1174:, and some carbamates are known to actually stimulate GCA production. Increased GCA activity results in a decrease of the concentration and metabolic half-life of glucuronic acid substrates, causing the plasma levels of glucuronidated drugs to fall below their therapeutic threshold. Excessive glucuronidation of the substrates may result in an inadequate response to traditional doses of affected medications and, unless the drug has a very wide therapeutic index, will generally result in the acute failure of the pharmacotherapy and necessitate the transition from one or more implicated drugs to an equivalent regimen of non-glucuronidated alternatives. A select number of antidepressants and a wide range of anti-psychotic agents are glucuronidation ligands, but due to their delayed mechanism of action and pharmacokinetic properties the decrease of their plasma concentrations may not be immediately apparent and tends to present as a sudden and intense relapse of symptoms instead of a gradual regression to the behaviors and thought patterns exhibited by the patient prior to the initiation of their pharmacological treatment.
362:
253:
1254:) results in chronically painful conditions being perceived as considerably more severe than they did previously while pre-existing tolerable yet occasionally painful activities can become more painful than before and will begin to be aggravated by briefer and less physically demanding activities. It can also cause equally painful responses to decreasingly noxious (irritating) stimuli, eventually resulting in considerable agony from stimuli which wouldn't cause any amount of pain to most individuals.
60:
1000:
51:
910:
Once this reaction is complete, and the starch/nitric acid mix turns clear (after giving off nitrogen dioxide gas), the solution can be diluted, and hydrolyzed with another mineral acid. Then the oxidation is slowly quenched with sodium hydroxide (or sodium bicarbonate), forming sodium glucuronate, which can be crystallized out of solution. With transition metals, it forms complexes such as
673:
1296:, formerly called L-hexuronic acid). Ascorbate can be biosynthesized by higher plants, algae, yeast and most animals. An adult goat produces ~13 g of vitamin C per day. This ability is lacking in some mammals (including humans and guinea pigs) and also in insects, invertebrates and most fishes. These species require external ascorbate supply, because they lack the biosynthetic enzyme
1139:
the rate of metabolism is reduced enough to produce a marked accumulation of all GCA substrates in the system; this often increases drug concentrations in the blood by medically relevant amounts. In the most severe cases permanent and debilitating organ damage (particularly the liver, kidneys, heart, and brain), and even death, have been known to occur.
580:
726:
909:
Sodium glucuronate can be produced by the direct oxidation of starch with concentrated nitric acid. In this preparation the low availability of water keeps the starch polymers from hydrolyzing and only oxidizes the free hydroxyls, in much the same way that nitrogen dioxide would oxidize the starch.
1138:
It is possible to exhaust the body's supply of glucuronic acid by combining multiple drugs/substances whose metabolism and excretion are primarily or entirely dependent on glucuronidation. Although most such substances have secondary metabolic routes which become prominent following GCA depletion,
1102:
more water-soluble, and, in this way, allows for their subsequent elimination from the body through urine or faeces (via bile from the liver) at a significantly increased rate. The carboxyl group is ionized at physiological pH, making the conjugated compound water-soluble. Compounds with molecular
1166:
are all capable of contributing to GCA depletion, with ethanol and acetaminophen being the most commonly implicated substances involved in cases of accidental overdoses which have been positively attributed to glucuronic acid depletion.
897:
Direct oxidation of an aldose affects the aldehyde group first. A laboratory synthesis of a uronic acid from an aldose requires protecting the aldehyde and hydroxy groups from oxidation, for example by conversion to cyclic
866:
The nonplanar pyranose rings can assume either chair (in 2 variants) or boat conformation. The preferred conformation depends on spatial interference or other interactions of the substituents. The pyranose form of
1103:
masses > 60,000 are too large for renal excretion and will be excreted with bile into the intestine. Neonates are deficient in this conjugating system, making them particularly vulnerable to drugs such as
1242:
to aggravate both acute and chronic inflammatory conditions as well as increasing the perceived severity of pain in patients with chronic pain conditions, via up-regulation of the production and release of
1393:
1222:) in mammals because sulfate formation is a high-affinity, low-capacity system (due to sulfate depletion), whereas glucuronidation is a low-affinity, high-capacity (although still exhaustible) system.
