96:
120:
108:
140:
artifacts which affect the image of the two layers identically which cancels out in the relative measurement. Alternatively, with a well calibrated microscope and if biaxial heterostrain is low enough, it is possible to determine twist and uniaxial heterostrain from the knowledge of the moiré period in all directions. On the contrary it is much more difficult to determine homostrain which necessitates a calibration sample.
149:
and to be the main factor in the flat band width of those systems. Heterostrain has a much larger impact on electronic properties than homostrain. It explains some of the sample variability which had previously been puzzeling. Research is now moving towards understanding the impact of spatial fluctuations of heterostrain.
148:
Heterostrain is generated during the fabrication of the 2D materials stack. It can result from a meta-stable configuration during bottom up assembly or from the layer manipulation in the tear and stack technique. It has been shown to be ubiquitous in twisted graphene layers near the magic twist angle
450:
Kapfer, Mäelle; Jessen, Bjarke S.; Eisele, Megan E.; Fu, Matthew; Danielsen, Dorte R.; Darlington, Thomas P.; Moore, Samuel L.; Finney, Nathan R.; Marchese, Ariane; Hsieh, Valerie; Majchrzak, Paulina; Jiang, Zhihao; Biswas, Deepnarayan; Dudin, Pavel; Avila, José (2023). "Programming twist angle and
139:
which provides images showing both the atomic lattice of the first layer and the moiré superlattice. Relating the atomic lattice to the moiré lattice allows to determine entirely the relative arrangement of the layers (biaxial, uniaxial heterostrain and twist). The method is immune to calibration
39:
in which the properties of 2D materials are controlled by strain. Recent works have reported a deterministic control of heterostrain by sample processing or with the tip of an AFM of particular interest in twisted heterostructures. Heterostrain alone (without twist) has also been identified as a
749:
Engelke, Rebecca; Yoo, Hyobin; Carr, Stephen; Xu, Kevin; Cazeaux, Paul; Allen, Richard; Valdivia, Andres Mier; Luskin, Mitchell; Kaxiras, Efthimios; Kim, Minhyong; Han, Jung Hoon; Kim, Philip (2022-07-16). "Non-Abelian topological defects and strain mapping in 2D moiré materials".
607:
Kapfer, Maëlle; Jessen, Bjarke S.; Eisele, Megan E.; Fu, Matthew; Danielsen, Dorte R.; Darlington, Thomas P.; Moore, Samuel L.; Finney, Nathan R.; Marchese, Ariane; Hsieh, Valerie; Majchrzak, Paulina; Jiang, Zhihao; Biswas, Deepnarayan; Dudin, Pavel; Avila, José (2023-08-11).
52:. It means that the two layers constituting the structure are subject to different strains. This is in contrast with homostrain in which the two layers as subject to the same strain. Heterostrain is designated as "relative strain" by some authors.
496:
Peña, Tara; Dey, Aditya; Chowdhury, Shoieb A.; Azizimanesh, Ahmad; Hou, Wenhui; Sewaket, Arfan; Watson, Carla L.; Askari, Hesam; Wu, Stephen M. (2023). "Moiré engineering in 2D heterostructures with process-induced strain".
919:
Kim, Kyounghwan; Yankowitz, Matthew; Fallahazad, Babak; Kang, Sangwoo; Movva, Hema C. P.; Huang, Shengqiang; Larentis, Stefano; Corbet, Chris M.; Taniguchi, Takashi; Watanabe, Kenji; Banerjee, Sanjay K. (2016-03-09).
681:
Mesple, Florie; Walet, Niels R.; Trambly de
Laissardière, Guy; Guinea, Francisco; Došenović, Djordje; Okuno, Hanako; Paillet, Colin; Michon, Adrien; Chapelier, Claude; Renard, Vincent T. (September 2023).
