118:
43:
274:(rendering the cells more excitable) since less positive charge is present extracellularly. When calcium ions are absent the voltage level required to open voltage gated sodium channels is significantly altered (less excitation is required). If the plasma Ca decreases to less than 50% of the normal value of 9.4 mg/dl, action potentials may be spontaneously generated, causing contraction of peripheral skeletal muscles. Hypocalcemia is not a term for tetany but is rather a cause of tetany.
135:
125:
Tetany is characterized by contraction of distal muscles of the hands (carpal spasm with extension of interphalangeal joints and adduction and flexion of the metacarpophalangeal joints) and feet (pedal spasm) and is associated with tingling around the mouth and distally in the limbs.
684:
669:
257:
increase the permeability of neuronal membranes to sodium ion, causing a progressive depolarization, which increases the possibility of action potentials. This occurs because calcium ions interact with the exterior surface of
749:
297:
Also, tetany can be demonstrated by tapping anterior to the ear, at the emergence of the facial nerve. A resultant twitch of the nose or lips suggests low calcium levels. This is now known as the
543:
Trousseau's sign refers to the involuntary contraction of the muscles in the hand and wrist (i.e., carpopedal spasm) that occurs after the compression of the upper arm with a blood pressure cuff.
117:
742:
735:
647:
Harrison's
Principles of Internal Medicine 16th Edition – Dennis L. Kasper, Eugene Braunwald, Stephen Hauser, Dan Longo, J. Larry Jameson, Anthony S. Fauci.
1496:
172:
binding of calcium such that the ionized (physiologically influencing) fraction of calcium is reduced; one common reason for low carbon dioxide levels is
242:
can cause tetany. Vomiting induced alkalosis and hyperventilation induced respiratory alkalosis also cause tetany because of neuronal irritability.
503:
437:
412:
368:
Sutters, M.; Gaboury, CL.; Bennett, WM. (Oct 1996). "Severe hyperphosphatemia and hypocalcemia: a dilemma in patient management".
42:
1345:
291:
531:
304:
EMG studies reveal single or often grouped motor unit discharges at low discharge frequency during tetany episodes.
1245:
1240:
699:
101:
are not classified as tetany; rather, they are due to a lack of inhibition to the neurons that supply muscles.
1340:
1136:
1330:
928:
322:
1393:
1352:
809:
1423:
891:
1455:
1357:
1280:
727:
688:
254:
102:
1192:
1182:
1177:
1086:
951:
849:
758:
186:
106:
1172:
983:
941:
799:
789:
710:
636:
591:
499:
476:
433:
408:
385:
350:
271:
235:
199:
55:
1501:
1308:
1187:
1146:
834:
776:
626:
616:
581:
573:
466:
377:
283:
239:
173:
91:
1450:
1383:
1320:
1295:
1285:
1262:
1252:
814:
287:
263:
259:
1275:
1440:
1403:
1154:
968:
956:
844:
829:
631:
604:
586:
471:
454:
179:
165:
693:
1490:
1475:
1418:
1016:
906:
866:
819:
804:
298:
64:
1413:
1230:
1106:
1099:
1094:
1036:
1021:
824:
784:
250:
220:
139:
83:
704:
520:
1460:
1435:
1335:
1303:
1270:
1226:
1040:
961:
896:
871:
854:
267:
158:
715:
562:"On the relation of tetany to the parathyroid glands and to calcium metabolism"
1398:
1216:
1211:
1202:
1131:
1065:
1055:
993:
916:
678:
134:
1470:
1430:
1408:
1388:
1362:
1325:
1313:
1221:
1164:
1141:
1070:
1060:
1050:
1031:
1001:
973:
946:
861:
621:
208:
151:
60:
640:
595:
480:
17:
561:
389:
354:
1367:
1207:
1045:
1026:
577:
381:
290:
by squeezing, to trigger cramps in the fingers. This is now known as the
224:
138:
Cow grazing on rapidly grown pasture with tetany of the neck suggesting
1445:
1116:
216:
191:
169:
147:
98:
78:
661:
1465:
1011:
1006:
978:
936:
794:
673:
87:
432:(12th ed.). Philadelphia, Pa.: Saunders/Elsevier. p. 856.