820:-glucuronic acid the C-1 hydroxy group is on the same side of the pyranose ring as the carboxyl group. In the free sugar acid, the β-form is prevalent (~64%), whereas in the organism, the α-form
1380:"Determination of mRNA Expression of Human UDP-Glucuronosyltransferases and Application for Localization in Various Human Tissues by Real-Time Reverse Transcriptase-Polymerase Chain Reaction"
1185:
present in intestinal microflora to the respective aglycone, which may be reabsorbed from the intestine and translocated back to the liver with the blood. The resulting cycle is called
170:
593:
1053:(UDP-GT), have been found in all major body organs, e.g., intestine, kidneys, brain, adrenal gland, spleen, and thymus. Analogous reactions occur with other
411:
1196:
processes. Covalent binding of the aglycone portions of several carboxylic acid (ester) glucuronides is known to occur to nucleophilic sites on
1598:
1454:
812:-configuration. Due to ring closure, cyclic sugars have another asymmetric carbon atom (C-1), resulting in two more stereoisomers, named
821:
1490:
712:
376:
690:
1045:
with thiol, amine and hydroxy groups, or esterification with the carboxyl and hydroxyl groups. This linkage process is known as
1384:
1049:(or glucuronide conjugation). Glucuronidation occurs mainly in the liver, although the enzymes responsible for its catalysis,
1189:. Compounds that undergo enterohepatic circulation are only slowly excreted and usually have a longer half-life in the body.
694:
1321:
produces the enzyme β-glucuronidase, which hydrolyzes the MUG molecule to a fluorescent product that is detectable under
600:
319:
1124:
1507:"Glucuronic acid and the ethanol metabolite ethyl-glucuronide cause toll-like receptor 4 activation and enhanced pain"
1251:
758:
340:
1027:
683:
1186:
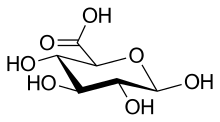
757:, with its sixth carbon atom oxidized to a carboxylic acid. In living beings, this primary oxidation occurs with
1362:
280:
286:
1116:
1050:
919:
1437:
Bock K, Köhle C (2005). "UDP-Glucuronosyltransferase 1A6: Structural, Functional, and
Regulatory Aspects".
911:
831:
Carbohydrate stereoisomers, which differ in configuration at only one (other) asymmetric C-atom, are named
248:
1628:
915:
1623:
1301:
1120:
1078:-glucuronides, its salts and esters are named glucuronates. The human body uses glucuronidation to make
86:
72:
977:
940:
816:. Depending on the configuration at C-1, there are two anomers of glucuronic acid, α- and β-form. In β-
506:
1250:
within the body. Long-term agonism of the TLR4 receptor (such as that which occurs from GCA, ETG, and
792:-glucose are capable of forming two furanose forms (α and β) and two pyranose forms (α and β). By the
558:
550:
542:
546:
534:
502:
843:
562:
554:
538:
526:
498:
357:
1618:
1339:
1079:
1062:
1054:
1023:
1015:
953:
136:
59:
1571:
1413:
1244:
1182:
1108:
793:
999:
1594:
1536:
1486:
1460:
1450:
1405:
1322:
1263:
1235:
981:
850:
808:-glucuronic acid, depending on its configuration at C-5. Most physiological sugars are of the
514:
385:
InChI=1S/C6H10O7/c7-1-2(8)4(5(10)11)13-6(12)3(1)9/h1-4,6-9,12H,(H,10,11)/t1-,2-,3+,4-,6-/m0/s1
395:
InChI=1/C6H10O7/c7-1-2(8)4(5(10)11)13-6(12)3(1)9/h1-4,6-9,12H,(H,10,11)/t1-,2-,3+,4-,6-/m0/s1
1563:
1526:
1518:
1442:
1397:
1313:
1231:
1215:
1128:
959:
887:
510:
434:
210:
328:
1211:
1104:
1087:
1046:
1042:
1008:
1004:
994:
971:
965:
836:
530:
146:
1379:
361:
252:
190:
1531:
1506:
1163:
883:
571:
518:
50:
37:
1446:
974:
occurs in large quantities in connective tissues, skin, cartilage, and synovial fluid.
