186:, with every data line paired with a dedicated return line. It is the voltage difference between these two lines that defines the mark and space, rather than, as in RS-232, the difference in voltage between a data line and a local ground. As the ground voltage can differ at either end of the cable, this required RS-232 to use signals with voltage magnitudes greater than 5 volts. Moving to dedicated return lines and always defining ground in reference to the sender allows RS-422 to use 0.4 V, allowing it to run at much higher speeds. RS-423 differs primarily in that it has a single return pin instead of one for each data pin.
242:
1374:
258:
termination, as well as the individual installation. Figure A.1 shows a maximum length of 1,200 meters (3,900 ft), but this is with a termination, and the annex discusses the fact that many applications can tolerate greater timing and amplitude distortion, and that experience has shown that the cable length may be extended to several kilometers. Conservative maximum data rates with 24
325:, often with each pair being shielded, and a ground wire. While a double-pair cable may be practical for many RS-422 applications, the RS-422 specification only defines one signal path and does not assign any function to it. Any complete cable assembly with connectors should be labeled with the specification that defined the signal function and mechanical layout of the connector, such as
149:
272:
RS-422 specifies the electrical characteristics of a single balanced signal. The standard was written to be referenced by other standards that specify the complete DTE/DCE interface for applications which require a balanced voltage circuit to transmit data. These other standards would define
257:
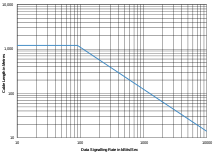
The maximum cable length is not specified in the standard, but guidance is given in its annex. (This annex is not a formal part of the standard, but is included for information purposes only.) Limitations on line length and data rate vary with the parameters of the cable length, balance, and
249:
Several key advantages offered by this standard include the differential receiver, a differential driver and data rates as high as 10 megabits per second at 12 meters (40 ft). Since the signal quality degrades with cable length, the maximum data rate decreases as cable length
269:) cable are 10 Mbit/s at 12 m (39 ft) to 90 kbit/s at 1,200 m (3,900 ft), as shown in the figure A.1. This figure is a conservative guide based on empirical data, not a limit imposed by the standard.
353:-8 connector. The ports could be put into either RS-232 or RS-422 mode, which changes the behavior of some of the pins while turning others on or off completely. These connectors are used to support RS-232 devices like
307:
signal, while MIL-STD-188-114B uses a signal symmetric about 0 V. However, the tolerance for common-mode voltage in both specifications allows them to interoperate. Care must be taken with the termination network.
167:, first issued in 1975, that specifies electrical characteristics of a digital signaling circuit. It was meant to be the foundation of a suite of standards that would replace the older
292:
RS-422 cannot implement a true multi-point communications network, such as with EIA-485, since there can be only one driver on each pair of wires. However, one driver can
171:
standard with standards that offered much higher speed, better immunity from noise, and longer cable lengths. RS-422 systems can transmit data at rates as high as 10
558:
361:
networking, RS-422 printers, and other peripherals. Two such ports were part of early Apple
Macintosh series designs until they were replaced, along with
814:
289:
connector) use RS-422 electrical signals. Some RS-422 devices have 4 screw terminals for pairs of wire, with one pair used for data in each direction.
1342:
1406:
971:
834:
230:
229:
The first version of RS-422 was issued in 1975, with revision A issued in
December 1978. Revision B, published in May 1994 was reaffirmed by the
641:
482:
195:
478:"V.11 : Electrical characteristics for balanced double-current interchange circuits operating at data signalling rates up to 10 Mbit/s"
1022:
693:
1369:
Interfaces are listed by their speed in the (roughly) ascending order, so the interface at the end of each section should be the fastest.
214:
specify the electrical characteristics of the balanced voltage digital interface circuit. RS-422 provides for data transmission, using
1075:
914:
844:
904:
64:
376:
RS-422 is a common transport mechanism for RS-232 extenders. These consist of RS-232 ports on either end of an RS-422 connection.
