218:, and domestic fowl show a similar reduction to their wild cousins. In a famous Russian farm fox experiment, foxes selectively bred for reduced aggression appeared to show other traits associated with domestication syndrome. This prompted the claim that domestication syndrome was caused by selection for tameness. The foxes were not selectively bred for smaller craniums and teeth, floppy ears, or skills at using human gestures, but these traits were demonstrated in the friendly foxes. Natural selection favors those that are the most successful at reproducing, not the most aggressive. Selection against aggression made possible the ability to cooperate and communicate among foxes, dogs and bonobos. The more docile animals have been found to have less testosterone than their more aggressive counterparts, and testosterone controls aggression and brain size. The further away a dog breed is genetically from wolves, the larger the relative brain size is.
134:
in neural crest related genes only reveals change in neural crest-derived features. In effect, it is not evidence of linked trait changes in different species due to pleiotropic neural crest mechanisms as claimed by the neural crest cell hypothesis. For example, all of the craniofacial skeleton is derived from the neural crest, so any animal population that experiences evolutionary change in craniofacial features will show changes in genes associated with the neural crest. The number and importance of neural crest cell features in all vertebrates means change in these features is almost inevitable under the major selective regime shifts experienced by animals making the wild to domestic transition.
31:
210:, are a close genetic cousin to humans, but unlike the chimpanzees, bonobos are not aggressive and do not participate in lethal inter-group aggression or kill within their own group. The most distinctive features of a bonobo are its cranium, which is 15% smaller than a chimpanzee's, and its less aggressive and more playful behavior. These, and other, features led to the proposal that bonobos are a 'self-domesticated' ape. In other examples, the
73:
shared selective regime changes following transition from wild to domestic environments are a more likely cause of any convergent traits. In addition, the sheer number, diversity, and phenotypic importance of neural crest cell-derived vertebrate features means that changes in genes associated with them are almost inevitable in response to any significant selective change.
126:
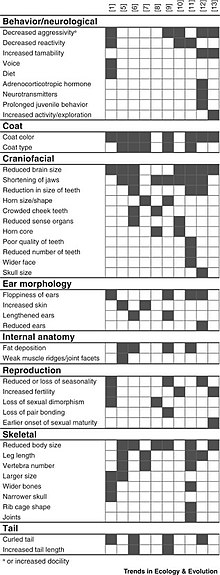
these traits include tameness, docility, floppy ears, altered tails, novel coat colors and patterns, reduced brain size, reduced body mass and smaller teeth. Other traits include changes in craniofacial morphology, alterations to the endocrine system, and changes to the female estrous cycles including the ability to breed all year-round.
109:
267:
similarly shared trait changes across different species--in effect, a series of partial trait convergences. They proposed four primary selective pathways that are commonly altered by the shift to a domestic selective context, and would often lead to similar shifts in different populations. These pathways are:
262:
under selection. But, the observation of changed neural crest cell genes between wild and domestic populations need only reveal changes to features derived from neural crest, it does not support the claim of a common underlying genetic architecture that causes all of the domestication syndrome traits
133:
cell behaviour may be modified by domestication, which then leads to those traits that are common across many domesticated animal species. This hypothesis has claimed support from many gene-based studies; e.g., However, recent publications have disputed this support; pointing out that observed change
157:
In 2018, a study identified 429 genes that differed between modern dogs and modern wolves. As the differences in these genes could also be found in ancient dog fossils, these were regarded as being the result of the initial domestication and not from recent breed formation. These genes are linked to
125:
in 1868 identified various behavioral, morphological, and physiological traits that are shared by domestic animals, but not by their wild ancestors. These shared traits became known as "the domestication syndrome", a term originally used to describe common changes in domesticated grains. In animals,
72:
cell regulating genes was the common cause of shared traits seen in many domesticated animal species. However, several recent publications have either questioned this neural crest cell explanation or cast doubt on the existence of domestication syndrome itself. One recent publication points out that
64:
Domesticated animals tend to be smaller and less aggressive than their wild counterparts, they may also have floppy ears, variations to coat color, a smaller brain, and a shorter muzzle. Other traits may include changes in the endocrine system and an extended breeding cycle. These animal traits have
284:
Because the 'Reproductive
Disruption' hypothesis explains domestication syndrome as a result of changed selective regimes, it can encompass multiple genetic or physiological ways that similar traits might emerge in the different domesticated species. For example, tamer behaviour might be caused by
250:
since the 1800s, and that the traits demonstrated by
Belyayev had occurred in the foxes prior to the breeding experiment. A 2019 opinion paper by Lord and colleagues argued that the results of the "Russian farm fox experiment" were overstated, although the pre-domesticated origins of these Russian
1736:
Kantar, Michael B.; Tyl, Catrin E.; Dorn, Kevin M.; Zhang, Xiaofei; Jungers, Jacob M.; Kaser, Joe M.; Schendel, Rachel R.; Eckberg, James O.; Runck, Bryan C.; Bunzel, Mirko; Jordan, Nick R.; Stupar, Robert M.; Marks, M. David; Anderson, James A.; Johnson, Gregg A.; Sheaffer, Craig C.; Schoenfuss,
170:
and can confer tameness, smaller jaws, floppy ears, and diminished craniofacial development, which distinguish domesticated dogs from wolves and are considered to reflect domestication syndrome. The study concluded that during early dog domestication, the initial selection was for behavior. This
266:
Gleeson and Wilson synthesised this debate and showed that animal domestication syndrome is not caused by selection for tameness, or by neural crest cell genetic pleiotropy. However, it could result from shared selective regime changes (which they termed 'reproductive disruption') leading to
254:
In 2020, Wright et al. argued Lord et al.'s critique refuted only a narrow and unrealistic definition of domestication syndrome because their criteria assumed it must be caused by genetic pleiotropy, and arises in response to 'selection for tameness'--as was claimed by
Belyaev, Trut, and the
1978:
Librado, Pablo; Gamba, Cristina; Gaunitz, Charleen; Der
Sarkissian, Clio; Pruvost, Mélanie; Albrechtsen, Anders; Fages, Antoine; Khan, Naveed; Schubert, Mikkel; Jagannathan, Vidhya; Serres-Armero, Aitor; Kuderna, Lukas F. K.; Povolotskaya, Inna S.; Seguin-Orlando, Andaine; Lepetz, Sébastien
2863:
Pearce, Stephen; Saville, Robert; Vaughan, Simon P.; Chandler, Peter M.; Wilhelm, Edward P.; Sparks, Caroline A.; Al-Kaff, Nadia; Korolev, Andrey; Boulton, Margaret I.; Phillips, Andrew L.; Hedden, Peter; Nicholson, Paul; Thomas, Stephen G. (1 December 2011).
255:
proposers of the neural crest hypothesis. In the same year, Zeder pointed out that it makes no sense to deny the existence of domestication syndrome on the basis that domestication syndrome traits were present in the pre-domesticated founding foxes.