35:, heterostrain can have important consequences on the electronic and optical properties of the resulting structure. As such, the control of heterostrain is emerging as a sub-field of
846:
Kerelsky, Alexander; McGilly, Leo J.; Kennes, Dante M.; Xian, Lede; Yankowitz, Matthew; Chen, Shaowen; Watanabe, K.; Taniguchi, T.; Hone, James; Dean, Cory; Rubio, Angel (2019).
174:
Huder, Loïc; Artaud, Alexandre; Le Quang, Toai; de
Laissardière, Guy Trambly; Jansen, Aloysius G. M.; Lapertot, Gérard; Chapelier, Claude; Renard, Vincent T. (2018-04-12).
312:
Mesple, Florie; Missaoui, Ahmed; Cea, Tommaso; Huder, Loic; Guinea, Francisco; Trambly de
Laissardière, Guy; Chapelier, Claude; Renard, Vincent T. (2021-09-17).
79:
signaling the regions where the atomic lattices of the two layers are in or out of registry. The shape of the moiré pattern depends on the type of strain.
71:
In nature, the two graphene layers usually stack with a shift of half a unit cell. This configuration is the most energetically favorable and is found in
31:
are stacked on top of each other. These layers can experience the same deformation (homostrain) or different deformations (heterostrain). In addition to
40:
parameter to tune the electronic properties of van der Waals structures as for example in twisted graphene layers with biaxial heterostrain.
86:
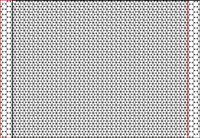
If the layer is strained in the same way along two directions (biaxial heterostrain), the moiré is a two-dimensional superstructure.
1134:
136:
1139:
27:
to simplify the designation of possible strain situations in van der Waals heterostructures where two (or more)
975:
Parker, Daniel E.; Soejima, Tomohiro; Hauschild, Johannes; Zaletel, Michael P.; Bultinck, Nick (2021-07-06).
64:
layers is considered. The description can be generalized for the case of different 2D materials forming an
28:
49:
1087:
998:
933:
869:
794:
705:
631:
573:
516:
470:
408:
335:
265:
197:
83:
If the layer is deformed along one direction (uniaxial heterostrain), the moiré is one dimensional.
95:
1111:
1077:
1046:
988:
901:
859:
784:
751:
695:
663:
621:
589:
563:
532:
506:
460:
432:
398:
367:
325:
289:
255:
221:
187:
771:
Artaud, A.; Magaud, L.; Le Quang, T.; Guisset, V.; David, P.; Chapelier, C.; Coraux, J. (2016).
132:
In
General, a layer can be deformed by an arbitrary combination of both types of heterostrain.
1103:
1038:
1030:
1022:
1018:
957:
949:
893:
885:
828:
810:
731:
723:
655:
647:
424:
386:
359:
351:
281:
213:
24:
1095:
1014:
1006:
941:
877:
818:
802:
713:
639:
581:
524:
478:
416:
343:
273:
205:
76:
976:
313:
175:
1091:
1002:
937:
921:
873:
798:
773:"Universal classification of twisted, strained and sheared graphene moiré superlattices"
709:
635:
577:
520:
474:
412:
339:
269:
201:
1065:
823:
772:
243:
65:
609:
119:
1128:
1115:
1050:
905:
667:
593:
536:
436:
371:
293:
36:
387:"Twist versus heterostrain control of optical properties of moiré exciton minibands"
225:
107:
1010:
847:
347:
209:
48:
Heterostrain is constructed from the Greek prefix hetero- (different) and the noun
945:
1099:
848:"Maximized electron interactions at the magic angle in twisted bilayer graphene"
277:
32:
420:
881:
1107:
1026:
953:
889:
814:
727:
651:
428:
355:
285:
643:
482:
1042:
961:
897:
832:
735:
718:
683:
659:
363:
314:"Heterostrain Determines Flat Bands in Magic-Angle Twisted Graphene Layers"
217:
72:
61:
922:"van der Waals Heterostructures with High Accuracy Rotational Alignment"
1034:
806:
585:
552:"Moiré engineering in 2D heterostructures with process-induced strain"
528:
551:
1082:
993:
864:
789:
756:
700:
684:"Giant Atomic Swirl in Graphene Bilayers with Biaxial Heterostrain"
626:
568:
511:
465:
403:
330:
260:
192:
176:"Electronic Spectrum of Twisted Graphene Layers under Heterostrain"
977:"Strain-Induced Quantum Phase Transitions in Magic-Angle Graphene"
610:"Programming twist angle and strain profiles in 2D materials"
75:. If one layer is strained while the other is left intact, a
385:
Zheng, Huiyuan; Zhai, Dawei; Yao, Wang (2021-10-01).
