33:
1494:
738:
As an example, a point is a hyperplane in 1-dimensional space, a line is a hyperplane in 2-dimensional space, and a plane is a hyperplane in 3-dimensional space. A line in 3-dimensional space is not a hyperplane, and does not separate the space into two parts (the complement of such a line is
1068:
In projective space, a hyperplane does not divide the space into two parts; rather, it takes two hyperplanes to separate points and divide up the space. The reason for this is that the space essentially "wraps around" so that both sides of a lone hyperplane are connected to each other.
733:
626:
511:
1178:. The intersection of P and H is defined to be a "face" of the polyhedron. The theory of polyhedra and the dimension of the faces are analyzed by looking at these intersections involving hyperplanes.
993:
890:
1049:
is a set of points with the property that for any two points of the set, all the points on the line determined by the two points are contained in the set. Projective geometry can be viewed as
1176:
931:
1057:(points at infinity) added. An affine hyperplane together with the associated points at infinity forms a projective hyperplane. One special case of a projective hyperplane is the
807:
772:
216:, there is no concept of half-planes. In greatest generality, the notion of hyperplane is meaningful in any mathematical space in which the concept of the dimension of a
840:
291:, and the notion of hyperplane varies correspondingly since the definition of subspace differs in these settings; in all cases however, any hyperplane can be given in
516:
In the case of a real affine space, in other words when the coordinates are real numbers, this affine space separates the space into two half-spaces, which are the
387:
330:
Several specific types of hyperplanes are defined with properties that are well suited for particular purposes. Some of these specializations are described here.
407:
65:
1425:
1146:
A hyperplane H is called a "support" hyperplane of the polyhedron P if P is contained in one of the two closed half-spaces bounded by H and
1737:
310:, and therefore must pass through the origin) and "affine hyperplanes" (which need not pass through the origin; they can be obtained by
637:
1528:
533:
1478:
1352:
1329:
1294:
1257:
415:
1418:
517:
1138:
of codimension 2 obtained by intersecting the hyperplanes, and whose angle is twice the angle between the hyperplanes.
1344:
1207:
1089:
1732:
936:
845:
1717:
1513:
1108:
1202:
179:
1411:
157:
149:
1722:
1448:
1022:
of codimension 1, only possibly shifted from the origin by a vector, in which case it is referred to as a
525:
319:
200:
In other kinds of ambient spaces, some properties from
Euclidean space are no longer relevant. For example, in
137:
1149:
895:
1727:
1656:
1651:
1631:
521:
53:
1641:
1636:
1616:
1131:
1100:
1003:
311:
164:
141:
76:
1646:
1626:
1621:
1317:
777:
355:
315:
129:
125:
1197:
217:
745:
1523:
1518:
1227:
1046:
1042:
250:
145:
57:
1697:
1538:
1493:
1286:
The
Foundations of Topological Analysis: A Straightforward Introduction: Book 2 Topological Ideas
1135:
1126:
between two non-parallel hyperplanes of a
Euclidean space is the angle between the corresponding
296:
816:
36:
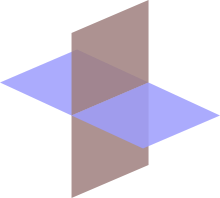
Two intersecting planes: Two-dimensional planes are the hyperplanes in three-dimensional space.
1533:
1386:
1367:
1348:
1325:
1303:
1290:
1253:
1192:
194:
133:
1284:
1463:
1311:
1096:
999:
288:
213:
175:
98:
95:
49:
365:
1508:
1453:
1280:
1104:
1078:
1054:
1050:
1027:
1023:
1019:
359:
307:
276:
153:
121:
109:
91:
88:
314:
of a vector hyperplane). A hyperplane in a
Euclidean space separates that space into two
1590:
1575:
1123:
392:
209:
1711:
1580:
1127:
1082:
223:
The difference in dimension between a subspace and its ambient space is known as its
205:
190:
84:
1088:
in n-dimensional
Euclidean space are separated by a hyperplane, a result called the
1600:
1565:
1458:
1187:
351:
343:
284:
280:
201:
72:
32:
1685:
1468:
1370:
810:
347:
264:
225:
204:, there is no concept of distance, so there are no reflections or motions. In a
1680:
1085:
1007:
292:
182:
69:
1661:
1570:
1483:
1434:
1394:
1375:
80:
61:
17:
1389:
1114:
The datapoint and its predicted value via a linear model is a hyperplane.