1469:
Statham, Mark J.; Trut, Lyudmila N.; Sacks, Ben N.; Kharlamova, Anastasiya V.; Oskina, Irina N.; Gulevich, Rimma G.; Johnson, Jennifer L.; Temnykh, Svetlana V.; Acland, Gregory M.; Kukekova, Anna V. (May 2011).
65:
been claimed to emerge across the different species in response to selection for tameness, which was purportedly demonstrated in a famous
Russian fox breeding experiment, though this claim has been disputed.
194:. Genes for resistance to parasites might be linked to those for the domestication syndrome; it is predicted that domestic animals are less resistant to parasites than their wild relatives.
3321:
121:
258:
The hypothesis that neural crest genes underlie some of the phenotypic differences between domestic and wild horses and dogs is supported by the functional enrichment of
190:
could have mediated the domestication of mammals. Domestication involves taming, which has an endocrine component; and parasites can modify endocrine activity and
3284:
3055:
940:
285:
reduced adrenal reactivity, by increased oxytocin production, or by a combination of these or other mechanisms, across the different populations and species.
202:
A dog's cranium is 15% smaller than an equally heavy wolf's, and the dog is less aggressive and more playful. Other species pairs show similar differences.
1030:, which is likely why they work so well in domestication: They are not new, and are relatively ready to have their magnitudes altered. In annual grains,
2915:
Stange, Madlen; Barrett, Rowan D. H.; Hendry, Andrew P. (February 2021). "The importance of genomic variation for biodiversity, ecosystems and people".
1472:"On the origin of a domesticated species: identifying the parent population of Russian silver foxes (Vulpes vulpes): THE ORIGIN OF RUSSIAN SILVER FOXES"
2555:
Fallahsharoudi, Amir; de Kock, Neil; Johnsson, Martin; Ubhayasekera, S. J. Kumari A.; Bergquist, Jonas; Wright, Dominic; Jensen, Per (2015-10-16).
3277:
2045:
Pendleton, Amanda L.; Shen, Feichen; Taravella, Angela M.; Emery, Sarah; Veeramah, Krishna R.; Boyko, Adam R.; Kidd, Jeffrey M. (December 2018).
1428:
3267:
3048:
2356:
1836:
Machugh, David E.; Larson, Greger; Orlando, Ludovic (2016). "Taming the Past: Ancient DNA and the Study of Animal
Domestication".
1314:"The taming of the neural crest: a developmental perspective on the origins of morphological covariation in domesticated mammals"
146:; however, whether this is true for domestication traits or merely for wild forms is less clear. Especially in the case of plant
2706:
1743:
3041:
3305:
171:
trait is influenced by those genes which act in the neural crest, which led to the phenotypes observed in modern dogs.
231:
3289:
3272:
2815:
2715:
1752:
1059:
3327:
3262:
2344:
1922:
1639:
1198:"The "Domestication Syndrome" in Mammals: A Unified Explanation Based on Neural Crest Cell Behavior and Genetics"
1047:
1010:
30:
3257:
3245:
3064:
307:
81:
58:
3193:
2917:
2129:
227:
108:
3348:
2261:"The self-domestication hypothesis: evolution of bonobo psychology is due to selection against aggression"
2127:
Lenser, Teresa; Theißen, Günter (2013). "Molecular mechanisms involved in convergent crop domestication".
175:
163:
2047:"Comparison of village dog and wolf genomes highlights the role of the neural crest in dog domestication"
1923:"The neural crest/domestication syndrome hypothesis, explained: reply to Johnsson, Henriksen, and Wright"
870:
818:
3250:
3128:
2972:
Purugganan, Michael D.; Fuller, Dorian Q. (2009). "The nature of selection during plant domestication".
1043:
327:
315:
97:
773:
277:
Changed resource availability and predation pressure affecting female fertility and offspring survival.
2372:
814:
3358:
2987:
2568:
2435:
1992:
1325:
1027:
936:
783:
243:
280:
Intensified potential for maternal stress, selecting for altered reproductive physiology in females.
2557:"Domestication Effects on Stress Induced Steroid Secretion and Adrenal Gene Expression in Chickens"
1873:"A striking example of developmental bias in an evolutionary process: The "domestication syndrome""
1578:"Shared reproductive disruption, not neural crest or tameness, explains the domestication syndrome"
299:
112:
In ten publications on domestication syndrome in animals, no single trait is included in every one.
77:
3315:
3310:
3019:
2954:
2845:
2743:
2649:
2537:
2509:
2490:
2462:
2440:
2416:
2326:
2280:
2260:
2024:
1523:
1289:
1261:
1161:
1103:
1035:
853:
830:
798:
743:
624:
612:
559:
536:
351:
150:, doubt has been cast because some domestication traits have been found to result from unrelated
54:
2700:
Chen, Erwang; Huang, Xuehui; Tian, Zhixi; Wing, Rod A.; Han, Bin (2019-04-29). "The
Genomics of
1014:
834:
682:
605:
528:
520:
380:
972:
584:
486:
3353:
3011:
3003:
2946:
2938:
2897:
2837:
2829:
2735:
2727:
2641:
2602:
2584:
2529:
2482:
2408:
2352:
2318:
2158:
2150:
2086:
2068:
2016:
2008:
1960:
1942:
1900:
1892:
1853:
1818:
1774:
1766:
1677:
1659:
1615:
1597:
1543:
1522:
Lord, Kathryn A.; Larson, Greger; Coppinger, Raymond P.; Karlsson, Elinor K. (February 2020).
1501:
1448:
1397:
1359:
1341:
1281:
1235:
1217:
1153:
1111:
1039:
599:
505:
463:
418:
235:
2995:
2974:
2930:
2926:
2887:
2877:
2819:
2719:
2633:
2592:
2576:
2521:
2474:
2400:
2310:
2272:
2218:
2189:
2142:
2076:
2058:
2000:
1950:
1934:
1884:
1845:
1808:
1756:
1667:
1651:
1605:
1589:
1535:
1491:
1483:
1440:
1349:
1333:
1273:
1225:
1209:
1145:
1095:
1031:
839:
758:
447:
441:
151:
931:
822:
737:
706:
628:
407:
3178:
2983:
2824:
2803:
2723:
1761:
1738:
1410:
1383:
1023:
966:
960:
954:
901:
886:
878:
777:
722:
698:
660:
645:
578:
572:
566:
497:
259:
39:
1849:
714:
690:
480:
2991:
2572:
1996:
1921:
Wilkins, Adam S; Wrangham, Richard; Fitch, W Tecumseh (2021-08-26). Peichel, C L (ed.).