242:
Bi, Zhen; Yuan, Noah F. Q.; Fu, Liang (2019-07-31).
1066:"Moiré disorder effect in twisted bilayer graphene"
1064:Nakatsuji, Naoto; Koshino, Mikito (2022-06-14).
56:Manifestation and measurement of heterostrain
8:
125:Graphene layers with uniaxial heterostrain
1081:
992:
863:
822:
788:
755:
717:
699:
625:
567:
510:
464:
402:
329:
259:
191:
113:Graphene layers with biaxial heterostrain
157:
23:was proposed in 2018 in the context of
7:
307:
305:
303:
237:
235:
169:
167:
165:
163:
161:
1019:1854/LU-01GQF91F1WRRP5WQDFR3XBHF2J
451:strain profiles in 2D materials".
101:Graphene layers in Bernal stacking
14:
144:Origin and impact of heterostrain
244:"Designing flat bands by strain"
135:Heterostrain can be measured by
118:
106:
94:
60:For simplicity, the case of two
1011:10.1103/PhysRevLett.127.027601
348:10.1103/PhysRevLett.127.126405
210:10.1103/PhysRevLett.120.156405
1:
137:scanning tunneling microscope
946:10.1021/acs.nanolett.5b05263
1100:10.1103/PhysRevB.105.245408
596:– via AIP Publishing.
278:10.1103/PhysRevB.100.035448
1156:
882:10.1038/s41586-019-1431-9
29:two-dimensional materials
421:10.1088/2053-1583/ac2d16
1135:Deformation (mechanics)
981:Physical Review Letters
644:10.1126/science.ade9995
499:Applied Physics Letters
483:10.1126/science.ade9995
318:Physical Review Letters
180:Physical Review Letters
719:10.1002/adma.202306312
16:Materials science term
1092:2022PhRvB.105x5408N
1003:2021PhRvL.127b7601P
938:2016NanoL..16.1989K
874:2019Natur.572...95K
799:2016NatSR...625670A
710:2023AdM....3506312M
636:2023Sci...381..677K
578:2023ApPhL.122n3101P
550:Tara, Pena (2023).
521:2023ApPhL.122n3101P
475:2023Sci...381..677K
413:2021TDM.....8d4016Z
340:2021PhRvL.127l6405M
270:2019PhRvB.100c5448B
202:2018PhRvL.120o6405H
777:Scientific Reports
688:Advanced Materials
1140:Materials science
1070:Physical Review B
807:10.1038/srep25670
620:(6658): 677–681.
586:10.1063/5.0142406
529:10.1063/5.0142406
459:(6658): 677–681.
248:Physical Review B
25:materials science
1147:
1120:
1119:
1085:
1061:
1055:
1054:
996:
972:
966:
965:
932:(3): 1989–1995.
916:
910:
909:
867:
858:(7767): 95–100.
843:
837:
836:
826:
792:
768:
762:
761:
759:
746:
740:
739:
721:
703:
694:(41): e2306312.