1612:
1366:
1334:
1289:
1267:
1197:
857:
616:
522:
475:
241:
33:
1575:
956:
is found in large quantities in cartilage, aorta, connective tissue, bone, and skin.
1417:
1278:
936:
308:
1214:-derived metabolites of aromatic hydrocarbons, are substrates for both UDP-GT and
1505:
Lewis SS, Hutchinson MR, Zhang Y, Hund DK, Maier SF, Rice KC, Watkins LR (2013).
1170:
Excessive quantities of GCA can also be hazardous to health. Tobacco smoke, most
1344:
1171:
1148:
1058:
797:
672:
636:
628:
492:
950:
is an inhibitor of blood coagulation, and occurs in mast cells, lung and liver.
1522:
1193:
1178:
1156:
1038:
1034:
1031:
777:
773:
750:
656:
640:
462:
201:
1293:
1247:
1201:
1131:, UDPGT activity is reduced or nearly absent due to mutations, resulting in
1112:
1099:
1091:
1071:
903:
1554:
Blanc P (February 1996). "Characterization of the tea fungus metabolites".
1540:
1464:
1409:
1401:
882:
Additional oxidation at C-1 to the carboxyl level yields the dicarboxylic
1282:
1144:
1132:
785:
781:
652:
221:
1107:, which is inactivated by the addition of glucuronic acid, resulting in
230:
1567:
1271:
1219:
1159:
1140:
947:
891:
769:
754:
697: in this section. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.
648:
295:
1262:
Determination of urinary steroids and of steroid conjugates in blood.
1207:
1152:
1083:
899:
832:
813:
1591:
Biochemical
Pathways: An Atlas of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology
570:
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their
17:
1481:
Tanya C McCarthy, Christopher J Sinal (2005), "Biotransformation",
269:
1095:
998:
724:
632:
181:
169:
159:
1239:
260:
1394:
American
Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics
725:
1218:. Glucuronides predominate with phenol or a phenol precursor (
666:
1230:
Glucuronic acid, as well as the glucuronidated metabolite of
345:
1192:
Certain glucuronides are electrophilic and may function in
480:
159 to 161 °C (318 to 322 °F; 432 to 434 K)
1485:, vol. 1 (2nd ed.), Elsevier, pp. 299–312,
1441:. Methods in Enzymology. Vol. 400. pp. 57–75.
737:-methyl glycoside of glucuronic acid in the low energy C
1311:-glucuronide (MUG) is used to test for the presence of
588:
1123:(20%), and unconjugated bilirubin (< 1%). In the
962:
is a proteoglycan in skin, heart, and blood vessels.
635:(hence the name "uronic acid"). It is found in many
1274:and are used to monitor alcohol use or dependence.
1439:Phase II Conjugation Enzymes and Transport Systems
307:
145:
935:Glucuronic acid is a common building block of
111:)-3,4,5,6-Tetrahydroxyoxane-2-carboxylic acid
8:
968:is found in the cornea, cartilage, and bone.
1074:resulting from glucuronidation are named β-
1589:Gerhard Michal, Dietmar Schomburg (2012),
360:
251:
209:
42:
1530:
796:, glucuronic acid has two stereoisomers (
713:Learn how and when to remove this message
327:
1270:are excreted in urine as metabolites of
1355:
1307:The glucuronide 4-methylumbelliferyl-β-
659:of microorganisms, plants and animals.
416:
381:
356:
285:
229:
1378:Ohno S, Nakajin, Shizuo (2008-10-06).
1277:Glucuronic acid and gluconic acid are
863:(C-5) are epimers of glucuronic acid.