407:(12th ed.). Philadelphia, Pa.: Saunders/Elsevier. p. 367.
498:(12th ed.). Philadelphia, Pa.: Saunders/Elsevier. p. 64.
1121:
1111:
253:
is the primary cause of tetany. Low ionized calcium levels in the
133:
116:
901:
881:
762:
195:
94:
frequency of muscle cells or of the nerves that innervate them.
27:
Medical condition, exhibiting involuntary contraction of muscles
731:
212:
154:(high phosphate-to-calcium ratio) can also trigger the spasms.
321:
Bill
Kvasnicka; Les J. Krysl. "Grass Tetany in Beef Cattle".
230:
Osteomalacia and rickets due to deficiency of vitamin D
90:, which may be caused by disorders that increase the
651:
1376:
1294:
1261:
1163:
1079:
992:
927:
769:
655:
286:(1801–1867) devised the maneuver of occluding the
54:
35:
609:Journal of Anaesthesiology Clinical Pharmacology
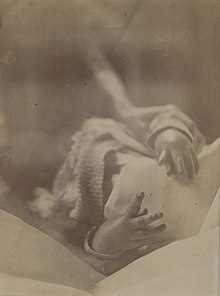
121:Position of Hands in the Spasm of Tetany (1905)
496:Guyton and Hall textbook of medical physiology
430:Guyton and Hall textbook of medical physiology
405:Guyton and Hall textbook of medical physiology
743:
455:"A New Syndrome, Magnesium-Deficiency Tetany"
146:The usual cause of tetany is a deficiency of
86:consisting of the involuntary contraction of
8:
105:(physiologic tetanus) have a broad range of
603:Williams, A; Abraham, D; Liddle, V (2011).
750:
736:
728:
652:
560:Maccallum, WG; Voegtlin, C (Jan 9, 1909).
234:Metabolic alkalosis with hypokalemia like
41:
32:
630:
620:
585:
470:
341:Haldimann, B.; Vogt, K. (Sep 1983). "".
313:
270:and hypocalcemia effectively increases
7:
566:The Journal of Experimental Medicine
459:Canadian Medical Association Journal
109:types, of which tetany is only one.
97:Muscle cramps caused by the disease
50:Hands of a baby affected with tetany
1497:Symptoms and signs: Nervous system
800:Festinating gait/Parkinsonian gait
530:. The Internet Archive: Elsevier.
25:
1394:Overpronation/Flexible flat feet
534:from the original on 2021-11-29
292:Trousseau sign of latent tetany
605:"Tetany: A diagnostic dilemma"
219:can trigger winter tetany, or
1:
168:cause tetany by altering the
845:Myopathic gait/Waddling gait
1518:
453:Grobin, W (May 14, 1960).
1246:Lower motor neuron lesion
1241:Upper motor neuron lesion
1046:Myotonia / Pseudomyotonia
761:relating to movement and
190:toxin, via inhibition of
161:gland can lead to tetany.
49:
40:
494:Hall, John, ed. (2010).
428:Hall, John, ed. (2010).
403:Hall, John, ed. (2010).
622:10.4103/0970-9185.83691
180:Low levels of magnesium
343:Schweiz Med Wochenschr
142:
122:
1353:Boutonniere deformity
202:, may lead to tetany.
157:Underfunction of the
137:
120:
1424:Clasp-knife response
578:10.1084/jem.11.1.118
382:10.1681/ASN.V7102056
324:Beef Cattle Handbook
103:Tetanic contractions
1456:Conversion disorder
1358:Swan neck deformity
1281:Locomotive syndrome
255:extracellular fluid
182:can lead to tetany.
1193:Spastic paraplegia
1183:Spastic paraplegia
1178:Periodic paralysis
1087:Abnormal posturing
952:Dysdiadochokinesia
888:Asynchronous gait
850:Trendelenburg gait
810:Marche à petit pas
759:Signs and symptoms
187:Clostridium tetani
143:
123:
113:Signs and symptoms
107:muscle contraction
1484:
1483:
1173:Flaccid paralysis
994:Abnormal movement
984:Hemimotor neglect
942:Cerebellar ataxia
892:Gunslinger's gait
790:Cerebellar ataxia
725:
724:
519:Hernandez, Anna.