678:
672:
671:
629:
604:
598:
597:
571:
556:Appl. Phys. Lett
547:
541:
540:
514:
493:
487:
486:
468:
447:
441:
440:
406:
382:
376:
375:
333:
309:
298:
297:
263:
239:
230:
229:
195:
171:
122:
110:
98:
1155:
1154:
1150:
1149:
1148:
1146:
1145:
1144:
1125:
1124:
1123:
1063:
1062:
1058:
974:
973:
969:
918:
917:
913:
845:
844:
840:
770:
769:
765:
748:
747:
743:
680:
679:
675:
606:
605:
601:
549:
548:
544:
495:
494:
490:
449:
448:
444:
384:
383:
379:
311:
310:
301:
241:
240:
233:
173:
172:
159:
155:
146:
130:
129:
128:
127:
126:
123:
115:
114:
111:
103:
102:
99:
66:heterostructure
58:
46:
17:
12:
11:
5:
1153:
1151:
1143:
1142:
1137:
1127:
1126:
1122:
1121:
1076:(24): 245408.
1056:
967:
911:
838:
763:
741:
673:
599:
562:(14): 143101.
542:
505:(14): 143101.
488:
442:
377:
324:(12): 126405.
299:
231:
186:(15): 156405.
156:
154:
151:
145:
142:
124:
117:
116:
112:
105:
104:
100:
93:
92:
91:
90:
89:
88:
87:
84:
57:
54:
45:
42:
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1152:
1141:
1138:
1136:
1133:
1132:
1130:
1117:
1113:
1109:
1105:
1101:
1097:
1093:
1089:
1084:
1079:
1075:
1071:
1067:
1060:
1057:
1052:
1048:
1044:
1040:
1036:
1032:
1028:
1024:
1020:
1016:
1012:
1008:
1004:
1000:
995:
990:
987:(2): 027601.
986:
982:
978:
971:
968:
963:
959:
955:
951:
947:
943:
939:
935:
931:
927:
923:
915:
912:
907:
903:
899:
895:
891:
887:
883:
879:
875:
871:
866:
861:
857:
853:
849:
842:
839:
834:
830:
825:
820:
816:
812:
808:
804:
800:
796:
791:
786:
782:
778:
774:
767:
764:
758:
753:
745:
742:
737:
733:
729:
725:
720:
715:
711:
707:
702:
697:
693:
689:
685:
677:
674:
669:
665:
661:
657:
653:
649:
645:
641:
637:
633:
628:
623:
619:
615:
611:
603:
600:
595:
591:
587:
583:
579:
575:
570:
565:
561:
557:
553:
546:
543:
538:
534:
530:
526:
522:
518:
513:
508:
504:
500:
492:
489:
484:
480:
476:
472:
467:
462:
458:
454:
446:
443:
438:
434:
430:
426:
422:
418:
414:
410:
405:
400:
397:(4): 044016.
396:
392:
388:
381:
378:
373:
369:
365:
361:
357:
353:
349:
345:
341:
337:
332:
327:
323:
319:
315:
308:
306:
304:
300:
295:
291:
287:
283:
279:
275:
271:
267:
262:
257:
254:(3): 035448.
253:
249:
245:
238:
236:
232:
227:
223:
219:
215:
211:
207:
203:
199:
194:
189:
185:
181:
177:
170:
168:
166:
164:
162:
158:
152:
150:
143:
141:
138:
133:
121:
109:
97:
85:
82:
81:
80:
78:
77:moiré pattern
74:
69:
67:
63:
55:
53:
51:
43:
41:
38:
37:straintronics
34:
30:
26:
22:
1073:
1069:
1059:
984:
980:
970:
929:
926:Nano Letters
925:
914:
855:
851:
841:
783:(1): 25670.