1872:
1610:
1577:
1329:
3083:
2892:
2865:
2597:
2556:
2388:
2081:
2046:
1955:
1672:
1496:
1471:
1354:
1313:
1230:
1197:
752:
748:
116:
1980:
3342:
3198:
3123:
3023:
2958:
2747:
2621:
2541:
2494:
2420:
2028:
1795:
Lord, Kathryn A.; Larson, Greger; Coppinger, Raymond P.; Karlsson, Elinor K. (2020).
1487:
1293:
359:
355:
179:
167:
2849:
2653:
2387:
Frantz, Laurent A. F.; Bradley, Daniel G.; Larson, Greger; Orlando, Ludovic (2020).
1638:
Johnsson, Martin; Henriksen, Rie; Wright, Dominic (2021-08-26). Peichel, C L (ed.).
1312:
Sánchez-Villagra, Marcelo R.; Geiger, Madeleine; Schneider, Richard A. (June 2016).
1165:
3163:
2802:
Chen, Kunling; Wang, Yanpeng; Zhang, Rui; Zhang, Huawei; Gao, Caixia (2019-04-29).
2373:
Study finds the brains of modern dog breeds are larger than those of ancient breeds
2330:
2284:
617:
491:
159:
130:
69:
2276:
2146:
306:, but with its own set of syndrome traits. In cereals, these include little to no
274:
Disrupted intra-sexual selection in males (reduced/altered male-male competition).
2620:
Herbeck, Yu. E.; Gulevich, R. G.; Shepeleva, D. V.; Grinevich, V. V. (May 2017).
3168:
3088:
1213:
792:
247:
239:
2934:
2525:
2478:
2314:
1938:
1813:
1796:
1655:
1539:
1277:
3148:
2637:
2404:
2298:
2241:
2138:
2063:
1133:
395:
311:
211:
207:
85:
50:
3007:
2942:
2833:
2731:
2645:
2588:
2194:
2177:
2154:
2072:
2012:
1946:
1896:
1770:
1663:
1601:
1452:
1345:
1221:
1157:
3224:
3118:
2223:
2210:
2004:
1737:
Tonya C.; Ismail, Baraem; Heimpel, George E.; Wyse, Donald L. (2016-04-29).
1640:"The neural crest cell hypothesis: no unified explanation for domestication"
991:
977:
347:
335:
331:
323:
183:
93:
35:
3033:
3015:
2950:
2901:
2841:
2739:
2606:
2533:
2486:
2412:
2322:
2162:
2090:
2020:
1964:
1904:
1857:
1822:
1778:
1681:
1619:
1593:
1547:
1505:
1363:
1285:
1239:
1115:
2882:
271:
Disrupted inter-sexual selection in males (reduced/altered female choice).
3229:
3183:
996:
669:
191:
187:
143:
17:
2999:
1797:"The History of Farm Foxes Undermines the Animal Domestication Syndrome"
1524:"The History of Farm Foxes Undermines the Animal Domestication Syndrome"
1337:
100:, and increased yield, as well as changes in color, taste, and texture.
3173:
3103:
2866:"Molecular Characterization of Rht-1 Dwarfing Genes in Hexaploid Wheat"
2804:"CRISPR/Cas Genome Editing and Precision Plant Breeding in Agriculture"
1444:
1149:
1107:
1083:
1038:
are by far the most common, and thus are the most interesting goals of
412:
385:
2580:
1888:
1196:
Wilkins, Adam S; Wrangham, Richard W; Fitch, W Tecumseh (2014-07-01).
3133:
3113:
3098:
3078:
665:
400:
339:
203:
2436:"Why Are These Foxes Tame? Maybe They Weren't So Wild to Begin With"
1981:"Ancient genomic changes associated with domestication of the horse"
1099:
2461:
Wright, Dominic; Henriksen, Rie; Johnsson, Martin (December 2020).
142:
Many similar traits – both in animals and plants – are produced by
3188:
3158:
3153:
3138:
2704:
Species
Provides Insights into Rice Domestication and Heterosis".
2463:"Defining the Domestication Syndrome: Comment on Lord et al. 2020"
1262:"Defining the Domestication Syndrome: Comment on Lord et al. 2020"
389:
343:
319:
107:
89:
34:
Reduction in size is regarded as a domestication syndrome trait -
29:
3208:
3143:
916:
861:
636:
544:
303:
226:
The domestication syndrome was reported to have appeared in the
215:
147:
3037:
2510:"Straw Foxes: Domestication Syndrome Evaluation Comes Up Short"
2259:
Hare, Brian; Wobber, Victoria; Wrangham, Richard (March 2012).
3203:
3108:
3093:
2211:"Addendum to "The parasite-mediated domestication hypothesis""
471:
426:
238:
found historical evidence that
Belyayev's foxes originated in
346:/grain number, altered color compounds, taste, and texture,
234:'s breeding experiment. However, in 2015 canine researcher
1260:
Wright, Dominic; Henriksen, Rie; Johnsson, Martin (2020).
1082:
Harlan, Jack R.; de Wet, J. M. J.; Price, E. Glen (1973).
2695:
2693:
2691:
2689:
2687:
2685:
2683:
2622:"Oxytocin: Coevolution of human and domesticated animals"
2797:
2795:
2793:
2791:
2789:
2787:
2785:
2783:
2781:
2779:
2777:
2681:
2679:
2677:
2675:
2673:
2671:
2669:
2667:
2665:
2663:
2122:
2120:
3322:
The
Variation of Animals and Plants Under Domestication
2775:
2773:
2771:
2769:
2767:
2765:
2763:
2761:
2759:
2757:
2118:
2116:
2114:
2112:
2110:
2108:
2106:
2104:
2102:
2100:
1582:
Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences
1576:
Gleeson, Ben Thomas; Wilson, Laura A. B. (2023-03-29).
1384:
https://academic.oup.com/jhered/article/70/5/301/813519
122:
The Variation of Animals and Plants Under Domestication
2389:"Animal domestication in the era of ancient genomics"
1731:
1729:
1727:
1725:
1723:
1721:
1719:
1717:
1715:
1713:
1711:
68:
Other research suggested that pleiotropic change in
1709:
1707:
1705:
1703:
1701:
1699:
1697:
1695:
1693:
1691:
1429:"Early Canid Domestication: The Farm-Fox Experiment"
3298:
3238:
3217:
3071:
214:'s cranium is 13% smaller than its wild cousin the
251:foxes were already a matter of scientific record.
370:Control of the syndrome traits in cereals is by:
2178:"The Parasite-Mediated Domestication Hypothesis"
3049:
2626:Russian Journal of Genetics: Applied Research
2382:
2380:
2301:(2005). "Human-like social skills in dogs?".
632:- small awn reduction/barbless awns - in rice
8:
2236:
2234:
1790:
1788:
3056:
3042:
3034:
455:on different subgenomes, Rht standing for
2891:
2881:
2823:
2596:
2222:
2193:
2080:
2062:
1954:
1812:
1760:
1671:
1609:
1495:
1476:Biological Journal of the Linnean Society
1353:
1229:
263:in all of the different animal species.
