
1610:
1581:
1580:
1547:
1542:
1541:
1532:
1530:
1524:
1523:
1519:
1510:
1508:
1500:
1499:
1495:
1475:
1474:
1467:
1457:
1455:
1447:
1446:
1442:
1432:
1430:
1425:
1424:
1420:
1411:
1409:
1406:Gaia Newsletter
1400:
1399:
1395:
1385:
1383:
1374:
1373:
1369:
1359:
1357:
1348:
1347:
1343:
1326:
1269:
1268:
1264:
1251:
1250:
1246:
1194:
1193:
1189:
1179:
1177:
1169:
1168:
1161:
1151:
1149:
1144:
1143:
1139:
1129:
1127:
1121:
1120:
1116:
1064:
1063:
1059:
1007:
1006:
1002:
992:
990:
986:
985:
981:
971:
969:
968:. 25 April 2018
964:
963:
959:
950:
948:
944:
937:
936:
929:
916:
915:
911:
901:
899:
887:Overbye, Dennis
885:
884:
880:
870:
868:
863:
862:
858:
848:
846:
841:
840:
836:
827:
825:
816:
815:
811:
802:
800:
791:
790:
786:
776:
774:
770:
765:
764:
760:
712:
711:
707:
658:
657:
653:
599:
598:
594:
586:
581:
580:
576:
559:
510:
509:
505:
497:
492:
491:
487:
477:
476:
472:
459:
458:
454:
444:
442:
432:
431:
420:
415:
398:
369:
356:
349:
346:
337:
334:
325:
322:
306:
299:
296:
287:
283:
274:
271:
262:
255:
222:
181:
159:
126:
117:
103:
90:
77:
55:star catalogues
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
1619:
1617:
1609:
1608:
1603:
1598:
1593:
1583:
1582:
1579:
1578:
1573:
1568:
1563:
1558:
1553:
1546:
1545:External links
1543:
1540:
1539:
1517:
1493:
1465:
1440:
1418:
1393:
1367:
1341:
1262:
1244:
1187:
1159:
1137:
1114:
1057:
1000:
979:
957:
927:
909:
889:(1 May 2018).
878:
856:
834:
809:
784:
758:
705:
651:
592:
574:
503:
485:
470:
452:
417:
416:
414:
411:
410:
409:
404:
397:
394:
368:
365:
355:
352:
351:
350:
347:
340:
338:
335:
328:
326:
323:
316:
310:Omega Centauri
305:
302:
301:
300:
297:
290:
288:
284:
277:
275:
272:
265:
263:
256:
249:
221:
218:
180:
177:
158:
155:
125:
122:
116:
113:
102:
99:
89:
86:
76:
73:
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1618:
1607:
1604:
1602:
1599:
1597:
1594:
1592:
1589:
1588:
1586:
1577:
1574:
1572:
1571:ESA Gaia page
1569:
1567:
1564:
1562:
1559:
1557:
1554:
1552:
1549:
1548:
1544:
1528:
1521:
1518:
1507:
1503:
1497:
1494:
1489:
1485:
1481:
1480:
1472:
1470:
1466:
1454:
1450:
1444:
1441:
1428:
1422:
1419:
1407:
1403:
1397:
1394:
1381:
1377:
1371:
1368:
1355:
1351:
1345:
1342:
1337:
1331:
1323:
1319:
1315:
1311:
1307:
1303:
1299:
1295:
1290:
1285:
1281:
1277:
1273:
1266:
1263:
1258:
1254:
1248:
1245:
1240:
1236:
1232:
1228:
1224:
1220:
1215:
1210:
1206:
1202:
1198:
1191:
1188:
1176:
1172:
1166:
1164:
1160:
1147:
1141:
1138:
1125:
1118:
1115:
1110:
1106:
1102:
1098:
1094:
1090:
1085:
1080:
1076:
1072:
1068:
1061:
1058:
1053:
1049:
1045:
1041:
1037:
1033:
1028:
1023:
1019:
1015:
1011:
1004:
1001:
989:
983:
980:
967:
961:
958:
947:, vol. 1
943:
942:
934:
932:
928:
923:
919:
913:
910:
898:
897:
892:
888:
882:
879:
866:
860:
857:
844:
838:
835:
823:
819:
813:
810:
799:
795:
788:
785:
769:
762:
759:
754:
750:
746:
742:
738:
734:
729:
724:
720:
716:
709:
706:
701:
697:
693:
689:
685:
681:
676:
671:
667:
663:
655:
652:
647:
643:
639:
635:
630:
625:
620:
615:
611:
607:
603:
596:
593:
585:
578:
575:
570:
564:
556:
552:
548:
544:
540:
536:
531:
526:
522:
518:
514:
507:
504:
496:
489:
486:
481:
474:
471:
466:
464:
456:
453:
441:
440:
435:
429:
427:
425:
423:
419:
412:
408:
405:
403:
400:
399:
395:
393:
391:
387:
386:
380:
378:
374:
366:
364:
360:
353:
344:
339:
332:
327:
320:
315:
313:
311:
303:
294:
289:
281:
276:
269:
264:
260:
253:
248:
246:
244:
238:
236:
232:
228:
219:
217:
214:
210:
206:
202:
198:
193:
185:
178:
176:
173:
169:
165:
156:
154:
152:
148:
144:
138:
136:
131:
123:
121:
114:
112:
109:
100:
98:
95:
87:
85:
82:
74:
72:
70:
64:
62:
61:
56:
52:
50:
41:
37:
32:
19:
1576:Gaia Archive
1531:. Retrieved
1520:
1509:. Retrieved
1505:
1496:
1478:
1456:. Retrieved
1452:
1443:
1431:. Retrieved
1421:
1410:, retrieved
1405:
1396:
1386:28 September
1384:. Retrieved
1379:
1370:
1358:. Retrieved
1353:
1344:
1330:cite journal
1279:
1275:
1265:
1256:
1247:
1204:
1200:
1196:
1190:
1178:. Retrieved
1174:
1150:. Retrieved
1140:
1128:. Retrieved
1117:
1074:
1070:
1066:
1060:
1020:(A14): A14.