242:
1593:(2nd ed.), Wiley, p. 145a,
644:
388:Key: AEMOLEFTQBMNLQ-WAXACMCWSA-N
189:
7:
1476:
1474:
768:Glucuronic acid, like its precursor
695:adding citations to reliable sources
875:-glucuronic acid prefer the chair C
398:Key: AEMOLEFTQBMNLQ-WAXACMCWBB
298:
268:
1288:Glucuronic acid is a precursor of
1094:, primary and secondary aliphatic
772:, can exist as a linear (carboxo-)
25:
1022:(UDPGA) is often involved in the
765:(UDPG), not with the free sugar.
1248:inflammatory signaling molecules
984:form the cell walls of bacteria.
671:
578:
446:
58:
49:
1385:Drug Metabolism and Disposition
682:needs additional citations for
574:(at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
452:
440:
1:
1511:Brain, Behavior, and Immunity
1447:10.1016/S0076-6879(05)00004-2
1151:, cyclooxygenase inhibitors (
655:tea and is important for the
631:that was first isolated from
871:-glucose and its derivative
1210:, quantitatively important
1149:paracetamol (acetaminophen)
1115:is excreted in the bile as
1645:
1483:Encyclopedia of Toxicology
1051:UDP-glucuronyltransferases
992:
31:
1523:10.1016/j.bbi.2013.01.005
1187:enterohepatic circulation
1041:. These linkages involve
776:(<1%), or as a cyclic
568:
484:
427:
407:
372:
129:
117:
85:
71:
66:
57:
48:
1204:reactions, for example.
32:Not to be confused with
1125:Crigler–Najjar syndrome
1117:bilirubin diglucuronide
788:). Aldohexoses such as
1402:10.1124/dmd.108.023598
1012:
920:copper(II) glucuronate
894:) of glucuronic acid.
828:(UDPGA) predominates.
746:
124:-Glucuronic acid, GlcA
80:-Glucopyranuronic acid
1556:Biotechnology Letters
1302:gulonolactone oxidase
1121:bilirubin glucuronide
1002:
912:iron(III) glucuronate
749:Glucuronic acid is a
728:
87:Systematic IUPAC name
1240:toll-like receptor 4
1177:Glucuronides may be
1007:by formation of a β-
916:iron(II) glucuronate
691:improve this article
1340:Isosaccharinic acid
1024:phase II metabolism
1003:Glucuronidation of
954:Chondroitin sulfate
890:is the self-ester (
470: g·mol
419:O=C(O)1O(O)(O)(O)1O
45:
1568:10.1007/BF00128667
1109:gray baby syndrome
1066:-galacturonic acid
1013:
982:galacturonic acids
978:Glycoglycerolipids
941:glycoglycerolipids
794:Fischer convention
747:
601:Infobox references
485:Related compounds
43:
1600:978-0-470-14684-2
1456:978-0-12-182805-9
1363:D-Glucuronic acid
1323:ultraviolet light
1310:
1299:
1264:Ethyl glucuronide
1236:ethyl glucuronide
1216:sulfotransferases
1077:
1065:
1019:
980:of glucuronic or
874:
870:
860:
853:
846:
839:
825:
819:
811:
807:
803:
791:
762:
744:
736:
723:
722:
715:
609:Chemical compound
607:
606:
515:Galacturonic acid
507:Arabinuronic acid
341:CompTox Dashboard
171:Interactive image
123:
79:
16:(Redirected from
1636:
1604:
1603:
1586:
1580:
1579:
1551:
1545:
1544:
1534:
1502:
1496:
1495:
1478:
1469:
1468:
1434:
1428:
1427:
1425:
1424:
1375:
1369:
1360:
1314:Escherichia coli
1308:
1297:
1129:Gilbert syndrome
1088:carboxylic acids
1075:
1063:
1043:glycosidic bonds
1020:-glucuronic acid
1017:
960:Dermatan sulfate
888:Glucuronolactone
872:
868:
858:
851:
844:
837:
826:-glucuronic acid
823:
817:
809:
805:
801:
789:
760:
742:
741:conformation of
734:
718:
711:
707:
704:
698:
675:
667:
646:
621:sweet wine, must
591:
585:
582:
581:
559:Xyluluronic acid
551:Tagaturonic acid
543:Ribuluronic acid
511:Fructuronic acid
469:
454:
448:
442:
435:Chemical formula
365:
364:
349:
347:
331:
311:
300:
289:
272:
255:
244:
233:
213:
193:
173:
149:
121:
77:
62:
53:
46:
44:Glucuronic acid
21:
1644:
1643:
1639:
1638:
1637:
1635:
1634:
1633:
1609:
1608:
1607:
1601:
1588:
1587:
1583:
1553:
1552:
1548:
1504:
1503:
1499:
1493:
1480:
1479:
1472:
1457:
1436:
1435:
1431:
1422:
1420:
1377:
1376:
1372:
1361:
1357:
1353:
1331:
1260:
1228:
1226:Role in disease
1183:β-glucuronidase
1164:benzodiazepines
1105:chloramphenicol
1047:glucuronidation
1009:glycosidic bond
1005:4-aminobiphenyl
997:
995:Glucuronidation
991:
989:Glucuronidation
972:Hyaluronic acid
966:Keratan sulfate
933:
928:
878:
835:. For example,
740:
719:
708:
702:
699:
688:
676:
665:
613:Glucuronic acid
610:
603:
598:
597:
596: ?)
587:
583:
579:
575:
547:Sorburonic acid
535:Psicuronic acid
531:Mannuronic acid
503:Altruronic acid
495:
467:
457:
451:
445:
437:
423:
420:
415:
414:
403:
400:
399:
396:
390:
389:
386:
380:
379:
368:
350:
343:
334:
314:
301:
287:Glucuronic+acid
275:
236:
216:
196:
176:
163:
152:
139:
125:
113:
112:
81:
41:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
1642:
1640:
1632:
1631:
1626:
1621:
1611:
1610:
1606:
1605:
1599:
1581:
1562:(2): 139–142.
1546:
1497:
1491:
1470:
1455:
1429:
1370:
1354:
1352:
1349:
1348:
1347:
1342:
1337:
1330:
1327:
1259:
1256:
1238:(ETG), act on
1227:
1224:
1162:, and certain
993:Main article:
990:
987:
986:
985:
975:
969:
963:
957:
951:
932:
929:
927:
924:
876:
861:-iduronic acid
738:
721:
720:
679:
677:
670:
664:
661:
608:
605:
604:
599:
577:
576:
572:standard state
569:
566:
565:
563:Xyluronic acid
555:Taluronic acid
539:Riburonic acid
527:Lyxuronic acid
519:Guluronic acid
499:Alluronic acid
496:
490:
487:
486:
482:
481:
478:
472:
471:
465:
459:
458:
455:
449:
443:
438:
433:
430:
429:
425:
424:
422:
421:
418:
410:
409:
408:
405:
404:
402:
401:
397:
394:
393:
391:
387:
384:
383:
375:
374:
373:
370:
369:
367:
366:
358:DTXSID40273973
353:
351:
339:
336:
335:
333:
332:
324:
322:
316:
315:
313:
312:
304:
302:
294:
291:
290:
283:
277:
276:
274:
273:
265:
263:
257:
256:
246:
238:
237:
235:
234:
226:
224:
218:
217:
215:
214:
206:
204:
198:
197:
195:
194:
186:
184:
178:
177:
175:
174:
166:
164:
157:
154:
153:
151:
150:
142:
140:
135:
132:
131:
127:
126:
119:
115:
114:
90:
89:
83:
82:
75:
69:
68:
64:
63:
55:
54:
38:Guluronic acid
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1641:
1630:
1629:Vicinal diols
1627:
1625:
1622:
1620:
1617:
1616:
1614:
1602:
1596:
1592:
1585:
1582:
1577:
1573:
1569:
1565:
1561:
1557:
1550:
1547:
1542:
1538:
1533:
1528:
1524:
1520:
1516:
1512:
1508:
1501:
1498:
1494:
1492:0-12-745354-7
1488:
1484:
1477:
1475:
1471:
1466:
1462:
1458:
1452:
1448:
1444:
1440:
1433:
1430:
1419:
1415:
1411:
1407:
1403:
1399:
1395:
1391:
1387:
1386:
1381:
1374:
1371:
1368:
1367:Sigma-Aldrich
1364:
1359:
1356:
1350:
1346:
1343:
1341:
1338:
1336:
1335:Gluconic acid
1333:
1332:
1328:
1326:
1324:
1320:
1316:
1315:
1305:
1303:
1295:
1291:
1290:ascorbic acid
1286:
1284:
1280:
1275:
1273:
1269:
1268:ethyl sulfate
1265:
1257:
1255:
1253:
1249:
1246:
1241:
1237:
1233:
1225:
1223:
1221:
1217:
1213:
1209:
1205:
1203:
1199:
1198:serum albumin
1195:
1190:
1188:
1184:
1180:
1175:
1173:
1168:
1165:
1161:
1158:
1154:
1150:
1146:
1142:
1136:
1134:
1130:
1126:
1122:
1118:
1114:
1110:
1106:
1101:
1097:
1093:
1089:
1085:
1081:
1073:
1069:
1067:
1060:
1056:
1052:
1048:
1044:
1040:
1036:
1033:
1029:
1025:
1021:
1010:
1006:
1001:
996:
988:
983:
979:
976:
973:
970:
967:
964:
961:
958:
955:
952:
949:
946:
945:
944:
942:
938:
937:proteoglycans
931:Proteoglycans
930:
925:
923:
921:
917:
913:
907:
905:
901:
895:
893:
889:
885:
884:glucaric acid
880:
864:
862:
855:
854:-galacturonic
848:
841:
834:
829:
827:
815:
799:
795:
787:
783:
779:
775:
771:
766:
764:
756:
753:derived from
752:
732:
727:
717:
714:
706:
696:
692:
686:
685:
680:This section
678:
674:
669:
668:
662:
660:
658:
654:
650:
642:
638:
634:
630:
626:
623:" and οὖρον "
622:
618:
614:
602:
595:
590:
573:
567:
564:
560:
556:
552:
548:
544:
540:
536:
532:
528:
524:
523:Iduronic acid
520:
516:
512:
508:
504:
500:
497:
494:
489:
488:
483:
479:
477:
476:Melting point
474:
473:
466:
464:
461:
460:
439:
436:
432:
431:
426:
417:
413:
406:
392:
382:
378:
371:
363:
359:
355:
354:
352:
342:
338:
337:
330:
326:
325:
323:
321:
318:
317:
310:
306:
305:
303:
297:
293:
292:
288:
284:
282:
279:
278:
271:
267:
266:
264:
262:
259:
258:
254:
250:
247:
245:
243:ECHA InfoCard
240:
239:
232:
228:
227:
225:
223:
220:
219:
212:
208:
207:
205:
203:
200:
199:
192:
188:
187:
185:
183:
180:
179:
172:
168:
167:
165:
161:
156:
155:
148:
144:
143:
141:
138:
134:
133:
128:
116:
110:
106:
102:
98:
94:
88:
84:
74:
70:
65:
61:
56:
52:
47:
39:
35:
34:Gluconic acid
30:
19:
1624:Uronic acids
1590:
1584:
1559:
1555:
1549:
1514:
1510:
1500:
1482:
1438:
1432:
1421:. Retrieved
1389:
1383:
1373:
1358:
1318:
1312:
1306:
1287:
1281:products in
1279:fermentation
1276:
1261:
1229:
1206:
1191:
1176:
1172:barbiturates
1169:
1137:
1070:
1059:uronic acids
1014:
934:
908:
896:
881:
865:
830:
767:
748:
730:
709:
700:
689:Please help
684:verification
681:
624:
620:
612:
611:
493:uronic acids
130:Identifiers
118:Other names
108:
104:
100:
96:
92:
29:
1345:Uronic acid
1039:endobiotics
1028:conjugation
856:(C-4), and
840:-mannuronic
798:enantiomers
629:uronic acid
428:Properties
249:100.026.807
191:CHEBI:28860
1619:Hepatology
1613:Categories
1423:2010-11-07
1351:References
1245:endogenous
1194:toxication
1179:hydrolyzed
1157:endogenous
1100:carbamates
1092:mercaptans
1072:Glycosides
1032:lipophilic
904:acetonides
847:-alluronic
778:hemiacetal
774:aldohexose
751:sugar acid
703:March 2023
663:Properties
657:metabolism
641:gum arabic
463:Molar mass
329:8A5D83Q4RW
202:ChemSpider
158:3D model (
137:CAS Number
73:IUPAC name
27:Sugar acid
1517:: 24–32.