1071:
1406:
1395:
2825:10.1146/annurev-arplant-050718-100049
2724:10.1146/annurev-arplant-050718-100320
2040:
2038:
1916:
1914:
1762:10.1146/annurev-arplant-043015-112311
1633:
1631:
1629:
1571:
1569:
1567:
1565:
1563:
1561:
1559:
1557:
1517:
1515:
1127:
1125:
1077:
1075:
890:(by increasing tiller number) in rice
874:(by increasing tiller number) in rice
7:
1850:10.1146/annurev-animal-022516-022747
1464:
1462:
1422:
1420:
1375:
1373:
1307:
1305:
1303:
1255:
1253:
1251:
1249:
1191:
1189:
1187:
1185:
1183:
1181:
1179:
1177:
1175:
3285:Domesticated animals of Austronesia
3268:Domestication of the Syrian hamster
1838:Annual Review of Animal Biosciences
1739:"Perennial Grain and Oilseed Crops"
1084:"Comparative Evolution of Cereals"
129:A recent hypothesis suggests that
25:
2514:Trends in Ecology & Evolution
2508:Zeder, Melinda A. (August 2020).
2467:Trends in Ecology & Evolution
1871:Wilkins, Adam S. (January 2020).
1801:Trends in Ecology & Evolution
1528:Trends in Ecology & Evolution
1266:Trends in Ecology & Evolution
976:gene family - reduced preharvest
751:), wheat, corn, barley, sorghum,
314:, shorter height (thus decreased
53:traits that are common to either
1488:10.1111/j.1095-8312.2011.01629.x
790:Specifically, four orthologs in
475:in one Japanese cultivar of rice
298:The same concept appears in the
166:development. These genes affect
1022:Many of these are mutations in
939:when defective in rice; can be
176:parasite-mediated domestication
2808:Annual Review of Plant Biology
2707:Annual Review of Plant Biology
1744:Annual Review of Plant Biology
27:Proposed biological phenomenon
1:
2277:10.1016/j.anbehav.2011.12.007
2147:10.1016/j.tplants.2013.08.007
451:(two orthologous versions of
3306:List of domesticated animals
2434:Gorman, James (2019-12-03).
2303:Trends in Cognitive Sciences
943:to produce the same compound
616:(by reducing or eliminating
342:protein content), increased
246:and had been bred there for
2248:. Penguin Publishing Group.
1877:Evolution & Development
1214:10.1534/genetics.114.165423
1134:"Das Domestikationssyndrom"
1011:Teosinte glume architecture
3377:
3290:Domestication of the sheep
3273:Domestication of the horse
2935:10.1038/s41576-020-00288-7
2526:10.1016/j.tree.2020.03.001
2479:10.1016/j.tree.2020.08.009
2315:10.1016/j.tics.2005.07.003
1814:10.1016/j.tree.2019.10.011
1540:10.1016/j.tree.2019.10.011
1318:Royal Society Open Science
1278:10.1016/j.tree.2020.08.009
1132:Hammer, Karl (June 1984).
1060:Agricultural weed syndrome
1048:chromosomal rearrangements
686:in rice, wheat, maize/corn
334:, increased grain weight,
3328:Genomics of domestication
3263:Domestication of the goat
2638:10.1134/S2079059717030042
2405:10.1038/s41576-020-0225-0
2345:Bruce Hood (psychologist)
2064:10.1186/s12915-018-0535-2
641:- awn elimination in rice
178:hypothesis suggests that
88:, shorter height, larger
3258:Domestication of the dog
3246:Domestication of the cat
3065:Domestication of animals
2195:10.18690/agricsci.20.1.1
1939:10.1093/genetics/iyab098
1656:10.1093/genetics/iyab097
649:- naked kernels in maize
80:has produced changes in
3194:Domesticated silver fox
2918:Nature Reviews Genetics
2393:Nature Reviews Genetics
2130:Trends in Plant Science
2005:10.1126/science.aam5298
1427:Trut, Lyudmila (1999).
302:process which produces
228:domesticated silver fox
2349:The Domesticated Brain
1594:10.1098/rspb.2022.2464
941:artificially disrupted
524:in maize/corn and rice
322:or fruit size, easier
164:central nervous system
113:
92:or fruit size, easier
49:refers to two sets of
47:Domestication syndrome
43:
38:skull compared with a
3251:cats in ancient Egypt
3129:Domestic Muscovy duck
2883:10.1104/pp.111.183657
2224:10.31219/osf.io/f92aj
1050:are far less common.
1044:copy number variation
1028:transcription factors
366:Cereal genes by trait
328:synchronous flowering
111:
98:synchronous flowering
33:
2182:Agricultura Scientia
937:2-Acetyl-1-pyrroline
784:Arabidopsis thaliana
747:in rice (especially
562:/LOC4345998 in rice.
330:, altered timing of
244:Prince Edward Island
59:domesticated animals
3000:10.1038/nature07895
2992:2009Natur.457..843P
2573:2015NatSR...515345F
1997:2017Sci...356..442L
1338:10.1098/rsos.160107
1330:2016RSOS....360107S
588:gene family in rice
300:plant domestication
78:plant domestication
55:domesticated plants
3316:Self-domestication
3311:Selective breeding
2561:Scientific Reports
2441:The New York Times
2246:The Genius of Dogs
2209:Skok, J. (2023b).
2176:Skok, J. (2023a).
1445:10.1511/1999.2.160
1433:American Scientist
1150:10.1007/BF02098682
1036:altered expression
847:Grain/fruit number
831:teosinte branched1
799:Phaseolus vulgaris
767:Determinate growth
466:in rice and barley
352:determinate growth
114:
44:
3336:
3335:
2581:10.1038/srep15345
2473:(12): 1059–1060.
1991:(6336): 442–445.
1889:10.1111/ede.12319
1405:Missing or empty
1272:(12): 1059–1060.
1138:Die Kulturpflanze
1040:mutation breeding
1004:Unspecified trait
948:Delayed sprouting
905:in rice and wheat
774:TERMINAL FLOWER 1
549:(smaller) in rice
338:(stickiness, not
236:Raymond Coppinger
16:(Redirected from
3366:
3058:
3051:
3044:
3035:
3028:
3027:
2969:
2963:
2962:
2927:Nature Portfolio
2912:
2906:
2905:
2895:
2885:
2876:(4): 1820–1831.
2870:Plant Physiology
2860:
2854:
2853:
2827:
2799:
2752:
2751:
2697:
2658:
2657:
2617:
2611:
2610:
2600:
2552:
2546:
2545:
2505:
2499:
2498:
2458:
2452:
2451:
2449:
2448:
2431:
2425:
2424:
2384:
2375:
2370:
2364:
2362:
2341:
2335:
2334:
2295:
2289:
2288:
2265:Animal Behaviour
2256:
2250:
2249:
2238:
2229:
2228:
2226:
2206:
2200:
2199:
2197:
2173:
2167:
2166:
2124:
2095:
2094:
2084:
2066:
2042:
2033:
2032:
1975:
1969:
1968:
1958:
1918:
1909:
1908:
1883:(1–2): 143–153.