505:978-1-4160-4574-8
439:978-1-4160-4574-8
414:978-1-4160-4574-8
282:French Professor
272:resting potential
236:Gitelman syndrome
200:neurotransmission
70:
69:
30:Medical condition
16:(Redirected from
1509:
1188:Spastic diplegia
1155:Tonic immobility
1147:Waxy flexibility
1091:Stooped posture
897:Hemiparetic gait
878:Asymmetric gait
777:Gait abnormality
752:
745:
738:
729:
653:
644:
634:
624:
599:
589:
546:
545:
540:
539:
525:
516:
510:
509:
491:
485:
484:
474:
450:
444:
443:
425:
419:
418:
400:
394:
393:
370:J Am Soc Nephrol
365:
359:
358:
338:
332:
331:
329:
318:
284:Armand Trousseau
240:Bartter syndrome
174:hyperventilation
92:action potential
45:
33:
21:
1517:
1516:
1512:
1511:
1510:
1508:
1507:
1506:
1487:
1486:
1485:
1480:
1451:Motion sickness
1384:Rachitic rosary
1372:
1321:Joint stiffness
1296:Range of motion
1290:
1257:
1253:Sleep paralysis
1237:General causes
1159:
1075:
988:
923:
835:Vestibular gait
815:Propulsive gait
765:
756:
726:
721:
720:
664:
650:
602:
559:
555:
550:
549:
537:
535:
523:
518:
517:
513:
506:
493:
492:
488:
452:
451:
447:
440:
427:
426:
422:
415:
402:
401:
397:
376:(10): 2056–61.
367:
366:
362:
340:
339:
335:
327:
320:
319:
315:
310:
288:brachial artery
280:
264:plasma membrane
260:sodium channels
248:
246:Pathophysiology
150:. An excess of
132:
115:
31:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
1515:
1513:
1505:
1504:
1499:
1489:
1488:
1482:
1481:
1479:
1478:
1473:
1468:
1463:
1458:
1453:
1448:
1443:
1441:Astasia-abasia
1438:
1433:
1428:
1427:
1426:
1416:
1411:
1406:
1404:Bow-leggedness
1401:
1396:
1391:
1386:
1380:
1378:
1374:
1373:
1371:
1370:
1365:
1360:
1355:
1350:
1349:
1348:
1343:
1338:
1328:
1323:
1318:
1317:
1316:
1311:
1300:
1298:
1292:
1291:
1289:
1288:
1283:
1278:
1273:
1267:
1265:
1259:
1258:
1256:
1255:
1250:
1249:
1248:
1243:
1235:
1234:
1233:
1224:
1219:
1214:
1205:
1197:
1196:
1195:
1190:
1180:
1175:
1169:
1167:
1161:
1160:
1158:
1157:
1152:
1149:
1144:
1139:
1134:
1129:
1124:
1119:
1114:
1109:
1104:
1103:
1102:
1097:
1089:
1083:
1081:
1077:
1076:
1074:
1073:
1068:
1063:
1058:
1053:
1048:
1043:
1034:
1029:
1024:
1019:
1014:
1009:
1004:
998:
996:
990:
989:
987:
986:
981:
976:
971:
969:Sensory ataxia
966:
965:
964:
959:
957:Pronator drift
954:
949:
939:
933:
931:
925:
924:
922:
921:
920:
919:
911:
910:
909:
904:
899:
894:
886:
885:
884:
876:
875:
874:
869:
859:
858:
857:
852:
847:
839:
838:
837:
832:
830:Truncal ataxia
827:
822:
817:
812:
807:
802:
797:
792:
787:
779:
773:
771:
767:
766:
757:
755:
754:
747:
740:
732:
723:
722:
719:
718:
707:
696:
681:
665:
660:
659:
657:
656:Classification
649:
648:
645:
615:(3): 393–394.
600:
556:
554:
553:External links
551:
548:
547:
511:
504:
486:
465:(20): 1034–5.
445:
438:
420:
413:
395:
360:
349:(35): 1231–3.