1002:
794:
524:
420:
164:
1346:
997:
966:
944:
1270:
1209:
1064:
728:
266:
341:
computers. This was implemented in a multi-pin connector that had enough pins to support the majority of the common
869:
634:
924:
1377:
1352:
1244:
899:
619:
175:, or may be sent on cables as long as 1,200 meters (3,900 ft) at lower rates. It is closely related to
1396:
934:
504:
TIA/EIA STANDARD, Electrical
Characteristics of Balanced Voltage Digital Interface Circuits, TIA/EIA-422-B
391:
219:
215:
183:
1401:
1198:
1151:
1007:
779:
627:
430:
576:"Maxim IC Application Note 723 'Selecting and Using RS-232, RS-422, and RS-485 Serial Data Standards'"
1194:
1047:
929:
380:
366:
537:
1106:
661:
650:
591:"Texas Instruments Application Report '422 and 485 Standards Overview and System Configurations'"
200:
ANSI/TIA/EIA-422-B Electrical
Characteristics of Balanced Voltage Differential Interface Circuits
321:
When used in relation to communications wiring, RS-422 wiring refers to cable made of 2 sets of
1096:
718:
654:
520:
362:
241:
829:
415:
406:
industry standard connector for RS-422, which is still found on broadcast equipment today.
959:
809:
789:
664:
384:
211:
1260:
954:
879:
804:
708:
683:
395:
387:
575:
1390:
1332:
1219:
1111:
1059:
1042:
824:
723:
713:
688:
68:
222:
or non-terminated transmission lines, point to point, or multi-drop. In contrast to
1069:
1012:
864:
769:
605:
590:
322:
262:
390:
facilities used RS-422A to remotely control the players/recorders located in the
1337:
1316:
1239:
1234:
1079:
1017:
992:
919:
703:
698:
346:
300:
179:, which uses the same signaling systems but on a different wiring arrangement.
1190:
889:
678:
1214:
1204:
1171:
1166:
1101:
976:
764:
749:
744:
358:
338:
148:
226:, RS-422/V.11 does not allow multiple drivers but only multiple receivers.
17:
1224:
1161:
894:
754:
606:"Texas Instruments Application Report SLLA067B 'Comparing Bus Solutions'"
435:
425:
403:
350:
477:
273:
protocols, connectors, pin assignments and functions. Standards such as
1357:
1311:
1295:
1121:
939:
884:
819:
774:
311:
293:
282:
274:
251:
250:
increases. Figure A.1 in the annex plotting this stops at 10
223:
172:
168:
1290:
1181:
1156:
1146:
1141:
1131:
949:
839:
799:
759:
342:
326:
315:
176:
1275:
1186:
1285:
1176:
1116:
1054:
1027:
909:
859:
784:
354:
286:
278:
240:
1280:
1265:
1126:
1037:
1032:
874:
399:
370:
304:
623:
1229:
854:
849:
379:
Before hard-disk-based playout and editing systems were used,
259:
455:
337:
One of the most widespread uses of RS-422 was on the early
303:, but they are not identical. RS-422 uses a nominal 0 to 5-
245:
Data rate versus line length chart, from RS-422 Annex A.1
314:
is a similar specification for unbalanced signaling (
299:
RS-422 can interoperate with interfaces designed to
1325:
1304:
1253:
1089:
985:
737:
671:
138:
130:
122:
114:
106:
98:
90:
82:
74:
60:
52:
47:
39:
34:
972:Coherent Accelerator Processor Interface (CAPI)
110:−6 to +6 V (maximum voltage for each line)
635:
517:Microcomputers and Modern Control Engineering
8:
163:, is a technical standard originated by the
585:. Maxim Integrated Products. December 2000.
642:
628:
620:
398:connection was used, which makes use of a
31:
194:RS-422 is the common short form title of
147:
447:
231:Telecommunications Industry Association
218:, with unidirectional/non-reversible,
152:RS-422 network with multiple receivers
483:International Telecommunication Union
349:, but this was quickly replaced by a
196:American National Standards Institute
7:
345:pins; the first models used a 9-pin
216:balanced, or differential, signaling
615:. Texas Instruments. October 2009.
519:, Reston Publishing Company, 1983
25:
202:and its international equivalent
27:Standard for serial communication
1373:
1372:
134:Tx+, Tx−, Rx+, Rx− (full duplex)
1407:Serial communication interfaces
600:. Texas Instruments. June 2002.