1868:
1862:
1861:
1833:
1827:
1826:
1816:
1792:
1783:
1782:
1764:
1733:
1686:
1685:
1675:
1635:
1624:
1623:
1613:
1573:
1552:
1551:
1519:
1510:
1509:
1499:
1466:
1457:
1456:
1424:
1415:
1414:
1408:
1403:
1401:
1393:
1391:
1390:
1381:academic.oup.com
1377:
1368:
1367:
1357:
1309:
1298:
1297:
1257:
1244:
1243:
1233:
1193:
1170:
1169:
1129:
1120:
1119:
1079:
1032:loss of function
1024:regulatory genes
840:apical dominance
815:PROSTRATE GROWTH
21:
3376:
3375:
3369:
3368:
3367:
3365:
3364:
3363:
3339:
3338:
3337:
3332:
3294:
3234:
3213:
3179:Domestic rabbit
3067:
3062:
3032:
3031:
2984:Nature Research
2971:
2970:
2966:
2914:
2913:
2909:
2862:
2861:
2857:
2801:
2800:
2755:
2699:
2698:
2661:
2619:
2618:
2614:
2554:
2553:
2549:
2507:
2506:
2502:
2460:
2459:
2455:
2446:
2444:
2433:
2432:
2428:
2386:
2385:
2378:
2371:
2367:
2359:
2343:
2342:
2338:
2297:
2296:
2292:
2258:
2257:
2253:
2240:
2239:
2232:
2208:
2207:
2203:
2175:
2174:
2170:
2126:
2125:
2098:
2044:
2043:
2036:
1977:
1976:
1972:
1920:
1919:
1912:
1870:
1869:
1865:
1835:
1834:
1830:
1794:
1793:
1786:
1735:
1734:
1689:
1637:
1636:
1627:
1575:
1574:
1555:
1521:
1520:
1513:
1468:
1467:
1460:
1426:
1425:
1418:
1404:
1394:
1388:
1386:
1379:
1378:
1371:
1311:
1310:
1301:
1259:
1258:
1247:
1195:
1194:
1173:
1131:
1130:
1123:
1100:10.2307/2406971
1081:
1080:
1073:
1068:
1056:
842:) in maize/corn
490:in sorghum and
368:
296:
294:Syndrome traits
291:
260:candidate genes
232:Dmitry Belyayev
224:
200:
140:
106:
76:The process of
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
3374:
3373:
3370:
3362:
3361:
3356:
3351:
3341:
3340:
3334:
3333:
3331:
3330:
3325:
3318:
3313:
3308:
3302:
3300:
3299:Related topics
3296:
3295:
3293:
3292:
3287:
3282:
3281:
3280:
3270:
3265:
3260:
3255:
3254:
3253:
3242:
3240:
3236:
3235:
3233:
3232:
3227:
3221:
3219:
3215:
3214:
3212:
3211:
3206:
3201:
3196:
3191:
3186:
3181:
3176:
3171:
3166:
3161:
3156:
3151:
3146:
3141:
3136:
3131:
3126:
3121:
3116:
3111:
3106:
3101:
3096:
3091:
3086:
3084:Bactrian camel
3081:
3075:
3073:
3069:
3068:
3063:
3061:
3060:
3053:
3046:
3038:
3030:
3029:
2964:
2907:
2855:
2816:Annual Reviews
2753:
2716:Annual Reviews
2659:
2632:(3): 235–242.
2612:
2547:
2520:(8): 647–649.
2500:
2453:
2426:
2399:(8): 449–460.
2376:
2365:
2357:
2336:
2290:
2271:(3): 573–585.
2251:
2230:
2201:
2168:
2096:
2034:
1979:(2017-04-28).
1970:
1910:
1863:
1828:
1807:(2): 125–136.
1784:
1753:Annual Reviews
1687:
1625:
1553:
1534:(2): 125–136.
1511:
1482:(1): 168–175.
1458:
1416:
1369:
1299:
1245:
1208:(3): 795–808.
1171:
1121:
1070:
1069:
1067:
1064:
1063:
1062:
1055:
1052:
1020:
1019:
1006:
1005:
1001:
1000:
987:
986:
982:
981:
950:
949:
945:
944:
927:
926:
922:
921:
912:
911:
907:
906:
897:
896:
892:
891:
883:
875:
867:
858:
849:
848:
844:
843:
827:
810:
809:
805:
804:
803:
802:
787:and orthologs
769:
768:
764:
763:
755:
753:foxtail millet
749:glutinous rice
733:
732:
728:
727:
719:
711:
703:
695:
687:
678:
677:
673:
672:
656:
655:
654:Flowering time
651:
650:
642:
633:
621:
609:
595:
594:
590:
589:
563:
556:
555:
551:
550:
541:
533:
525:
516:
515:
511:
510:
502:
494:
476:
468:
460:
457:reduced height
437:
436:
432:
431:
423:
415:
404:
392:
376:
375:
367:
364:
350:independence,
295:
292:
290:
287:
282:
281:
278:
275:
272:
230:cultivated by
223:
220:
199:
196:
139:
136:
117:Charles Darwin
105:
102:
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
3372:
3371:
3360:
3357:
3355:
3352:
3350:
3349:Domestication
3347:
3346:
3344:
3329:
3326:
3324:
3323:
3319:
3317:
3314:
3312:
3309:
3307:
3304:
3303:
3301:
3297:
3291:
3288:
3286:
3283:
3279:
3276:
3275:
3274:
3271:
3269:
3266:
3264:
3261:
3259:
3256:
3252:
3249:
3248:
3247:
3244:
3243:
3241:
3237:
3231:
3228:
3226:
3223:
3222:
3220:
3218:Invertebrates
3216:
3210:
3207:
3205:
3202:
3200:
3199:Water buffalo
3197:
3195:
3192:
3190:
3187:
3185:
3182:
3180:
3177:
3175:
3172:
3170:
3167:
3165:
3162:
3160:
3157:
3155:
3152:
3150:
3147:
3145:
3142:
3140:
3137:
3135:
3132:
3130:
3127:
3125:
3124:Domestic duck
3122:
3120:
3117:
3115:
3112:
3110:
3107:
3105:
3102:
3100:
3097:
3095:
3092:
3090:
3087:
3085:
3082:
3080:
3077:
3076:
3074:
3070:
3066:
3059:
3054:
3052:
3047:
3045:
3040:
3039:
3036:
3025:
3021:
3017:
3013:
3009:
3005:
3001:
2997:
2993:
2989:
2985:
2981:
2977:
2976:
2968:
2965:
2960:
2956:
2952:
2948:
2944:
2940:
2936:
2932:
2928:
2924:
2920:
2919:
2911:
2908:
2903:
2899:
2894:
2889:
2884:
2879:
2875:
2871:
2867:
2859:
2856:
2851:
2847:
2843:
2839:
2835:
2831:
2826:
2821:
2817:
2813:
2809:
2805:
2798:
2796:
2794:
2792:
2790:
2788:
2786:
2784:
2782:
2780:
2778:
2776:
2774:
2772:
2770:
2768:
2766:
2764:
2762:
2760:
2758:
2754:
2749:
2745:
2741:
2737:
2733:
2729:
2725:
2721:
2717:
2713:
2709:
2708:
2703:
2696:
2694:
2692:
2690:
2688:
2686:
2684:
2682:
2680:
2678:
2676:
2674:
2672:
2670:
2668:
2666:
2664:
2660:
2655:
2651:
2647:
2643:
2639:
2635:
2631:
2627:
2623:
2616:
2613:
2608:
2604:
2599:
2594:
2590:
2586:
2582:
2578:
2574:
2570:
2566:
2562:
2558:
2551:
2548:
2543:
2539:
2535:
2531:
2527:
2523:
2519:
2515:
2511:
2504:
2501:
2496:
2492:
2488:
2484:
2480:
2476:
2472:
2468:
2464:
2457:
2454:
2443:
2442:
2437:
2430:
2427:
2422:
2418:
2414:
2410:
2406:
2402:
2398:
2394:
2390:
2383:
2381:
2377:
2374:
2369:
2366:
2360:
2358:9780141974866
2354:
2350:
2346:
2340:
2337:
2332:
2328:
2324:
2320:
2316:
2312:
2309:(9): 439–44.