1585:
1548:
1473:
742:
Any hyperplane of a
Euclidean space has exactly two unit normal vectors:
295:
as the solution of a single (due to the "codimension 1" constraint)
242:
186:
168:
41:
1595:
306:
is a vector space, one distinguishes "vector hyperplanes" (which are
1552:
998:
Affine hyperplanes are used to define decision boundaries in many
322:
that fixes the hyperplane and interchanges those two half spaces.
31:
1130:. The product of the transformations in the two hyperplanes is a
728:{\displaystyle a_{1}x_{1}+a_{2}x_{2}+\cdots +a_{n}x_{n}>b.\ }
1407:
621:{\displaystyle a_{1}x_{1}+a_{2}x_{2}+\cdots +a_{n}x_{n}<b\ }
813:), then one can define the affine subspace with normal vector
185:, and the hyperplanes are the hypersurfaces consisting of all
506:{\displaystyle a_{1}x_{1}+a_{2}x_{2}+\cdots +a_{n}x_{n}=b.\ }
1403:
1065:, which is defined with the set of all points at infinity.
1250:
Projective
Geometry: From Foundations to Applications
1152:
939:
898:
848:
819:
780:
748:
640:
536:
418:
395:
368:
1335:
Victor V. Prasolov & VM Tikhomirov (1997, 2001)
87:. Two lower-dimensional examples of hyperplanes are
1673:
1609:
1547:
1501:
1441:
1228:"Excerpt from Convex Analysis, by R.T. Rockafellar"
358:, such a hyperplane can be described with a single
1170:
988:{\displaystyle {\hat {n}}\cdot (x-{\tilde {b}})=0}
987:
925:
885:{\displaystyle {\tilde {b}}\in \mathbb {R} ^{n+1}}
884:
834:
801:
766:
727:
620:
505:
401:
381:
362:of the following form (where at least one of the
1271:Polytopes, Rings and K-Theory by Bruns-Gubeladze
1248:Beutelspacher, Albrecht; Rosenbaum, Ute (1998),
1026:. Such a hyperplane is the solution of a single
1002:algorithms such as linear-combination (oblique)
809:equipped with the conventional inner product (
1419:
124:, each of which separates the space into two
8:
1018:In a vector space, a vector hyperplane is a
27:Subspace of n-space whose dimension is (n-1)
1426:
1412:
1404:
1289:. Cambridge University Press. p. 13.