333:
312:
311:
309:
306:
279:
276:
247:
244:
232:
231:
228:
204:
203:
194:-mediated and
183:
177:
166:carbon dioxide
164:Low levels of
162:
155:
131:
128:
114:
111:
68:
67:
58:
52:
51:
47:
46:
38:
37:
29:
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1514:
1503:
1500:
1498:
1495:
1494:
1492:
1477:
1476:Dancing mania
1474:
1472:
1469:
1467:
1464:
1462:
1459:
1457:
1454:
1452:
1449:
1447:
1444:
1442:
1439:
1437:
1434:
1432:
1429:
1425:
1422:
1421:
1420:
1419:Hyperreflexia
1417:
1415:
1412:
1410:
1407:
1405:
1402:
1400:
1397:
1395:
1392:
1390:
1387:
1385:
1382:
1381:
1379:
1375:
1369:
1366:
1364:
1361:
1359:
1356:
1354:
1351:
1347:
1344:
1342:
1339:
1337:
1334:
1333:
1332:
1331:Hypermobility
1329:
1327:
1324:
1322:
1319:
1315:
1312:
1310:
1307:
1306:
1305:
1302:
1301:
1299:
1297:
1293:
1287:
1284:
1282:
1279:
1277:
1274:
1272:
1269:
1268:
1266:
1264:
1260:
1254:
1251:
1247:
1244:
1242:
1239:
1238:
1236:
1232:
1228:
1225:
1223:
1220:
1218:
1215:
1213:
1209:
1206:
1204:
1201:
1200:
1198:
1194:
1191:
1189:
1186:
1185:
1184:
1181:
1179:
1176:
1174:
1171:
1170:
1168:
1166:
1162:
1156:
1153:
1150:
1148:
1145:
1143:
1140:
1138:
1137:Joint locking
1135:
1133:
1130:
1128:
1125:
1123:
1120:
1118:
1115:
1113:
1110:
1108:
1105:
1101:
1098:
1096:
1093:
1092:
1090:
1088:
1085:
1084:
1082:
1078:
1072:
1069:
1067:
1064:
1062:
1059:
1057:
1054:
1052:
1049:
1047:
1044:
1042:
1038:
1035:
1033:
1030:
1028:
1025:
1023:
1020:
1018:
1017:Fasciculation
1015:
1013:
1010:
1008:
1005:
1003:
1000:
999:
997:
995:
991:
985:
982:
980:
977:
975:
972:
970:
967:
963:
960:
958:
955:
953:
950:
948:
945:
944:
943:
940:
938:
935:
934:
932:
930:
926:
918:
915:
914:
912:
908:
907:Antalgic gait
905:
903:
900:
898:
895:
893:
890:
889:
887:
883:
880:
879:
877:
873:
870:
868:
867:Steppage gait
865:
864:
863:
860:
856:
853:
851:
848:
846:
843:
842:
840:
836:
833:
831:
828:
826:
823:
821:
820:Stomping gait
818:
816:
813:
811:
808:
806:
805:Magnetic gait
803:
801:
798:
796:
793:
791:
788:
786:
783:
782:
780:
778:
775:
774:
772:
768:
764:
760:
753:
748:
746:
741:
739:
734:
733:
730:
717:
713:
712:
708:
706:
702:
701:
697:
695:
691:
690:
686:
682:
680:
676:
675:
671:
667:
666:
663:
658:
654:
646:
642:
638:
633:
628:
623:
618:
614:
610:
606:
601:
597:
593:
588:
583:
579:
575:
572:(1): 118–51.