2308:
2304:
2300:
2294:
2291:
2286:
2282:
2278:
2274:
2270:
2266:
2262:
2255:
2252:
2247:
2243:
2237:
2235:
2231:
2225:
2220:
2216:
2212:
2205:
2202:
2196:
2191:
2187:
2183:
2179:
2172:
2169:
2164:
2160:
2156:
2152:
2148:
2144:
2140:
2136:
2132:
2131:
2123:
2121:
2119:
2117:
2115:
2113:
2111:
2109:
2107:
2105:
2103:
2101:
2097:
2092:
2088:
2083:
2078:
2074:
2070:
2065:
2060:
2056:
2052:
2048:
2041:
2039:
2035:
2030:
2026:
2022:
2018:
2014:
2010:
2006:
2002:
1998:
1994:
1990:
1986:
1982:
1974:
1971:
1966:
1962:
1957:
1952:
1948:
1944:
1940:
1936:
1932:
1928:
1924:
1917:
1915:
1911:
1906:
1902:
1898:
1894:
1890:
1886:
1882:
1878:
1874:
1867:
1864:
1859:
1855:
1851:
1847:
1843:
1839:
1832:
1829:
1824:
1820:
1815:
1810:
1806:
1802:
1798:
1791:
1789:
1785:
1780:
1776:
1772:
1768:
1763:
1758:
1754:
1750:
1746:
1745:
1740:
1732:
1730:
1728:
1726:
1724:
1722:
1720:
1718:
1716:
1714:
1712:
1710:
1708:
1706:
1704:
1702:
1700:
1698:
1696:
1694:
1692:
1688:
1683:
1679:
1674:
1669:
1665:
1661:
1657:
1653:
1649:
1645:
1641:
1634:
1632:
1630:
1626:
1621:
1617:
1612:
1607:
1603:
1599:
1595:
1591:
1587:
1583:
1579:
1572:
1570:
1568:
1566:
1564:
1562:
1560:
1558:
1554:
1549:
1545:
1541:
1537:
1533:
1529:
1525:
1518:
1516:
1512:
1507:
1503:
1498:
1493:
1489:
1485:
1481:
1477:
1473:
1465:
1463:
1459:
1454:
1450:
1446:
1442:
1438:
1434:
1430:
1423:
1421:
1417:
1412:
1399:
1385:
1382:
1376:
1374:
1370:
1365:
1361:
1356:
1351:
1347:
1343:
1339:
1335:
1331:
1327:
1324:(6): 160107.
1323:
1319:
1315:
1308:
1306:
1304:
1300:
1295:
1291:
1287:
1283:
1279:
1275:
1271:
1267:
1263:
1256:
1254:
1252:
1250:
1246:
1241:
1237:
1232:
1227:
1223:
1219:
1215:
1211:
1207:
1203:
1199:
1192:
1190:
1188:
1186:
1184:
1182:
1180:
1178:
1176:
1172:
1167:
1163:
1159:
1155:
1151:
1147:
1143:
1140:(in German).
1139:
1135:
1128:
1126:
1122:
1117:
1113:
1109:
1105:
1101:
1097:
1093:
1089:
1085:
1078:
1076:
1072:
1065:
1061:
1058:
1057:
1053:
1051:
1049:
1045:
1041:
1037:
1033:
1029:
1026:, especially
1025:
1018:in maize/corn
1017:
1016:
1012:
1008:
1007:
1003:
1002:
998:
994:
993:
989:
988:
985:Altered color
984:
983:
979:
975:
974:
969:
968:
963:
962:
957:
956:
952:
951:
947:
946:
942:
938:
934:
933:
929:
928:
924:
923:
919:
918:
914:
913:
909:
908:
904:
903:
899:
898:
894:
893:
889:
888:
884:
881:
880:
876:
873:
872:
868:
865:
863:
859:
856:
855:
851:
850:
846:
845:
841:
837:
836:
832:
828:
825:
824:
820:
816:
812:
811:
807:
806:
801:
800:
796:and eight in
795:
794:
789:
788:
786:
785:
780:
779:
775:
771:
770:
766:
765:
761:
760:
756:
754:
750:
746:
745:
740:
739:
735:
734:
731:Glutinousness
730:
729:
725:
724:
720:
717:
716:
712:
709:
708:
704:
701:
700:
696:
693:
692:
688:
685:
684:
680:
679:
675:
674:
671:
667:
663:
662:
658:
657:
653:
652:
648:
647:
643:
640:
638:
634:
631:
630:
626:
622:
619:
615:
614:
610:
608:
607:
602:
601:
597:
596:
593:Threshability
592:
591:
587:
586:
581:
580:
575:
574:
569:
568:
564:
561:
558:
557:
553:
552:
548:
546:
542:
539:
538:
534:
531:
530:
526:
523:
522:
518:
517:
513:
512:
508:
507:
503:
500:
499:
495:
493:
489:
488:
483:
482:
477:
474:
473:
469:
467:
465:
461:
458:
454:
450:
449:
444:
443:
439:
438:
434:
433:
429:
428:
424:
421:
420:
416:
414:
410:
409:
405:
402:
398:
397:
393:
391:
387:
383:
382:
378:
377:
373:
372:
371:
365:
363:
361:
360:seed dormancy
357:
356:vernalization
353:
349:
345:
341:
337:
336:glutinousness
333:
329:
325:
321:
317:
313:
309:
305:
301:
293:
288:
286:
279:
276:
273:
270:
269:
268:
264:
261:
256:
252:
249:
245:
241:
237:
233:
229:
221:
219:
217:
213:
209:
205:
197:
195:
193:
189:
185:
181:
180:endoparasites
177:
172:
169:
168:embryogenesis
165:
161:
155:
153:
149:
145:
137:
135:
132:
127:
124:
123:
118:
110:
103:
101:
99:
95:
91:
87:
83:
79:
74:
71:
66:
62:
60:
56:
52:
48:
41:
37:
32:
19:
3320:
3164:Domestic pig
2979:
2973:
2967:
2922:
2916:
2910:
2873:
2869:
2858:
2811:
2807:
2711:
2705:
2701:
2629:
2625:
2615:
2567:(1): 15345.