780:
776:
766:
744:
691:
687:
676:
617:
613:
602:
559:
555:
545:
502:
498:
491:
456:
452:
445:
394:
391:2D Materials
390:
380:
321:
317:
251:
247:
183:
179:
147:
134:
131:
70:
59:
47:
21:heterostrain
20:
18:
1129:Categories
1083:2204.06177
994:2012.09885
865:1812.08776
790:1605.07356
757:2207.05276
701:2308.13230
627:2209.10696
569:2210.03480
512:2210.03480
466:2209.10696
404:2110.01487
331:2012.02475
261:1902.10146
193:1803.03505
153:References
1116:248157360
1108:2469-9950
1051:229331622
1027:0031-9007
954:1530-6984
906:199057045
890:0028-0836
815:2045-2322
728:0935-9648
668:252438585
652:0036-8075
594:252762502
537:252762502
437:238259645
429:2053-1583
372:227305789
356:0031-9007
294:118982311
286:2469-9950
44:Etymology
19:The term
1043:34296891
962:26859527
898:31367030
833:27181495
736:37615204
660:37561852
364:34597066
226:21734003
218:29756887
73:graphite
62:graphene
1088:Bibcode
1035:1821673
999:Bibcode
934:Bibcode
870:Bibcode
824:4867435
795:Bibcode
706:Bibcode
632:Bibcode
614:Science
574:Bibcode
517:Bibcode
471:Bibcode
453:Science
409:Bibcode
336:Bibcode
266:Bibcode
198:Bibcode
1114:
1106:
1049:
1041:
1033:
1025:
960:
952:
904:
896:
888:
852:Nature
831:
821:
813:
734:
726:
666:
658:
650:
592:
535:
435:
427:
370:
362:
354:
292:
284:
224:
216:
50:strain
1112:S2CID
1078:arXiv
1047:S2CID
989:arXiv
902:S2CID
860:arXiv
785:arXiv
752:arXiv
696:arXiv
664:S2CID
622:arXiv
590:S2CID
564:arXiv
533:S2CID
507:arXiv
461:arXiv
433:S2CID
399:arXiv
368:S2CID
326:arXiv
290:S2CID
256:arXiv
222:S2CID
188:arXiv
33:twist
1104:ISSN
1039:PMID
1031:OSTI
1023:ISSN
958:PMID
950:ISSN
894:PMID
886:ISSN
829:PMID
811:ISSN
732:PMID
724:ISSN
656:PMID
648:ISSN
425:ISSN
360:PMID
352:ISSN
282:ISSN
214:PMID
1096:doi
1074:105
1015:hdl
1007:doi
985:127
942:doi
878:doi
856:572
819:PMC
803:doi
714:doi
640:doi
618:381
582:doi
560:122
525:doi
503:122
479:doi
457:381
417:doi
344:doi
322:127
274:doi
252:100
206:doi
184:120
1131::
1110:.
1102:.
1094:.
1086:.
1072:.
1068:.
1045:.
1037:.
1029:.
1021:.
1013:.
1005:.
997:.
983:.
979:.
956:.
948:.
940:.
930:16
928:.
924:.
900:.
892:.
884:.
876:.
868:.
854:.
850:.
827:.
817:.
809:.
801:.
793:.
779:.
775:.
730:.
722:.
712:.
704:.
692:35
690:.
686:.
662:.
654:.
646:.
638:.
630:.
616:.
612:.
588:.
580:.
572:.
558:.
554:.
531:.
523:.
515:.
501:.
477:.
469:.
455:.
431:.
423:.
415:.
407:.
393:.
389:.
366:.
358:.
350:.
342:.
334:.
320:.
316:.
302:^
288:.
280:.
272:.
264:.
250:.
246:.
234:^
220:.
212:.
204:.
196:.
182:.
178:.
160:^
68:.
1118:.
1098::
1090::
1080::
1053:.
1017::
1009::
1001::
991::
964:.
944::
936::
908:.
880::
872::
862::
835:.
805::
797::
787::
781:6
760:.
754::
738:.
716::
708::
698::
670:.
642::
634::
624::
584::
576::
566::
539:.
527::
519::
509::
485:.
481::
473::
463::
439:.
419::
411::
401::
395:8
374:.
346::
338::
328::
296:.
276::
268::
258::
228:.
208::
200::
190::
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.