1252:, Cambridge University Press, p. 10,
263: − 1, or equivalently, of
1151:
965:
964:
941:
940:
938:
911:
907:
906:
897:
870:
866:
865:
850:
849:
847:
821:
820:
818:
787:
783:
782:
779:
753:
752:
747:
707:
697:
678:
668:
655:
645:
639:
603:
593:
574:
564:
551:
541:
535:
485:
475:
456:
446:
433:
423:
417:
394:
373:
367:
1171:{\displaystyle H\cap P\neq \varnothing }
524:of the hyperplane, and are given by the
112:, in which case the hyperplanes are the
1341:Translations of Mathematical Monographs
1219:
1165:
1099:, hyperplanes are a key tool to create
926:{\displaystyle x\in \mathbb {R} ^{n+1}}
7:
104:Most commonly, the ambient space is
802:{\displaystyle \mathbb {R} ^{n+1}}
25:
167:, the ambient space might be the
132:across a hyperplane is a kind of
1492:
774:. In particular, if we consider
229:. A hyperplane has codimension
1324:, page 7, Krieger, Huntington
976:
970:
955:
946:
855:
826:
767:{\displaystyle \pm {\hat {n}}}
758:
1:
1345:American Mathematical Society
1208:Supporting hyperplane theorem
1090:hyperplane separation theorem
83:is one less than that of the
326:Special types of hyperplanes
1109:natural language processing
409:is an arbitrary constant):
259:is a subspace of dimension
1754:
1738:Multi-dimensional geometry
1203:Arrangement of hyperplanes
835:{\displaystyle {\hat {n}}}
189:through a point which are
1694:
1490:
1339:, page 22, volume 200 in
144:between points), and the
48:is a generalization of a
138:geometric transformation
1101:support vector machines
842:and origin translation
54:three-dimensional space
1172:
1039:Projective hyperplanes
1034:Projective hyperplanes
989:
927:
886:
836:
803:
768:
729:
622:
507:
403:
383:
178:, or more generally a
165:non-Euclidean geometry
152:by the reflections. A
37:
1318:Heinrich Guggenheimer
1173:
990:
928:
887:
837:
804:
769:
730:
623:
508:
404:
384:
382:{\displaystyle a_{i}}
356:Cartesian coordinates
279:or more generally an
237:Technical description
50:two-dimensional plane
35:
1610:Dimensions by number
1198:Ham sandwich theorem
1150:
937:
896:
846:
817:
778:
746:
638:
534:
518:connected components
416:
393:
366:
68:, a hyperplane is a
1733:Projective geometry
1322:Applicable Geometry
1142:Support hyperplanes
1047:projective subspace
1043:projective geometry
172:-dimensional sphere
58:mathematical spaces
1718:Euclidean geometry
1539:Degrees of freedom
1442:Dimensional spaces
1387:Weisstein, Eric W.
1368:Weisstein, Eric W.
1168:
1134:whose axis is the
1103:for such tasks as
1014:Vector hyperplanes
985:
923:
892:as the set of all
882:
832:
799:
764:
725:
618:
503:
399:
389:s is non-zero and
379:
334:Affine hyperplanes
299:of degree 1.
297:algebraic equation
254:-dimensional space
148:of all motions is
38:
1705:
1704:
1514:Lebesgue covering
1479:Algebraic variety
1312:Allyn & Bacon
1304:Charles W. Curtis
1193:Decision boundary
973:
949:
858:
829:
761:
724:
617:
502:
402:{\displaystyle b}
340:affine hyperplane
180:pseudo-Riemannian
118: − 1)
16:(Redirected from
1745:
1502:Other dimensions
1496:
1464:Projective space
1428:
1421:
1414:
1405:
1400:
1399:
1381:
1380:
1300:
1272:
1269:
1263:
1262:
1245:
1239:
1238:
1232:
1224:
1177:
1175:
1174:
1169:
1097:machine learning
1063:ideal hyperplane
1055:vanishing points
1000:machine learning
994:
992:
991:
986:
975:
974:
966:
951:
950:
942:
932:
930:
929:
924:
922:
921:
910:
891:
889:
888:
883:
881:
880:
869:
860:
859:
851:
841:
839:
838:
833:
831:
830:
822:
808:
806:
805:
800:
798:
797:
786:
773:
771:
770:
765:
763:
762:
754:
734:
732:
731:
726:
722:
712:
711:
702:
701:
683:
682:
673:
672:
660:
659:
650:
649:
627:
625:
624:
619:
615:
608:
607:
598:
597:
579:
578:
569:
568:
556:
555:
546:
545:
512:
510:
509:
504:
500:
490:
489:
480:
479:
461:
460:
451:
450:
438:
437:
428:
427:
408:
406:
405:
400:
388:
386:
385:
380:
378:
377:
318:, and defines a
308:linear subspaces
289:projective space
267: 1 in
232:
214:projective space
176:hyperbolic space
171:
160:of half-spaces.