2564:
2560:
2550:
2517:
2513:
2503:
2470:
2466:
2456:
2445:. Retrieved
2439:
2429:
2396:
2392:
2368:
2348:
2339:
2306:
2302:
2293:
2268:
2264:
2254:
2245:
2214:
2204:
2185:
2181:
2171:
2134:
2128:
2054:
2050:
1988:
1984:
1973:
1930:
1926:
1880:
1876:
1866:
1841:
1837:
1831:
1804:
1800:
1748:
1742:
1647:
1643:
1585:
1581:
1531:
1527:
1479:
1475:
1436:
1432:
1407:|title=
1387:. Retrieved
1380:
1321:
1317:
1269:
1265:
1205:
1201:
1144:(1): 11–34.
1141:
1137:
1091:
1087:
1021:
1009:
990:
971:
965:
959:
953:
930:
915:
910:Spike number
900:
895:Panicle size
885:
877:
869:
860:
852:
829:
813:
808:Standability
797:
791:
782:
772:
757:
742:
736:
721:
713:
705:
697:
689:
681:
676:Grain weight
659:
644:
635:
623:
611:
604:
598:
583:
577:
571:
565:
543:
535:
527:
519:
504:
496:
492:pearl millet
485:
479:
470:
462:
456:
452:
446:
440:
435:Plant height
425:
417:
406:
394:
388:, rice, and
379:
369:
354:, lesser/no
297:
283:
265:
257:
253:
225:
201:
173:
160:neural crest
156:
141:
131:neural crest
128:
120:
119:'s study of
115:
75:
70:neural crest
67:
63:
46:
45:
3359:Agriculture
3169:Fancy mouse
3089:Bali cattle
3072:Vertebrates
2986:: 843–848.
2818:: 667–697.
2718:: 639–665.
2351:. Pelican.
2299:Hare, Brian
2242:Hare, Brian
2141:: 704–714.
2051:BMC Biology
1844:: 329–351.
793:Glycine max
248:fur farming
208:chimpanzees
3343:Categories
3149:Guinea pig
2929:: 89–105.
2447:2020-11-18
2188:(1): 1–7.
2139:Cell Press
1755:: 703–29.
1439:(2): 160.
1389:2024-03-05
1094:(2): 311.
1066:References
514:Grain size
459:) in wheat
390:maize/corn
374:Shattering
318:), larger
312:abscission
308:shattering
212:guinea pig
198:In animals
86:abscission
82:shattering
51:phenotypic
3225:Honey bee
3119:Dromedary
3024:205216444
3008:0028-0836
2959:223559538
2943:1471-0056
2834:1543-5008
2748:140266038
2732:1543-5008
2646:2079-0597
2589:2045-2322
2542:216513400
2495:221636622
2421:214809393
2155:1360-1385
2073:1741-7007
2057:(1): 64.
2029:206656021
2013:0036-8075
1947:1943-2631
1897:1520-541X
1771:1543-5008
1664:1943-2631
1602:0962-8452
1453:0003-0996
1346:2054-5703
1294:221636622
1222:1943-2631
1158:0075-7209
1088:Evolution
978:sprouting
935:produces
925:Fragrance
920:in barley
668:, wheat,
620:) in rice
348:daylength
332:flowering
324:threshing
289:In plants
240:fox farms
222:Challenge
192:microRNAs
184:helminths
174:The 2023
144:orthologs
94:threshing
40:chihuahua
36:grey wolf
18:Glutinous
3354:Genetics
3278:theories
3230:Silkworm
3184:Reindeer
3016:19212403
2982:(7231).
2951:33067582
2902:22013218
2850:73471425
2842:30835493
2740:31035826
2654:21631875
2607:26471470
2534:32668211
2487:32917395
2413:32265525
2347:(2014).
2323:16061417
2244:(2013).
2163:24035234
2091:29950181
2021:28450643
1965:34849912
1927:Genetics
1905:31545016
1858:27813680
1823:31810775
1779:26789233
1682:34849908
1644:Genetics
1620:36946116
1611:10031412
1588:(1995).
1548:31810775
1506:21625363
1398:cite web
1364:27429770
1286:32917395
1240:25024034
1202:Genetics
1166:42389667
1116:28564784
1054:See also
1042:, while
997:pericarp
995:- white
710:in wheat
670:ryegrass
509:in wheat
464:GA20ox-2
422:in wheat
188:protozoa
182:such as
3239:History
3174:Poultry
3104:Chicken
2988:Bibcode
2893:3327217
2598:4608001
2569:Bibcode
2363:Preface
2331:9311402
2285:3415520
2082:6022502
1993:Bibcode
1985:Science
1956:8633094
1673:8633120
1497:3101803
1355:4929905
1326:Bibcode
1231:4096361
1108:2406971
999:in rice
980:in rice
970:in the
882:in rice
866:in rice
857:in rice
826:in rice
762:in rice
726:in rice
718:in rice
702:in rice
694:in rice
582:in the
540:in rice
532:in rice
501:in rice
478:either
430:in rice
413:soybean
403:of rice
399:in the
386:sorghum
358:, less
316:lodging
310:/fruit
206:, like
204:Bonobos
84:/fruit
3134:Ferret
3114:Donkey
3099:Cattle
3079:Alpaca
3022:
3014:
3006:
2975:Nature
2957:
2949:
2941:
2900:
2890:
2848:
2840:
2832:
2746:
2738:
2730:
2652:
2644:
2605:
2595:
2587:
2540:
2532:
2493:
2485:
2419:
2411:
2355:
2329:
2321:
2283:
2161:
2153:
2137:(12).