538:"First Macintosh Press Release"
204:ITU-T Recommendation T-REC-V.11
421:Electronic Industries Alliance
165:Electronic Industries Alliance
78:10 (1 driver and 10 receivers)
1:
967:Intel Ultra Path Interconnect
945:Intel QuickPath Interconnect
935:Direct Media Interface (DMI)
86:1,200 meters (3,900 ft)
102:100 kbit/s – 10 Mbit/s
1423:
930:Compute Express Link (CXL)
559:Sony 9-Pin Remote Protocol
1366:
1167:IEEE-1284 (parallel port)
1082:logical device interface)
296:to up to ten receivers.
402:connector. This is the
729:List of bus bandwidths
392:central apparatus room
246:
184:differential signaling
153:
431:List of network buses
244:
151:
1172:IEEE-1394 (FireWire)
910:PCI Extended (PCI-X)
540:. stanford.edu. 1984
515:Douglas A. Cassell,
394:. In most cases the
381:broadcast automation
367:Universal Serial Bus
48:Protocol information
1013:Parallel ATA (PATA)
583:MaximIntegrated.com
126:Positive difference
118:Negative difference
99:Maximum binary rate
920:PCI Express (PCIe)
247:
210:. These technical
154:
1384:
1383:
1370:
1097:Apple Desktop Bus
1074:PCI Express (via
1033:Serial ATA (SATA)
719:Network on a chip
182:RS-422 specifies
146:
145:
131:Available signals
91:Mode of operation
67:, unidirectional
16:(Redirected from
1414:
1376:
1375:
1368:
830:HP Precision Bus
644:
637:
630:
621:
616:
610:
601:
595:
586:
580:
562:
556:
550:
549:
547:
545:
534:
528:
513:
507:
501:
495:
494:
492:
490:
474:
468:
467:
465:
463:
452:
416:Differential TTL
301:MIL-STD-188-114B
206:, also known as
198:(ANSI) standard
159:, also known as
83:Maximum distance
61:Network topology
32:
21:
1422:
1421:
1417:
1416:
1415:
1413:
1412:
1411:
1387:
1386:
1385:
1380:
1371:
1362:
1321:
1300:
1249:
1162:IEEE-488 (GPIB)
1085:
981:
960:Infinity Fabric
790:Europe Card Bus
733:
667:
648:
608:
604:
593:
589:
578:
574:
571:
569:Further reading
566:
565:
557:
553:
543:
541:
536:
535:
531:
514:
510:
502:
498:
488:
486:
476:
475:
471:
461:
459:
454:
453:
449:
444:
412:
385:post-production
335:
281:connector) and
239:
237:Characteristics
192:
139:Connector types
75:Maximum devices
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
1420:
1418:
1410:
1409:
1404:
1399:
1389:
1388:
1382:
1381:
1367:
1364:
1363:
1361:
1360:
1355:
1350:
1340:
1335:
1329:
1327:
1323:
1322:
1320:
1319:
1314:
1308:
1306:
1302:
1301:
1299:
1298:
1293:
1288:
1283:
1278:
1273:
1271:Intel HD Audio
1268:
1263:
1261:ADAT Lightpipe
1257:
1255:
1251:
1250:
1248:
1247:
1242:
1237:
1232:
1227:
1222:
1217:
1212:
1207:
1202:
1184:
1179:
1174:
1169:
1164:
1159:
1154:
1149:
1144:
1139:
1134:
1129:
1124:
1119:
1114:
1109:
1104:
1099:
1093:
1091:
1087:
1086:
1084:
1083:
1072:
1067:
1062:
1057:
1052:
1051:
1050:
1045:
1035:
1030:
1025:
1020:
1015:
1010:
1005:
1000:
995:
989:
987:
983:
982:
980:
979:
974:
969:
964:
963:
962:
955:HyperTransport
952:
947:
942:
937:
932:
927:
922:
917:
912:
907:
902:
897:
892:
887:
882:
877:
872:
867:
862:
857:
852:
847:
842:
837:
832:
827:
822:
817:
812:
807:
802:
797:
792:
787:
782:
777:
772:
767:
762:
757:
752:
747:
741:
739:
735:
734:
732:
731:
726:
721:
716:
711:
709:Bus contention
706:
701:
696:
691:
686:
684:Front-side bus
681:
675:
673:
669:
668:
665:computer buses
649:
647:
646:
639:
632:
624:
618:
617:
602:
587:
570:
567:
564:
563:
551:
529:
508:
496:
469:
446:
445:
443:
440:
439:
438:
433:
428:
423:
418:
411:
408:
388:linear editing
334:
331:
238:
235:
191:
190:Standard scope
188:
144:
143:
140:
136:
135:
132:
128:
127:
124:
120:
119:
116:
112:
111:
108:
104:
103:
100:
96:
95:
92:
88:
87:
84:
80:
79:
76:
72:
71:
65:Point-to-point
62:
58:
57:
54:
53:Physical media
50:
49:
45:
44:
41:
37:
36:
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1419:
1408:
1405:
1403:
1400:
1398:
1397:EIA standards
1395:
1394:
1392:
1379:
1365:
1359:
1356:
1354:
1351:
1348:
1344:
1341:
1339:
1336:
1334:
1333:Multidrop bus
1331:
1330:
1328:
1324:
1318:
1315:
1313:
1310:
1309:
1307:
1303:
1297:
1294:
1292:
1289:
1287:
1284:
1282:
1279:
1277:
1274:
1272:
1269:
1267:
1264:
1262:
1259:
1258:
1256:
1252:
1246:
1243:
1241:
1240:External PCIe
1238:
1236:
1233:
1231:
1228:
1226:
1223:
1221:
1220:Parallel SCSI
1218:
1216:
1213:
1211:
1208:
1206:
1203:
1200:
1196:
1192:
1188:
1185:
1183:
1180:
1178:
1175:
1173:
1170:
1168:
1165:
1163:
1160:
1158:
1155:
1153:
1150:
1148:
1145:
1143:
1140:
1138:
1135:
1133:
1130:
1128:
1125:
1123:
1120:
1118:
1115:
1113:
1112:Commodore bus
1110:
1108:
1105:
1103:
1100:
1098:
1095:
1094:
1092:
1088:
1081:
1077:
1073:
1071:
1068:
1066:
1063:
1061:
1060:Fibre Channel
1058:
1056:
1053:
1049:
1046:
1044:
1041:
1040:
1039:
1036:
1034:
1031:
1029:
1026:
1024:
1021:
1019:
1016:
1014:
1011:
1009:
1006:
1004:
1001:
999:
996:
994:
991:
990:
988:
984:
978:
975:
973:
970:
968:
965:
961:
958:
957:
956:
953:
951:
948:
946:
943:
941:
938:
936:
933:
931:
928:
926:
923:
921:
918:
916:
913:
911:
908:
906:
903:
901:
898:
896:
893:
891:
888:
886:
883:
881:
878:
876:
873:
871:
868:
866:
863:
861:
858:
856:
853:
851:
848:
846:
843:
841:
838:
836:
833:
831:
828:
826:
823:
821:
818:
816:
813:
811:
808:
806:
803:
801:
798:
796:
793:
791:
788:
786:
783:
781:
778:
776:
773:
771:
768:
766:
763:
761:
758:
756:
753:
751:
748:
746:
743:
742:
740:
736:
730:
727:
725:
724:Plug and play
722:
720:
717:
715:
714:Bus mastering
712:
710:
707:
705:
702:
700:
697:
695:
692:
690:
689:Back-side bus
687:
685:
682:
680:
677:
676:
674:
670:
666:
663:
659:
657:
652:
645:
640:
638:
633:
631:
626:
625:
622:
614:
607:
603:
599:
592:
588:
584:
577:
573:
572:
568:
560:
555:
552:
539:
533:
530:
526:
522:
518:
512:
509:
505:
500:
497:
485:
484:
479:
473:
470:
457:
451:
448:
441:
437:
434:
432:
429:
427:
424:
422:
419:
417:
414:
413:
409:
407:
405:
401:
397:
393:
389:
386:
382:
377:
374:
372:
368:
364:
360:
356:
352:
348:
344:
340:
332:
330:
328:
324:
319:
317:
313:
309:
306:
302:
297:
295:
290:
288:
284:
280:
276:
270:
268:
264:
261:
255:
253:
243:
236:
234:
232:
227:
225:
221:
217:
213:
209:
205:
201:
197:
189:
187:
185:
180:
178:
174:
170:
166:
162:
158:
150:
142:Not specified
141:
137:
133:
129:
125:
121:
117:
113:
109:
105:
101:
97:
93:
89:
85:
81:
77:
73:
70:
69:multidrop bus
66:
63:
59:
55:
51:
46:
42:
38:
33:
30:
19:
1402:Serial buses
1136:
865:TURBOchannel
655:
613:Focus.TI.com
612:
598:Focus.TI.com
597:
582:
554:
542:. Retrieved
532:
516:
511:
503:
499:
489:19 September
487:. Retrieved
481:
472:
460:. Retrieved
458:. foldoc.org
450:
383:systems and
378:
375:
336:
333:Applications
323:twisted pair
320:
310:
298:
291:
271:
256:
248:
228:
207:
203:
199:
193:
181:
160:
156:
155:
94:Differential
56:Twisted pair
29:
1338:CoreConnect
1317:ExpressCard
1245:Thunderbolt
1235:Camera Link
1018:Bus and Tag
704:Address bus
699:Control bus
694:Daisy chain
347:D connector
161:TIA/EIA-422
43:TIA/EIA-422
1391:Categories
1191:ACCESS.bus
1090:Peripheral
890:InfiniBand
885:HP GSC bus
679:System bus
525:0835943658
506:, May 1994
442:References
396:Sony 9-pin
365:ports, by
220:terminated
18:ITU-T V.11
1152:Lightning
1102:Atari SIO
977:SpaceWire
810:Zorro III
750:S-100 bus
745:SS-50 bus
738:Standards
658:standards
651:Technical
456:"EIA-423"
373:in 1998.
359:AppleTalk
339:Macintosh
233:in 2005.
212:standards
1378:Category
1353:Wishbone
1326:Embedded
1305:Portable
1225:Profibus
1157:DMX512-A
1043:Parallel
895:Ethernet
805:Zorro II
755:Multibus
656:de facto
527:page 569
436:Profibus
426:Fieldbus
410:See also
404:de facto
351:mini-DIN
123:Space(0)
40:Standard
1358:SLIMbus
1312:PC Card
1296:TOSLINK
986:Storage
940:RapidIO
820:FASTBUS
775:STD Bus
672:General
369:on the
312:EIA-423
294:fan-out
283:EIA-449
275:EIA-530
224:EIA-485
169:RS-232C
115:Mark(1)
107:Voltage
1291:S/PDIF
1182:1-Wire
1147:RS-485
1142:RS-423
1137:RS-422
1132:RS-232
993:ST-506
950:NVLink
800:STEbus
760:Unibus
544:8 July
523:
462:8 July
355:modems
343:RS-232
327:RS-449
316:RS-423
252:Mbit/s
177:RS-423
173:Mbit/s
157:RS-422
35:RS-422
1286:McASP
1254:Audio
1199:SMBus
1195:PMBus
1177:UNI/O
1117:HP-IL
1070:SATAe
1055:ESCON
1028:HIPPI
860:NuBus
815:CAMAC
785:Q-Bus
780:SMBus
765:VAXBI
662:wired
609:(PDF)
594:(PDF)
579:(PDF)
287:DC-37
279:DB-25
1343:AMBA
1281:MADI
1266:AES3
1127:MIDI
1080:NVMe
1076:AHCI
1038:SCSI
1023:DSSI
998:ESDI
875:SBus
835:EISA
770:MBus
660:for
653:and
546:2021
521:ISBN
491:2022
464:2021
400:DE-9
371:iMac
305:volt
267:POTS
208:X.27
1347:AXI
1276:I²S
1230:USB
1215:D²B
1210:SPI
1205:I3C
1187:I²C
1122:HIL
1107:DCB
1078:or
1065:SSA
1048:SAS
1008:SMD
1003:IPI
925:AGP
915:PXI
905:PCI
900:UPA
880:VLB
870:MCA
855:VPX
850:VXS
845:VXI
840:VME
825:LPC
795:ISA
363:ADB
318:).
263:UTP
260:AWG
1393::
1197:,
1193:,
611:.
596:.
581:.
480:.
357:,
329:.
254:.
1349:)
1345:(
1201:)
1189:(
643:e
636:t
629:v
561:.
548:.
493:.
466:.
285:(
277:(
265:(
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.