119:
107:
96:zero-dimensional
21:
1753:
1752:
1748:
1747:
1746:
1744:
1743:
1742:
1723:Affine geometry
1708:
1707:
1706:
1701:
1690:
1669:
1605:
1543:
1497:
1488:
1454:Euclidean space
1437:
1432:
1385:
1384:
1366:
1365:
1362:
1297:
1281:Binmore, Ken G.
1279:
1276:
1275:
1270:
1266:
1260:
1247:
1246:
1242:
1230:
1226:
1225:
1221:
1216:
1184:
1148:
1147:
1144:
1120:
1118:Dihedral angles
1105:computer vision
1079:convex geometry
1075:
1051:affine geometry
1036:
1028:linear equation
1016:
935:
934:
905:
894:
893:
864:
844:
843:
815:
814:
781:
776:
775:
744:
743:
703:
693:
674:
664:
651:
641:
636:
635:
599:
589:
570:
560:
547:
537:
532:
531:
481:
471:
452:
442:
429:
419:
414:
413:
391:
390:
369:
364:
363:
360:linear equation
344:affine subspace
336:
328:
277:Euclidean space
239:
230:
169:
154:convex polytope
113:
110:Euclidean space
105:
94:in a plane and
89:one-dimensional
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
1751:
1749:
1741:
1740:
1735:
1730:
1728:Linear algebra
1725:
1720:
1710:
1709:
1703:
1702:
1695:
1692:
1691:
1689:
1688:
1683:
1677:
1675:
1671:
1670:
1668:
1667:
1659:
1654:
1649:
1644:
1639:
1634:
1629:
1624:
1619:
1613:
1611:
1607:
1606:
1604:
1603:
1598:
1593:
1591:Cross-polytope
1588:
1583:
1578:
1576:Hyperrectangle
1573:
1568:
1563:
1557:
1555:
1545:
1544:
1542:
1541:
1536:
1531:
1526:
1521:
1516:
1511:
1505:
1503:
1499:
1498:
1491:
1489:
1487:
1486:
1481:
1476:
1471:
1466:
1461:
1456:
1451:
1445:
1443:
1439:
1438:
1433:
1431:
1430:
1423:
1416:
1408:
1402:
1401:
1382:
1361:
1360:External links
1358:
1357:
1356:
1333:
1315:
1308:Linear Algebra
1301:
1295:
1274:
1273:
1264:
1258:
1240:
1218:
1217:
1215:
1212:
1211:
1210:
1205:
1200:
1195:
1190:
1183:
1180:
1167:
1164:
1161:
1158:
1155:
1143:
1140:
1128:normal vectors
1124:dihedral angle
1119:
1116:
1074:
1071:
1041:, are used in
1035:
1032:
1015:
1012:
1004:decision trees
984:
981:
978:
972:
969:
963:
960:
957:
954:
948:
945:
920:
917:
914:
909:
904:
901:
879:
876:
873:
868:
863:
857:
854:
828:
825:
796:
793:
790:
785:
760:
757:
751:
736:
735:
721:
718:
715:
710:
706:
700:
696:
692:
689:
686:
681:
677:
671:
667:
663:
658:
654:
648:
644:
629:
628:
614:
611:
606:
602:
596:
592:
588:
585:
582:
577:
573:
567:
563:
559:
554:
550:
544:
540:
514:
513:
499:
496:
493:
488:
484:
478:
474:
470:
467:
464:
459:
455:
449:
445:
441:
436:
432:
426:
422:
398:
376:
372:
335:
332:
327:
324:
238:
235:
210:elliptic space
208:space such as
206:non-orientable
193:to a specific
66:plane in space
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1750:
1739:
1736:
1734:
1731:
1729:
1726:
1724:
1721:
1719:
1716:
1715:
1713:
1700:
1699:
1693:
1687:
1684:
1682:
1679:
1678:
1676:
1672:
1666:
1664:
1660:
1658:
1655:
1653:
1650:
1648:
1645:
1643:
1640:
1638:
1635:
1633:
1630:
1628:
1625:
1623:
1620:
1618:
1615:
1614:
1612:
1608:
1602:
1599:
1597:
1594:
1592:
1589:
1587:
1584:
1582:
1581:Demihypercube
1579:
1577:
1574:
1572:
1569:
1567:
1564:
1562:
1559:
1558:
1556:
1554:
1550:
1546:
1540:
1537:
1535:
1532:
1530:
1527:
1525:
1522:
1520:
1517:
1515:
1512:
1510:
1507:
1506:
1504:
1500:
1495:
1485:
1482:
1480:
1477:
1475:
1472:
1470:
1467:
1465:
1462:
1460:
1457:
1455:
1452:
1450:
1447:
1446:
1444:
1440:
1436:
1429:
1424:
1422:
1417:
1415:
1410:
1409:
1406:
1397:
1396:
1391:
1388:
1383:
1378:
1377:
1372:
1369:
1364:
1363:
1359:
1354:
1353:0-8218-2038-9
1350:
1347:, Providence
1346:
1342:
1338:
1334:
1331:
1330:0-88275-368-1
1327:
1323:
1319:
1316:
1313:
1309:
1305:
1302:
1298:
1296:0-521-29930-6
1292:
1288:
1287:
1282:
1278:
1277:
1268:
1265:
1261:
1259:9780521483643
1255:
1251:
1244:
1241:
1236:
1235:u.arizona.edu
1229:
1223:
1220:
1213:
1209:
1206:
1204:
1201:
1199:
1196:
1194:
1191:
1189:
1186:
1185:
1181:
1179:
1162:
1159:
1156:
1153:
1141:
1139:
1137:
1133:
1129:
1125:
1117:
1115:
1112:
1110:
1106:
1102:
1098:
1093:
1091:
1087:
1084:
1080:
1072:
1070:
1066:
1064:
1060:
1056:
1052:
1048:
1044:
1040:
1033:
1031:
1029:
1025:
1021:
1013:
1011:
1009:
1005:
1001:
996:
982:
979:
967:
961:
958:
952:
943:
918:
915:
912:
902:
899:
877:
874:
871:
861:
852:
823:
812:
794:
791:
788:
755:
749:
740:
719:
716:
713:
708:
704:
698:
694:
690:
687:
684:
679:
675:
669:
665:
661:
656:
652:
646:
642:
634:
633:
632:
612:
609:
604:
600:
594:
590:
586:
583:
580:
575:
571:
565:
561:
557:
552:
548:
542:
538:
530:
529:
528:
527:
523:
519:
497:
494:
491:
486:
482:
476:
472:
468:
465:
462:
457:
453:
447:
443:
439:
434:
430:
424:
420:
412:
411:
410:
396:
374:
370:
361:
357:
353:
349:
345:
341:
333:
331:
325:
323:
321:
317:
313:
309:
305:
300:
298:
294:
290:
286:
282:
278:
274:
270:
266:
262:
258:
255:
253:
248:
244:
236:
234:
228:
227:
221:
219:
215:
211:
207:
203:
198:
196:
192:
191:perpendicular
188:
184:
181:
177:
173:
166:
161:
159:
155:
151:
147:
143:
139:
135:
131:
127:
123:
120:-dimensional
117:
111:
108:-dimensional
102:
100:
97:
93:
90:
86:
85:ambient space
82:
78:
74:
71:
67:
63:
60:of arbitrary
59:
55:
51:
47:
43:
34:
30:
19:
1696:
1662:
1601:Hyperpyramid
1566:Hypersurface
1560:
1459:Affine space
1449:Vector space
1393:
1374:
1371:"Hyperplane"
1340:
1336:
1321:
1307:
1285:
1267:
1249:
1243:
1234:
1222:
1188:Hypersurface
1145:
1121:
1113:
1094:
1076:
1073:Applications
1067:
1062:
1058:
1038:
1037:
1017:
997:
741:
739:connected).