2089:
2079:
2071:
2027:
2019:
2011:
1963:
1953:
1945:
1903:
1895:
1856:
1821:
1777:
1769:
1680:
1670:
1662:
1618:
1608:
1600:
1546:
1504:
1494:
1451:
1362:
1352:
1344:
1292:
1284:
1238:
1228:
1220:
1164:
1156:
1114:
1106:
759:SBEIIb
666:barley
448:Rht-D1
442:Rht-B1
401:rachis
340:gluten
104:Origin
3189:Sheep
3159:Llama
3154:Horse
3139:Gayal
3020:S2CID
2955:S2CID
2925:(2).
2846:S2CID
2814:(1).
2744:S2CID
2714:(1).
2702:Oryza
2650:S2CID
2538:S2CID
2491:S2CID
2417:S2CID
2327:S2CID
2281:S2CID
2025:S2CID
1933:(1).
1751:(1).
1650:(1).
1290:S2CID
1162:S2CID
1104:JSTOR
932:BADH2
871:PROG1
864:/RAE2
823:PROG1
819:Prog1
738:GBSSI
707:GASR7
639:/RAE2
629:LABA1
560:SPL14
554:Yield
547:/RAE2
453:Rht-1
408:qPDH1
344:fruit
320:grain
304:crops
148:crops
138:Cause
90:grain
42:skull
3209:Zebu
3144:Goat
3012:PMID
3004:ISSN
2947:PMID
2939:ISSN
2898:PMID
2838:PMID
2830:ISSN
2736:PMID
2728:ISSN
2642:ISSN
2603:PMID
2585:ISSN
2530:PMID
2483:PMID
2409:PMID
2353:ISBN
2319:PMID
2159:PMID
2151:ISSN
2087:PMID
2069:ISSN
2017:PMID
2009:ISSN
1961:PMID
1943:ISSN
1901:PMID
1893:ISSN
1854:PMID
1819:PMID
1775:PMID
1767:ISSN
1678:PMID
1660:ISSN
1616:PMID
1598:ISSN
1544:PMID
1502:PMID
1449:ISSN
1411:help
1360:PMID
1342:ISSN
1282:PMID
1236:PMID
1218:ISSN
1154:ISSN
1112:PMID
1046:and
1034:and
967:pyl6
961:pyl4
955:pyl1
917:vrs1
902:DEP1
887:AAP3
879:Gn1a
862:GAD1
854:An-1
778:TFL1
744:Waxy
723:TGW6
699:GLW2
661:VRN1
646:tga1
637:GAD1
625:An-2
618:awns
613:An-1
603:and
579:pyl6
573:pyl4
567:pyl1
545:GAD1
537:An-1
498:Ghd7
216:cavy
186:and
162:and
152:loci
3204:Yak
3109:Dog
3094:Cat
2996:doi
2980:457
2931:doi
2888:PMC
2878:doi
2874:157
2820:doi
2720:doi
2634:doi
2593:PMC
2577:doi
2522:doi
2475:doi
2401:doi
2311:doi
2273:doi
2219:doi
2215:OSF
2190:doi
2143:doi
2077:PMC
2059:doi
2001:doi
1989:356
1951:PMC
1935:doi
1931:219
1885:doi
1846:doi
1809:doi
1757:doi
1668:PMC
1652:doi
1648:219
1606:PMC
1590:doi
1586:290
1536:doi
1492:PMC
1484:doi
1480:103
1441:doi
1350:PMC
1334:doi
1274:doi
1226:PMC
1210:doi
1206:197
1146:doi
1096:doi
1015:tga
973:PYL
835:tb1
781:in
741:or
715:GW5
691:GW5
683:GW2
664:in
606:Nud
585:PYL
529:GS5
521:GS3
484:or
481:dw3
472:KO2
427:LG1
411:in
396:sh4
384:in
381:SH1
242:on
154:.
57:or
3345::
3018:.
3010:.
3002:.
2994:.
2978:.
2953:.
2945:.
2937:.
2923:22
2921:.
2896:.
2886:.
2872:.
2868:.
2844:.
2836:.
2828:.
2812:70
2810:.
2806:.
2756:^
2742:.
2734:.
2726:.
2712:70
2710:.
2662:^
2648:.
2640:.
2628:.
2624:.
2601:.
2591:.
2583:.
2575:.
2563:.
2559:.
2536:.
2528:.
2518:35
2516:.
2512:.
2489:.
2481:.
2471:35
2469:.
2465:.
2438:.
2415:.
2407:.
2397:21
2395:.
2391:.
2379:^
2325:.
2317:.
2305:.
2279:.
2269:83
2267:.
2263:.
2233:^
2217:.
2213:.
2186:20
2184:.
2180:.
2157:.
2149:.
2135:18
2133:.
2099:^
2085:.
2075:.
2067:.
2055:16
2053:.
2049:.
2037:^
2023:.
2015:.
2007:.
1999:.
1987:.
1983:.
1959:.
1949:.
1941:.
1929:.
1925:.
1913:^
1899:.
1891:.
1881:22
1879:.
1875:.
1852:.
1840:.
1817:.
1805:35
1803:.
1799:.
1787:^
1773:.
1765:.
1749:67
1747:.
1741:.
1690:^
1676:.
1666:.
1658:.
1646:.
1642:.
1628:^
1614:.
1604:.
1596:.
1584:.
1580:.
1556:^
1542:.
1532:35
1530:.
1526:.
1514:^
1500:.
1490:.
1478:.
1474:.
1461:^
1447:.
1437:87
1435:.
1431:.
1419:^
1402::
1400:}}
1396:{{
1372:^
1358:.
1348:.
1340:.
1332:.
1320:.
1316:.
1302:^
1288:.
1280:.
1270:35
1268:.
1264:.
1248:^
1234:.
1224:.
1216:.
1204:.
1200:.
1174:^
1160:.
1152:.
1142:32
1136:.
1124:^
1110:.
1102:.
1092:27
1090:.
1086:.
1074:^
992:Rc
964:,
958:,
576:,
570:,
487:d2
362:.
326:,
96:,
61:.
3057:e
3050:t
3043:v
3026:.
2998::
2990::
2961:.
2933::
2904:.
2880::
2852:.
2822::
2750:.
2722::
2656:.
2636::
2630:7
2609:.
2579::
2571::
2565:5
2544:.
2524::
2497:.
2477::
2450:.
2423:.
2403::
2361:.
2333:.
2313::
2307:9
2287:.
2275::
2227:.
2221::
2198:.
2192::
2165:.
2145::
2093:.
2061::
2031:.
2003::
1995::
1967:.
1937::
1907:.
1887::
1860:.
1848::
1842:5
1825:.
1811::
1781:.
1759::
1684:.
1654::
1622:.
1592::
1550:.
1538::
1508:.
1486::
1455:.
1443::
1413:)
1409:(
1392:.
1366:.
1336::
1328::
1322:3
1296:.
1276::
1242:.
1212::
1168:.
1148::
1118:.
1098::
1013:/
838:(
833:/
821:/
817:/
776:/
627:/
600:Q
506:Q
445:/
419:Q
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.