571:
567:
563:
558:
557:
552:
544:
533:
529:
522:
515:
512:
507:
501:
497:
490:
487:
482:
478:
473:
468:
464:
460:
456:
449:
446:
441:
435:
431:
424:
421:
416:
410:
406:
399:
396:
391:
387:
383:
379:
375:
371:
364:
361:
356:
352:
348:
344:
337:
334:
326:
325:
317:
314:
307:
305:
302:
300:
299:Chvostek sign
295:
293:
289:
285:
277:
275:
273:
269:
265:
261:
256:
252:
245:
243:
241:
237:
229:
226:
222:
218:
214:
210:
207:An excess of
206:
205:
201:
197:
193:
189:
188:
184:
181:
178:
175:
171:
167:
163:
160:
156:
153:
149:
145:
144:
141:
136:
129:
127:
119:
112:
110:
108:
104:
100:
95:
93:
89:
85:
81:
80:
74:
66:
65:endocrinology
62:
59:
57:
53:
48:
44:
39:
34:
19:
1414:Hyporeflexia
1309:Bethlem sign
1276:Gowers' sign
1231:Quadruplegia
1126:
1107:Opisthotonus
1100:Osteoporosis
1095:Camptocormia
1037:Hyperkinesia
1022:Fibrillation
929:Coordination
882:Leaping gait
825:Spastic gait
795:Choreic gait
785:Scissor gait
709:
698:
683:
668:
612:
608:
569:
565:
542:
536:. Retrieved
527:
514:
495:
489:
462:
458:
448:
429:
423:
404:
398:
373:
369:
363:
346:
342:
336:
323:
316:
303:
296:
281:
251:Hypocalcemia
249:
233:
221:grass tetany
185:
140:grass tetany
124:
96:
84:medical sign
76:
72:
71:
1461:Shell shock
1436:Hypnic jerk
1336:Gorlin sign
1304:Contracture
1271:Hemiparesis
1227:Tetraplegia
1041:Hypokinesia
962:Dyssynergia
872:Toe walking
855:Pigeon gait
528:Osmosis.org
268:nerve cells
159:parathyroid
18:Heat tetany
1491:Categories
1399:Knock-knee
1217:Hemiplegia
1212:Paraplegia
1203:Monoplegia
1199:Syndromes
1132:Hypertonia
1066:Echopraxia
1056:Stereotypy
917:Lotus gait
913:Deformity
711:DiseasesDB
538:2022-03-31
308:References
1471:Catatonia
1431:Shivering
1409:Back knee
1389:Flat feet
1363:Scoliosis
1326:Ankylosis
1314:Club foot
1222:Triplegia
1165:Paralysis
1151:Grimacing
1142:Catalepsy
1080:Posturing
1071:Echolalia
1061:Akathisia
1051:Hypotonia
1032:Myoclonus
1002:Athetosis
974:Asterixis
947:Dysmetria
862:Foot drop
841:Muscular
278:Diagnosis
225:ruminants
211:in grass
209:potassium
152:phosphate
61:Neurology
56:Specialty
1368:Kyphosis
1263:Weakness
1208:Diplegia
1027:Myokymia
641:21897517
596:19867238
532:Archived
481:20326284
77:tetanic
1502:Tetanus
1446:Vertigo
1117:Trismus
705:D013746
632:3161471
587:2124703
472:1938332
390:8915965
355:6623048
262:in the
217:pasture
198:-ergic
192:glycine
170:albumin
148:calcium
99:tetanus
88:muscles
79:seizure
1466:Stupor
1286:Ptosis
1127:Tetany
1012:Tremor
1007:Chorea
979:Abasia
937:Ataxia
639:
629:
594:
584:
524:(html)
502:
479:
469:
436:
411:
388:
353:
130:Causes
73:Tetany
36:Tetany
1377:Other
1122:Cramp
1112:Spasm
716:29143
694:781.7
679:R29.0
328:(PDF)
223:, in
82:is a
902:Limp
781:CNS
770:Gait
763:gait
700:MeSH
689:9-CM
637:PMID
592:PMID
521:"MD"
500:ISBN
477:PMID
434:ISBN
409:ISBN
386:PMID
351:PMID
238:and
196:GABA
1346:HSD
1341:EDS
685:ICD
670:ICD
627:PMC
617:doi
582:PMC
574:doi
467:PMC
378:doi
347:113
266:of
215:or
213:hay
75:or
1493::
1229:/
1210:/
1039:/
714::
703::
692::
677::
674:10
635:.
625:.
613:27
611:.
607:.
590:.
580:.
570:11
568:.
564:.
541:.
526:.
475:.
463:82
461:.
457:.
384:.
372:.
345:.
301:.
294:.
63:,
751:e
744:t
737:v
687:-
672:-
662:D
643:.
619::
598:.
576::
508:.
483:.
442:.
417:.
392:.
380::
374:7
357:.
330:.
227:.
176:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.