737:
630:
526:inequalities
515:
352:affine space
339:
337:
329:
303:
301:
285:vector space
281:affine space
272:
271:. The space
268:
260:
256:
251:
246:
240:
224:
222:
220:is defined.
202:affine space
199:
162:
158:intersection
115:
103:
73:hypersurface
45:
39:
29:
1686:Codimension
1665:-dimensions
1586:Hypersphere
1469:Free module
1310:, page 62,
1086:convex sets
1008:perceptrons
811:dot product
348:codimension
316:half spaces
312:translation
293:coordinates
265:codimension
226:codimension
140:preserving
126:half spaces
101:on a line.
18:Hyperplanes
1712:Categories
1681:Hyperspace
1561:Hyperplane
1214:References
933:such that
522:complement
320:reflection
247:hyperplane
197:geodesic.
183:space form
130:reflection
46:hyperplane
1571:Hypercube
1549:Polytopes
1529:Minkowski
1524:Hausdorff
1519:Inductive
1484:Spacetime
1435:Dimension
1395:MathWorld
1376:MathWorld
1314:, Boston.
1166:∅
1163:≠
1157:∩
971:~
962:−
953:⋅
947:^
903:∈
862:∈
856:~
827:^
759:^
750:±
688:⋯
584:⋯
466:⋯
275:may be a
187:geodesics
150:generated
81:dimension
64:. Like a
62:dimension
1698:Category
1674:See also
1474:Manifold
1337:Geometry
1283:(1980).
1182:See also
1136:subspace
1132:rotation
1083:disjoint
1059:infinite
1020:subspace
350:1 in an
243:geometry
218:subspace
142:distance
77:subspace
42:geometry
1596:Simplex
1534:Fractal
1320:(1977)
1306:(1968)
520:of the
342:is an
283:, or a
156:is the
122:"flats"
1553:shapes
1390:"Flat"
1351:
1328:
1293:
1256:
1081:, two
1006:, and
723:
616:
501:
249:of an
195:normal
134:motion
99:points
79:whose
1657:Eight
1652:Seven
1632:Three
1509:Krull
1231:(PDF)
1053:with
1045:. A
354:. In
287:or a
146:group
92:lines
1642:Five
1637:Four
1617:Zero
1551:and
1349:ISBN
1326:ISBN
1291:ISBN
1254:ISBN
1122:The
1107:and
1024:flat
714:>
631:and
610:<
245:, a
128:. A
75:, a
70:flat
44:, a
1647:Six
1627:Two
1622:One
1095:In
1077:In
1061:or
346:of
338:An
302:If
241:In
212:or
174:or
163:In
56:to
52:in
40:In
1714::
1392:.
1373:.
1343:,
1233:.
1111:.
1092:.
1030:.
1010:.
995:.
233:.
1663:n
1427:e
1420:t
1413:v
1398:.
1379:.
1355:.
1332:.
1299:.
1237:.
1160:P
1154:H
983:0
980:=
977:)
968:b
959:x
956:(
944:n
919:1
916:+
913:n
908:R
900:x
878:1
875:+
872:n
867:R
853:b
824:n
795:1
792:+
789:n
784:R
756:n
720:.
717:b
709:n
705:x
699:n
695:a
691:+
685:+
680:2
676:x
670:2
666:a
662:+
657:1
653:x
647:1
643:a
613:b
605:n
601:x
595:n
591:a
587:+
581:+
576:2
572:x
566:2
562:a
558:+
553:1
549:x
543:1
539:a
498:.
495:b
492:=
487:n
483:x
477:n
473:a
469:+
463:+
458:2
454:x
448:2
444:a
440:+
435:1
431:x
425:1
421:a
397:b
375:i
371:a
304:V
273:V
269:V
261:n
257:V
252:n
231:1
170:n
136:(
116:n
114:(
106:n
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.