1396:: 32–40.
1294:vitamin C
1202:acylation
1200:via trans
1113:Bilirubin
926:Functions
619:γλεῦκος "
147:6556-12-3
1576:34822312
1541:23348028
1465:16399343
1410:18838504
1329:See also
1283:Kombucha
1160:steroids
1145:morphine
1133:jaundice
1127:and the
1080:alcohols
1061:(e. g.,
902:(e. g.,
786:pyranose
782:furanose
763:-glucose
745:-glucose
653:kombucha
639:such as
627:") is a
491:Related
222:DrugBank
1532:3641160
1418:5150289
1319:E. coli
1272:ethanol
1252:opiates
1232:ethanol
1220:benzene
1208:Phenols
1141:Ethanol
1119:(80%),
1084:phenols
948:Heparin
900:acetals
892:lactone
849:(C-3),
842:(C-2),
833:epimers
814:anomers
770:glucose
755:glucose
649:xanthan
645:approx.
594:what is
592: (
468:194.139
296:PubChem
231:DB03156
1597:
1574:
1539:
1529:
1489:
1463:
1453:
1416:
1408:
1153:NSAIDs
1098:, and
1096:amines
1037:- and
1016:UDP-α-
918:, and
822:UDP-α-
804:- and
759:UDP-α-
651:, and
647:18%),
615:(from
589:verify
586:
412:SMILES
309:441478
270:C00191
211:392615
67:Names
1572:S2CID
1414:S2CID
1392:(1).
1285:tea.
1030:) of
633:urine
625:urine
617:Greek
377:InChI
182:ChEBI
160:JSmol
1595:ISBN
1537:PMID
1487:ISBN
1461:PMID
1451:ISBN
1406:PMID
1266:and
1212:P450
1035:xeno
939:and
729:The
637:gums
320:UNII
281:MeSH
261:KEGG
18:GlcA
1564:doi
1527:PMC
1519:doi
1443:doi
1398:doi
1365:at
1258:Use
1181:by
1155:),
1068:).
1055:UDP
906:).
800:),
784:or
693:by
346:EPA
299:CID
36:or
1615::
1570:.
1560:18
1558:.
1535:.
1525:.
1515:30
1513:.
1509:.
1473:^
1459:.
1449:.
1412:.
1404:.
1390:37
1388:.
1382:.
1325:.
1317:.
1304:.
1234:,
1147:,
1143:,
1135:.
1111:.
1090:,
1086:,
1082:,
943::
922:.
914:,
886:.
879:.
561:,
557:,
553:,
549:,
545:,
541:,
537:,
533:,
529:,
525:,
521:,
517:,
513:,
509:,
505:,
501:,
450:10
120:β-
107:,6
103:,5
99:,4
95:,3
91:(2
76:β-
1578:.
1566::
1543:.
1521::
1467:.
1445::
1426:.
1400::
1309:D
1300:-
1298:L
1292:(
1076:D
1064:D
1057:-
1026:(
1018:D
1011:.
877:1
873:D
869:D
859:L
852:D
845:D
838:D
824:D
818:D
810:D
806:L
802:D
790:D
780:(
761:D
743:D
739:1
735:D
733:-
731:β
716:)
710:(
705:)
701:(
687:.
643:(
584:N
456:7
453:O
447:H
444:6
441:C
348:)
344:(
162:)
122:D
109:R
105:R
101:S
97:S
93:S
78:D
40:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.