1017:
1013:
1009:
1003:
991:. Retrieved
982:
970:. Retrieved
960:
949:, retrieved
940:
921:
912:
900:. Retrieved
894:
881:
871:15 September
869:. Retrieved
859:
849:16 September
847:. Retrieved
837:
826:. Retrieved
812:
801:. Retrieved
797:
787:
775:. Retrieved
761:
718:
714:
708:
665:
661:
654:
609:
605:
595:
577:
563:cite journal
520:
516:
512:
506:
488:
473:
462:
455:
443:. Retrieved
437:
389:
383:
381:
372:
370:
367:Gaia Archive
361:
357:
307:
258:
239:
230:
226:
223:
208:
200:
196:
194:
190:
167:
163:
160:
150:
146:
142:
139:
127:
118:
107:
104:
93:
91:
80:
78:
68:
65:
58:
48:
47:
45:
39:
35:
1453:www.esa.int
1433:23 February
1180:12 December
951:10 December
1591:Astrometry
1585:Categories
1533:2019-11-21
1527:"Gaia Sky"
1511:2020-12-15
1458:15 October
1360:29 January
1289:2012.02061
1214:2012.03380
1152:31 January
1084:1804.09366
1077:(A2): A2.
1027:1804.09377
993:2 December
828:2022-09-23
803:2022-09-23
728:1511.01896
675:1609.07255
619:2012.01916
413:References
51:catalogues
1322:227255512
1314:0004-6361
1239:227342958
777:17 August
753:119126039
646:248245902
638:0004-6361
530:1207.6042
71:archive.
1412:21 March
1130:10 March
1109:54497421
1052:52838272
972:26 April
700:46661611
555:27564967
465:Archive"
445:8 August
396:See also
385:Gaia Sky
220:Gaia DR3
179:Gaia DR2
157:Gaia DR1
18:Gaia DR2
1294:Bibcode
1282:: 649.
1219:Bibcode
1207:: 649.
1089:Bibcode
1032:Bibcode
922:NPR.org
733:Bibcode
721:: A26.
680:Bibcode
535:Bibcode
500:. DPAC.
286:groups.
172:Tycho-2
1502:"Gaia"
1429:. 2022
1320:
1312:
1237:
1107:
1050:
751:
698:
668:: A5.
644:
636:
612:: A3.
553:
392:data.
1318:S2CID
1284:arXiv
1235:S2CID
1209:arXiv
1126:. ESA
1105:S2CID
1079:arXiv
1048:S2CID
1022:arXiv
945:(pdf)
902:1 May
771:(PDF)
749:S2CID
723:arXiv
696:S2CID
670:arXiv
642:S2CID
614:arXiv
587:(PDF)
551:S2CID
525:arXiv
498:(PDF)
377:stars
213:ICRF3
1460:2023
1435:2022
1414:2020
1388:2019
1362:2019
1336:link
1310:ISSN
1197:Gaia
1182:2020
1154:2019
1132:2018
1067:Gaia
1010:Gaia
995:2017
974:2018
953:2019
904:2018
873:2016
851:2016
779:2022
634:ISSN
569:link
463:Gaia
447:2024
390:Gaia
373:Gaia
371:The
259:Gaia
231:Gaia
227:Gaia
209:Gaia
205:ICRS
201:Gaia
197:Gaia
170:and
168:Gaia
164:Gaia
151:Gaia
147:Gaia
143:Gaia
108:Gaia
94:Gaia
81:Gaia
69:Gaia
60:Gaia
53:are
49:Gaia
46:The
40:Gaia
36:Gaia
1484:doi
1380:ESA
1354:ESA
1302:doi
1227:doi
1175:ESA
1097:doi
1075:616
1040:doi
1018:616
822:ESA
798:BBC
741:doi
719:586
688:doi
666:595
624:doi
610:649
543:doi
521:426
439:ESA
1587::
1504:.
1468:^
1451:.
1404:,
1378:.
1352:.
1332:}}
1328:{{
1316:.
1308:.
1300:.
1292:.
1280:A6
1278:.
1274:.
1255:.
1233:.
1225:.
1217:.
1205:A2
1203:.
1173:.
1162:^
1103:.
1095:.
1087:.
1073:.
1046:.
1038:.
1030:.
1016:.
930:^
920:.
893:.
796:.
747:.
739:.
731:.
717:.
694:.
686:.
678:.
664:.
640:.
632:.
622:.
608:.
604:.
565:}}
561:{{
549:.
541:.
533:.
519:.
436:.
421:^
1536:.
1514:.
1490:.
1486::
1462:.
1437:.
1390:.
1364:.
1338:)
1324:.
1304::
1296::
1286::
1259:.
1241:.
1229::
1221::
1211::
1184:.
1156:.
1134:.
1111:.
1099::
1091::
1081::
1054:.
1042::
1034::
1024::
997:.
976:.
924:.
906:.
875:.
853:.
831:.
806:.
781:.
755:.
743::
735::
725::
702:.
690::
682::
672::
648:.
626::
616::
589:.
571:)
557:.
545::
537::
527::
467:.
461:"
449:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.